Quizam 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Standardized recipies
a recipe producing a known quality and quantity of food for a specific operation
It specifies (1) the type and amount of each ingredient, (2) the preparation + cooking procedures and (3) the yield + portion size
Have specific operation attached: cooking time, temperatures and utensils
Recipie costing basics
Cost per unit equation = A.P. cost/number of units = cost per unit
Unit cost: the price paid to acquire one of the specific units
Cost per portion
total recipe cost/number of portions = cost per portion
Total recipe cost
The total cost of ingredients for a particular recipe; it does not reflect overhead, labor, fixed expenses or profit
Overhead costs
expenses related to operating a business, including but not limited to costs for advertising, equipment, leasing, insurance, property rent, supplies and utilities
Food cost percentage
The ratio of the cost of foods used to the total food sales during a set period, calculated by dividing the cost of food used by the total sales in a restaurant
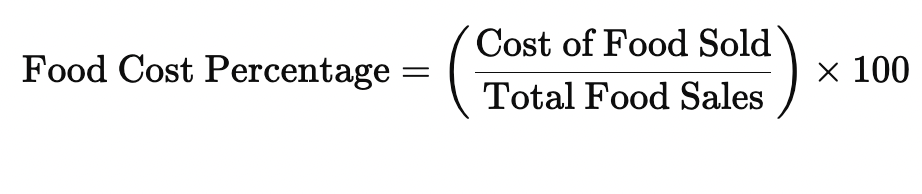
Selling price
Plate cost/desired cost % = selling price
A.P. cost
the condition or cost of an item as it is purchased or received from the supplier
E.P. cost
The amount of a food item available for consumption or use after trimming or fabrication; a smaller, more convenient portion of a larger or bulk unit
Yield percentage
Formula: E.P. weight/A.P. weight = yield percentage
Definition: the ratio of the unusable weight of an ingredient after cleaning and trimming for the quantity purchased, calculated by dividing the trimmed weight by the as-purchased weight of an ingredient
How to factor a recipe and cost individual ingredients (including the use of yield % and weights and equivalent measures)

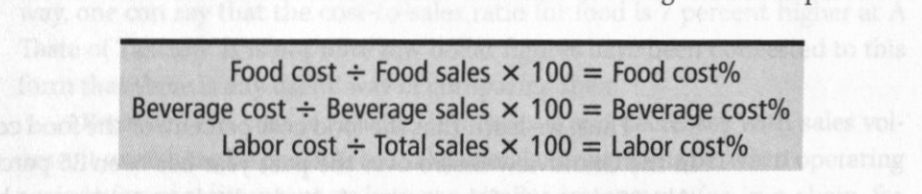
How to calculate and interpret cost percentages (Cost/sales=cost%)
Take the overall total sales if specific sales are not available
You can find really every kind of percentage you need by taking the cost you are looking at dividing it by total sales and multiplying it by 100
Covers
One diner (person) = a cover

Seat turnover
Seat turnover = number of customers served/number of seats
Calculated sales per server
average sale for server = total sales for server/number of customers for server

Variable costs vs. fixed costs and their differences and characteristics
Fixed costs:
normally unaffected by changes in sales volume. little direct relationship to the business volume
examples: insurance premiums, real estate taxes, depreciation on equipment
these should never be taken to mean static or unchanging but merely to indicate that any changes that may occur in such costs are related only indirectly or distinctly to changes in volume
Variable costs:
clearly related to business volume
As business volume increases, variable costs will increase, as volume decreases, variable costs should decrease as well
Directly variable costs: directly linked to vomule of business, so that every increase and decrease in volume brings a corresponding increase or decrease in cost
Examples: payroll costs, food, beverages
Semivariable cost:
A portion of it should change with short-term changes in business volume and another portion should not
salaries + wages
Controllable costs
can be changed in the short term
food + beverages (controlled through changing portion sizes)
Variable costs
Normally controllable
Uncontrollable costs
cannot normally be changed in the short term
rent, interest on mortgage, real estate taxes, license fees + depreciation
Average check
average check = total dollar sales/total number of covers
Prime cost
refers to the costs of materials + labor: food, beverages and payroll
Sales mix
the relative quantity sold of any menu item as compared with other items in the same category
Formula: take the number sold of that item and divide it by the total amount sold of all the items. Then multiply that answer by 100
Menu pricing factors and concepts. How to calculate menu sales price (prime cost method)
Raw food cost (also labeled as entree cost or food cost)
Direct labor cost (labor all together)
Prime factor (also called prime-cost factor)
Prime cost: the cost of food, beverages, and direct labor (all labor together) added together

Basic terminology and definitions from each chapter and lecture
Menu engineering- the difference between star, plowhorse, puzzle, and dog; be able to conduct menu engineering analysis including menu mix %, CM, categorization, and classification.
Menu engineering takes a look at every item and sees if it is profitable
Star
H/H
High contribution margin compared to normal and high volume compared to normal item percentage
Dog
L/L
Low contribution margin compared to normal and low volume compared to normal item percentage
Puzzle
H/L
High contribution margin compared to normal and low volume compared to normal item percentage
Plowhorse
L/H
Low contribution margin compared to normal and high volume compared to normal item percentage
Menu mix %
CM
To get the CM for an item you take the sales price and minus the food cost price
Sales price-food cost= CM
Menu cost
to get the menu cost of an item you take the portions of the item sold and times it by the food cost price
portion amount (amount sold) x food cost (cost of ingredients) = menu cost
Menu revenues
to get menu revenues you take the amount sol of an item and multiply that by the sales price of it
amount sold (portion amount) x sales price = menu revenue
Menu CM
the menu CM is the amount sold times the CM
amount sold x CM of item = menu CM
Average contribution margin (CM)
you take the total CM (all of the item CM added together) and divide it by the total number of items sold
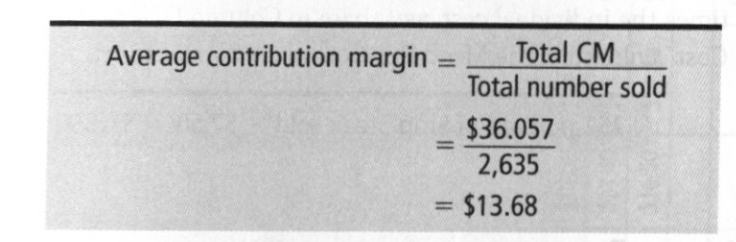
Item percentage
this is the amount of item you have on the menu divided by one. This is then multiplied by .7
