Biology 3.1 Biological Molecules
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AQA A Level Biology Biological Molecules
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
All organisms share a common chemistry; there are the same groups of carbon-based compounds in cells.
What provides indirect evidence for evolution?
2
New cards
Small units from which large molecules are made.
Define monomer.
3
New cards
Molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together.
Define polymer.
4
New cards
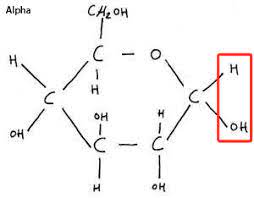
Hydrogen is above Carbon 5.
Structure of alpha-glucose.
5
New cards
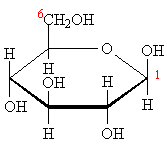
Hydrogen is below Carbon 5.
Structure of beta-glucose.
6
New cards
Glucose, fructose and galactose
\
C6H12O6
\
C6H12O6
Name the three hexose sugars and there molecular formula
7
New cards
Glycosidic
What bond forms when monosaccharides react
8
New cards
C12H22O11
What is the chemical formula for Maltose, Sucrose and Lactose
9
New cards
Equal vols benidict’s solution + sample
heat in a water bath
\+ = Blue → Orange/brick red ppt
\
Semi quantitative as darker colour = stronger sugar
\
heat in a water bath
\+ = Blue → Orange/brick red ppt
\
Semi quantitative as darker colour = stronger sugar
\
What is the benidict’s test for reducing sugars
10
New cards
Hydrolase non-reducing sugars e.g. sucrose into monomers by adding 1cm3 HCl and heat
Neutralise using sodium carbonate until turns litmus paper green
Add benidict’s + = Blue → Orange/brick red ppt
\
Neutralise using sodium carbonate until turns litmus paper green
Add benidict’s + = Blue → Orange/brick red ppt
\
Describe the test for non reducing sugars
11
New cards
iodine + = orange → blue/black
Describe the test for starch
12
New cards
make standard solutions with known concs and record absorbance
\
plot calib curve
\
record absorbance for unknown samples use calib curve to read concs
\
plot calib curve
\
record absorbance for unknown samples use calib curve to read concs
Outline how colourimetry could be used to give qualitative results for the presence of sugars and starch’s
13
New cards
\- energy reserve for plants
\- polysaccharide made up of alpha-glucose
\- unbranched, coiled amylose – therefore it’s compact and good for storage
\- branched amylopectin – therefore enzymes can hydrolyse bonds easily and release energy quickly
\- insoluble + doesn’t affect water potential, therefore good for storage
\- polysaccharide made up of alpha-glucose
\- unbranched, coiled amylose – therefore it’s compact and good for storage
\- branched amylopectin – therefore enzymes can hydrolyse bonds easily and release energy quickly
\- insoluble + doesn’t affect water potential, therefore good for storage
Structure and function of starch.
14
New cards
\-energy reserve for animals
\- polysaccharide made up of alpha-glucose
\- branched with a lot of side branches – therefore enzymes can hydrolyse bonds easily and release energy quickly
\- compact therefore good for storage
\- polysaccharide made up of alpha-glucose
\- branched with a lot of side branches – therefore enzymes can hydrolyse bonds easily and release energy quickly
\- compact therefore good for storage
Structure and function of glycogen.
15
New cards
Glucose + Glucose
How is maltose made
16
New cards
Glucose + Fructose
How is sucrose made
17
New cards
Glucose + Galactose
How is Lactose made
18
New cards
\- polysaccharide made up of beta-glucose
\- forms long, unbranched, straight cellulose chains
\- chains are linked with hydrogen bonds to form strong microfibrils
\- provides structural support for cells
\- forms long, unbranched, straight cellulose chains
\- chains are linked with hydrogen bonds to form strong microfibrils
\- provides structural support for cells
Structure and function of cellulose.
19
New cards
The hydrocarbon tail which can be saturated or unsaturated.
What is the R group of a fatty acid?
20
New cards
\-energy storage molecule – the long hydrocarbon tails release a lot of energy when broken down
\- insoluble + doesn’t affect water potential – the hydrophobic tails face inwards and the hydrophilic heads face outwards, forming droplets
\- Slow conductor of heat, good insulator
\- insoluble + doesn’t affect water potential – the hydrophobic tails face inwards and the hydrophilic heads face outwards, forming droplets
\- Slow conductor of heat, good insulator
Properties of triglycerides.
21
New cards
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids to form an ester bond
How are triglycerides formed?
22
New cards
\- makes up the bilayer of cell membranes
\- hydrophilic heads face outwards, hydrophobic tails face inwards, waterproofing
\- the centre is hydrophobic so water-soluble substances can’t pass through
\- hydrophilic heads face outwards, hydrophobic tails face inwards, waterproofing
\- the centre is hydrophobic so water-soluble substances can’t pass through
Properties of phospholipids.
23
New cards
Ester bond
What bonds are found in triglycerides?
24
New cards
Dissolve the solid sample in ethanol add equal vol water and shake
\
\+= Milky white emulsion
\
\+= Milky white emulsion
How do you test for lipids?
25
New cards
Sat: Only single bonds Unsat: C=C bonds
Sat: Straight chains, many contact points Unsat: Kinked chains, min contact
Sat: high mp, solid at room tempt Unsat: liquid at room tempt
Sat: found in animals Unsat: Found in plants
Sat: Straight chains, many contact points Unsat: Kinked chains, min contact
Sat: high mp, solid at room tempt Unsat: liquid at room tempt
Sat: found in animals Unsat: Found in plants
How do saturated and unsaturated fatty acids differ to one another?
26
New cards
\
Glyercol backbone
Mix of sat and unsat fatty acids
Contain C,H and O only
Formed via a condensation reaction
Glyercol backbone
Mix of sat and unsat fatty acids
Contain C,H and O only
Formed via a condensation reaction
How are phospholipids and triglycerides similar
27
New cards
Phos: 2 fatty acids 1 phosphate Trig: 3 fatty acids
Phos: Hydrophillic head + hydrophobic tail Trig: whole molecule is hydrophobic
Phos: Used mainly as membrane Trig: Used mainly as energy storage
Phos: Hydrophillic head + hydrophobic tail Trig: whole molecule is hydrophobic
Phos: Used mainly as membrane Trig: Used mainly as energy storage
How are triglycerides and phospholipids different?
28
New cards
NO, do not have repeating units
\
They are macromolecules
\
They are macromolecules
Are phospholipid and triglycerides polymers?
29
New cards
They have different variable side groups (R groups).
20 different aminos
20 different aminos
How do amino acids differ from one another?
30
New cards
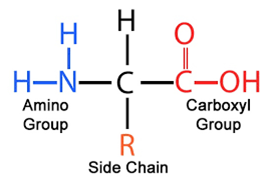
NH2 amine group
COOH carboxyl group
R side chain
COOH carboxyl group
R side chain
What is the general structure of an amino acid?
31
New cards
Biurets Test
Equal vol sodium hydroxide to sample
small amount of dilute copper (II) sulphate
mix
\+= blue → Purple
Equal vol sodium hydroxide to sample
small amount of dilute copper (II) sulphate
mix
\+= blue → Purple
How do you test for proteins
32
New cards
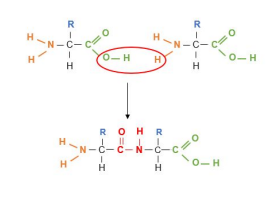
A dipeptide joined by a peptide bond (CNOH)
more than two is a polypeptide
more than two is a polypeptide
What does a condensation reaction between two amino acids form?
33
New cards
Sequence of amino acids
determined by codons in mRNA
determined by codons in mRNA
What is the primary structure of a protein?
34
New cards
H bonding and then either Alpha helix or Beta pleated sheets
What is the secondary structure of a protein?
35
New cards
3D shape determined by folding
disulfate bridges
ionic bonding
H bonds
\
Can be impacted by 1st structure due to amino sequence determining where bonds can occur
disulfate bridges
ionic bonding
H bonds
\
Can be impacted by 1st structure due to amino sequence determining where bonds can occur
What is the tertiary structure of a protein
36
New cards
May contain may polypeptides
May have a prosthetic such as a metal
May have a prosthetic such as a metal
What is quaternary protein structure
37
New cards
\- substrate binds to the active site to form an enzyme-substrate complex
\- lowers activation energy of reaction by putting strain on the bonds in a molecule or reducing repulsion between two molecules
\- lowers activation energy of reaction by putting strain on the bonds in a molecule or reducing repulsion between two molecules
How do enzymes catalyse a reaction?
38
New cards
spherical/compact
Hydrophilic R group that faces outwards Hydrophobic faces inwards usually water soluble
\
involves in metabolic process e.g. enzymes/haemoglobin
Hydrophilic R group that faces outwards Hydrophobic faces inwards usually water soluble
\
involves in metabolic process e.g. enzymes/haemoglobin
what is the structure/function of a globular protein?
39
New cards
Can form long chains/fibbers
insoluble
\
good structure/support e.g. collagen in skin
insoluble
\
good structure/support e.g. collagen in skin
Structure/function of fibrous proteins
40
New cards
Use a capillary tube to put mixture onto pencil line of origin and place paper in solvent
\
allow solvent to run until it almost reaches the other end of the paper
\
Use UV to see the spots
\
Each amino will have a different Rf value
\
allow solvent to run until it almost reaches the other end of the paper
\
Use UV to see the spots
\
Each amino will have a different Rf value
How can chromatography be used to identify an amino acid?
41
New cards
\- the enzyme’s active site and the substrate are exactly complementary to each other
\- they bond to form an enzyme-substrate complex
Describe the ‘lock and key’ model.
42
New cards
\- the active site and substrate are specific to each other but not exactly complementary
\- they bind to form an enzyme-substrate complex, the active site changing shape slightly to complete the fit
Describe the ‘induced fit’ model.
43
New cards
\- the active site is determined by the tertiary structure
\- changes in pH and temperature affect the bonds in the tertiary structure, so active site changes shape so it’s no longer complementary to its substrate
How is the tertiary structure related to an enzyme’s active site?
44
New cards
Enzyme conc
Substrate conc
Inhibitors conc
pH
Tempt
Substrate conc
Inhibitors conc
pH
Tempt
5 factors that effect enzyme ROR
45
New cards
If enzyme conc is fixed rate increases in propotion to substate conc
\
Rate levels off when max no, of E-S are formed
\
Rate levels off when max no, of E-S are formed
How do substrate conc effect enzyme ROR
46
New cards
Rate increases as Ke increases and peaks at optimum tempt
above optimum ionic and H bonds in 3rd structure of protein break
active site changes shape, no longer complimentary (denatured)
above optimum ionic and H bonds in 3rd structure of protein break
active site changes shape, no longer complimentary (denatured)
How does tempt effect enzyme ROR
47
New cards
Comp: Similar shape to substrate, binds to active site Non-comp: Bind to allosteric site
Comp: do not stop reactions ES complex can reform when inhibitor is released Non-Comp: can change active site shape and permanently stop reaction
Comp: increasing substate complex can decrease effect Non-comp: increasing con has no impact
\
Comp: do not stop reactions ES complex can reform when inhibitor is released Non-Comp: can change active site shape and permanently stop reaction
Comp: increasing substate complex can decrease effect Non-comp: increasing con has no impact
\
Contrast the two type of enzyme inhibitors
48
New cards
pH = -log10\[H+\]
How do you calculate pH
49
New cards
Outside optimum H+/OH- interact with H bonds in 3rs structure
How does pH effect enzyme ROR
50
New cards
a grpah showing ROR against time
draew a tangent where time = 0
draew a tangent where time = 0
How can results from a practical measuring enzyme activity be used to find the initial rate of reaction?
51
New cards
immerse equal vols of trypsin and milk stored in different test tubes in a water for 5 mins
mix together and time how long until the milk is hydrolysed (becomes a colourless solution)
test a differnt tempts
mix together and time how long until the milk is hydrolysed (becomes a colourless solution)
test a differnt tempts
How can you practically measure the effect of temperature on enzyme activity using trypsin and milk?
52
New cards
1/time
How do you calculate ROR
53
New cards
(Uncertainty/measured value) x100
How do you calculate uncertainty
54
New cards
Holds genetic information.
What is the role of DNA?
55
New cards
Transfers genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
What is the role of RNA?
56
New cards
RNA and proteins.
Components of ribosomes.
57
New cards
Deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, and an organic base (adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine).
Components of a DNA nucleotide.
58
New cards
Ribose sugar, phosphate group, and an organic base (adenine, uracil, cytosine or guanine).
Components of an RNA nucleotide.
59
New cards
Double helix with two polynucleotide chains held together by hydrogen bonds between specific complementary base pairs.
Describe a DNA molecule.
60
New cards
Phosphodiester
What bonding occurs between nucleotides?
61
New cards
Double helix with two polynucleotides chains held together via H bonds to specific bases
Describe a DNA molecule
62
New cards
DNA helicase breaks the H bonds between base pairs
Each strand acts as a template
free nucleotides from nucellar sap attach to exposed bases due to base pairing
DNA polymerase catalyses a condensation reaction that joins adjacent strands
H bonds reform
Each strand acts as a template
free nucleotides from nucellar sap attach to exposed bases due to base pairing
DNA polymerase catalyses a condensation reaction that joins adjacent strands
H bonds reform
How does semiconservative replication happen?
63
New cards
Bacteria grown in medium containing heavy isotope N15 for many generations
some bacteria were moved toa medium containing light isotope N14 and extracted after 2 DNA replication cycles
Bacteria centrifuged formed a pellet heavy DNA settled at the bottom
some bacteria were moved toa medium containing light isotope N14 and extracted after 2 DNA replication cycles
Bacteria centrifuged formed a pellet heavy DNA settled at the bottom
Describe the Meselson and Stahl experiment
64
New cards
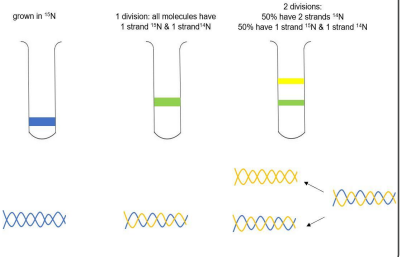
How does the Meselson Stahl experiment validate semiconservative replication
65
New cards
Ensures genetic continuity.
Why is semi-conservative replication of DNA important?
66
New cards
mRNA; Comp to 1 gene from DNA with introns spliced out, codons can be translated into polypeptides by ribosomes
rRNA: component of ribosomes
tRNA: Supplies complimentary aminos to codons during translation
rRNA: component of ribosomes
tRNA: Supplies complimentary aminos to codons during translation
What is the role of different types of RNA in living cells
67
New cards
A + G = 2 rings, purines
T/U + C 1 ring, pyrimidines
T/U + C 1 ring, pyrimidines
Which bases are purine and which are pyrimidines
68
New cards
A +T, 2 H bonds
G + C, 3 H bonds
G + C, 3 H bonds
What are the complimentary base pairs in DNA
69
New cards
\- hydrogen bonds between the bases are broken by DNA helicase, unwinding the double helix
\- the two strands act as templates
\- free DNA nucleotides are attracted to the exposed bases by complementary base pairing
\- DNA polymerase joins up the adjacent nucleotides, forming a sugar-phosphate backbone
Describe the process of semi-conservative replication.
70
New cards
Ribose sugar, three phosphate groups and an adenine base.
Components of ATP.
71
New cards
Sugar phosphate backbone/H bonds, stability
Long molecule, lots of info
Helix can compact for storage in nucleus
Base sequence of triplets codes for aminos
double stranded for semi-conservative replication
weak h bonds to easily separate for replication
\
Long molecule, lots of info
Helix can compact for storage in nucleus
Base sequence of triplets codes for aminos
double stranded for semi-conservative replication
weak h bonds to easily separate for replication
\
How does DNA structure relate to its function
72
New cards
Long nucleotide, still shorter than DNA, breaks down quickly
contains uracil instead of thymine
single stranded and linear with no base pairing
\
contains uracil instead of thymine
single stranded and linear with no base pairing
\
RNA structure/function
73
New cards
single stranded
clover shape
anticodon on one end amino binding on other
anticodon binds to comp mRNA codon
amino acid corresponds to anticoding
clover shape
anticodon on one end amino binding on other
anticodon binds to comp mRNA codon
amino acid corresponds to anticoding
RNA structure
74
New cards
Condensation reaction between ADP and Pi, catalysed by ATP synthase during photosynthesis or respiration.
Describe ATP synthesis.
75
New cards
ATP (Catalysed by ATP hydrolase) → ADP + Pi
Energy released coupled with metabolic reactions
phosphate group (Pi) phosphorylates compounds to make them more reactive
Energy released coupled with metabolic reactions
phosphate group (Pi) phosphorylates compounds to make them more reactive
What’s the role of ATP in cells
76
New cards
high energy bonds between phosphate groups
small amount of energy released at a time to prevent wastes
single step hydrolysis
easily resynthesized
small amount of energy released at a time to prevent wastes
single step hydrolysis
easily resynthesized
Why is ATP suitable as the energy currency of cells
77
New cards
Chemically simple, few components
Why was it doubted that DNA carried the genetic code
78
New cards
DNA, double stranded RNA, single
DNA, deoxyribose RNA, ribose
DNA, Thymine RNA, Uracil
DNA, Longer RNA, Shorter
DNA, deoxyribose RNA, ribose
DNA, Thymine RNA, Uracil
DNA, Longer RNA, Shorter
Compare DNA to RNA
79
New cards
\- each molecule is made up of an oxygen atom covalently bonded to two hydrogen atoms
\- each molecule is polar due to the electronegativity of oxygen
\- there is hydrogen bonding between molecules
Structure of water.
80
New cards
\- metabolite
\- solvent
\- cohesion
\- high specific heat capacity – buffers changes in temperature
\- high latent heat of vaporisation – provides cooling effect with little loss of water
\- solvent
\- cohesion
\- high specific heat capacity – buffers changes in temperature
\- high latent heat of vaporisation – provides cooling effect with little loss of water
5 Properties of water.
81
New cards
\- found in cytoplasm and body fluids
\- H+ - determines pH
\- Fe2+ - binds to oxygen in haemoglobin
\- Na+ - used in co-transport of glucose and amino acids
\- PO43- - components of DNA, RNA and ATP
\- H+ - determines pH
\- Fe2+ - binds to oxygen in haemoglobin
\- Na+ - used in co-transport of glucose and amino acids
\- PO43- - components of DNA, RNA and ATP
Location and roles of inorganic ions.