Anatomy chapter 2
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
The human body has over ___ types of cells
200
cells are the smallest ‘_____ ___ in our bodies
living unit
basic cellular function
obtain and use nutrients, get rid of waste, replicate/regenerate,repair
the three functions of a cell are carried out by the cells
organelles
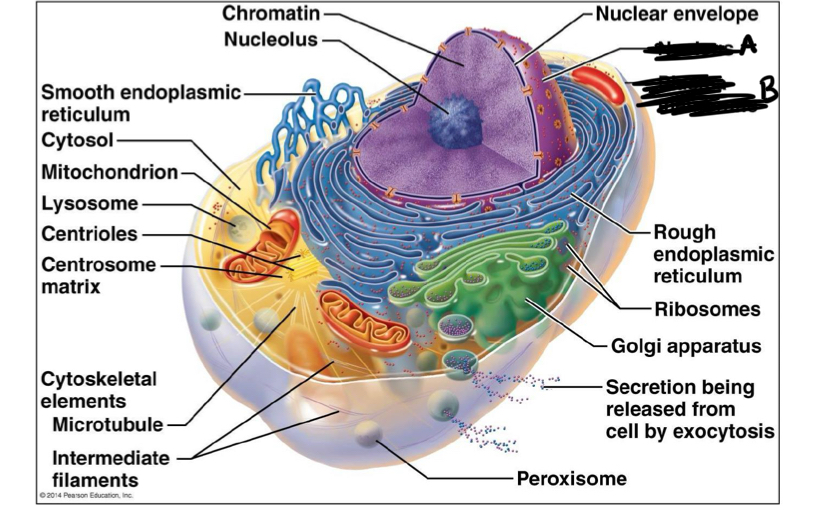
What is A
nucleus
what is B
Plasma membrane
fluid mosaic model proves
the plasma membrane is made up of many structures
phospholipids
fats, amphipathic (hydrophobic and hydrophilic), creates framework for the plasma membrane, makes up 75% of membrane lipids
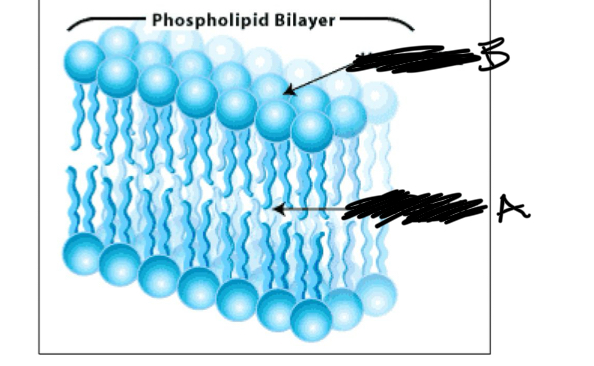
B is
hydrophilic

A is
hydrophobic
Membrane proteins
integral, peripheral
Integral protein
imbedded in the by layers, extend across both layers
peripheral protein
does not extend across the bilayer, easily separated from it
transmembrane protein tells us its a
integral protein
Main function of plasma membrane
Protective barrier, cellular communications, regulates movements of substances coming in and out
the plasma membrane is selectively
permeable
permeable
ability to cross
integral proteins act as ____ to assist the entrance of ____ molecules
transporters, impermeant
carriers are associated with ___ transport
passive
pumps are associated with
active
pumps need the energy because they are
moving molecules against the natural gradients
Natural gradient
high to low
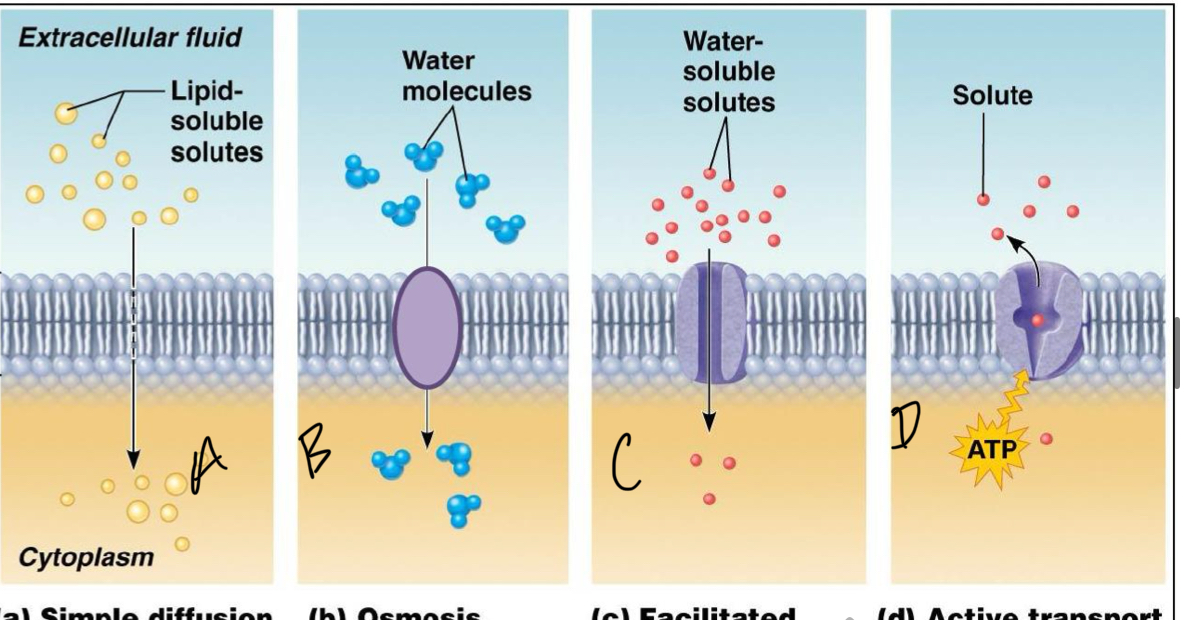
which are passive transports
A,b,c
if something is hydrophilic it often times is
lypophobic
Inorder to pass through it has to also be
lypophyllic
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane
why cant water pass The lipid bilayer alone
The tails are hydrophobic
is osmosis a protein acts as a ____ so the water molecules can go through
channel
facilitated diffusion
An integral protein opens up and allows solute across the membrane (carrier)
Carriers vs channels
a channel opens like a tunnel, carriers open hinge like
carriers and channels are associated with
passive transport
vesicular membrane transport
pieces of a plasma membrane that get pinched off to form a plasma membrane bubble
three ways vesicles are used for endocytosis
phagocytosis, pinocytosis
Phagocytosis
(cell eating) brings bigger molecules in, plasma membrane will extend up and form these arms (pseudopods), they then fuse together top hinges off and the bubble migrates down into the cell
Vessel bringing stuff in if its phagocytosis
phagosome
Pinocytosis
cell drinking, creates a pit extracellular fluid (all dissolved solutes) will go into the pit, two ends will fuse together
receptor- mediated endocytosis
like pino but requires a receptor to bind to the surface, when the binding occurs it will signal to kick off the process
Vessicular membrane exocytosis
the vesicle is a bilayer, vesicle migrates to the edge of the cell, phospholipids fuse together allows vesiclle to open up and release any molecules
cytoplasm is composed of
cytoplasm, organelles, inclusions
endocytosis and exocytosis
act as yin and yang balance of replenishing phospholipids and also bringing in cells
as we bring some of the cells in they will fuse together top hingesgether with the ____
organelles
cytosol
jelly like fluid which all other intracellular elements are suspended (all the stuff sits in)
what would be found in cytosol
water, ions, enzymes
what occurs in the cytosol
many chemical reactions (using the enzymes)
organelles
specialized structures within a cell that have a characteristic shapes and perform specific functions
inclusions
temporary strucures because these molecules are broken down (not permenant)
example of inclusions
pigments, crystals of proteins, food stores
what are some basic organelles
mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, centrioles
ribosomes
protein synthesis , made up of two dif proteins + ribosomes eat RNA that are two different subunits
Location of ribosomes
cytosol (free ribosomes), or attatched to the endoplasmic reticulum (rough endoplasmic reticulum)
endoplasmic reticulum
network writhing the cytoplasm, network of membrane enclosed cavities
rough ER function
protein synthesis
smooth ER
no ribosomes, making and breaking down lipids, calcium storage
cavities in ER
Cisterne (flattened sacs or tubules)
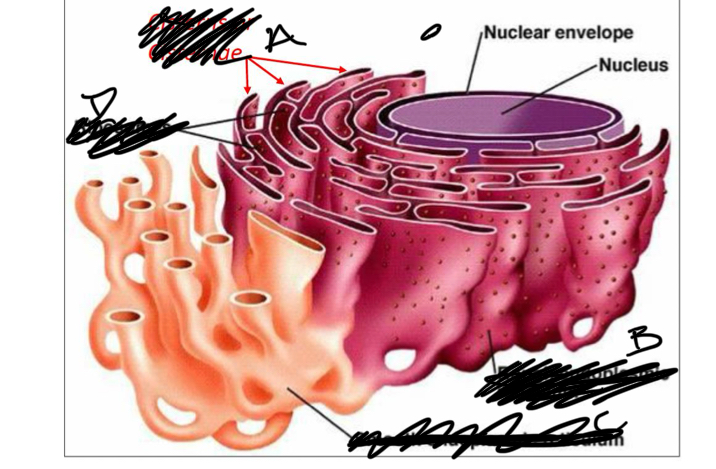
What is a
cisterns
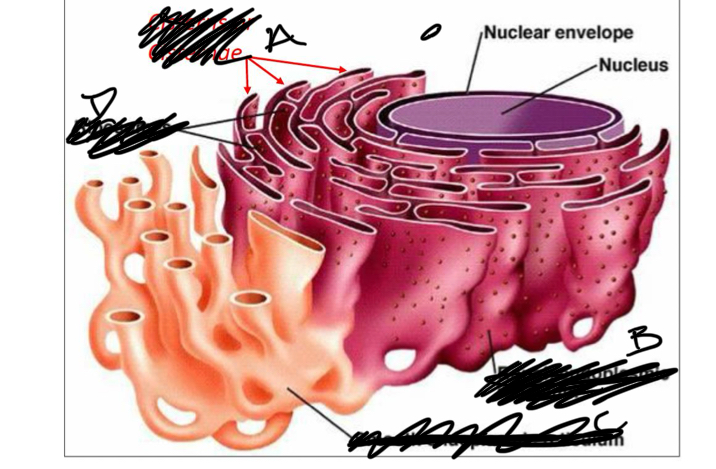
What is b
rough er
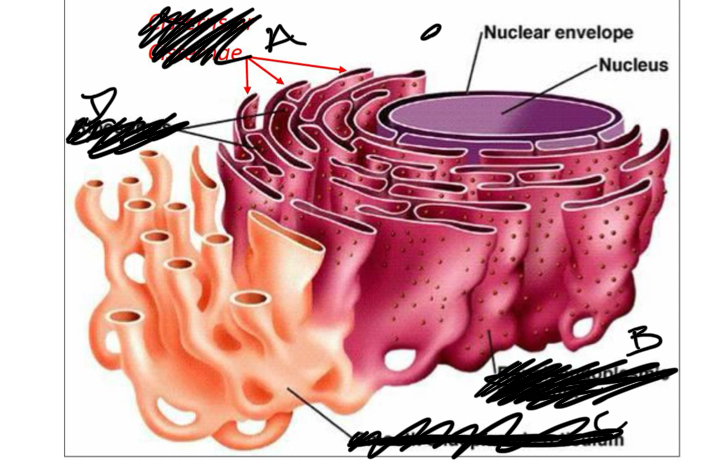
What is C
smooth ER
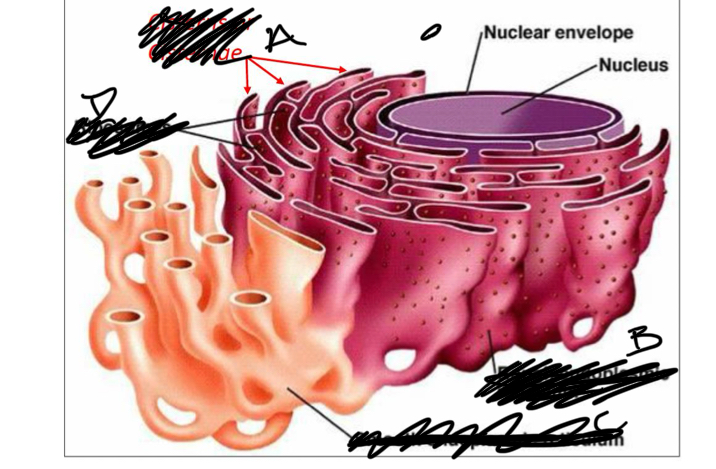
What is D
ribosomes
the ER is all extending from the
nucleus
goblin apparatus is known for
the processing center of the cell
Proteins and lipids get transported to the Golgi apparatus and
gets processed if anything needs to be added or cut
a protein would get packaged into
Golgi has two sides the receiving side is called
cis
Protein through the golgi
cis face, then flattened in cisternae, then is sorted, then reaches trans face (shipping side),Golgi pinch offs a piece of itself with the protein and then goes off to a final destination
Coordination of organelles
pinching off of ER, then cis space of Golgi, through cisternae, exits out transface pinches off Golgi, then can take avoupkle different pathways
if a protein is meant for a diff cell
It will fuse with the membrane and is destined for an exocytosis
Meant to be an integral protein
inserts into the plasma membrane
protein must be destroyed
breaks the protein secretory vessicle will fuse worth the lysosome, and the lysosome has acidic enzymes to break it down
peroxisomes vs lysosomes
lysosmes (digestion), peroxisomes (detox)
peroxisomes
removes toxic wastes by using special enzymes
An example of a cytoskeleton microfillament
actin
cytoskeleton intermediate fillaments
woven like a rope
cytoskeleton mictrotubules
hollow tubes of spherical protein subunits called tubulins
centrioles are
an individual organelle made up of multiple microtubules
centrosome
pair of two centrioles
microfillaments
edge of the cell m
microvilli is __ a microfillament
not
microfillament are
finger like projections of the plasma membrane with actin on the inside
What acts as the structural rods to keep the microvilli up
actin
microtubules
largest diameter
microtubules dont have to be ___ but can be
motile
example of microtubules
chilling and flagella
Flagella
sperm
intermediate fillaments
stabilize organelle position in the cytoskeleton and attatch cells to one another
the nucleus
control center of the cell n
nucleolous
synthesis of ribosomes (RNA will help for the ribosomes)
chromatin q
genetic material
nuclear envelope
a double membrane on the nucleus

D, glyco proteins, cellular adhesion and recognition