Muscle Structure, Function, and Fiber Types: A Comprehensive Guide
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
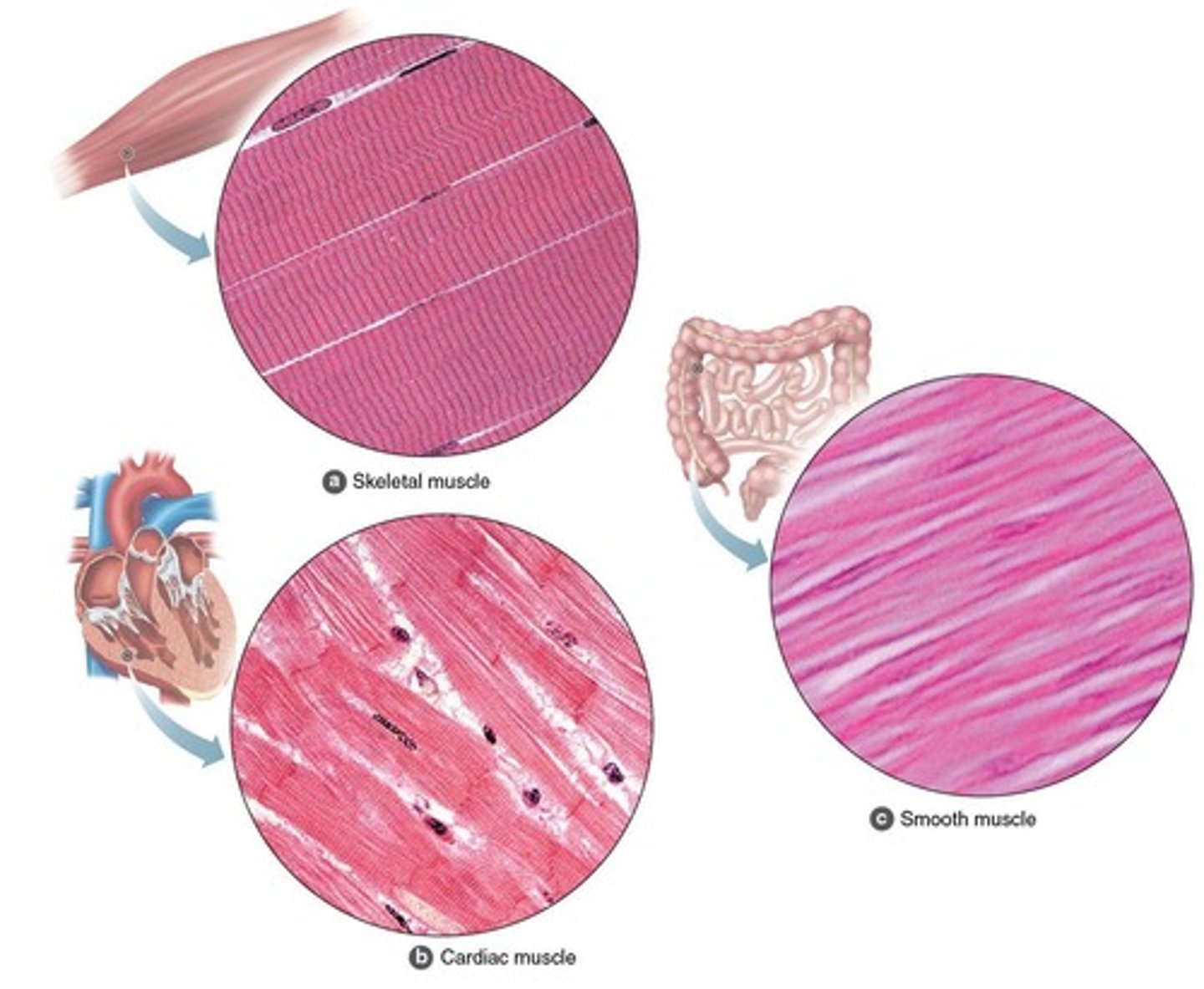
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal (voluntary), Smooth (involuntary, hollow organs), Cardiac (involuntary, heart).
What is the functional unit of skeletal muscle?
Sarcomere.
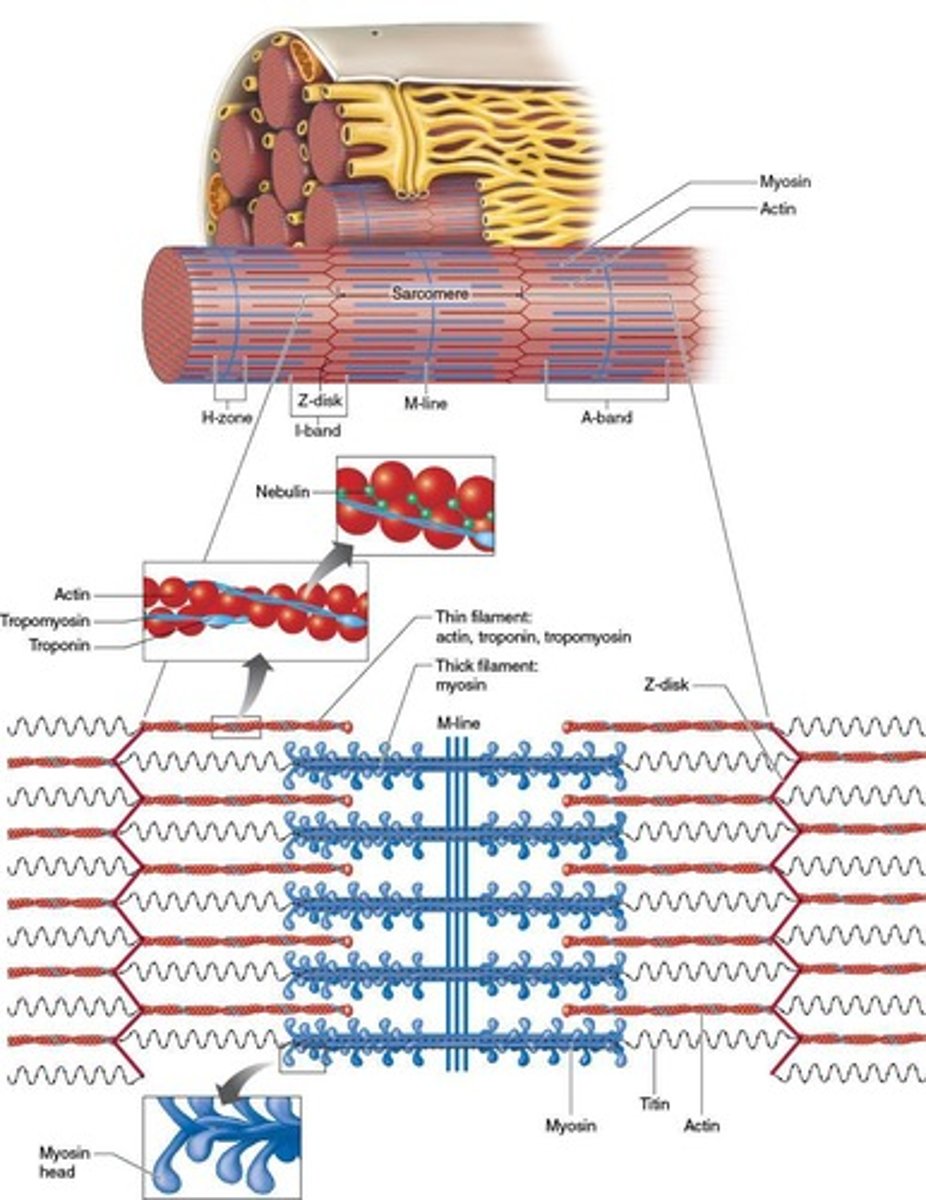
What is the organization of skeletal muscle from largest to smallest unit?
Muscle → fasciculi → muscle fiber → myofibril → sarcomere.
What surrounds a muscle fiber?
Endomysium.
What gives the sarcomere its distinctive striped appearance?
Striations formed by the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments.
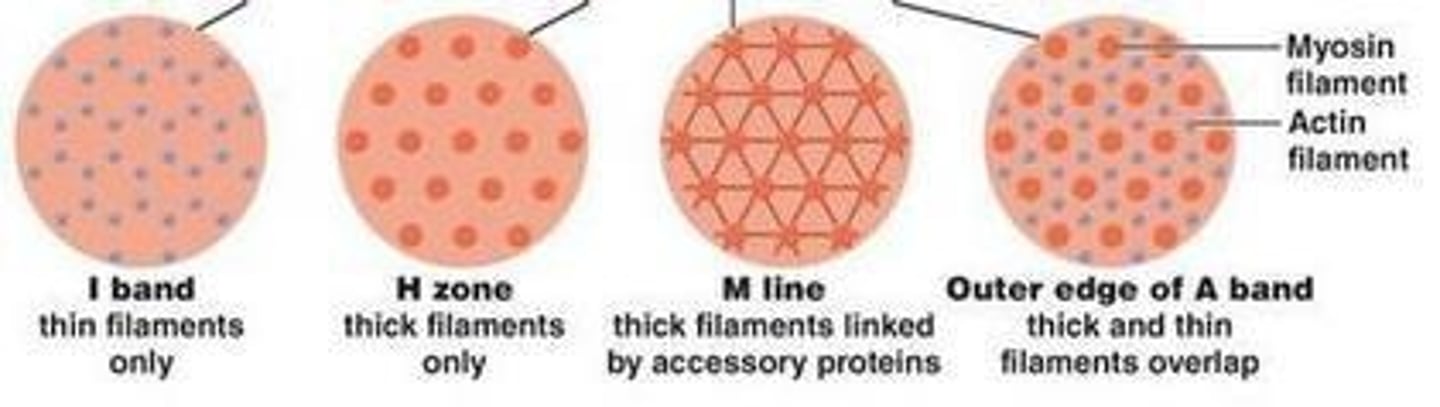
What are the components of the A-band in a sarcomere?
Dark stripes containing both actin and myosin.
What is the H-zone in a sarcomere?
The middle of the A-band that contains only myosin.
What anchors actin to the Z-disk?
Nebulin.
What are the three proteins that make up actin?
Actin (with myosin binding site), Tropomyosin (covers active binding site at rest), Troponin (moves tropomyosin upon calcium binding).
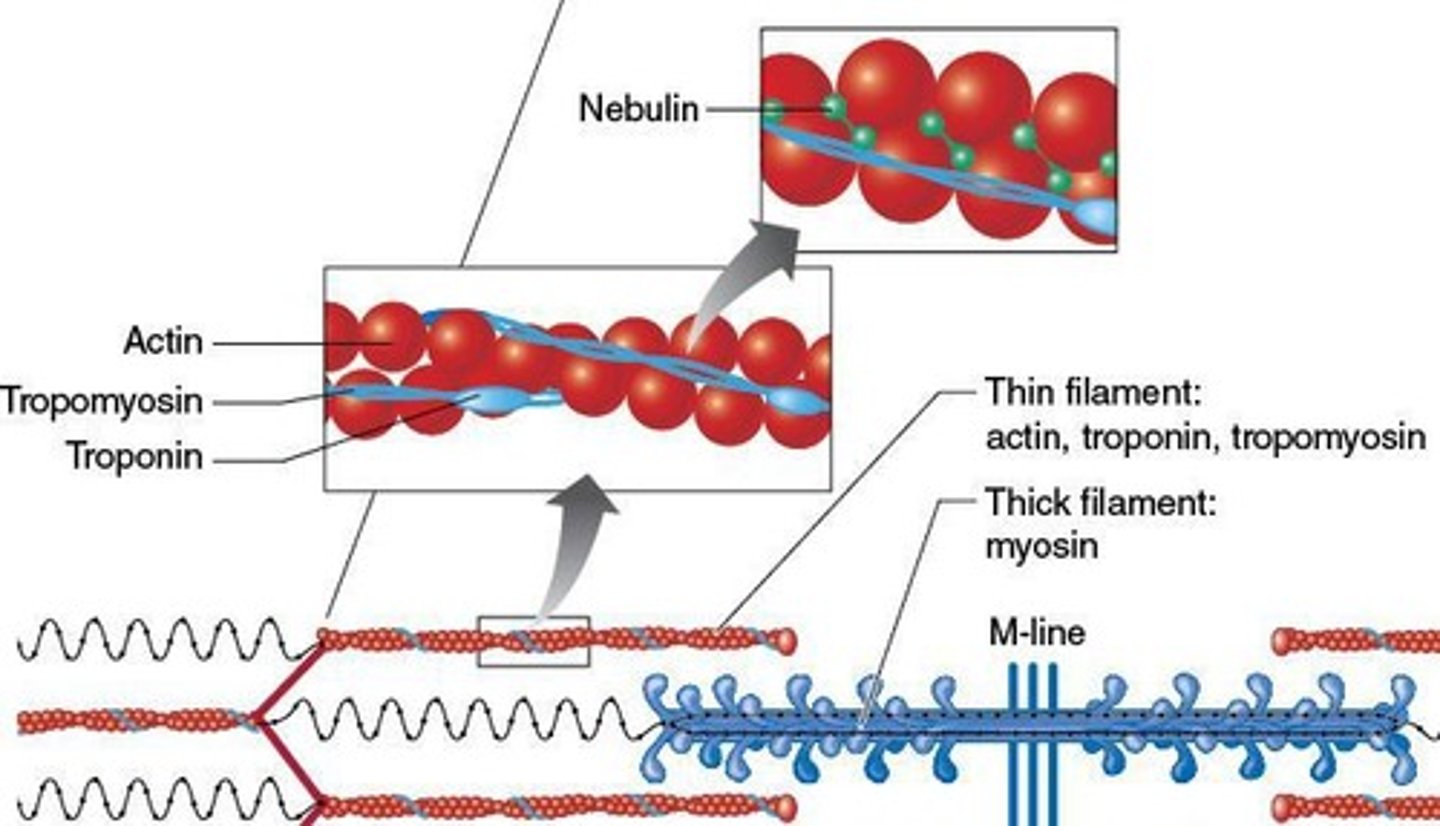
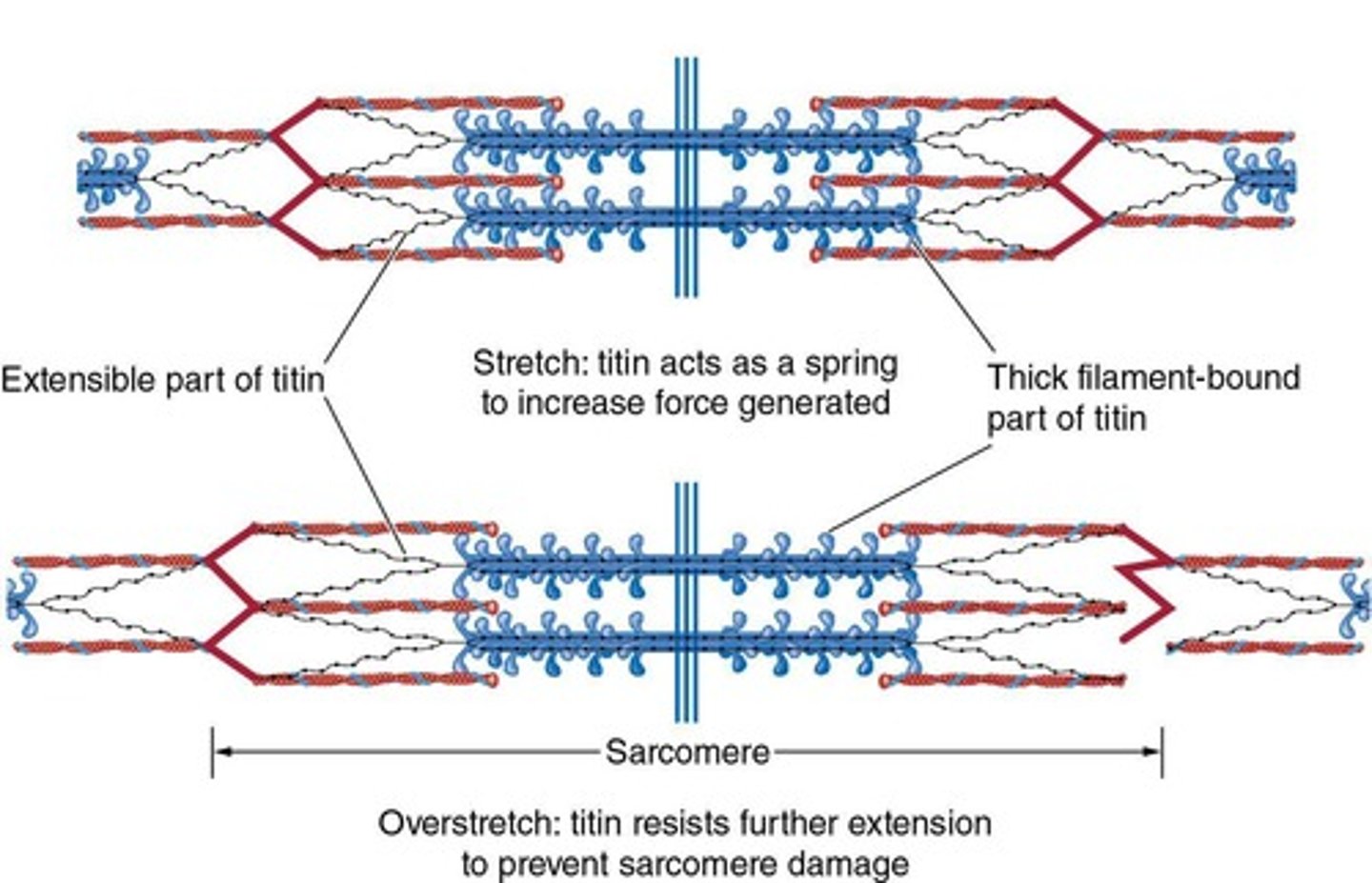
What role does titin play in muscle contraction?
It attaches myosin to the Z-disk and maintains equal spacing between actin filaments.
What happens to the I-band during muscle contraction?
It shortens.
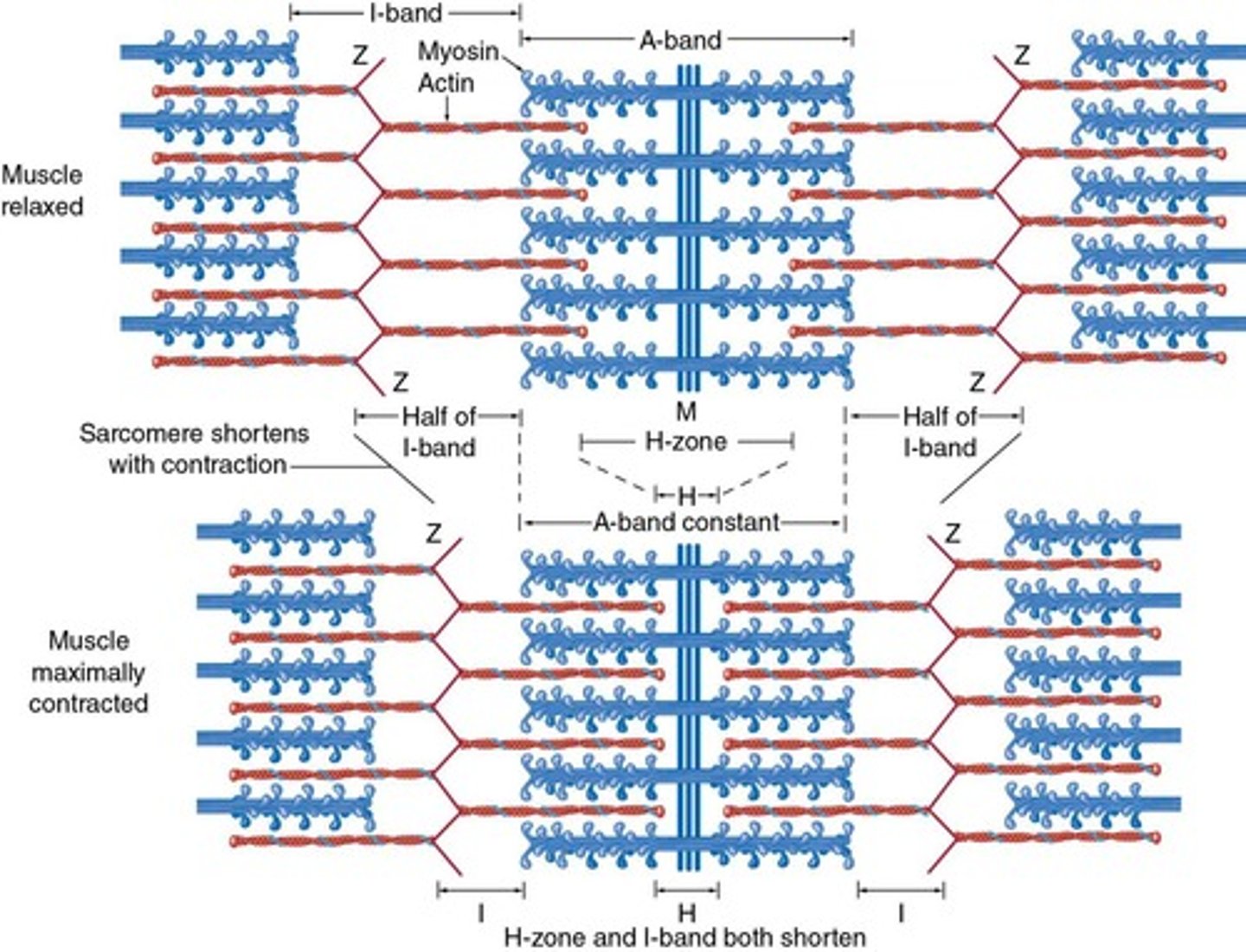
What remains the same during muscle contraction in the sarcomere?
The A-band.
What is the role of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
Involved in growth, repair, and adaptations.
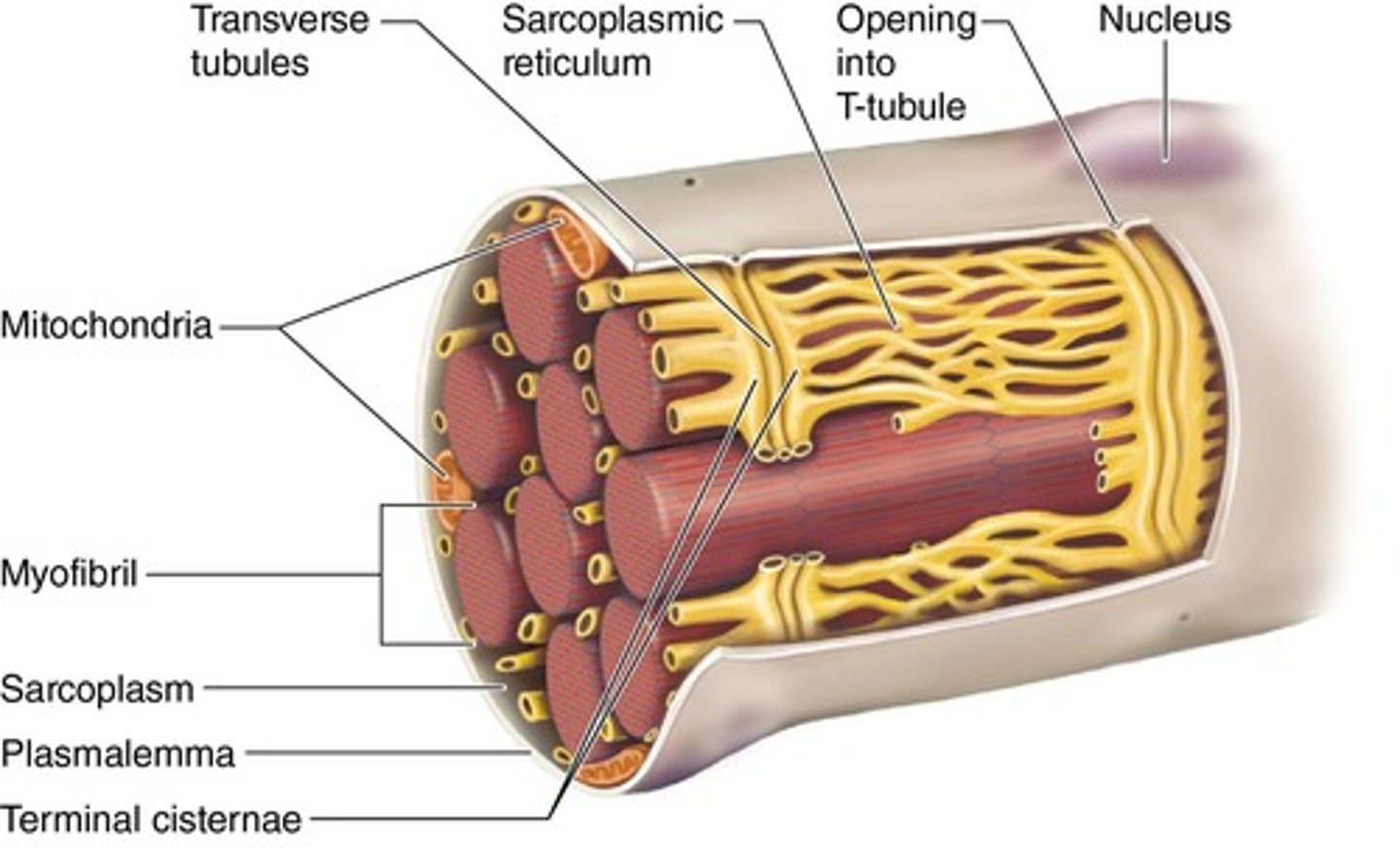
What is the significance of the sarcolemma?
It is the cell membrane of a muscle fiber.
What are transverse tubules?
Extensions of the sarcolemma that penetrate into the muscle fiber.
What is the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
It stores calcium ions necessary for muscle contraction.
What is the role of sarcoplasm?
It is the cytoplasm of a muscle cell, containing myofibrils and other organelles.
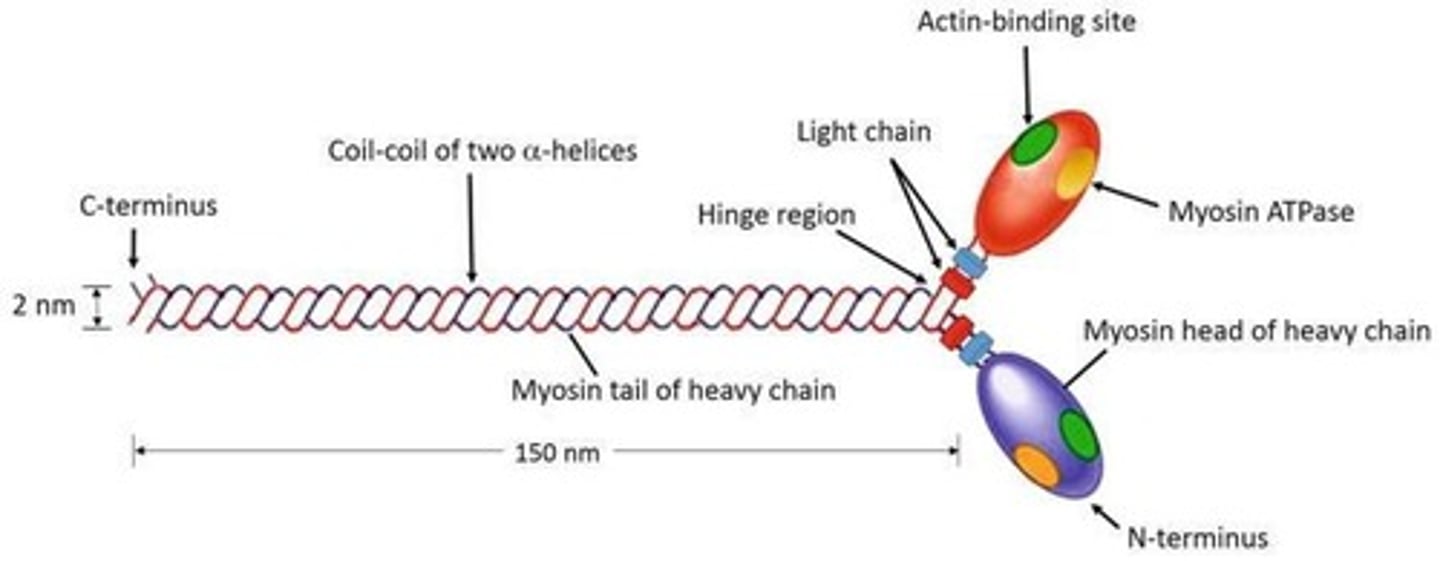
What is the functional role of myosin in muscle contraction?
Myosin heads interact with actin to produce contraction.
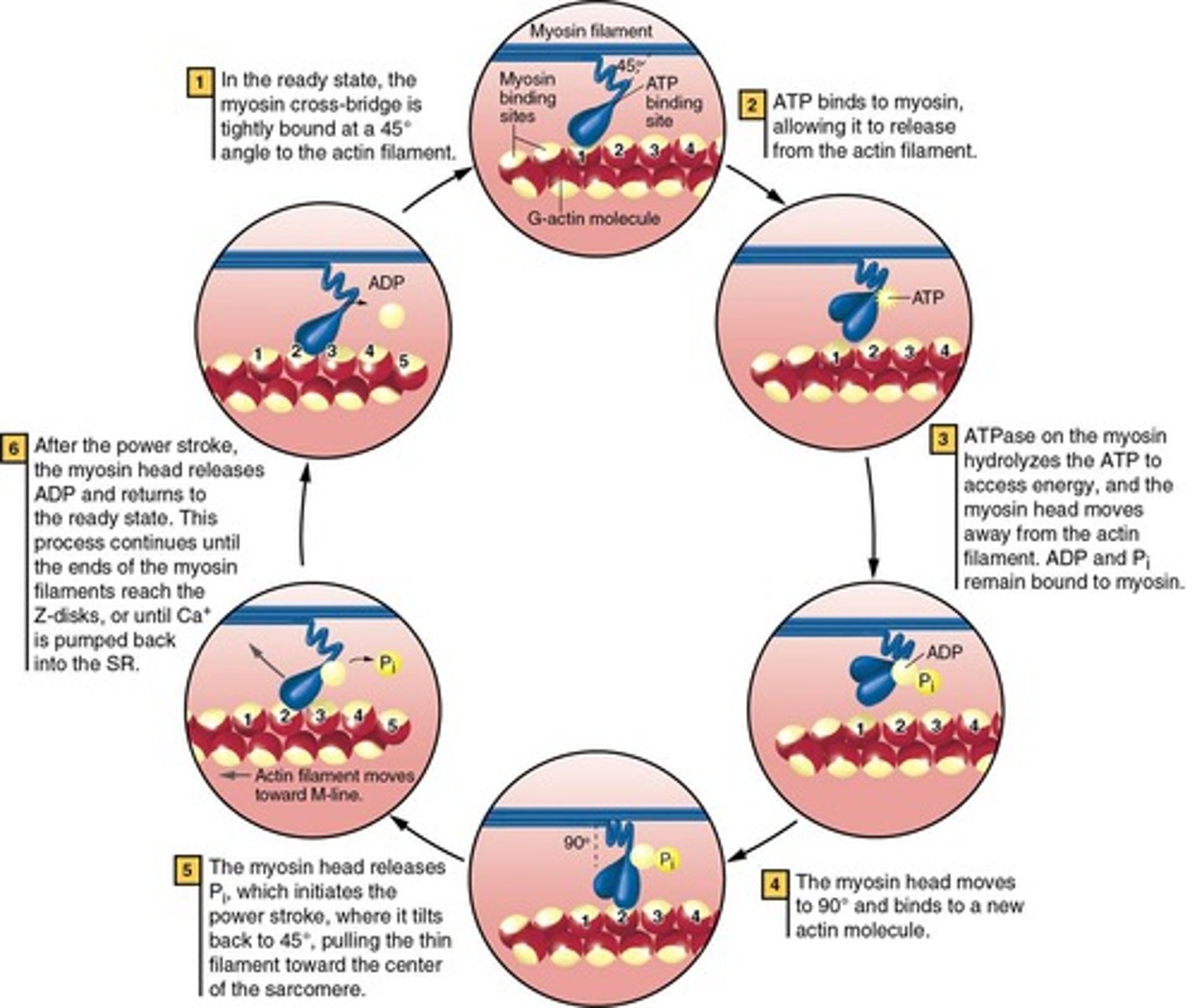
What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
Calcium binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to move and expose binding sites on actin.
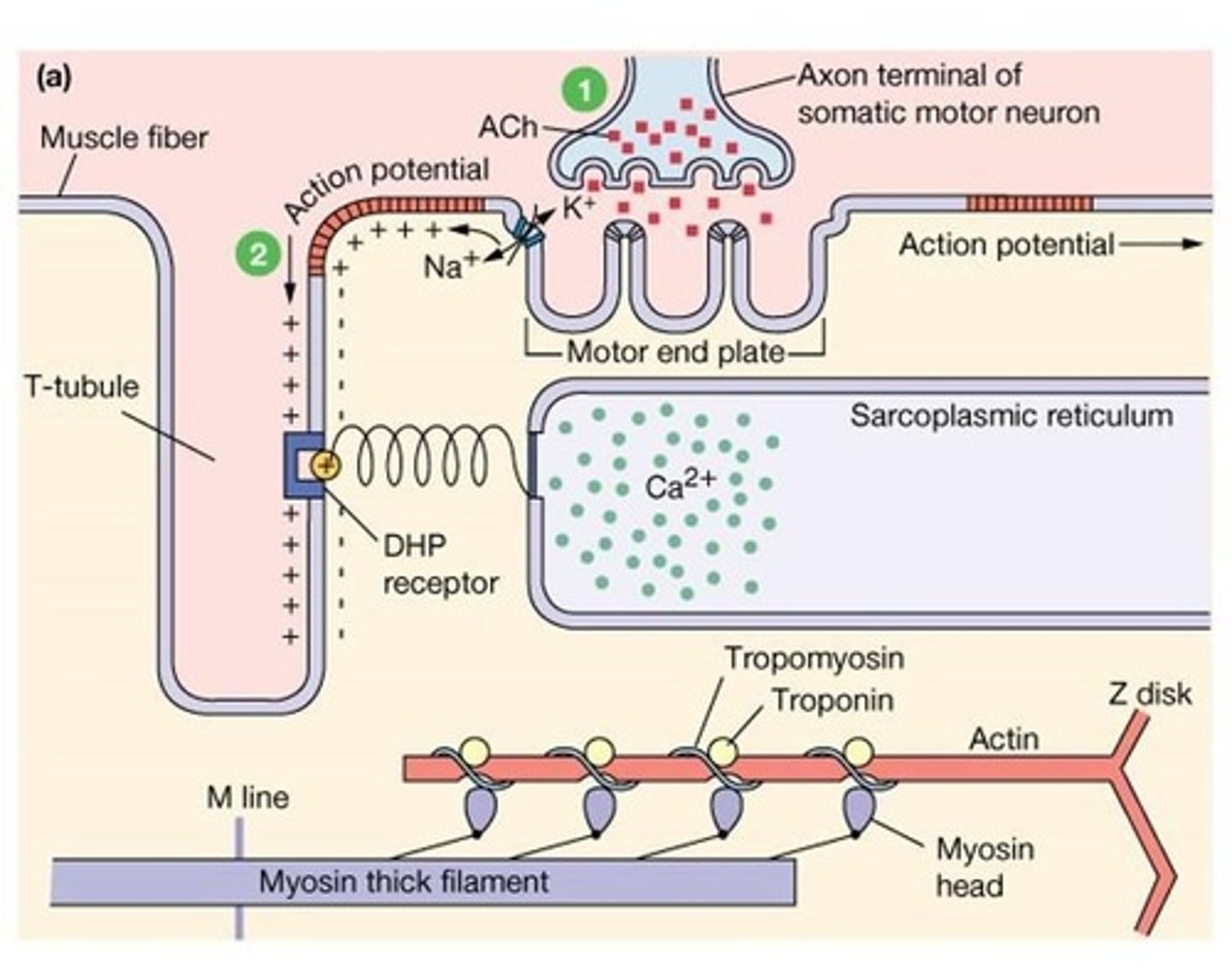
What is the significance of the M line in a sarcomere?
It is the middle of the H-zone where myosin filaments are anchored.
What prevents overstretching of the muscle during contraction?
Titin acts like a spring, increasing stiffness.
What is the relationship between excitation-contraction coupling and muscle contraction?
Excitation-contraction coupling is the process that links the electrical signal to muscle contraction.
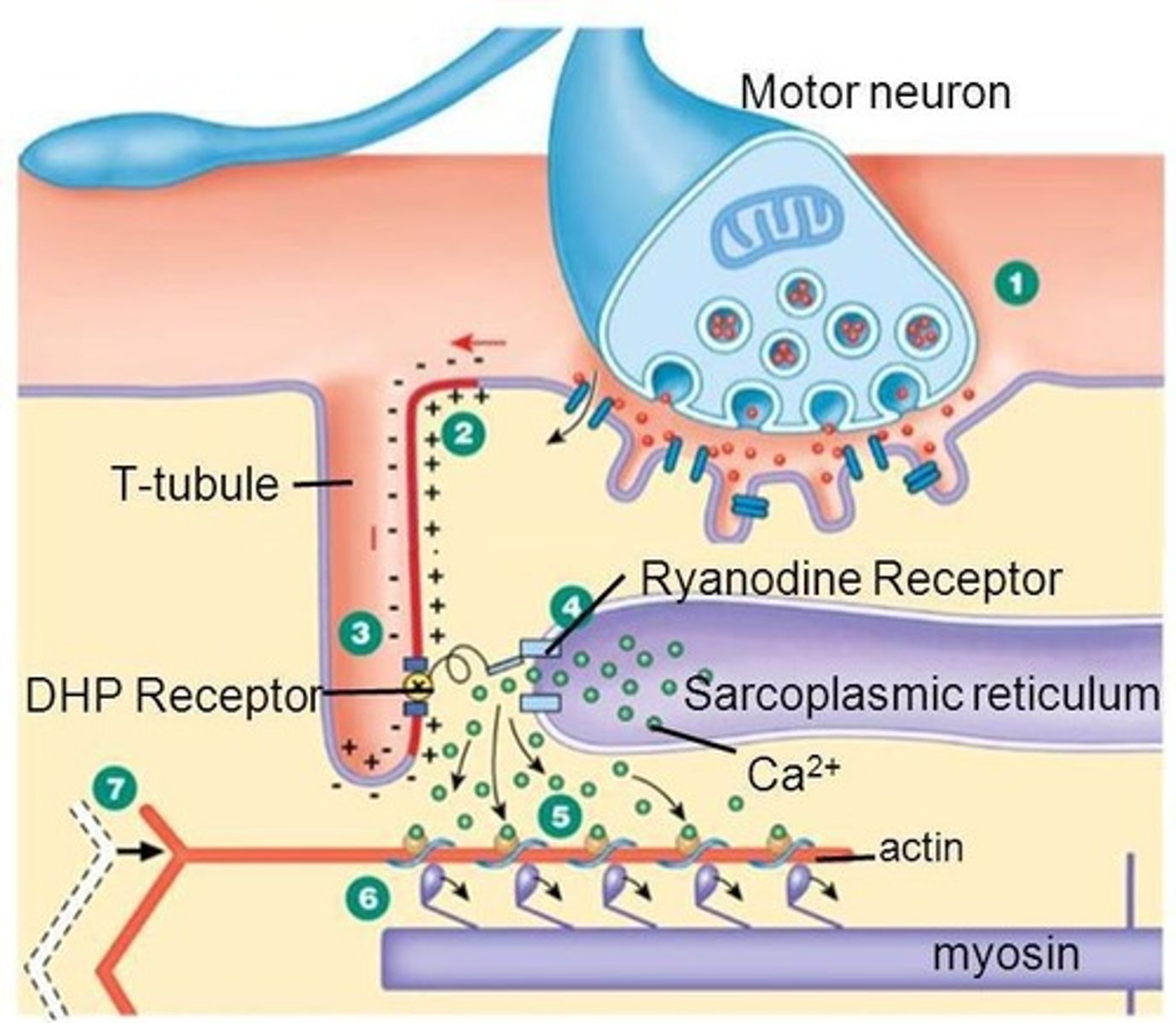
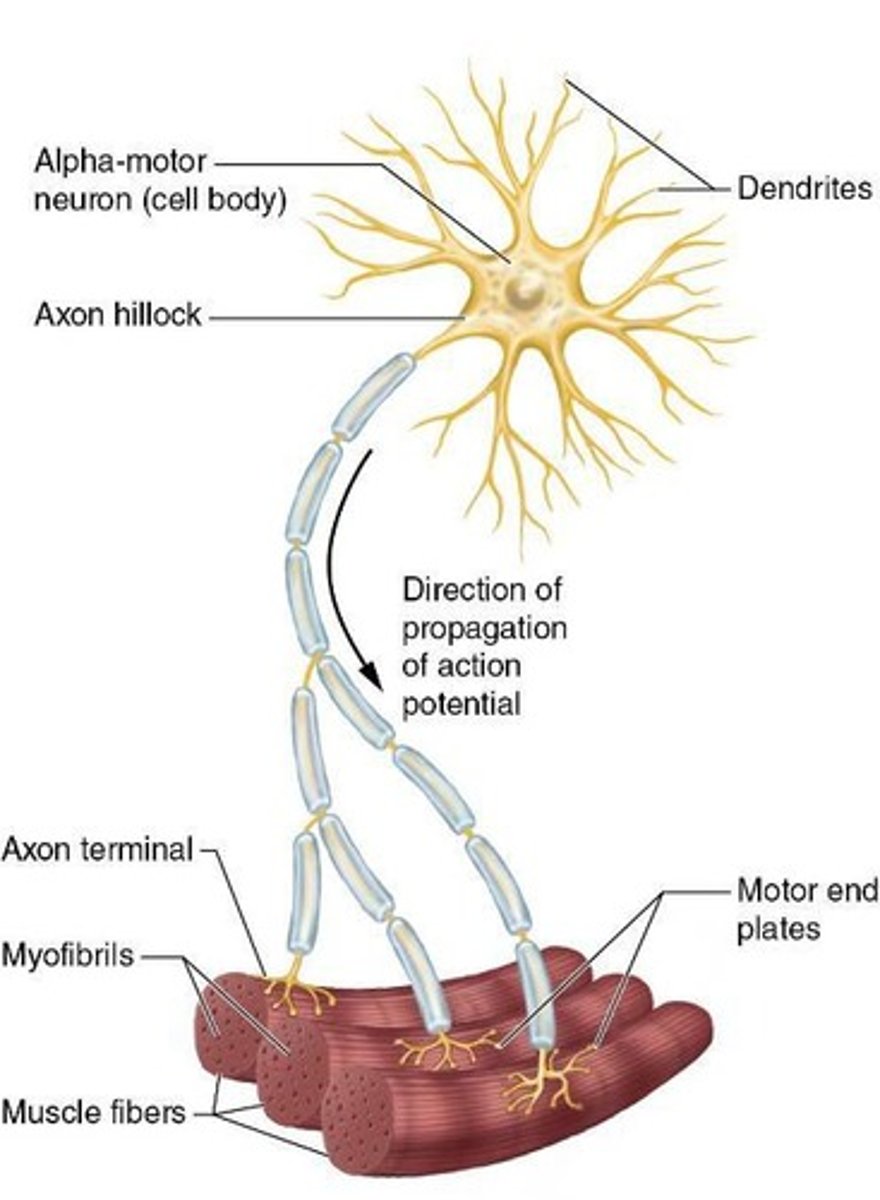
What is a motor unit?
A single alpha motor neuron and the myofibrils it innervates.
What is the sequence of events leading to muscle shortening called?
Excitation-contraction coupling.
What is the role of ATP in muscle contraction?
ATP is necessary for muscle contraction and relaxation.
What type of ATPase is found on the myosin head?
Myosin ATPase.
What does SERCA stand for?
Sarcoplasmic and endoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase.
What type of ATPase is the sodium-potassium pump?
Sodium-potassium pump ATPase.
What is malignant hyperthermia?
A life-threatening genetic predisposition where exposure to certain anesthetics causes unchecked ryanodine receptor activation.
How does malignant hyperthermia affect muscle contraction?
It causes uncontrolled calcium release, preventing muscles from relaxing properly.
What is the effect of botulinum toxin on muscle contraction?
It prevents the release of ACh from the presynaptic axon terminal, blocking the contraction process.
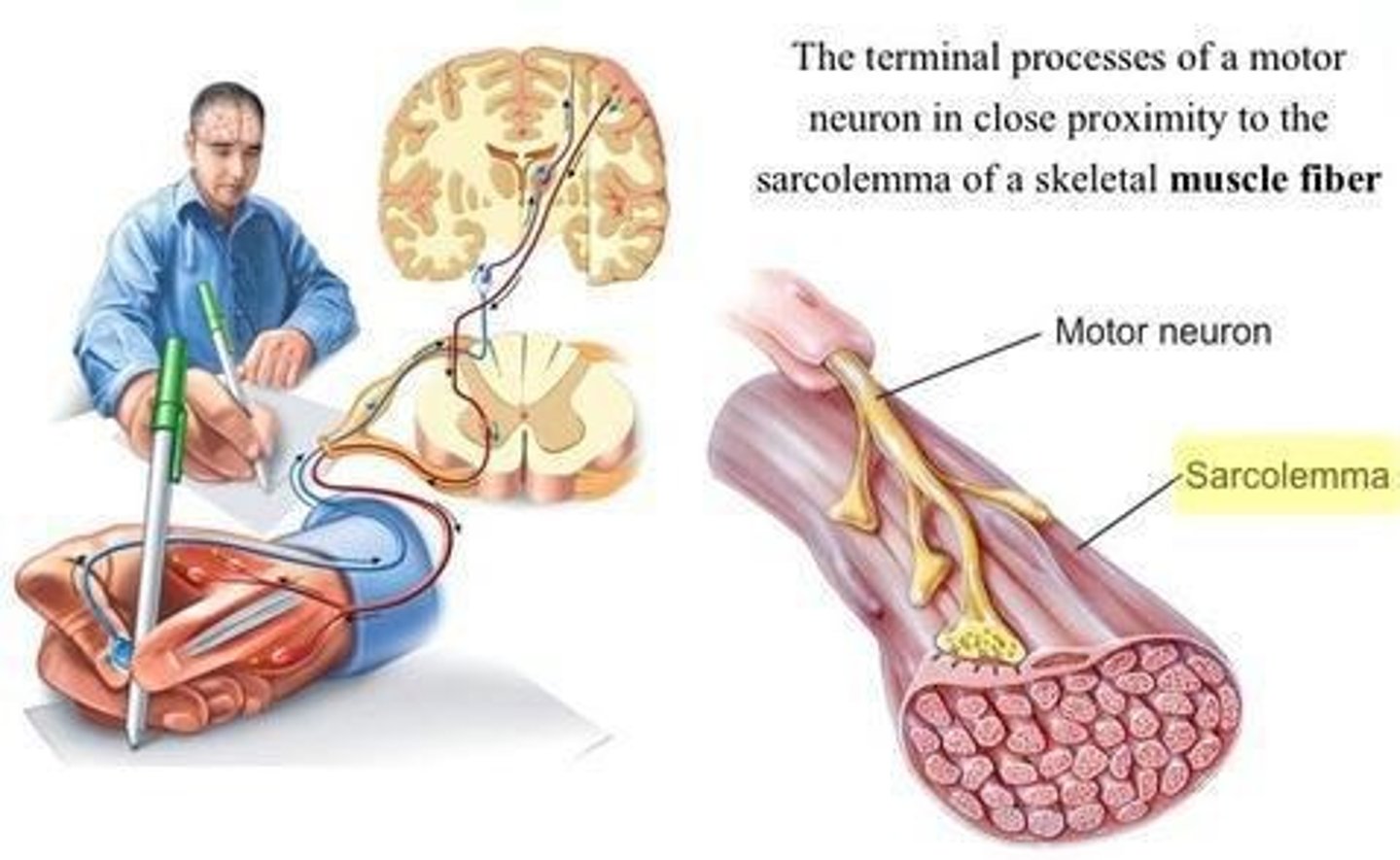
What is myasthenia gravis?
An autoimmune disease affecting the neuromuscular junction, where antibodies block nicotinic ACh receptors.
How does myasthenia gravis affect muscle contraction?
It weakens the synaptic signal, making it insufficient to trigger a muscle action potential.
What does the length-tension relationship describe?
The relationship between muscle length and the tension it can produce.
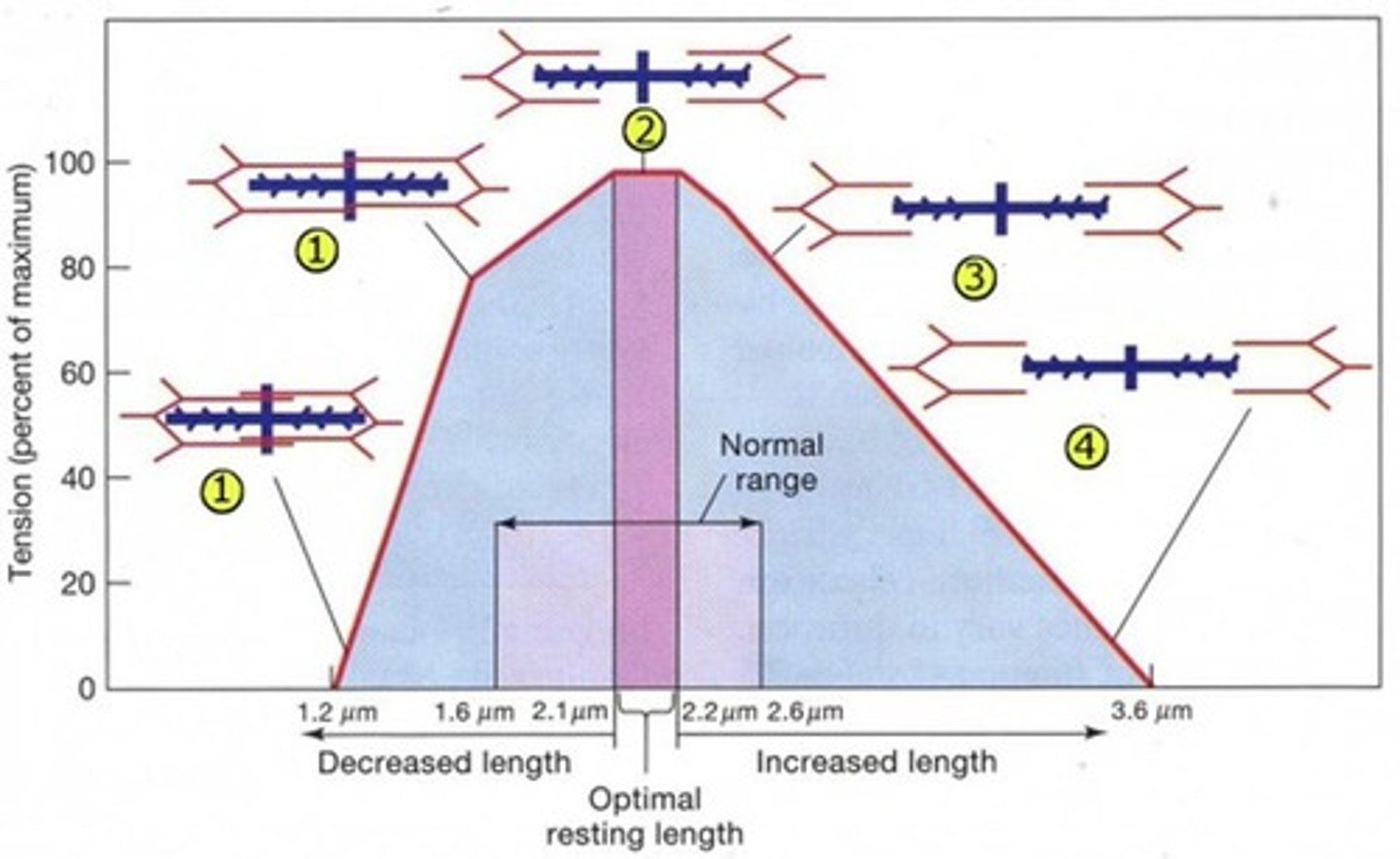
What does titin do in muscle contraction?
It prevents overstretching and damage to the sarcomere by resisting active stretching.
What is the winding myofilament theory?
It describes how titin contributes to muscle stiffness and force production.
What is the force-velocity curve for muscle contractions?
Eccentric > Isometric > Concentric.
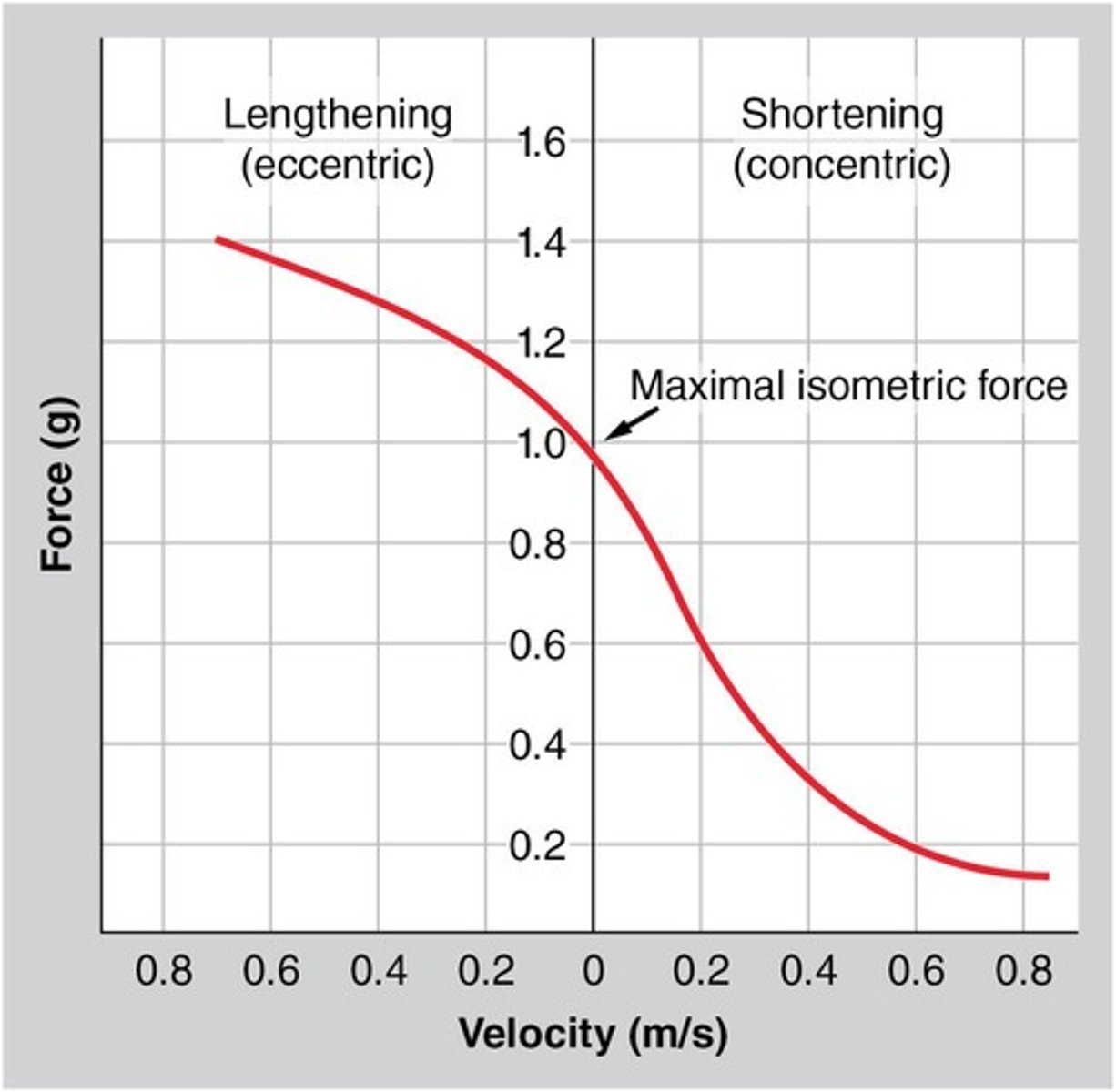
What type of contractions produce more force?
Eccentric contractions produce more force than concentric contractions.
What type of contractions produce less force?
Concentric contractions produce less force than eccentric contractions.
Why is controlling intracellular calcium levels important for skeletal muscle function?
Calcium levels regulate muscle contraction and relaxation.
What happens if SERCA does not efficiently pump calcium?
Calcium levels remain elevated, leading to prolonged muscle contraction and fatigue.
What triggers the termination of excitation-contraction coupling?
The removal of calcium from the cytoplasm.
What are the two main types of muscle fibers?
Type I (slow twitch) and Type II (fast twitch).
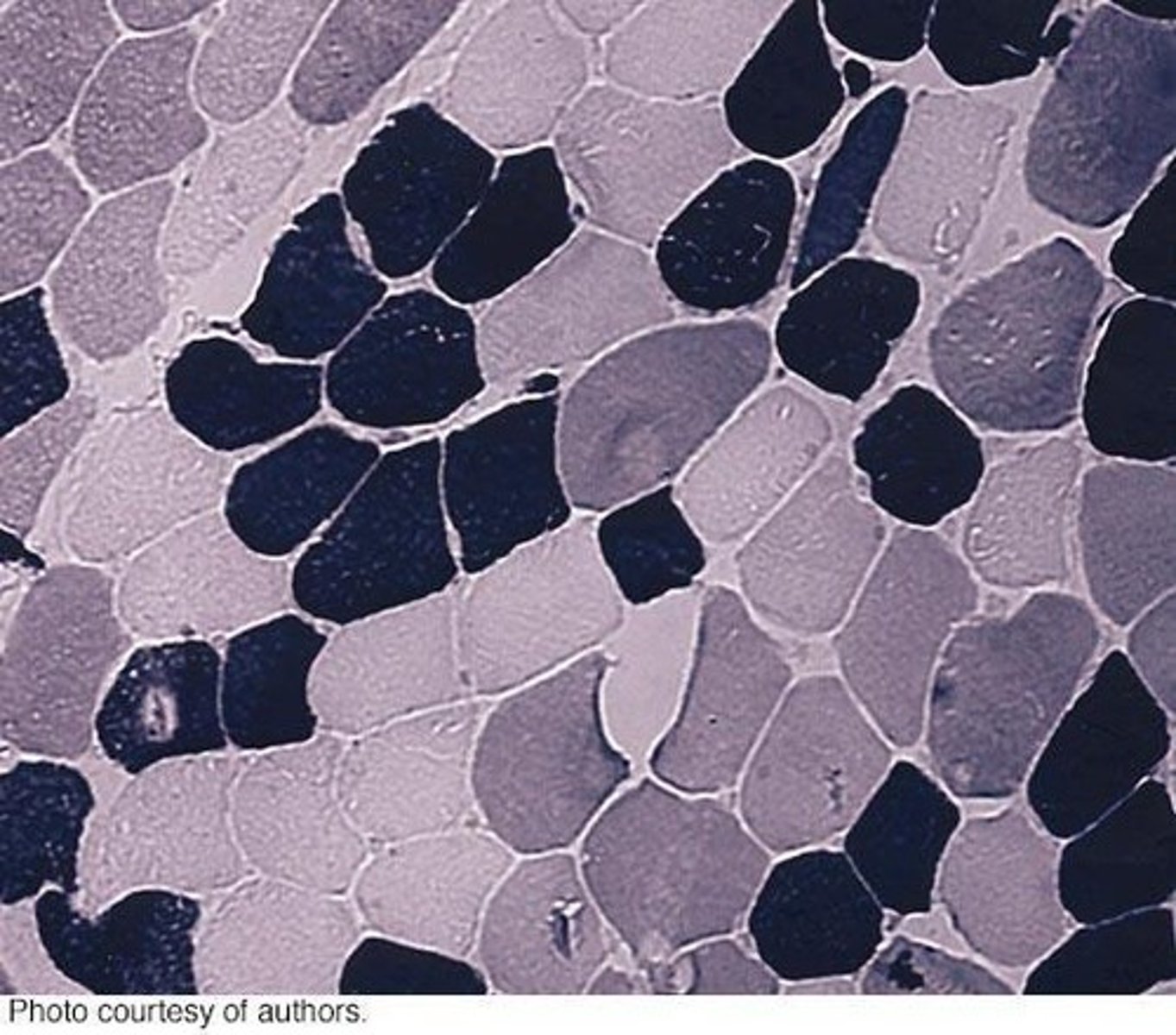
What is the peak tension time for Type I muscle fibers?
Peak tension in 110 ms (slow twitch).
What is the peak tension time for Type II muscle fibers?
Peak tension in 50 ms (fast twitch).
What percentage of fibers in an average muscle are Type IIc fibers?
Approximately 1%-3%.
How do muscle fiber type ratios aid in athletic performance?
They can help predict sport selection and performance.
Which muscle is known to be Type I in everyone?
The soleus.
What are the three classification systems for muscle fiber types?
System 1: Type I, Type IIa, Type IIx; System 2: Slow twitch (ST), Fast twitch a (FTa), Fast twitch x (FTx); System 3: Slow oxidative (SO), Fast oxidative/glycolytic (FOG), Fast glycolytic (FG).
What are the oxidative and glycolytic capacities of Type I fibers?
Type I fibers have high oxidative capacity and low glycolytic capacity.
What is the contractile speed and fatigue resistance of Type IIx fibers?
Type IIx fibers have fast contractile speed and low fatigue resistance.
What is the motor unit strength and size for Type IIa fibers?
Type IIa fibers have high motor unit strength and large motor unit size (greater than 300 fibers).
What is the conduction velocity of Type I muscle fibers?
Slower than Type II fibers.
What is the contraction speed in milliseconds for Type IIa fibers?
50 ms.
What is the primary enzyme concentration in Type IIx fibers?
Anaerobic.
Which fiber type has the highest peak power?
Type IIx.
What factors influence the fatigability of muscle fibers?
Mitochondria, capillarization, oxidative enzymes, and contraction speeds.
What are the determinants of muscle fiber type distribution?
Genetic factors and training factors.
What happens to Type II motor units with aging?
There is a loss of Type II motor units.
How is muscle fiber type distribution determined?
Through biopsy, staining, and examination under a microscope.
What principle describes the orderly recruitment of motor units?
Henneman's size principle.
What is rhabdomyolysis and what are its common causes?
Rhabdomyolysis is extreme muscle damage leading to myoglobin and creatine kinase leaking into circulation, commonly caused by eccentric exercise, heat, dehydration, medications, and genetics.
How can rhabdomyolysis be prevented?
By knowing athletes' fitness levels and prescribing appropriate exercise volume-load.
What is the myonuclear domain theory related to muscle fiber changes?
During atrophy, myonuclei are not lost, only muscle fibers.
What is the difference between hypertrophy and hyperplasia in muscle fibers?
Hypertrophy refers to an increase in muscle fiber size, while hyperplasia refers to an increase in the number of muscle fibers.
What are some symptoms of rhabdomyolysis?
Symptoms include muscle pain, weakness, swelling, and dark urine.
What changes occur in muscle fiber types with training and detraining?
Type IIx can convert to Type IIa with training, and Type IIa can convert to Type IIx with detraining.
How can fiber typing predict sport performance?
By assessing the ratio of muscle fiber types to match the demands of specific sports.
What fiber type characteristics allow for greater oxidative capacity in Type I fibers?
High capillarization and oxidative enzyme concentration.
What fiber type characteristics allow for greater power and strength production in Type II fibers?
High glycolytic capacity and fast contractile speed.