biochemisty, biomolecules, carbohydrates, and lipids
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
what is an anabolic reaction?
when smaller molecules are joined together to make larger molecules; this requires energy
what is a catabolic recation?
larger molecules break apart into smaller molecules; this releases energy
what is dehydration synthesis?
the creation of larger molecules from smaller monomers where a water molecule is released (pushes out water to create larger molecules)
how do you make a disaccharide
it has to go through dehydration synthesis
what is a functional group
a specific group of atoms and bonds in a compound that give the compound specific characteristics
what are the different types of functional groups?
hydroxyl, carbonyl (carbonyl, aldehyde, and ketone), carboxyl, sulfhydryl, amino, and phosphate
what is the functional group “hydroxyl”?
when one hydrogen atom is covalently bonded to an oxygen atom (can be multiple hydroxyl’s in one atom)
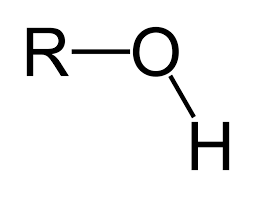
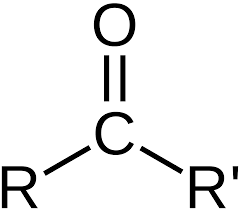
what is the functional group “carbonyl”?
a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom (three types: carbonyl, aldehyde, and ketone)
what is the subgroup ”carbonyl”?
carbonyl carbon (just the normal oxygen being double bonded to a carbon)
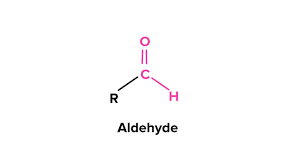
what is the subgroup “aldehyde”?
carbonyl C attached to a C (carbon) and an H (hydrogen)
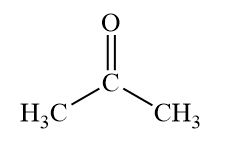
what is the subgroup “ketone”?
carbonyl C attached to two carbons
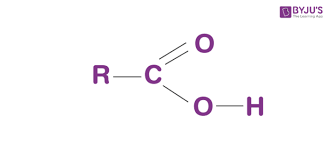
what is the functional group “carboxyl”?
a carbon atom combined with a hydroxyl and a carbonyl
what is the functional group “sulfhydryl”?
a sulfide atom bonded to a hydrogen atom
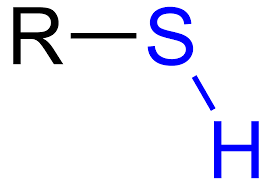
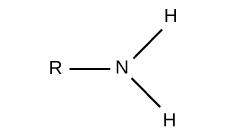
what is the functional group “amino”?
a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms
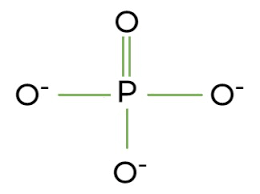
what is the functional group “phosphate”?
when a phosphorus atom is bonded to 4 oxygen atoms
what are biomolecules also referred to as?
macromolecules
what are the four types of macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins
each macromolecule has its own building block that is called what?
a monomer
what is made when multiple monomers are put together?
polymers
what are carbohydrates made up of?
made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
what is a type of monomer for carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
what does saccharide mean?
sugar
what is a type of polymers for carbohydrates?
polysaccharides
what does the ending -ose signify?
that the atom is most likely a carbon
what are carbohydrates used for?
all living things main source of energy (quick short term energy)
plants use them for structural purposes
what does monosaccharide mean?
1 sugar
what does disaccharide mean?
2 sugars
what does polysaccharide mean?
multiple sugars
what are some common polysaccharides?
starch, glycogen, and cellulose
starch?!
a polysaccharide
only found in plants
many glucose molecules are put together to make starch
glycogen?!
can be a polysaccharide
only found in animals
liver bonds together many, many molecules of glucose to form glycogen
cellulose?!
a polysaccharide
the stringy, fibrous material in the cell wall of plants
major component of wood and paper
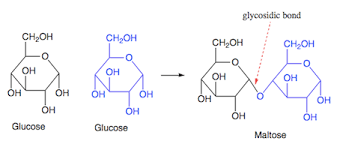
carbohydrates bond with what?
glyosidic linkages
what chemical ID tests are used for what (carbohydrates) ?
benedicts solution is used for monosaccharides, and lugols solution is used for polysaccharides
what are lipids made up of?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen without a specific ratio
monomers for lipids equal what?
fatty acids and glycerol
polymers for lipids equal what?
triglycerides or phospholipids
are lipids water soluble?
nope
lipids hold what?
lipids hold more energy per unit weight than any other macromolecule
what is a triglyceride?
when a lipid has 3 fatty acid tails, it forms a triglyceride
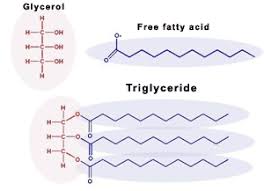
what is a phospholipid?
when a lipid has 2 fatty acids and a phosphate head, it is a phospholipid. This helps form our cell membrane.

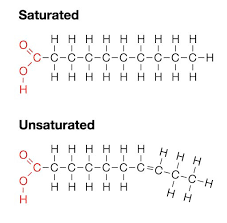
what is a saturated fatty acid?
a saturated fatty acid has all the carbon it can hold. There is no double bond and appears in a straight line. It tends to be solid at room temperature.
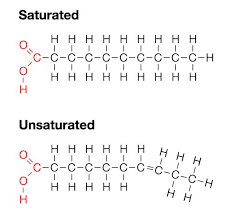
what is an unsaturated fatty acid?
an unsaturated fatty acid has a double bond and will show a kink in the tail. it tends to be liquid at room temperature.
what are the functions of lipids?
lipids make up the cell membrane
they take longer to break down/long term energy storage
form waterproof coverings on feathers, fruits, leaves, etc.
cushion and insolate internal organs
what do steroids do (lipids)?
regulate fluidity in the cell membrane. not too rigid or fluid
acts as hormones in the body
has a 4 fused ring structure
what are waxes (lipids)?
they are completely water insoluble
solid at room temperature
serves as water repellant on some leaves and feathers
serves as energy storage for some organisms (like phytoplankton)
what are phospholipids (lipids)?
make up the cell membrane
regulate homeostasis in the cell
contains polar head and non-polar tail
surrounds cells for protective layers
amphipathic/amphiphilic (goes with point 3)
what does amphipathic mean
having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts
what is another word for amphipathic?
amphiphilic
what special covalent bonds do lipids use
ester linkages
what chemical ID tests are used for lipids??
Translucence test, solubility test, and sudan II test
what are the common functional groups for lipids?
carbonyl, carboxyl, and phosphate
what does esterlinkage connect?
fatty acids and glycerol
foods that lipids are found in?
mayo, butter, nuts, and olive oil