The Peripheral Nervous System: Afferent Division; Special Senses
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Human Physiology - From Cells to Systems (Lauralee Sherwood) Chapter 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
CNS
Brain and spinal cord
ENS
controls the motility and secretion functions of the digestive system
innervates the gastrointestinal tract
PNS
made up of nerves and ganglion
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Rest & digest
Sympathetic Nervous System
prepares body for stressful situations
“fight or flight”
stimulus
change detectable by the body
Sensory stimuli
carry conscious input
five senses
sight, sound, smell, touch, taste
Visceral stimuli
carry subconscious input
Complex stimulation
touch, pinch, heat, cutting, crush, and vibration
Photoreceptors
in the retina of the eye that function to detect light and convert it into electrical signals that the brain can interpret as vision
Mechanoreceptors
detect mechanical stimuli
pressure, touch, and sound waves
Thermoreceptors
detect changes in temperature
Osmoreceptors
in the hypothalamus that detect changes in osmotic pressure
Chemoreceptors
detect chemical changes in the body’s fluids
blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and saliva
Nociceptors
detect and transmit pain signals to the brain
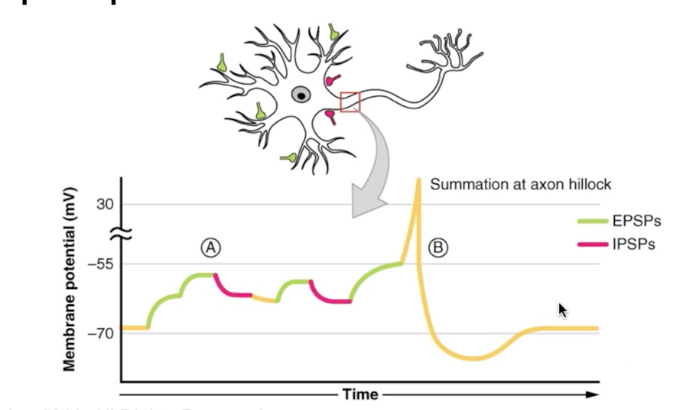
Receptor potential
A receptor is going to detect a stimuli, determine if it’s important enough, then cause an action potential to occur to be able to send the signal down to the brain to integrate (determine what will happen)
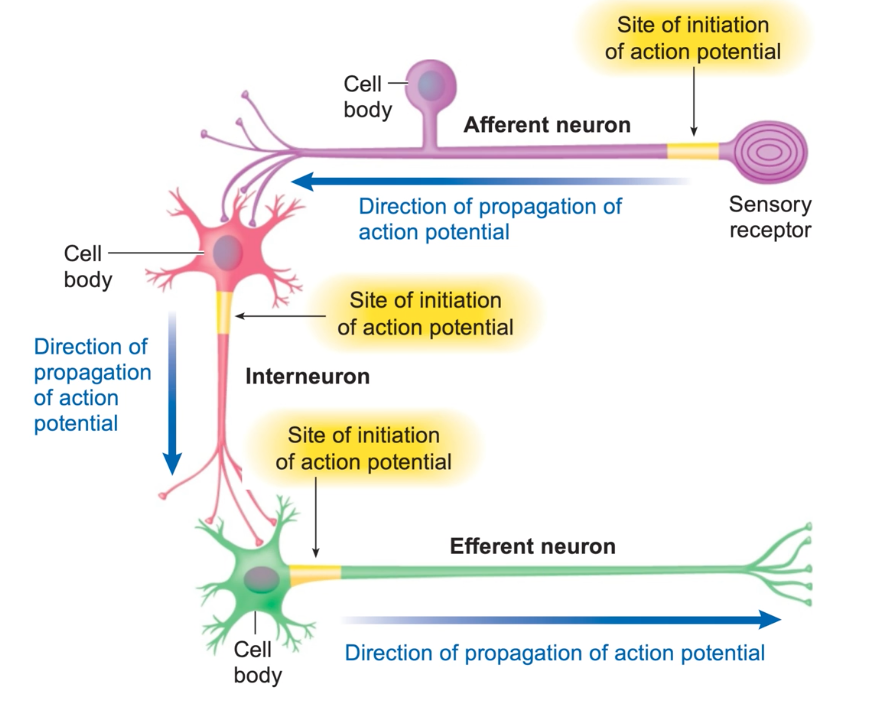
Afferent & efferent neurons
Understand the image.
pain
Nociceptors are sensitive to ______.
a.) sound
b.) osmolarity
c.) pain
d.) light
Tactile
Mechanoreceptors are a type of ________ receptor.
Hair receptor
hair movement and very gentle touch
Merkel’s disc
light, sustained touch
Pacinian Corpuscle
vibrations and deep pressure
Ruffini endings
ONLY deep pressure
Meissner’s corpuscle
light, fluttering touch
Tonic receptor
a sensory receptor that slowly adapts to a stimulus and continues to produce action potentials as long as the stimulus is present
e.g., thermoreceptors, pain receptors, joint capsule, muscle spindle, & Ruffini corpuscle
Phasic receptors
sensory receptors that respond quickly to stimuli but stop responding when the stimulus is constant
e.g., Pacinian corpuscle, thermoreceptors, and touch receptors
Phantom pain
may arise from extensive remodeling of the brain region that originally handled sensation
e.g., amputation of a limb
visceral afferent
What kind of nerves carry subconscious input information?
a.) sensory afferent
b.) sensory efferent
c.) visceral afferent
d.) visceral efferent
First order neuron
Which type of neuron? First, second, or third?
responsible for directly receiving sensory information from the periphery (like skin, muscle, or organs) and transmitting it to the central nervous system (CNS)
Second order neuron
Which type of neuron? First, second, or third?
receives signals from the first-order neuron (sensory receptor) and then transmits the information further up the neural pathway
passes the spinal cord or brainstem
Third order neuron
Which type of neuron? First, second, or third?
Nerve cells that relay sensory information from the thalamus to the cerebral cortex
Acurity
how accurately a stimulus can be located
influenced by receptive field or lateral inhibition
Receptive field
region of the skin surface surrounding the somesthetic sensory neuron
Lateral inhibition
each activated signal pathway inhibits the pathways next to it
Perception
conscious awareness of surroundings
Pain
a protective mechanism triggered on stimulation of danger-sensing nociceptors
brings to conscious awareness the tissue damage that is occurring or about to occur
Pain receptors
Categories of what?
Mechanical (physical), thermal (temp), and polymodal (respond to multiple types of sensory stimulation, such as heat, touch, and chemicals)
Delta fibers and C fibers
types of nerve fibers that transmit pain and temperature sensations
A-delta fibers
nerve fibers that are:
responsible for the initial perception of sharp pain
fast
C fibers
nerve fibers that:
transmit duller burning pain
slow
A-delta fibers
What nerve fibers constitute the “fast pain” pathway?
a.) A-alpha fibers
b.) A-delta fibers
c.) A-beta fibers
d.) C fibers
Analgesic system
a pain control system in the brain and spinal cord that reduces pain perception
endorphins released during exercise
stress-induced
acupuncture
eyelashes; lacrimal
Protective mechanisms that help prevent eye injuries:
eyelids and ______
tears and ________ gland
Accommodation
increases the strength of the lens for near vision
strength depends on its shape
regulated by the ciliary muscle
ciliary muscle
The strength of the lens depends on its shape, which in turn is regulated by what muscle?
a.) constrictor muscle
b.) radial muscle
c.) suspensory muscle
d.) ciliary muscle
Rods
provide indistinct gray vision at night
high sensitivity
low acuity
vision in shades of gray
Cones
provide sharp color vision during the day
low sensitivity
high acuity
color vision
Phototransduction
convert light stimuli into neural signals
by retinal cells
photoreceptors: rods and cones
Trichromatic theory
explains how humans perceive color by combining red, green, and blue light
Opponent processing theory
brain perceives color in terms of opposing pairs, such as red-green, blue-yellow, and black-white
Visual information Processing
modified and separated before reaching the visual cortex
thalamus and visual cortex elaborate the visual message
depth perception
hierarchy of visual cortical processing
Visual field
field of view that can be seen without moving the head
external, middle, inner
What are the three parts of the ear?
Hearing
neural perception of sound energy
Sound waves
traveling vibrations of air
pitch, intensity, timbre
What are the three sound characteristics?
pitch
tone
intensity
loudness
timbre
quality
External ear
plays a role in sound localization
pinna (ear, external auditory meatus (ear canal), & tympanic membrane (eardrum)
Tympanic membrane
vibrates in unison with sound waves in the external ear
stretch across entrance to the middle
vibrates when struck by sound wave (like drum)
Cochlea
pea-sized, snail-shaped, “hearing” portion of the inner ear
contains the organ of Corti, the sense organ for hearing
hair cells in the organ of Corti transduce fluid movement into neural cells
Ossicles
Pitch discrimination
depends on the region of the basilar membrane that vibrates
ability to distinguish among various frequencies of incoming sound waves
basilar membrane
Pitch discrimination depends on the shape and properties of the _______.
a.) basilar membrane
b.) ossicles
c.) stereocilia
d.) microvilli
Semicircular canals
sense head movement and maintain balance
Otolith organs
detect linear acceleration and gravity
Chemoreceptors
receptors for taste and smell
salty, sour, sweet, bitter, umami
Taste buds include what 5 taste bud receptors?
s_____, s______, s______, and u______
pheromones