Integrated Marketing Communications Overview
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Promotion
Communication to build and maintain relationships.
Communication
Sharing of meaning between sender and receiver.
Source
Sender of the message in communication.
Receiver
Individual or group decoding the message.
Encoding Process
Converting meaning into signs or symbols.
Decoding Process
Interpreting signs into concepts and ideas.
Message
Physical form of communication from sender to receiver.
Communication Channel
Medium transmitting the encoded message.
Noise
Anything reducing communication clarity and accuracy.
Feedback
Receiver's response communicated back to sender.
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC)
Coordinated promotional efforts for maximum impact.
Message Integration
Tactical alignment of promotional messages.
Strategic Integration
Long-term alignment of communication strategies.
Push Strategy
Promoting products by pushing them to consumers.
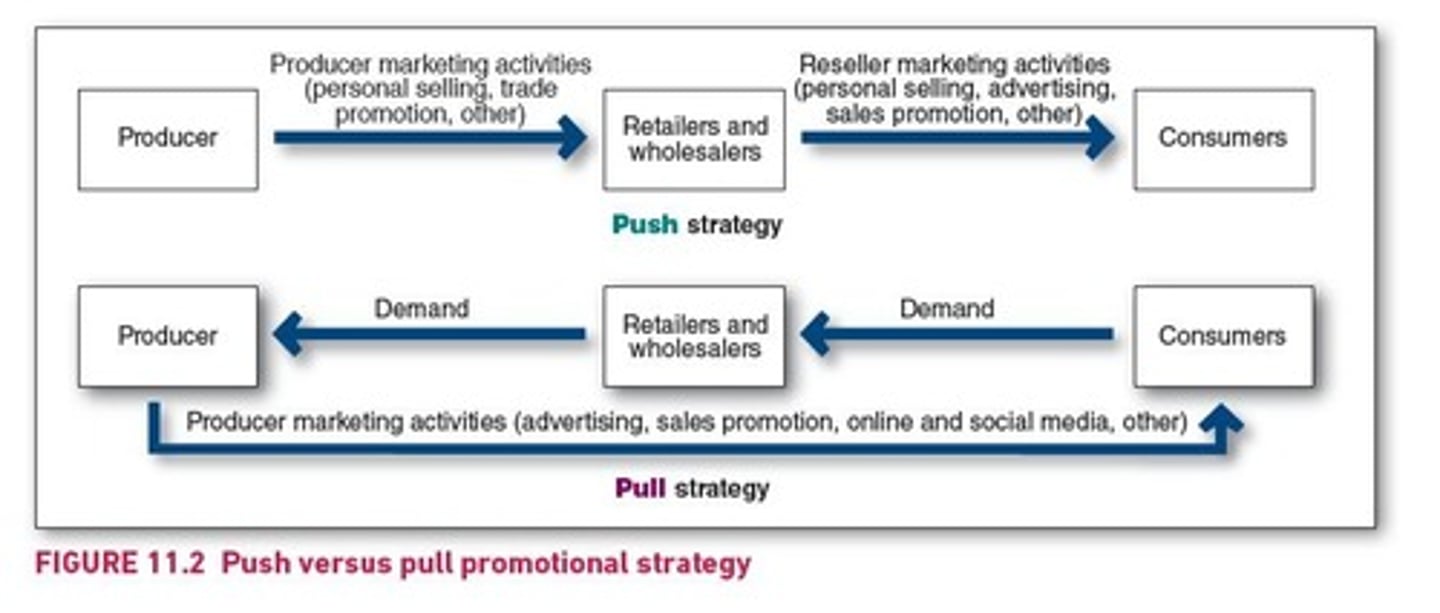
Pull Strategy
Encouraging consumers to seek out products.
Advertising
Paid, non-personal communication about products.
Advantages of Advertising
Control, wide reach, brand equity, low cost.
Disadvantages of Advertising
Impersonal, clutter, credibility issues, difficult measurement.
Hierarchy of Effects
Model for setting advertising objectives.
Copy
Verbal portion of advertisements.
Artwork
Visual elements including illustrations and layout.
Layout
Arrangement of ad's illustrations and copy.
Appeal
Emotional or rational attraction in advertising.
Rational appeal
Focuses on factual information and logical reasoning.
Emotional appeal
Evokes feelings like humor, fear, or warmth.
Telemarketing Code of Practice
Requires disclosure of identity and call purpose.
Direct Marketing Code
Testimonials must be current, typical, and verifiable.
ISP SPAM Code
Mandates spam filter information for consumers.
Free-to-Air Broadcasting Code
Ensures news programming is truthful and accurate.
Self-Regulation of Advertising
Voluntary system for maintaining advertising standards.
Advertising Standards Complaints Board
Anyone can complain about any advertisement.
Benefits of Self-Regulation
Industry bears costs, allowing flexibility and less interference.
Public Relations (PR)
Activities to manage company image and public perception.
Publicity
Uncontrolled public commentary about a brand or company.
PR Advantages
Credibility, lower cost, and consumer engagement.
PR Disadvantages
Less control and time-consuming processes.
Press Release
Short copy distributed to announce news or events.
Proactive PR
Anticipates and addresses potential public relations issues.
Reactive PR
Responds to negative publicity or crises.
Personal Selling
Paid communication to inform and persuade customers.
Sales Promotion
Short-term incentives to boost sales.
Consumer Sales Promotion
Promotions aimed directly at consumers.
Premiums
Merchandise offered free or at low cost.
Sales Promotion Advantages
Stimulates short-term sales and creates excitement.
Sales Promotion Disadvantages
Can harm long-term brand equity and lead to trade wars.
Service
Application of efforts to people or objects.
Intangibility
Cannot be perceived by senses; non-physical.
Inseparability
Produced and consumed simultaneously; shared responsibility.
Perishability
Unused service capacity cannot be stored.
Heterogeneity
Variation in quality due to human behavior.
Tangible Cues
Physical elements used to reduce service anxiety.
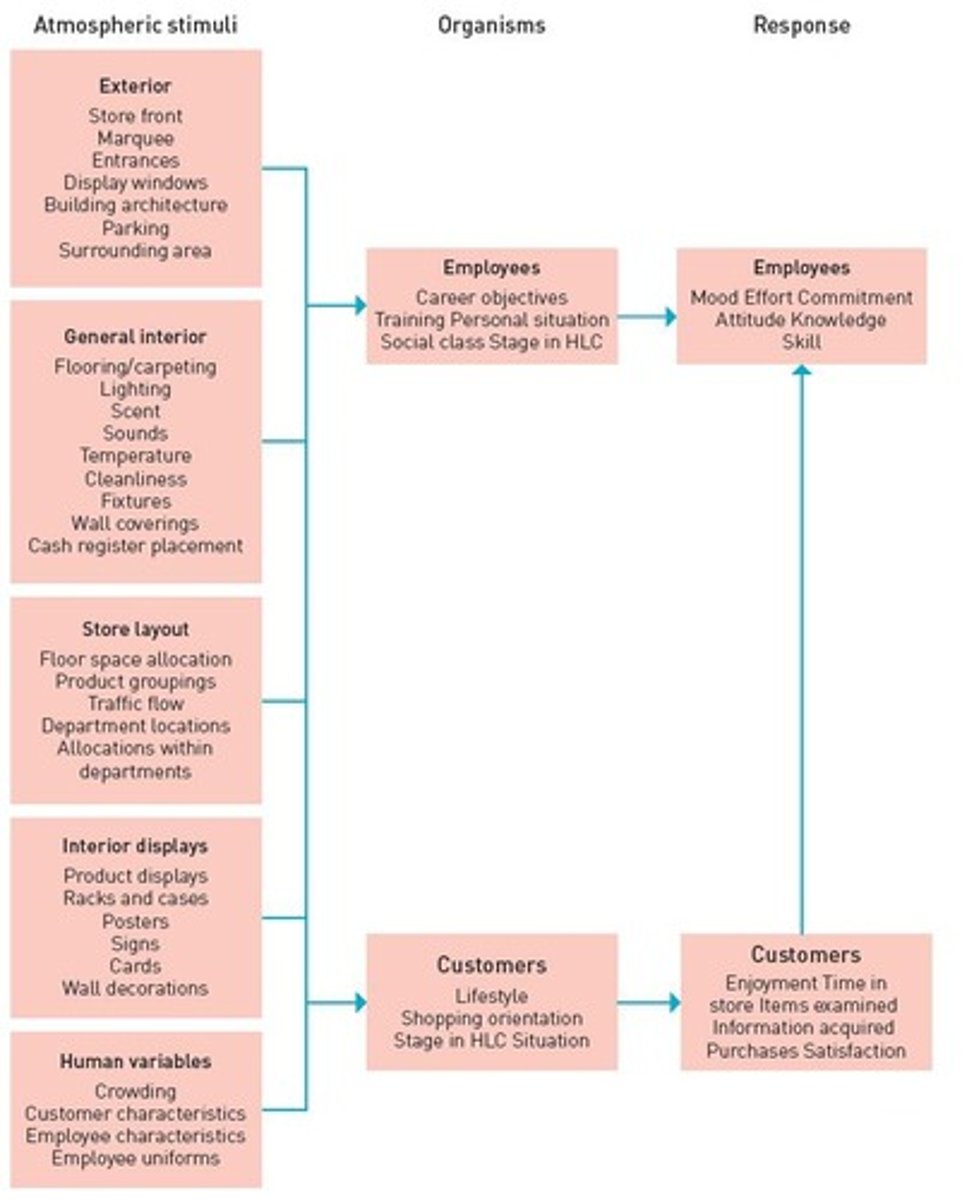
Servicescape
Physical environment where service is delivered.
Brand Image
Importance increases with service intangibility.
Service Industries
Sectors primarily providing services, not goods.
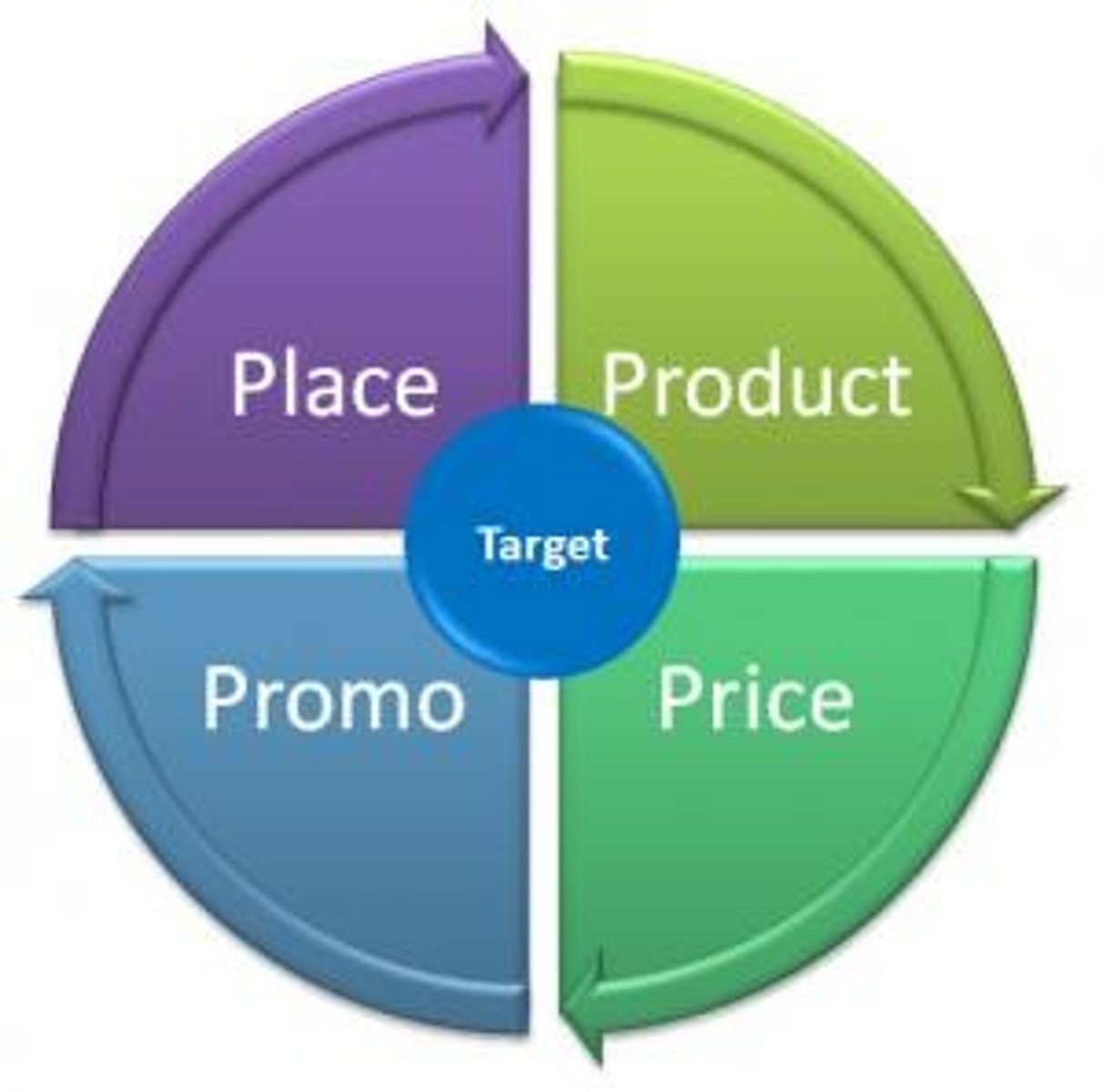
Marketing Mix
Controllable variables in strategic marketing planning.
Customer Presence
Required for service consumption; cannot take home.
Quality Control
Methods to ensure consistent service delivery.
Employee Training
Improves service consistency and quality.
Flexible Pricing
Adjusting prices to balance supply and demand.
Reservation Systems
Manage demand and service capacity effectively.
Yield Management
Pricing strategy to maximize revenue from services.
Service Delivery Systems
Standardized processes to enhance service quality.
Direct Sale Channel
Only method for delivering certain services.
Co-Creation
Shared responsibility in service production.
Customer Expectations
Managing perceptions to improve service satisfaction.
Mystery Shoppers
Used for quality control assessments.
Labor Intensiveness
Higher labor leads to greater service variability.
Core Service
Main service offered to customers.
Supplementary Service
Additional services enhancing core service.
Tangibilising
Making intangible services more concrete.
Service Pricing
Prices based on tasks, time, and demand.
Quality Indicator
Price often reflects perceived service quality.
Distribution Channels
Direct channels reduce service inseparability.
Low-Contact Service
Service delivery with minimal customer interaction.
Promotional Cues
Tangible symbols representing the service offered.
Visualisation
Creating mental images to represent services.
Association
Linking services to familiar concepts or brands.
Physical Representation
Tangible items representing the service experience.
Documentation
Written materials supporting service understanding.
Expanded Marketing Mix
Includes 7Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Processes, Physical Evidence.
People Variable
Human aspect involved in service delivery.
Personnel
Employees representing the company to customers.
Aesthetic Labour
Employee appearance enhancing service perception.
Emotional Labour
Managing emotions to fulfill service roles.
C2C Interaction
Customer interactions influence service experiences.
Physical Evidence
Tangible clues validating service quality.
Atmospherics
Environmental factors influencing customer perceptions.
Processes
Flow of customer engagement with services.
Customer Journey
Total experience from service purchase to consumption.
Touch Points
Moments of customer interaction with the company.