BIO 168 - Lab 01 - Orientation to the Human Body - K. Pescosolido
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
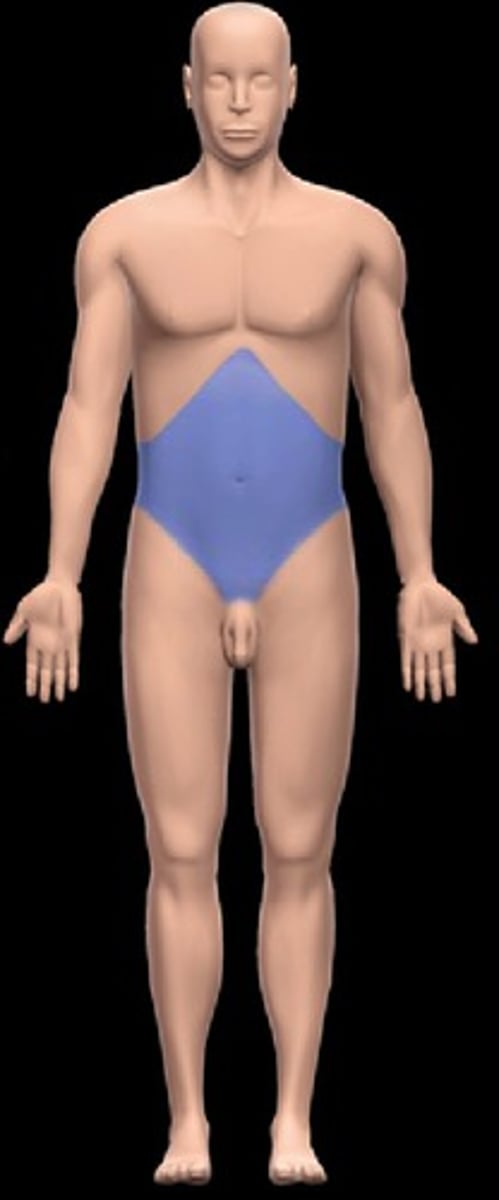
abdominal
the region of the abdomen
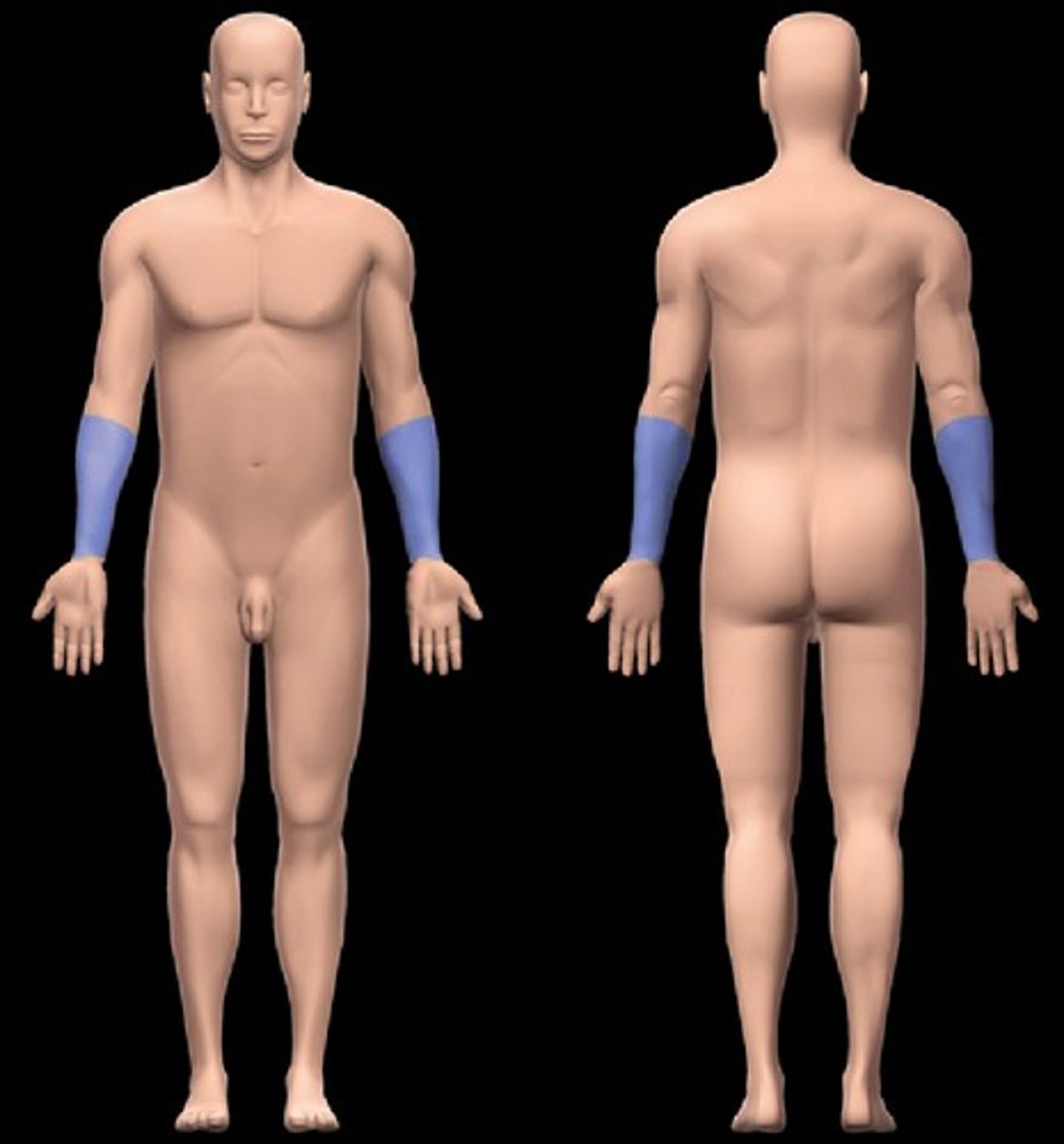
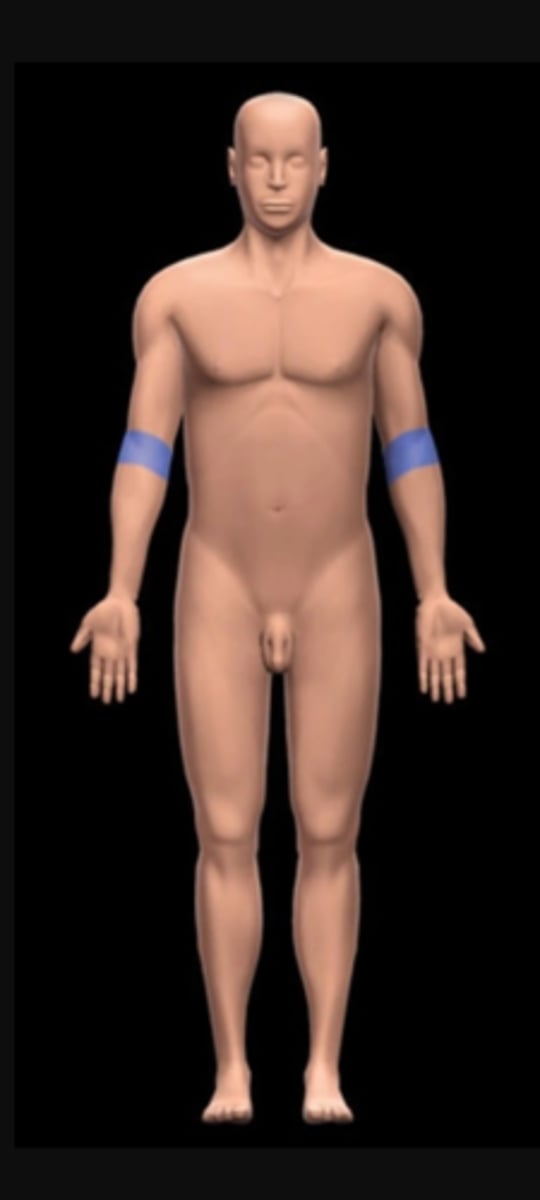
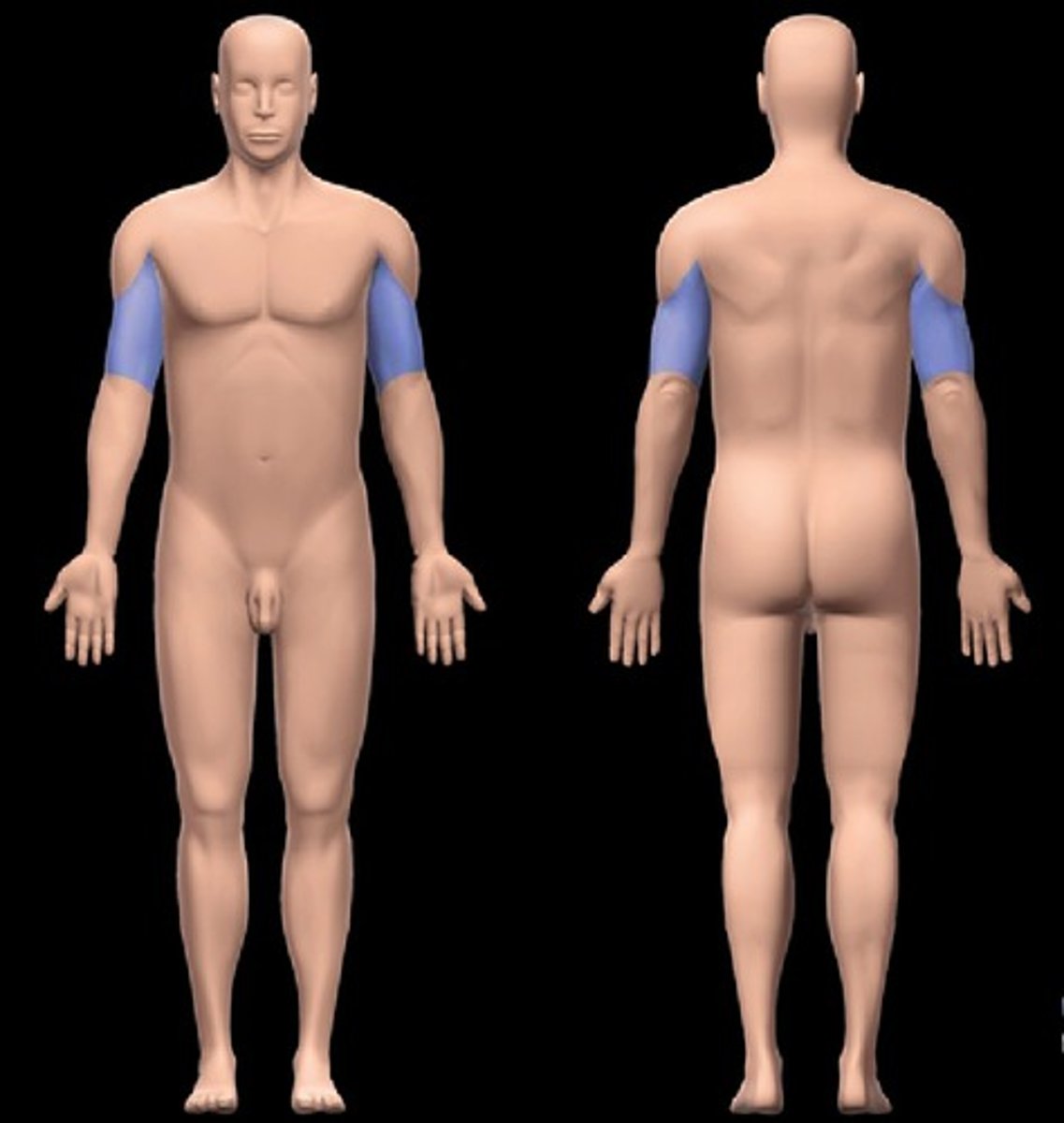
Antebrachial
forearm
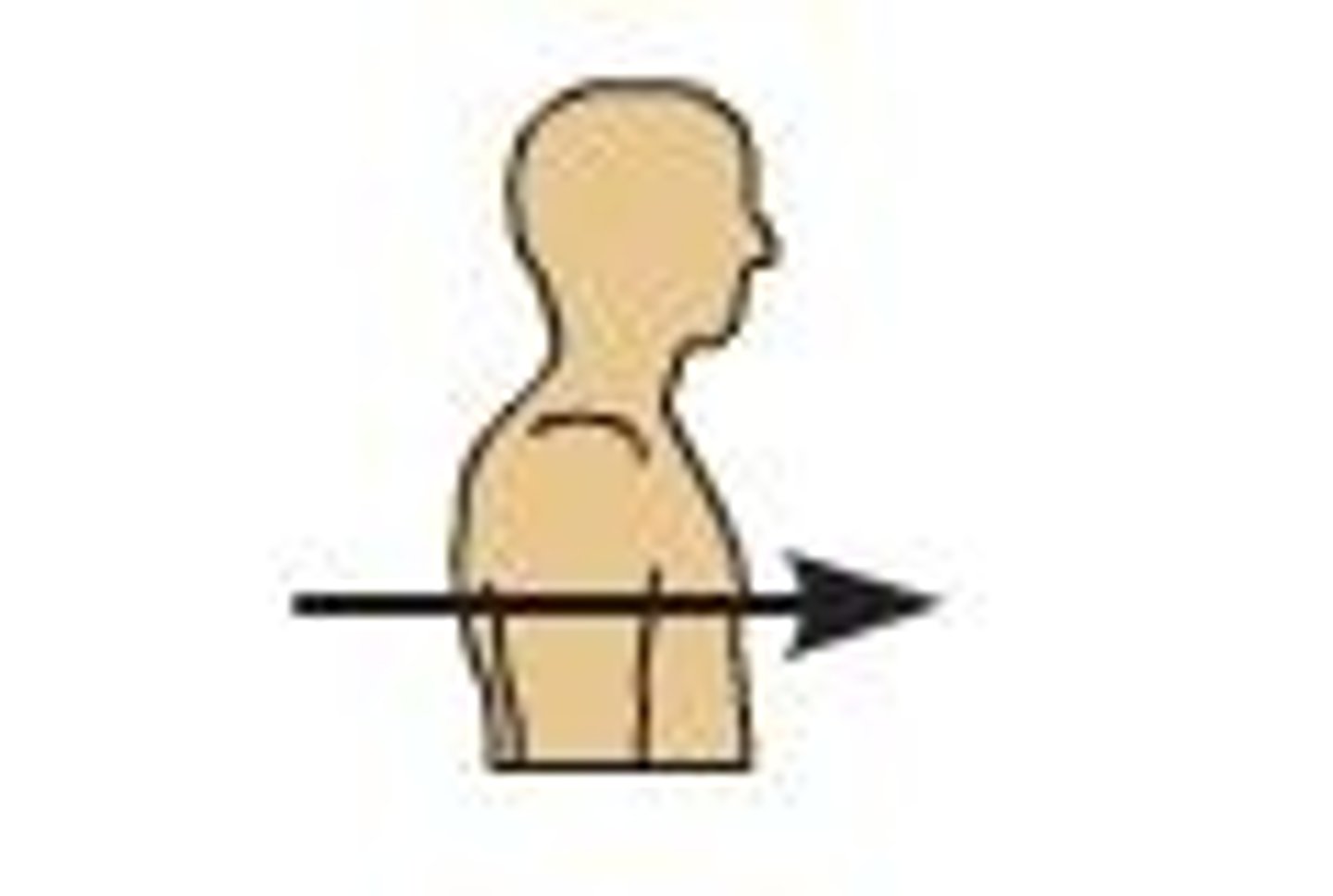
Antecubital
front of elbow
Axillary
armpit
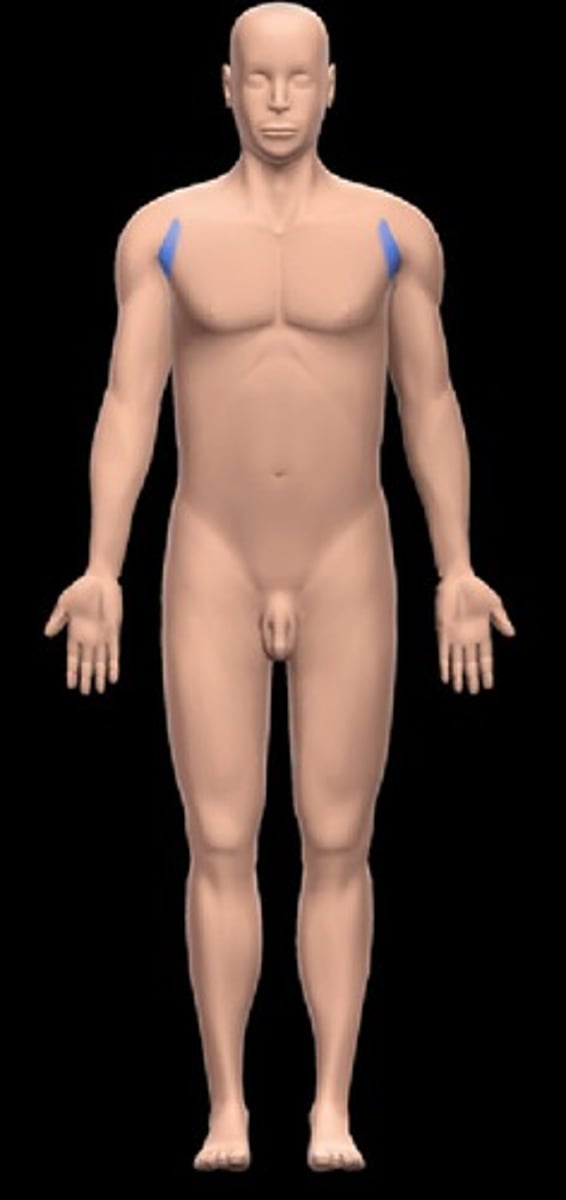
Brachial
upper arm
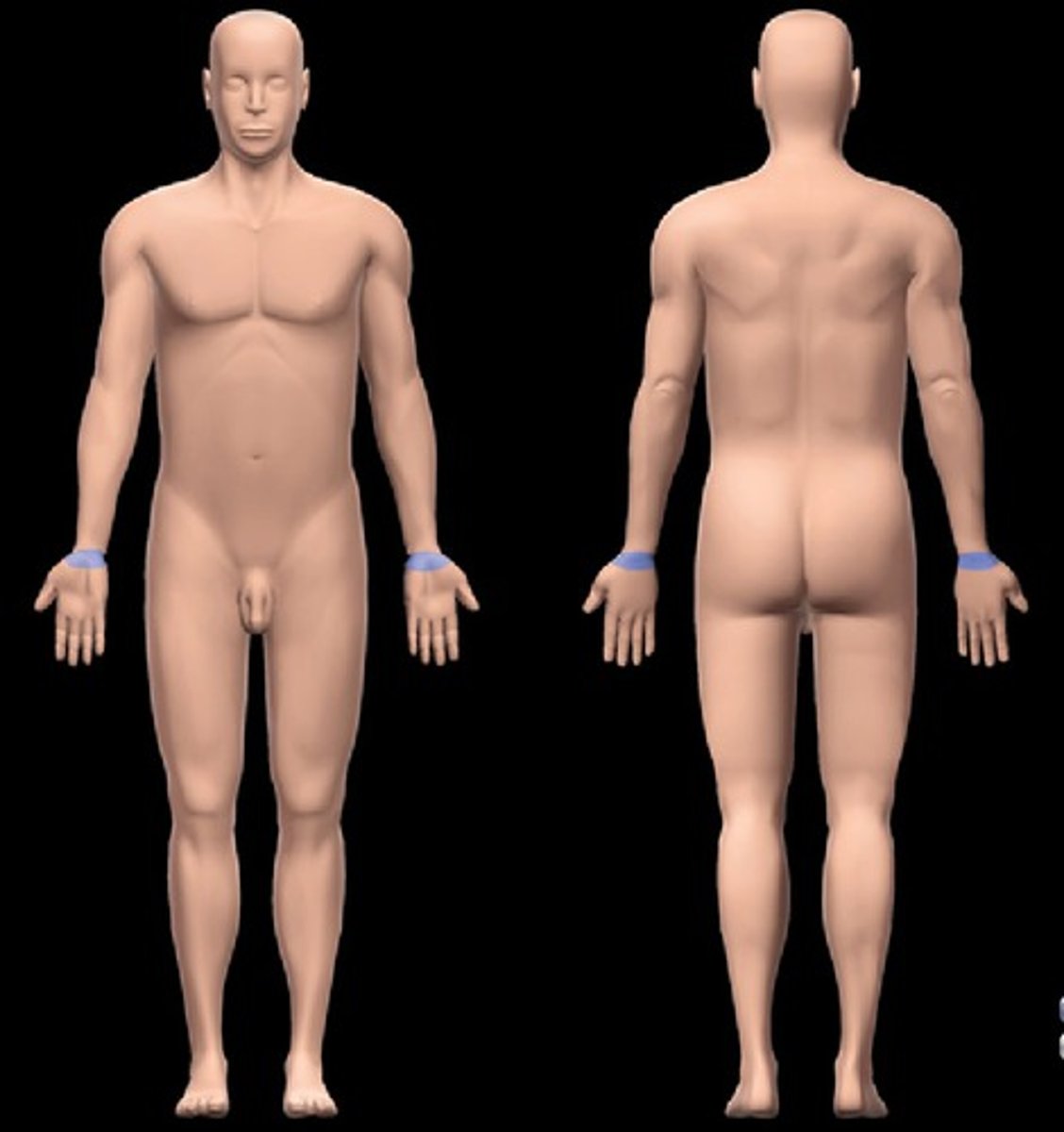
carpal
wrist area
cephalic
head
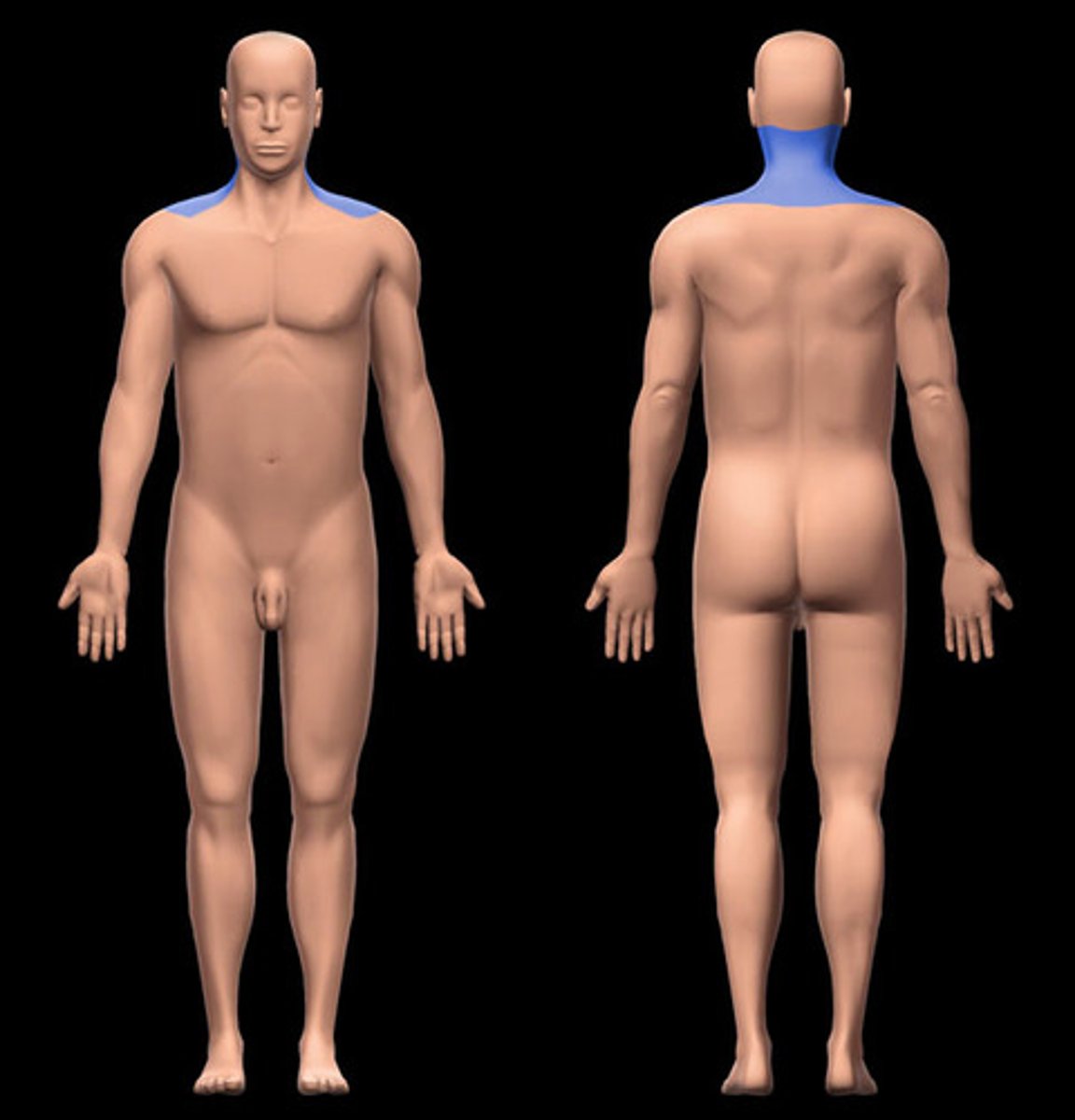
cervical
neck
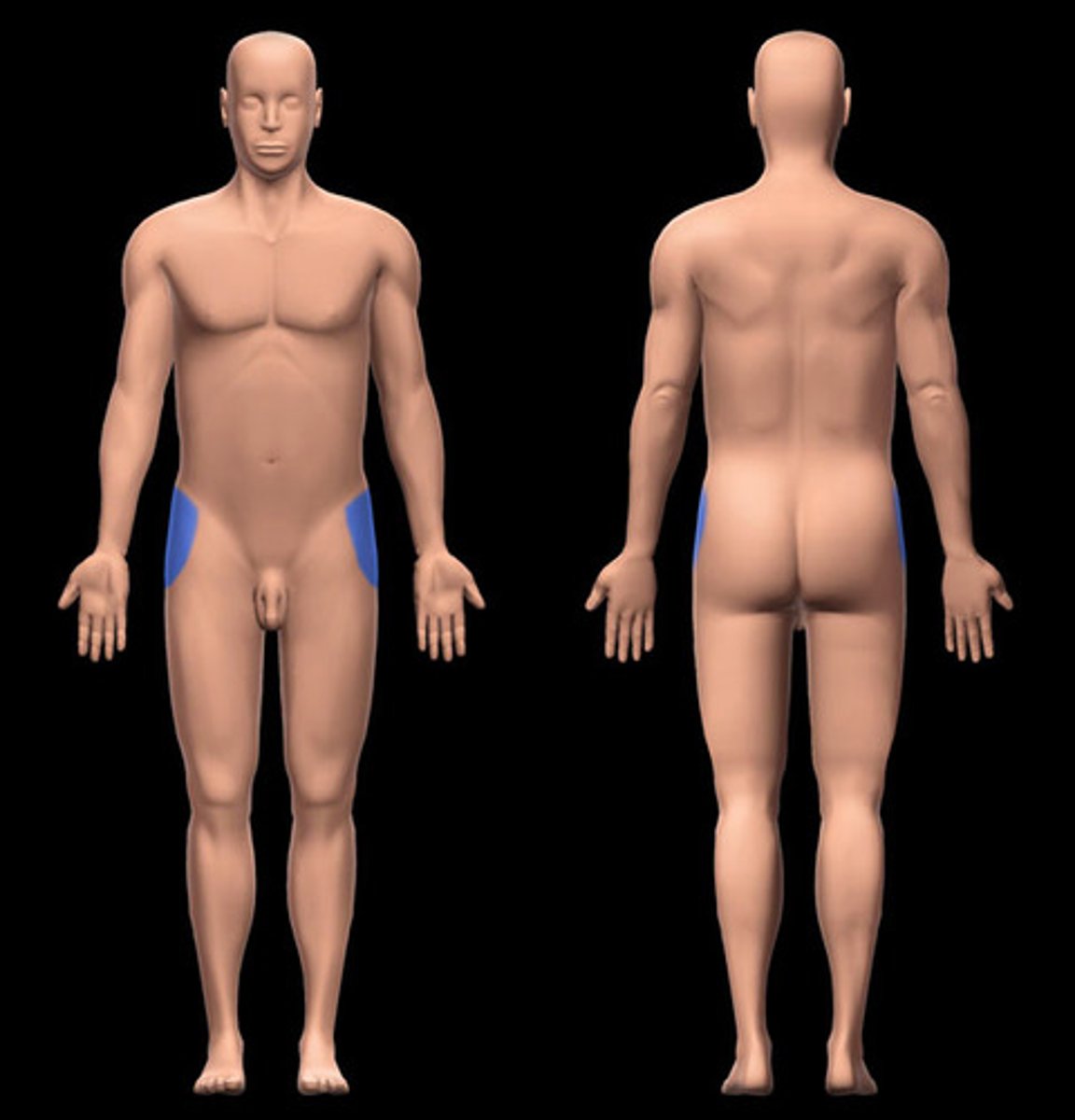
Coxal
hip
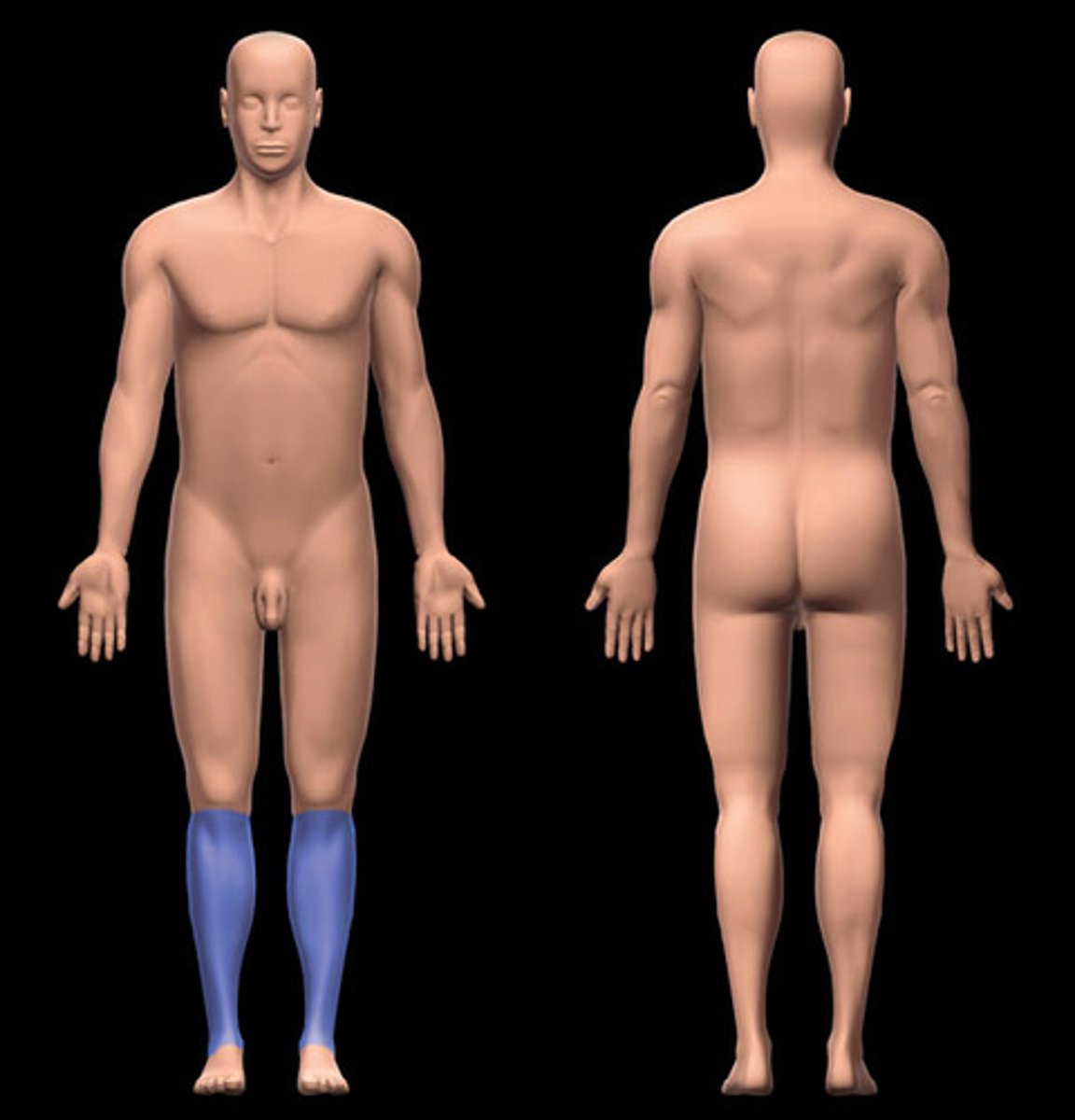
crural
lower leg (shin)
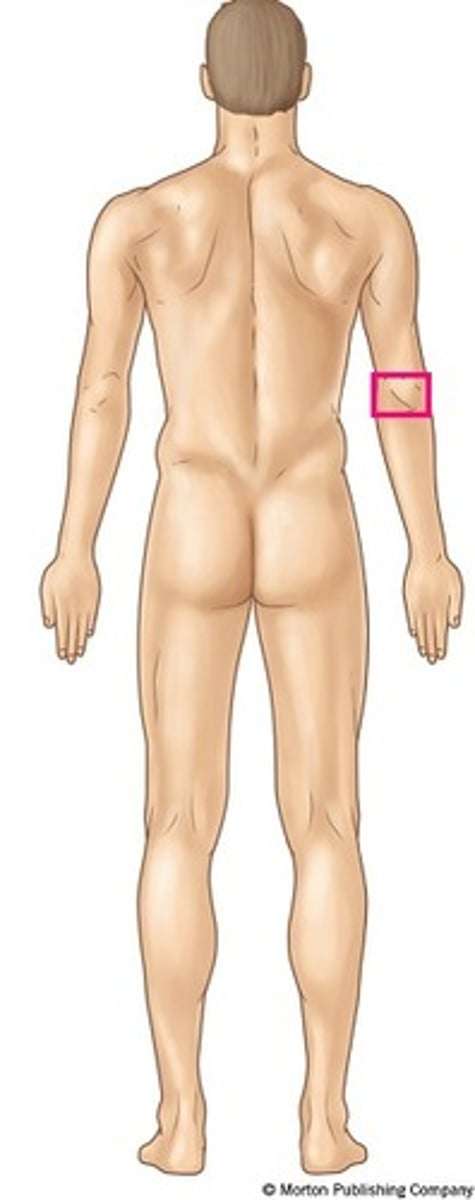
cubital/olecranal
elbow
digital
fingers and toes
femoral
thigh
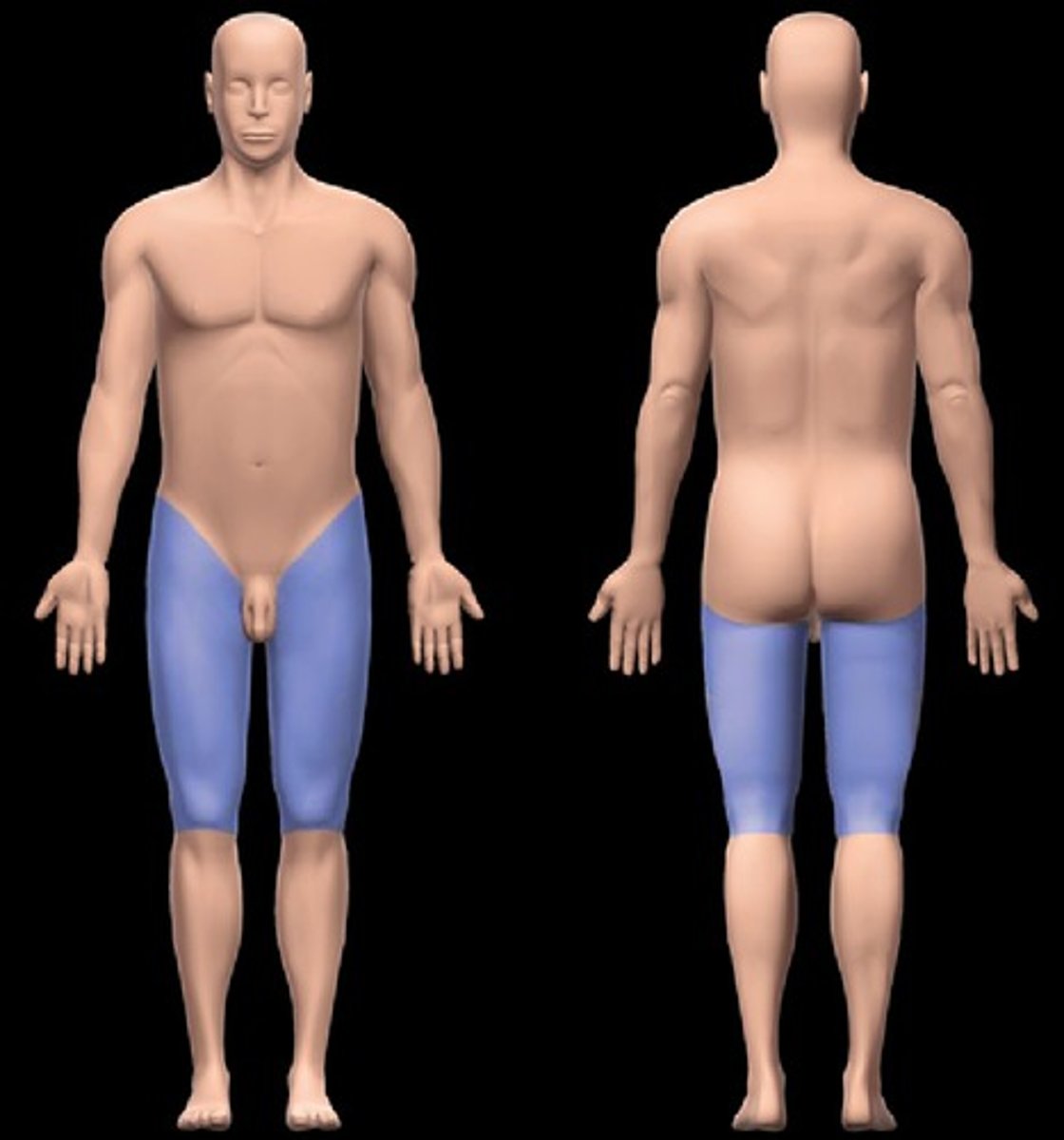
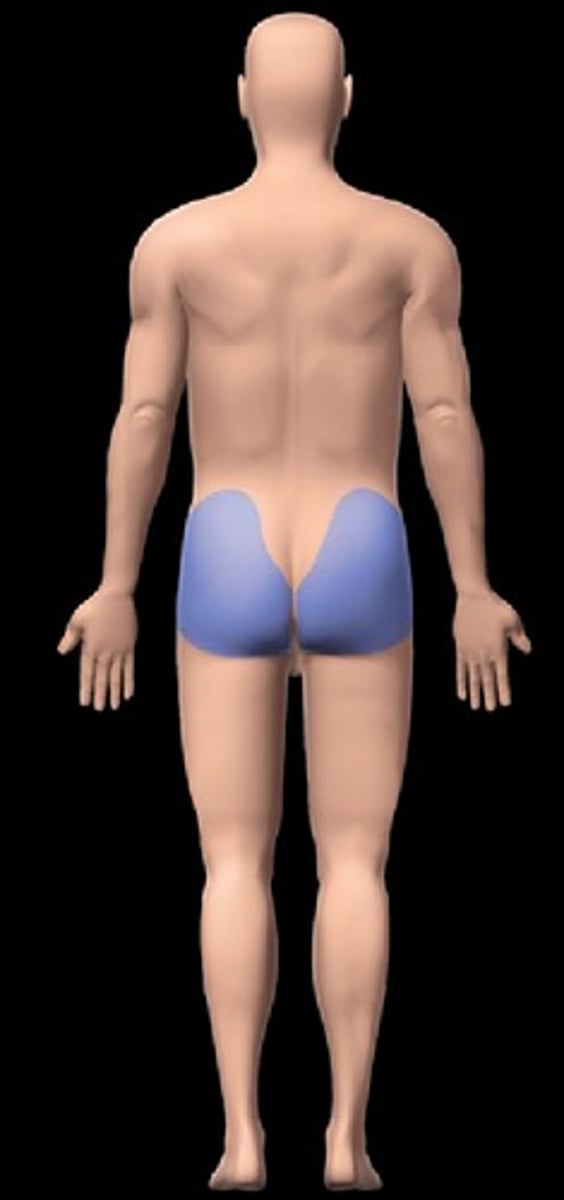
gluteal
buttock
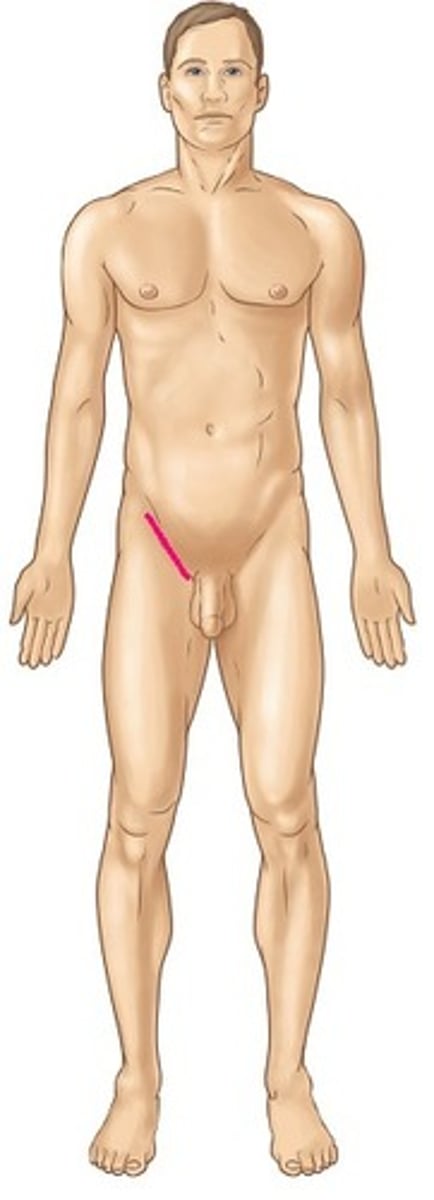
inguinal
groin
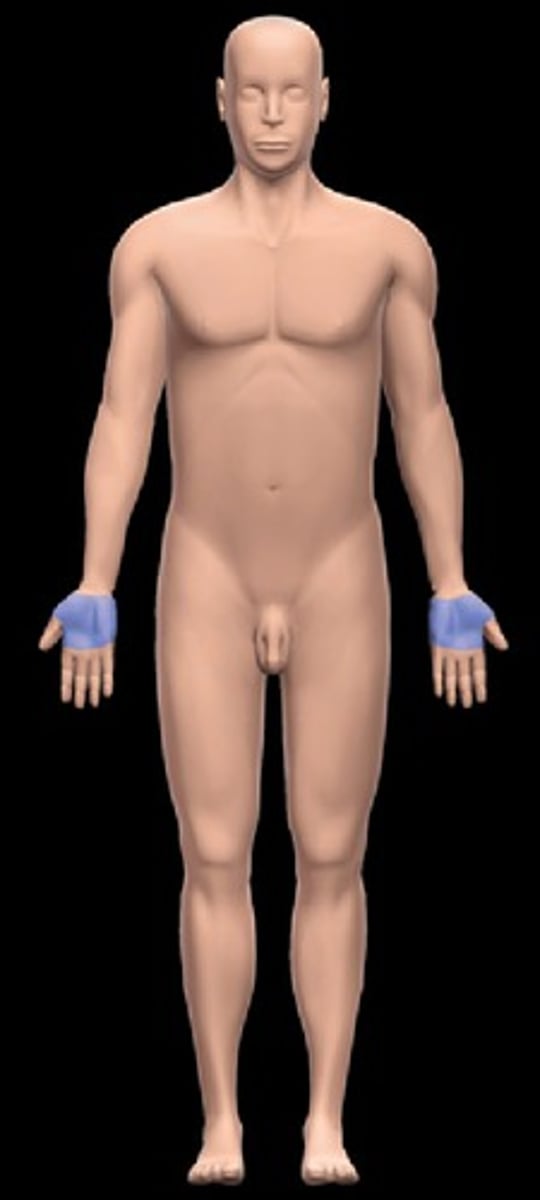
Palmar
palm of hand
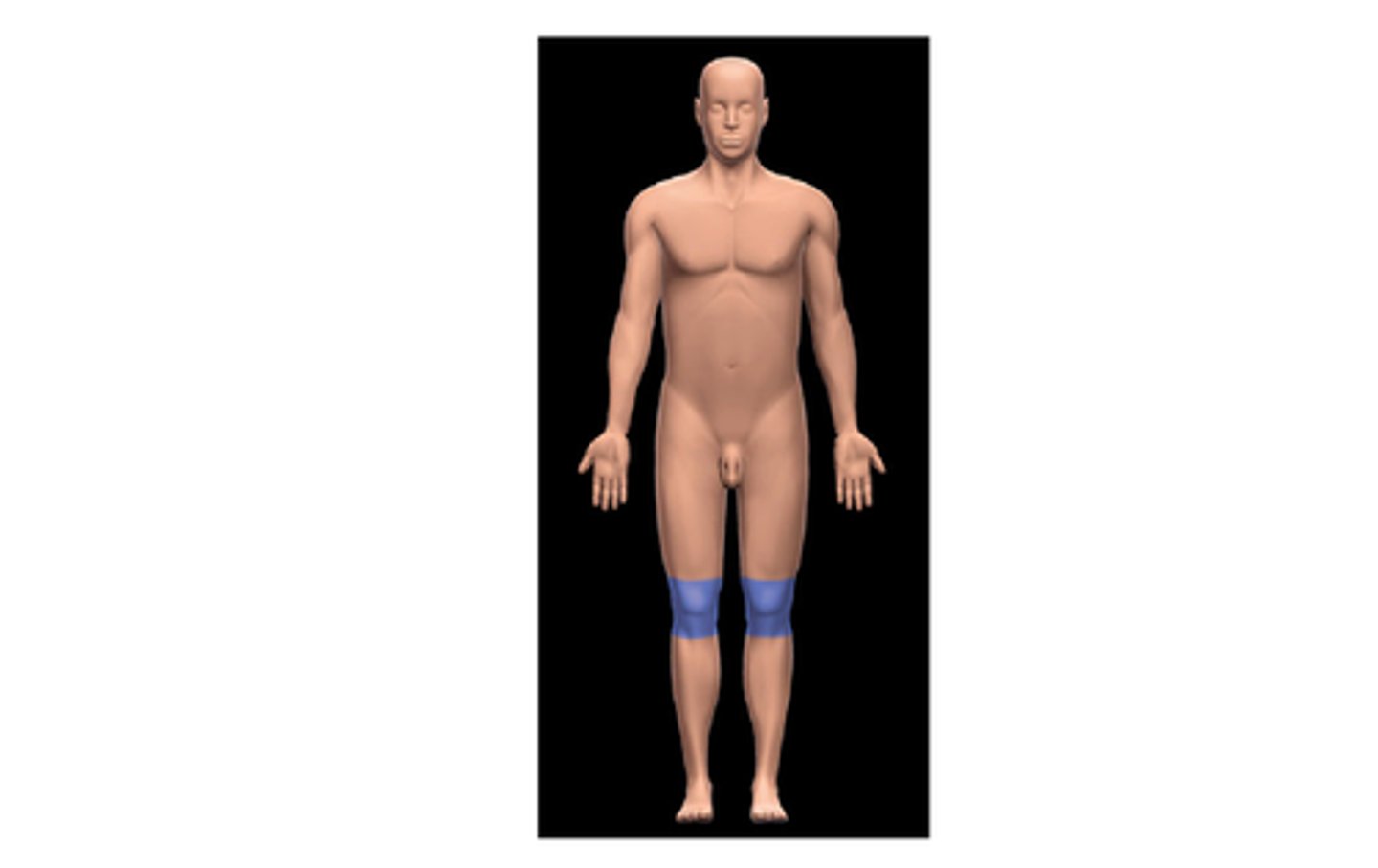
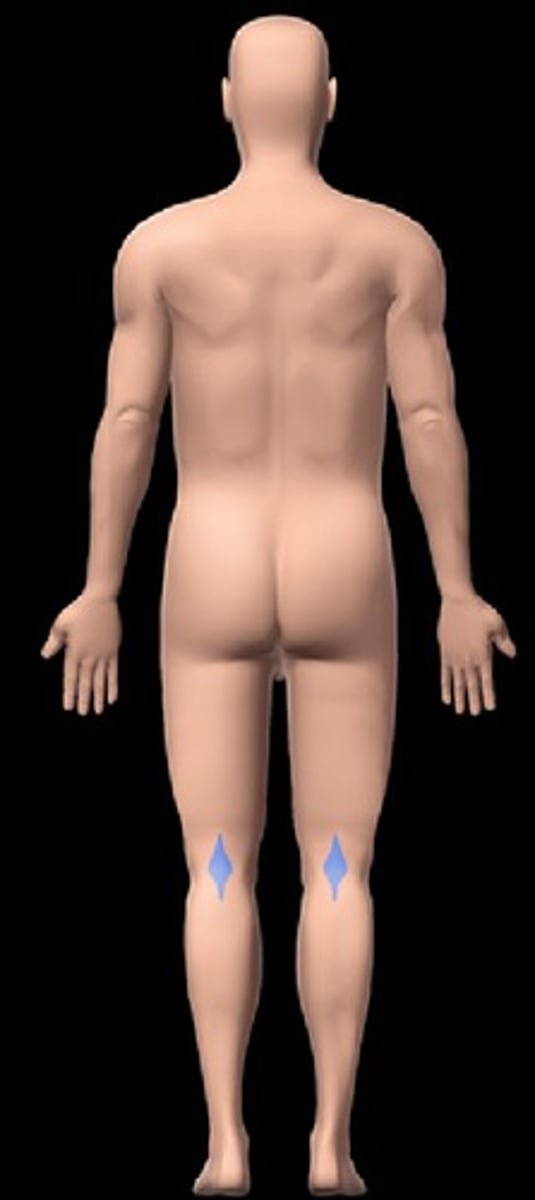
patellar
knee cap
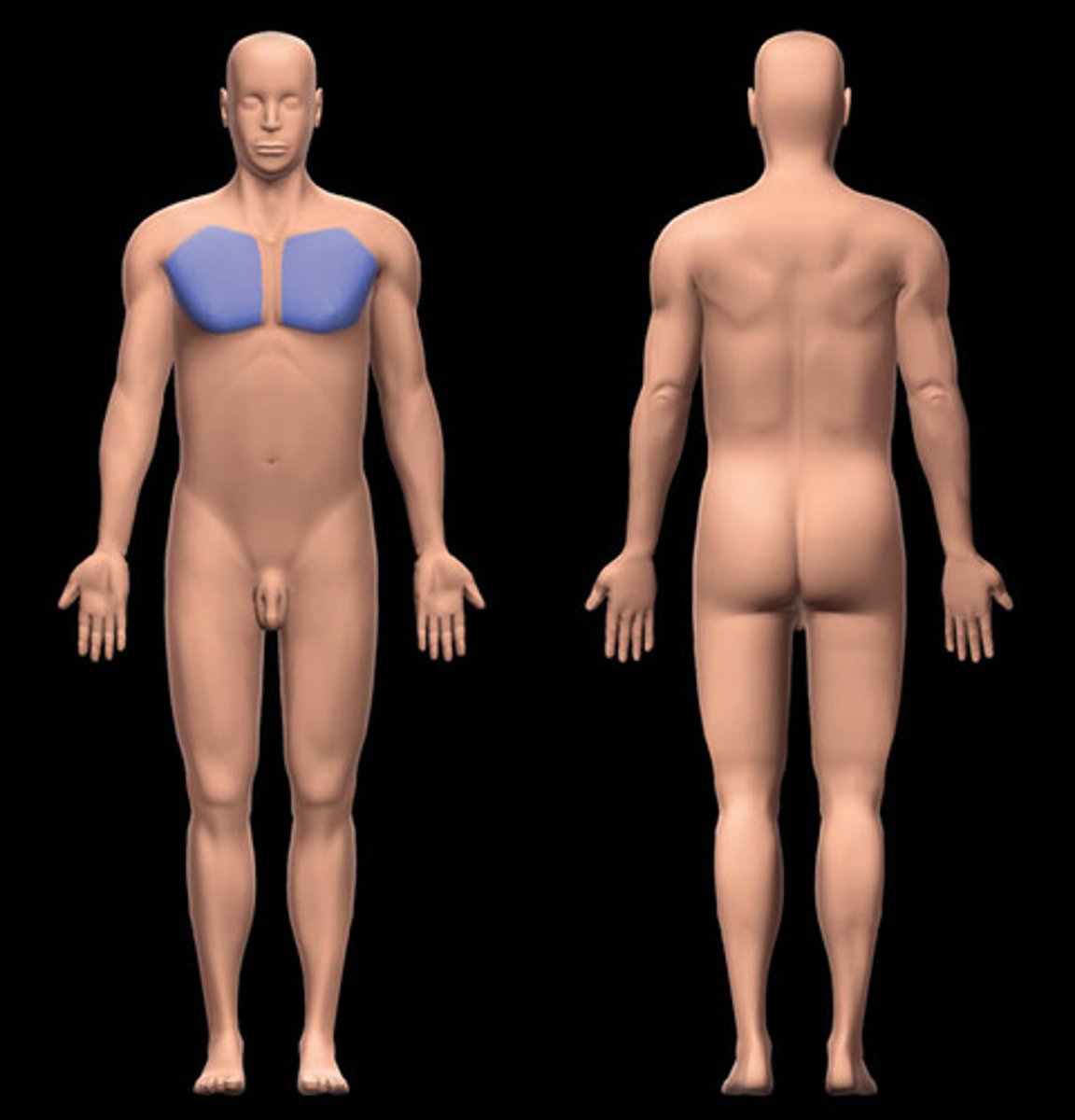
Pectoral
chest
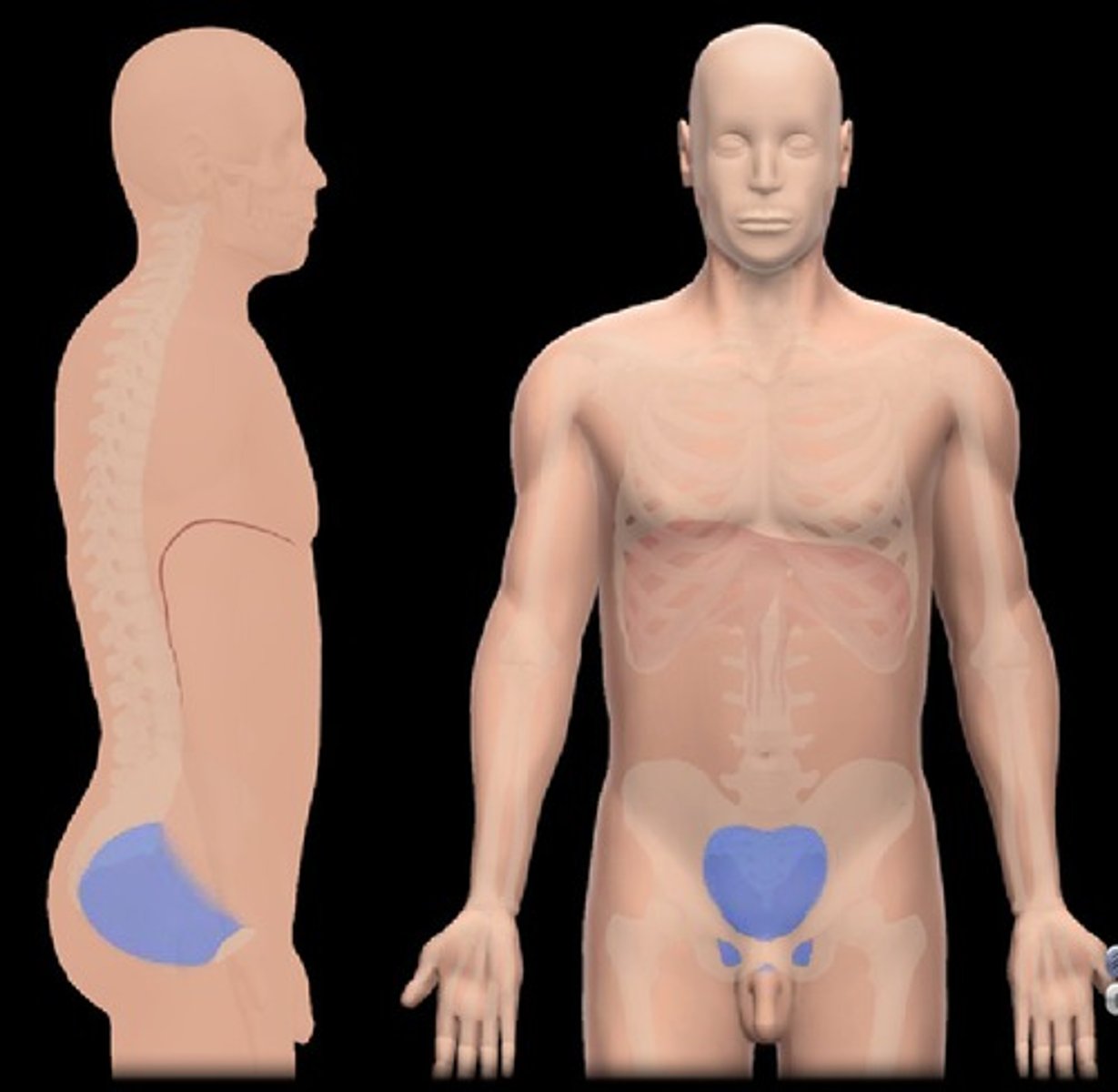
pelvic
area overlaying the front of the pelvis; pubic region
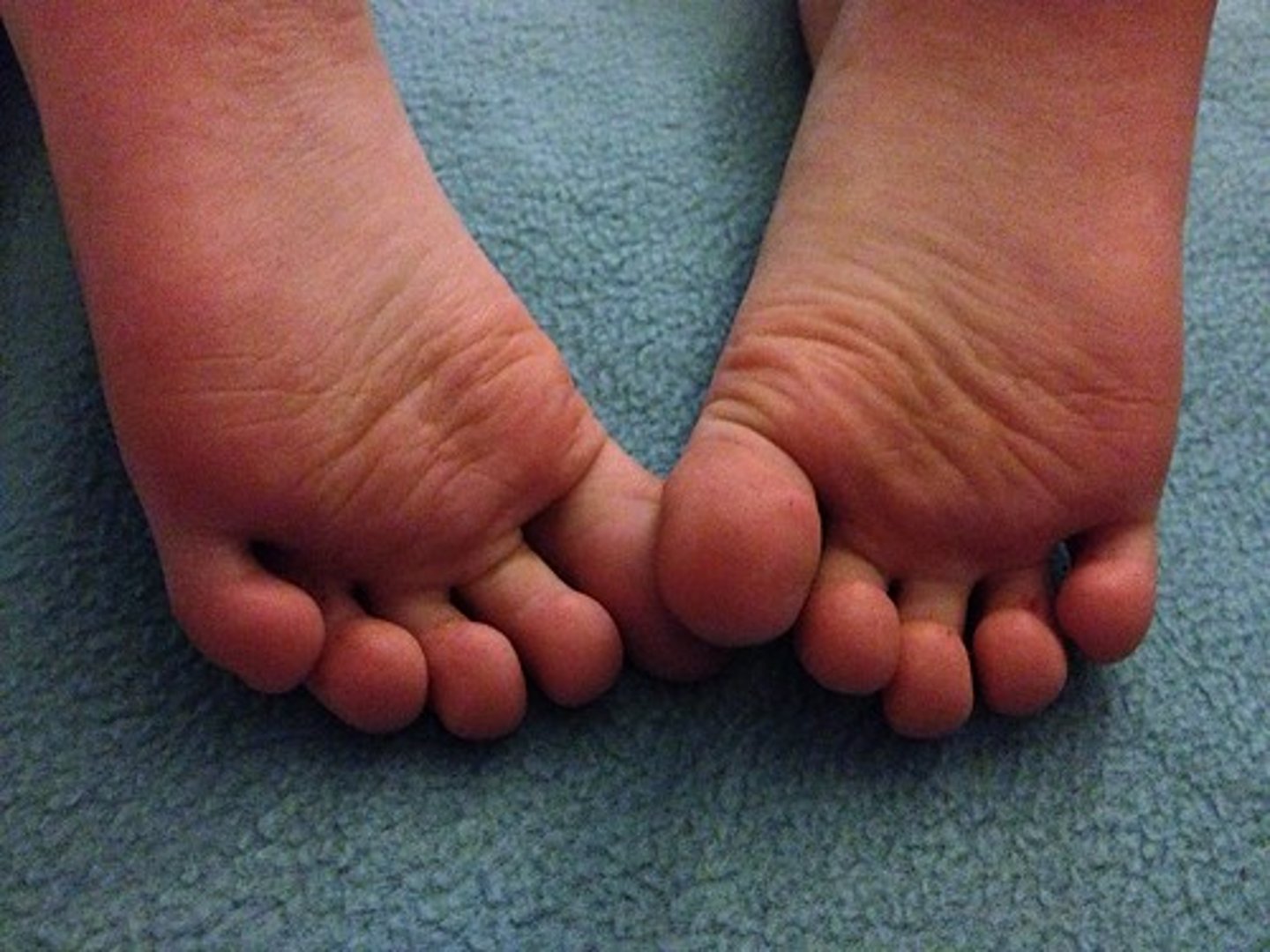
plantar
bottom of foot
Popliteal
back of knee
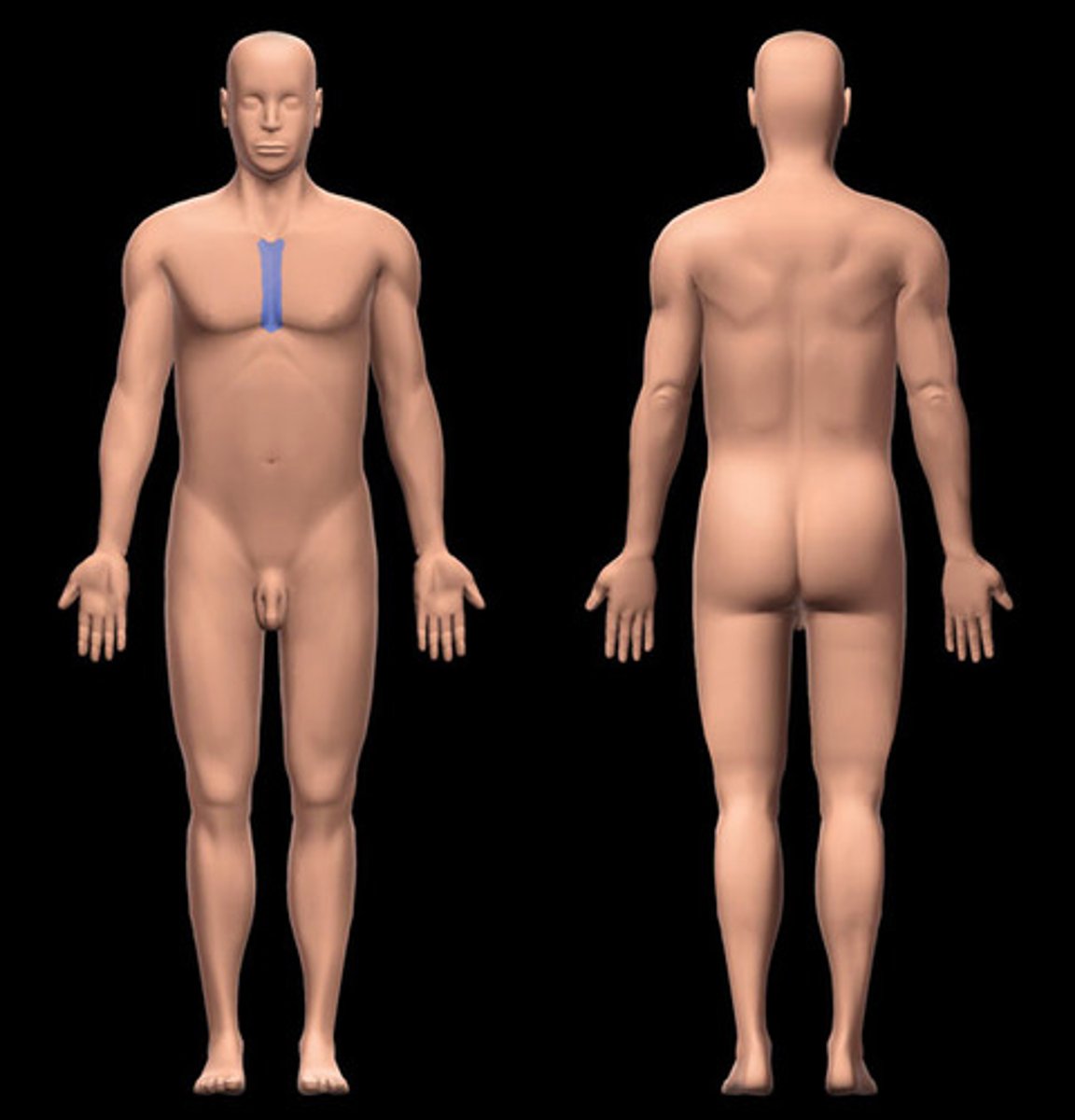
sternal
breastbone area
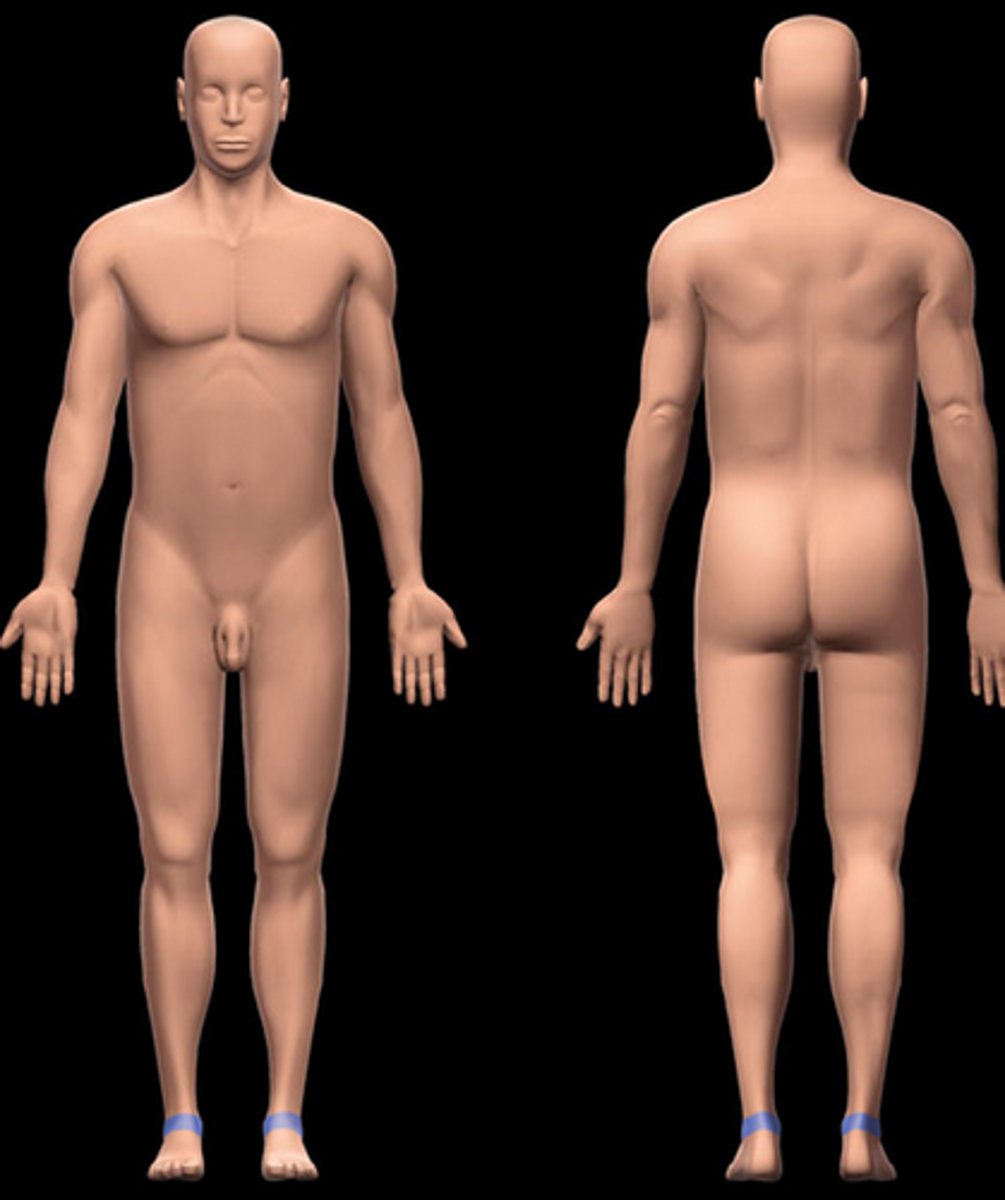
tarsal
ankle region
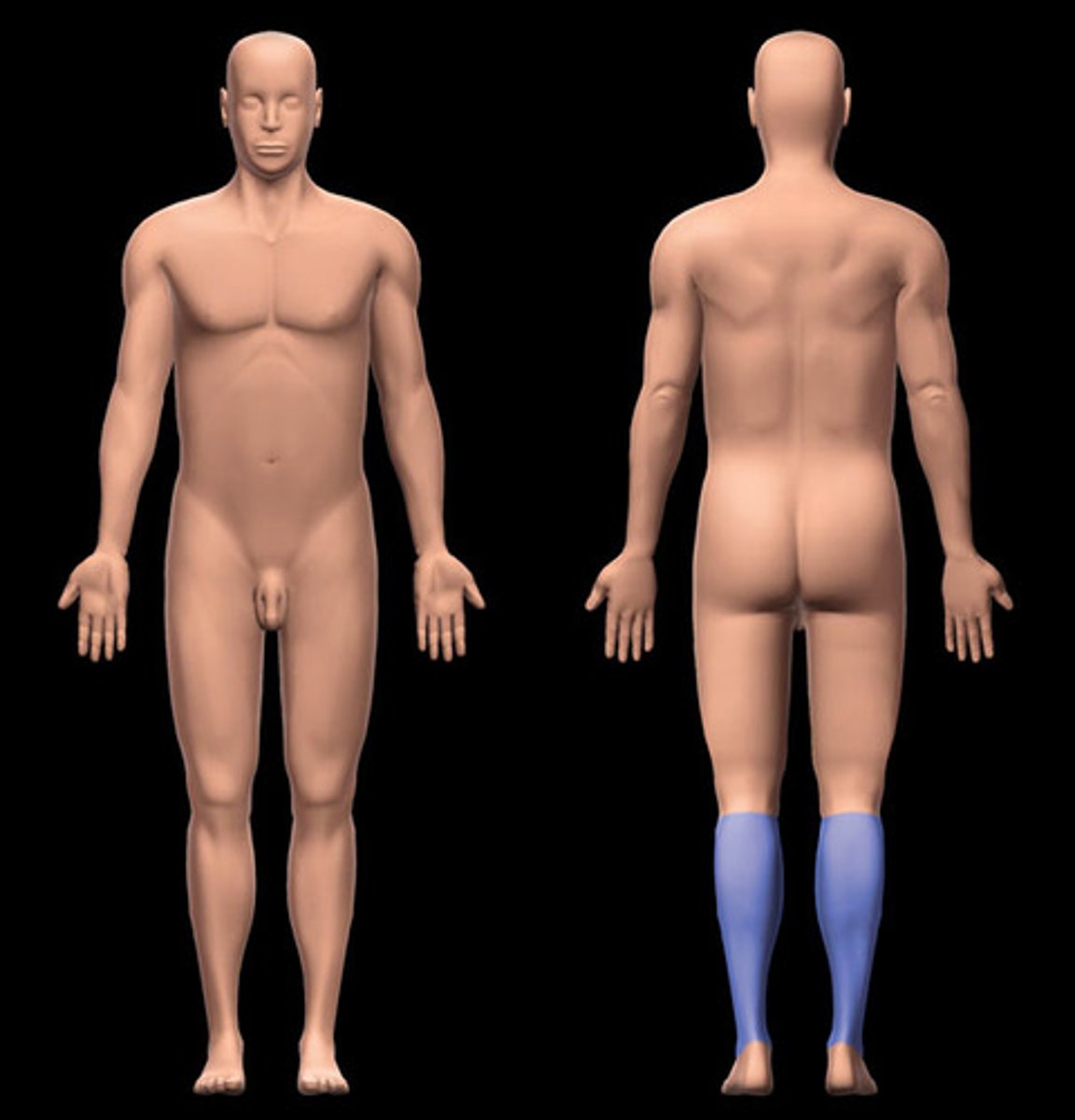
Sural
calf (back of leg)
vertebral
area of the spine
Adrenal Gland
Sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones that help arouse the body in times of stress.

Brain
The mass of nerve tissue that is the main control center of the body
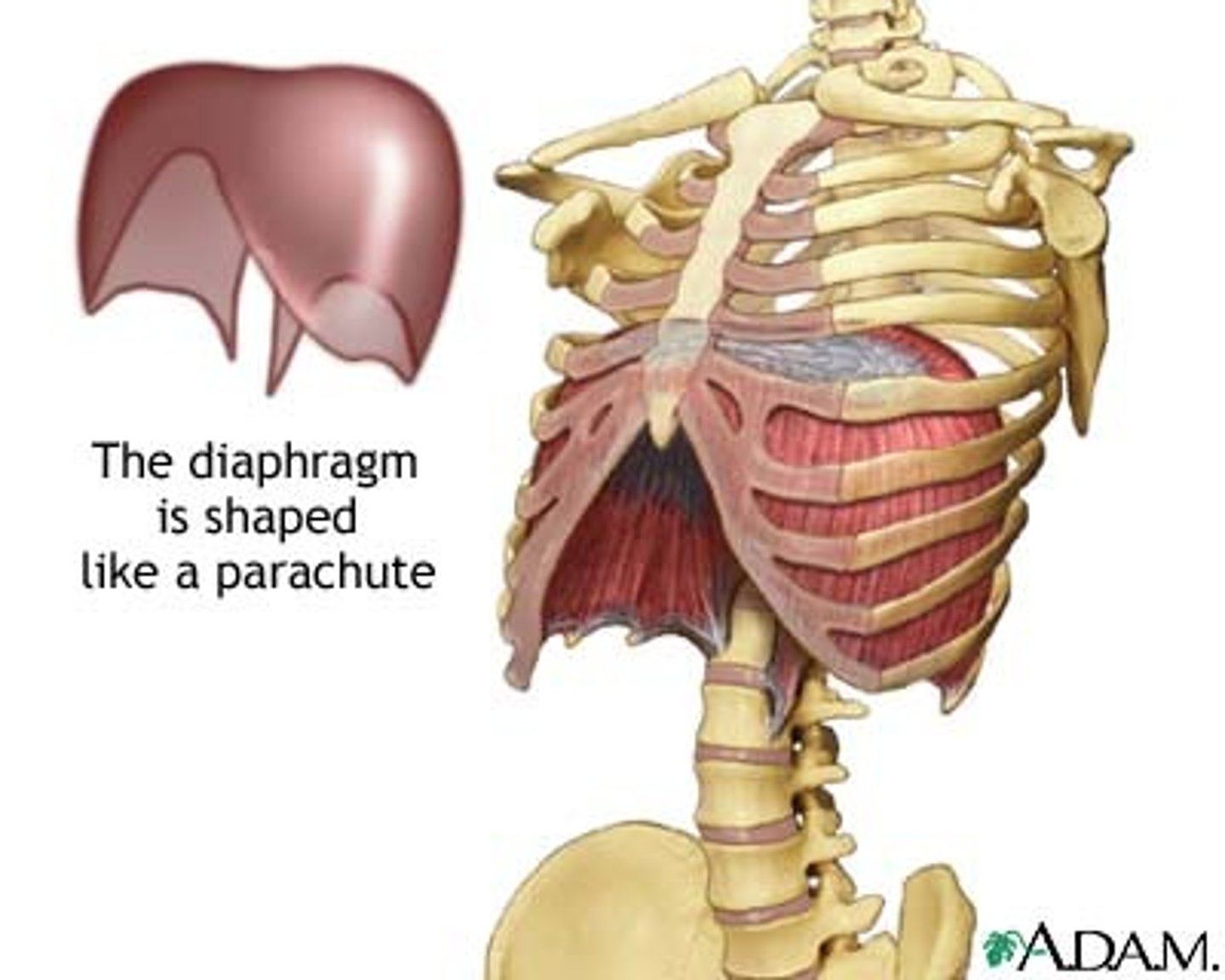
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
heart
A hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
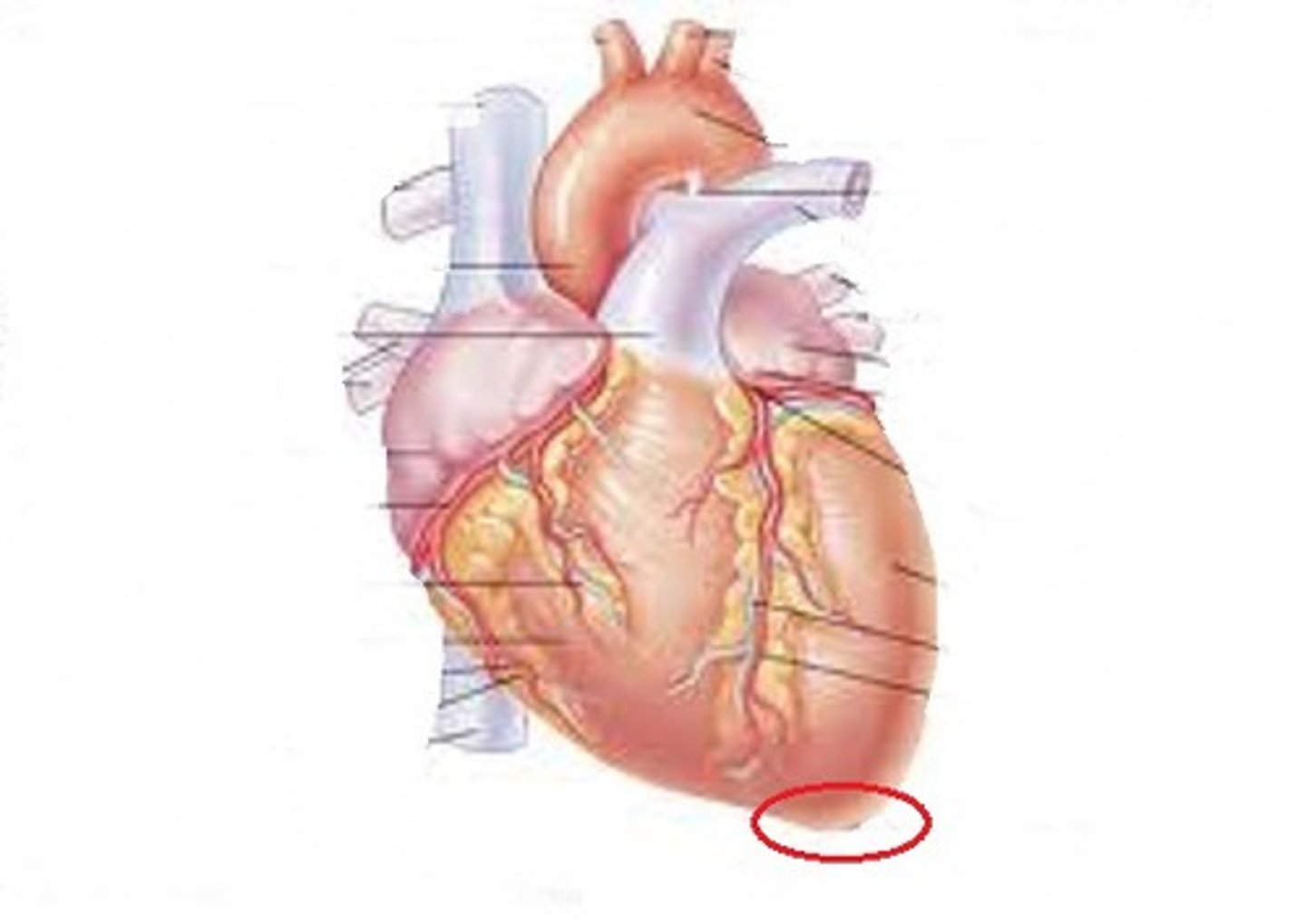
Kidneys
Filter blood from the renal arteries and produce urine as waste
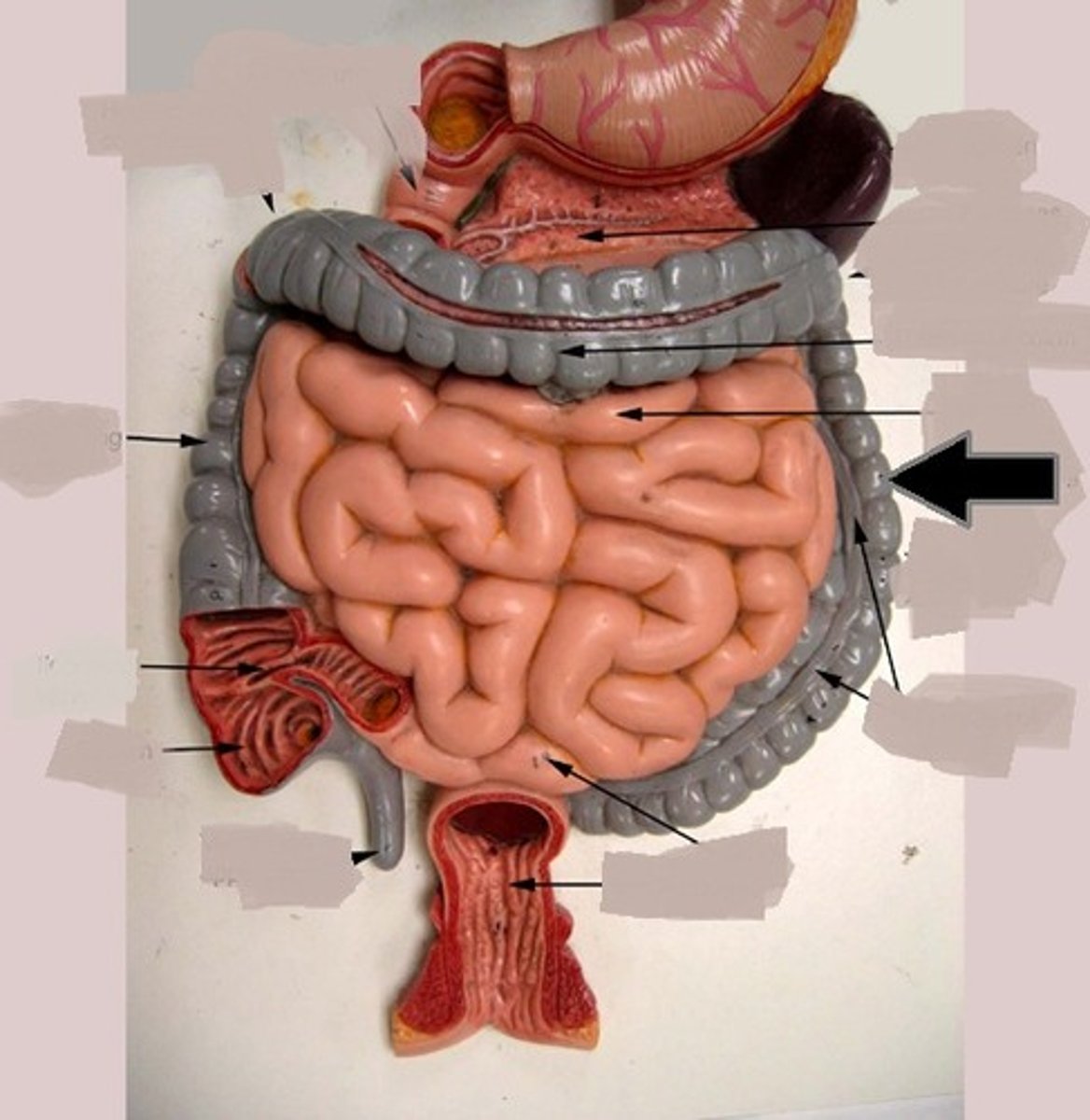
large intestine
The last section of the digestive system, where water is absorbed from food and the remaining material is eliminated from the body
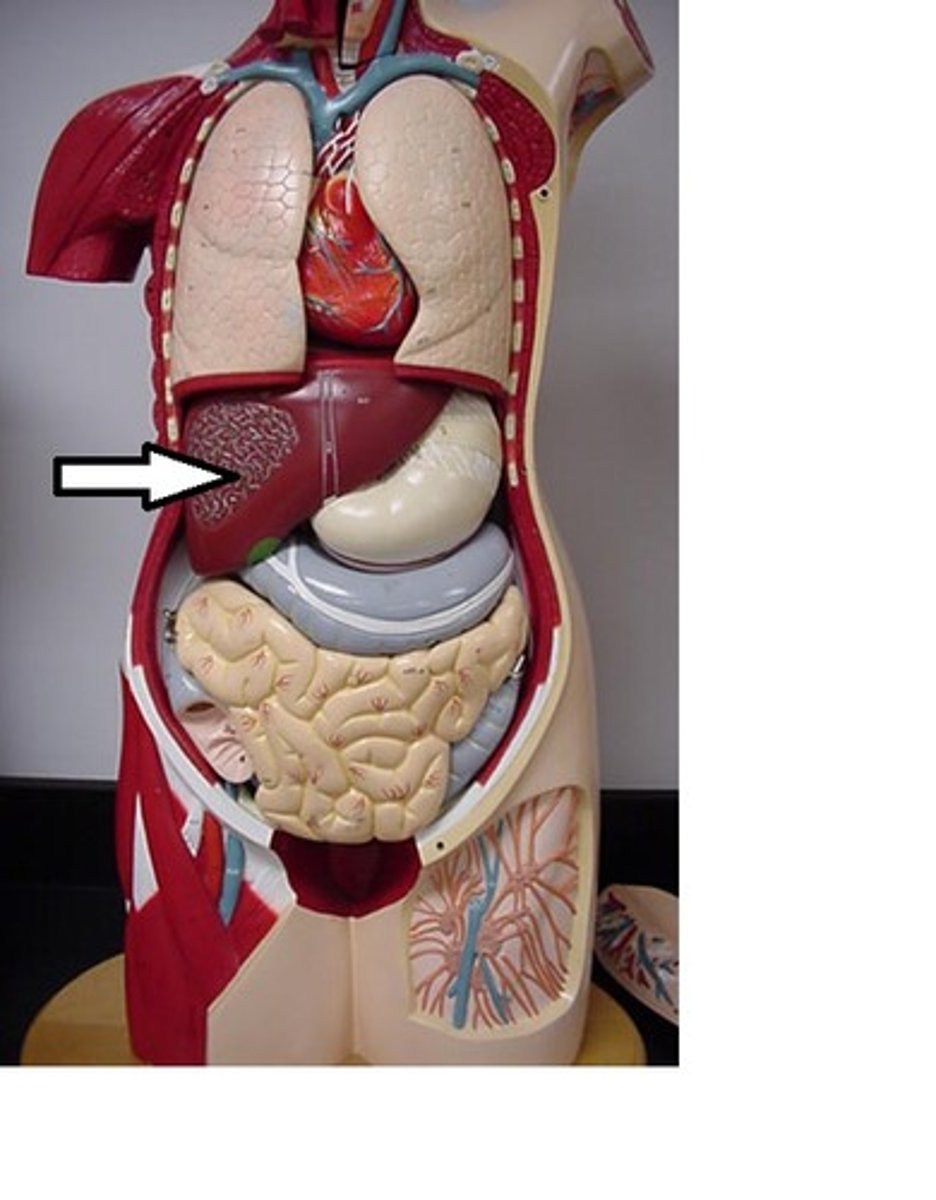
Liver
produces bile (a substance used to digest fats)
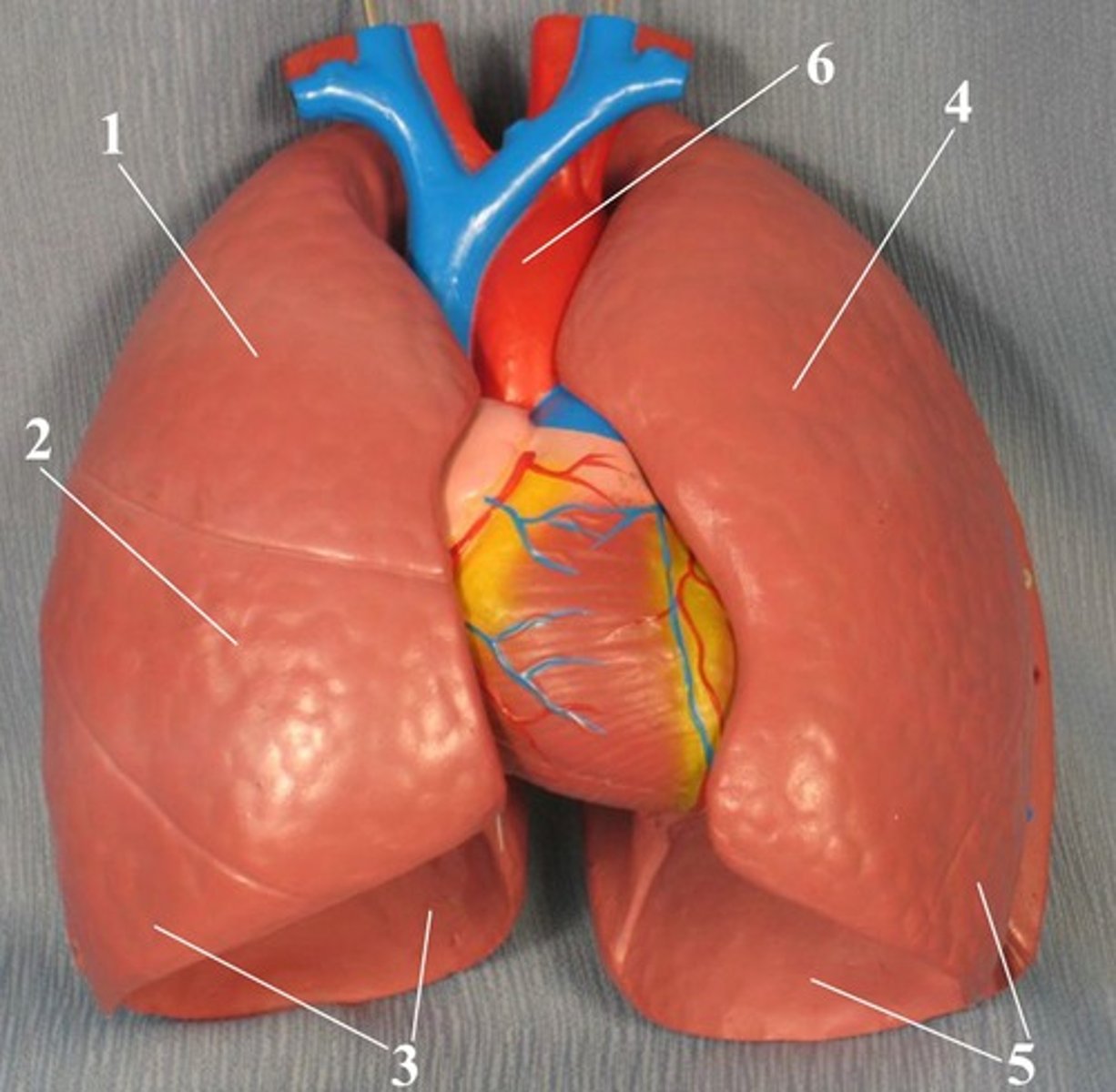
Lungs
Where gas exchange takes place
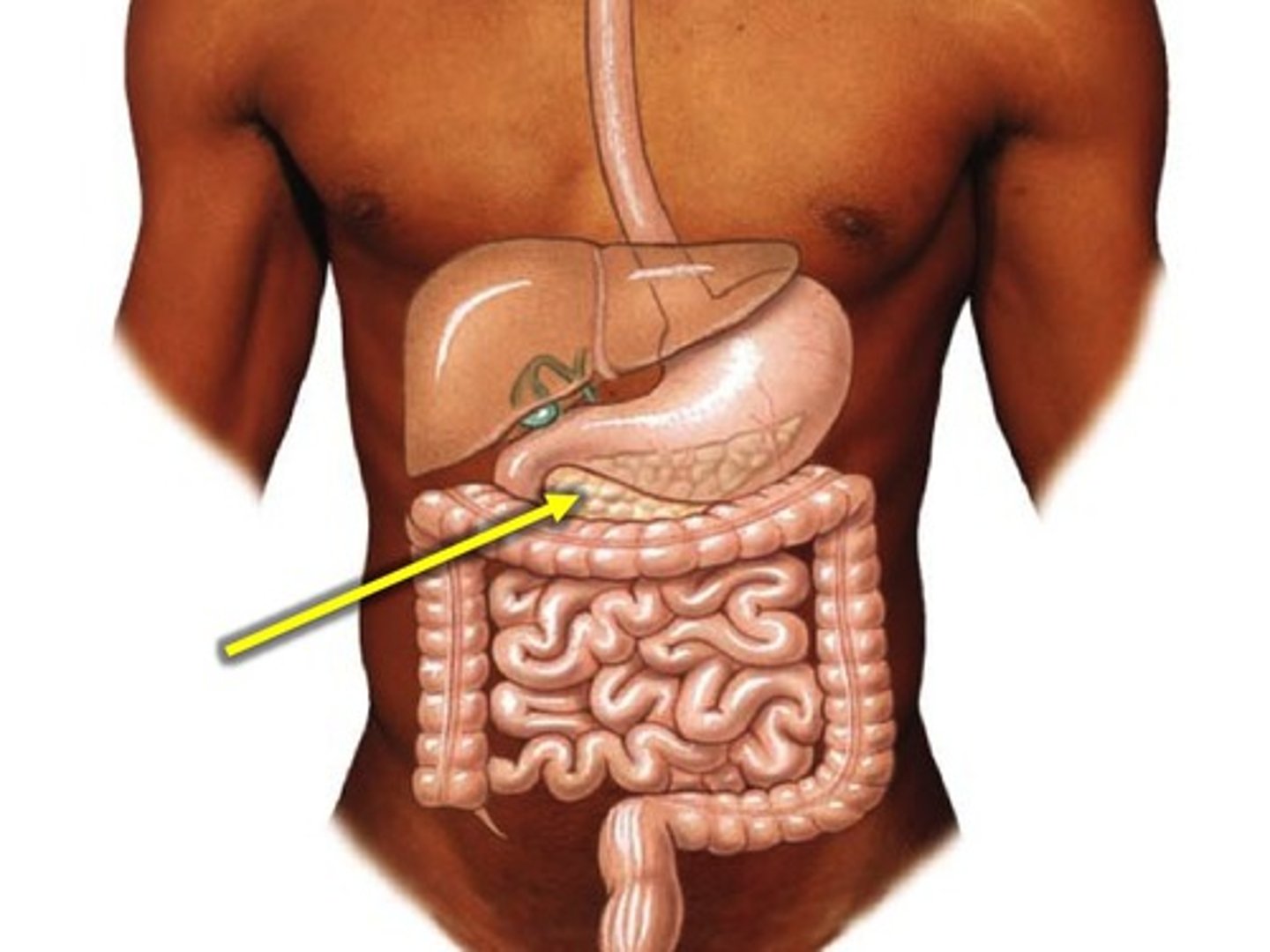
Pancreas
Regulates the level of sugar in the blood, produces the hormone, insulin
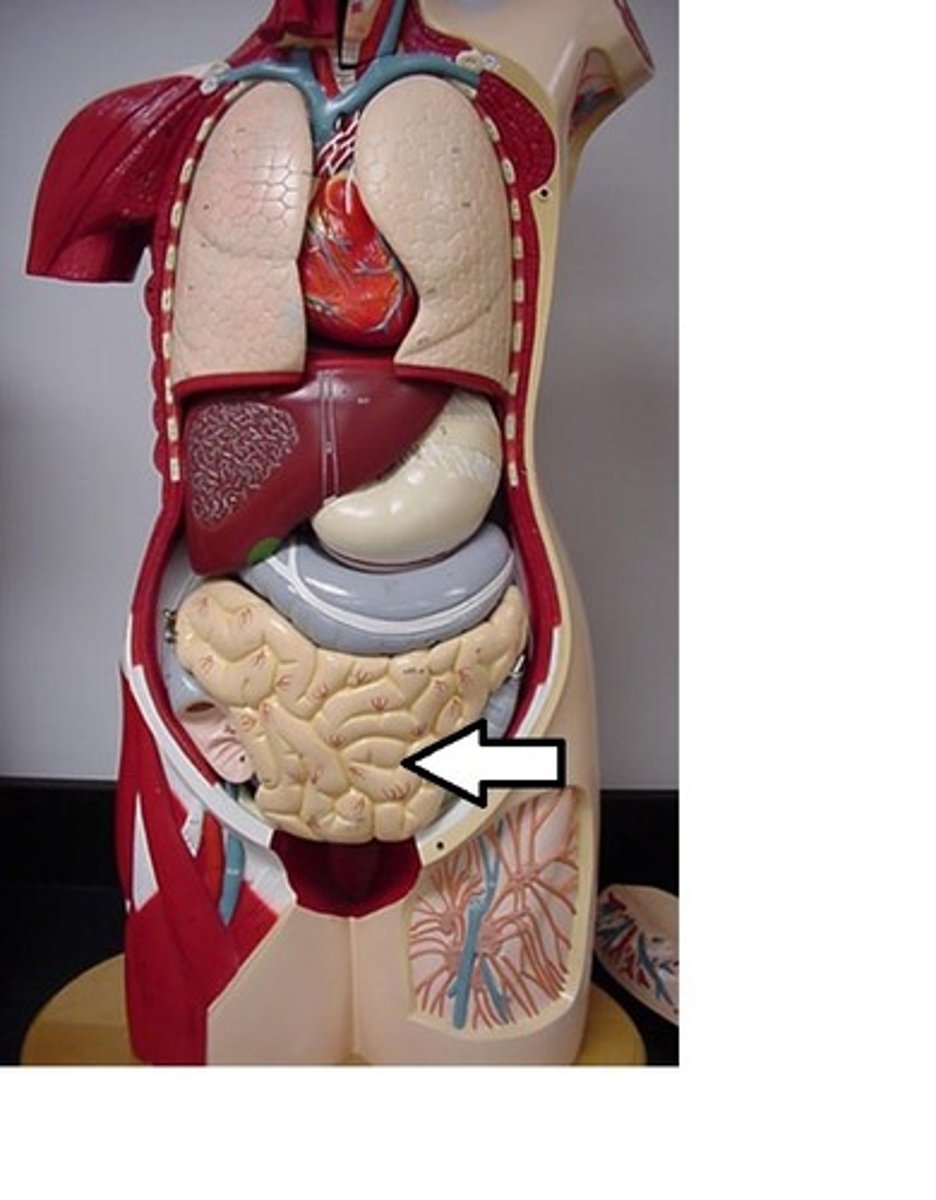
Small Intestine
Chemically digests and absorbs food
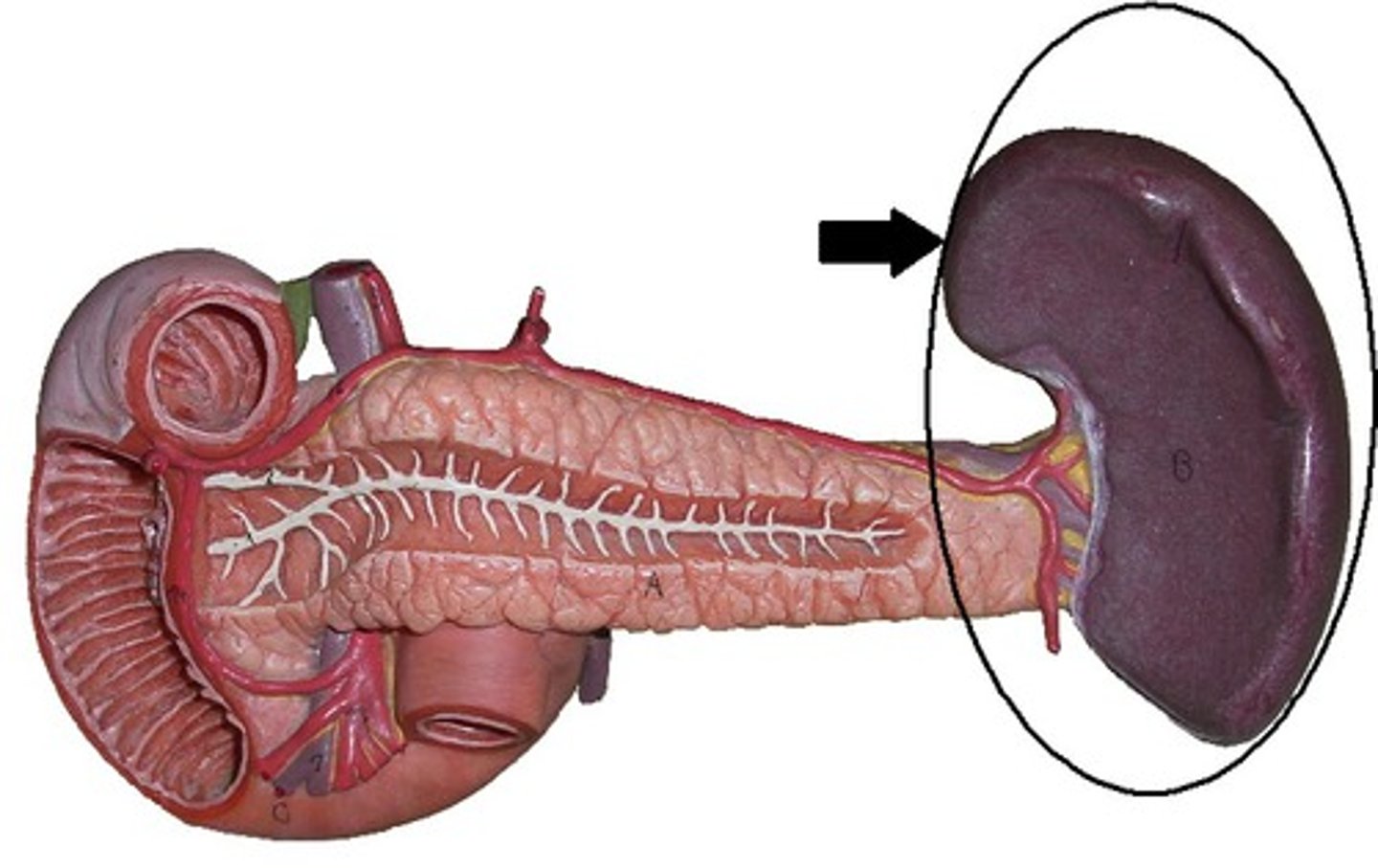
Spleen
Organ near the stomach that stores, and eliminates blood cells and germs.
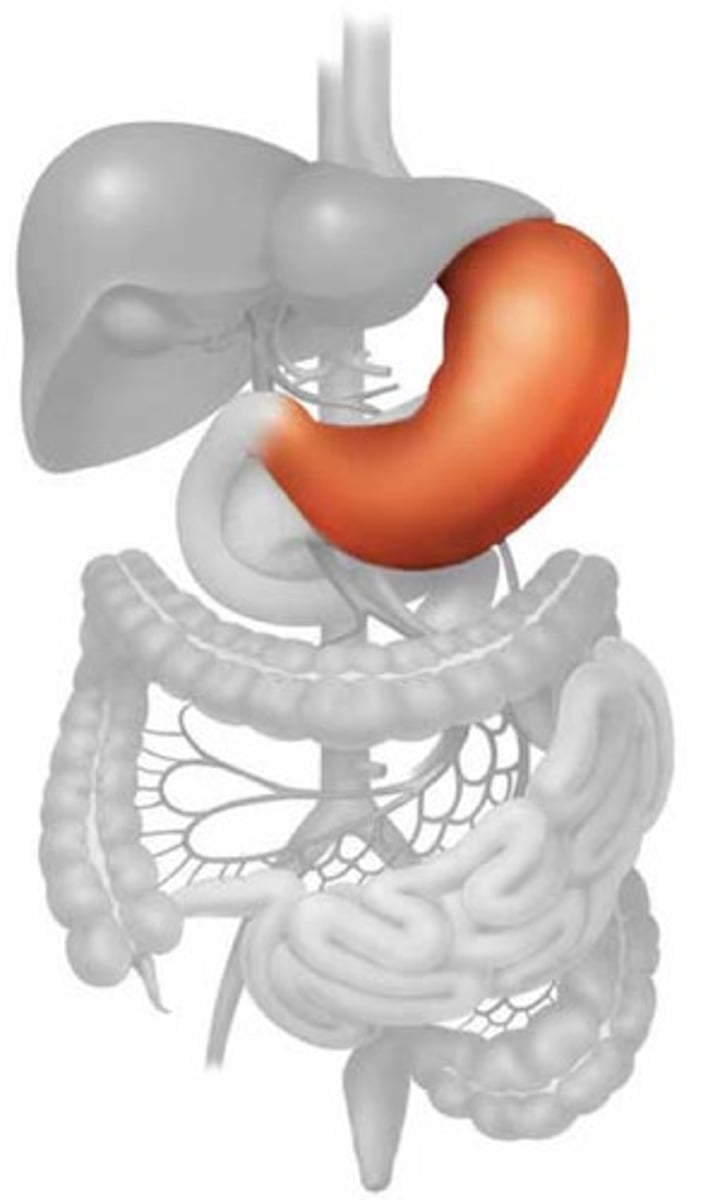
Stomach
large muscular sac that continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
Thyroid Gland
located in front of the neck; secretes triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and calcitonin (hormones)
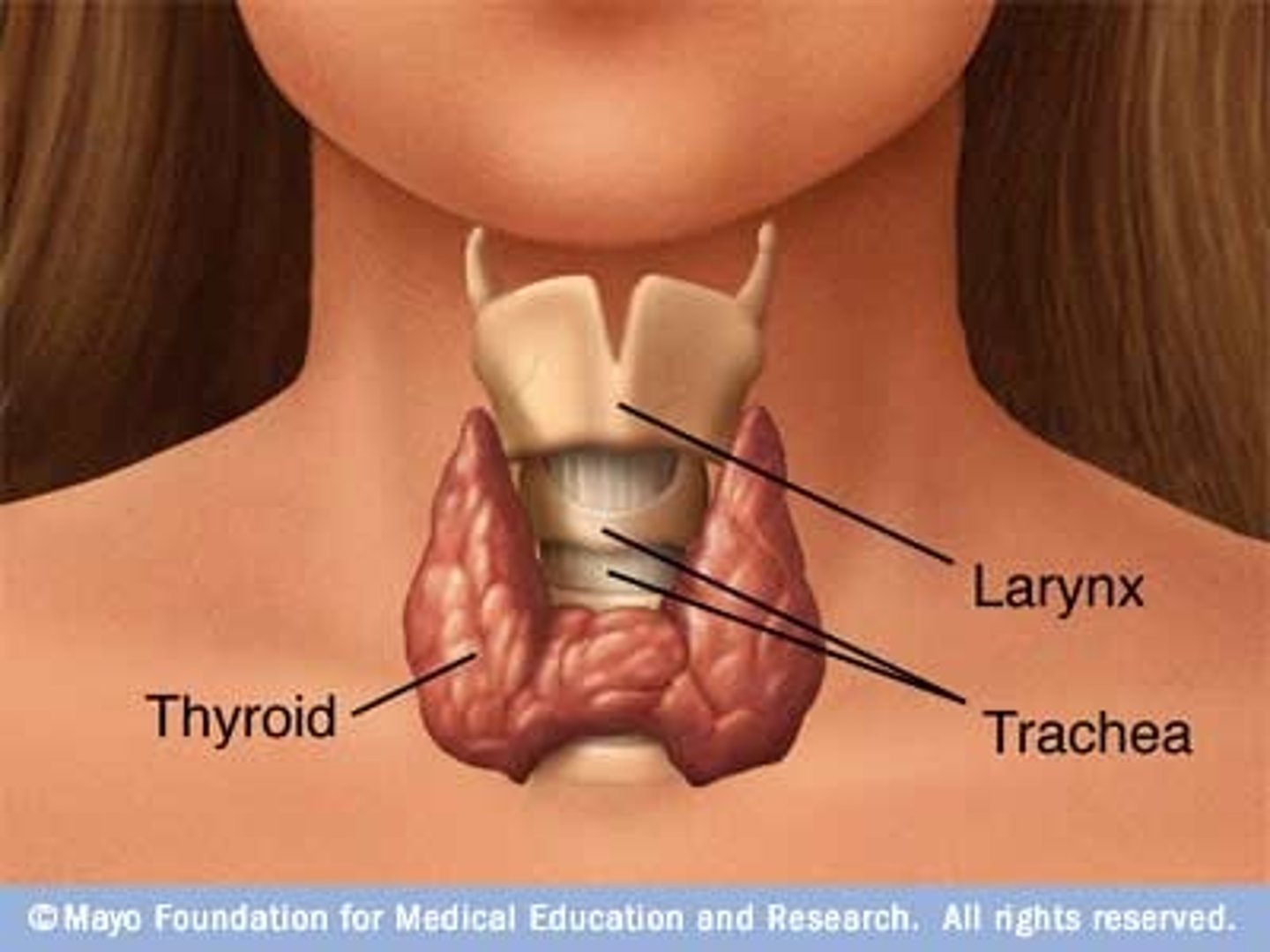
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
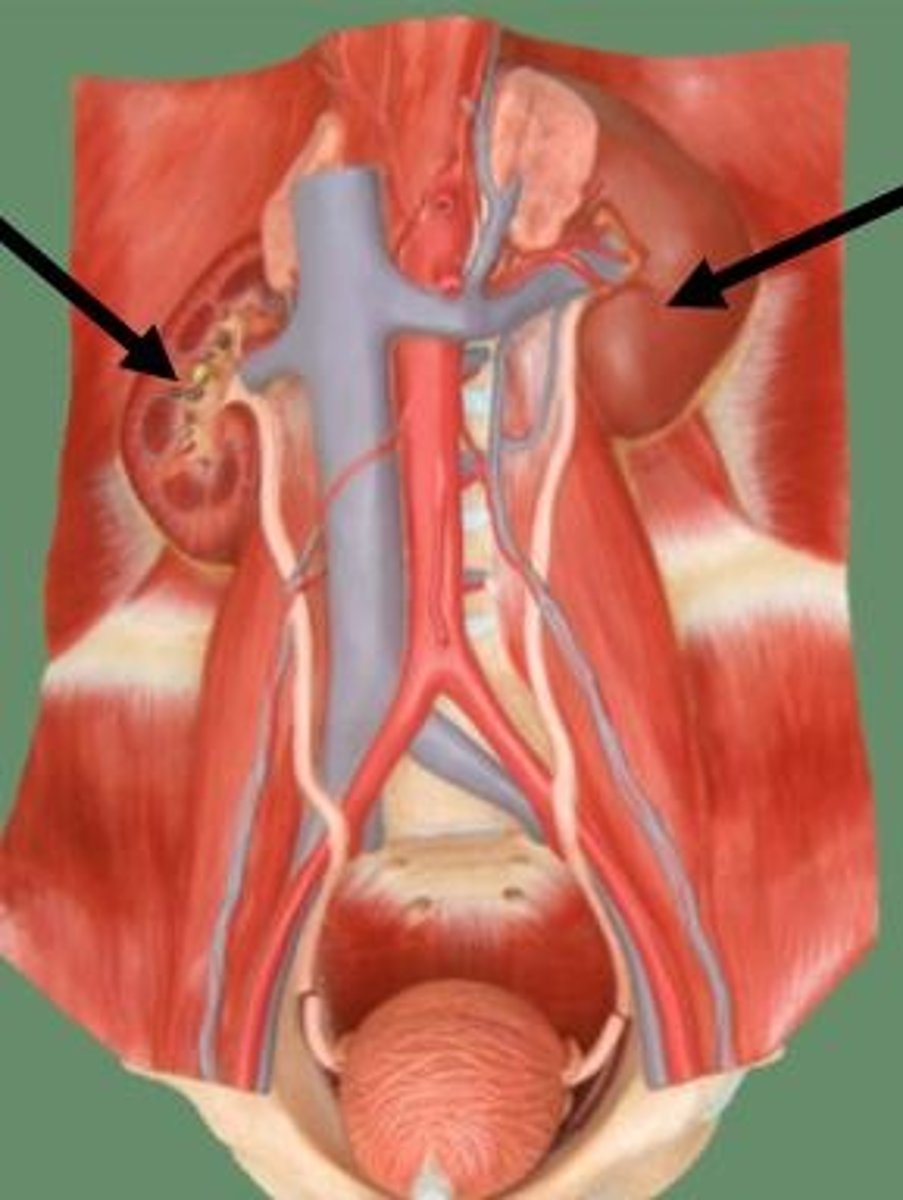
Ureters
The tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
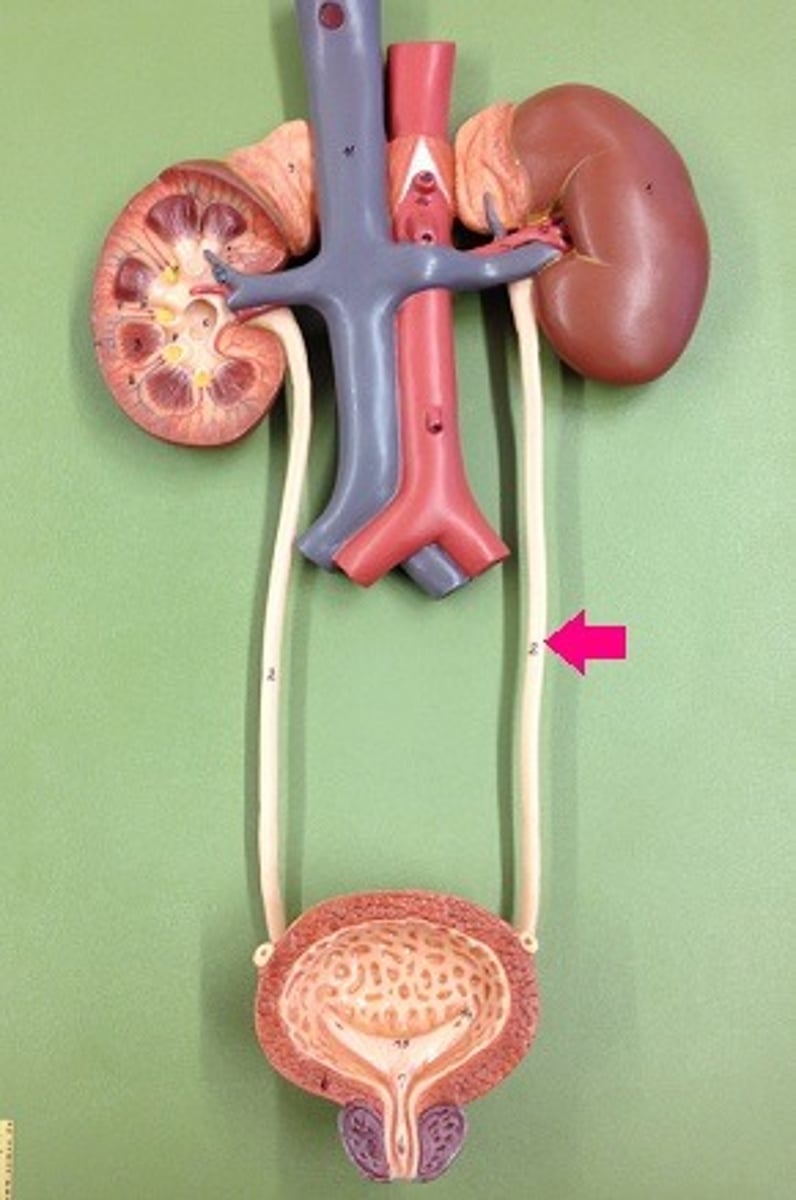
Urinary Bladder
stores urine

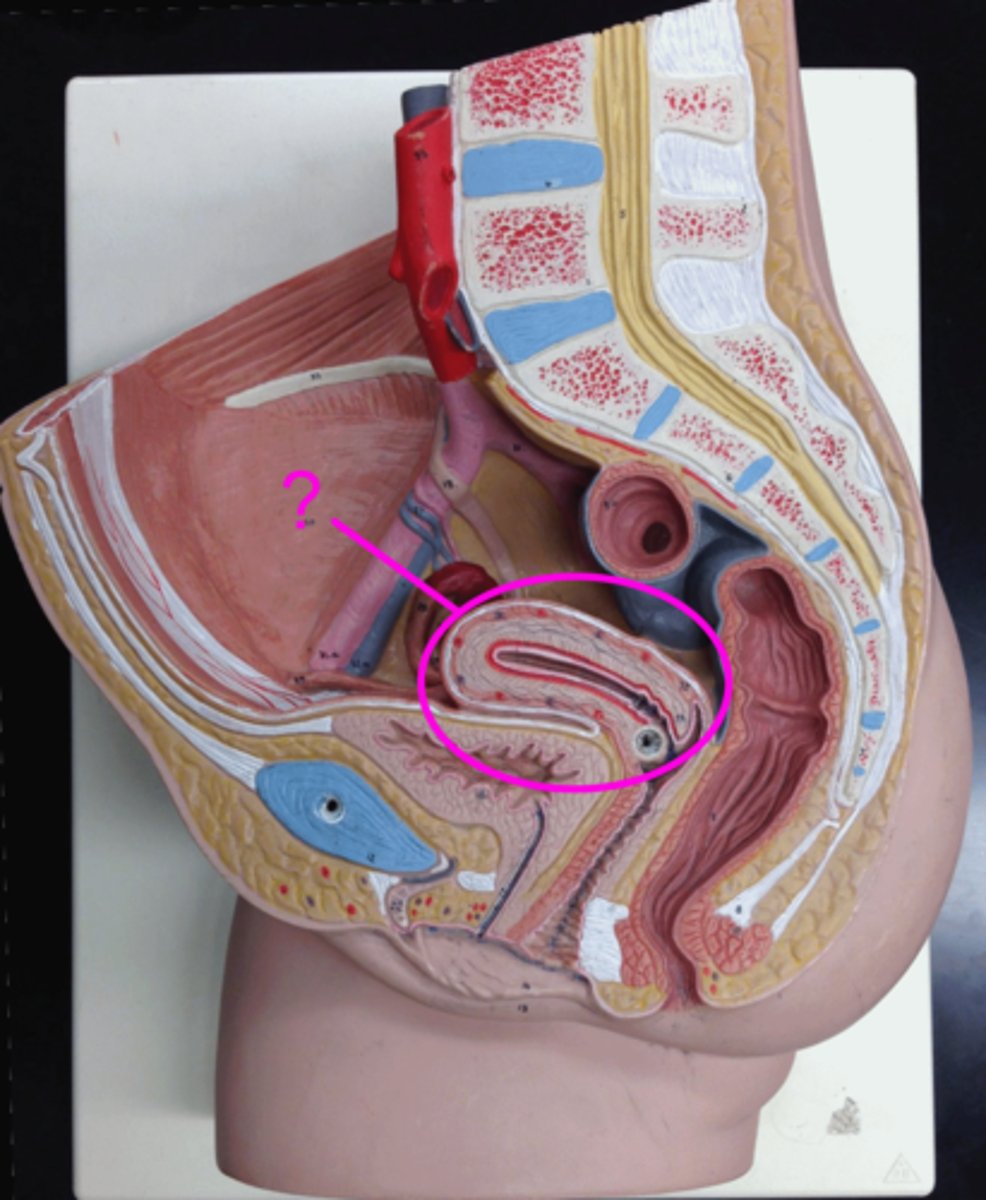
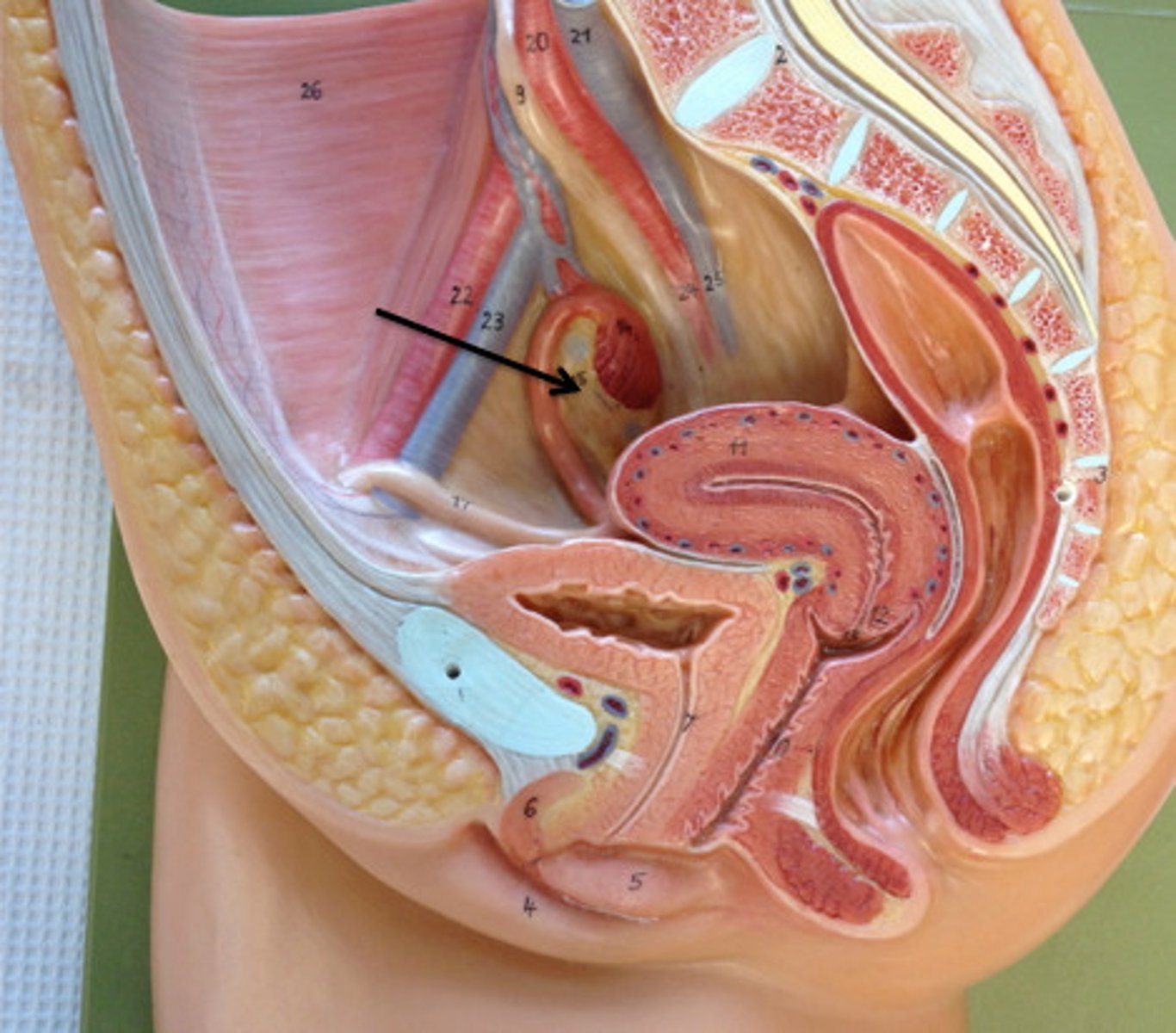
testis
male reproductive organ that produces sperm and hormones
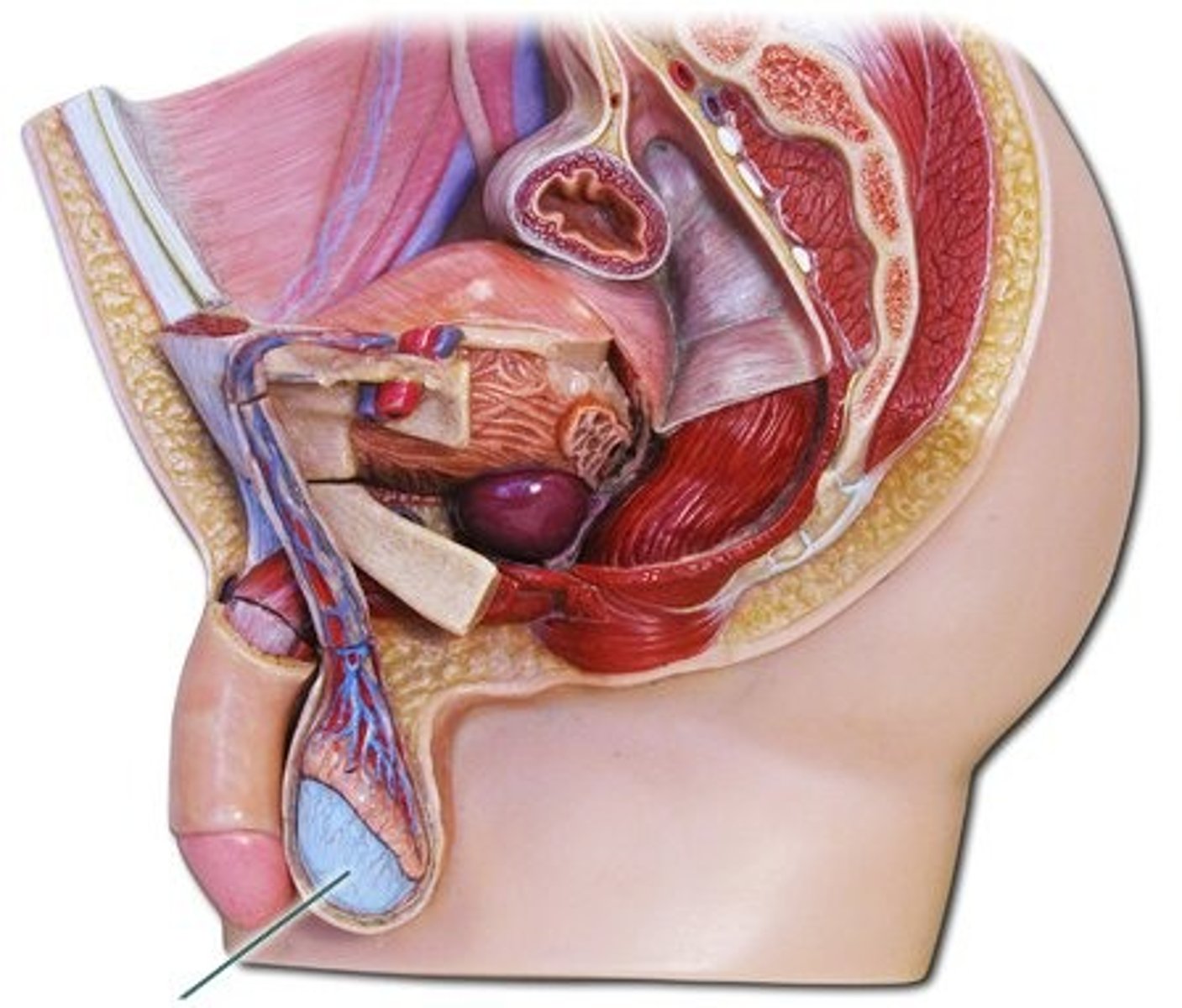
uterus
Used to house the developing fetus.
ovary
produces eggs
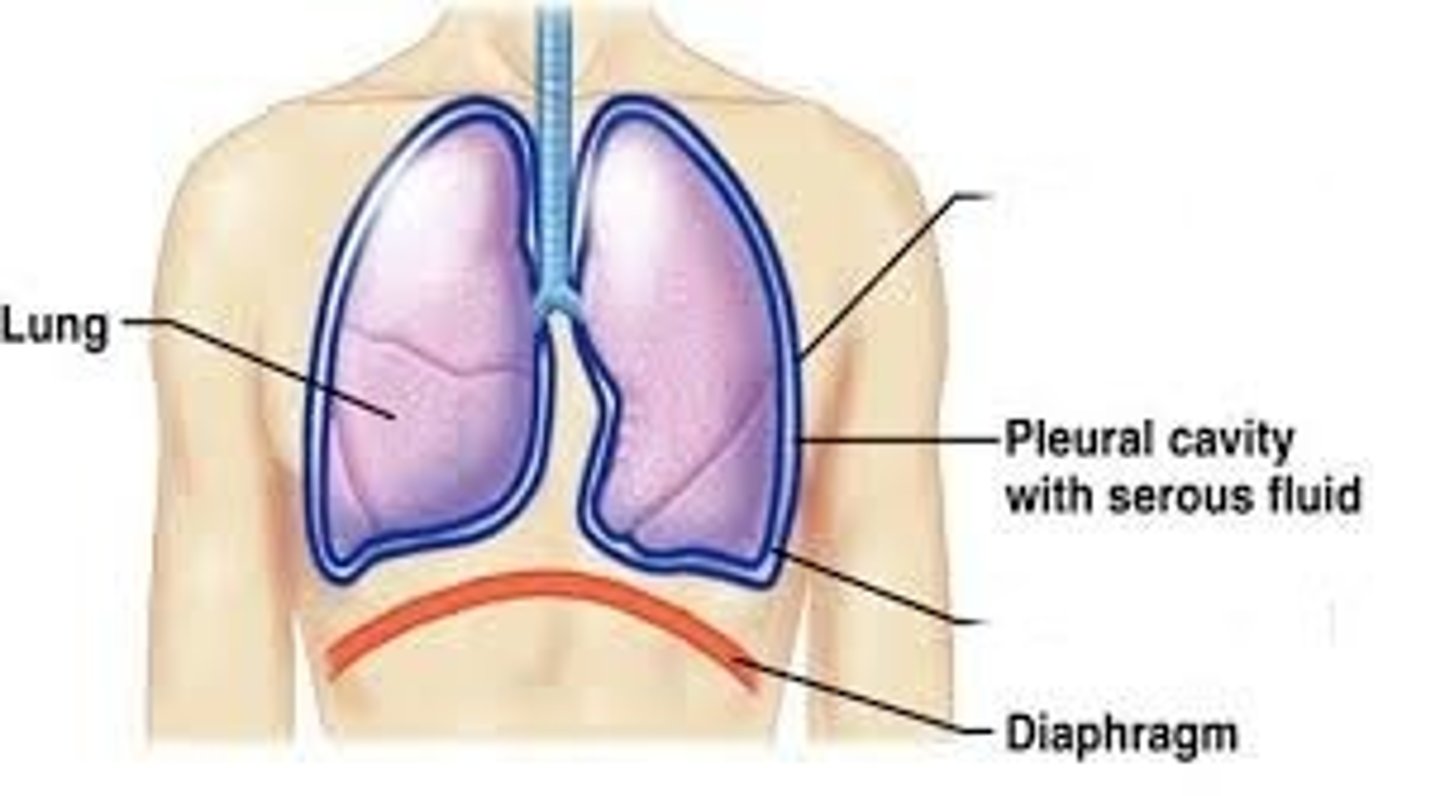
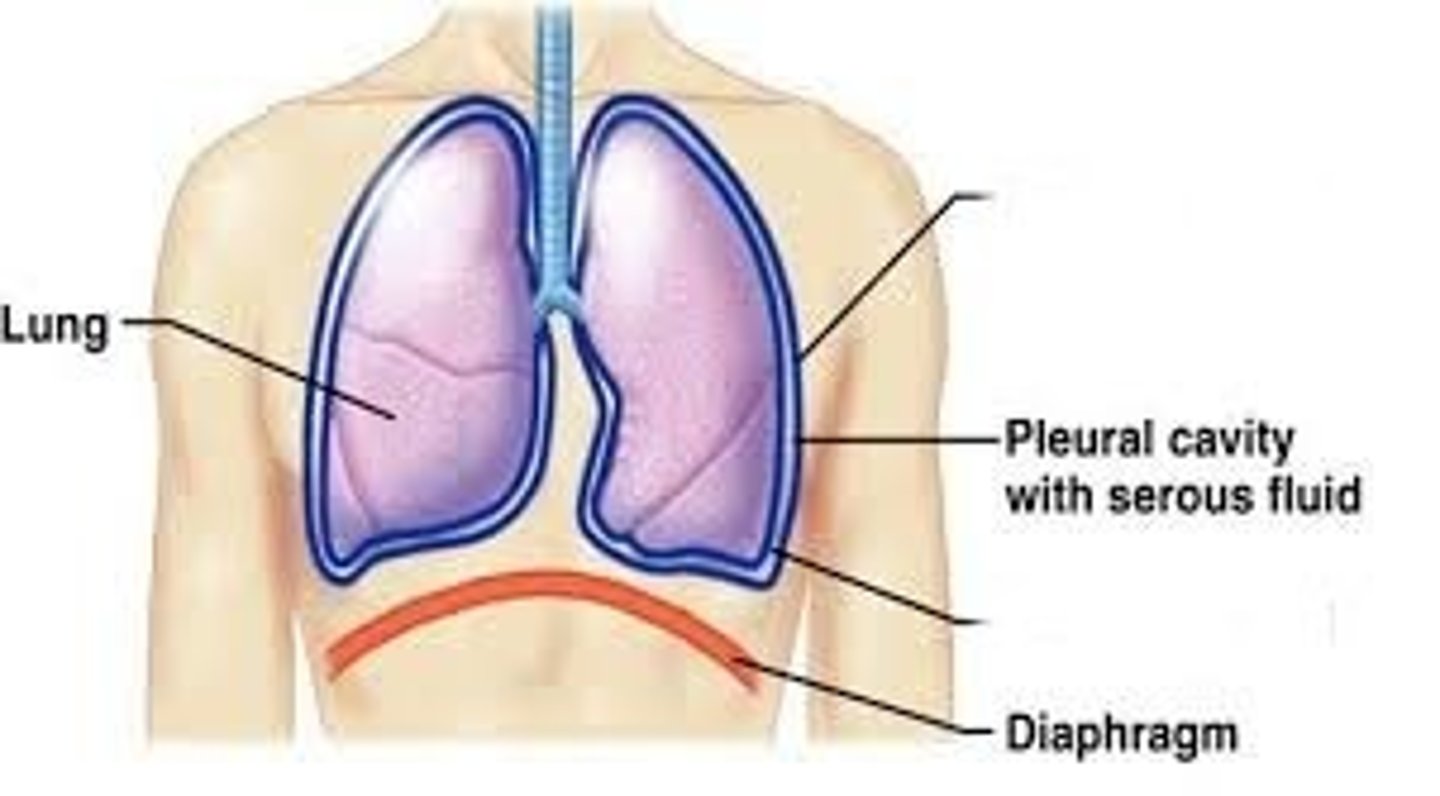
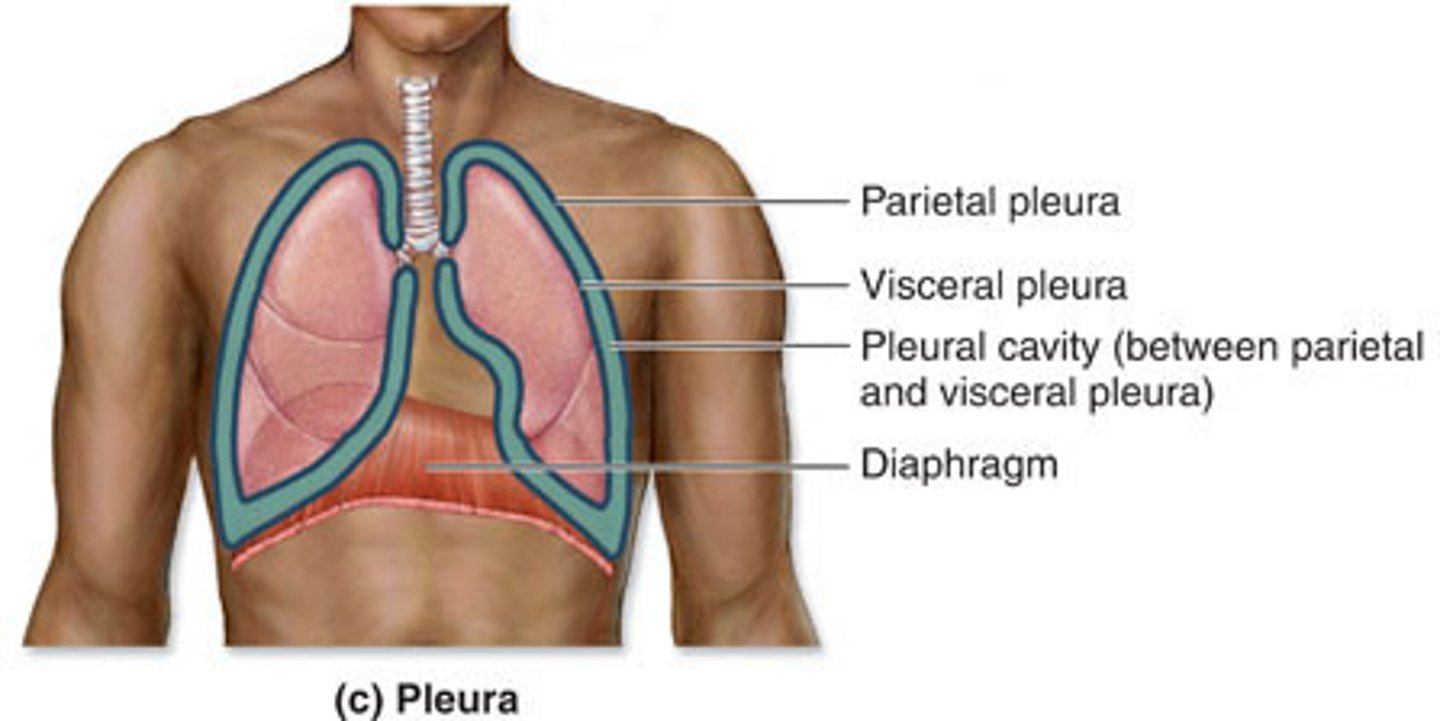
Visceral Pleura
The serous membrane that directly covers the lungs.
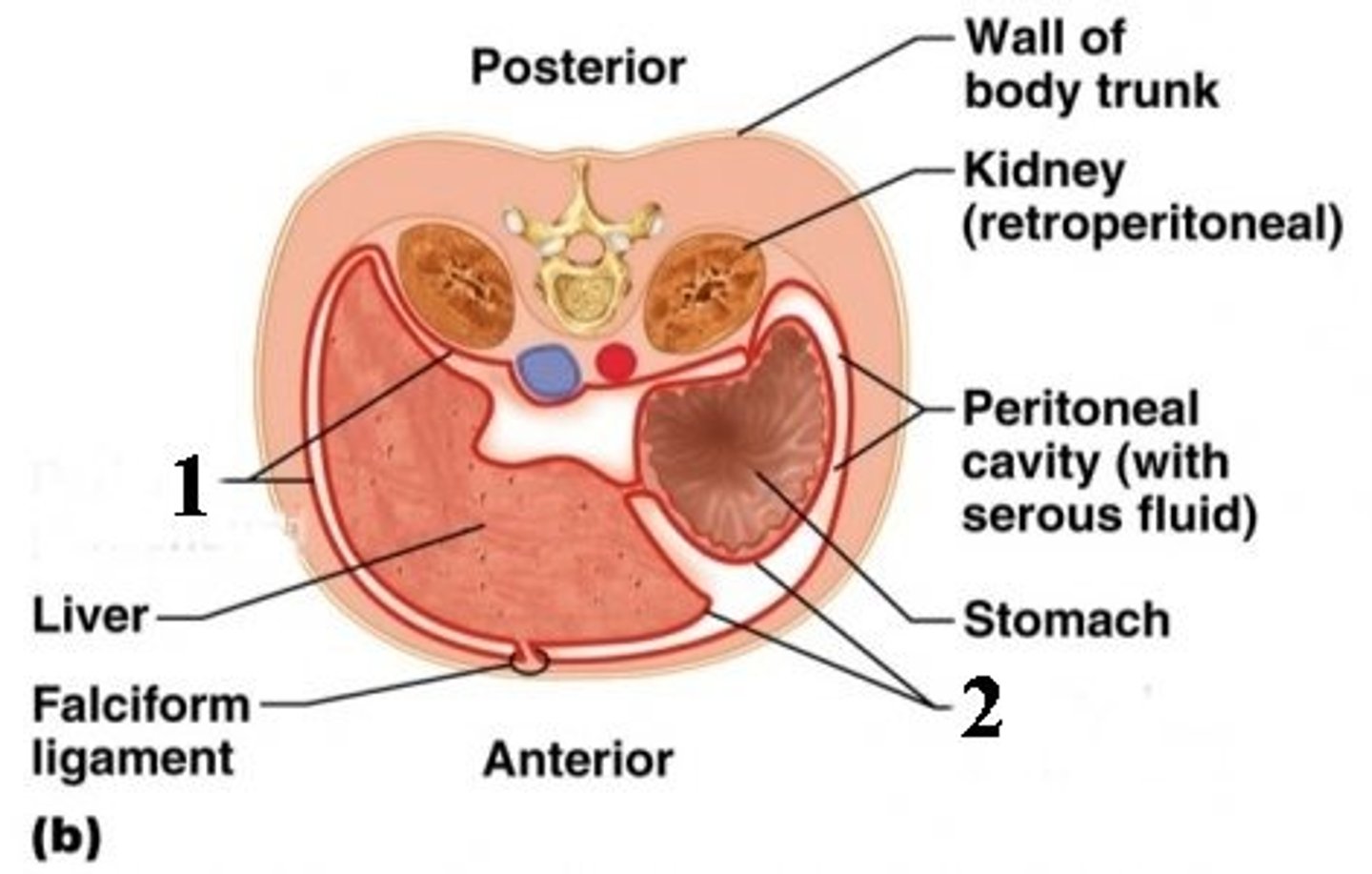
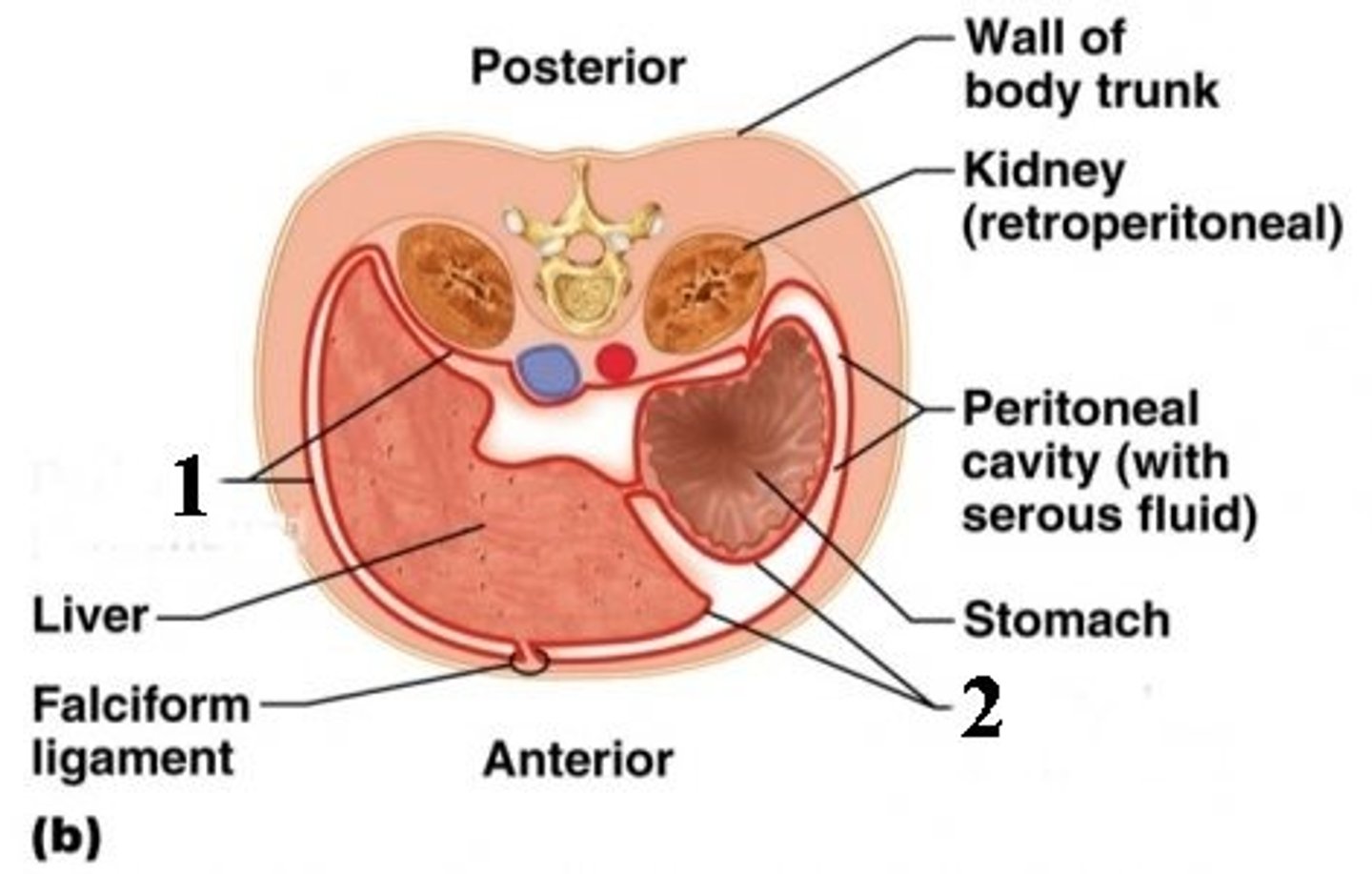
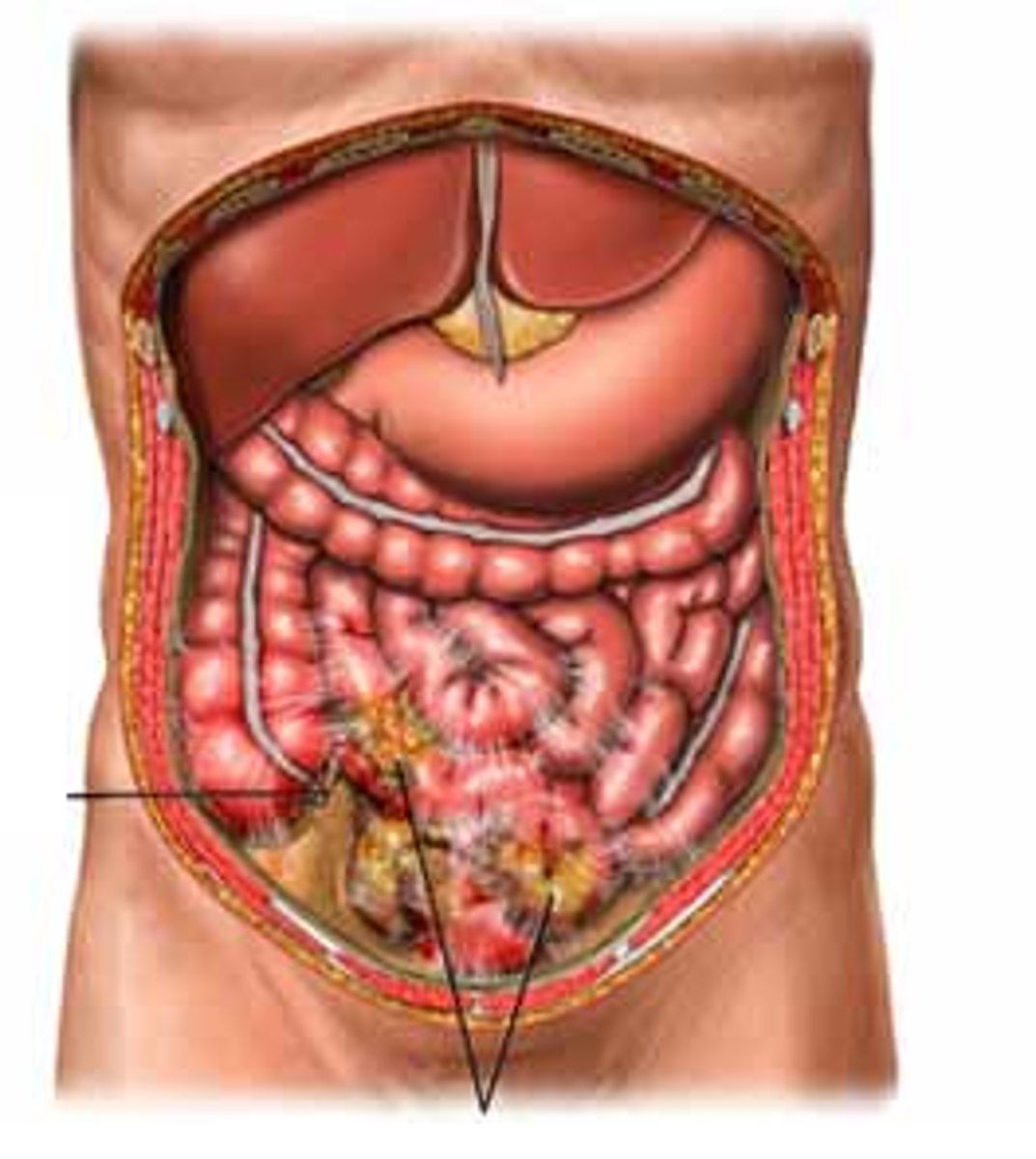
Parietal Peritoneum
The serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity (1)
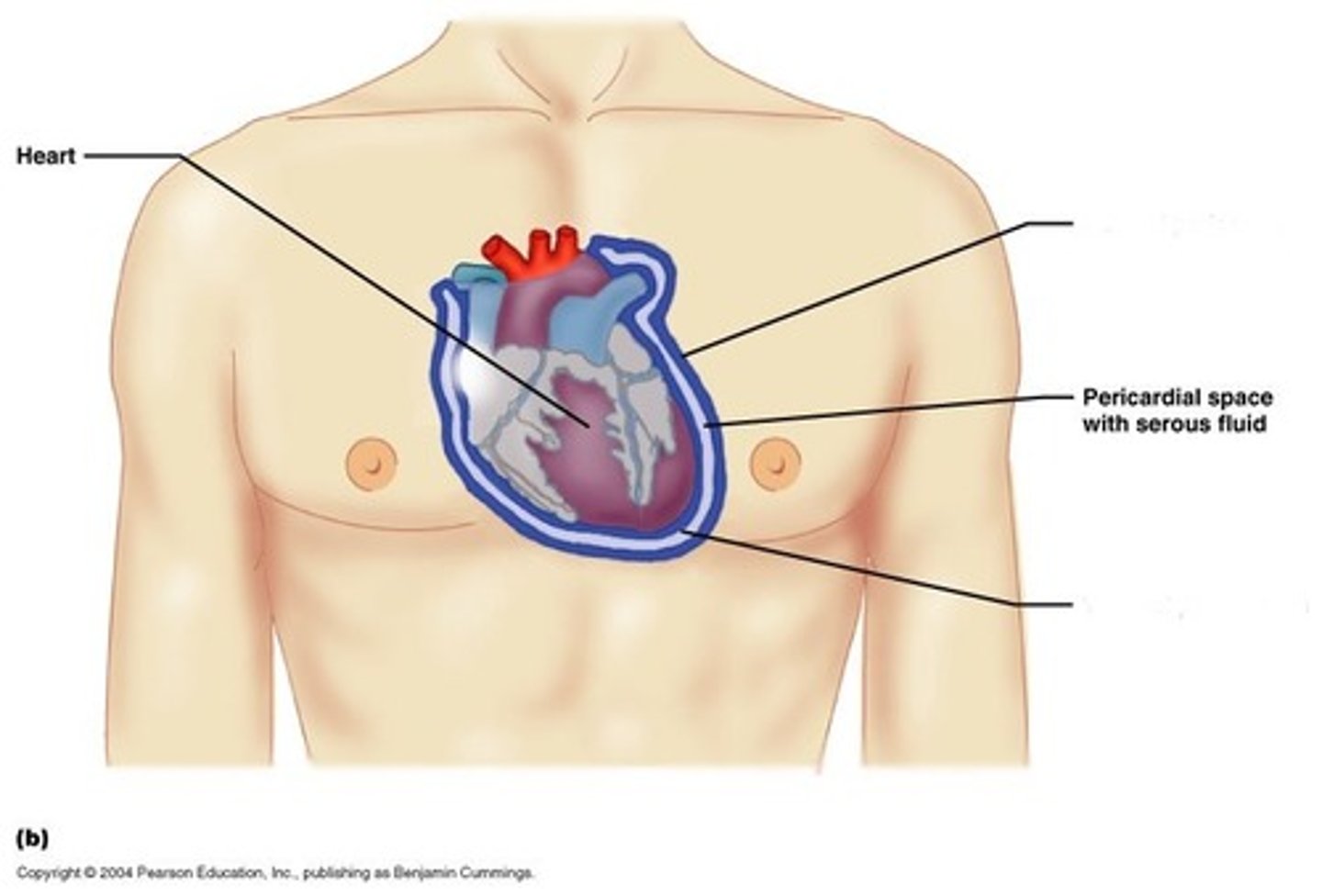
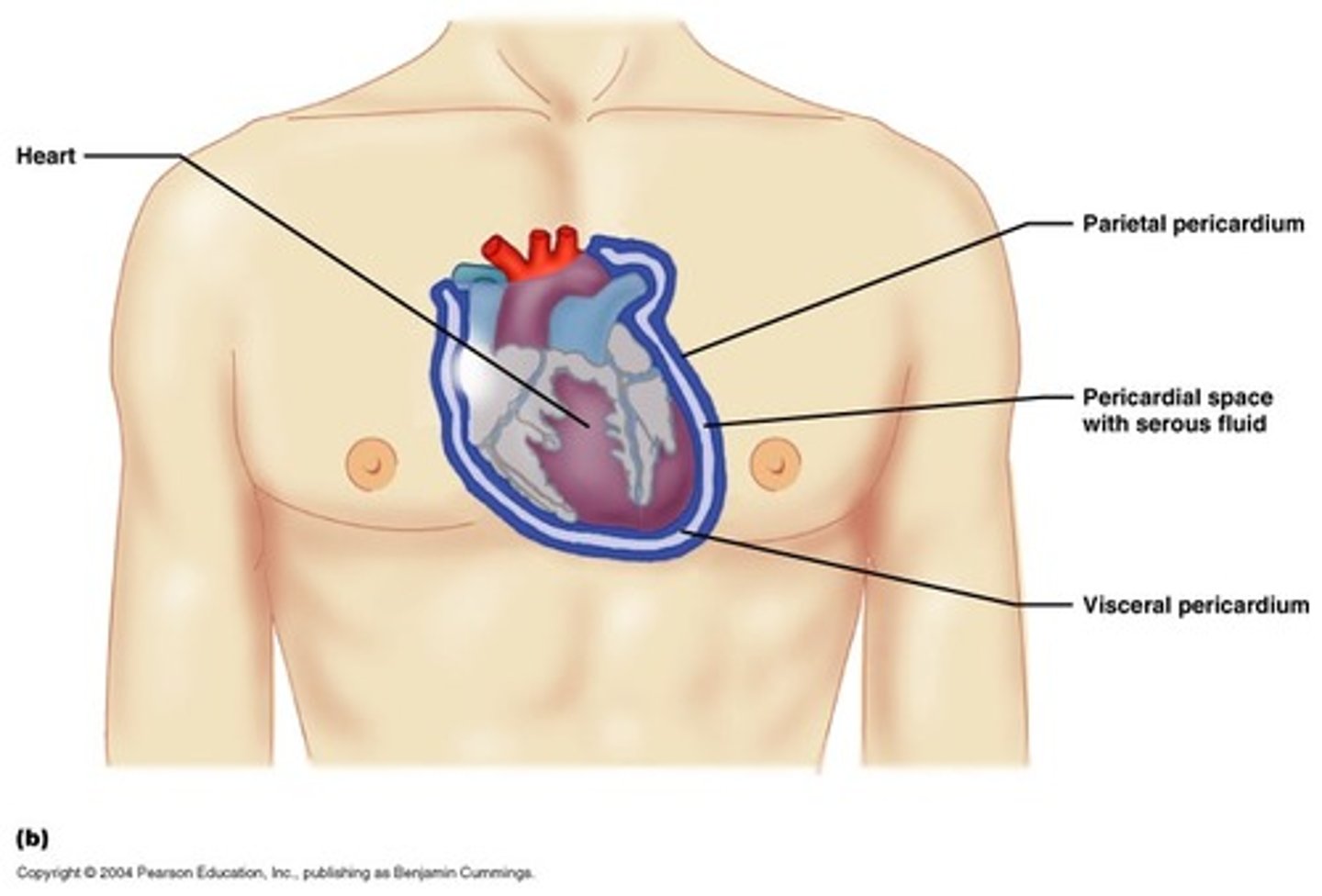
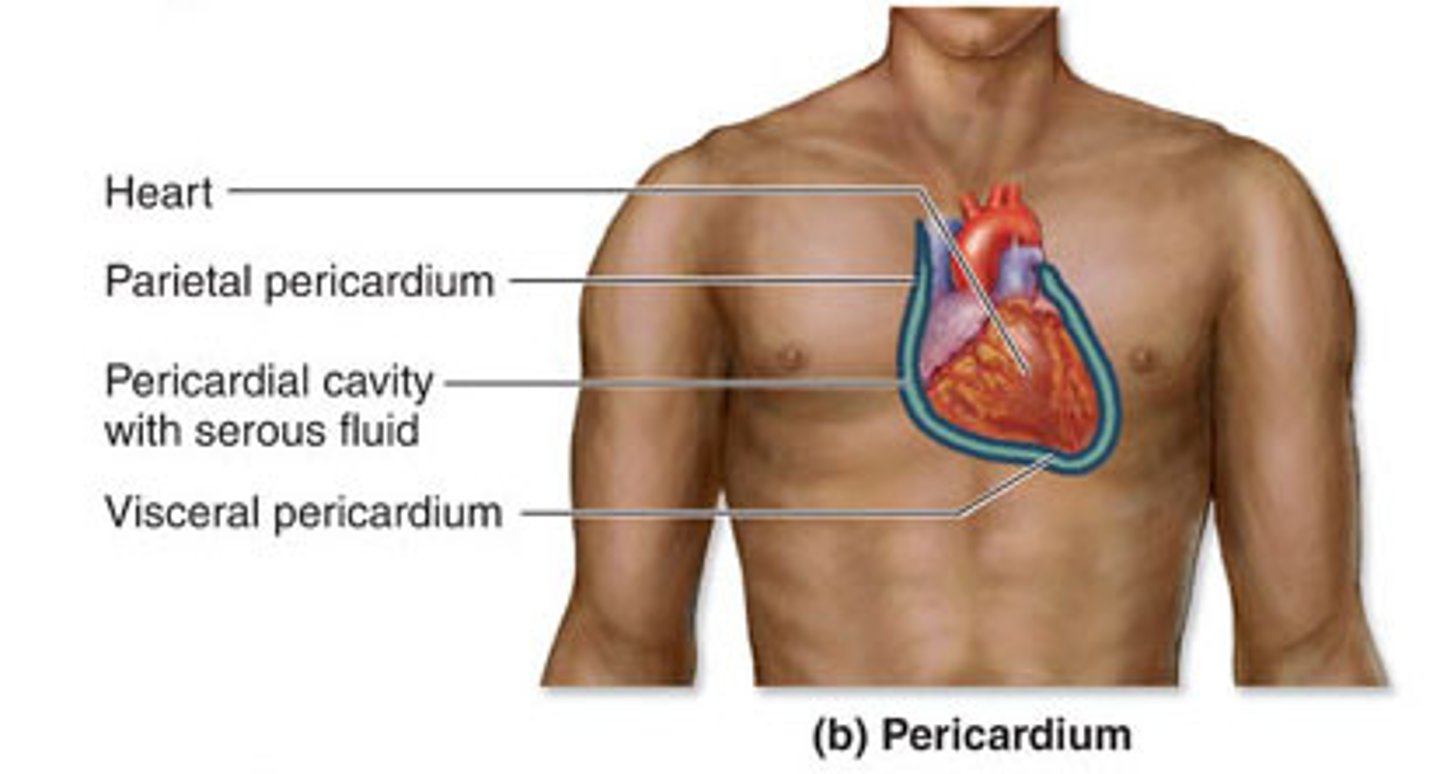
Visceral Pericardium
The serous membrane that directly covers the heart.
Parietal Pleura
The serous membrane that lines the pleural cavity.
Visceral Peritoneum
The serous membrane that directly covers the abdmoinopelvic organs. (2)
Parietal Pericardium
The serous membrane that lines the pericardial cavity.
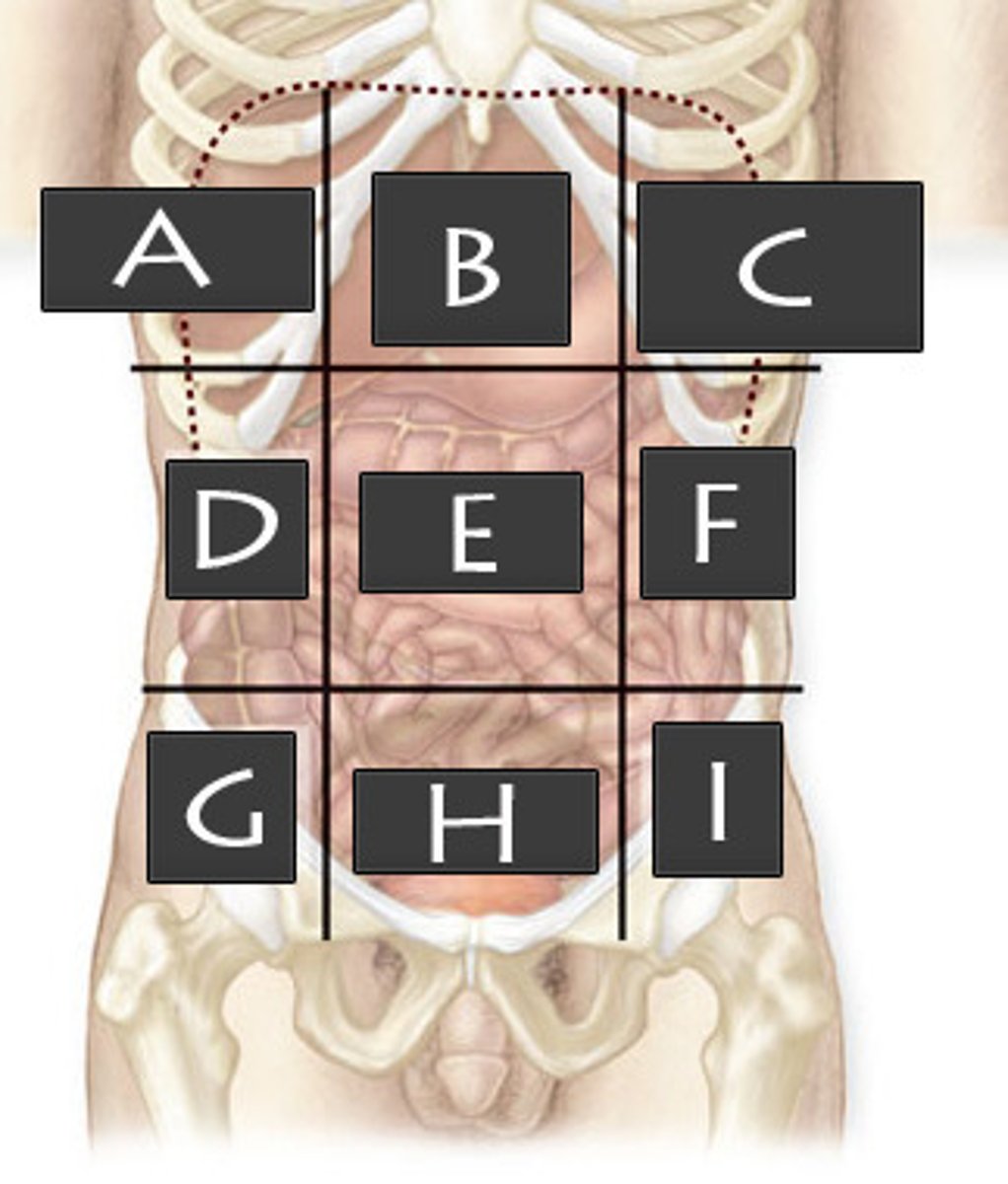
Right Hypochondriac Region
What abdominopelvic region is A?
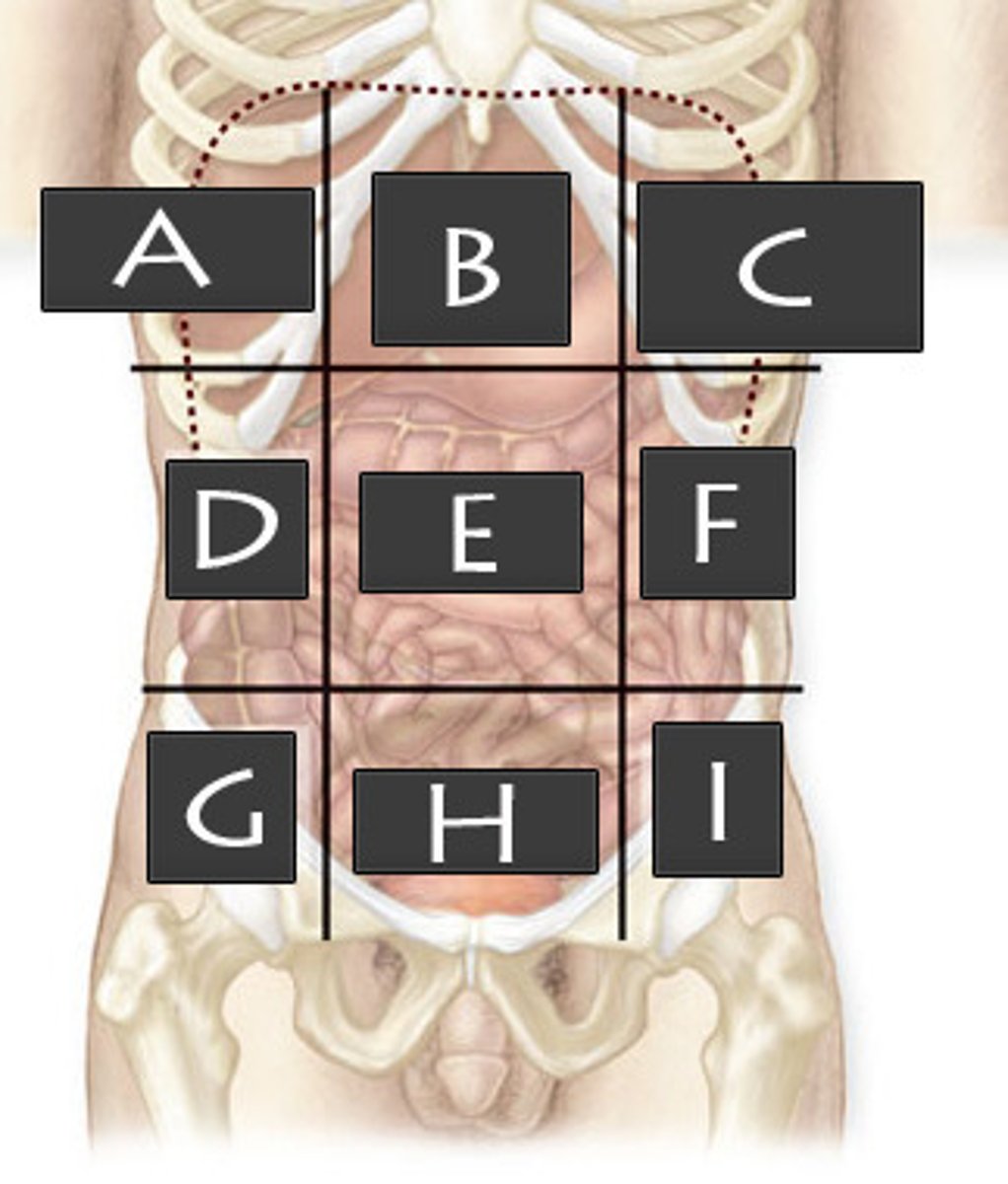
Epigastric Region
What abdominopelvic region is B?
Left Hypochondriac Region
What abdominopelvic region is C?
Right Lumber Region
What abdominopelvic region is D?
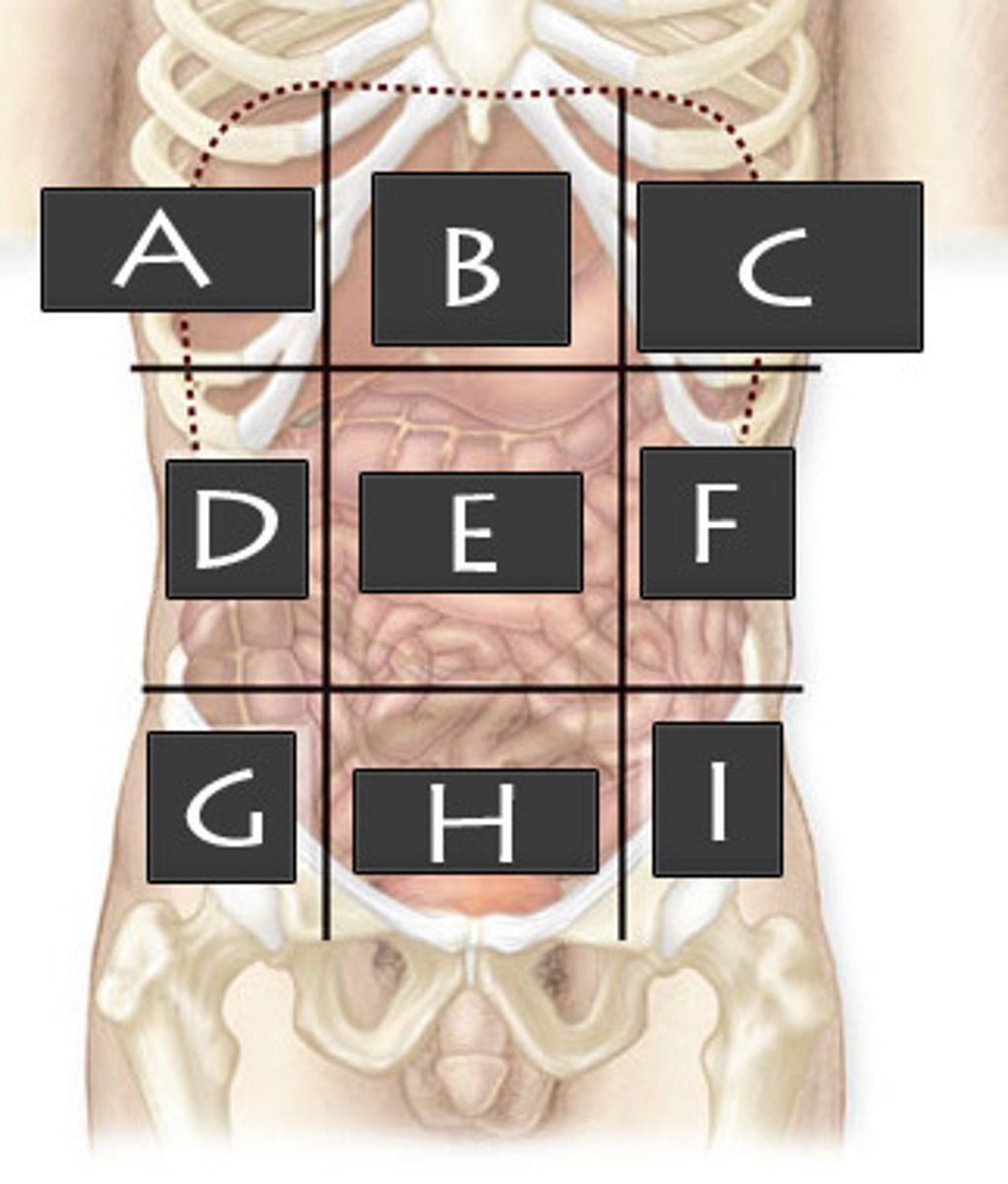
Umbilical Region
What abdominiopelvic region is E?
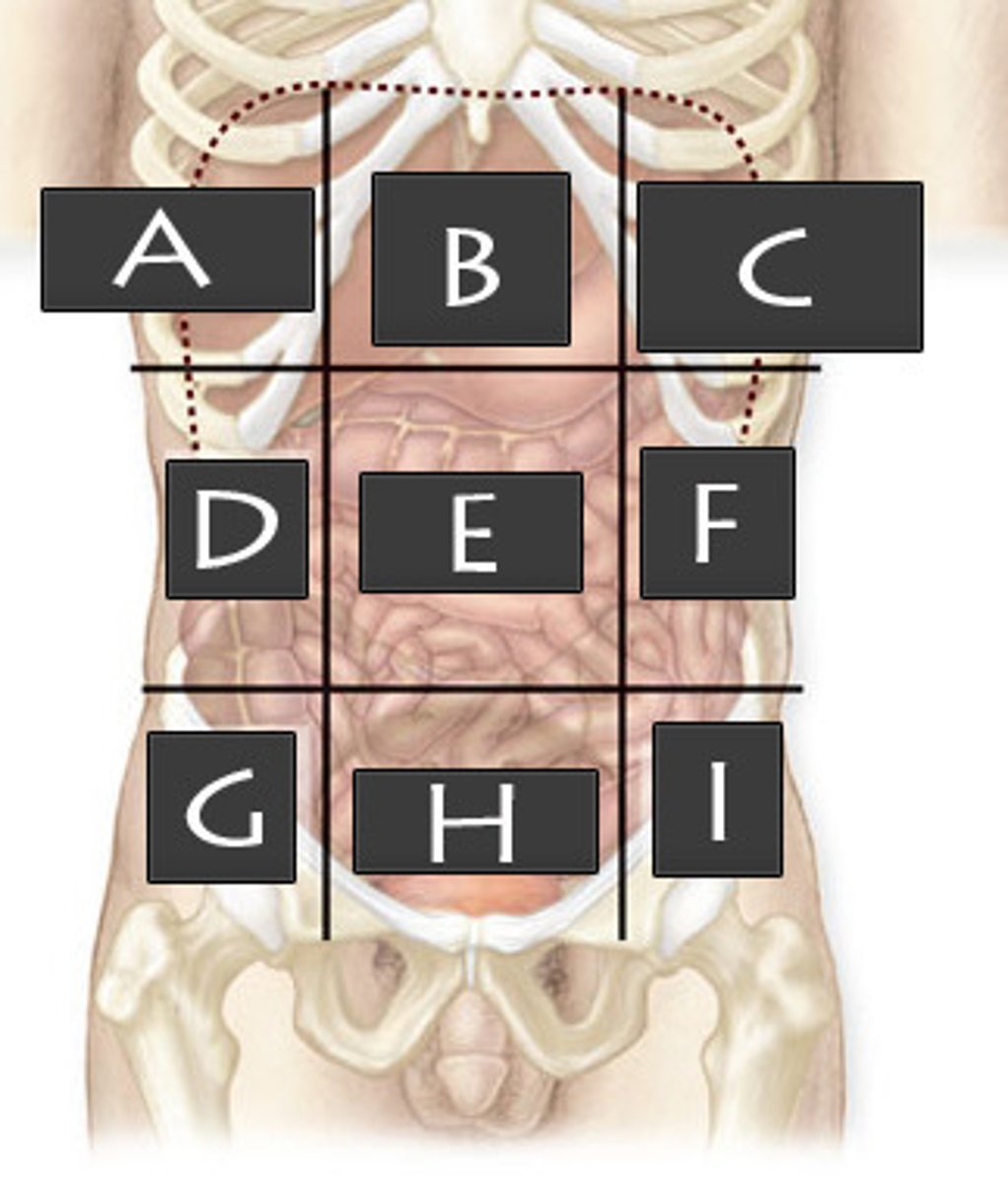
Left Lumbar Region
What abdominopelvic region is F?
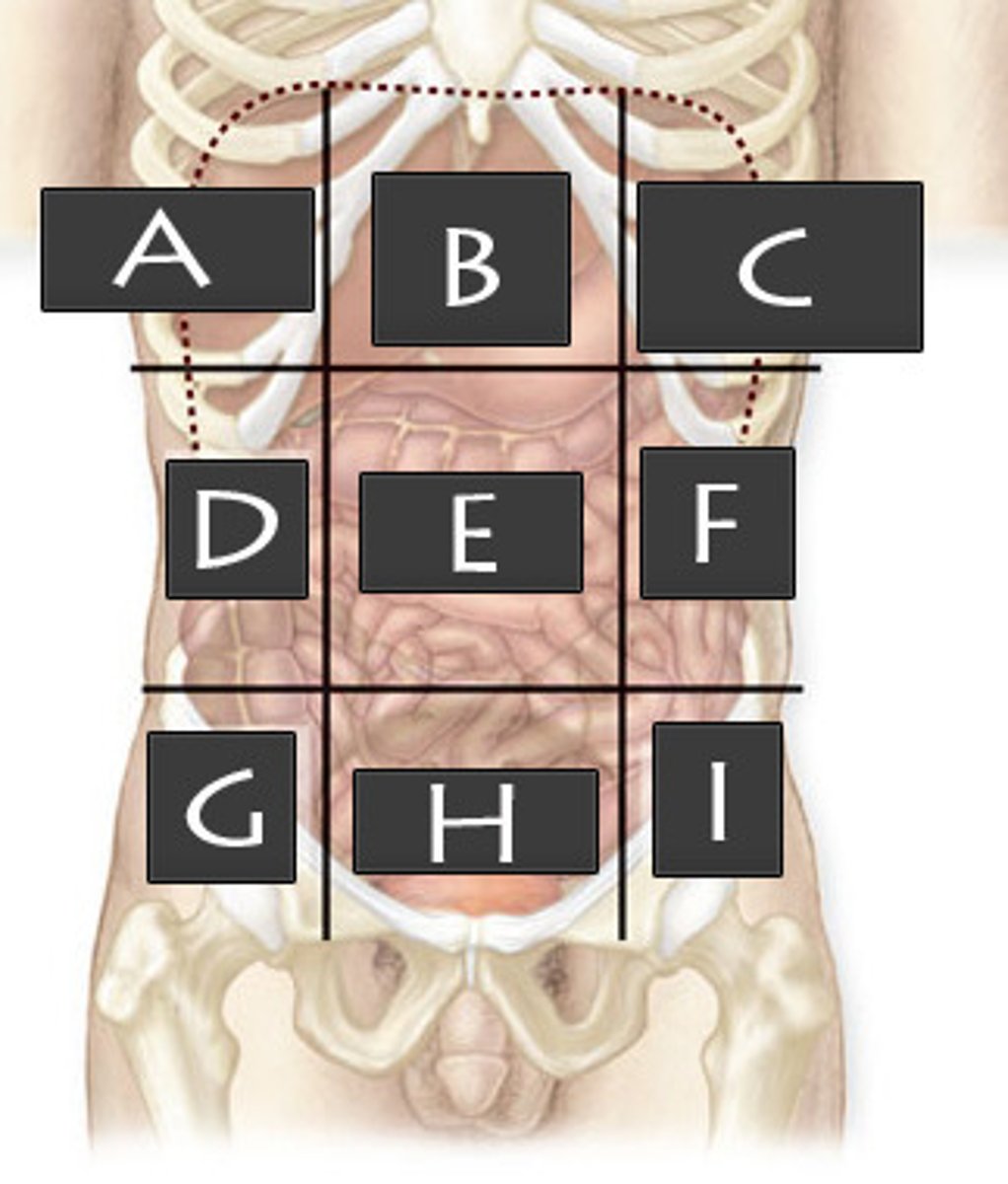
Right Iliac Region
What abdominopelvic region is G?
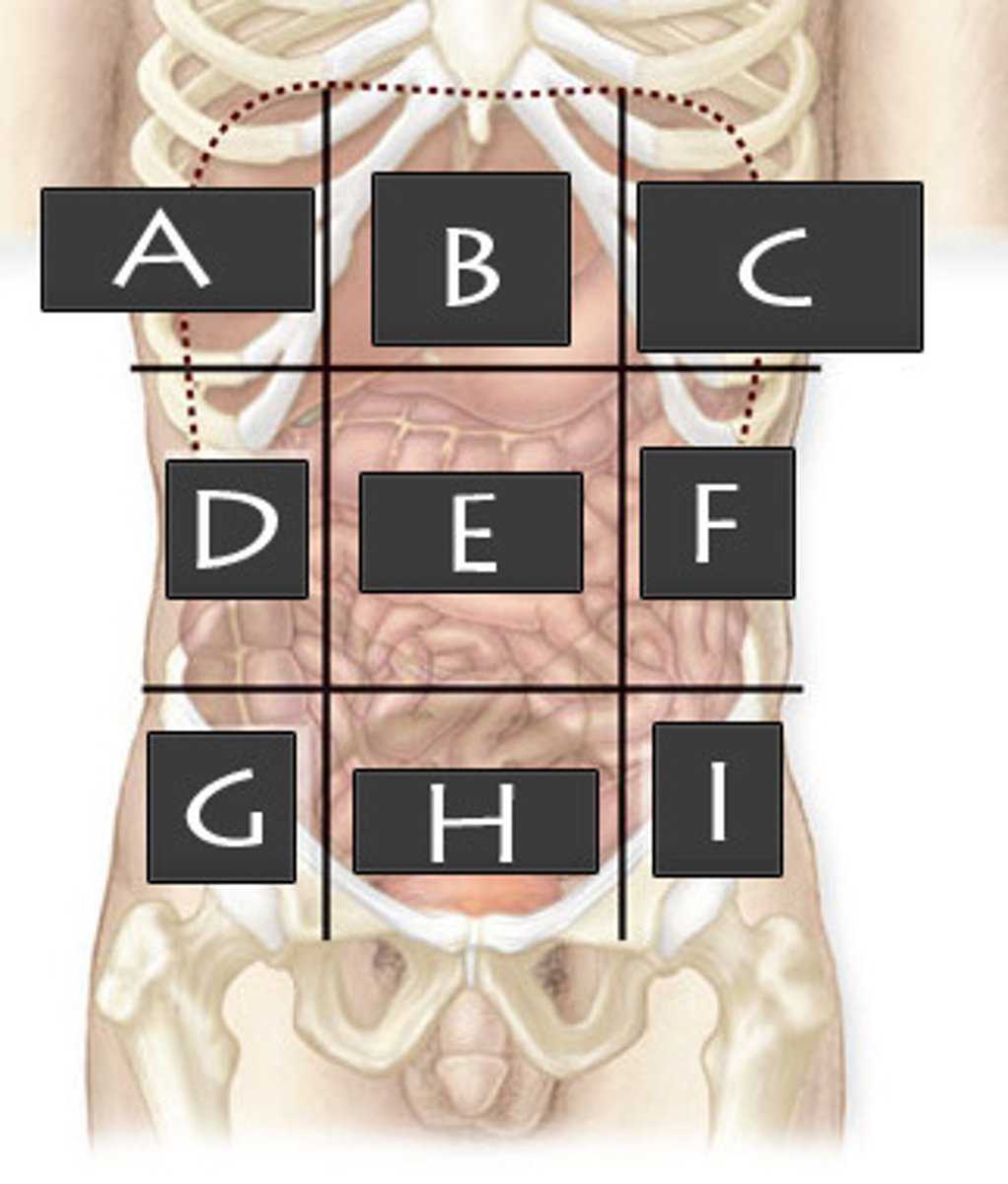
Hypogastric Region
What abdominopelvic region is H?
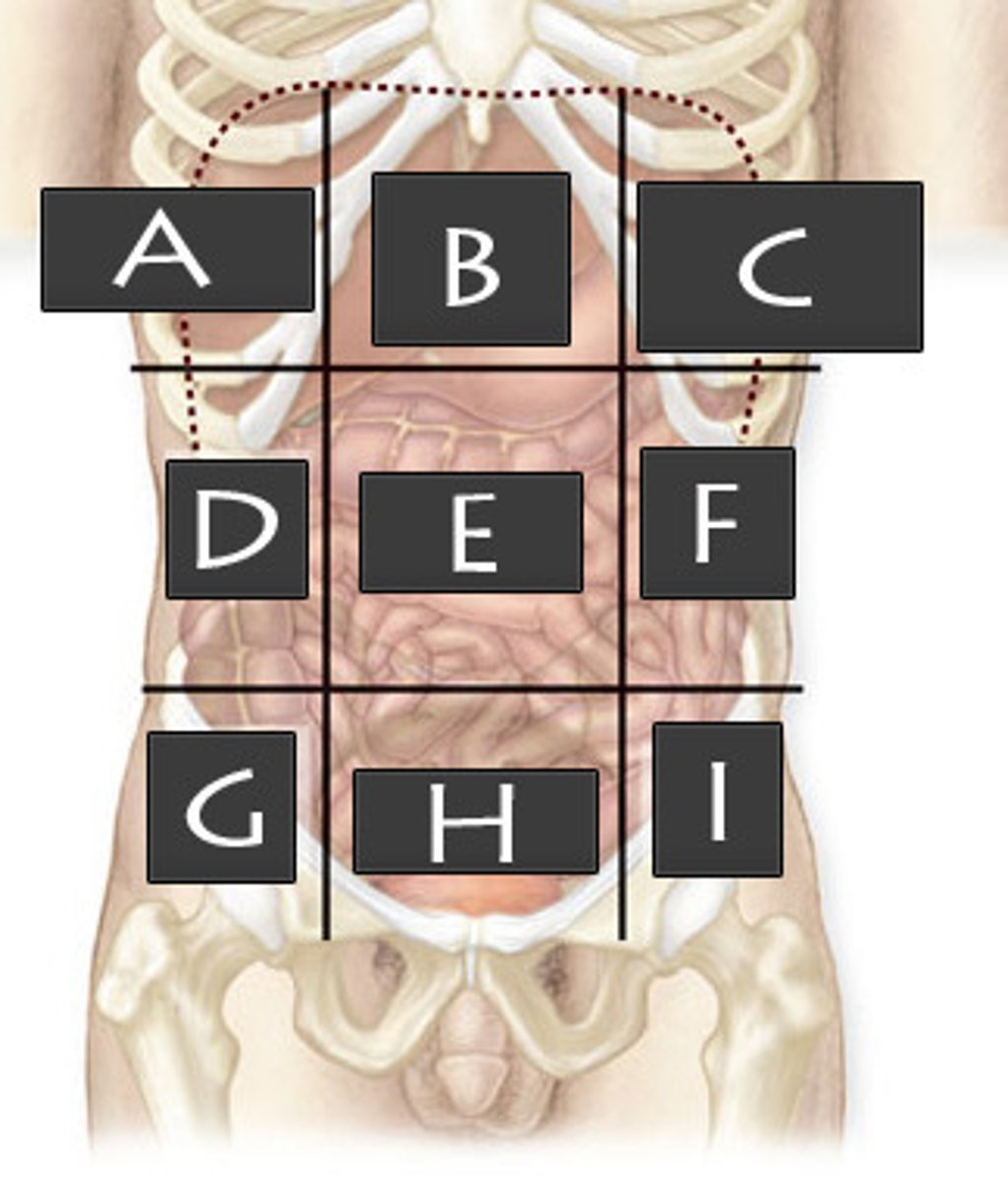
Left Iliac Region
What abdominopelvic region is I?
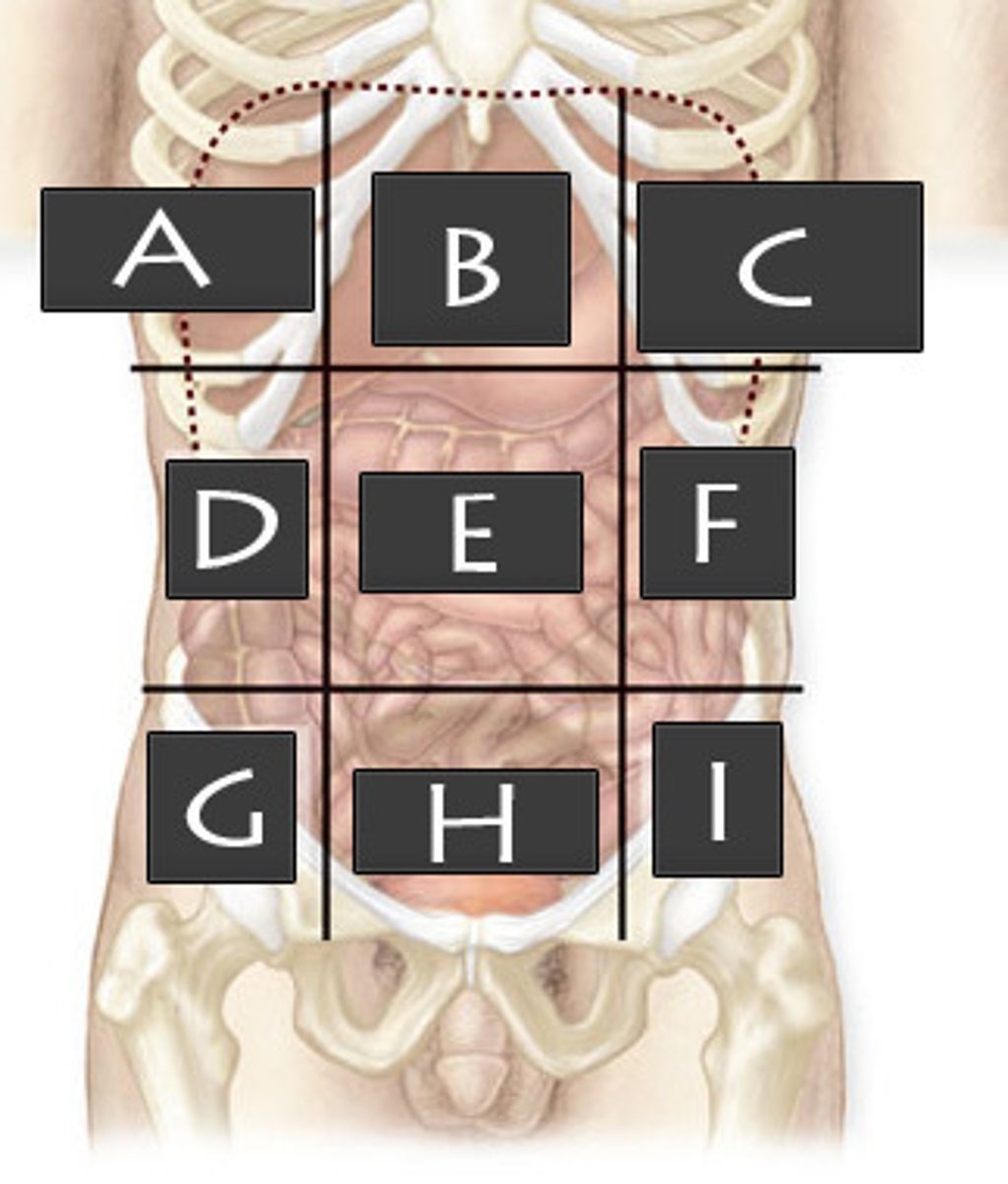
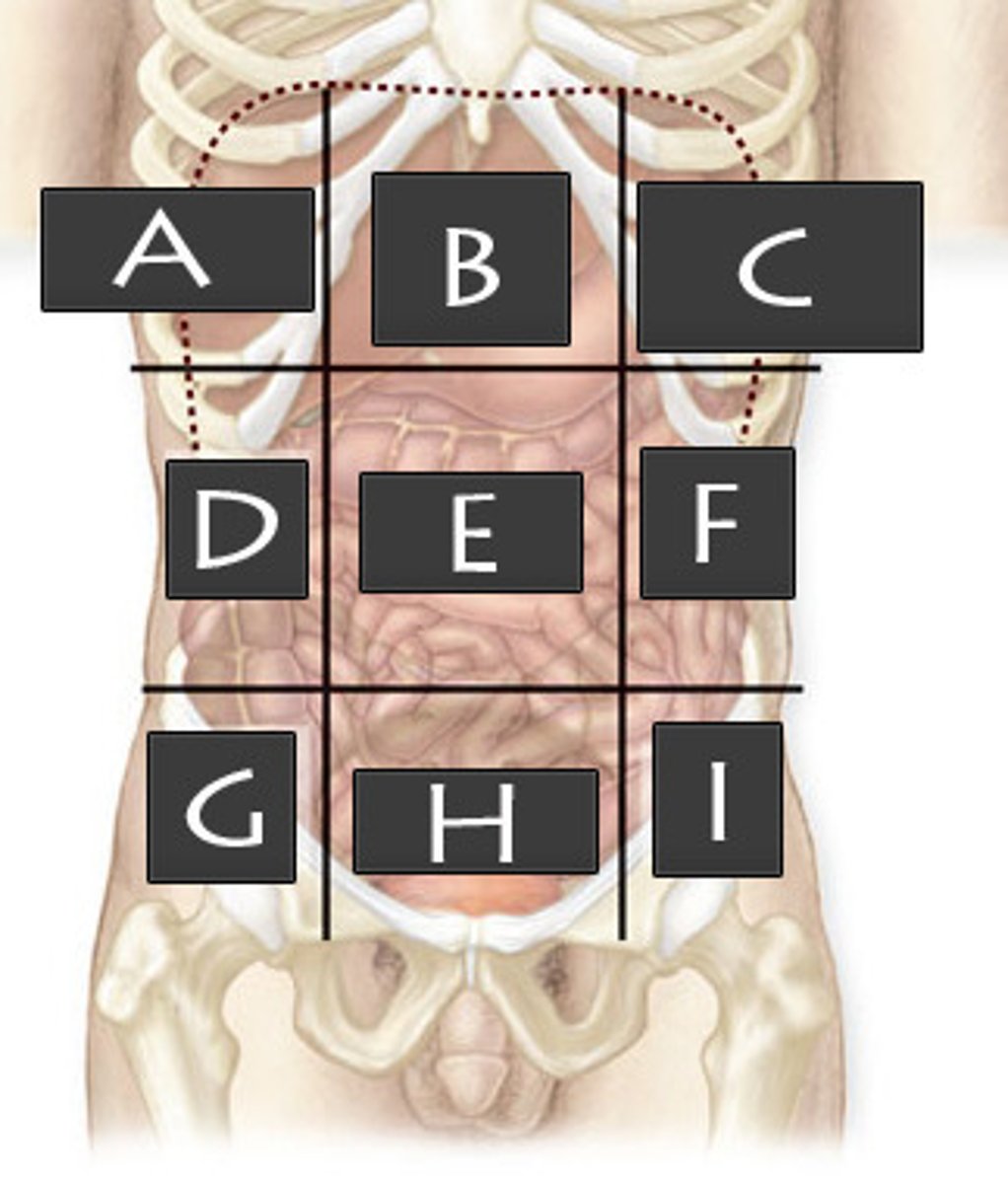
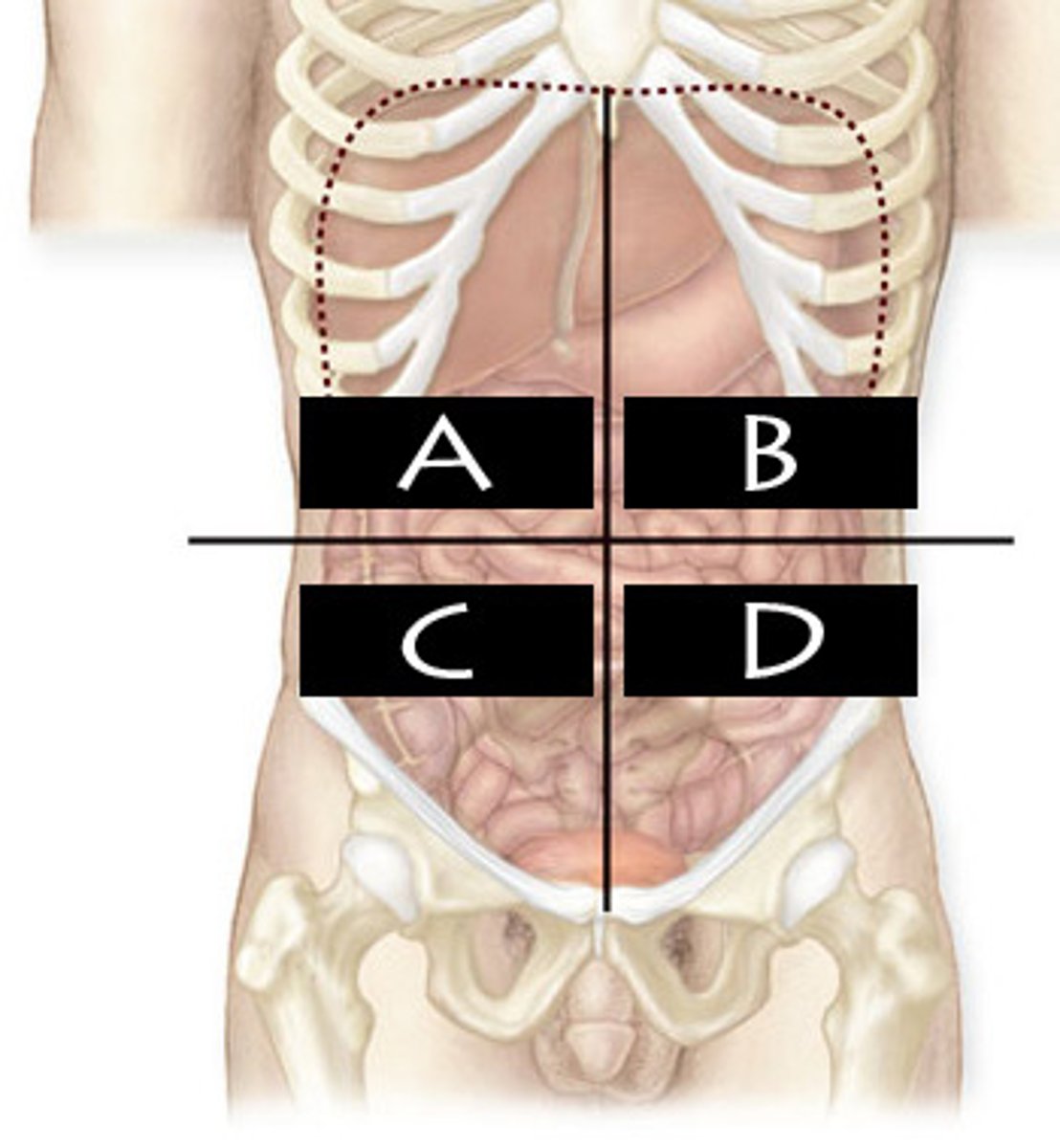
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
What abdominopelvic quadrant is A?
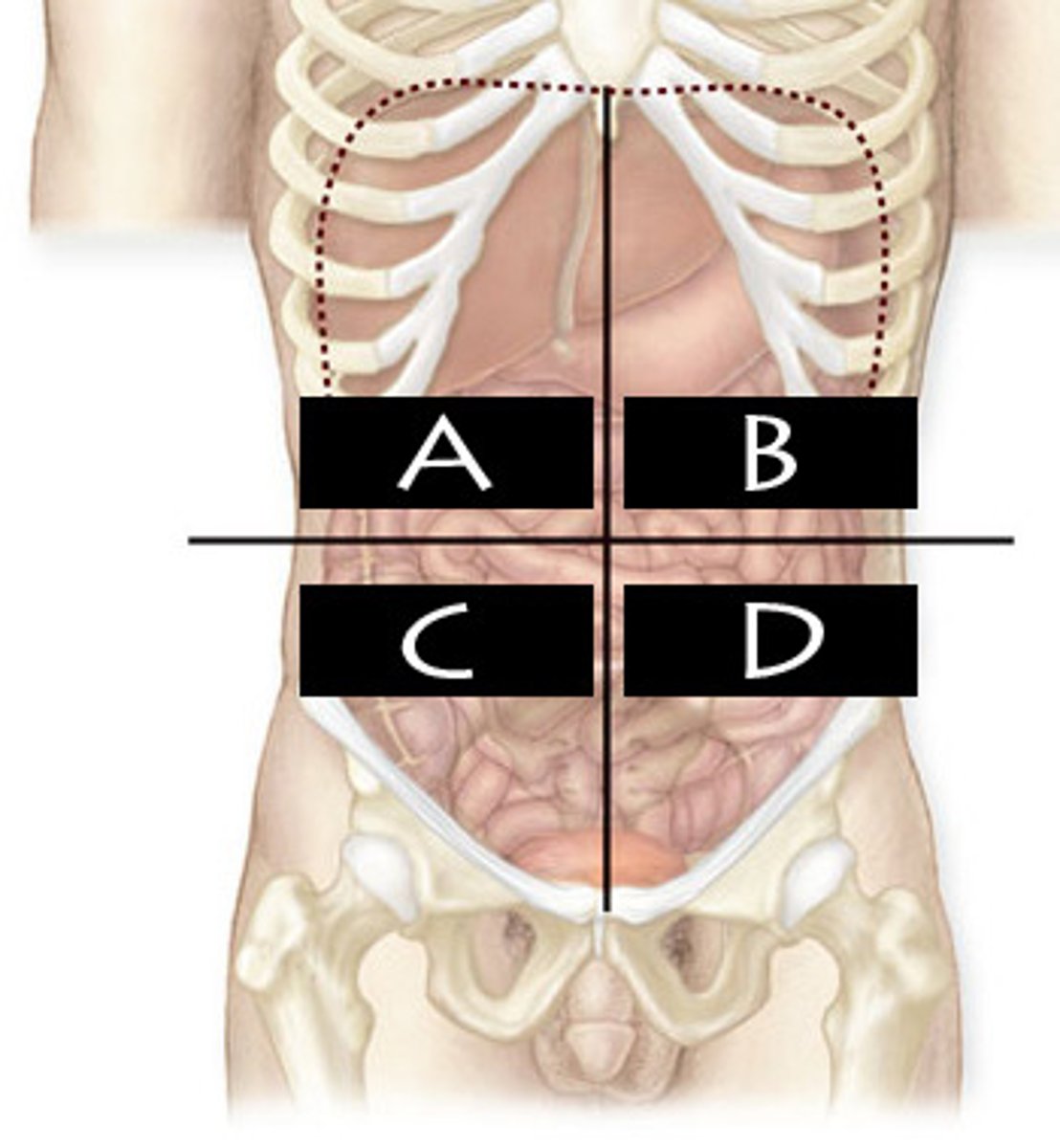
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
What abdominopelvic quadrant is B?
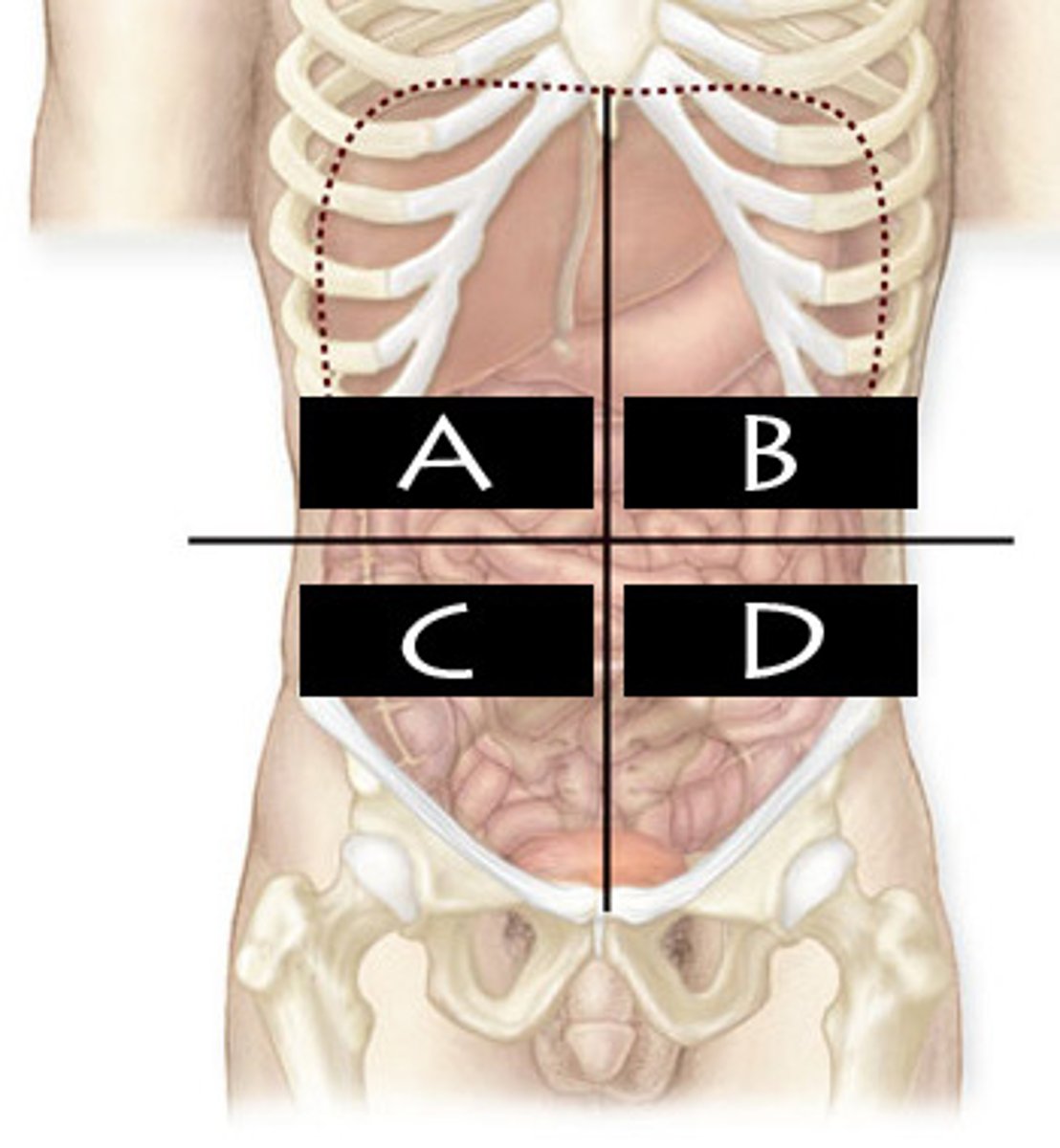
Righter Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
What abdominopelvic quadrant is C?
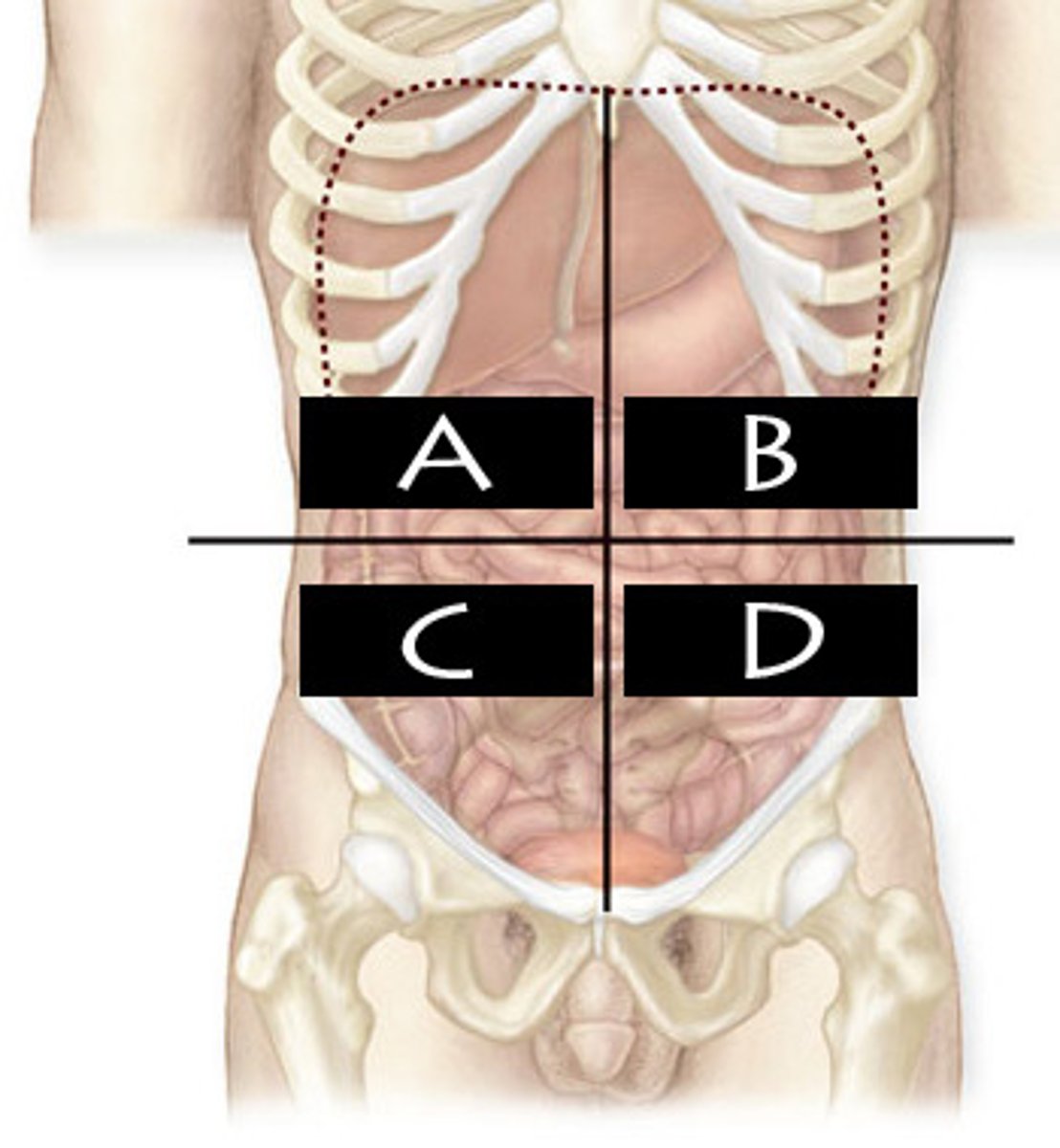
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
What abdominopelvic quadrant is D?
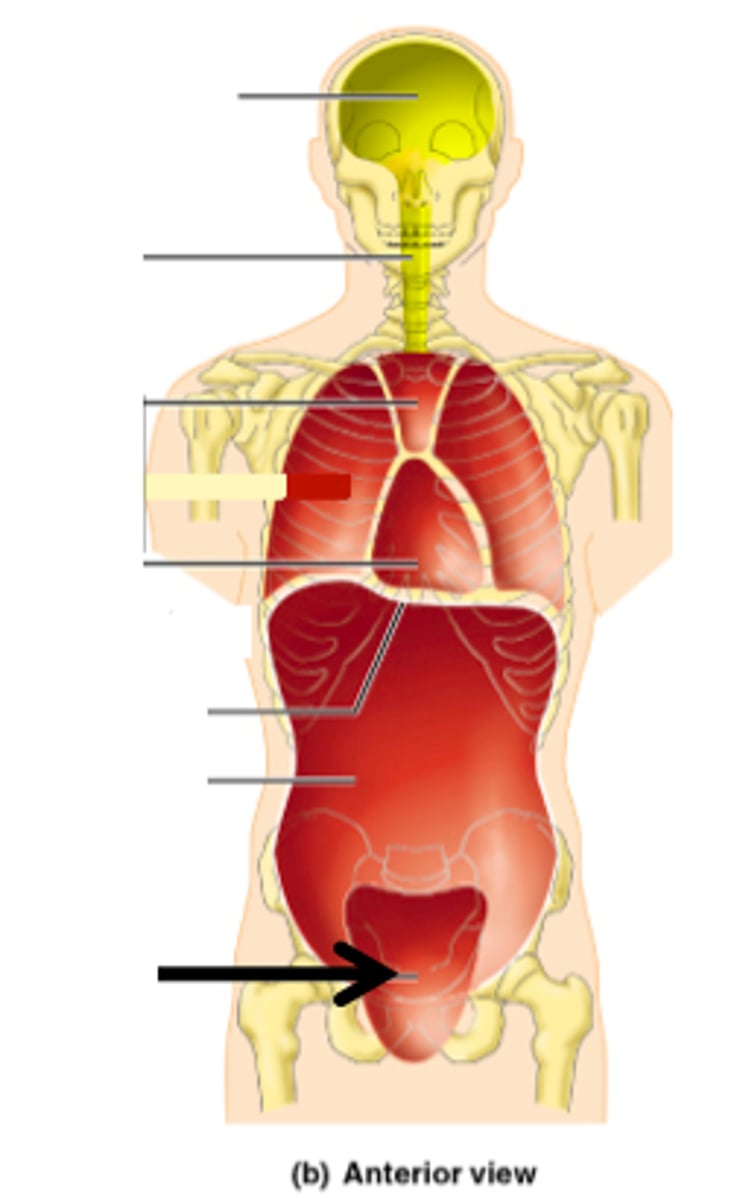
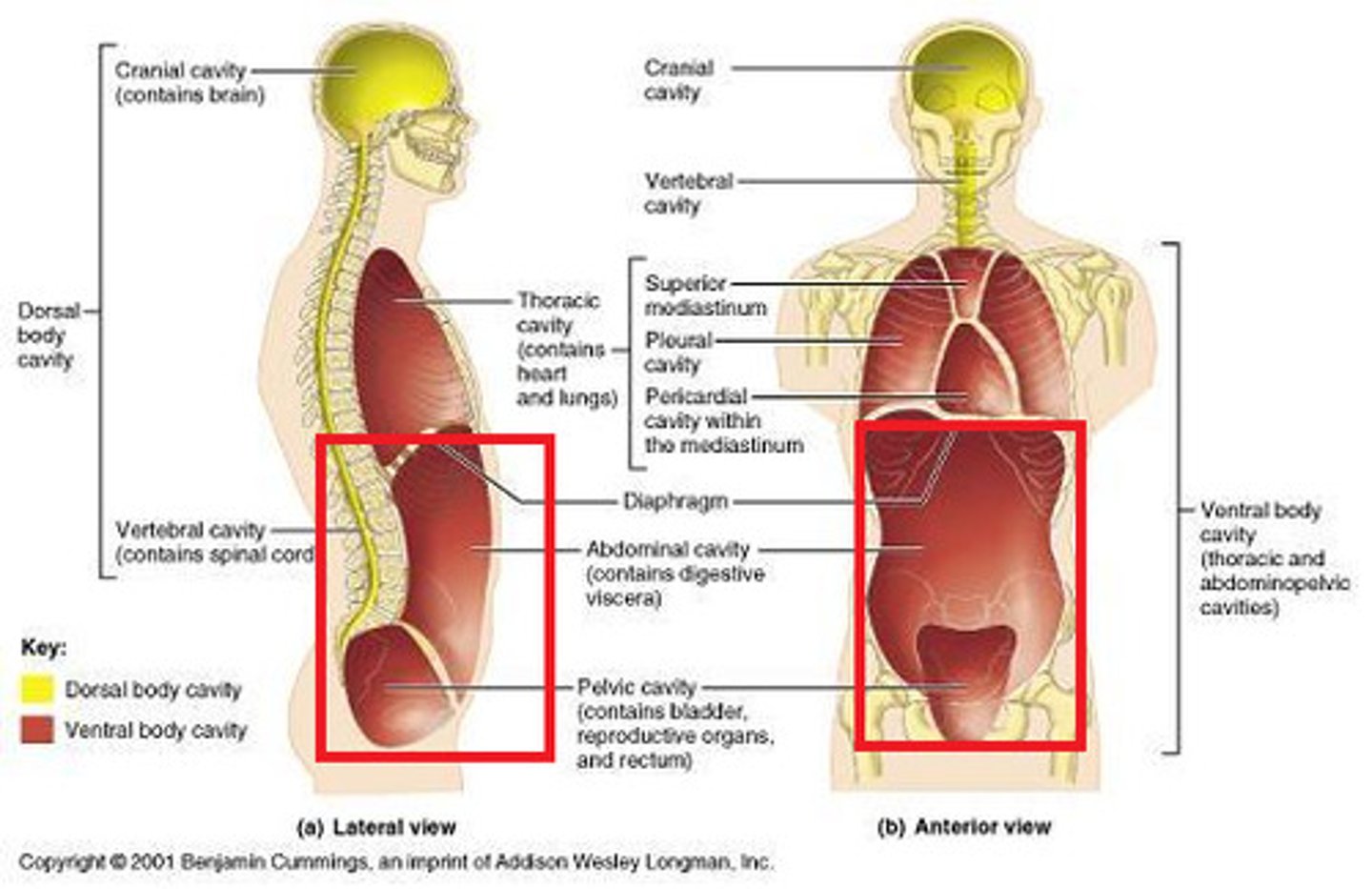
Pleural Cavity
contains the lungs
pericardial cavity
contains the heart
Mediastinum
Centrally located space between the lungs
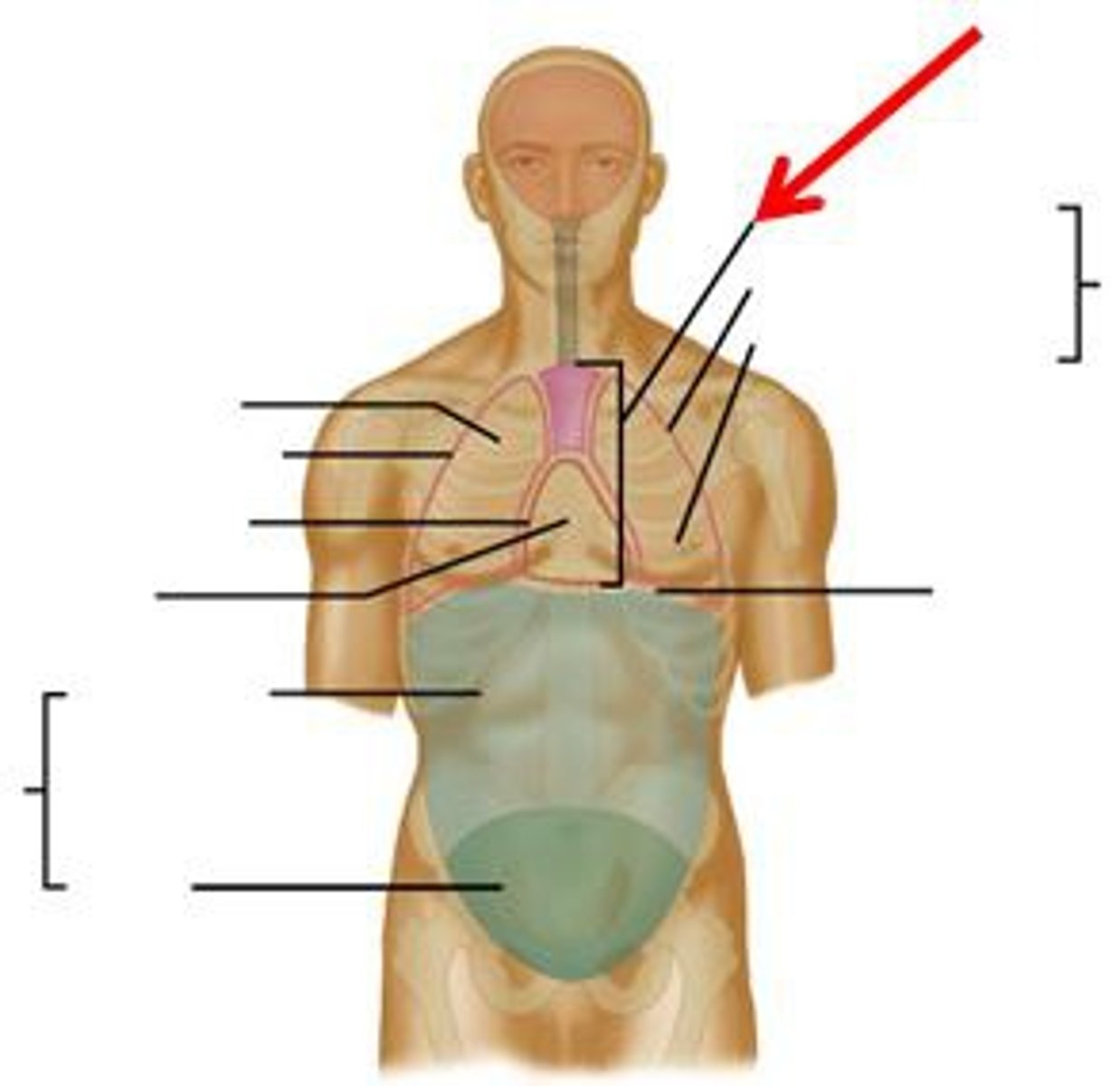
abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
pelvic cavity
contains urinary bladder, portions of large intestine, and internal organs of reproduction
cranial cavity
contains the brain
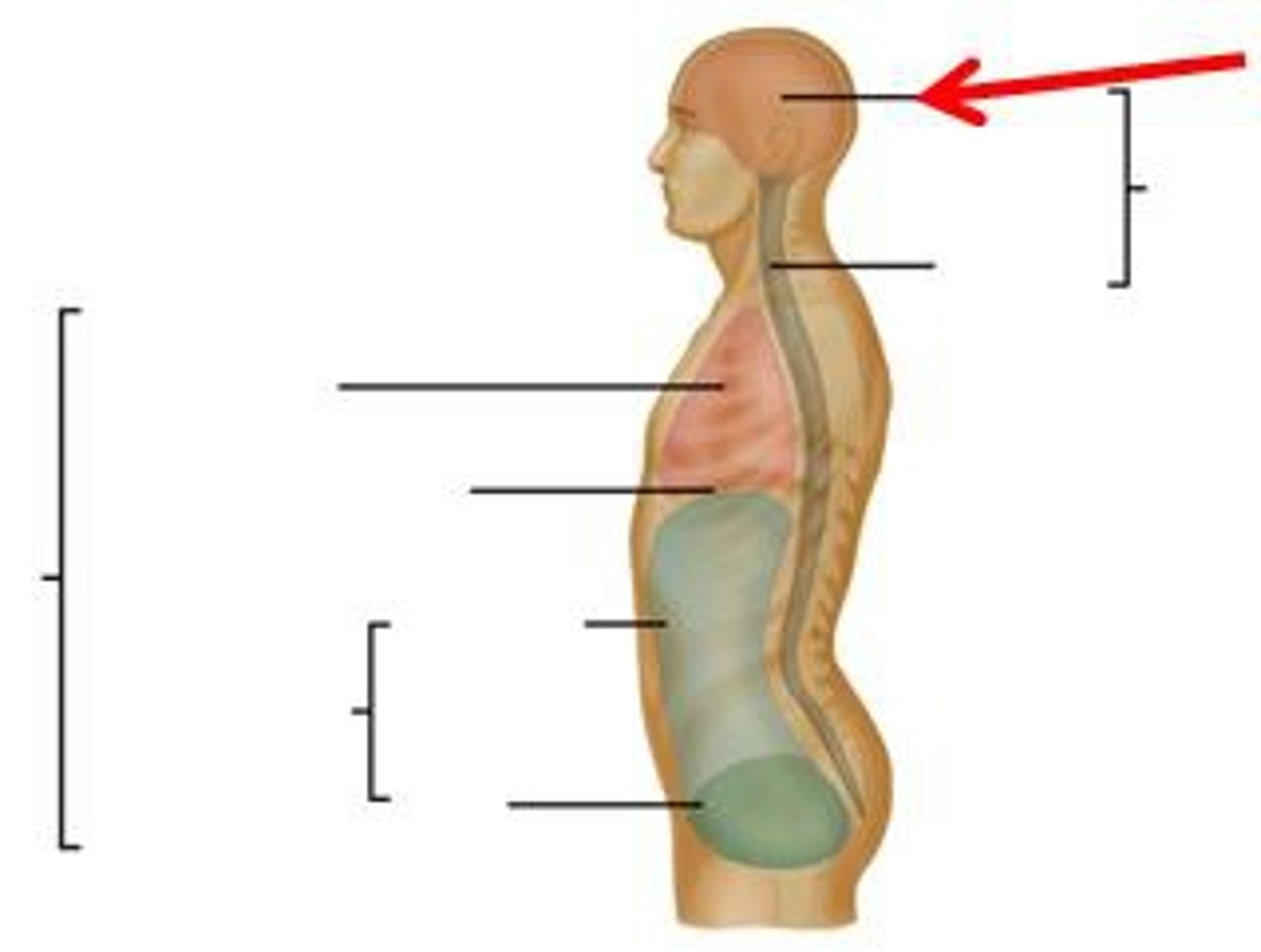
Vertebral Cavity (Spinal Cavity)
contains the spinal cord
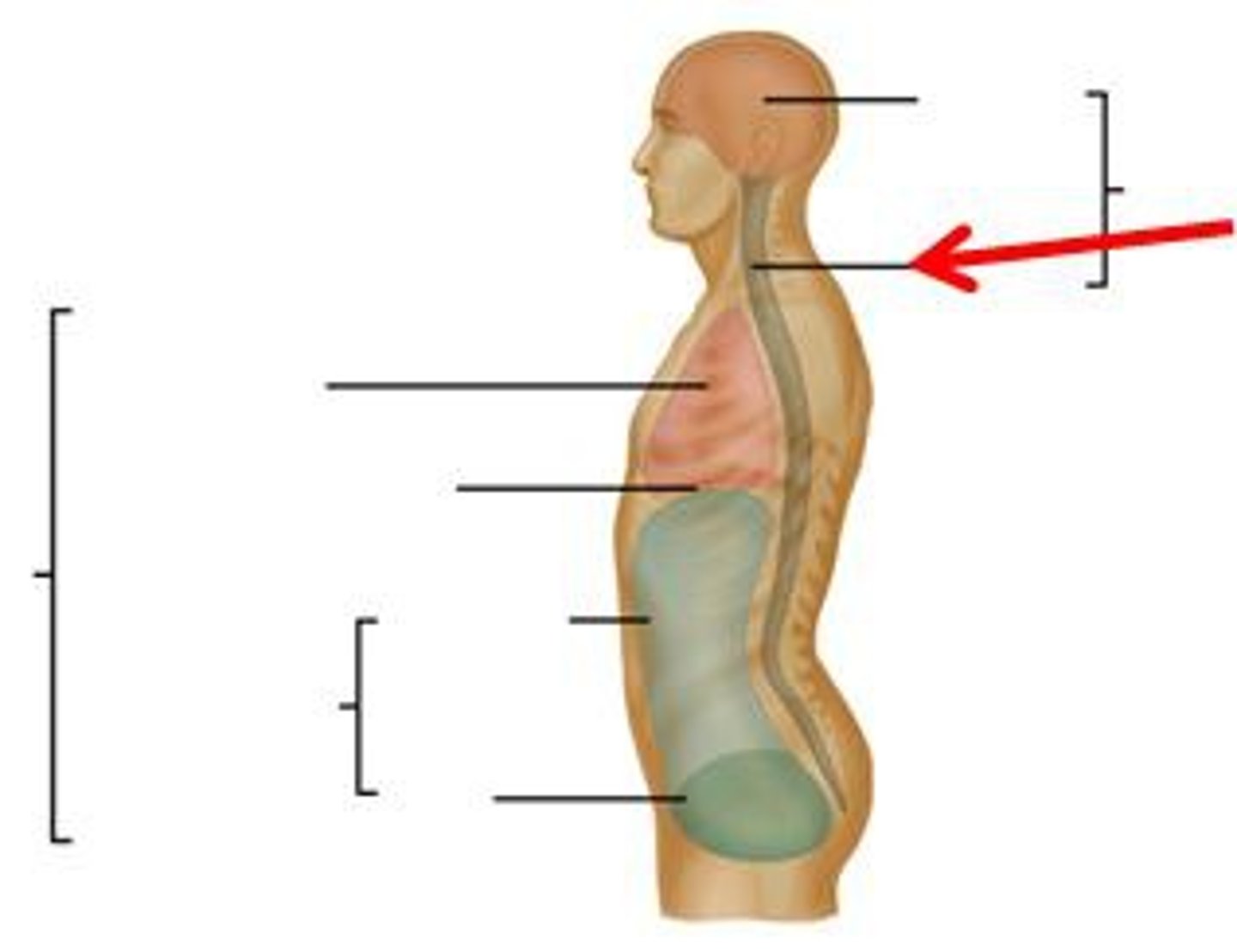
Posterior (dorsal)
back of body
abdominopelvic cavity
both the pelvic and abdominal cavities
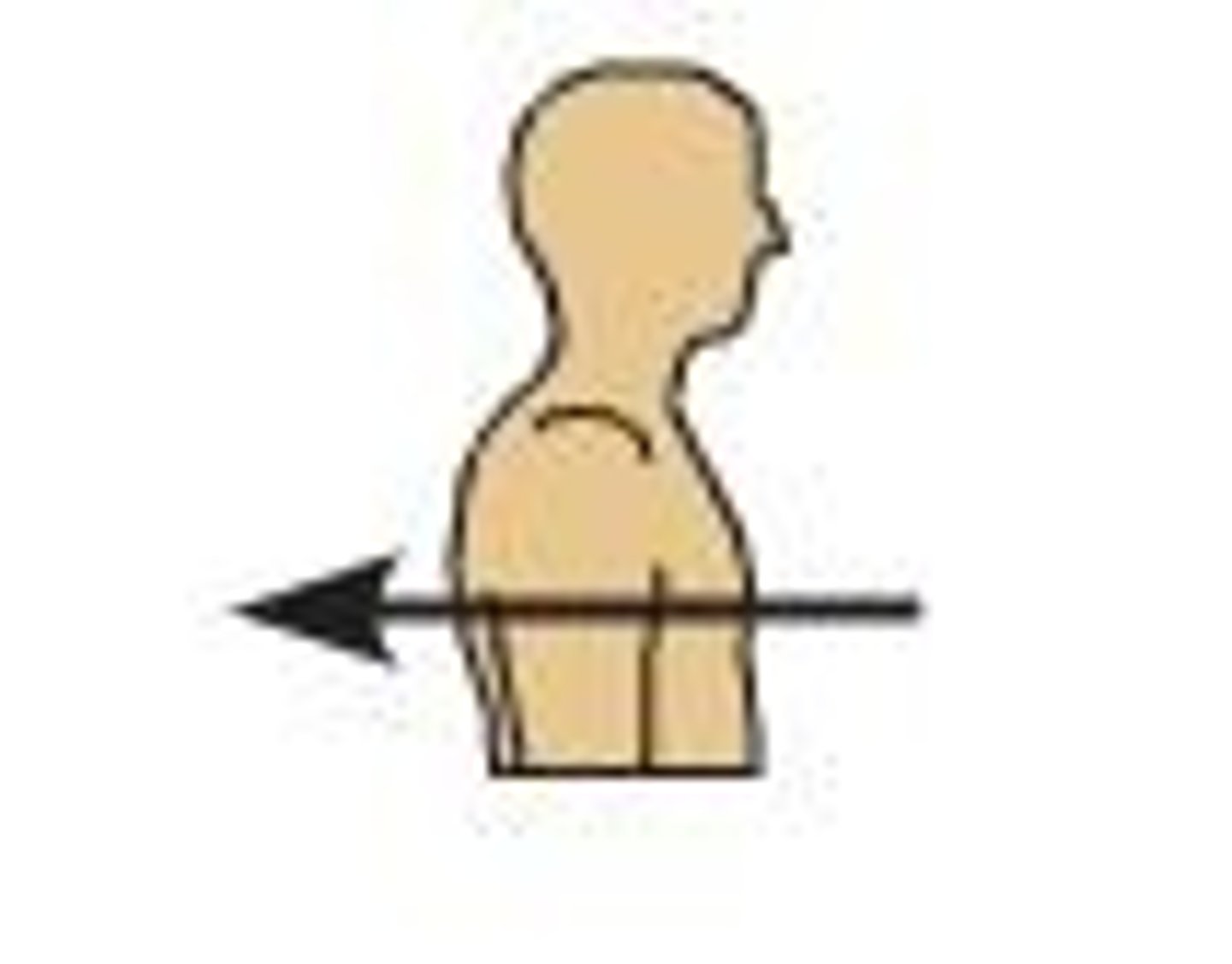
lateral
body parts away from the midline
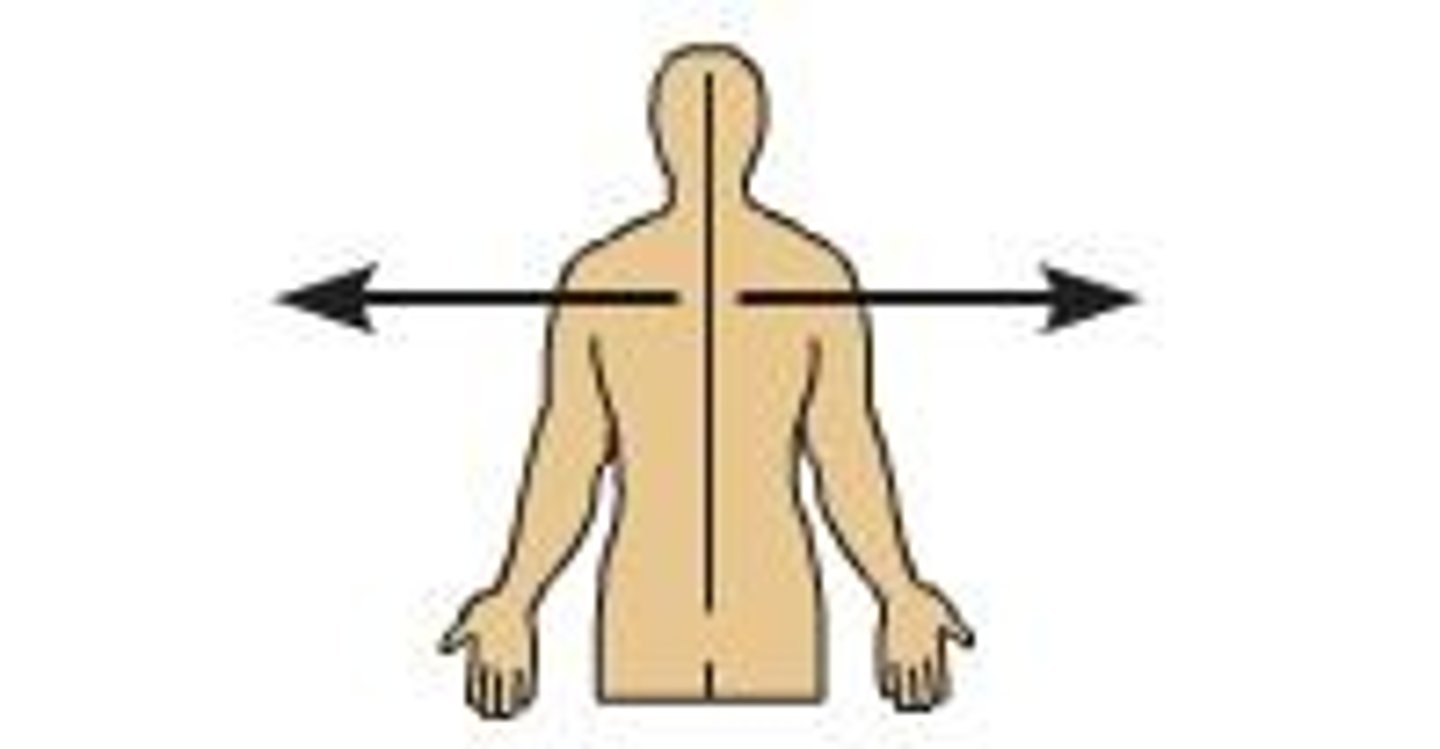
medial
body parts close to the midline
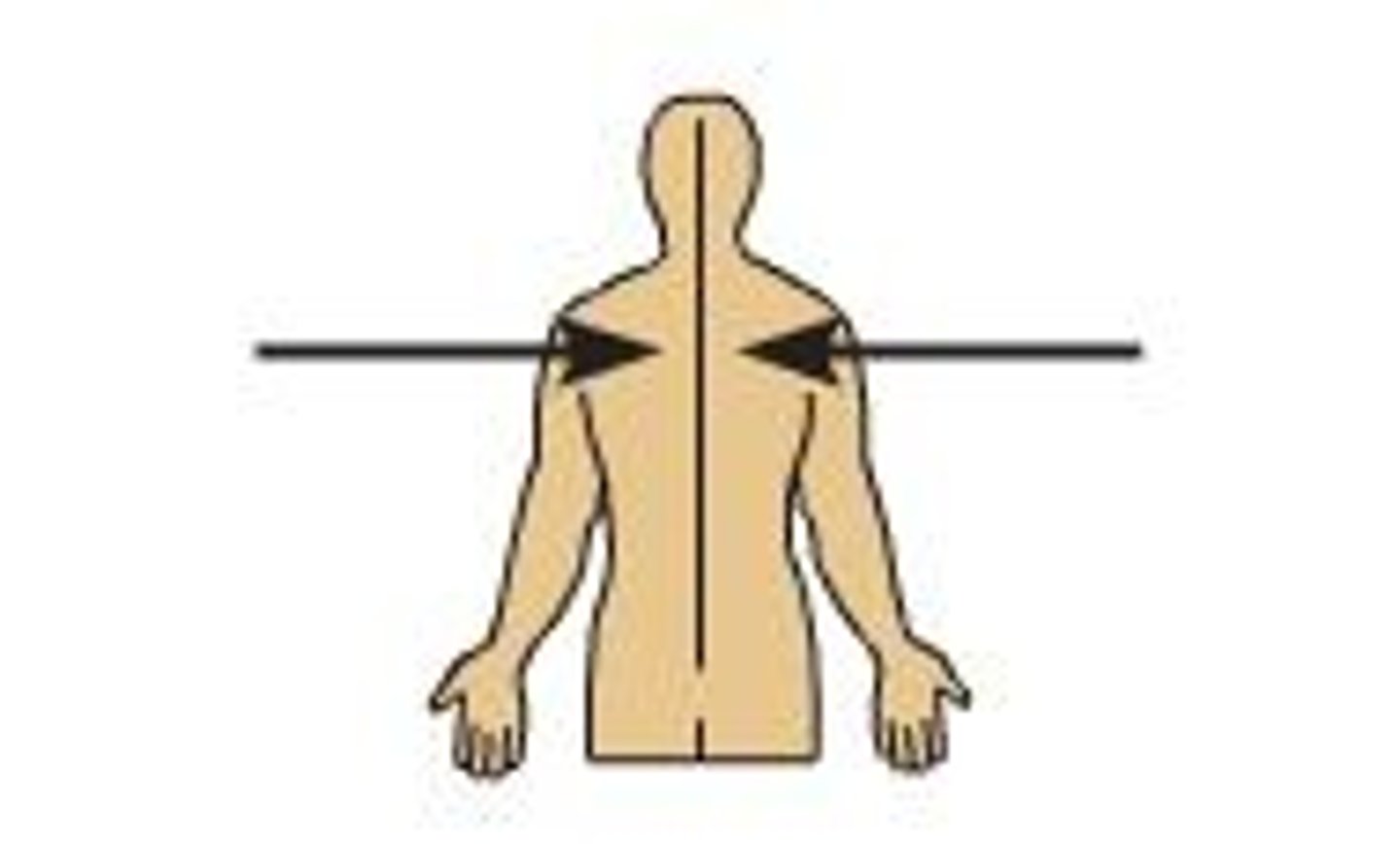
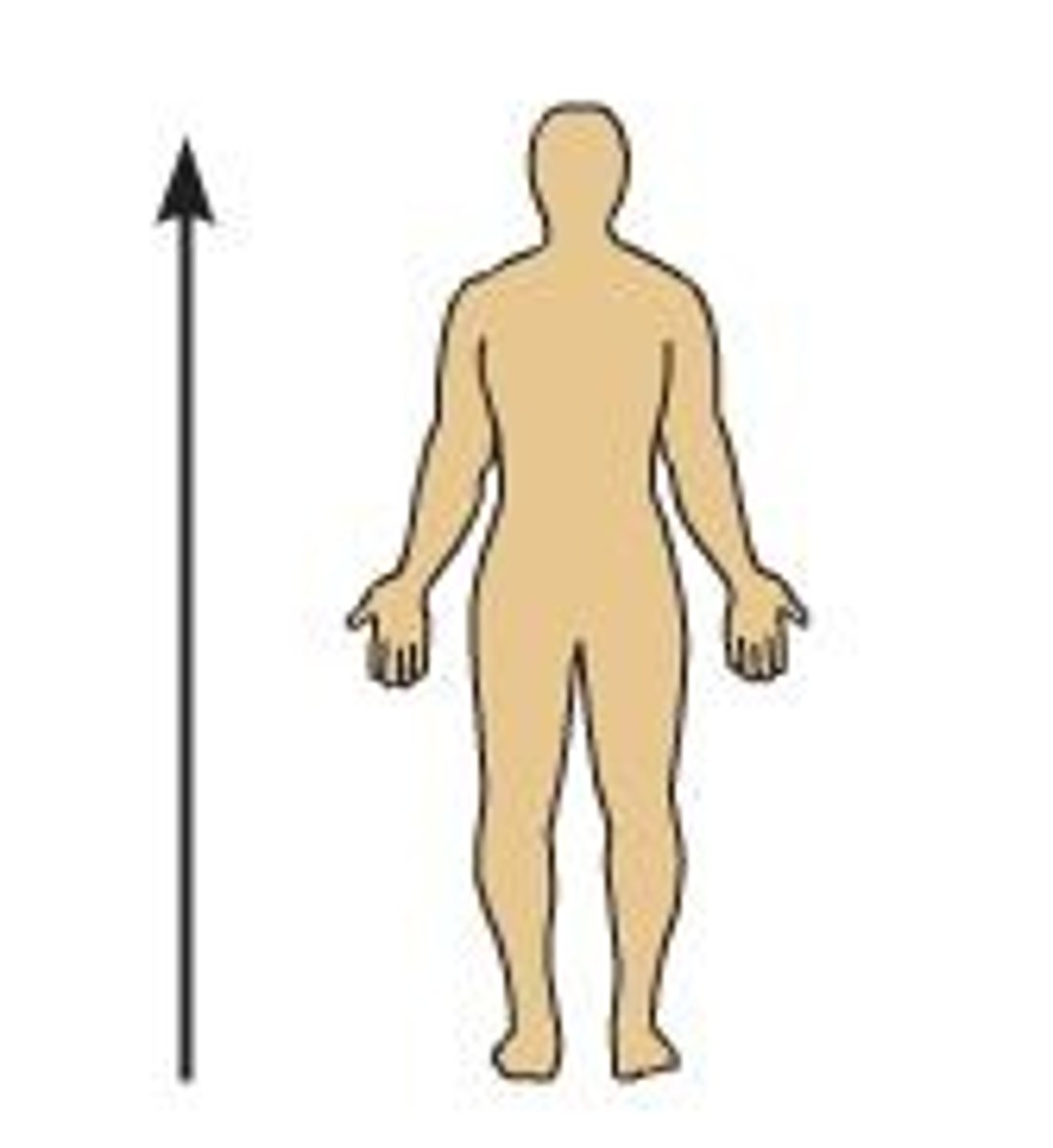
Superior
Above another structure; Ex: forehead is ___________ to your nose
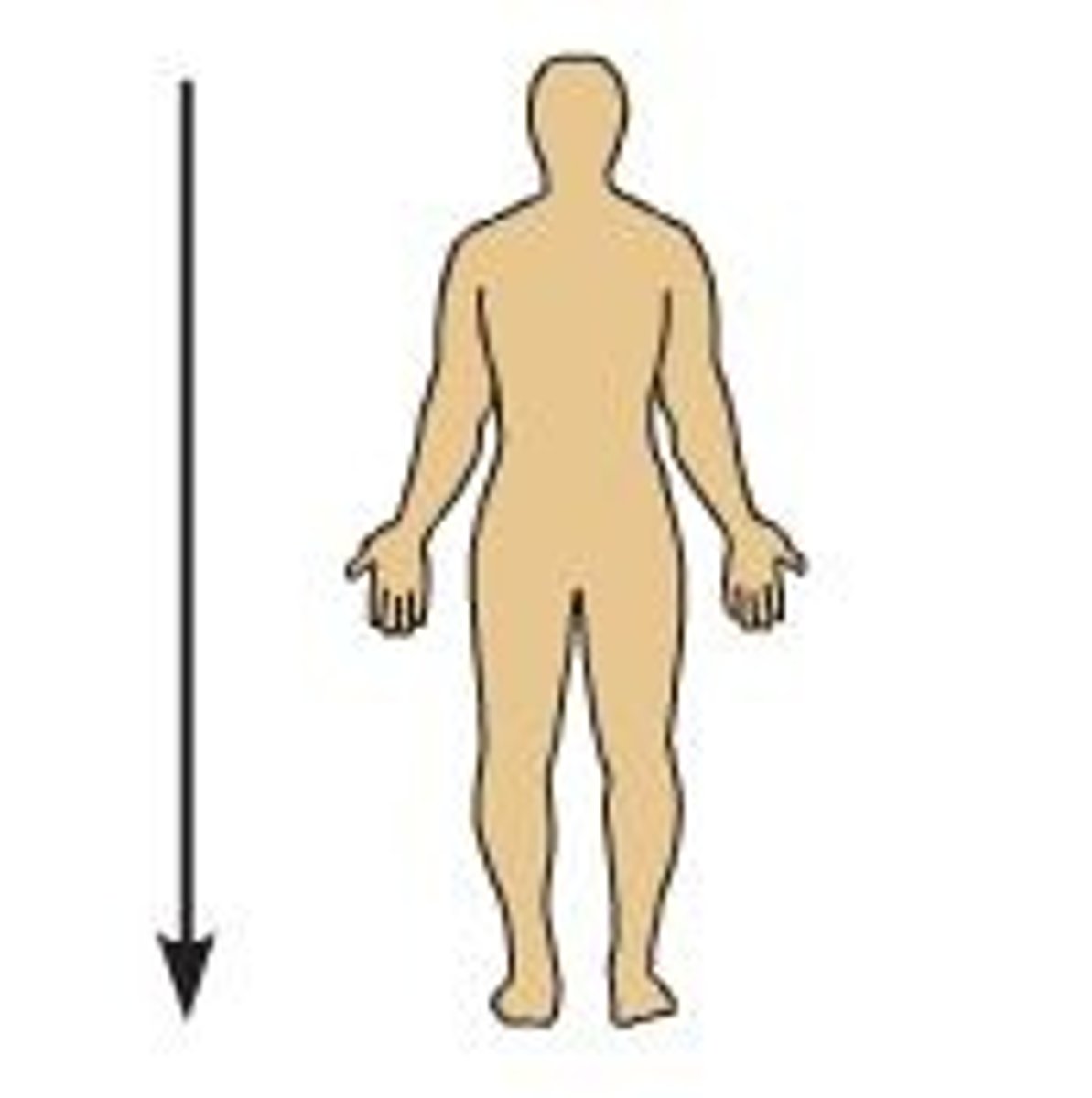
Inferior
below another structure; Ex: your chin is ____________ to your mouth
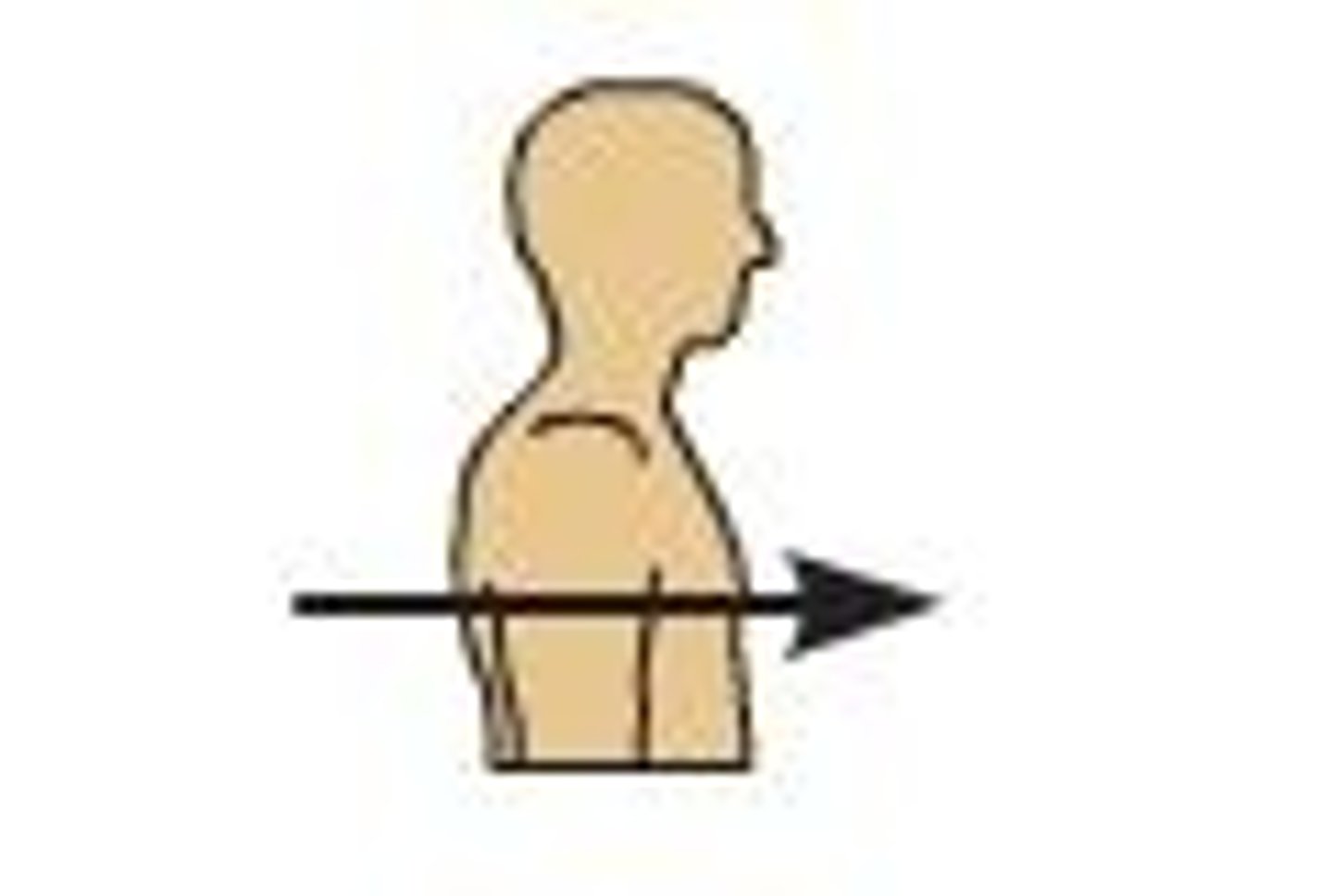
Anterior
structure is toward the front of the body; Ex: your chest is ____________ to your spine
Posterior
structure is toward the back of the body; Ex: your tongue is ____________ to your teeth
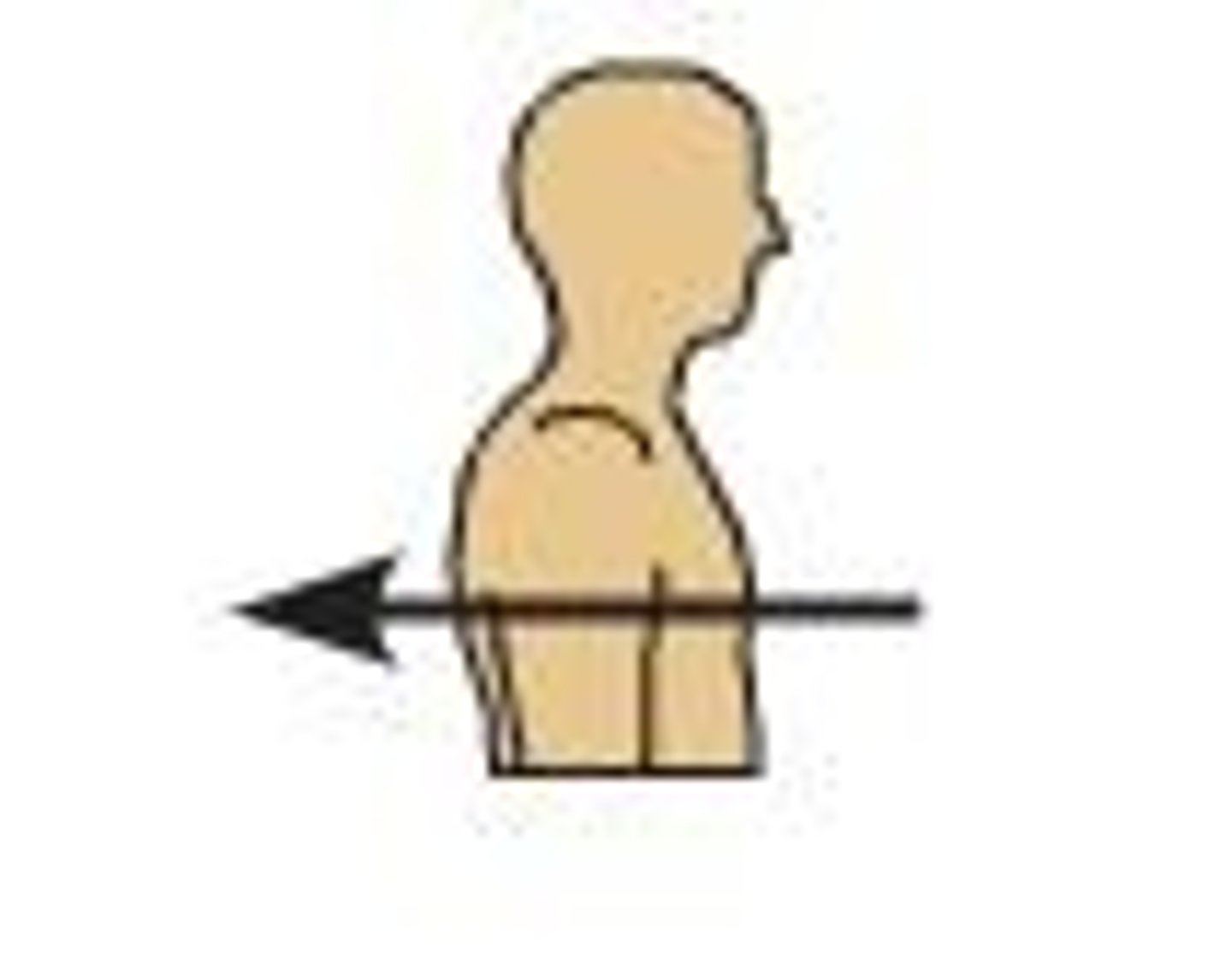
Proximal
structure closer to the attachment point; Ex: the elbow is ___________ to your wrist (attachment point is the shoulder)
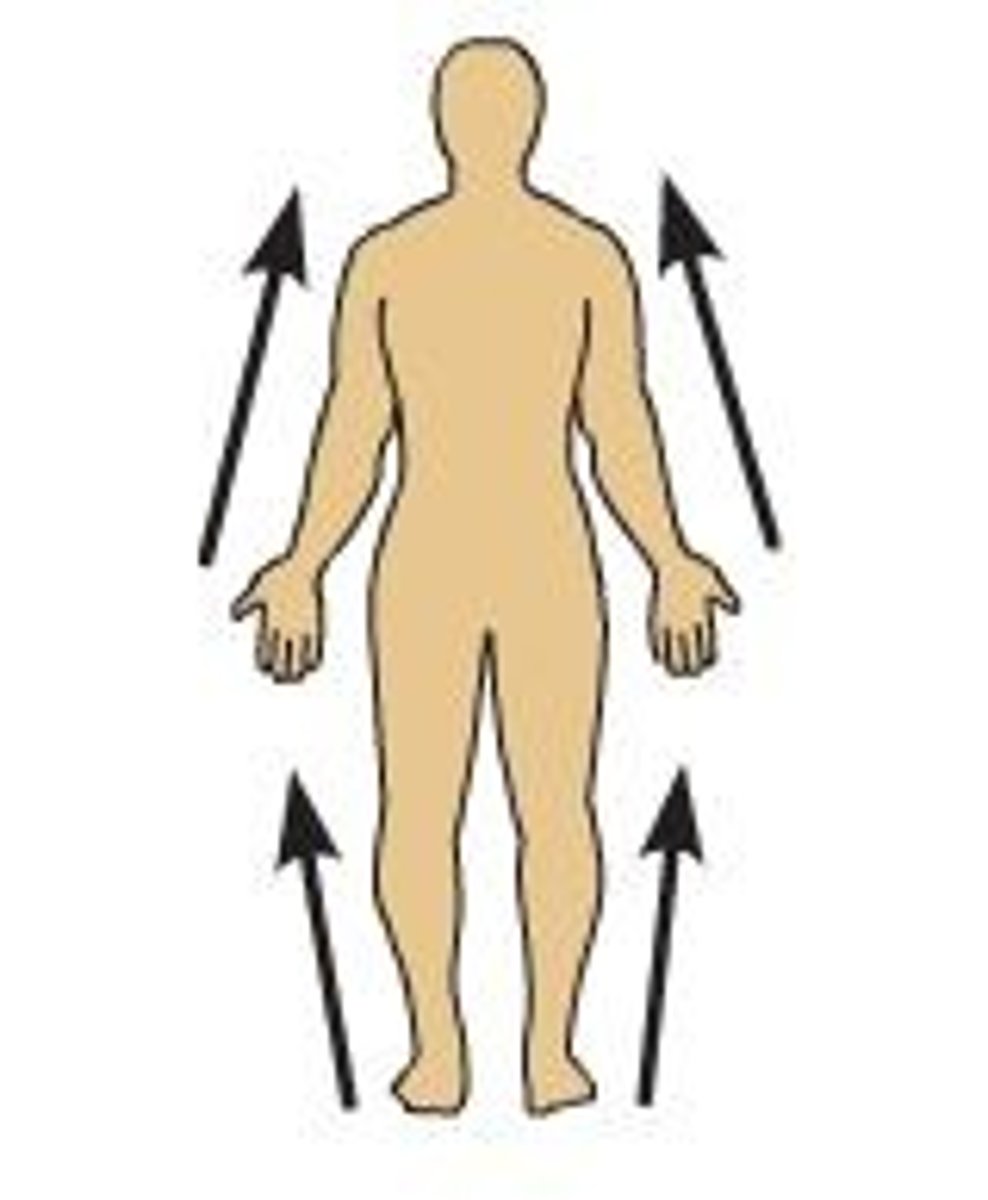
Distal
structure is further away from the attachment point; Ex: fingernails are ________ to your knuckles (attachment point is the wrist or shoulder)
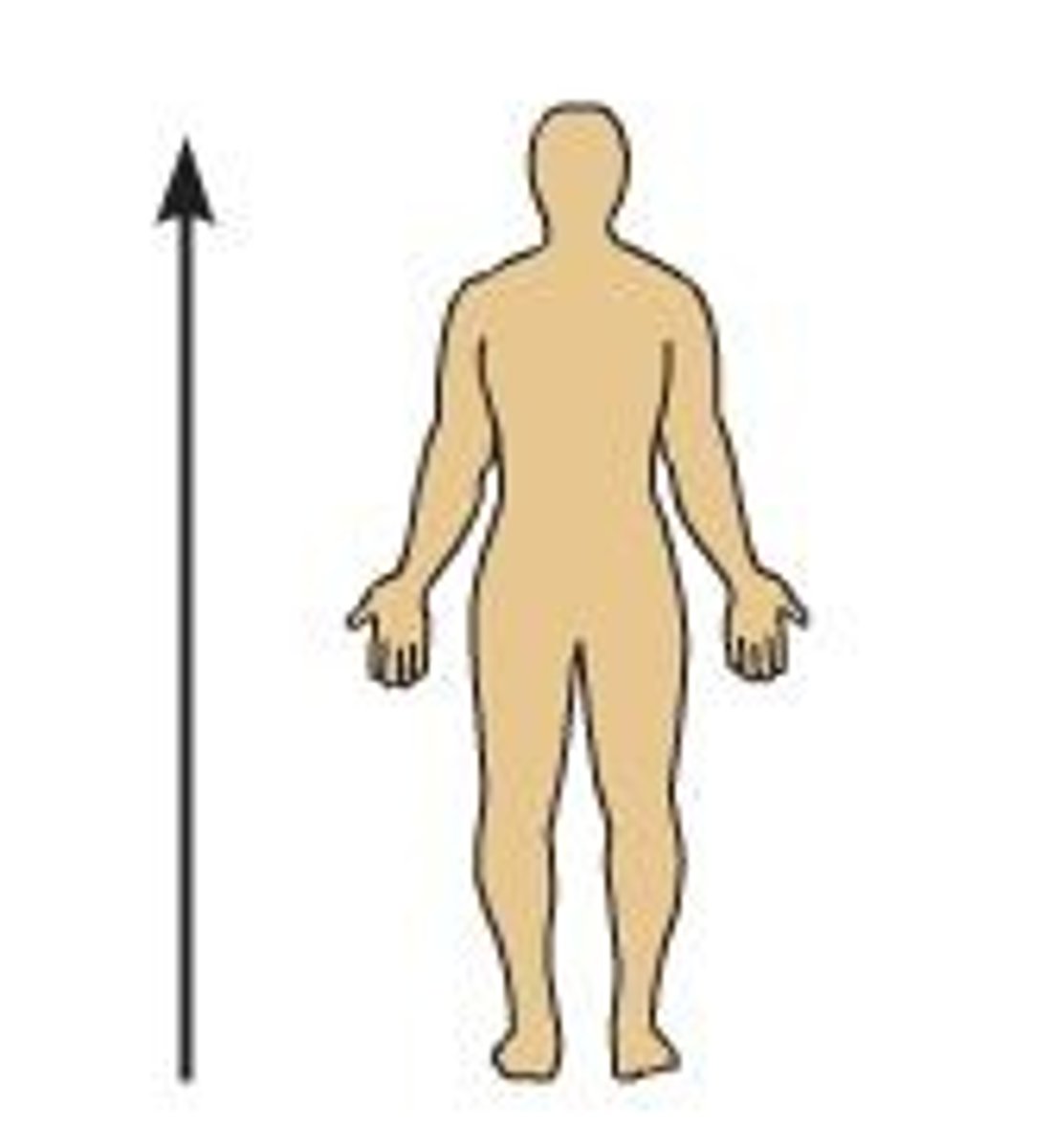
Cranial
structure toward the head; same as superior in humans; in four-legged animals, it is the same as anterior; Ex: neck is ________ to your belly button
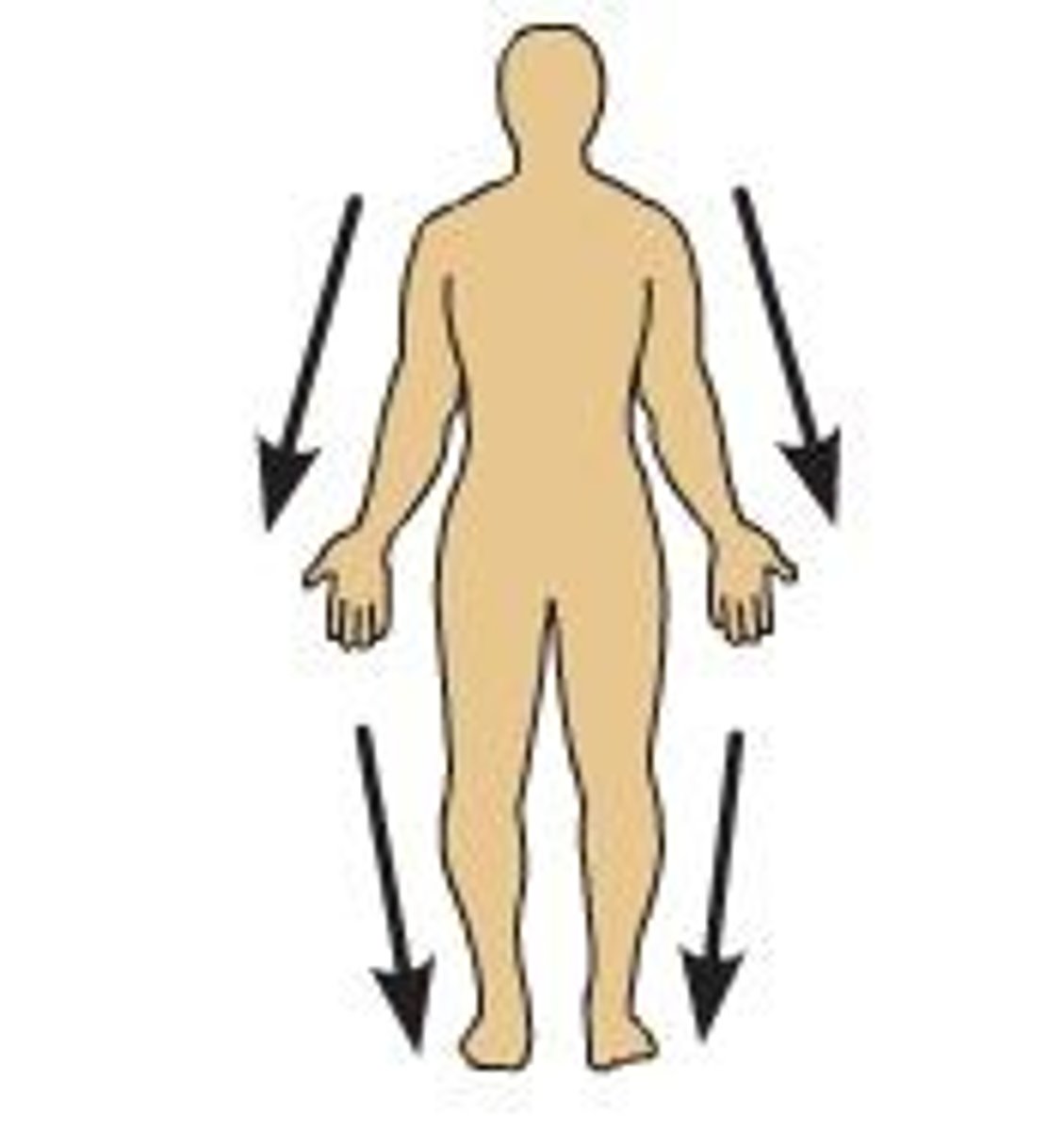
Caudal
structure toward the tail or rear; same as inferior in humans; in four-legged animals, it is the same as posterior; Ex: shoulders are __________ to your head
Dorsal
term describes an organism on all fours; refers to upper structures - toward the back; Ex: backbone is ____________ to your chest (on all fours); top of the foot is ____________ to the bottom of foot (in humans)
Ventral
term describes an organism on all fours; refers to lower structures, toward the belly; Ex: your chest is ____________ to your backbone