Geography - population+ migration
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Birth rate
The number of babies born per 1000 people in a country
Death rate
The number of deaths per 1000 people in a country
Natural change
Difference between birth rate and death rate
Why do gov need to know about birth rates
To plan for increased population ( housing, healthcare, employment )
Why do gov need to know about death rates
To see how heath system is or if there is disease
Population pyramid
Graph showing makeup of population ( age gender )
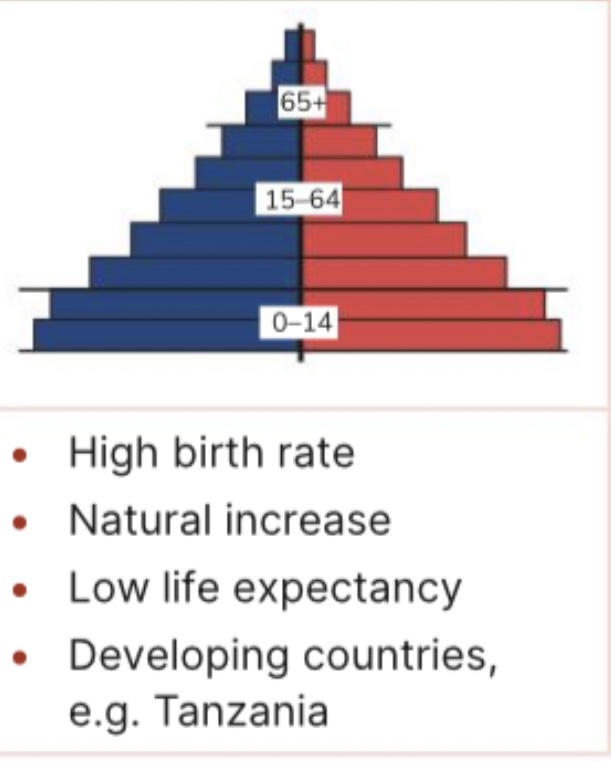
What type of population pyramid is this
Expanding
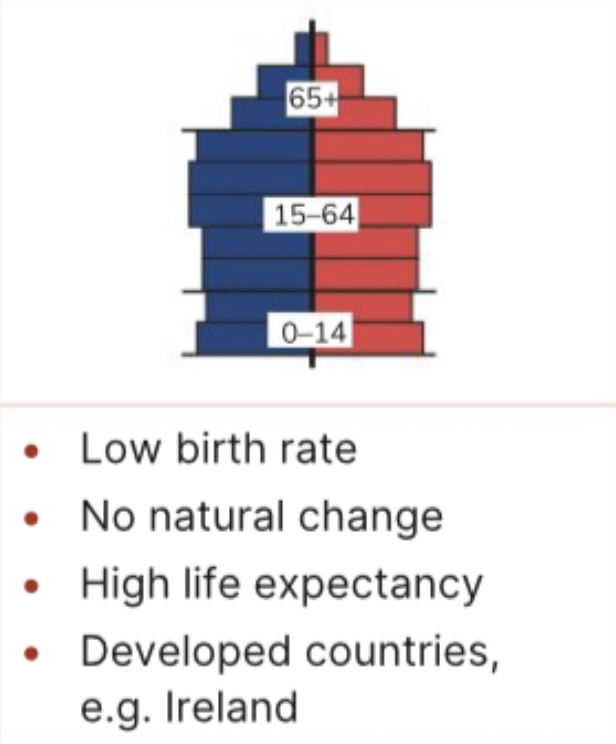
What type of population pyramid is this
Stationary
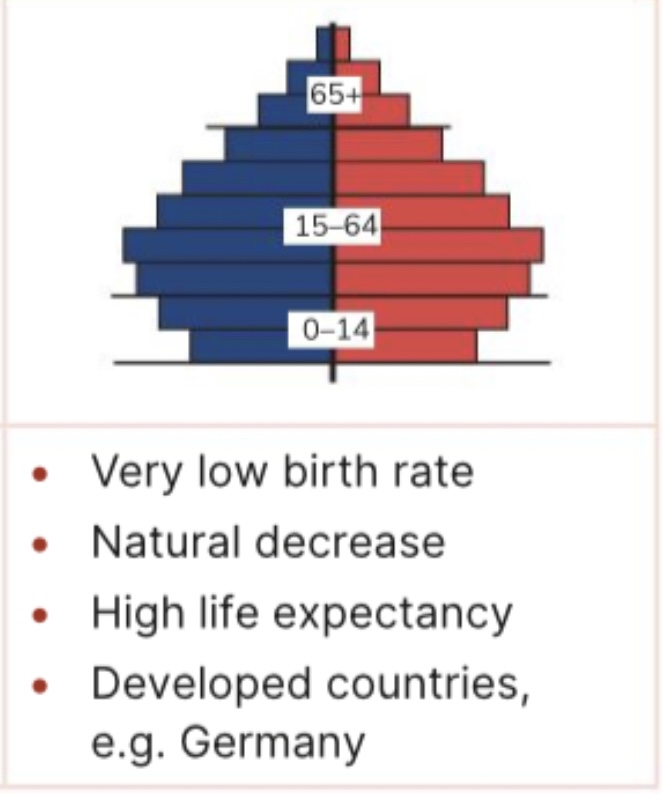
What type of population pyramid is this
Contracting
Life expectancy
How long a person is expected to live
How does food supply affect population
More nutrition = healthier population = longer healthier lives
How does technology affect population
Modern farming = increased food supply, better housing
How does healthcare affect population
Reduces death rate, vaccines stop disease, medical devices
How does war affect population
War deaths, lack of supplies, baby boom when soilders come home
How does the status of women affect population
Younger marriages = more time at home = more time to start family
How does education affect population
If females leave school early more kids younger
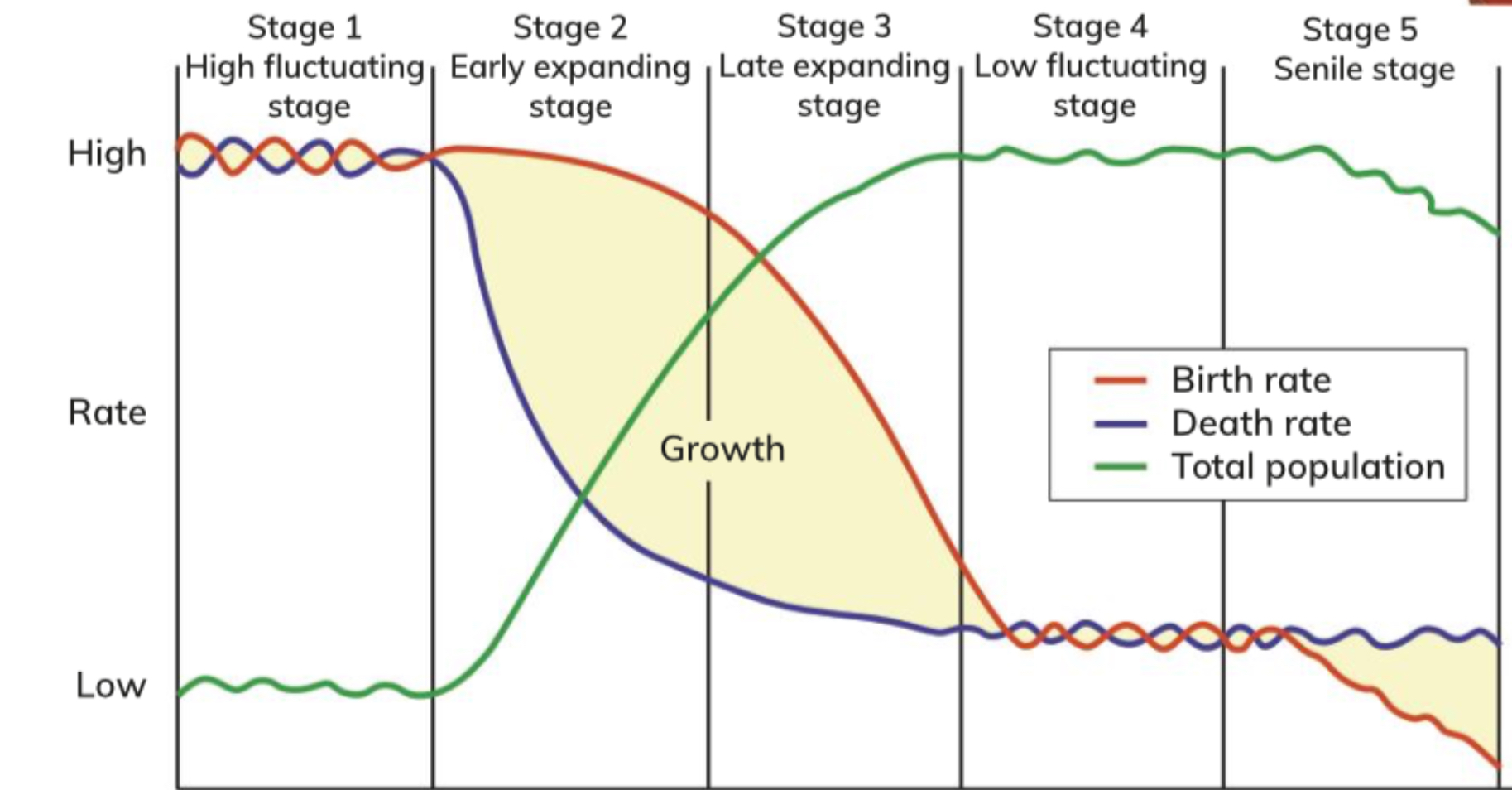
What is this graph called
Population cycle
What is stage 1
High fluctuating stage
What is stage 2
Early expanding stage
What is stage 3
Late expanding stage
What is stage 4
Low fluctuating stage
What is stage 5
Senile stage
Describe high fluctuating stage
High birth/death rate fluctuating. No population change
Explanation of stage 1
Famine/war cause high death rate which cancells high birth rate, caused by more kids to ensure some make it to adulthood
Countries in stage 1
None currently
Describe early expanding stage
Birth rate remains high, death rate falls quick, population increases quickly
Explain stage 2
Whatever was causing high death rate stops, improvement of economy/ facilities birth rate remains high causing big population
Describe late expanding stage
Birth rate decreases quickly, death rate decreases slower, population grows slowly
countries in stage 3
Afghanistan, Tanzania
Explain stage 3
More babies grow so less need for many kids. Fewer improvements of facilities so death rate slower
Describe low fluctuating stage
Birth/ death rates low but fluctuating population is level
Explain stage 4
Facilities developed, long life expectancy, babies expensive so less born
Countries in stage 4
Ireland
Describe senile stage
Birth rate decreases below death rate, population decreases
Explain stage 5
People decide to have less kids, natural decrease
Countries in stage 5
Germany, Italy
What is population density
How many people live in an area
How do you find the population density of an area
Average people per km2
What are the 5 factors affecting population density
Relief, climate, history, resources, economic development
How does relief affect population density
The higher up land is the harder it is to access and build on
How does climate affect population density
People want a climate not too hot/cold, farming
How does resources affect population density
Ores, wood, fertile soil draw people to an area
How does economic development affect population density
People abandon rural areas for work
Migration
The movement of people from once place to another
Immigrant
A person who moves INto an area
emigrant
A person who moves out of a country
Economic migrant
A person who migrates for work opportunities
Asylum seeker
Immigrant who asks for permission to stay in a country to avoid persecution
Refugee
An immigrant who is granted permission to stay in another country Becuase their home is unsafe
Barrier to migration
Something stopping a person from migrating
What are 5 barriers to migration
Cultural, physical, financial, political, personal
Individual migration
One person/ family decide to move
Mass migration
Movement of large group of people
Pull factors
A factor making a person want to move into an area
Push factors
A factor making a person want to move away from an area
1 example of organised mass migration
Ulster plantations
When did the ulster plantations occur
1609
What happened in the ulster plantations
King James I took Land away from Irish and gave it to English settlers
Where do migrants move from
A source region
Where do migrants go
A destination region
Economic impacts in source
Less people less services needed less money going into local economy
Economic impacts in destination
Migrants cheap labour bring skills increased people increased economy
Social impacts on destination
Migrants bring culture, migrants may be discriminated