Chapter 6 - Intro to Viruses - (NSU - BIOL 251) - Microbiology by Talaro
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
All viruses have capsids which are ____________________________________.
protein coats that enclose & protect their nucleic acid.
each capsid is made of identical subunits called ______________ made of ______________.
capsomers
proteins
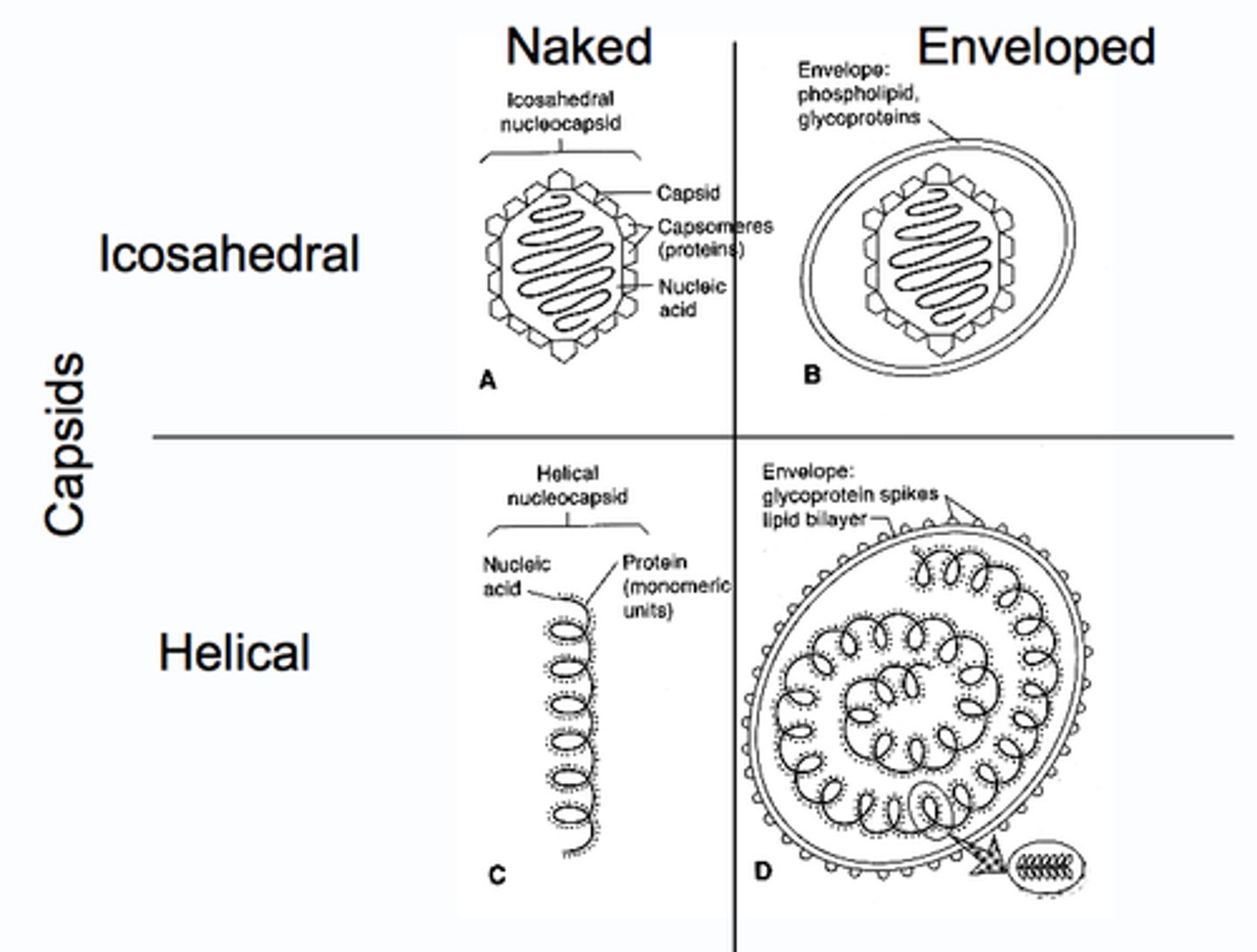
What are the two shapes of capsids?
-helical
-iscosahedral
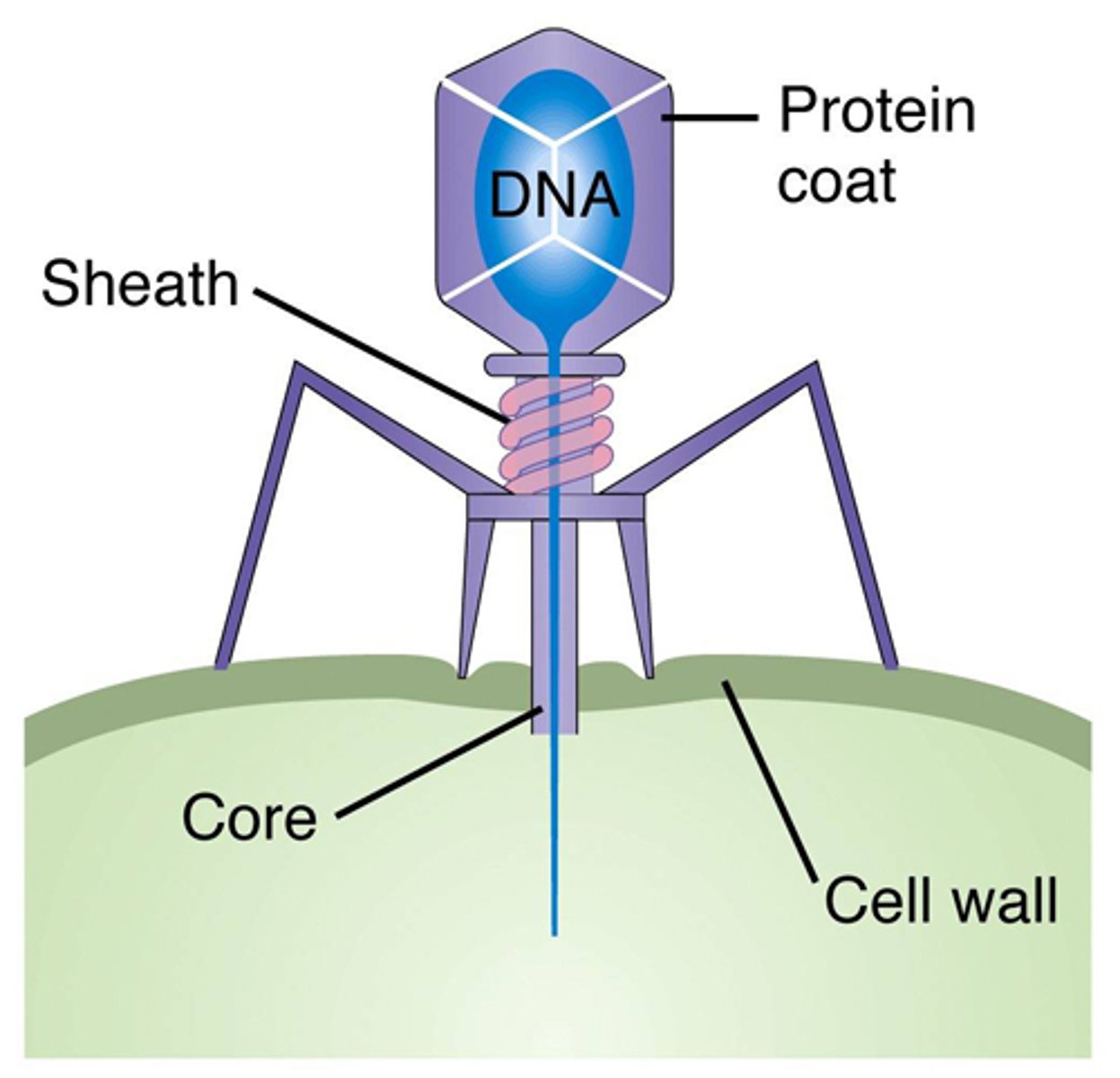
What is the specialized capsid only with bacteriophages?
complex
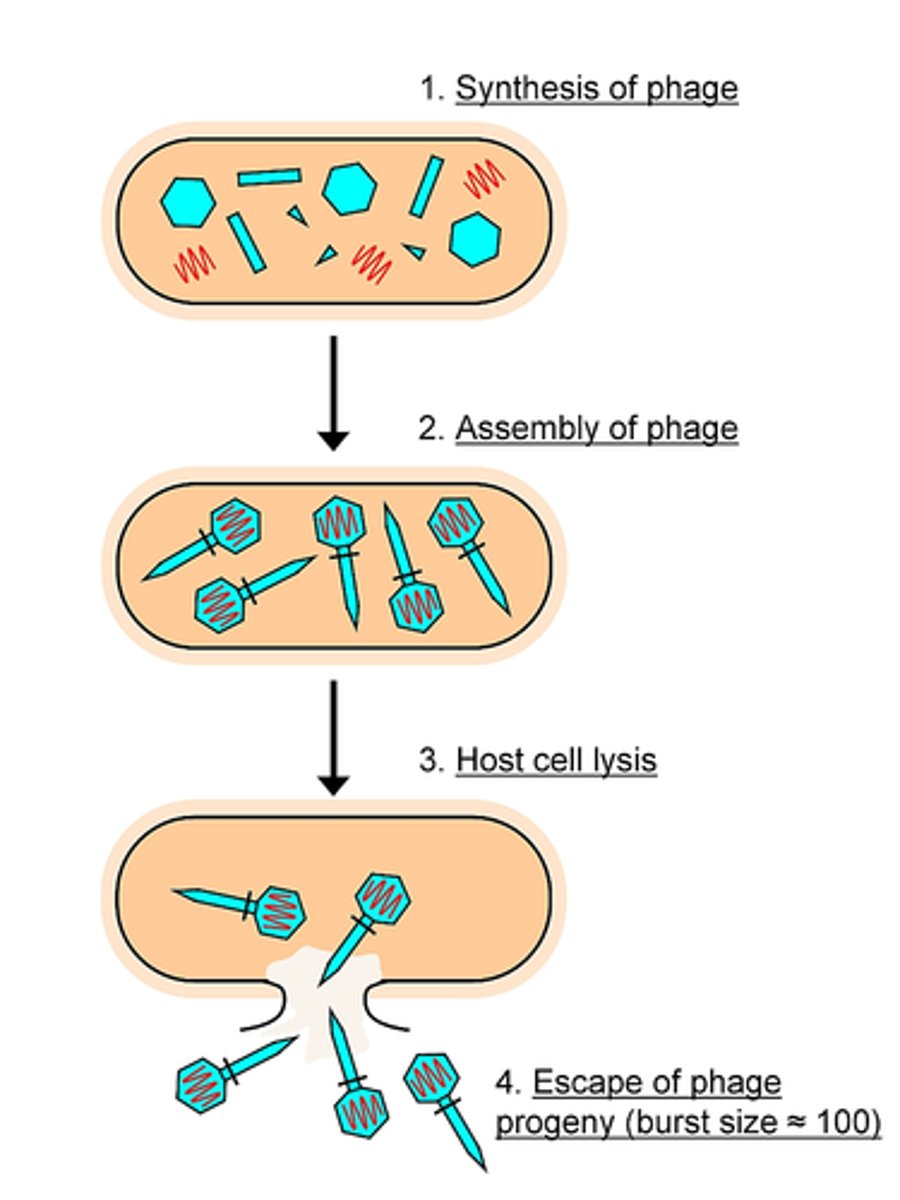
What are the 6 steps in virus replication? describe them.
adsorption - binding of virus to receptor
penetration -genome enters host cell
replication - viral components produced
assembly - viral components assembled
maturation - completion of viral formation
release - viruses leave cell to infect other cells
Lysogeny
bacterial chromosome carries phage DNA
What must a cell have for a virus to infect it? (2)
have a specific receptor on its surface for viral attachment
has to contain all of the enzymes and materials needed to produce new virions
What are the three Differences between phage and animal virus replication?
Animal virus replication is more complex than phage replication because host cells are more complex.
Animal viruses cannot inject their DNA.
Lysogeny for phage, latency for animal viruses
What are the two way viruses penetrate?
- via a vesicle (endocytosis)
-goes through membrane (only enveloped)
RNA viruses compared to DNA are _________
unstable and senstitive
What are the seven Cytopathic effects- virus-induced damage to cells?
1. changes in ______________.
2. Cytoplasmic ______ _________.
3. Nuclear _________ ________.
4. Cells that form ___________.
5. Cell ____________.
6. alter __________.
7. ________________ genes.
1. changes in size & shape
2. cytoplasmic inclusion bodies
3. nuclear inclusion bodies.
4. cells fuse to form multinucleated cells
5. cell lysis
6. alter DNA
7. oncogenic genes
how do we grow viruses?
via the required appropriate cells to replicate
What are the 3 media used to grow viruses?
live animals tissues
bird embryos
cell culture (human cells and culture)
What are prions? what do they cause?
misfolded proteins, contain no nucleic acid
encephalopathies - holes in the brain
what is the size range of viruses?
0.02-0.3 nanometres
What do viruses possess that allows adhesion to cells?
glycoprotien spikes
What are the two cycles viruses can go through (both animal and phage)
Lytic and Lysogenic (dont mix up with lysogeny vc latent)
Describe the lytic cycle
- the viral genome directs the cell to manufacture new capsid proteins and replicate the viral genome
- new viruses are assembled inside the cell
-the new viruses either bud from the cell surface or erupt en masse from the cell, killing the host cell
Describe the Lysogenic Cycle
- viral genome is inserted into host genome (prophage/ provirus)
--the viral genome remains in a latent state or lysogeny without causing disease
-- each time the cell replicates, the viral genome is copied
- stressor = viral genome is activated and proceeds to direct the production of new viruses entering the lytic cycle
What is the immune response to viruses?
initially by monocytes and lymphocytes and inflammation site of viral entry - antibody production follows
A fully formed extracellular particle that is virulent is a?
virion
Some animal viruses remain ________ and bacteriopahges remain ________ where they do not enter the lytic stage and lyse cells?
latent
lysogenic
When growing viruses on tissue you detect them when you see ___________.
plaques
Why are viral infections hard to treat?
the drugs that attack viral replication also have serious side effects in host
Viruses
Small (usually <0.2 um) noncellular particles with a definite size, shape and chemical composition
Ecological niche for viruses
Obligate intracellular parasites
Capsid
the protein shell enclosing the viral genome; may be rod-shaped, polyhedral, or more complex in shape; made from protein subunits (capsomeres)
Nucleocapsid
Capsid together with the nucleic acid in a virus
Viral Envelope
a membrane, derived from membranes of the host cell, that cloaks the capsid; vesicles can leave (exocytosis)
naked viruses
Viruses lacking an envelope
Helical
Continuous helix, of capsomers forming a cylindrical nucelocapsid
Icosahedral
20-sided with 12 corners
are spikes considered a virulence factor?
Yes
Complex viruses: atypical viruses
Poxviruses and bacteriophages
Lipoproteins
Proteins attached to fats/lipid molecule
Viral genome
Either DNA or RNA, never both; carries necessary genes needed to invade host cells and redirect cell's activity to make new viruses
Obligate parasite
is a parasitic organism that is completely dependent on its host for survival and reproduction
Central core of a virus
Nucleic Acid molecules; (DNA OR RNA) and Matrix Proteins enzymes ( not found in all viruses)
Covering of a virus
-capsid
-envelope (not found in all viruses)
nucleocapsid
capsid and nucleic acid together
envelopes are made of...
phospholipid bilayer
naked virus
virus without an envelope
Functions of Capsid/Envelope
Protects the nucleic acid when the virus is outside of the host cell
Helps the virus bind to a cell surface and assists the penetration of the viral DNA or RNA into a suitable host cell
Complex Viruses
a typical viruses such as poxviruses and bacteriophages
lipoproteins
proteins attached to fats/lipid molecule
viral genome
either DNA or RNA but never both
DNA viruses
Usually double stranded (ds) but may be single stranded (ss)
Circular or linear
RNA viruses
Usually single stranded, may be double stranded, may be segmented into separate RNA pieces
ssRNA genomes
-range from 2300 to 31,000 bases
-generally have fewer genes
-more fragile than double stranded nucleic acids
positive sense RNA
Single-stranded RNA genomes ready for immediate translation into proteins
negative sense RNA
RNA genomes that need to be converted into the proper form to be made into proteins
replicase
copy RNA
polymerase
an enzyme that brings about the formation of a particular polymer, especially DNA or RNA.
reverse transcriptase
An enzyme encoded by some certain viruses (retroviruses) that uses RNA as a template for DNA synthesis.
host range
the spectrum of host cells a virus can infect
budding
exocytosis; nucleocapsid binds to membrane which pinches off and sheds the viruses gradually; cell is not immediately destroyed
lysis
nonenveloped and complex viruses released when cell dies and ruptures
scrapie
prion disease in sheep
BSE (Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy)
prion disease in cattle; mad cow disease
wasting disease
prion disease in elk
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
progressive, incurable, neurologic disease caused by infectious prions
Transmission of HIV
Sexual contact, shared needles, contact with blood, mother to baby
Treatment for HIV
1. Antiretroviral therapy:
Can increase the length of time between a person getting infected with HIV and developing symptoms of AIDS, significantly helping to prolong life.
2. Check T-lymphocyte cell count
HIV targets and destroys
Helper T cells
3 stages of HIV
acute, chronic, AIDS
influenza
(flu) is a viral respiratory illness that results from infection of the nose, throat, and occasionally lungs
transmission of flu
aerosol droplets
at risk population of flu
everyone
post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection
"Long COVID": ongoing, relapsing, or new symptoms or conditions present 30 or more days after COVID infection
transmission of SARS-CoV-2
respiratory droplets