developmental psychology ch7
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are emotions?
Emotions: feeling states, often caused by an event, includes multiple components:
External emotion: Expression
Internal emotion: Subjective evaluation and Physiological arousal.
What is emotional regulation?
All processes by which we influence which emotions we have, and how we experience them.
Plays a central role in well-being.
Becomes more complex over the lifespan.
Process Model of Emotion Regulation:
Situation selection: Avoidance.
Situation modification: Problem solving, situation modification.
Attentional deployment: Distraction, rumination.
Cognitive change: Acceptance, Reappraisal.
Response Modulation: Suppresion.
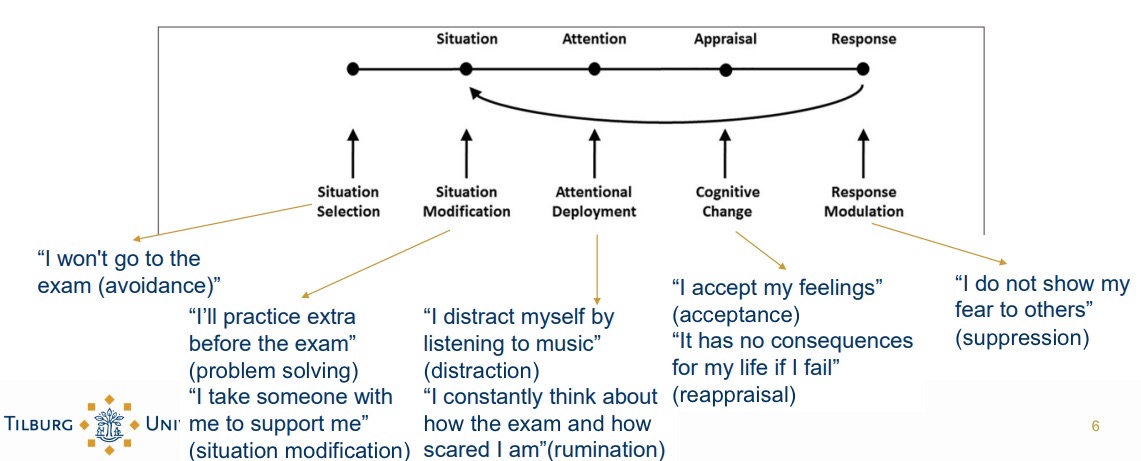
Maladaptive vs adaptive strategies
Rumination vs Problem solving
Suppression - Reassessment
Avoidance - Acceptance
More psychopathology - Less psychopathology
But: sometimes actually useful to suppress feelings → strategies are not inherently good/bad → depends on context
Current research focuses on emotion regulation flexibility.
Development of emotions in infants:
Emotions are observable in the first days of life. Become more complex with age - depends on cognitive development.
Babies are observed in certain situations - emotion research in infants.
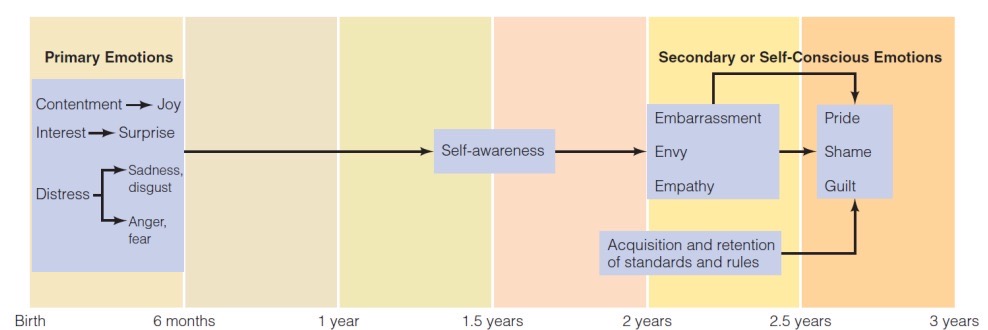
What emotions are shown in infants?
Biological basis, but also environmental influence: Children mirror emotional expressions of caregiver.
Mothers respond selectively to their babies’ expressions → learning: infants show more happy faces and emotion socialisation
Development of emotions in infants by months
Around 9 months: social referencing
Emotional communication: infants and young kids understand emotions and express them - parents play a crucial role (Still face - Tronick)
0–12 months:
Use simple strategies (e.g., turning away, sucking on a pacifier)
Seek support from caregivers
18–24 months:
Try to control upsetting situations (e.g., pushing others)
Use distraction to cope with frustration
Early signs of suppression (e.g., knitting brows, compressing lips)
End of 2nd year (symbolic thought & language):
Begin cognitive regulation (e.g., repeating comforting words)
Shift from behavioural to cognitive strategies
Age 3–4 (prefrontal cortex development):
Improved emotion regulation
Better control over negative emotions
What emotion regulation strategies are seen in infants aged 0–12 months?
Use of simple strategies (e.g., turning away or sucking on a pacifier)
Seeking support from caregivers
What emotion regulation strategies are common at 18–24 months?
Attempt to control upsetting stimuli (e.g., pushing others)
Cope with frustration through distraction
Show early signs of suppression (e.g., knitting brows or compressing lips)
What emotion regulation developments occur by the end of the 2nd year?
Emergence of cognitive regulation of distress (e.g., repeating comforting words)
Shift from mainly behavioral (motor) to also include cognitive strategies
Enabled by symbolic thought and language
What changes in emotion regulation happen by ages 3 to 4?
Improvements in emotion regulation
Better regulation of negative emotions
Supported by development of the prefrontal cortex
Emotion expression in infants:
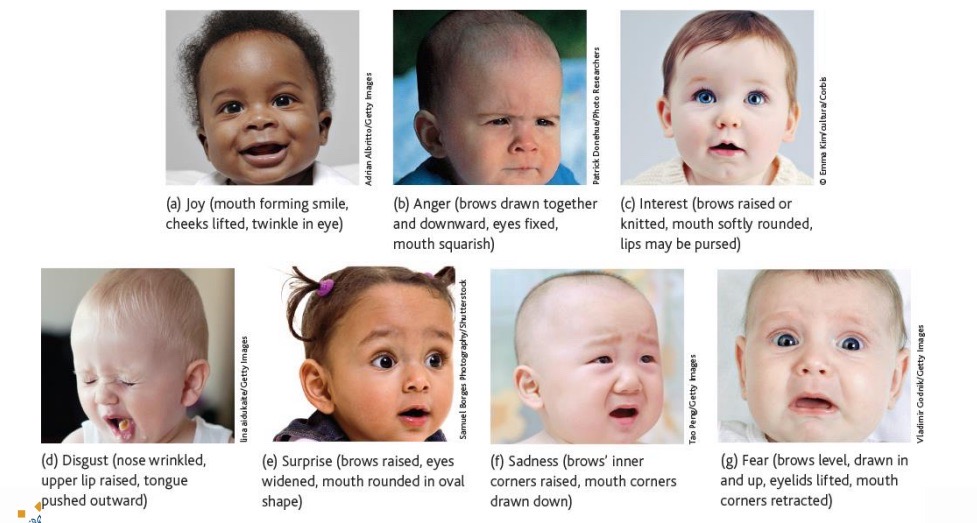
How do emotions develop in children?
Further improvement of emotional competence - concept of mixed emotions, mental time travel, improved ability to suppress or hide negative emotional reactions.
More complex use of emotion regulation strategies - focusing feelings elsewhere, more effective emotion regulation through cognition, empathy development.
Emotional competence important predictor of social competence.
Emotional display rules, gap between internal and external emotions widens - Understanding on emotions, display and skills for self control.
Cultural differences in emotional display rules:
Individualistic cultures:
Preference for self-directed emotions, encouragement for expression.
Collectivistic cultures:
Preference for emotions directed at others (ex. empathy)
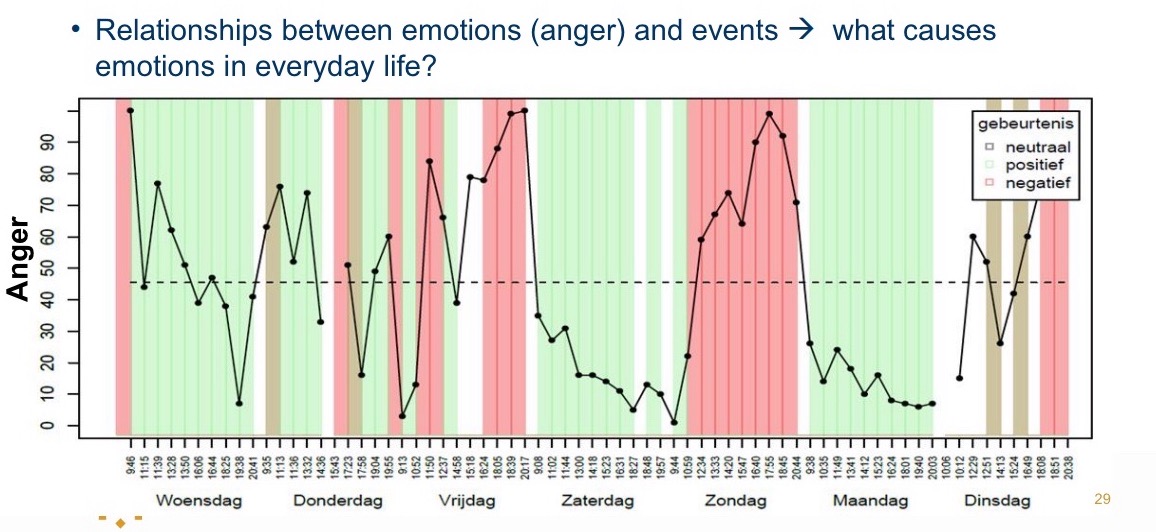
Research method: Emotion development in adolescents
Measuring state-level of emotions, cognitions, behaviours in daily life through an app:
Experience Sampling Method (ESM):
Multiple times a day
Diary Study (diary diary):
Only one questionnaire at the end of the day.
Advantages: low recall bias, high ecological validity, study of short-term dynamics
Disadvantages: high burden on subjects, measurement reactivity
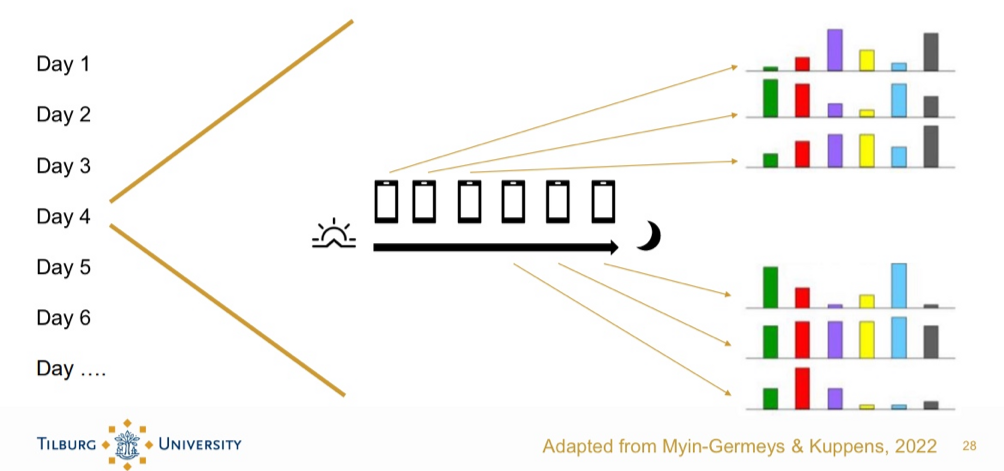
Example ESM
Stereotype of a moody teenager:
More negative emotions, less positive ones
More extreme emotions and fluctuations
Adolescence - Emotion intensity: longitudinal study
Daily diaries 3 weeks per year for positive/negative emotions:
less positive emotions, stronger decline for girls
more negative emotions, but girls score higher on average
Emotion regulation goals: Adolescents
Adolescents have different emotion regulation goals than adults:
Goals:
Broaden horizons
Acquire knowledge
Meet new people
Taking risks
Behavioural set of exploration: Accumulation of information in preparation for future necessity
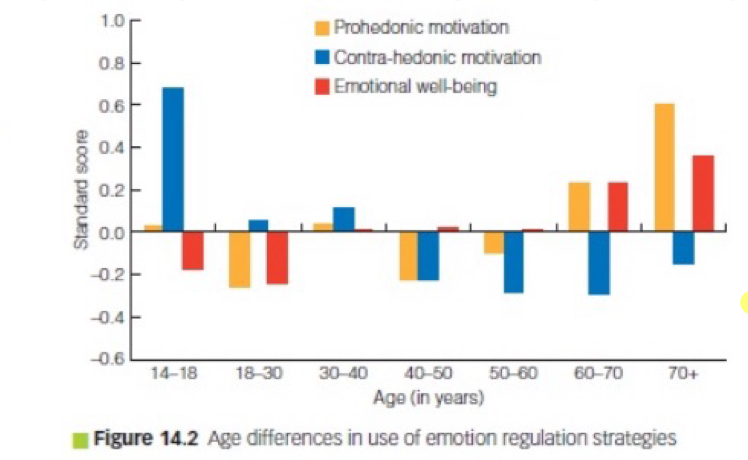
Age differences in use of emotional regulation strategies:
14-18: Mainly contra-hedonic - to feel sad or bad, prohedonic positive, emotional well-being negative
18-30: Mainly prohedonic - to feel good, rest negative
30-40: Mainly contrahedonic, but rest not negative
40-50 and 50-60: Mainly emotional well-being, rest negative
60-70: Prohedonic and Emotional well-being, contrahedonic negative
70: The most - prohedonic, then emotional well-being, contrahedonic negative
Adolescence: Emotional stability
More extreme mood swings than children and adults.
Many changes in adolescence + ineffective emotion regulation (executive functions not yet fully developed) → combination leads to more negative/extreme emotions
Variability becomes less over adolescence → improvement
How do emotions develop in adults?
Developmental changed continue through adult years.
Effort to create lifestyles that are emotionally satisfying, predictable and manageable by making many decisions.
Midlife at the intersection of growth and decline:
Decline path:
Functional health, speed of processing, working memory
Growth Path:
Knowledge, experience, emotion regulation
Midlife - well-being:
Temporary dip in well-being.
Life transitions may bring stress and uncertainty.
Social comparisons may put pressure on individuals (SOC)
Challenges in older age:
Decline in health and memory
Lost opportunities
Confrontation with mortality
Loss of loved ones
Loss of independence
Loss of purpose, loneliness
Finances
Emotions in older age:
On average positive emotions remain more stable and negative emotions become less frequent → better emotional balance.
Older adults can detect and feel negative emotions, but they control the amount of time spent on negative emotions.
Few changes in happiness, large decreases in stress.
Positivity bias (or negative avoidance):
A form of selective attention, relatively more attention and better memory for positive information.
Brain regions involved in emotions degenerate less with age than cognition ones.
+ Socio-emotional selectivity theory - Cartensen
Emotional choices in older age:
Time horizons become shorter - goals change - focus on goals that are realised during the very pursuit of the goal itself: meaning, satisfaction.
Goals: live in the moment, savour life, see clearly what matters, invest in sure things, deepen relationships.
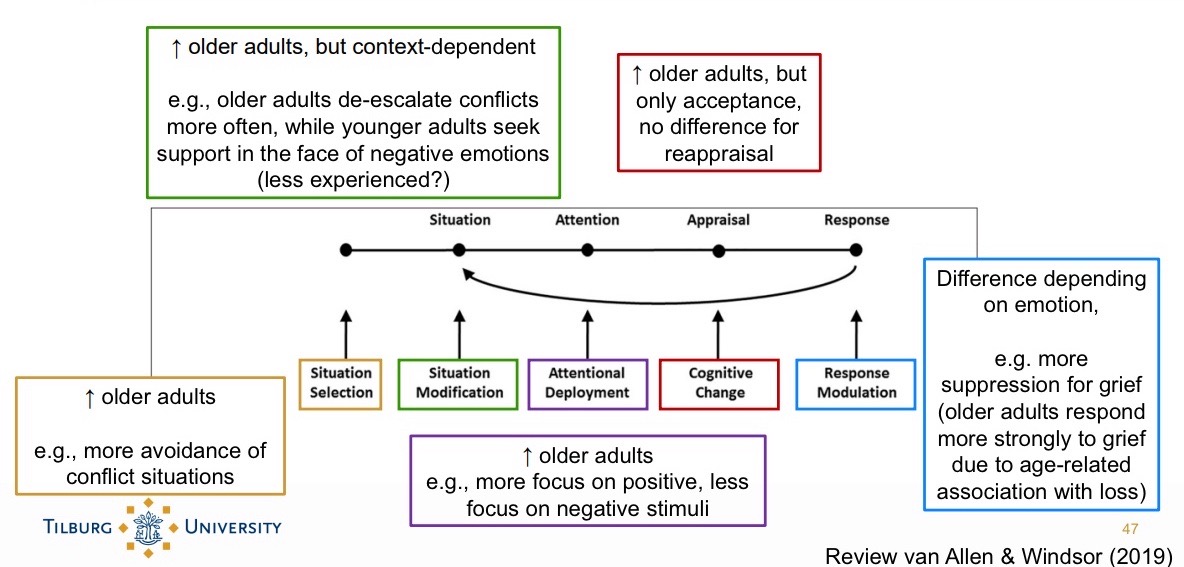
Emotion regulation in older age:
Older adults show less variability in their emotion regulation strategies.
Explanations:
Less variability in context → less need to adjust strategies
Stable patterns of regulation→ they developed it already.
Selective narrowing of social networks:
Size of inner circle remains the same.
Fewer relationships with people of outer circle → if they no longer lead to positive emotions u drop them.
Emotional well-being goes up as networks are narrowed.
Empirical examination of SST:
Questions: If u had limited time vs unlimited time who would u meet? A very good friend, an interesting person you met lately or a famous book author you love.
No time limit:
Young adults - pick all three options the same.
Old adults - a good friend
With time limit:
Both groups choose good friend. Perhaps future time perspective changed.
Limitations for experience of well-being:
The years close to death, well-being declines.