Sensing the Environment
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
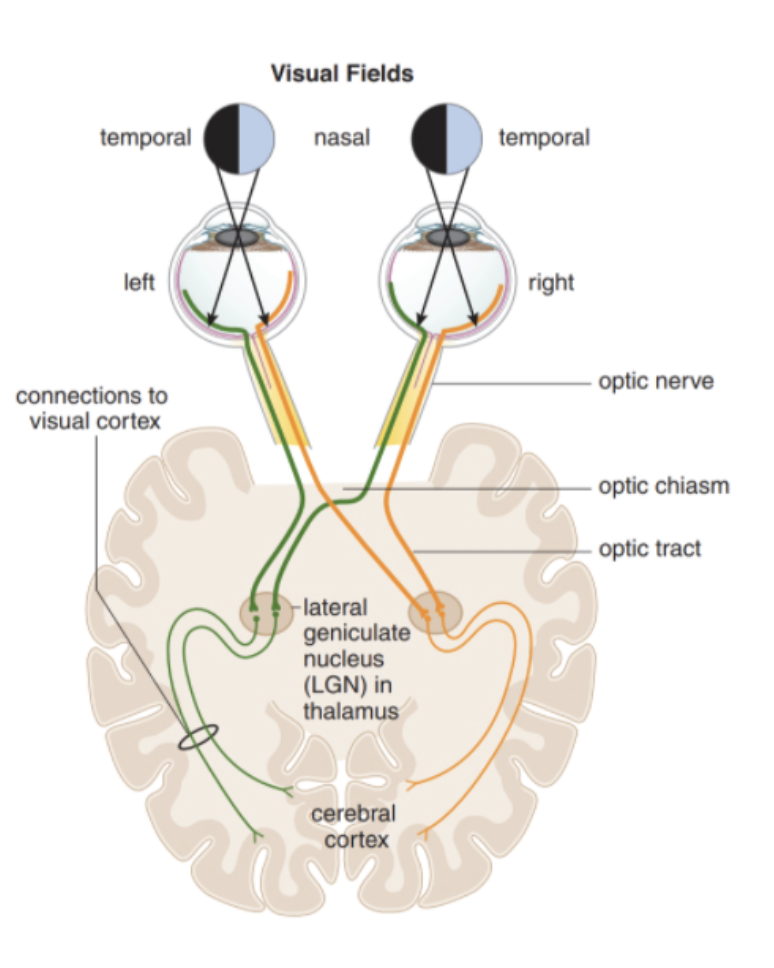
describe the visual pathway
light enters the eye through cornea and passes through the aqueous humor
light hits the photoreceptors within the rod and cone cells of the retina
stimulated rods and cones transmit a signal that passes through the retinal cells to the optic nerve
the optic nerve ends at the lateral geniculate nucleus and relays information to the occipital lobe
what controls the amount of light let into the eye?
iris
sphincter muscles close the pupil (less light in)
contraction of dilator muscles let more light in as they relax
parvocellular cells are responsible for ___ that allow for detailed image detection
high spatial resolution
optic chiasm
where signals from the nasal retina crossover (conveys information form the temporal visual fields)
fovea
area of the eye with only cones (no rods)
central part of the macula
rods
make up a majority of the photoceptor cells in the eye
visual pigment = rhodopsin
primarily contribute to scotopic vision
vision at night
top-down processing
immediate recognition based on prior experience and context
ability to perceive objects that aren’t/are partially there
interposition
when one object covers or obscures another, the object that covers the other is closer
motion parallax
closer objects appear to move faster than distant objects
proprioception
the sense of balance that allows people to be aware of the body’s positions
change in movememnent
mechanoreception
detects stimuli like pressure and vibration
touch and sound
nocioreception
somatosensory perception of pain
somatosensation
overall term for the detection and interpretation of stimuli
touch
farsightedness
hyperopia
eye is too short
lens cannot bend light enough
only see far away objects
nearsightedness
eye is too long
lens bends light too much
only sees objects closeby
retina
has photoreceptors that receive lights
cones (full-color range)
in the center region of retina
rods (grey-scale image, cover most of retina)
in the perimeter of the retina
phototransduction
process by which rods and cones convert photons into electrical signals in the reina
occur b/c opsins (pigments)
left visual field projects onto the ___ side of the rina
right
right visual field projects onto the __ side of the retina
left
spatial resolution
the ability to distinguish differences in the smaller details of an object
temporal rosulution
refers to how quickly the visual information is changing in our visual field
parvocellular cells
in thalamus
LGN
high spatial resolution of stationary objects
magnocellular cells
moving objects
high temporal resolution (shape and color)
no fine details
in LGN
parallel processing
humans interpret visual information simultaneously
olfactory chemoreceptors
nerves that detect the aroma of a given molecule
located in the upper part of the nasal cavity
stimuli binds to chemoreceptors causing a chemical signal
pheromones
chemicals secreted by one animal which elicit a response from another animal of the same species
taste pathway
information travels from taste buds (has chemoreceptors) —> brain stem —> thalamus
The thalamus passes signals to the frontal lobe and flavors are determined
somatosensory system includes
skin
mucous membranes
limbs
joints
perception
being aware of the world around you, integrated information
sensation
process of obtaining raw sensory information
bottom up processing
the usage of real-time visual stimuli to perceive an image
no prior knowledge of stimuli
face pareidolia
seeing facing in things that are not there
depth perception
relies on visual cues to determine their distance
relative size
objects appear larger the closer they are
constancy
we perceive characteristics of an object to remain the same despite changes in the stimuli and environment
gestalt principles
our tendency to perceive and interpret certain configurations at the level of the simpler whole
law of proximity
we perceive objects closer together as a group
law of similarity
our tendency to group similar objects together
law of continuation
our tendency to perceive “good” continuous patterns
subjective contours
perceiving contours that are not really there
law of closure
our brains fill in the missing parts for an image and we perceive it as a whole
which muscles in the retina focus light?
ciliary muscles
change the shape of the lens
signals in the somatic sensory system are sent where in the brain?
somatosensory cortex
parietal lobe