Molecular Bio
1/684
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
685 Terms
how was immunology discovered
edward jenner observed that milkmaids that got cow pox never got small pox even with close proximity to the virus
cow pox symptoms were much more mild so he injected material from a fresh cow pox vesicle into James Phipps
6 weeks later, Phipps was inoculated with small pox but never developed the disease
what are the big two types of immune responses
innate or non-acquired response
acquired or adaptive response
what two lines of defense are nonspecific
first line of defense
skin
mucous membranes
secretions of skin and membranes
second line of defense
phagocytic white blood cells
antimicrobial proteins
inflammatory response
what line of defense is specific
third line of defense
lymphocytes
antibodies
what are examples of anatomical and physiological barriers
intact skin
ciliary clearance
low stomach pH
lysozyme in tears and saliva
what are involved in cellular innate immunity
natural killer cells
neutrophils
eosinophils
mast cells
macrophages
dendritic cells
what are involved in humoral innate immunity
complement
mannose binding lectin
antimicrobial peptides
LPS binding protein
C-reactive protein
what is involved in cellular adaptive immunity
T cells and B cells
what is involved in humoral adaptive immunity
antibodies
characteristics of innate immune response
non-specific and fast
doesn’t improve with subsequent exposures
first line of defense
4 components
physical barriers
physiological barriers
vascular system
phagocytic component
what are some examples of physical barriers
tightly packed together epithelial cells
keratin in skin = waterproofing
epithelial shedding
mucous coat
what are examples of physiological barriers
fever - less microbial replication
low ph - less microbes
coughing/sneezing
blinking
commensals
antimicrobial molecules
interferon alpha/beta - decreases infections in neighboring cells
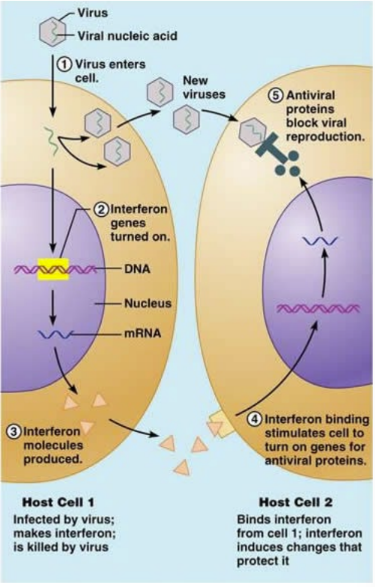
role of interferons
released from virus-infected cells
IFN binds to surface receptors on neighbor cells
inducing uninfected cells to synthesize antiviral proteins that interfere with or inhibit viral replication
what are interleukins
a type of cytokine
soluble molecules that mediate interactions between cells
role of IL-1 and IL-6
induces fever and increases immune response
role of IL-8
chemotaxis for neutrophil recruitment
role of IL-2
stimulates lymphocyte proliferation
role of lysozyme
found in tears, saliva, in granules of neutrophils
degrades bacterial peptidoglycan cell wall
bacteria succumbs to osmotic gradient and dies
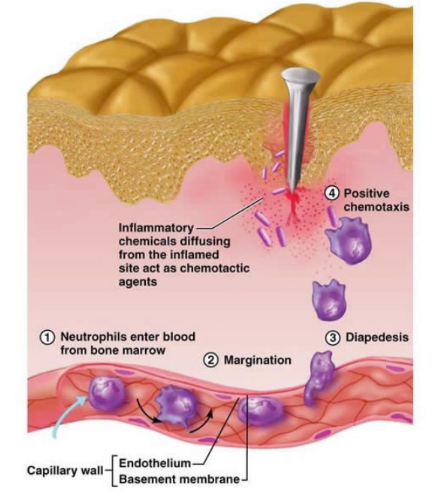
role of the vascular/phagocytic response
acute inflammatory response upon penetration
increases vascular permeability
immune cells recruited from blood to remove invading pathogens
general function of complement
trigger inflammation
immune cell recruitment
coats pathogens to increase phagocytosis
kills pathogens
components of the complement response
9 proteins that are broken down to form pore in pathogen that leads to death
3 pathways can lead to complement activation
classical pathway
lectin pathway
alternative pathway
what happens in the classical pathway
antibody mediated
C1 binds to Fc portion of IgG or IgM which starts cascade
splits C2 and C4 to form C3 convertase (C4bC2a)
C3b is opsonized
ultimately leads to C5 convertase
what are the active fragments of the complement
C3a and C5a
role of C3a
induce release of histamine by mast cells
attracts neutrophils
role of C5a
induce release of histamine by mast cells
attracts neutrophils
strongly chemotactic for leukocytes and increases their adhesion to endothelial cells
how does the complement cause lysis
targets lysis by MAC
metabolism and osmotic balance of target is disruptedDNA and protein synthesis stops
fluids enter and target swells and bursts
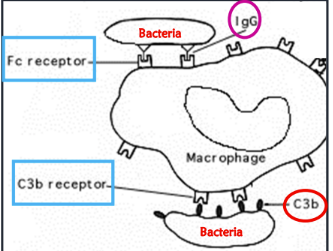
what are the types of opsonins
C3b and antibodies
bind to foreign molecules
what are IgG antibodies and C3b recognized by
IgG recognized by Fc receptors on immune cells
C3b recognized by C3b receptor on immune cells
what parts of a microbe are recognized by pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMP)
LPS and flagellin
what are some types of pattern recognition receptors
mannose receptors: sugars on pathogens → phagocytosis
CD14
toll-like receptors
role of toll-like receptors
stimulates production of cytokines, chemokines, and antimicrobial peptides
acts as pattern recognition receptor
alert immune system of infection
kills pathogens
what cells are part of the immune response
granulocytes
platelets
mononuclear cells
dendritic cells
lymphocytes
where are all cells of the immune response derived from
haematopoeitic stem cell (bone marrow)
what regulates the production of cells of the immune response
colony stimulating factors
what does IL-7 regulate
lymphoid cells (T cells, B cells, and NK cells)
dendritic cell lineage
what does IL-3 regulate
common lymphoid progenitor and haemopoietic stem cell
what does granulocyte-monocyte CSF (GM-CSF) regulate
along with granulocyte CSF, helps to regulate production of granulocytes
mast cells
basophils
neutrophils
eosinophils
what does monocyte CSF regulate
monocytes → macrophages
what does granulocyte CSF regulate
along with GM-CSF, regulates granulocytes
eosinophils
neutrophils
basophils
mast cells
what are the types of granulocytes
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
mast cells
general features of granulocytes
produced in bone marrow
50 billion in circulations
release contents of cytoplasmic granules to kill pathogens
what granulocyte arrives first to the scene of the immune response
neutrophils
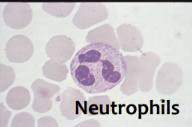
what are the general features of neutrophils
95% of circulating granulocytes
multilobes nucleus
aka polymorphonuclear neutrophils
migrate rapidly to site of infection
phagocytose and destroy foreign organisms
produce myeloperoxidase and lysozyme
what makes up the majority of circulating granulocytes
neutrophils - 95% of circulating granulocytes
function of neutrophils
produce myeloperoxidase and lysozyme
phagocytose and destroy foreign organisms
release reactive oxygen species and phagolysosome enzymes to kill pathogens
what receptors do neutrophils have to aid in pathogen detection
Fc receptor
complement receptors
toll-like receptors
defining physical characteristic of neutrophils
multilobed nucleus
stains purple
defining physical characteristic of eosinophils
bilobed nucleus
stains pink with eosin
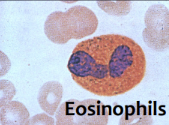
what is the main function of eosinophils
bind to Ig coated parasites
release granules to kill helminths
involved in allergies and produces histamine/pro-inflammatory molecules
where do most eosinophils reside
connective tissue
frequency of eosinophils
makes up 2-5% of white blood cells
frequency of basophils
0.2% of white blood cells
where do most basophils reside
in blood stream
same function as mast cells, but those are in the tissue
physical characteristics of basophils
hard to see nucleus
lots of molecules
stains blue with hematoxylin
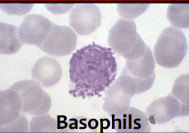
function of basophils
release histamine and inflammatory molecules
allergen must cross link IgE molecules bound to its surface
often linked to hypersensitivity reactions
function of mast cells
release histamines when allergen is encountered
mucosal mast cell
connective tissue mast cell
function of platelets aka thrombocytes
blood clotting
involved in inflammation
adhere to endothelial surface of damaged blood vessel and release factors to:
modulate capillary permeability
leukocyte recruitment
what are macrophages derived from
monocytes in blood and become macrophages in tissue
defining physical characteristics of mononuclear phagocytes
largest in size of circulating WBCs
horseshoe shaped nucleus
frequency of mononuclear phagocytes
2-8%
naming convention of mononuclear phagocytes
names vary on location
ex. kupffer cells in liver
microglia in brain
function of mononuclear phagocytes
innate immune response
phagocytosis
release chemoattractive factors for other immune cells to boost immune response
release leukotrienes and prostaglandins to increase vascular permeability/cell recruitment
assist acquire immune response
a type of antigen presenting cell
present antigen to T cells
how do macrophages assist the acquired immune response
when macrophage digests a pathogen, some antigen is saved on the MHC (major histocompatibility complex)
APC to secondary lymphoid tissue activates T cell that recognizes antigen to generate immune response
where are MHC class I molecules located
on all nucleated cells
where are MHC class I and II molecules located
on antigen presenting cells (APCs)
aka macrophages, dendritic cells, B cells
what is a normal MHC filled with
self protein
what is an MHC filled with in the case of infection
filled with antigen from invading organism
definition of antigen
immunogen
something that induces immune response
definition of epitope
3D molecular arrangement on antigen recognized by immune system
definition of hapten
too small for immune response unless attached to larger molecule
what makes up MHC I
3 alpha chains
1 beta microglobulin
what makes up MHC II
2 alpha chains
2 beta chain
specific T cell will recognize foreign antigen in MHC II molecule and stimulate immune response
where are class II and class I molecules located on chromosomes
short arm of chromosome 6
HLA region is most polymorphic gene cluster of entire human genome
where do dendritic cells reside
in most tissue and organs
function of dendritic cells
professional antigen presenting cells
capture, process, and present antigens to T-cells to initiate adaptive immune response
function of lymphocytes
specificity and memory function of acquired immune response
have antigen receptor that recognizes one specific epitope
once programmed, cannot be changed
how much of total lymphoid cells do B cells make up
5-15% of B cells
function of B cells
humoral response
binds to antigens in bodily fluids
have antibodies on their cell surface to recognize foreign antigens
characteristics of B cell antigen receptor
membrane-bound antibody receptor
unique antigen-binding site
once bound, antigen is internalized and processed to be presented to helper T cells
steps of B cell activation
B cell finds antigen which matches its receptors
it waits until it’s activated by a T helper cell
B-cell the divides to produce plasma and memory cells
plasma cells produce antibodies that attach to current type of invader
what is clonal selection
each lymphocyte is specific to a particular antigen
what is clonal expansion
production of daughter cells that share the same antigen specificity
what are the two types of cells produced by B cells
plasma cells
memory cells
characteristics of plasma cells
live only a few days
secrete antibody that bind the same epitope (specificity)
characteristics of memory cells
persist in circulation for a long time
persist even longer if they encounter the same antigen
what is the primary response to an antigen
first exposure to antigen
lag phase: lasts days to weeks
IgM first produced
what is the secondary response to an antigen
second exposure to antigen
shorter lag phase
more antibody produced
IgG > IgM
what determines the isotype of an antibody
amino acids of heavy constant chain
what are the two components of an antigen binding site
variable end of heavy chain + variable end of light chain
how are antibodies cleaved
enzyme breaks disulfide linkages in hinge area to separate Fc and Fab regions
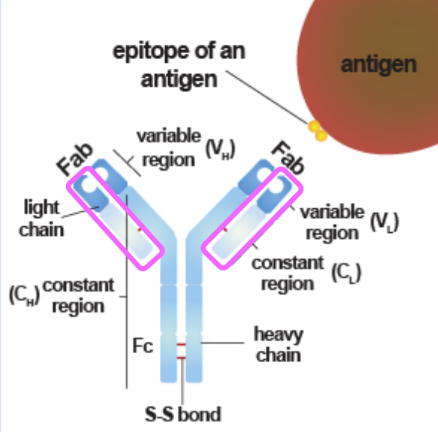
what is the Fab region
antigen binding fragment
each arm is an antigen binding region
what is the Fc region
interacts with:
complement
immune cells
neutrophils
macrophages
other phagocytes
structure of an antibody
2 identical heavy and light chains
constant and variable end regions
isotypes: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, IgD
what is the most abundant antibody in serum
IgG (70-75%)
how many subclasses does IgG have
four - IgG 1 to IgG 4
which antibody has the highest half life
IgG - 3 weeks
characteristics of IgG
main antibody in secondary response
passes through placenta for neonate immunity
activates complement
antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity
what is the abundance of IgA
15-20%
major antibody present in mucous secretions such as saliva, tears, breast milk in the form of dimer called secretory IgA
what is the half-life of IgA
6 days
characteristics of IgA
two forms - IgA1 and IgA2
monomeric in circulation
associated with another protein called secretory component