Schedule 2 - Influences on Businesses
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What is the business cycle?
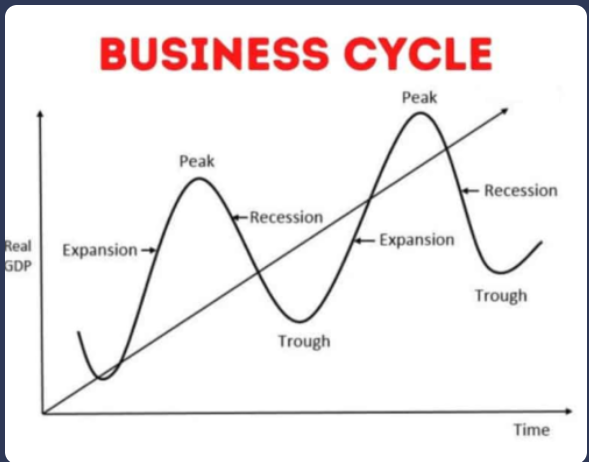
Economic climate
The state of an economy in a country e.g. the level of goods and services produced and the number of jobs available.
What effects the economic climate?
Amount of production
Level of income
Amount of consumer spending
Amount of jobs available
What are the signs of an improving economy?
Increased production
Increased income levels
Rising consumer spending
Rising levels of employment
What are the signs of a weakening economy?
Reduced production
Reduced income levels
Falling consumer spending
Falling levels of employment
Interest rates
The cost of borrowing money or the reward for saving money.
What happens to the cost of borrowing if the interest rate increases?
Cost of borrowing increases
What happens to the reward for saving money if interest rates increase?
The reward increases
If the interest rates rise, will consumers/ businesses want to spend more or save more?
Save more
What might businesses do to keep money in the bank?
Delay growth.
If the economy is strong, will the levels of employment be high or low and why?
High as more workers will be needed to produce goods and provide services.
What happens if the economy weakens in terms of employment?
Employment levels and wages fall.
What does an increase in employment rate lead to?
Higher sales
Increased employment costs
Explain why an increase in employment rates leads to a change in sales.
More people have a job -> more income -> more disposable cash -> higher spending power -> higher consumer spending.
Explain why an increase in employment rates leads to a change in employment costs
Wages increase to attract more employees as less employees available -> higher costs -> profit may decrease.
Consumer spending
Value of goods and services bought by consumers over a period of time
What happens to consumer spending if their jobs are at risk and why?
Lowers as they will want to save money for when they have to income.
Businesses providing essential products may experience what?
A less significant drop in sales - income inelastic
Businesses providing luxury products may experience what?
A more significant drop in sales - income elastic
Why does a strengthening economy lead to more production?
There is more demand.
What higher demand lead to?
Rising levels of employment.
Why do levels of employment rise when there is more demand?
More production needed to keep up with the demand.
What happens if levels of employment increase?
Higher income levels.
What happens if there are higher income levels?
Consumers have more disposable cash
What happens if consumers have more disposable cash?
Increased consumer spending.
What happens if consumer spending increases?
Higher sales.
What happens to operations if consumer incomes decrease?
- Cut production levels
- Cheaper versions of products
What happens to finance if consumer incomes decrease?
- Update budgets
- Revise cash flows
- Borrowing money
What happens to HR if consumer incomes decrease?
- Reduce employees' hours
- Make redundancies
What happens to marketing if consumer incomes decrease?
- Cut prices
- Revise advertising strategy
What are methods of digital communication? (3)
- Texts
- Webchat
- Teleconferencing and video-conferencing
- Apps
- Social media
Advantages of ICT
- Easier to contact customers - customer support
- Businesses can re-order supplies automatically which can lower storage costs and ensure the business has enough supplies
Disadvantages of ICT
- Training
- Expensive
- Technical problems and hackers
Advantages of e-commerce
- Reach more customers
- Speed the flow of goods and information
- Improve customer service
- Don't need a physical store
- Larger range of products can be found by customers and sold
Disadvantages of e-commerce
- Expensive to keep up with technology
- Customer security concerns
Ethical
Doing the right thing.
Examples of ethical business practises
- using recyclable material/ packaging
- fair trade
- paying workers a fair wage
- having good work environments
Examples of unethical business practises
- Animal testing
- Underpaying staff
- Slavery/ child labour
What does it mean if a product has fairtrade?
The producer receives a guaranteed and fair price.
Advantages of a business being ethical
- Improved reputation
- USP
- Higher prices can be charged
- Better employee motivation and recruitment - more productivity
- Additional sources of finance from ethical investors
Disadvantages of a business being ethical
- More expensive materials
- Focus on core activities such as satisfying customers could be lost
What are the 3 main categories of law?
- Employment law
- Health and safety law
- Consumer law
What are the sections of Employment law?
- National minimum/ living wage
- Discrimination - Equality Act
- Paid holidays and maternity leave
What is the Health and Safety law?
Prevents business putting employees in danger and so protects the workforce.
What are some areas the health and safety law could cover?
- Installation and maintenance of safety equipment and clothing
- Providing protection against dangerous substances
- Maintenance of workplace temperatures
- Fitting guards on dangerous machinery
What are some things the consumer law prevents?
- Selling goods and services that are not as described
- Selling products that are unsafe
- Selling products that do not work properly or at unfair prices
- Selling information about consumers to other business without permission
What does the consumer rights act cover?
- Rights to return goods
- Rights to repair/ replace
- Delivery rights
- Product quality
Advantages of employment law
- Employee friendly practices increases motivation
- More likely to get the most out of employees as they gain access to greater experience and expertise
Disadvantages of employment law
- Can increase costs which lowers profit
- May make hiring employees less attractive to business and they may get replaced with machinery
Advantages of health and safety law
- Reduces chance of fines or lawsuits as it is less likely for an employee to get injured
- Avoid reputational damage for taking bad care of employees
Disadvantages of health and safety law
- Expensive to implement safety measures and regular checks
- Time consuming to implement safety measures - could delay business actions e.g. expansion
Advantages of consumer law
- Consumers will be more confident to buy expensive products
- Clear framework which applies to all competitors - fairer contest
Disadvantages of consumer law
- Higher costs to get higher quality products and delivery requirements
- Expensive to replace or refund
- Reduction in potential revenue due to strict consumer data protection
What could low competition for a business lead to for a consumer?
- Higher price
- Lower quality
How does governments ensure monopolies don't occur?
- introduce price gaps
- Prevent specific mergers and takeovers
- Introduce consumer protection and legislation
How will a business compete in moderate competition?
- Competitively price
- Launch new products
- Compete through advertising
How will a business compete in high competition?
- Competitively price
- Product or service differentiation - USP
Risk
Possibility of something going wrong which can be measured in some way.
Uncertainty
When a situation is hard to measure due to lack of information so the
How can a business minimise risk?
- Business plans
- Train staff
- Use experts and consultants
- Sell in different markets
What is internal risk?
Risk from within a business - easier to manage e.g. equipment failure
What is external risk?
Risk from the external environment - outside the business' control so harder to manage e.g. pandemic
Globalisation
Process through which world economies become more interconnected
Impacts of globalisation
- Increased volume of trade between countries
- People live and work in different countries
- Creation and growth of multinational companies
Factors contributing to globalisation
- Improved transportation technologies
- Improved communication technologies
- Increasing incomes
Advantages of globalisation
- Rapid growth - expanding into different countries, takeovers, economies of scale
- Inward investment - foreign businesses invest money into a country
- Cheaper resources
Disadvantages of globalisation
- New competition
- Fierce competition - if they have cheaper resources they can price more competitively
- Threat of takeovers as MNCs can buy businesses to grow quicker
- Job losses e.g. they move production abroad
What does it mean if a currency has greater purchasing power?
It has appreciated - increase in value against another currency
What does it mean if a currency lower has purchasing power?
depreciation - decrease in value against another currency
What does SPICED stand for?
Strong Pound Imports Cheaper Exports Dearer
What does WPIDEC stand for?
Weak Pound Imports Dearer Exports Cheaper