ISB203B-Exam 2
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Earthquake hazard assessment/mitigation and volcanoes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
What are earthquake hazards?
ground shaking
liquefaction
landslides
fire
tsunamis
what are the effects of ground shaking?
building collapse from direct shaking
rupturing of gas/electrical lines
secondary effects
what are the effects of liquefaction?
building collapse
sinkholes
what are the effects of landslides?
destroy everything in its path
can we predict earthquakes?
in the short term, no
in the long term, we can predict the probability of it happening
can we prevent earthquakes?
NO
what questions can we ask to evaluate earthquake hazards?
what is the probability of an it happening in a region?
how large might it be?
how will the fault move? what parts will move the most?
what kind of damage might be expected?
what is being evaluated when we investigate the tectonic environment of a potential earthquake?
is it on a subduction zone? this could cause a tsunami
how large can it get?
what is being evaluated when we investigate where the faults are of a potential earthquake?
where are the areas that could slip and cause an earthquake located?
what is being evaluated when we investigate the character of past earthquakes?
where have earthquakes happened in the past?
how often do earthquakes happen?
how long since the last one?
how large are the earthquakes?
can track this through newspapers, merchant records, old stories, folk tales and paleo-seismology
what is being evaluated when we investigate the present day activity in an area that has a possibility of earthquales?
present say seismicity isn’t always a good indication of earthquake potential
an area of a fault showing a high rate of strain accumulation is likely to move more during an earthquake
what is being evaluated when we investigate the ground/surface conditions of an area with a potential earthquake?
softer ground creates worse damage for earthquakes
seismic hazard maps
seismic hazard map
%g—percent gracity and predicted amount of ground shaking
predictions for levels of peak ground shaking based on probability, higher numbers with smaller probability, low numbers with higher probability
depends on the fault
paleo-seismology
study of earthquakes that happened in the past
firepits under tsunami sand
ghost forests
tsunami deposits
tsunami records
recurrance charts
NOT WATER ON ROCKS
what cause ghost forests?
trees in marshes die because they’re dropped down into seawater because of a tsunami
tsunami deposits
broad layers of sand and sediment brought over an area
can dig into the earth and see where/when the tsunami came from
recurrance charts
are based on recurrence intervals
provide predictions of when earthquakes could happen
not exact
what can we do to mitigate earthquake hazards?
building construction and zoning regulations
earthquake early warning
tsunami warning signs
education about earthquake hazards
wood stuctures and earthquakes
withstands earthquakes well—almost as good as reinforced concrete
elastic—building wiggles and absorbs ground shaking but stays together
brick structure/concrete block structure and earthquakes
don’t withstand earthquakes well
dislodges concrete blocks, mortar crumbles and separates, building collapses
reinforced concrete structures and earthquakes
withstands earthquakes well
expensive, not frequently used
when used with steel structures, pancaking occurrs
highway overpasses and earthquakes
concrete and interior steel supports
bad for vertical earthquake motion—crushes rebar like a tin can
how can buildings be better constructed for earthquake mitigation?
Adding steel corner struts, braces, and connectors can strengthen a wood-frame house
Buildings are less likely to collapse if they're wider at the base and if crossbeams are added for strength
Wrapping a bridges support columns in cables and bolting the span to the columns will prevent the bridge from collapsing so easily—cables and anchor bolts
Placing buildings on rollers or shock absorbers lessens the severity of vibrations—isolation
seismic retrofitting
adding things to existing buildings so that they can come through earthquakes better
Foundation anchor plates—strengthen the house to foundation connection; drilled into frame of house and foundation to keep them together
Cripple walls
Add things to structures to control where the damage goes
Wrapping steel cable around bridges
non-structural mitigation
things that can be done in your house to mitigate hazards
Strapping water heaters to walls so they can't fall over
Bolding things to walls
Not putting pictures above bed
Bolt appliances to wall
Replace copper gas lines to plastic lines
building zoning
evaluating areas of a city that may be more susceptible to hazards and making building codes
earthquake early warning
Advance warning of arrival of damaging seismic waves AFTER earthquake has begun
GPS/GNNS Waveforms
Seismometers
Seconds to minutes of warning before shaking starts
what can be done with the seconds to minutes of warning provided before shaking starts during an earthquake
Slow or stop trains
Prepare first responders
Protect power infrastructure
Stop surgeries
Secure sensitive equipment, shut down protection lines
Personal safety measures: drop and cover, stop vehicles
tsunami warning systems
can give hours of warning before waves hit the shore
DART buoys
warning steps as tsunami warning system
process: get information about seismic event and revise things
Preliminary analysis of earthquake—tsunami info statement, tsunami advisory, watch, or warning
Refinement of earthquake information, tsunami model estimates, additional data about tsunami gathered (repeated)--tsunami advisory, watch, or warnings may change
Report of tsunami wave heights/damage
DART buoys
Deep-ocean Assessment and Reporting of Tsunami (Tsunameter)
Pressure recorder bolted to ocean floor
Communicates with satellite and satellite send message to receiving center
Tsunami travel times
tsunami travel times
the hours of how long the tsunami wave will take to hit other buoys/areas of the ocean
tsunami warning signs
Signs along coasts in areas prone to tsunamis
Evacuation routes to higher ground as quickly as possible
People don't always listen
tsunami shelters
specially designed buildings to help people get to higher ground and built to withstand tsunamis
Purpose built tsunami shelters
education about earthquake hazards
Telling people what to do and how to stay safe during earthquakes and tsunamis
Aware of hazards in their region
resilience
Ability to maintain normal services and lives after a major event
Rapid recovery with minimal social disruption
Final state of affairs better or as good as before the event
how to improve resilience
Identify vulnerable facilities and systems
Develop scenarios to assess what could happen during an event
Set goals for improved response and develop plans for achieving goals
how to work towards the goals of increasing resilience
Engineering and retrofitting
Earthquake early warning
Analysis of tsunami inundation to plan evacuation routes, future development of schools, medical centers, other critical facilities
Awareness and education
why should we care about resilience?
Impacts business/government of, potentially, the entire country
Trans-pacific cables—disrupted communications with other countries
Ports/shipping
Economic impacts
Earthquakes can happen in the Midwest and in eastern North American
benefits of volcanoes
Create new land
Enrich soil for farming
Create mineral deposits
Create picturesque landscapes/tourism
drawbacks of volcanoes
Destroy communities
Destroy existing crops
Displace populations
Kill people and animals
Can change human history, can cause devastation across many countries around the world from one event
how are explanations of volcanoes different than earthquakes?
Earthquakes: many animals, not a lot of personification
Volcanoes: supernatural forces, assigning nature a personality
what is the basic anatomy of a volcano
Bottom: source of magma
Magma travels to surface via a conduit
Magma erupts to the surface through the vent
magma
molten rock below the surface pf the earth
lava
molten rock that has reached the surface of the earth and is either still molten or solidified
tephra
fragments of material produced during a volcanic eruption
ash
lapilli
bombs
ash
fragments of tephra smaller than 2mm in diameter
lapilli
fragments of tephra between 2 and 64mm in diameter; sometimes called cinders
bombs
fragments of tephra larger than 64mm in diameter
what are the 4 types of volcanoes?
fissures
stratovolcano
shield
cinder cone
fissure volcanoes
Long cracks in the ground where lava comes up and pours out on either side
Made up of layers of lava
Rifts and divergent margins
stratovolcanoes
"generic volcano;" most common above-air volcano on Earth
Triangle point
Made up of alternating layers of tephra and lava (cake layers)
Steep slopes due to tephra, but lava layers make it stronger
found in subduction zones
shield volcanoes
Broad and rounded, gentlest slope
Only made up of layers of lava, small slopes because of this
Massive
Start off as fissures
cinder cone volcanoes
No lava, just tephra around a vent
Smaller because tephra is unstable but can have steep slopes
angle of repose
slope at which that material is stable, any more, it will slide off
Different angles for different materials
where are volcanoes found?
Happen in patterns
Clusters
Arcs
The Ring of Fire
island arc or oceanic arc
oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary (subduction zone)
Usually stratovolcanoes
Can occasionally have shield volcanoes
continental arc or volcanic arc
chain that forms in continental-oceanic convergent boundary (subduction zone)
Known for stratovolcanoes
Can also have shield volcanoes, domes, cider condes; more variety
continental rift systems
Fissure eruptions
Can have cinder cones, shield volcanoes, and stratovolcanoes because of the variation of crust material
Off-rift axis volcanoes
hot spot volcanism
Shield volcanoes, fissures
HUGE volumes of lava
Prone to caldera formation
Flood basalts/large igneous provinces
mid-ocean ridges
Divergent boundary
Most common volcano type on Earth
Fissure eruptions; most common volcano type found under the ocean
Over time, may develop domes and seamounts (circular volcanic structures)
the ring of fire
Many clusters of volcanoes around the edges of the Pacific Ocean
types of volcanic arcs
island arc/oceanic arc
continental arc/volcanic arc
continental rift systems
hot spot volcanism
mid-ocean ridges
flood basalts/large igneous provinces
Rapid outpouring of vast amounts of lava, HUGE amount of material is what makes it unique
Fissure eruptions
Continental rifting? Hot spot? Combination of both? We don't really know the causes
off-rift axis volcanoes
the hot material doesn't come up into the rift valley, it goes off to either side, volcanoes develop along the sides of the rift
shield volcanoes or stratovolcanoes instead of fissure eruptions
magma
Mixture of melt (liquid rick), gas bubbles, and mineral crystals
density
mass/volume
number and weight of molecules = amount of mass
2 major ways to get magma
wet partial melting
decompression melting
wet partial melting
the introduction of volatiles (like water) to generate melt
decompression melting
moving the mantle around to reduce pressure and generate melt
occurs in mantle plumes, rifts, mid-ocean ridges
bouyancy —bring hot material up into cooler material (mantle convection)
heat transfer melting
minor way to generate melt
cannot generate melt by itself, needs melt and magma already there
already existing magma encounters something cooler, melts around the edges
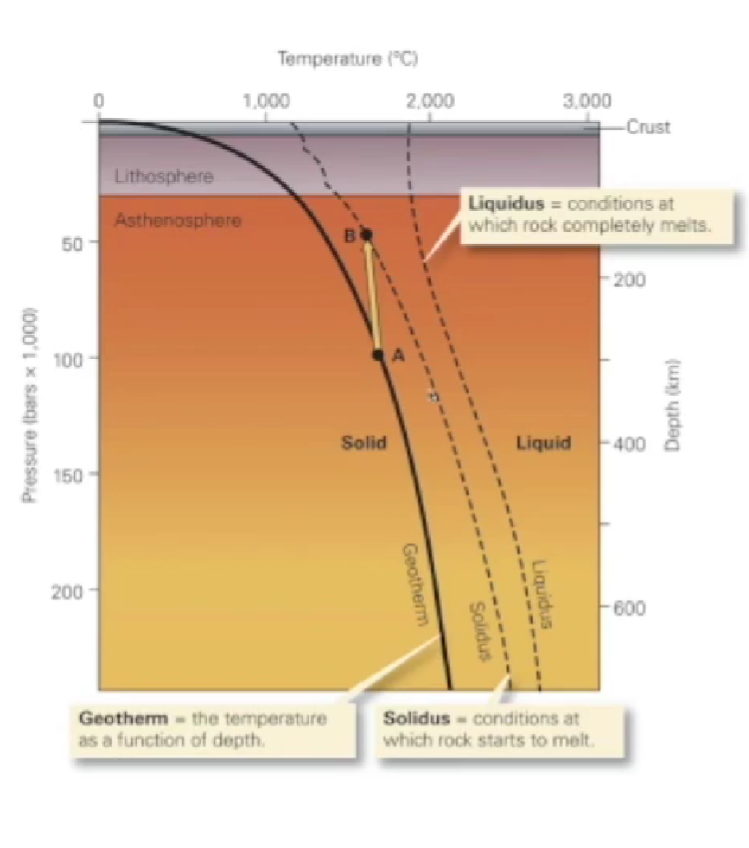
liquidus
conditions at which rock completely melts
Solidus
conditions at which rock starts to melt
geotherm
the temperature as a function of depth
oxide
oxygen combined with another element, a chemical naming convention
Silica, or SiO
Magnesium Oxide, or MgO
mineral
a crystalline solid with a regular atomic arrangement; has a specific composition and crystal structure
Quartz is SiO^2 in a regularly arranged pattern of molecules
Weight Percent (wt. %)
calculate total weight of all oxides using the periodic table -
to take weight of specific oxide divided by the total weight of all oxides
Common volcanic minerals
Olivine
Pyroxene
Hornblende (amphibole)
K-Na feldspar
Quartz
Magma compositions
Basaltic
45-52% silica
Mafic
Andesitic
52-62% silica
Intermediate
Dacitic
62-70% silica
Intermediate
Rhyolitic
More than 70% silica
Felsic
Factors that control magma composition
Source rock—what melted?
Partial melting—temperature of the system
Assimilation
Magma mixing
Fractional crystallization
Fractional crystallization (Bowens Reaction Series)
Magma eventually starts cooling (rises enough that it is in cool surrounding environment, water and other volatiles leave and raise the melting temperature)
Not all parts of the magma freeze at the same time—different components have different melting/freezing points
Zoning/mineral crystals due to composition changes
intrustive
lava erupted and cooled below surface of the earth, takes longer to cool, large crystals can develop
extrusive
lava erupted and it cooled at the surface of the earth, chills immediately, small/non-existent crystals
types of rocks
sedimentary
igneous
metamorphic
sedimentary rock
made of sediments (grains or fragments or rock) that accumulate and compact over a long time period; sandstone
igneous rock
volcanic rock
classified through composition and texture
More silica = bigger explosions and lighter color
extrusive composition of igneous rock
Basalt 45-52% silica
Andesite 52-62% silica
Dacite 62-70% silica
Rhyolite More than 70% silica
intrusive composition of igneous rock
Gabbro 45-52% silica
Diorite 52-62% silica
Granite More than 70% silica
texture of igneous rock
Glassy
Crystalline
Fine grained (aphanitic)
Coarse grained (phaneritic)
Porphyritic
Extrusive rocks have small/fine-grained crystals
Intrusive rocks have large/coarse crystals
Fragmental/pyroclastic--made up of a lot of materials
Vesicular—have gas bubbles in them
metamorphic rock
any type of rock that has been subjected to high temperatures or pressure and changed due to this; marble (from limestone)
volcanic products
lava flows
volcaniclastic debris
types of lava flows
basaltic
andesitic
felsic
basaltic lava flow
low viscosity and can flow long distances, lava fountains
Pahoehoe—smooth ropes/wrinkles at the surface of the lava flow; 'skin'
'a 'a—blocky/chunks that flow on top of the flow because it's cooler
lava tubes
columnar jointing
pillow basalts
lava tubes
can change surrounding rock as lava flows into it; instead of spreading out, it becomes channeled into a main stream, crust can form on top and an empty tube structure is left over; can become quite large
columnar jointing
the lava flow cools rapidly and becomes rubbly; joints and cracks form because layers of lava cool differently
pillow basalts
form underwater, skin forms immediately and pillow shape forms as a result
andesitic lava flow
too viscous to flow far and tends to break up as it flows
felsic lava flow
so viscous that it may pile up in a dome-shaped mass
volcaniclasic debris
debris formed when existing volcanic rock is blown apart during the eruption
Accumulates after landslides on the volcano or after being transported by water
Debris formed as lava flows break up or shatter
pyroclastic debris
volcanic gases