Anatomy & Physiology I Lab (D2L Quiz- Skeletal System Introduction) Practical 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
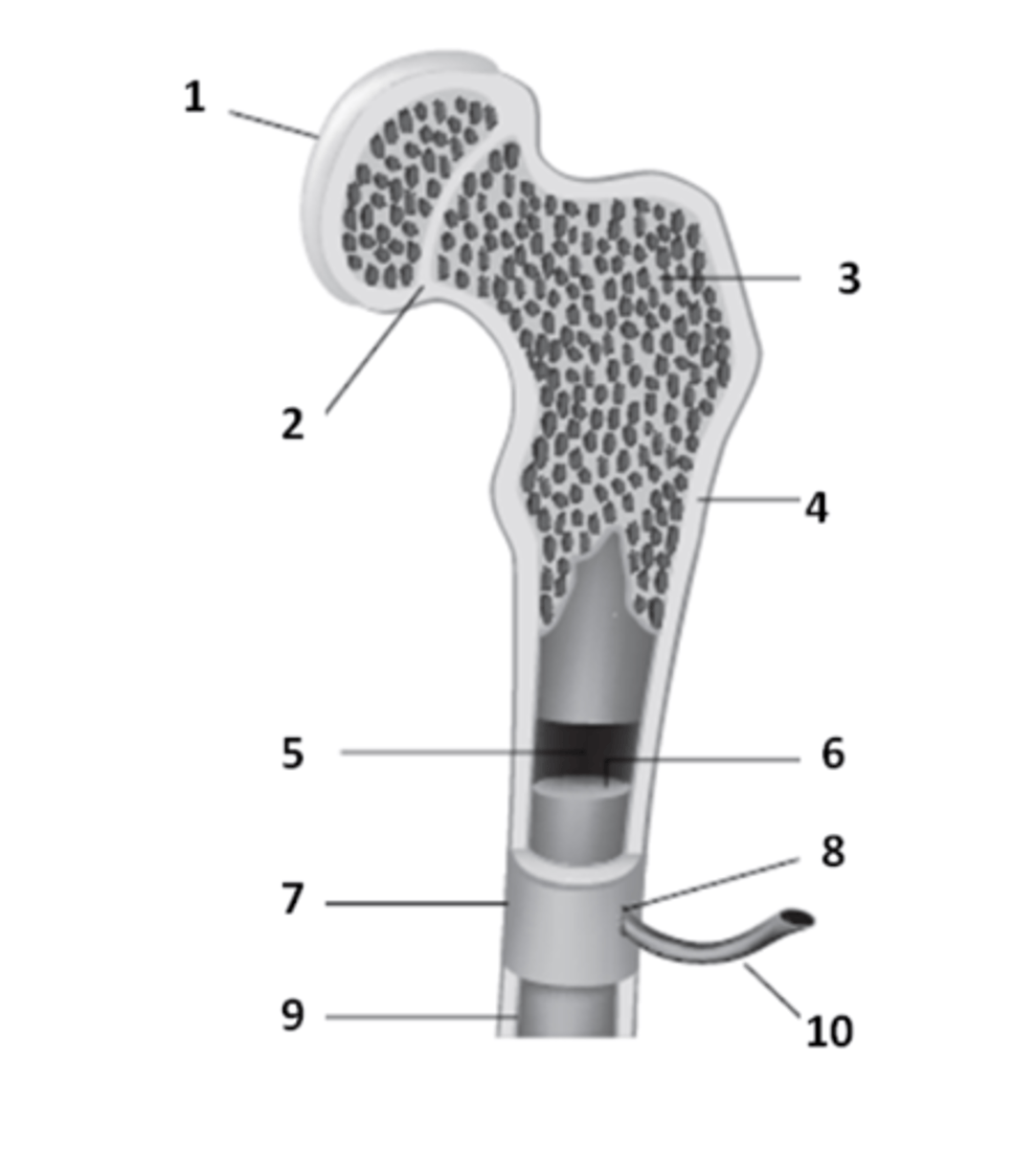
epiphyseal line
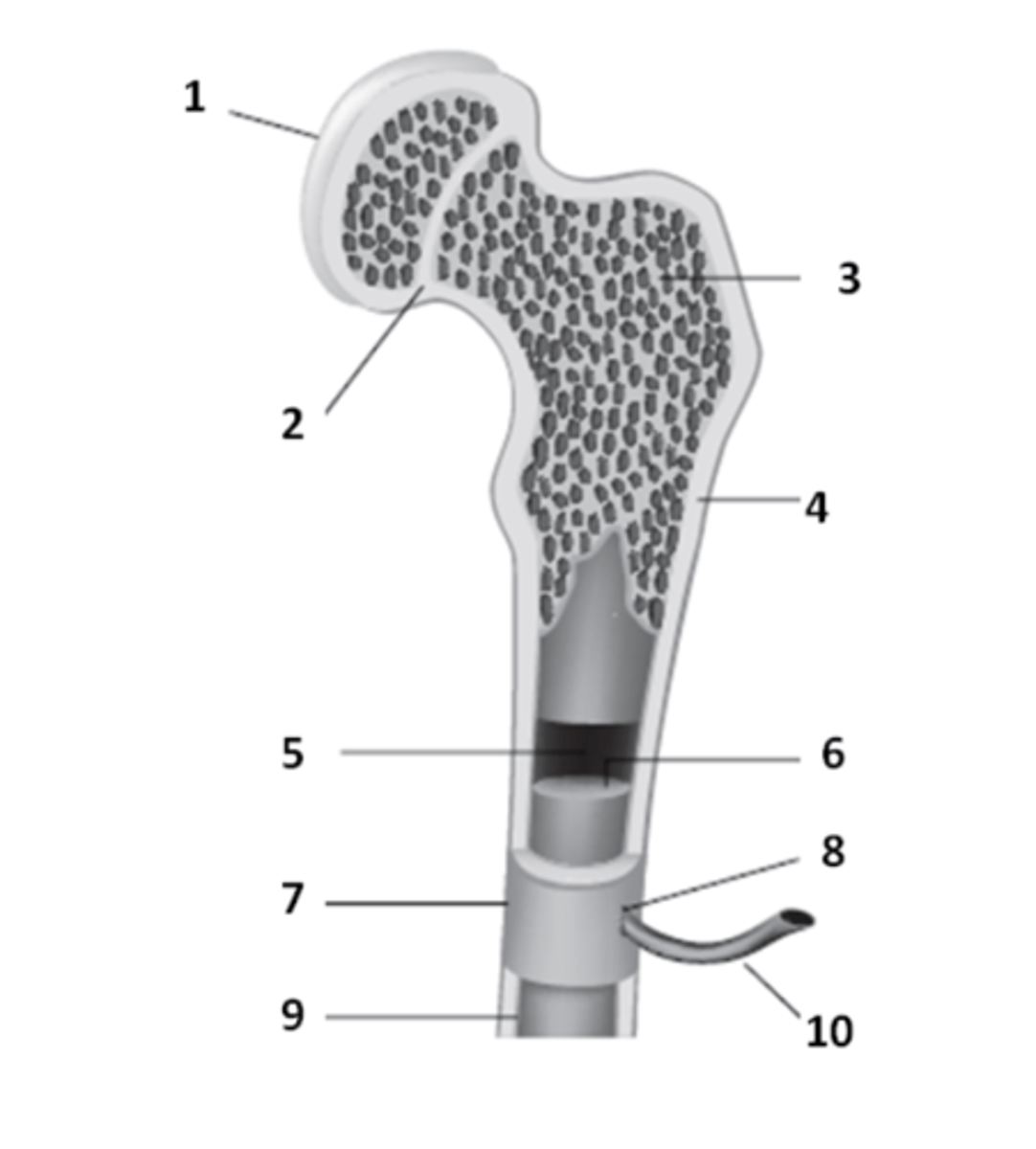
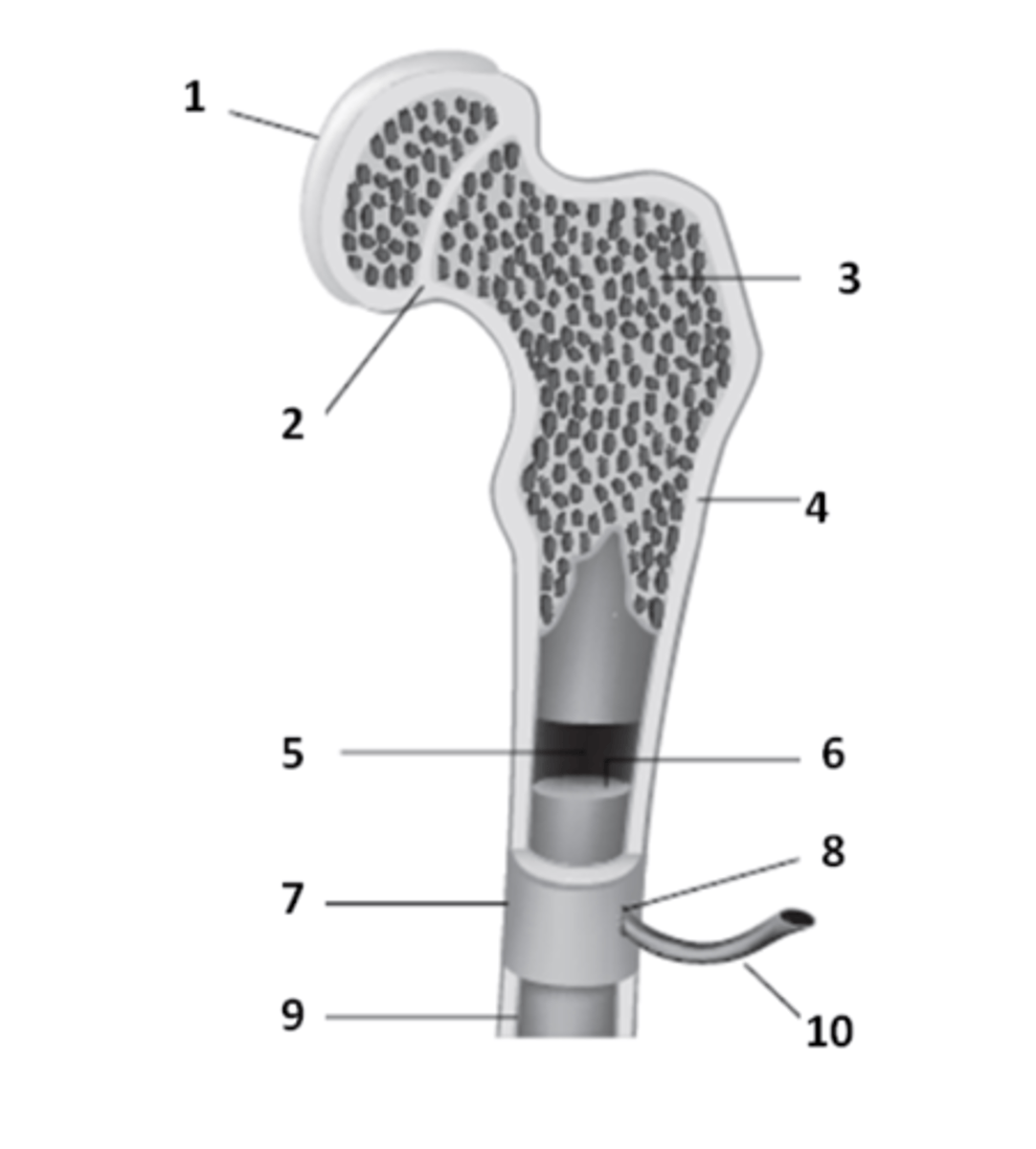
What is the structure that is a remnant of the epiphyseal plate? An area which contains hyaline cartilage that provides longitudinal growth of the bones during adolescence.
periosteum
What is the tough sheath covering the outer surface of the bones called? It is held to bone by perforating fibers.
epiphyseal line
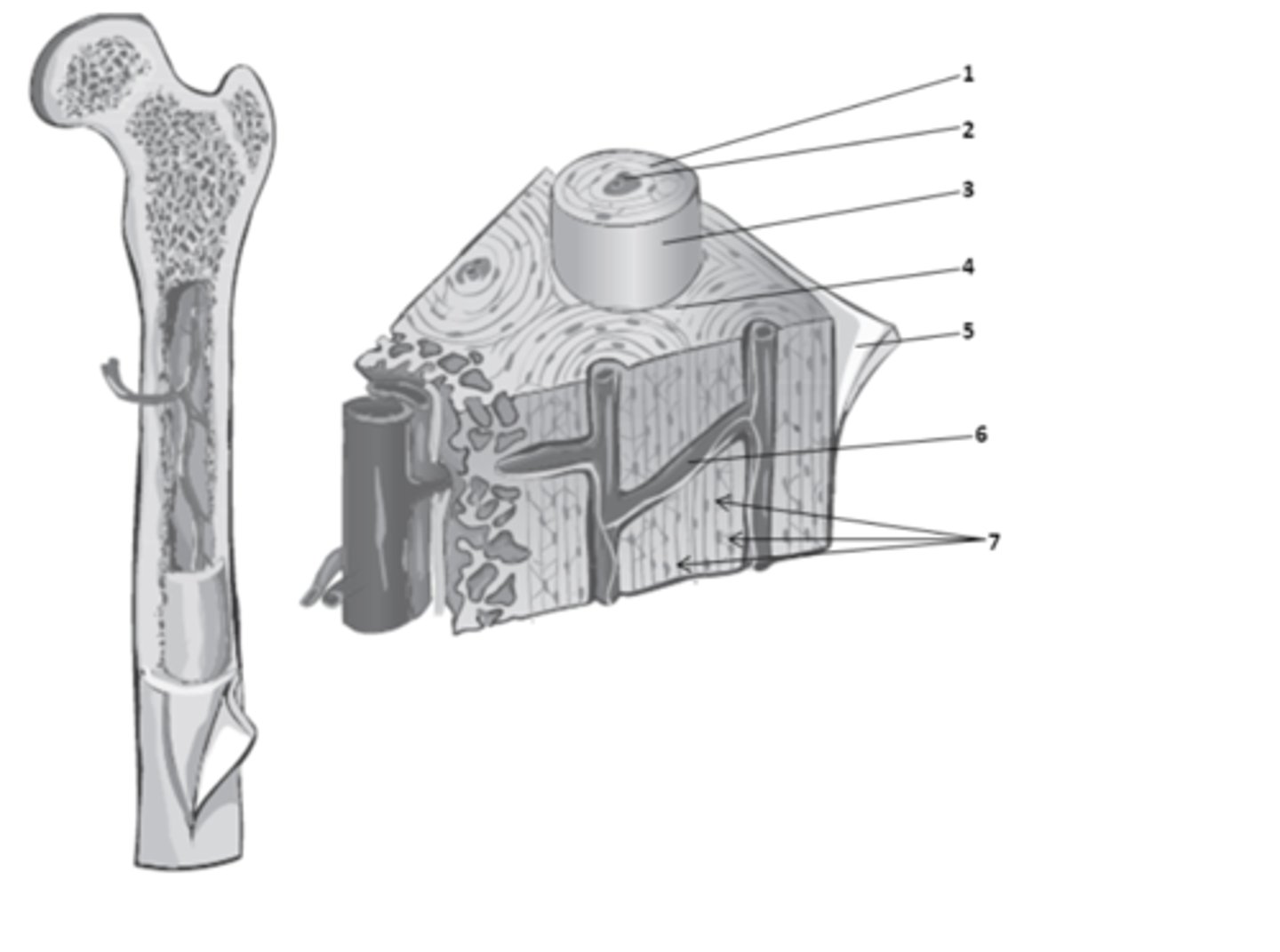
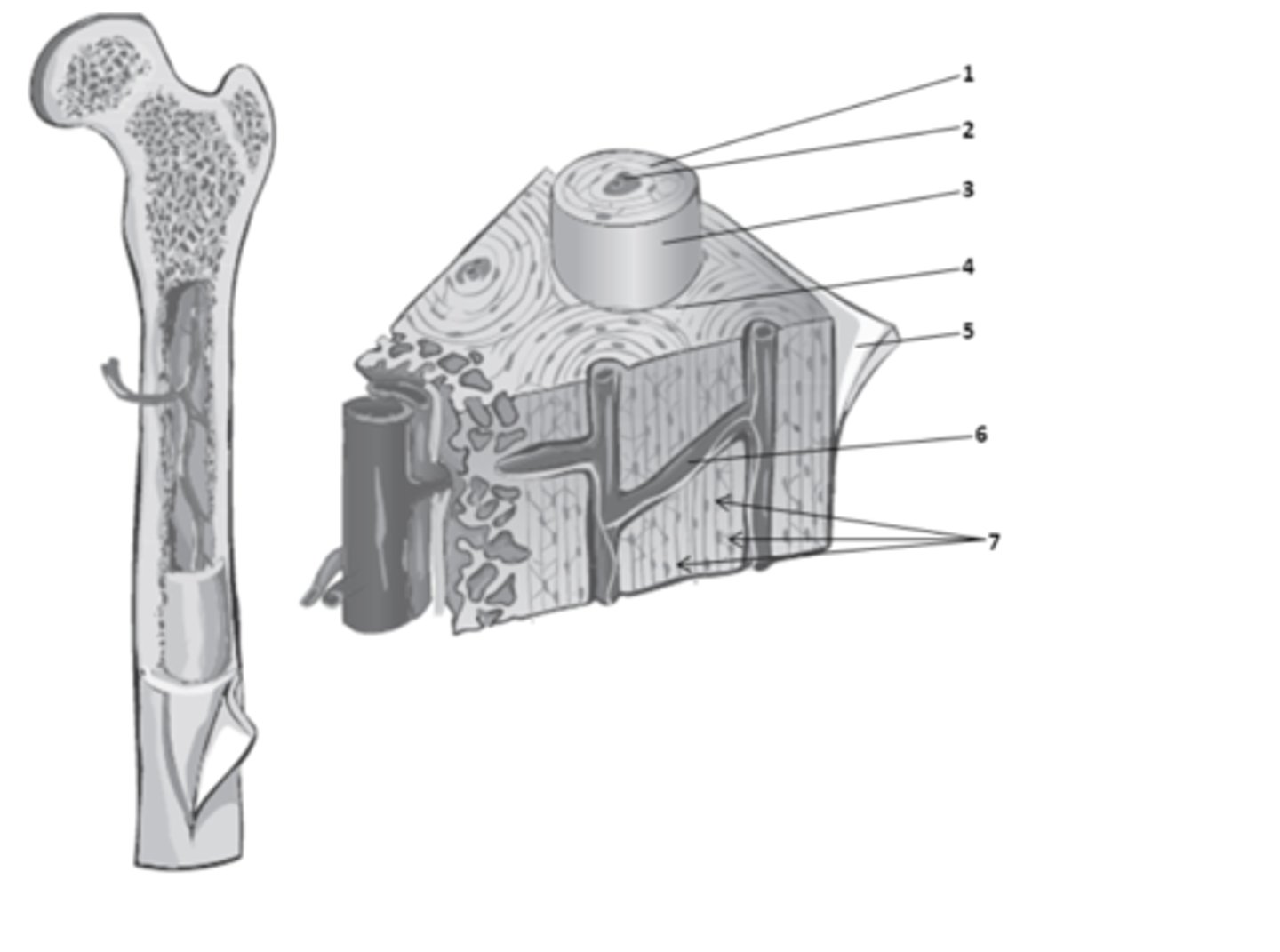
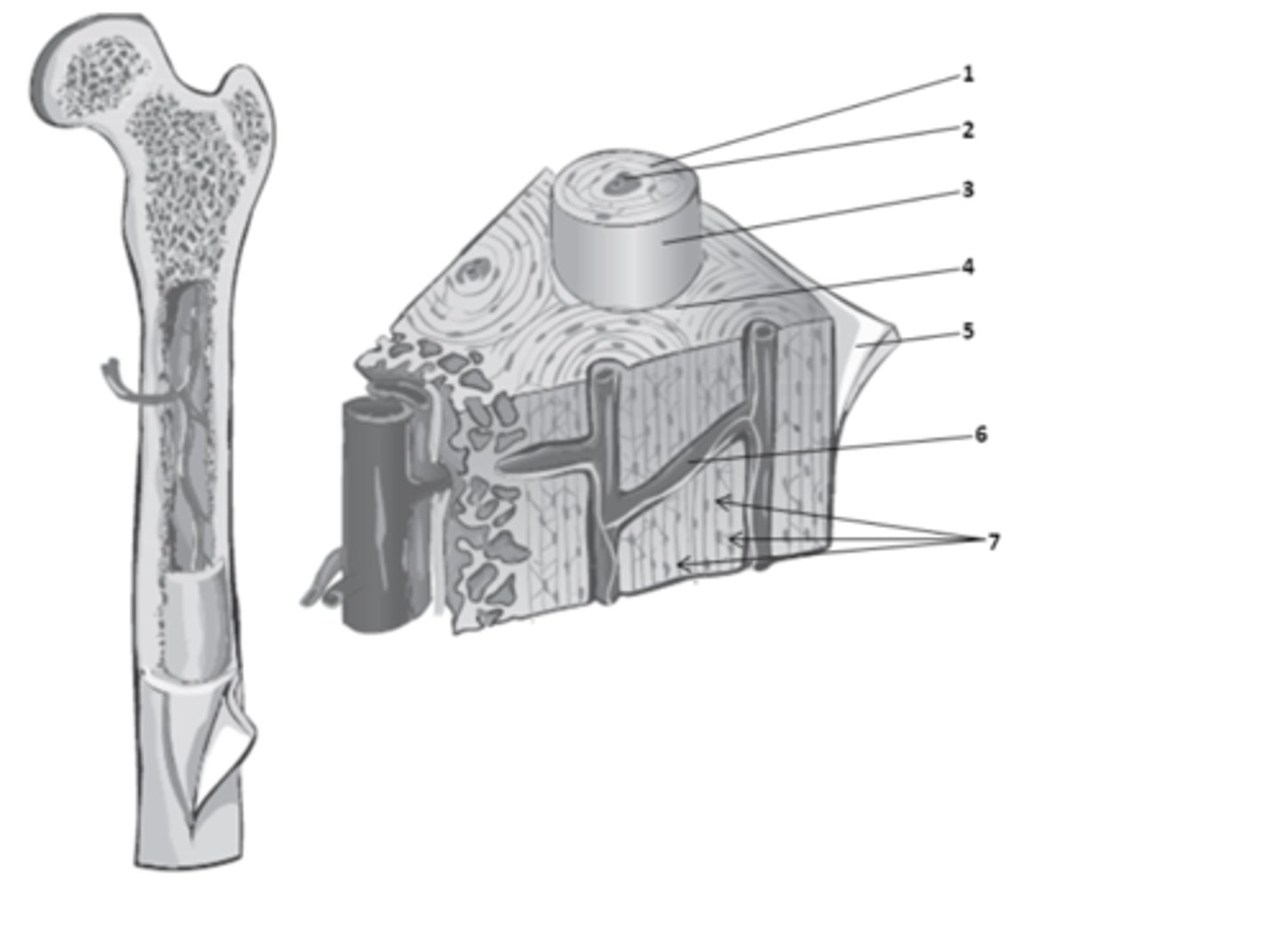
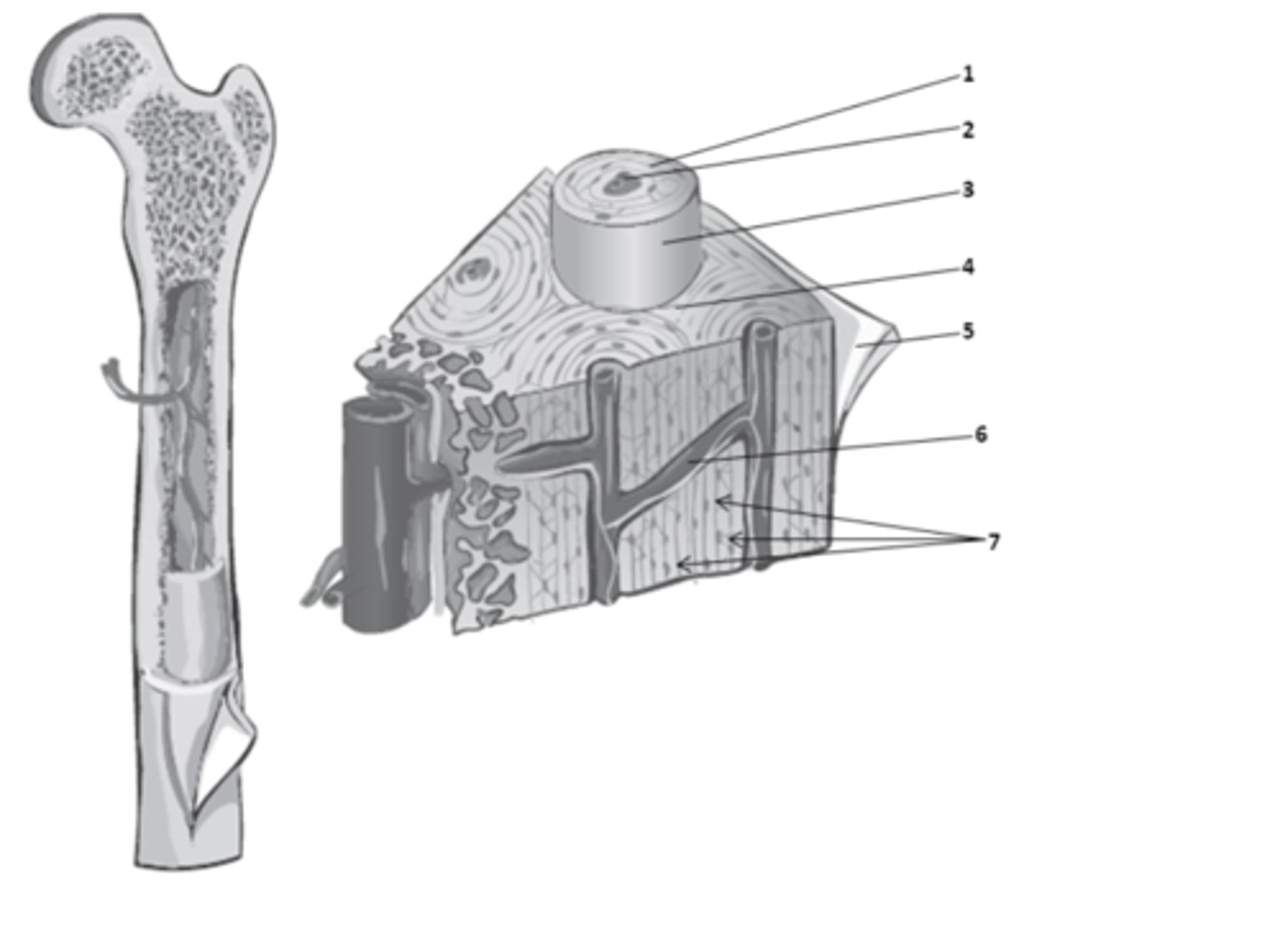
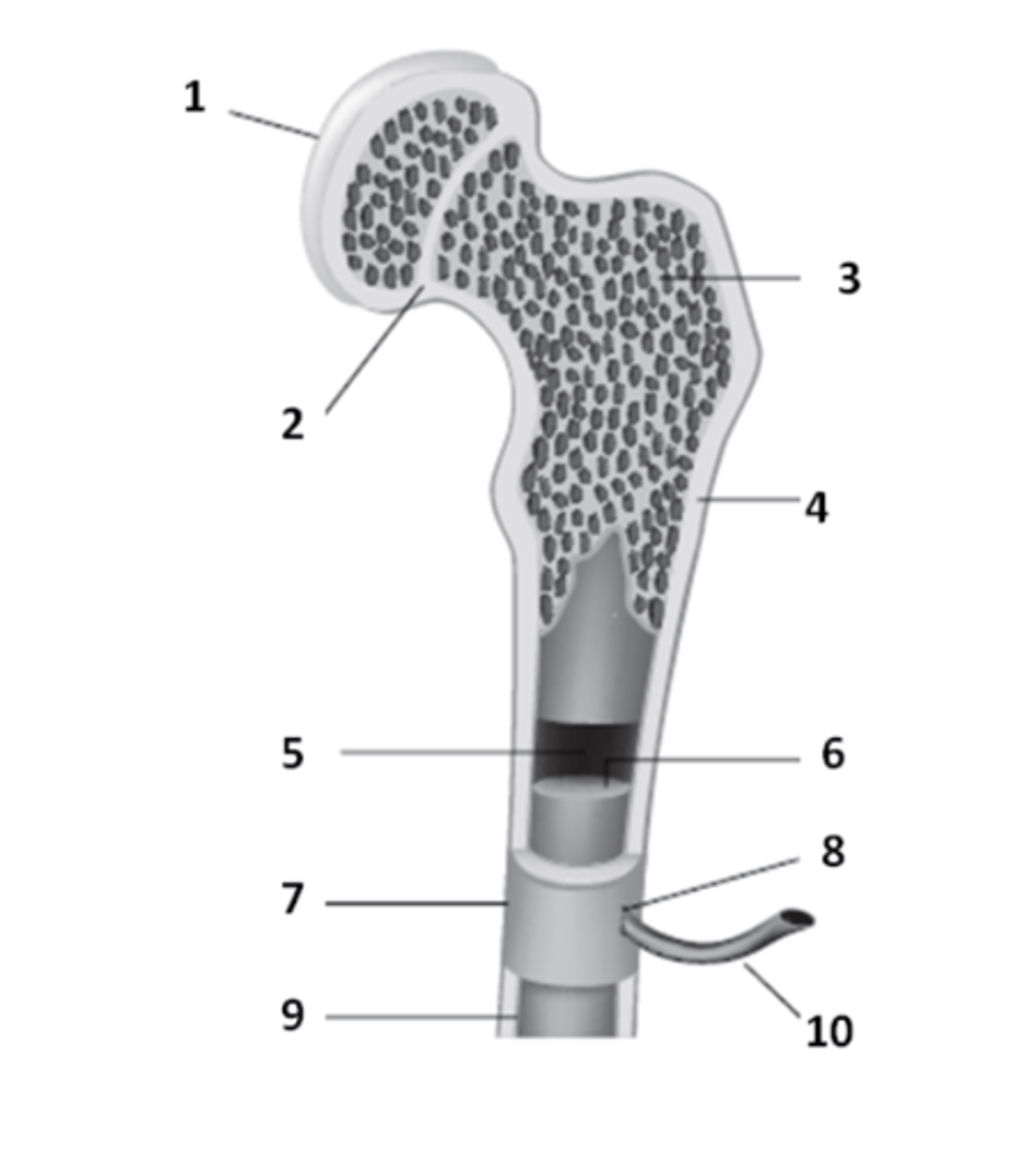
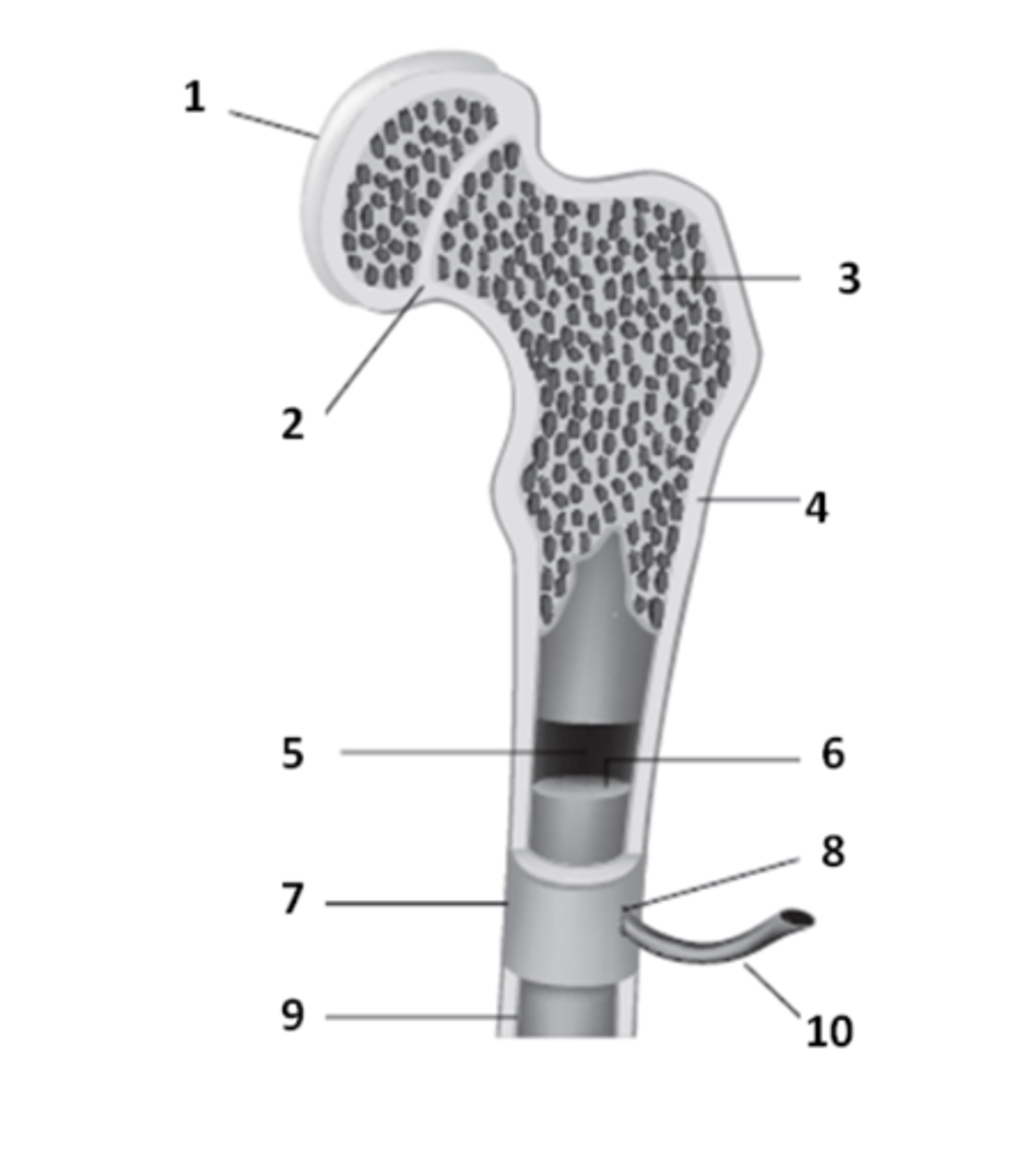
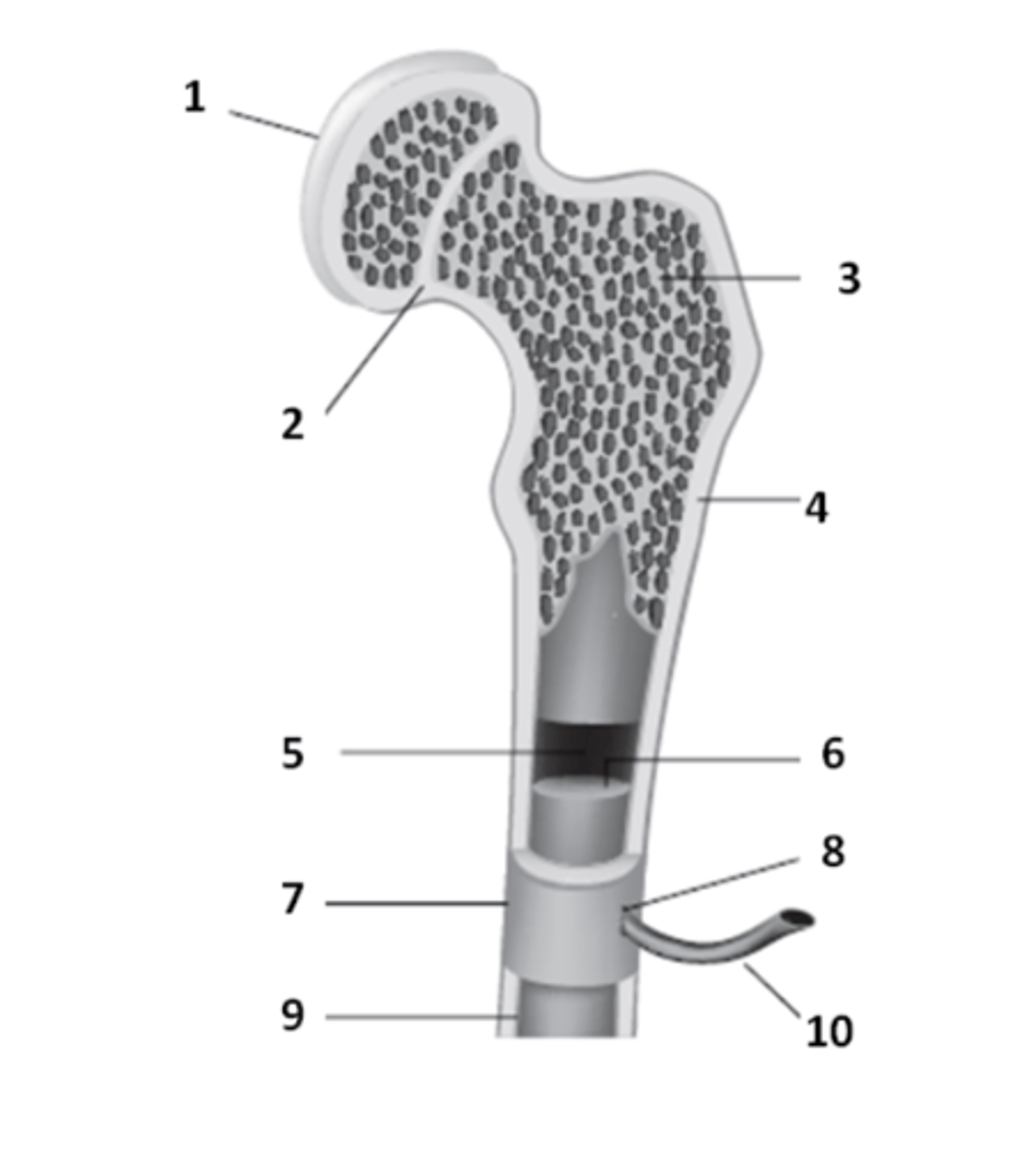
What structure of the bone anatomy is 2?
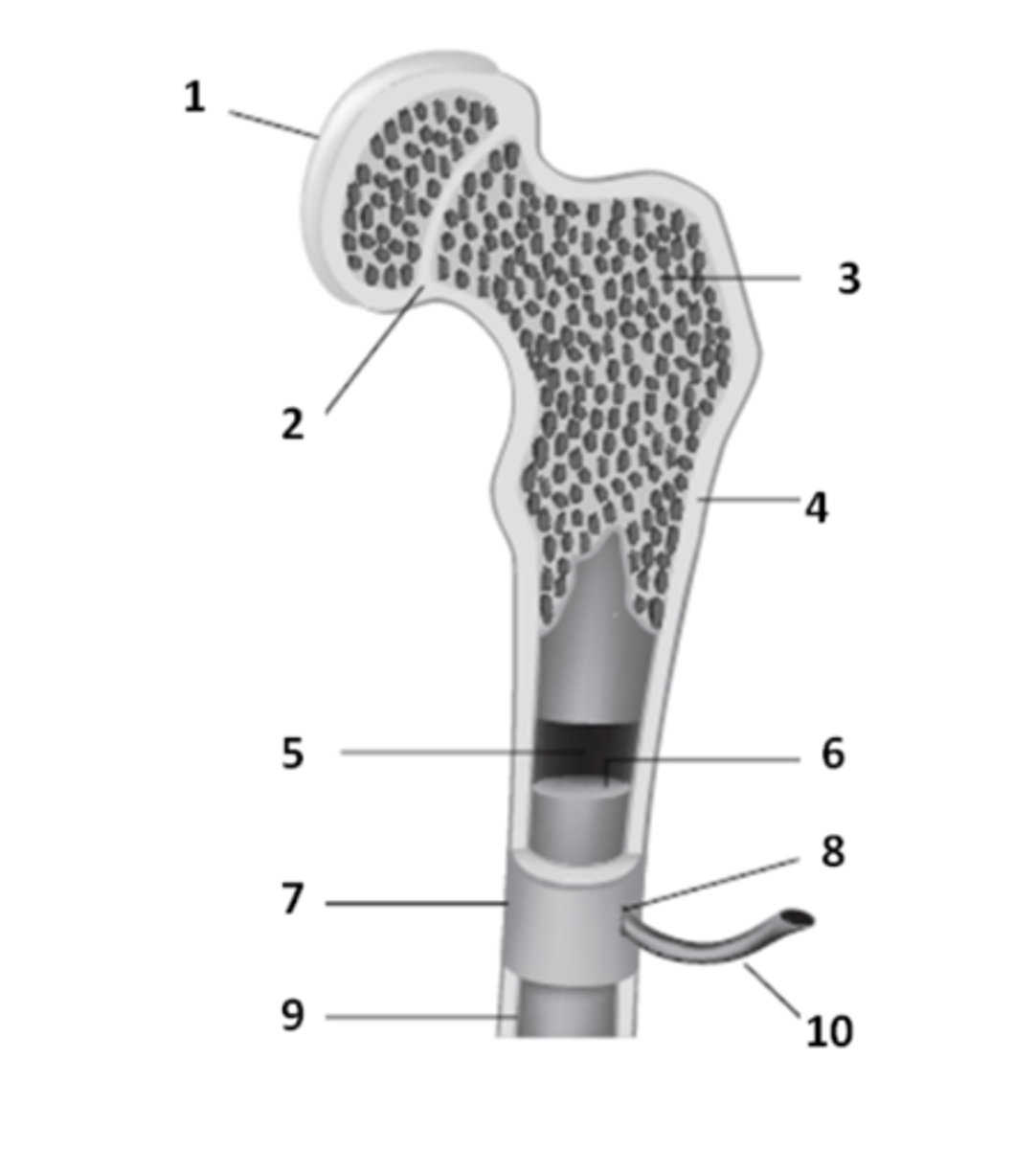
epiphysis
The ends of a typical long bone are called the _____________.
canaliculi
What are the hairlike canals in compact bone that allow osteocytes to connect to each other and exchange substances called?
axial skeleton
The __________ _____________ refers to the bones that make up the part of the skeleton which includes the skull, vertebrae, ribs, & sternum.
compact, spongy
Bones in the adult skeleton are composed of 2 types of osseous tissue. The 2 types of osseous tissue are ______________ bone & _______________ bone.
bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons
The skeletal system has 4 major components. Those 4 components are:
1.) _______________
2.) ______________
3.) ______________
4.) ______________
central canal
What do we call the hollow center of the osteon? It contains blood vessels & nerves.
long bone
The bone shape classification for a bone whose length is much greater than its width.
osteons
What are the weight-bearing cylinders found in compact bone?
circumferential lamellae
The bone matrix in compact bone that surrounds the outer surface of the diaphysis is called?
appendicular skeleton
The _______________ _________________ refers to the bones that make up the part of the skeleton that includes the upper & lower limbs, the pectoral girdle, & the pelvic girdle.
lacunae
The small cavities that house osteocytes are called?
endosteum
What is the thin membrane lining the medullary cavity that covers the trabeculae of the spongy bone called?
medullary cavity
What structure of bone anatomy is 5?
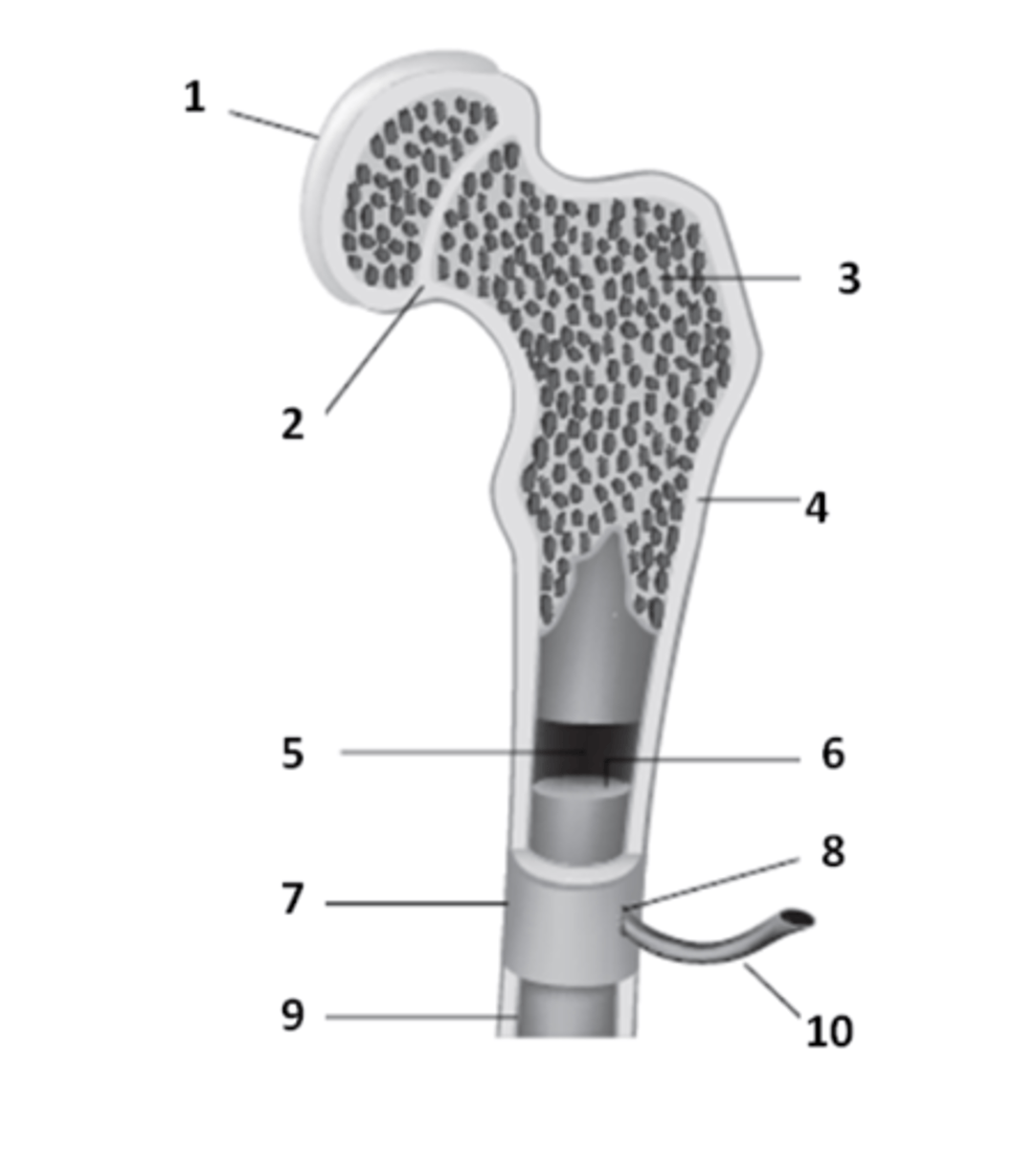
articular cartilage
The hyaline cartilage which covers the epiphyseal surface & provides a smooth surface to reduce friction is called?
yellow bone marrow
What type of bone marrow is the site of fat storage?
concentric lamellae
The rings in the bone matrix of compact bone, superficial to the central canal are called?
epiphyseal plate
What is the area of hyaline cartilage in a growing bone that provides longitudinal growth?
central canal
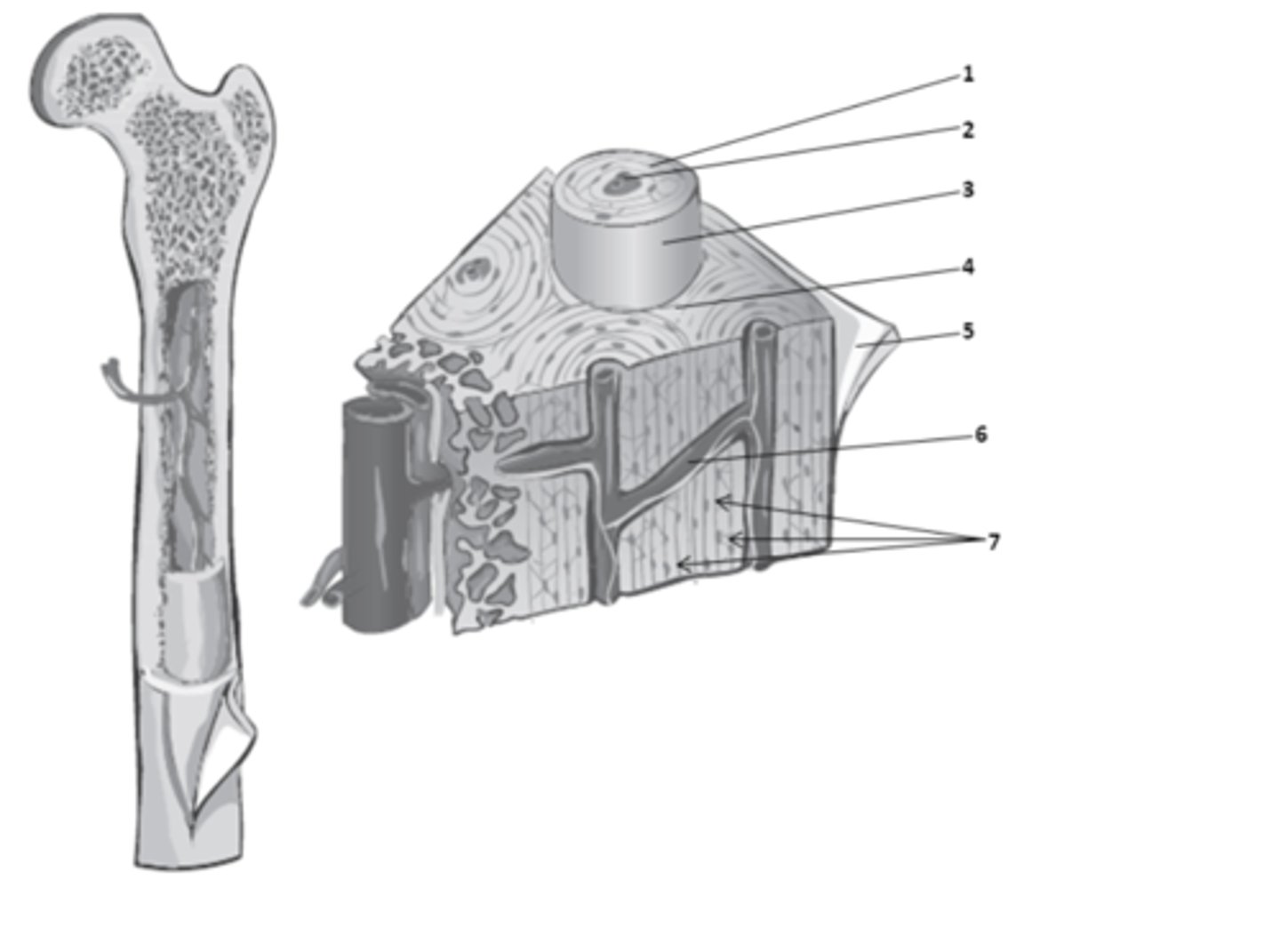
What structure of compact bone is 2?
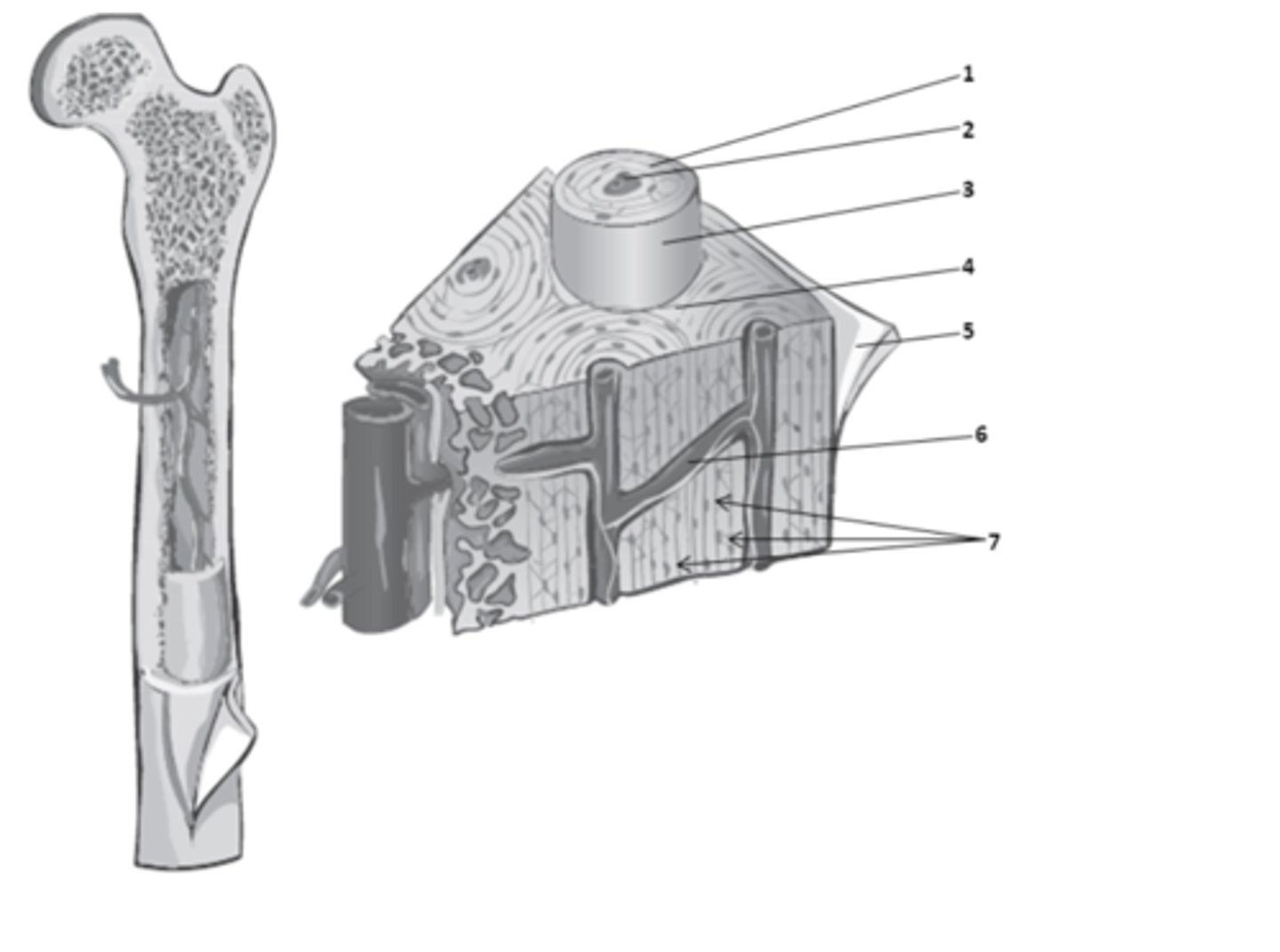
interstitial lamellae
What structure of compact bone is 4?
irregular bone
Any bone that has a shape which does not fall into any other category is said to be what type of bone?
diaphysis
The long shaft of a typical long bone which is called the _____________.
perforating canal
What structure of compact bone is 6?
short bone
The bone shape classification for a bone whose length and width is nearly equal is called?
concentric lamellae
What structure of compact bone is 1?
spongy bone
What structure of bone anatomy is 3?
sutural bone
A type of irregular bone that develops between the joints of the cranial bones is called what type of bone?
perforating canals
In compact bone, what are the structure which connect blood and nerve supplies between osteons, the periosteum, and the medullary cavity called?
endosteum
What structure of bone anatomy is 9?
articular cartilage
What structure of bone anatomy is 1?
periosteum
What structure of bone anatomy is 7?
interstitial lamellae
The bone matrix in compact bone, found between the osteons is called?
lacuna
What structure of compact bone is 7?
compact bone
What structure of bone anatomy is 4?
flat bone
The bone shape classification for a bone that is thin & plate-like is called?
bone marrow
What structure of bone anatomy is 6?
osteon
What structure of compact bone is 3?
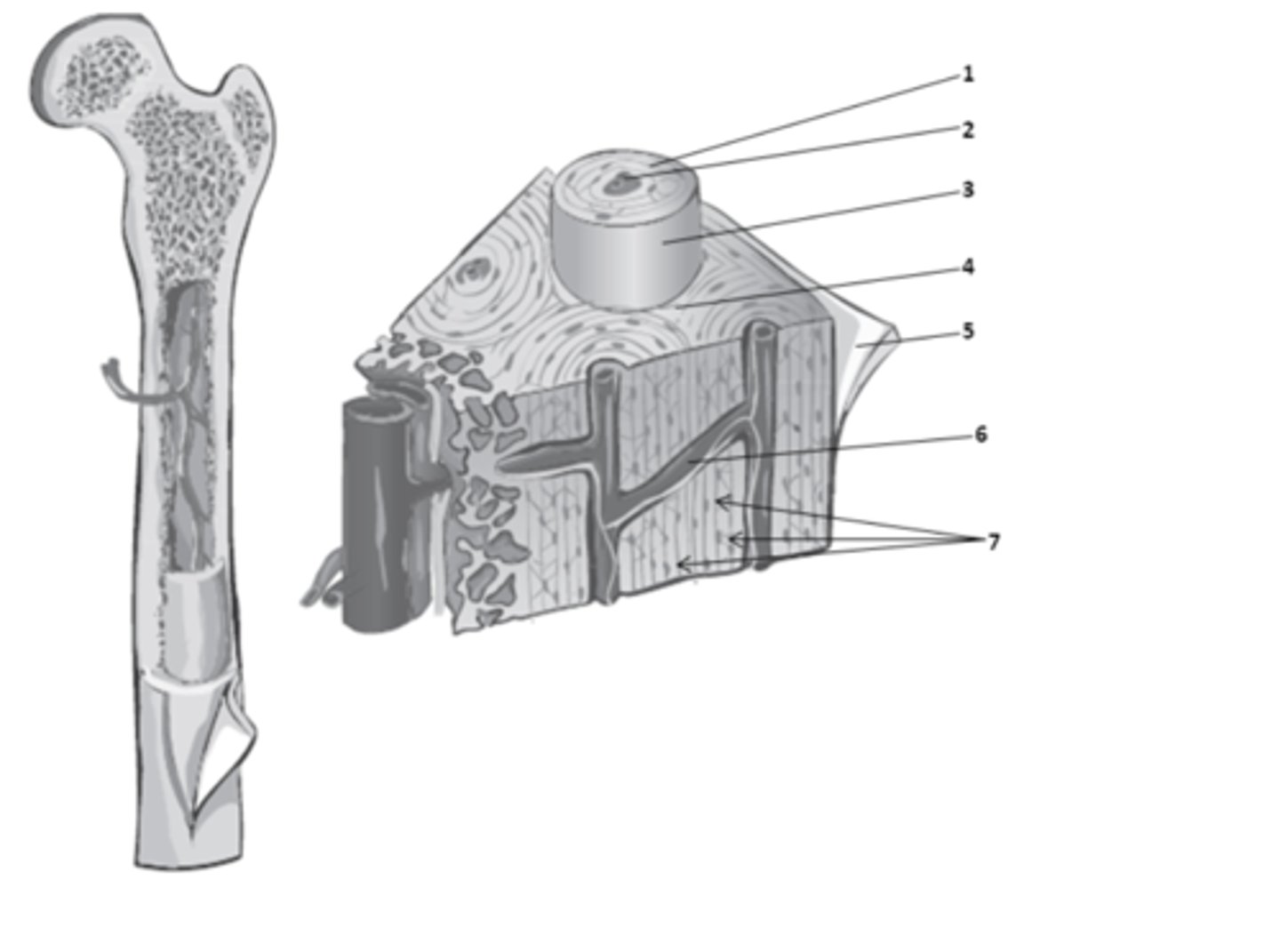
osteons
The functional unit of compact bone are long columns of tissues that run parallel to the longitudinal axis of the bone. What do we call these functional units of compact bone?
medullary cavity
Name the large cavity inside the diaphysis that contains bone marrow.
calcium, phosphate
Name 2 minerals that are stored in bones.
red bone marrow
What type of bone marrow is the site of new blood formation (hematopoiesis)?
bone marrow
What fills the spaces between the needle-like structures in spongy bone?
deep
Spongy bone is located ______________ to compact bone.
true
True or False: Bones are the site where new blood cells are formed.
perforating fibers
What fibrous structures hold the periosteum to the outer surface of the bone?
trabeculae
What are the needle-like structures in spongy bone?
sesamoid bone
Any irregular bone that is embedded in a tendon at a joint is said to be what type of bone?
periosteum
What structure of compact bone is 5?