Economic Development Global Economy Part 2
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Economic development
the sustainable increase in living standards for a country, typically characterized by increase in life span, education level, and income
Economic growth
an increase in real GDP over the previous years
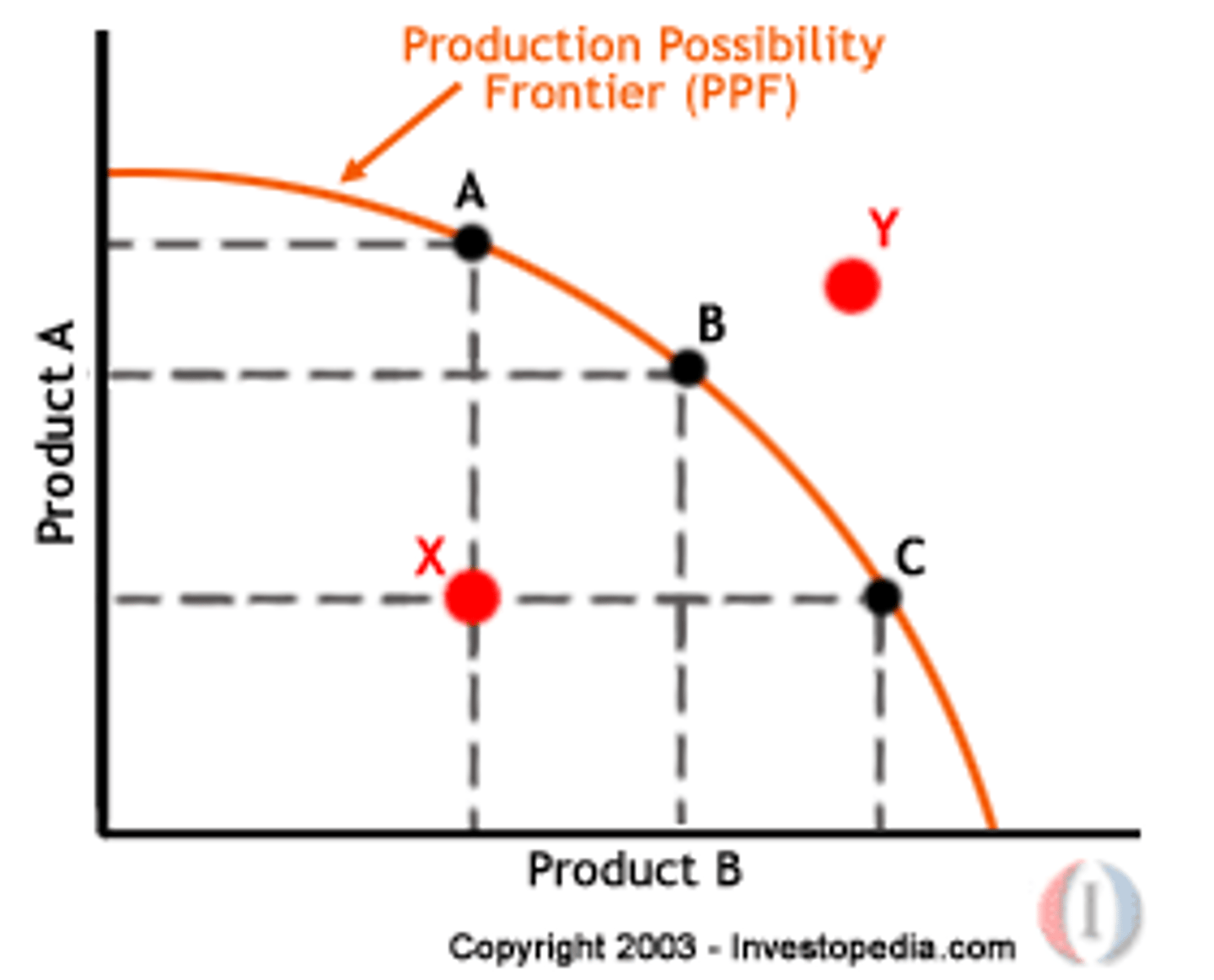
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
A graph that describes the maximum amount of one good that can be produced for every possible level of production of the other good.
Growth of actual production: shift of AD (GDP)
Growth of potential production: shift of the LRAS
Source of economic growth (5)
1. The natural resource base
2. physical capital
3. appropriate technologies
4. Human capital
5. Institutional factors
-------------------------
Natural resource base
- what to do about each natural resource
Physical capital
- buildings, equipments
- Capital widening: extension of capital good to larger segment of workers (more farmers using simple tools)
- Capital deepening: increase in the quality of the capital and ratio of capital per worker (all farmers using better farm tools)
Appropriate technology
Human capital
- increase healthcare
- encourage immigration to increase labor force
- education
Institutional factors
- Political stability
- stable banking system
- orderly legal system
Components of Growth without Development (3)
What to produce?
When comparative advantage of a country does not benefit themselves
- Resource extraction by multinational corporations (MNCs)
- Agricultural commodities reliance
How to produce?
Deterioration of environment and society as produced (negative externalities)
- deforestation
- land degradation
- water pollution
- over-fising
- air pollution
- climate change
For whom do you produce?
When there are some that do not benefit
- income equality
Development with/without growth?
Development with growth
- high correlation
- high income with high development
Development without growth
- low GDP per capita
- low income but high education
- wise investment in prenatal care and education
Common characteristics of economically less developed countries (LDCs) (5)
[IB GAP]
1. High birth rates/large dependency ratios
2. Low capita GDP
3. High agricultural dependence (50-80%)
4. Large urban informal sector
5. Poverty cycle
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
- Global average 20 births per 1000 women of childbearing age per year
- LDCs, 40-55 births per 1000 women of childbearing age per year (2-3 times more)
Dependency ratio
the percentage of old age adults and below-working aged children relative to number of working-age adults
- LDCs high dependency ratio
Measurement of poverty
Extreme poverty: less than $1.25 in purchasing power parity (ppp) adjusted
Moderate poverty: earning $2.00 per day, ppp-adjusted
Informal sector
sector that is unorganized, unregistered, and unsupported by state and its institution
- black market
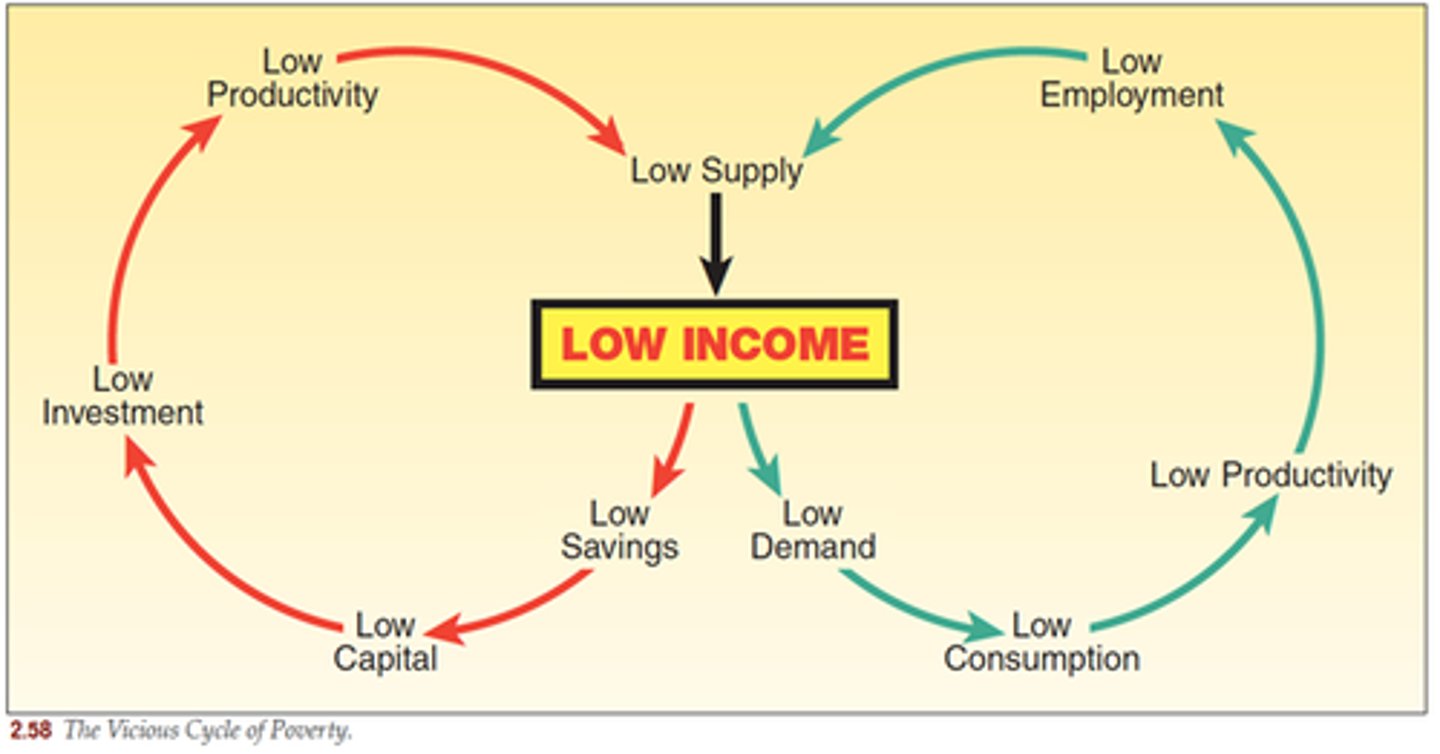
Poverty cycle
low income --> low saving --> low capital investment --> low productivity
Diversity among LDCs (5)
[PS RCH]
1. Resource endowments
2. Climate
3. History
4. Political system
5. Degree of political stability
Single indicators (def. and 3)
indicators of economic development through a specific area
1. Income indicators
2. Health indicators
3. Education indicators
Income indicators (3)
- single indicator
1. Per capita GDP v. per capita GNI
- GNI: Gross national income (all production from factors of production owed by a country) (GNI = GDP - net income flows)
- GDP: Gross national production (all production from factors of production in the boundaries of a specific region/country)
=> LDCs: per capita GDP> capita GNI
- more economic activity than amount labor is paid
=> MDCs (more developed country): per capita GDP < Capita GNI
- less economic activity than amount labor is paid
-------------
2. Purchasing power parity (PPP)
- law of one price: an identical good in one country should cost the same in another country
------------
3. Gini Coefficient
- distribution of income across a nation
- 0= completely equal in income distribution
- 100= completely unequal income distribution
Health indicators
1. fertility rate
- LDCs: high
2. mortality rate
- LDCs: high
3. Life span
- Low
Education indicators
Student per teacher ratio
adult literary rate
Composite indicator
a group of indicators and put them together in an attempt to get a broad picture of a country's level of development usually expressed an an index
Human Development Index (HDI)
- created by United Nations
- Evaluates
1. Health: Life expectancy
2. Education: Adult literary and enrollments ratio
3. Income: GDP per Capita (PPP-adjusted)
0 to 1
- 0 is low
- 1 is high
Domestic obstacles to economic (5)
1. poverty trap
2. natural resource trap
3. Geography trap
4. Education/poor governance trap
5. Conflict trap
Natural resource trap
2 reasons
1. no natural resources
2. cannot export resources to earn foreign exchange
Curse of natural resource
- breed domestic conflict over control of one resource
resource poor country --> no exportable commodities --> limited foreign income --> inability to import capital good --> low productivity and low income --> poverty
Geography trap
- land-locked and surrounded by poor countries
- Key access to sea ports
Country is landlocked with hostile neighbors --> no access to global market --> no foreign income from export --> low domestic employment --> low income --> poverty
Education/poor governance trap
- corrupt government does not help education
poor education makes a country
-less attractive to FDI
- limit amount of capital available to workers
- low skill workforce
- lower income
- less tax revenue
Poor education system --> low quality human capital --> low productivity --> low income --> low revenue/corrupt gov --> minimal spending on public goods
Conflict trap
- worse poverty trap
civil unrest and violence --> political and economic uncertainty --> reduced investment from abroad --> intense resource scarcity
Institutional and political obstacle to economic development (6)
1. ineffective taxation structure
2. lack of property rights
3. political instability
4. inequality in distribution of income
5. lack of infrastructure
6. lack of access to credit (banking and loans)
Social and cultural obstacles to economic development (2)
1. religion
2. tradition
Domestic factors that contribute to economic development (4)
1. education
2. Health
3. banking, credit, micro-credit
4. empowerment of women
International obstacles to economic development
1. Narrow range of exports
2. Over dependence on primary products
Narrow range of exports
LDCs have currency that is non-convertible on foreign exchange markets
need to gain "hard currency" through exports and use those capital to acquire needed physical capital to increase productivity
Over-dependence on primary products
consequence
- influence greatly by global commodity market fluctuation
- little pricing power
A highly inelastic supply means
- small change in quantity demanded, big change in price
International factors that contribute to economic development (5)
1. import substitution policies
2. export promotion policies
3. trade liberalization
4. acquire help from organization (WTO)
5. Diversification of national output
Import substitution policies
protectionist policies aiming to reduce domestic consumers' dependence on imported goods
- promote domestic industries with high import tariffs
BAD:
- could lead to tariff wars
- inefficient production at home (more expensive)
Export promotion policies
Protectionist measures aimed to increase competitiveness of domestic producers in foreign market
- subsidies for domestic producers of exportable goods
- intentional devaluation of national currency
BAD:
- export-led growth may be too dependent on foreign consumers
- government reduce revenue
- domestic producers' lack of incentive to increase quality or productivity due to government aid
- devaluation makes import less attractive to domestic country
Foreign direct investment
a long-term investment by foreign firms into domestic markets of other countries
- Add into the low capital/productivity area in poverty cycle
Greenfield investment: MNC construct new facilities from scratch
Brownfield investment: MNC purchase or lease existing facilities
Multinational corporation (MNCs)
large company with trading, manufacturing or service operations across several countries
Why MNCs are attracted to developing countries (6)
1. low-cost labor
2. natural resources
3. political stability
4. large domestic market
5. relaxed regulatory environment
6. liberalized free market conditions
Advantages of FDI (3)
1. Capital improvements
2. income, employment, training
3. Market efficiency and choice
Disadvantages of FDI (3)
1. muted effects on employment
2. limited income benefits
3. limited capital injections
MNC Power (5)
1. influence over regulatory environment
2. reduced tax burden
3. minimal environmental regulation
4. local worker right limited
5. overwhelming competition with local industry (enjoy economies of scale)
Aid
long or short term loans, grants, and/or technical assistance
Official development assistance (ODA) or bilateral aid
Aid given by a foreign government; when a country's government gives directly to another country
Non-governmental Organizations (NGO)
aid by non-governmental organisation
Type of aids (5)
1. debt relief grants
2. technical assistance
3. development assistance
4. humanitarian aid
5. Commodity assistance
Donor motivation for giving aid (3)
1. political and strategic
2. Economic
3. Humanitarian
Arguments for foreign aid (2)
1. It is only the delivery of aid that is problem, not the aid itself
2. aid addresses areas where growth alone will not cover
Arguments against foreign aid (5)
1. Aid is inefficient
2. Corruption squanders aid
3. Aid rarely gets to those who are in need
4. Aid displaces local investments and market
5. Aid fosters dependency
6. cost lead to international debt
Arguments for Trade to cope with development (4)
1. Rich countries eliminate subsidies and expand market for LDC
2. allow diversification
3. more efficiency
4. reduce dependency on foreign aid
Arguments against trade to cope with development (2)
1. cut in subsidies would cause rise in food prices (LDS import a lot from aboard)
2. Aid will go where trade don't go (poor villages)
International debt
comprises short and long term loan obligation owed to foreign government, NGOs, and private sources
Origins of international debt
1. inelastic demand of certain product (oil)
2. LDCs engaging in a rush lending and borrowing from banks
3. high interest rates that cannot be paid back
4. funds poorly used
Consequence of indebtedness
Debt trap
1. big non-concessional (market interest rate) loans
2. Large debt service payments
3. poor credit rating
4. fewer loans, high interest rate
5. public and private investment crowded out
6a. reduced business growth/lower employment/lower income
6b. decreased government spending on health, education, infrastructure
7a. slow reduced economic growth, less income for debt repayment
7b. lack of development
Market oriented growth and development policies
any policy that requires little or no role for government in promoting economic development through the unregulated activities of free market
Positives of market oriented policies (4)
1. privatizations and deregulation
2. improved efficiency in the provision of public good (problem with subsidizing natural monopoly)
3. price mechanism work (price controls (ceilings/floors) don't work)
4. improved efficiency in the international flow of goods, services and capital (bad export/import promotion, bad trade barriers)
Weaknesses of market oriented policies
- assume once merit goods are privatized efficiency will be achieved (neglect externalities)
Where Complementary approach (government intervention) is needed the most (3)
1. education (under allocated)
2. social safety nets
3. Infrastructures (under allocated)
Appropriate Technology
Technologies that are well-suited to a country's particular economic, geographical, ecological and climate conditions. Often used in connection with labour-abundant countries that require labour-intensive (as opposed to capital-intensive) technologies.
Micro-Credit
A programme to provide credit (loans) in small amounts to people who do not ordinarily have access to credit. 'Micro' is the Greek word for 'small', and refers to the small amounts of the loans, the very small size of businesses or activities that are financed by the loans (very small businesses are known as 'micro-enterprises') and the short repayment periods involved.
Empowerment
Creation of conditions for equality of opportunities; involves increasing the political, social and economic power of individuals or groups of individuals.
Import Substitution
Also known as import-substituting industrialization, refers to a growth and trade strategy where a country begins to manufacture simple consumer goods oriented towards the domestic market (such as shoes, textiles, beverages, electrical appliances) in order to promote its domestic industry; it presupposes the imposition of protective measures (tariffs, quotas, etc.) that will prevent the entry of imports that compete with domestic producers.
Export Promotion
Refers to a growth and trade strategy where a country attempts to achieve economic growth by expanding its exports. As a trade strategy, it looks outwards towards foreign markets and is based on stronger links between the domestic and global economies.
Trade Liberalization
The policy of liberalizing (freeing up) international trade by eliminating trade protection and barriers to trade (ie: tariffs, quotas, etc.)
Diversification
Generally refers to change involving greater variety, and is used to refer to increasing the variety of goods and services produced and/or exported by a country.
Capital Liberalization
Refers to the free movement of financial capital in and out of a country, occurring through the elimination by the government of exchange controls (government restrictions on the quantity of foreign exchange that can be bought by domestic residents of a country).
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Refers to investment by firms based in one country (the home country) in productive activities in another country (the host country). Firms that undertake FDI are called multinational corporations.
Multinational Corporation (MNC)
A firm involved in foreign direct investment (FDI); it is a firm that is based in one country (the home country) and that undertakes productive investments in another country (the host country).
Foreign Aid
Consists of concessional financial flows from the developed world to economically less developed countries and includes concessional loans and grants.
Concessional Loans
Loans that are offered as part of foreign aid, made on concessional terms (i.e. they are offered at interest rates that are lower than commercial rates, with longer repayment periods).
Grants
A type of foreign aid consisting of funds that are in effect gifts (they do not have to be repaid).
Humanitarian Aid
Foreign aid extended in regions where there are emergencies caused by violent conflicts or natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes and tsunamis, intended to save lives, ensure access to basic necessities such as food, water, shelter and health care, and provide assistance with reconstruction.
Development Aid
Foreign aid intended to help economically less developed countries; may involve project aid, programme aid, technical assistance or debt relief.
Project Aid
Foreign aid involving support for specific projects, such as building schools, clinics, hospitals, irrigation systems, and other agricultural infrastructure, or others.
Programme Aid
Foreign aid involving financial support to sectors, such as education, health care, agriculture, urban development, the financial sector (credit, banking, insurance), the environment, or others.
Official Development Assistance (ODA)
The more important part of foreign aid, referring to foreign aid that is offered by countries or by international organizations composed of a number of countries (it does not include aid offered by non-governmental organizations).
Tied Aid
The practice whereby donors make the recipients of foreign aid spend a portion of the borrowed funds on the purchase of goods and services from the donor country. It occurs only in the context of bilateral (not multilateral) aid.
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
Non-profit organizations that provide a very wide range of services and humanitarian functions; in developing countries they provide foreign aid, all of which takes the form of grants (there are no loans involved). They are involved with an enormous range of activities, including emergency assistance, promotion of sustainable development, poverty alleviation, protection of child health, provision of technical assistance, and many more.
Multilateral Development Assistance
Lending to developing countries for the purpose of assisting their development on non-concessional terms (market rates of interest and repayment periods) by multilateral organizations, i.e. organizations composed of many countries, including development banks such as the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund.
World Bank
A development assistance organization, composed of 185 member countries which are its joint owners, that extends long-term credit (loans) to developing country governments for the purpose of promoting economic development and structural change. It consists of two organizations: the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), which lends to middle income countries on non-concessional (i.e. commercial) terms (and therefore its activities and lending do not form part of foreign aid); and the International Development Association (IDA), which has similar activities to the IBRD but extends loans to low income countries on highly concessional terms; these activities form part of foreign aid. About 75% of World Bank lending is through the IBRD.
Conditional Assistance
Refers to development assistance provided by bilateral or multilateral development organizations, which is extended to countries on condition that they satisfy certain requirements, usually requiring that they adopt particular policies.
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
An international financial institution composed of 185 member countries, whose purpose is to make short-term loans to governments on commercial terms (i.e. non-concessional) in order to stabilize exchange rates, alleviate balance of payments difficulties and help countries meet their foreign debt obligations.
Foreign Debt
Refers to external debt, meaning the total amount of debt (public and private) incurred by borrowing from foreign creditors (i.e. lenders). The global problem of debt involves large volumes of public (i.e. government) debt.
Market-Oriented Policies
A policy in which government intervention is limited, economic decisions are made mainly by the private decision-makers (firms and consumers) and the market has significant freedom to determine resource allocation.
Interventionist Policies
Any policy based on government intervention in the market.
Social Safety Net
A system of government transfers of cash or goods to vulnerable groups, undertaken to ensure that these groups do not fall below a socially acceptable minimum standard of living.
Governance
Refers to the way of governing, and the exercise of power in the management of an economy's economic and social resources, in order to achieve particular objectives such as economic growth and development.
Economically Less Developed Countries
According to the World Bank's classification, includes countries that have a per capita GNI below a particular level (which changes from year to year); some common characteristics include low levels of GDP per capita, high levels of poverty, large agricultural sectors and large urban informal sectors (though it is dangerous to generalize about these characteristics).
Economically More Developed Countries
According to the World Bank's classification system, includes countries that have a per capita GNI above a particular level (which changes from year to year); they generally have relatively high levels of GDP per capita, relatively low levels of poverty, small agricultural sectors, and large industrial and service sectors (although it is dangerous to generalize about these characteristics).
Urban Informal Sector
That part of an urban economy that lies outside the formal economy, consisting of economic activities that are unregistered and legally unregulated. In developing countries these activities are often a very large part of the urban economy; unlike in developed countries, where they are usually pursued to avoid taxes and labour laws, in developing countries they are a matter of physical survival of substantial portions of the population.
Dual Economy
Arises when there are two different and opposing sets of circumstances that exist simultaneously, often found in economically less developed countries, such as for example wealthy, highly educated groups co-existing with poor, illiterate groups, a formal and informal urban sector, and a low-productivity agricultural sector and a high-productivity urban industrial sector.
Poverty Cycle (Poverty Trap)
Arises when low incomes result in low (or zero) savings, permitting only low (or zero) investment in physical, human and natural capital, and therefore low productivity of labour and of land, which in turn gives rise to low, if any, growth in income (sometimes growth may be negative), and hence low incomes once again. A poverty cycle may occur in a family, a community, a part of an economy, or in an economy as a whole. An important feature of the poverty cycle is that poverty is transmitted from generation to generation.
GNI per Capita
Gross national income divided by the number of people in the population; is an indicator of the amount of income in an economy per person in the population.
GDP per Capita
Gross domestic product divided by the number of people in the population; is an indicator of the amount of domestic output per person in the population.
Composite Indicators
A summary measure of more than one indicator, often used to measure economic development; for example the Human Development Index (HDI), that measures income, education and health indicators.
Human Development Index (HDI)
A composite indicator of development which includes indicators that measure three dimensions of development: income per capita, levels of health and educational attainment; is considered to be a better indicator of development than single indicators such as GNI per capita.