BSC 111 Lab Exam-1
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Evolution
Change in characteristics over a period of time.
How does natural selection contribute to evolution?
Organisms more adapted to the environment are more likely to survive and pass on the genes that aided their success.
Necessary components of natural selection
Struggle for existence, variation, and inheritance.
Positive selection
An allele favored by natural selection
Negative selection
Removal of an allele NOT favored by natural selection
Taxonomic levels (most to least inclusive)
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
“Did King Philip Come Over For Good Soup?”
Binomial Nomenclature
Divided by genus and then species.
Genus must be capitalized. Species is lowercase. Latin root words and is either underlined or italicized.
Three domains of life and their characteristics
-Bacteria: Peptidoglycan cell wall, prokaryotic, single-celled
-Archaea: Prokaryotic, single-celled,
-Eukarya: Eukaryotic, multicellular,
Evolutionary changes demonstrated by the organisms within the Volvocine line
Increases in complexity of colonies, increased contact between cells of colonies
Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotes: No true nucleus, unicellular, asexual reproduction, no membrane bound organelles
Eukaryotes: True nucleus, multicellular, sexual (and asexual) reproduction, membrane bound organelles
Most prokaryotes are not _, and many engage in _ relationships with other organisms
pathogenic, mutualistic
Extremophile
Organisms that live in extreme conditions
Autotroph
Organism able to form their own food for energy from carbon. Undergoes photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Heterotroph
Eats other organisms for energy.
Binary Fission
Asexual reproduction by separation of the body.
Anaerobic
Doesn’t need oxygen.
Three common shapes of bacteria
Oil immersion technique- why is it used?
To increase the resolving power/magnification of the microscope by immersing both the lens and specimen in the oil.
Difference between a wet mount slide and a prepared slide
Wet mount: Live specimen with a drop of water. Not permanent.
Prepared slide: Already has been made and is preserved using chemicals. Permanent.
Gram stain (interpret)
Purple = Gram positive (thick peptidoglycan)
Pink/red = Gram negative (thin peptidoglycan)
Nitrogen fixing bacteria and their importance to plants
Transforms atmospheric nitrogen into fixed nitrogen. Has a symbiotic relationship with plants by living in root nodules and providing nitrogen to plant. Plant supplies carbon to bacteria.
What are cyanobacteria
Bacteria capable of oxygenic photosynthesis. Releases oxygen and uses water.
What does Oscillatoria look like?

What does Nostoc look like?
What does Gloeoclaspa look like?
How does a bacterial sensitivity plate work?
Shows the growth versus no growth of an organism. 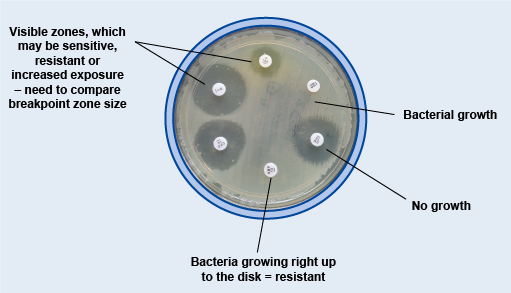
What can be learned from measuring zone of inhibition?
Determines the organism’s ability to grow and survive with certain nutrients.
Why are protists no longer classified as a kingdom
Protists themselves don’t have much in common with each other.
Protists are all _, but they posses a great diversity of other _
Eukaryotes, characteristics
How protists gain nutrition
Algae: by photosynthesis
Protozoa: by phagocytosis
How some protists defend themselves
Fast movement, release of toxins, presence of cellulose or silica walls, etc.
Algae are distinguished by their cellular organization
-Unicellular
-Filamentous
-Colonial
Three most common methods of movement among single-celled protists
-Cilia (little hairs)
-Flagella
-Pseudopodia
Photosynthetic algae
Green algae (Volvox), diatoms (silica cell walls), dinoflagellates (Peridinium/red tides), euglenoids (Euglena)
Green Algae under microscope
Volvox (circles within a circle), chlamyodomona (circle), spirogyra (spirals within a line)
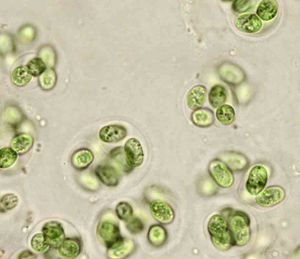
Diatom under microscope
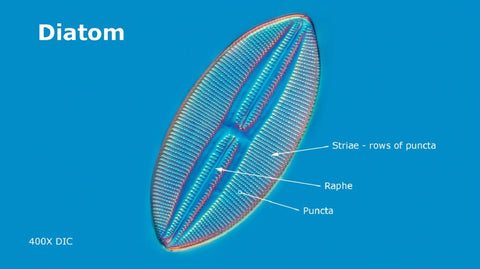 Little jewels!
Little jewels!
Peridinium under microscope

Euglena under microscope
Heterotrophic prozoa
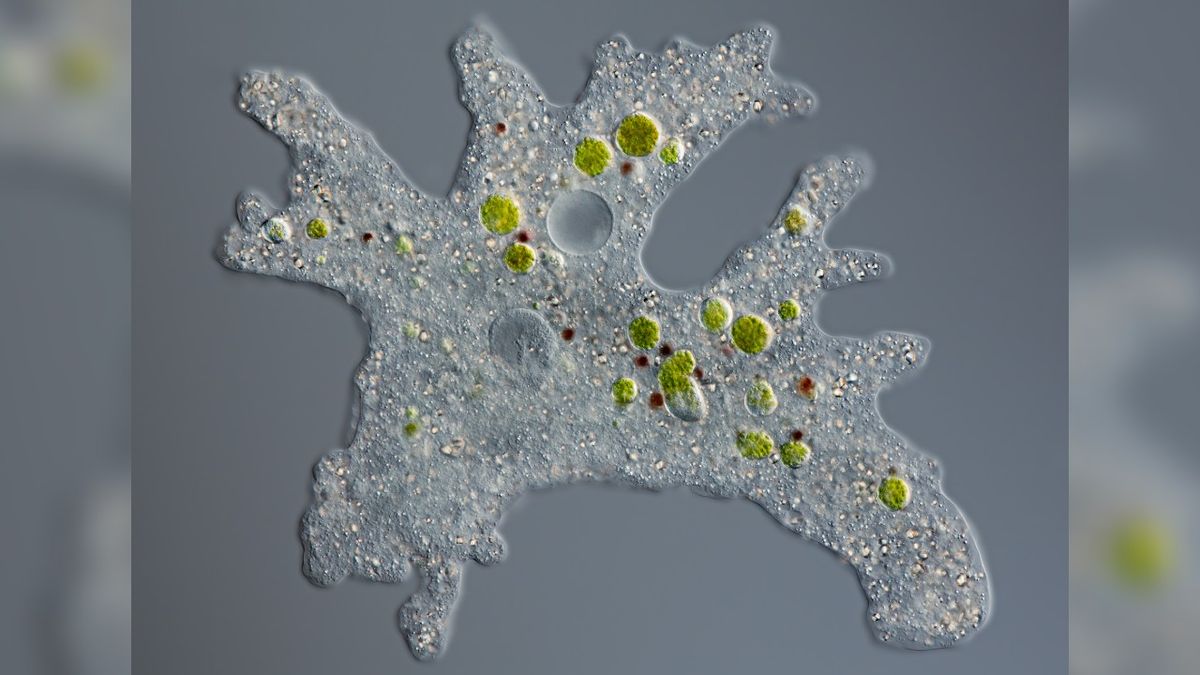
-Amoebas: amoeba (false arms)
-Flagellates: Trypanosoma (parasitic)
-Ciliates: Paramecium (capable of conjugation and binary fission)
-Plasmodium (cause of malaria- moves by cilia)
Amoeba under microscope
Trypanosoma under microscope

Paramecium under microscope

Plasmodium under microscope

General characteristics of fungi
Eukaryotes, reproduce by spores, heterotrophic
Ecological and economic role of fungi
Ecological: can be a decomposer
Economic: Includes the production of cheese, beer, mushroom
Generalized life cycle of fungi

Absorptive heterotrophs
Feeds externally by digesting organic matter and then absorbing the nutrients
Saprotrophs
Eats decaying matter
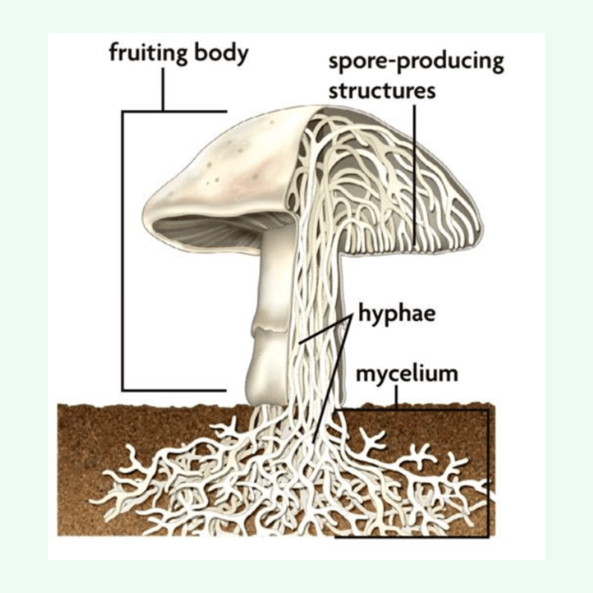
Parts of a fungi
Hyphae: Branching filaments
Mycelium: Consists of hyphae
Chitin: Exoskeleton or inner skeleton of most fungi
Sporangia: Makes and stores spores
Spores: Reproductive
Phylum Zygomycota (sexual vs asexual)

What mycorrhizae are
Symbiotic relationship between fungus and plant.
Fungus attaches to the root of plants and become an extension of the plant’s root system. The fungi gets nutrients from the plant while the plant gains more nutrients.
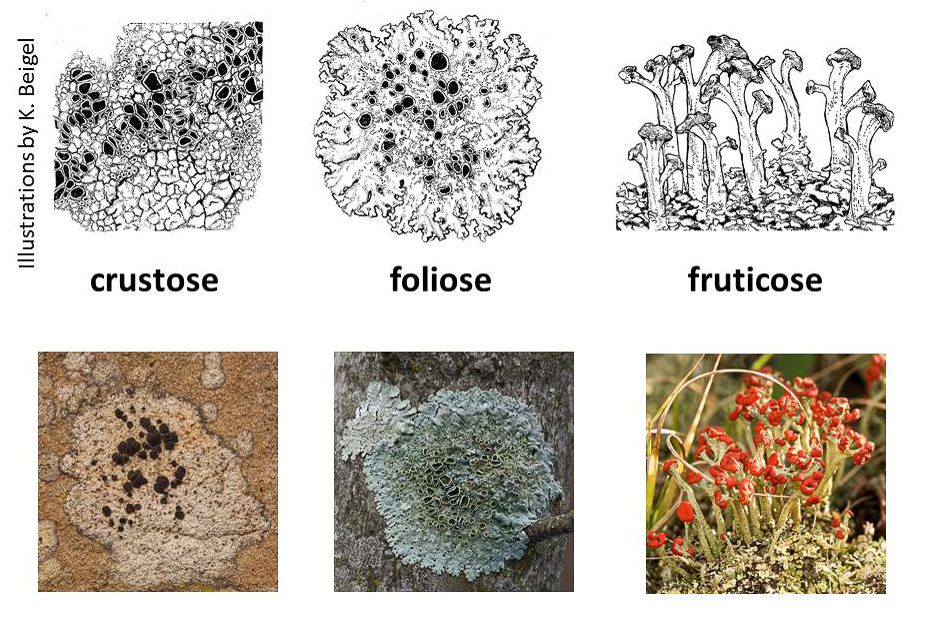
What lichen is
Symbiotic relationship between fungi and algae.
The fungus attaches to the log or rock, and absorbs nutrients while the algae uses the nutrients absorbed to photosynthesize.
Three shapes of lichens

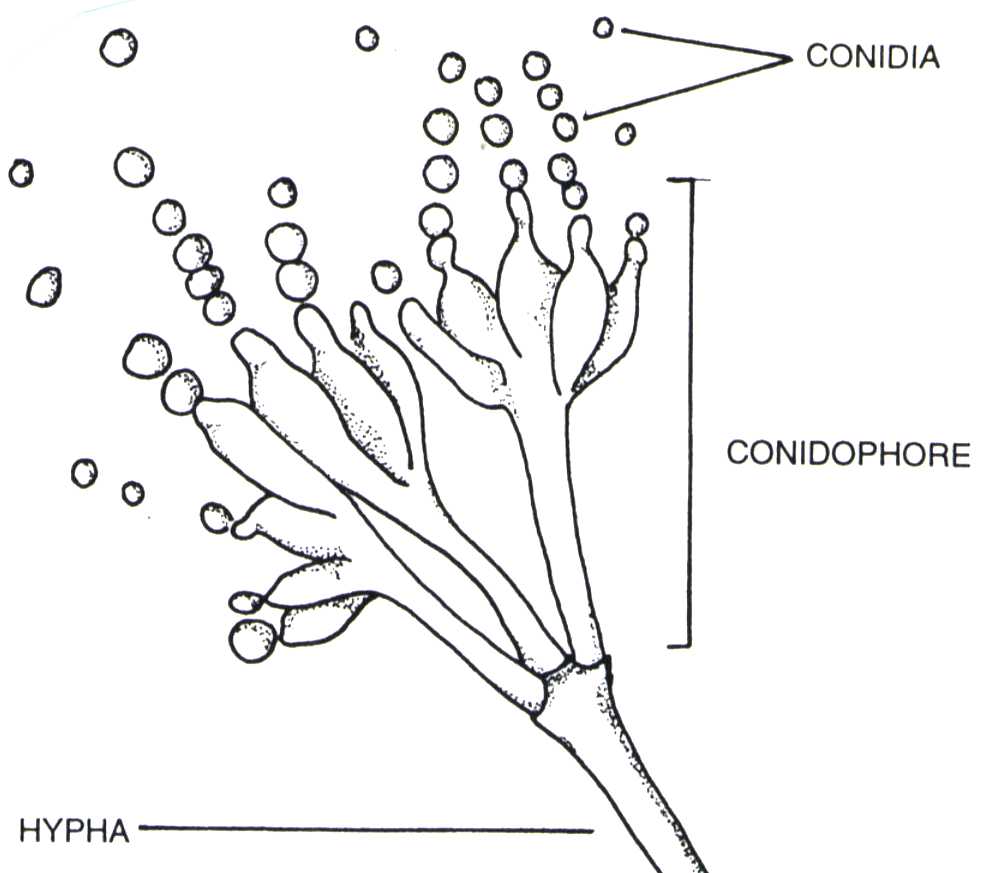
Identify the conidiophores produced by Penicillium
Identify the budding cells in Saccharomyces
Recognize the structures involved in sexual reproduction in Peziza
 the eight ascospores in the ascus in the ascocarp
the eight ascospores in the ascus in the ascocarp
Recognize the structures in sexual reproduction in Coprinus
 the four
the four
basidiospores produces in the basidium within the gills of the basidiocarp
Symbiotic relationships
(98).jpg)
Diagram of a mushroom (part 2)
 Basidiocarp: Fruiting body in which sexually produced spores are formed on the surface of.
Basidiocarp: Fruiting body in which sexually produced spores are formed on the surface of.
