NCSU ANS 110 Exam 2 me
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
EIPH disease
exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage
-seen in performance animals
-capillary walls rupture
-bleeding from nose
- can be seen in the throat
Epistaxis
bleeding from the nose
Lasix
decreases blood pressure, makes horses pee to prevent eiph and make them run faster in races
-has decreased effect over time/usage
Hypoxemia
low blood oxygen level
Heaves
COPD in horses
-chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder
-caused by respiratory irritants
-treat by removing the irritants (hay, bedding, etc), putting them outside more, and/or bronchiodilators
-develop large abdominal muscles from trying to breathe
Circulatory System
supplies the body with nutrients and removes waste
Arteries
carry blood away from the heart
Veins
carry blood to the heart
Average horse heart weight
8 lbs
% body weight that is blood
9%
Components of blood
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, plasma
How to take a blood sample
From the jugular vein, collected in tubes containing an anticoagulant
Hematocrit (PCV)
percentage of RBC's in the horse's blood
-30-45% is normal
-low is anemic
-high can be from stress or exercise/dehydration
SPLEEN stores and releases RBC's during exercise
Nervous system
sends signals through brain and nerves
Endocrine system
the glands and the hormones they produce
ex; pituitary, thyroid, ovaries, testes
Sight
wide range of vision
eyes on either side of head
-mostly monocular (one eye)
-some binocular in very front (both eyes)
-blind spot immediately behind and in front
Eye
-flattened
-retina closer to the lens at the bottom
-dichromatic vision; they can see blues, yellows, and greens, but NOT reds
Tapetrum Lucidum
night vision - eyes reflect in flash photos
Hearing
-better than humans
-deteriorates with age
- sound waves -> eardrum vibration -> electrical impulses
Ears rotate...
180 degrees using 16 muscles
Taste
-highly linked to smell
-taste buds in papillae on tongue
-horses prefer SWEET tastes
Smell
-selection of food
-predator detection
-communication; social and reproductive
-smell droppings of another horse; see who was there
Vomeronasal organ
Jacobson's organ
-specialized olfactory cells used to detect pheromones
-horses life their upper lip to expose cells to "smell" pheromones
Touch
-nerve endings in the skin transmit signals to the brain when touched
-very sensitive over the ribs
-communication
Axial Skeleton
bones that run along the central axis of the body
-skull to tail
Parietal Bone
top of skull
Frontal bone (skull)
between the eyes
Nasal bone
bridge of nose
Maxilla bone
upper jaw bone, under the eye
Temporal bone
behind the eye
Mandible
lower jaw bone
Cervical vertebrae
neck to shoulder
-starts at the atlas and axis
-7 total (not including atlas and axial)
-small dorsal process
Thoracic Vertebrae
area from shoulder to behind
-doesn't have much movement
-18 total and all have rib pairs
-large dorsal process
# of ribs in the horse
18
Lumbar vertebrae
backside/tail area
-6 total
-medium sized dorsal process
IM Injection site of horse
triangle shape in the middle of the neck area

Appendicular Skeleton
Bones of the limbs and limb girdles that are attached to the axial skeleton
How are the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton attached?
at the pectoral girdle and the pelvic girdle
Scapula
shoulder blade
Humerus
upper arm bone
Ulna and Radius
bones that are fused together to make the large part of the forearm; where the elbow is found
Carpus/carpal bones
"wrist" bones in the knee (forelimb) of horse
Splint bones
remnants of II and IV toes (metacarpal/metatarsal)
Cannon bone
third metacarpal (metatarsal) of the horse
Sesamoid bones
"knuckles"
-proximal (closer to body)
-distal (closer to foot) aka navicular
humans only have these in the thumb
Long Pastern
proximal phalanx, P1
Short Pastern
Middle phalanx, P2
Coffin bone
distal phalanx, P3
Femur
largest bone of the body; the thigh
Patella
"kneecap" below the femur (hindlimb)
Tibia and fibula
fused together
Tarsus
"ankle" bone; hock
From splint bone down on a horse...
front and back legs are the SAME
Joints
union of bones
Joint capsule
-synovial fluid
-articular cartilage
Flexion
decreasing the angle of a joint
Extension
increasing the angle of a joint
Shoulder joint
-hinge joint
-flex AND extend
Knee joint
-fetlock joint
-flex AND extend
Hip joint
-not like a human ball and socket, but can have a little rotation
Hock joint
ankle (4 joints)
Stifle joint
"knee" joint of hindlimb
Arthritis
inflammation of the joints
-inflamed joint capsule or synovial fluid
-can cause infection and deterioration of the joint
-treat with steroids, supplements, anti-inflammatories, and hyaleuronic acid injections, as well as rest/pain meds
Muscles
-cardiac: heart
-smooth: digestive tract, arteries
-skeletal: contraction and relaxation for limb movement
Masseter (muscle)
jaw muscle
Rhomboideus
diamond shaped muscle at top of neck to the shoulder
Splenius
extends and rotates head
-higher up in the neck
Brachiocephalicus
moves the head up and down
-top of ear to bottom of shoulder
Sternocephalicus
to flex or incline the head and neck
-throatlatch region
Deltoid
over the shoulder blade
Triceps
Back of upper arm, below deltoid
Pectoral muscle
chest muscle
Trapezius
trapezoid shaped muscle at the base of the neck and top of spine, moves neck and shoulders
Latissimus dorsi
above the ribs on the back (muscle)
Intercostals
muscles between the ribs
Abdominals
lower stomach muscles, helps to breathe
NO muscles below the...
knee and hock
Gluteals
top of rump
Quadriceps
front part of femur, near pelvis (muscle)
Gastrocnemius
"calf muscle" on the tibia
Semimembranosus
hamstring muscle on back part of femur
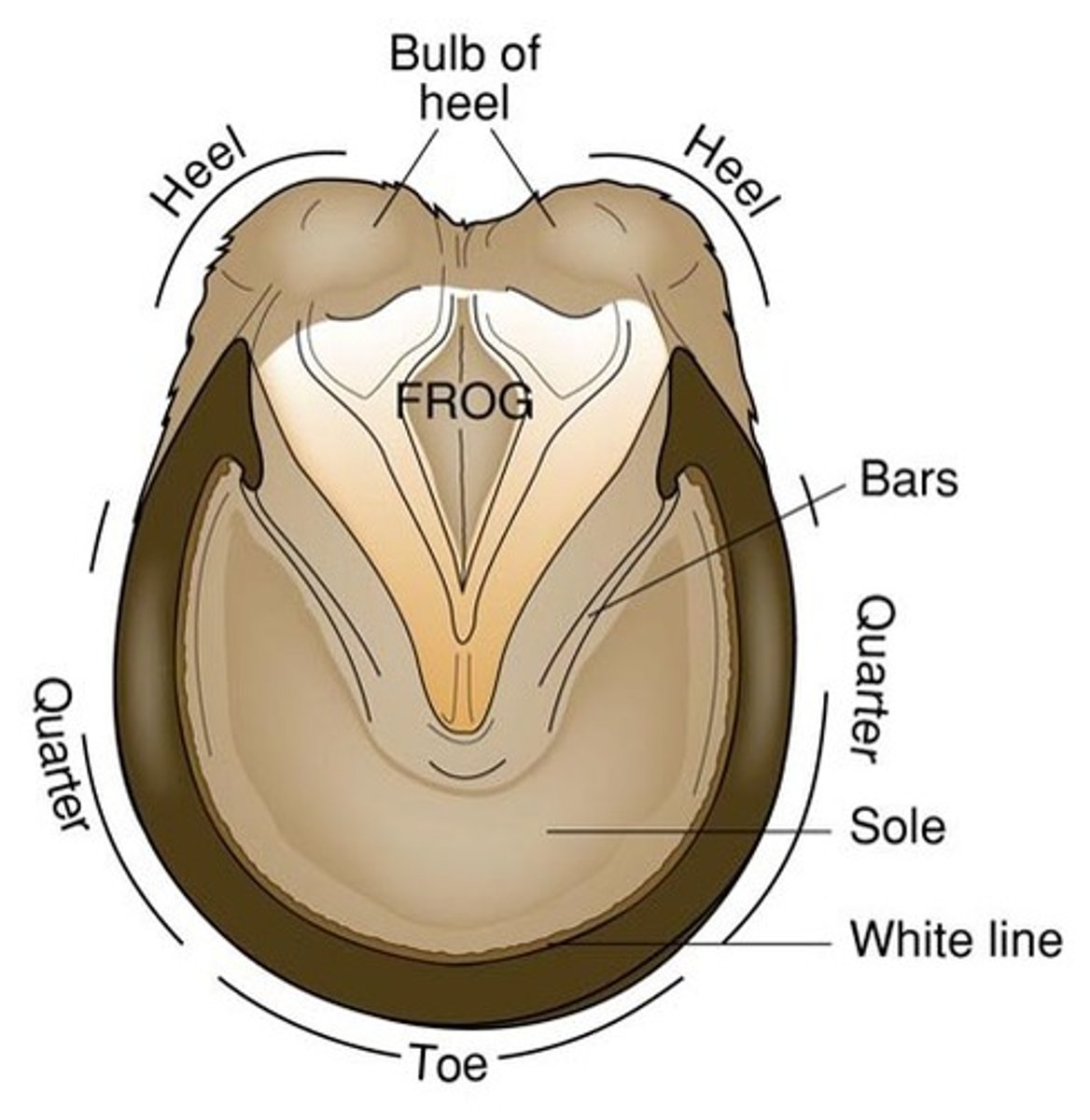
Hoof functions
-protection
-support weight
-circulation of blood
-prevent slipping
Hoof Anatomy
Laminitis
inflammation of the sensitive lamina under the wall of the hoof
-coffin bone rotates in severe cases
-more critical in front feet
-ICE THEM 1st
-acute or chronic
-caused by sepsis, grain overload, obesity, rich pasture, trauma, weight bearing
-treat by anti-inflammatory meds, ice feet, corrective shoeing, hoof wall resection (removal in severe cases)
Lower limb functions
-support weight of the horse (60% in front, 40% in back)
-most of weight is on the coffin bone
-No muscles below the hock; joints move by tendons and ligaments
Tendons
muscle to bone
Flexor tendon
contract to bend/flex a joint (back of the joint)
-common digital
-lateral digital
Extensor tendon
contract to straighten/extend a joint (front of the joint)
-superficial digital
-deep digital
Ligaments
bone to bone
-hold tendons and joints in place
Check ligaments
help support flexor tendons
-superior and inferior
Suspensory ligaments
between the cannon bone and beep digital flexor tendon
-supports full weight of horse
-stay apparatus
Stay apparatus
allows the horse to lock is limbs and stay standing when asleep
-uses minimal energy
-locking patella in hind limb
-locking stifle and hock
Sole bruises
caused by trauma or underlying abscess
Sole corns
bruise at the "seat of corn" between hoof wall and bars
Cracked hoof wall
-crack is distinguished by location (toe, heel)
Thrush of the hoof
bacterial infection of the frog
-black, white crumbles, bad odor
-dirty environment is usually the cause
Navicular disease
degeneration of the navicular bone in horses due to chronic wear and injury
-deep digital flexor is commonly affected
-caused by strain, overuse, poor conformation
-manage by rest, shoeing, anti-inflammatory meds, surgery
Sidebone
Ossification of the lateral cartilage on either side of the coffin bone within the hoof.
Ringbone
bony growth in joints
-secondary to arthritis
-high; pastern joint
-low; coffin joint
-degenerative
-treat with injections
Spavins
bony growth in hock
-type of arthritis
-BOG spavin: swollen hock
-BLOOD spavin: distension of veins in hock