Grays Anatomy - Chapter 1
1/313
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
314 Terms
Regional approach
each region of the body is studied separately and all aspects of that region are studied at the same time
Systemic approach
each system of the body is studied and followed throughout the entire body
Sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
Coronal plane
divides body into anterior and posterior parts
Median sagittal plane
passes vertically through the midline of the body, dividing it into left and right halves
Transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into superior and inferior portions
Cranial
towards the head
Caudal
towards the tail
Rostral
used to describe the position of a structure in reference to the nose
Superficial
near the surface
Levels of interaction of X rays in the body
bone > water > fat > air
Bone on an x ray appear white
due to the lack of exposure to X rays
Air appears black in X rays
due to the abundance of exposure to X rays
Images acquired via CT scans
in the axial plane and viewed such that the observer looks from below and upward towards the head
-the right side of the patient is the left side of the image
-the uppermost border of the image is anterior
Axial skeleton
consists of bones of the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum
Appendicular skeleton
bones of the upper and lower limbs
Cartilage
avascular form of connective tissue consisting of extracellular fibers embedded in a matrix that contains cells localized in small cavities
-nourished by diffusion and has no blood vessels, lymphatics, or nerves
The amount and kind of extracellular fibers is based on
the type of cartilage
In heavy weightbearing areas or areas prone to pulling forces, the amount of collagen
greatly increases and cartilage is almost inextensible
Cartilage contains elastic fibers and fewer collagen fibers in areas
lighter weightbearing demands and stresses are placed
Functions of cartilage
-support soft tissues
-provide a smooth, gliding surface for bone articulations at joints
-enable the development and growth of long bones
Types of cartilage
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrocartilage
Hyaline cartilage
matrix contains a moderate amount of collagen fibers (articular surfaces of bones)
-most common
Elastic cartilage
matrix contains collagen fibers along with a large number of elastic fibers (external ear)
Fibrocartilage
matrix contains a limited number of cells and ground substance amidst a substantial amount of collagen fibers (intervertebral discs)
Bone functions
-supportive structures of the body
-protects vital organs
-reservoirs of calcium and phosphorous
-levers for muscles to act to produce movement
-contains blood producing cells
Compact bone (trabecular)
dense bone that forms the outer shell of all bones and surrounds the spongy layer
Spongy bone (cancellous)
consists of spicules of bone enclosing cavities containing blood forming cells
Classification of bones
-long
-short
-flat
-irregular
-sesamoid
Long bones
tubular
-humerus and femur
Short bones
cuboidal
-bones of the wrist and ankle
Flat bones
consist of two compact bone plates separated by spongy bone
-skull
Irregular bones
bones of various shapes
-face
Sesamoid bones
round or oval bones that develop in tendons
Artery adjacent to bone
gives off nutrient artery that directly enters the internal cavity of the bone and supplies the marrow, spongy bone, and inner layers of compact bone
All bones are covered externally by
periosteum (fibrous connective tissue membrane)
In the area of a joint where articular cartilage is present
periosteum is not present
Periosteum
fibrous membrane covering bone that has the ability of forming new bone
-receives blood vessels
Nerves that pass into the internal cavity of bone alongside the nutrient artery
vasomotor fibers
Vasomotor fibers
nerves that regulate blood flow inside the bone
All bones come from
mesenchyme by either intramembranous ossification or endochodral ossification
Intramembranous ossification
mesenchymal models of bone undergo ossification
Endochondral ossification
cartilaginous models of bones form from mesenchyme and undergo ossification
Determination of skeletal age
the nondominant hand is radiographed and compared to a series of standard radiographs
Red bone marrow (myeloid tissue)
produces blood cells, platelets, and most white blood cells
Yellow bone marrow
dominanted by fat globules with some white blood cells produced
As a person ages red bone marrow
is converted to yellow bone marrow in the medulla of long and flat bones
Hemopoietic stem cell
produce white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets
Mesenchymal stem cell
differentiates into structures that form bone, cartilage, and muscle
Bone fracture
bone gives way after abnormal load or stress
Bone fractures in children
occur across growth plate or across the shaft
-partial cortical disruption
After a fracture occurs
-blood clot forms between the fracture margins
-jelly like matrix is formed and further migration of collagen producing cells occur
-calcium hydroxyapatite is produced by osteoblasts and forms insoluble crystals and bone matrix is laid down
-callus forms across the fracture site
Fracture line reduction
used in the treatment of a fracture
Avascular necrosis
cellular death of bone resulting from a temporary or permanent loss of blood supply to the bone
Osteoporosis
disease in which the bone mineral density is significantly reduced
Osteoporotic fractures
typically occur in the femoral necks, vertebra, and the wrist
Epiphyseal fractures
fractures that occur in growth plate and metaphyseal regions
-these regions are more vulnerable between the ages of 7-10 and puberty due to rapid growth
Synovial joints
skeletal elements are separated by an articular cavity
Features of synovial joints
-layer of cartilage covers the articulating surfaces of the skeletal elements (usually hyaline cartilage)
-joint capsule
-contain additional structures such as articular discs, fat pads, and tendons
Joint capsule
consists of an inner synovial joint and an outer fibrous membrane
Solid joints
no cavity separating the skeletal elements and the components are held together by connective tissue
Types of solid joints
fibrous and cartilaginous
The synovial membrane attaches to
margins of the joint surfaces at the interface between the cartilage and bone
Synovial membrane
membrane lining the capsule of a joint
-highly vascular and produces synovial fluid
Closed sacs of synovial membranes
can occur outside of joints and form synovial bursae or tendon sheaths
Synovial bursae
intervene between structures such as tendons and bones, tendons and joints, and skin and bones
Purpose of synovial bursae
reduce friction of one structure when it moves over the other
Tendon sheaths
surround tendons and reduce friction
Articular discs
absorb compression forces, adjust to changes in the contours of the joint surfaces, and increase the range of movements
-composed of primarily fibrocartilage
Fat pads
occur between synovial membranes and the capsule
-these move into and out of the region as the joint contours
Synovial joints are based upon
shape and movement
Synovial joints based on shape
based on their articular surfaces
-described as plane (flat), hinge, pivot, bicondylar (two sets of contact points), condylar (ellipsoid), saddle, and ball and socket
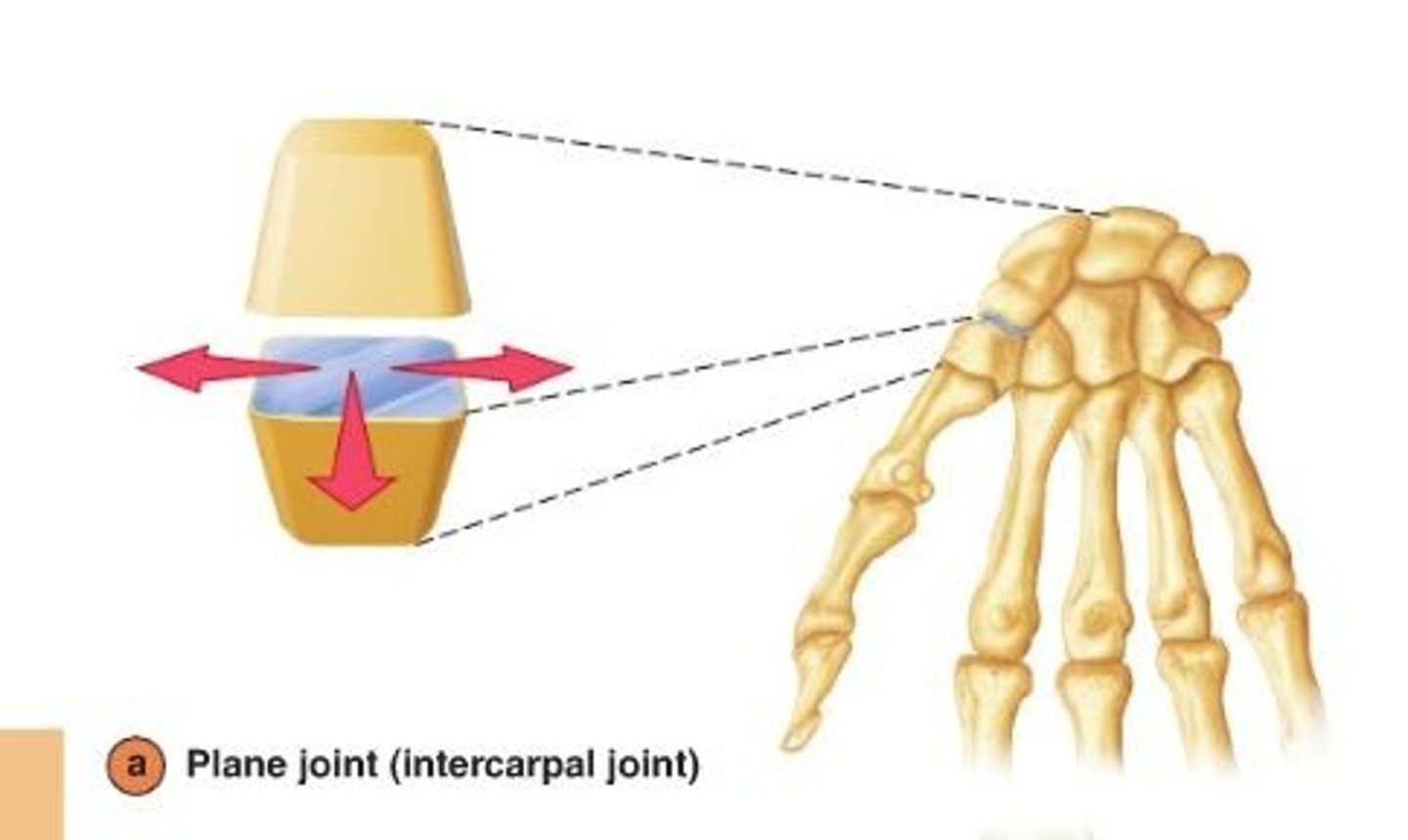
Plane synovial joint
allow sliding or gliding movements when one bone moves across the surface of another
ex: acromioclavicular joint
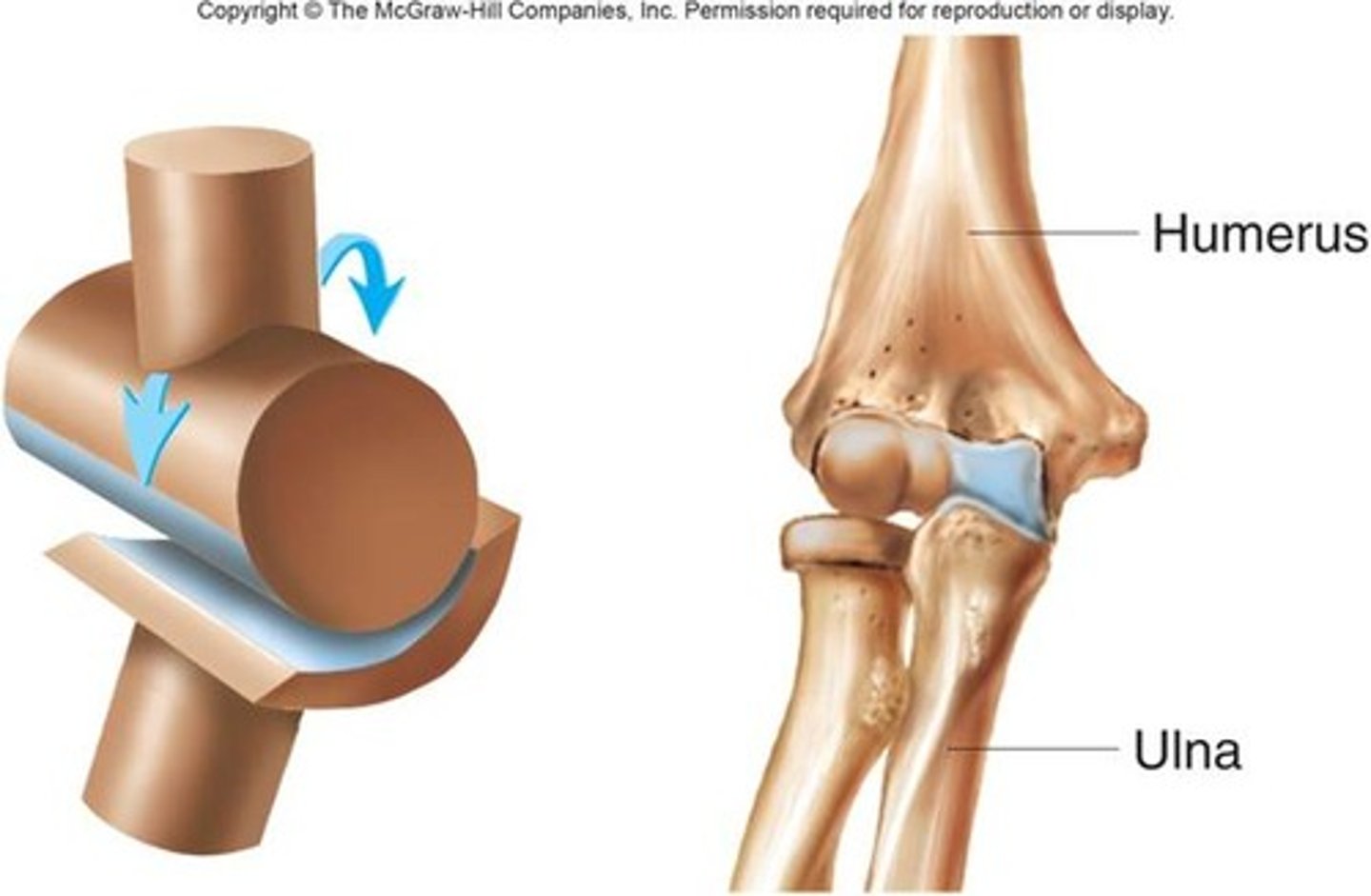
Hinge synovial joint
allow movement around one axis that passes transversely through the joint
-permits extension and flexion
ex: elbow joint
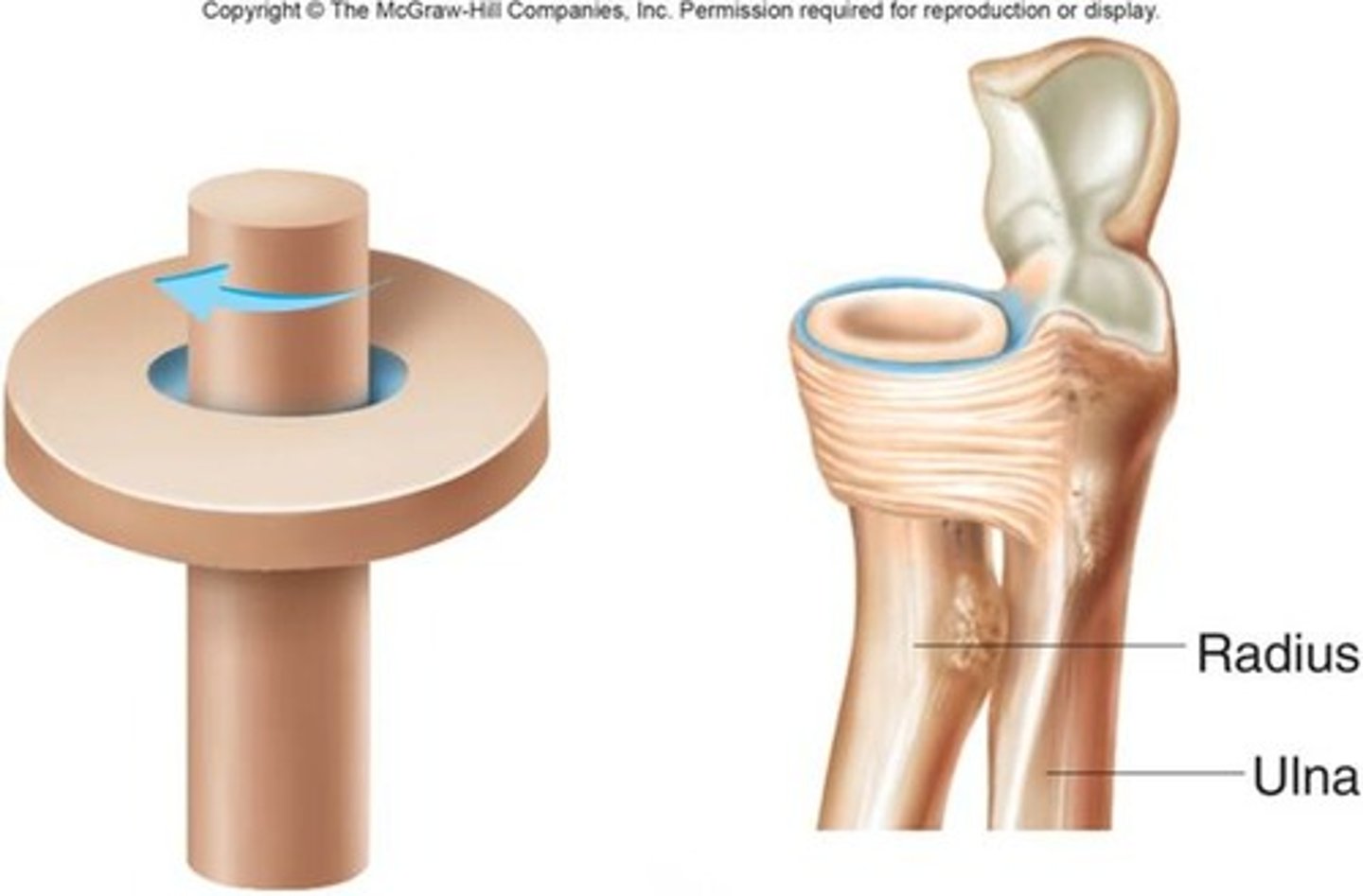
Pivot synovial joint
allow movement around one axis that passes longitudinally along the shaft of the bone
-permits rotation
ex:atlanto-axial joint
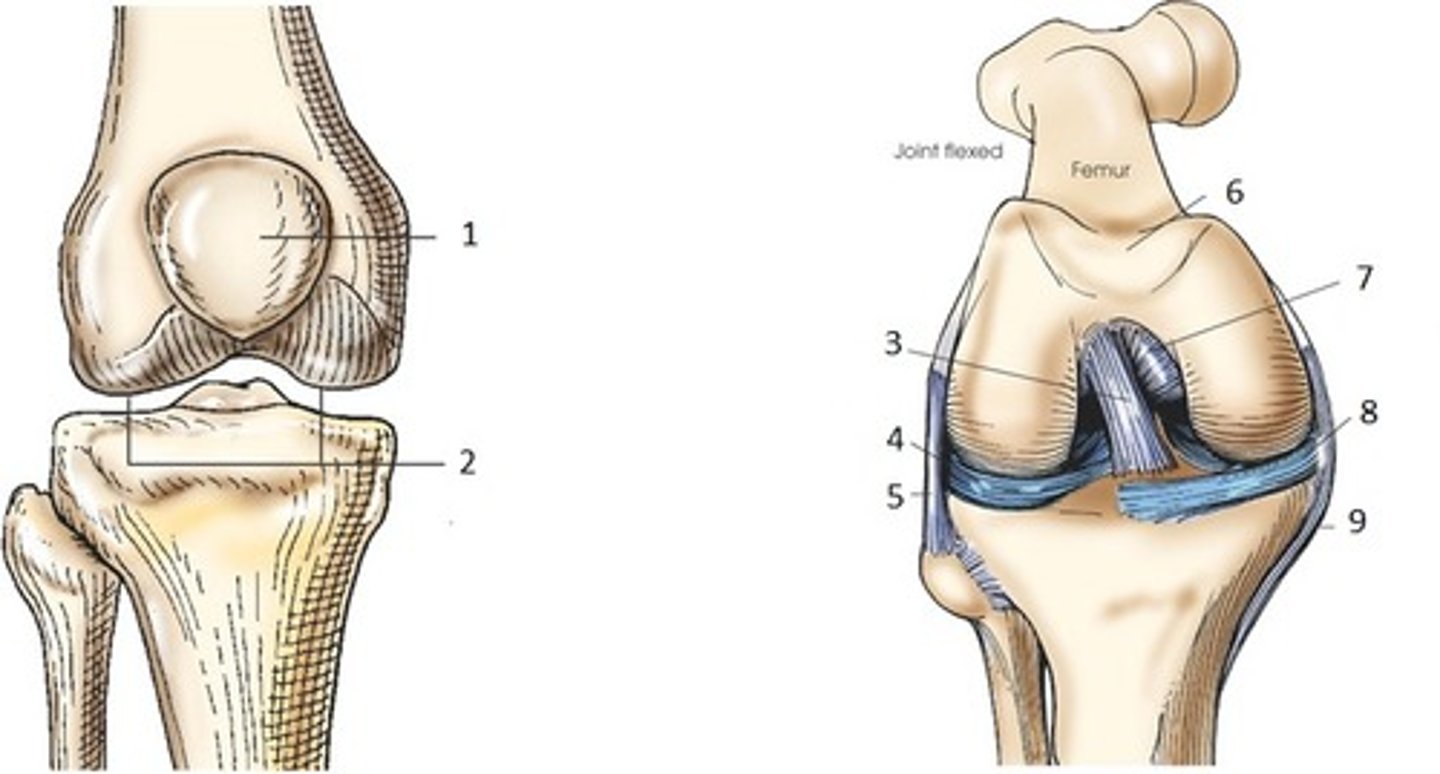
Bicondylar synovial joint
allow movement mostly in one axis with limited rotation around a second axis
-formed by two convex condyles that articulate with concave or flat surfaces
ex: knee joint
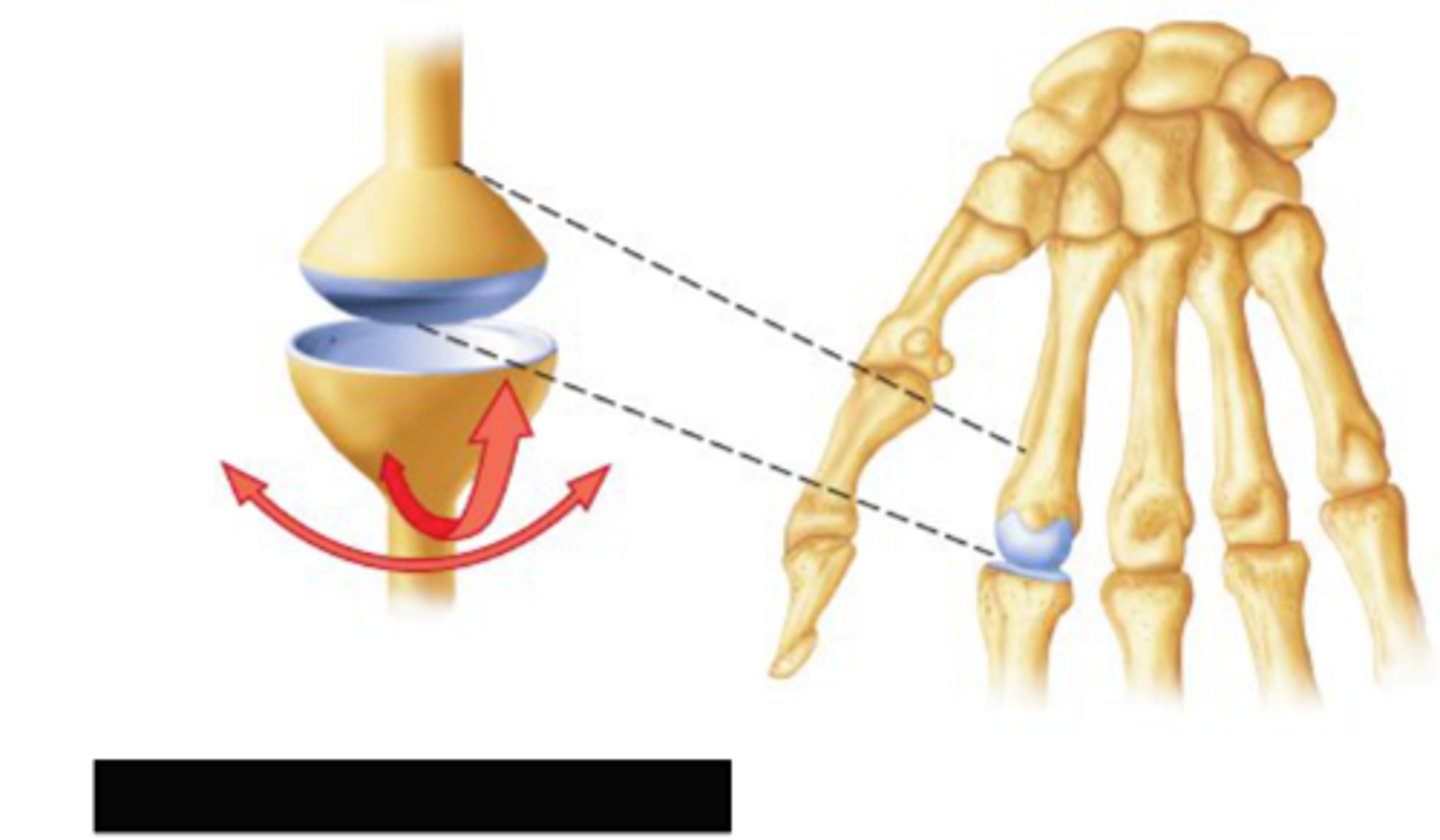
Condylar synovial joint
allow movement around two axes that are at right angles to each other
-permits flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction
ex: wrist joint
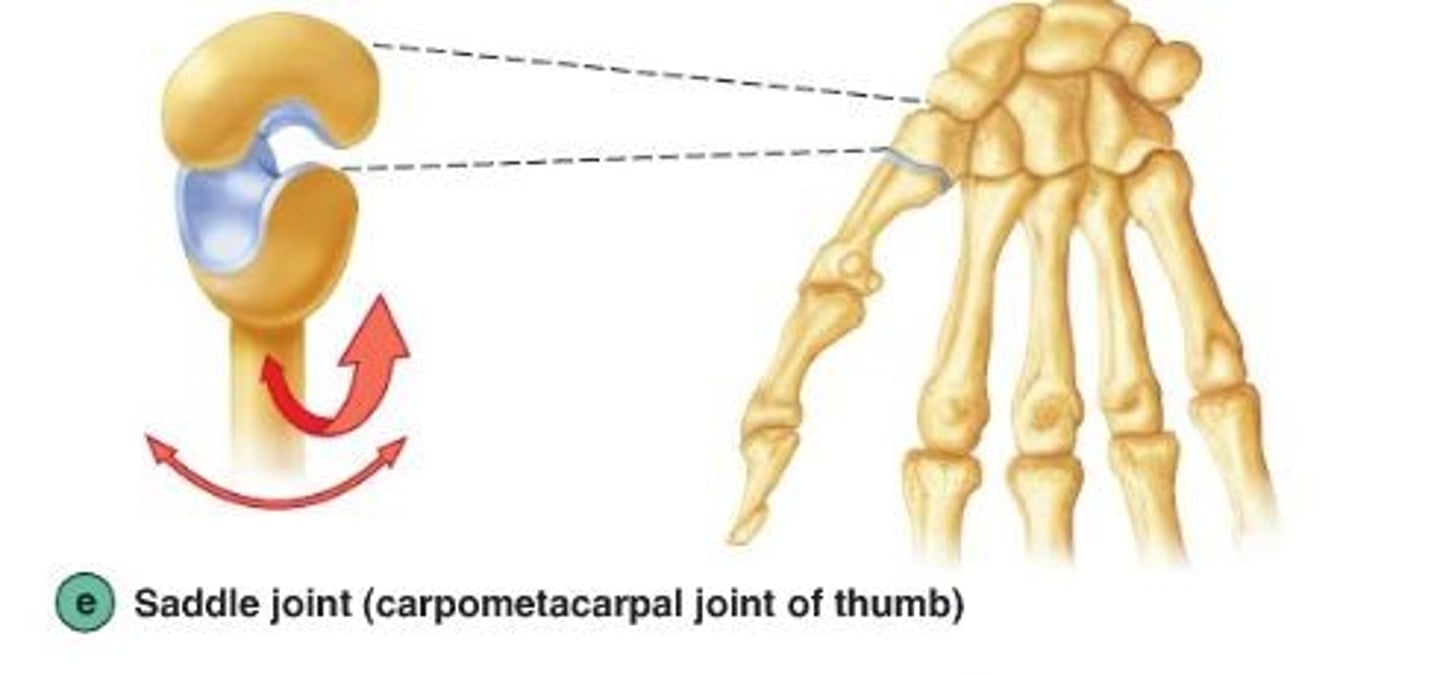
Saddle synovial joint
allow movement around two axes that are at right angles to each other
-articular surfaces are saddle shaped permitting flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and circumduction
ex: carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
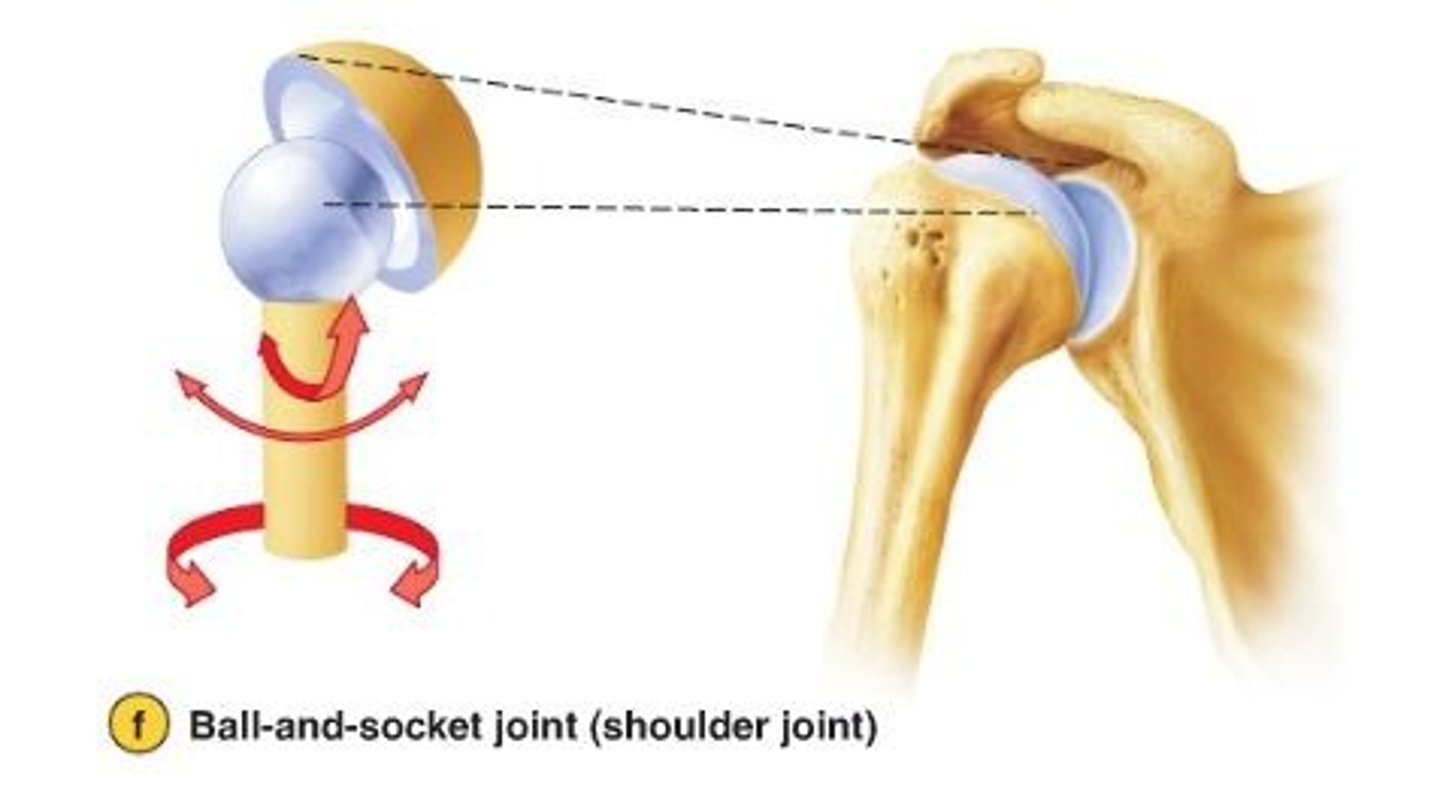
Ball and socket synovial joint
allow movement around multiple axes
-permits extension, flexion, abduction, adduction, circumduction, and rotation
ex: hip joint
Synovial joints based on movement
described as uniaxial (movement in one plane), biaxial (movement in two planes), multiaxial (movement in three planes)
A hinge joint has what type of movement
uniaxial
A ball and socket joint has what type of movement
multiaxial
Subtraction angiography
imaging technique where images are taken before the injection of the contrast media
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
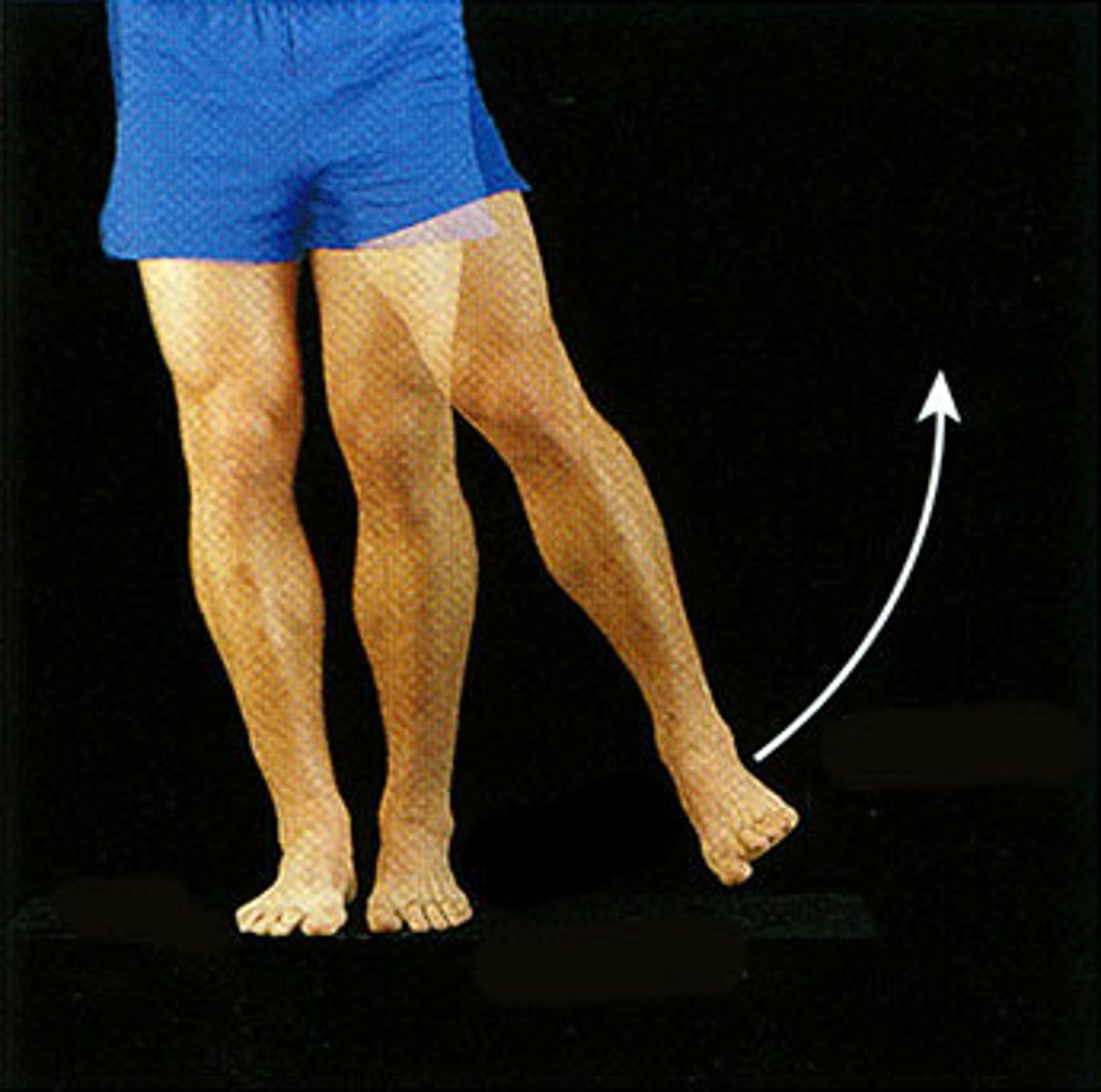
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
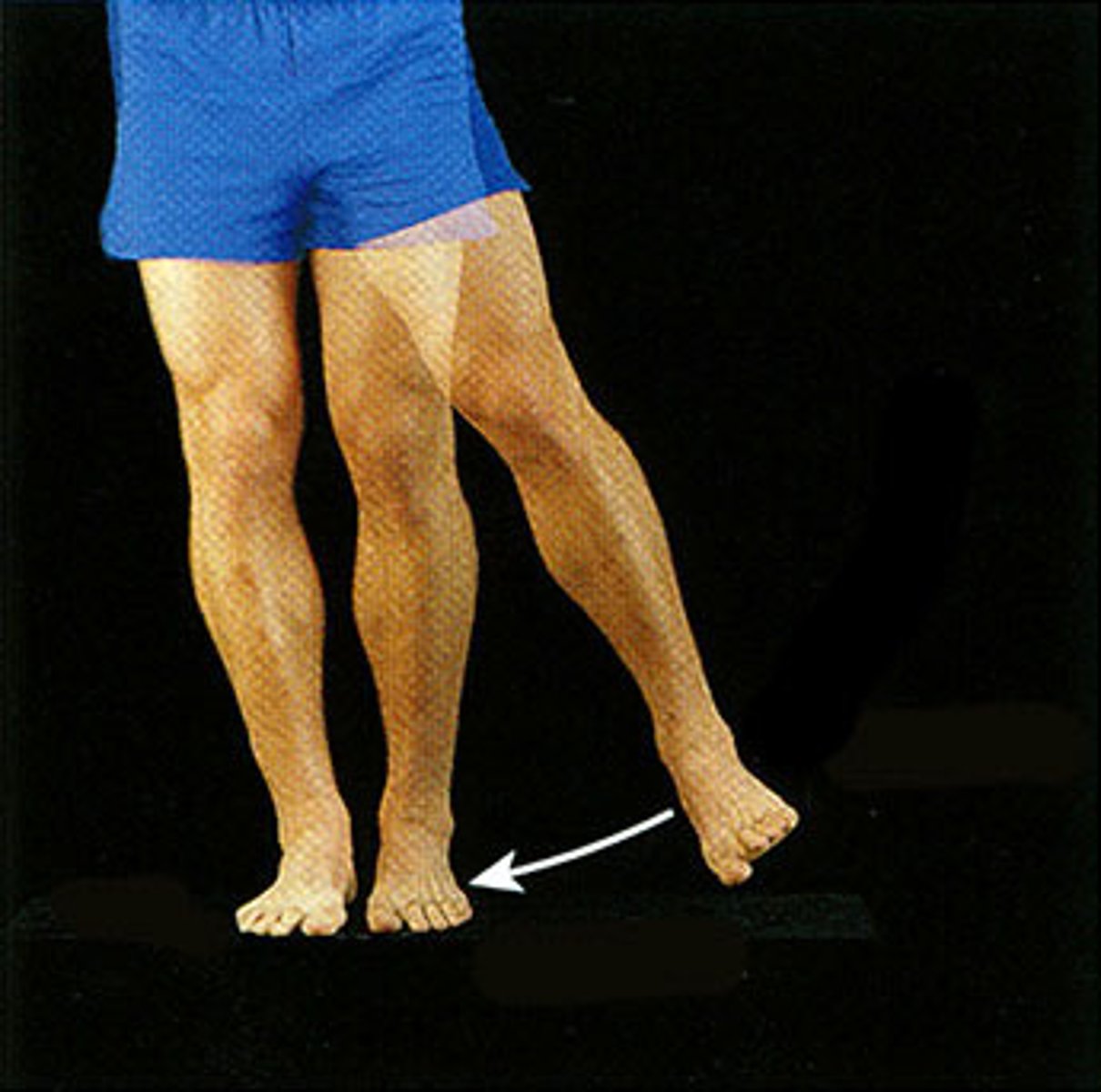
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
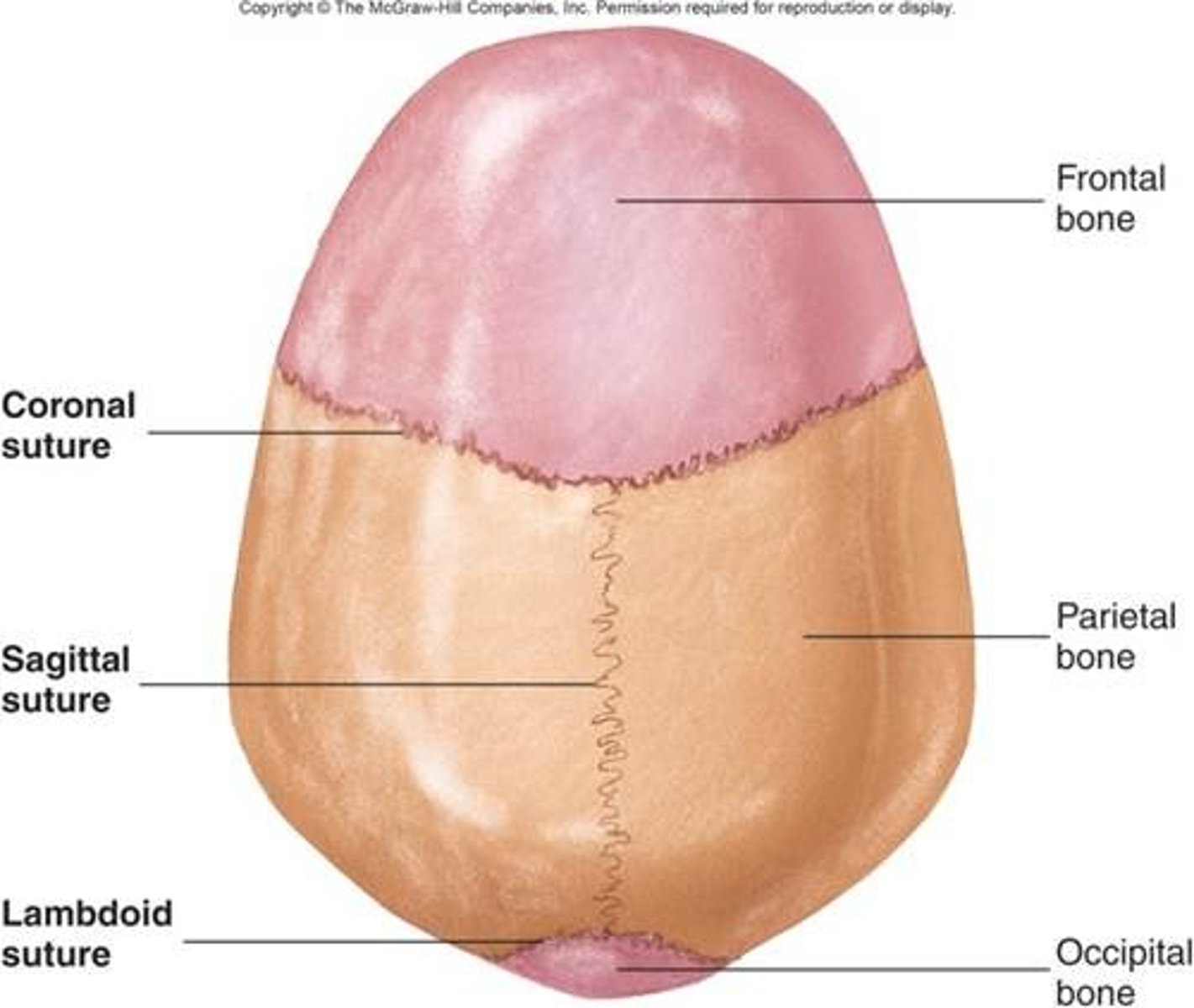
Types of fibrous joints
-suture
-gomphoses
-syndesmoses
Fibrous joints
consists of inflexible layers of dense connective tissue, holds the bones tightly together
-solid joints
Sutures
occurs only in the skull where adjacent bones are linked by a thin layer of connective tissue
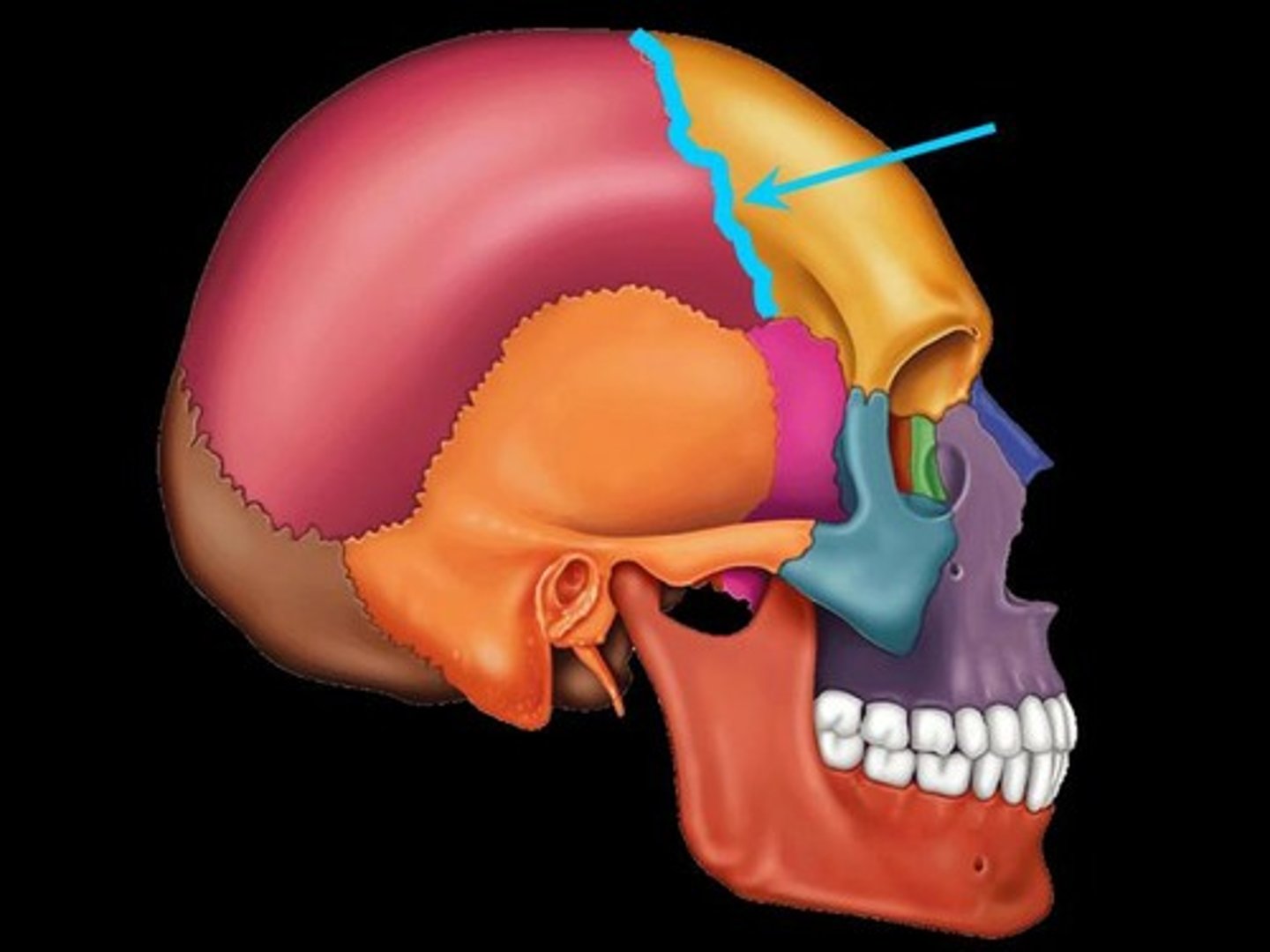
Sutural ligament
thin layer of dense connective tissue that joins flat bones of the skull together
Types of cartilaginous joints
-synchondroses
-symphyses
Synchodroses
occur when two ossification centers in a developing bone remain separated by a layer of cartilage
-allows for bone growth
The type of joint at the growth plate between the head and shaft of a long bone
synchodroses
Symphyses
occur where two separate bones are interconnected by cartilage
Type of joint that occurs at the midline, including the pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs
symphyses
Degenerative joint disease
osteoarthritis
-decreases in water and proteoglycan content with the cartilage
Osteophytes
juxta-articular bony nodules that are formed as a result of osteoarthritis
As a result of osteophytes
this leads to deformations which alter the biomechanics of the joint
Etiology of osteoarthritis
not clear however this can occur after other joint diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and infection
Arthtoscopy
technique used to visualize the inside of a joint. using a small telescope
-most commonly used on the knee, shoulder, ankle, and hip