8.1 - muscle phyisology
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
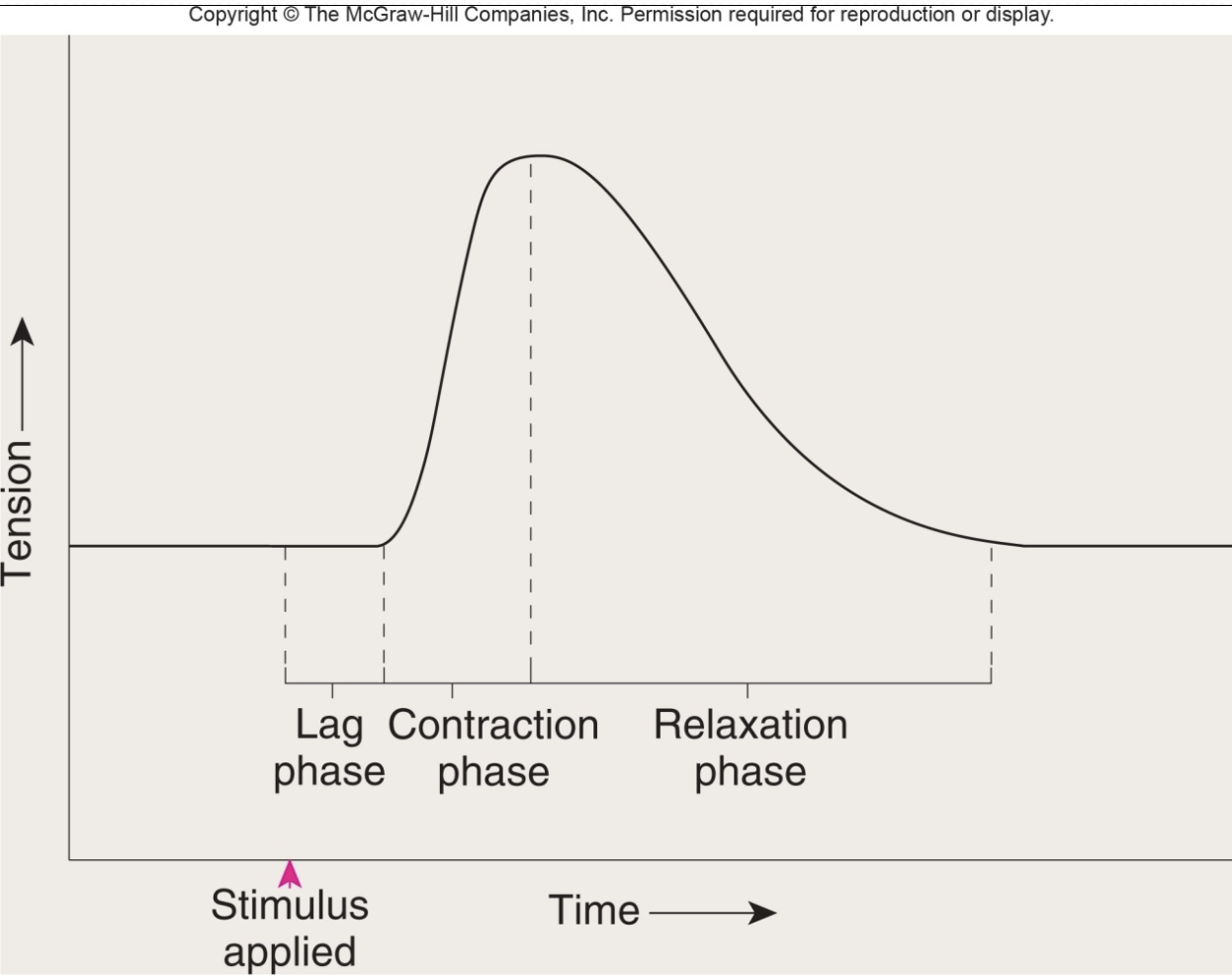
muscle twitch
contraction = response to stimulus = ap in 1+ muscle fiber, phases - lag/latent, contraction, relaxation
how are stronger contractions made
restim of muscle fiber before it completely relaxes, added to the first = causes a stronger contraction
tetanus
rapid arrival of ap causes twitches = peak level of contraction, sustatined muscle contraction evoked when motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle = emits ap at high rate
types of muscle fibers
slow muscle fibers - slow oxidative
fast aerobic - fast oxidative glycolytic fibers
fast anaerobic fibers - fast glycolytic fg
they diff in mitochondria and amt of atp produce
slow muscle fibers
small, weaker contractions- resist fatigue (postural muscles)
slow contraction as atp hydrolyzed on myosin head is slow, and has high amt of myoglobin = good supply of oxygen
fast aerobic fibers
intermed size and strength, with some fatigue, contract quick and powerful, but fatigue faster than slow muscle fibers = endurance
describe what fast anaerobic fibers are like
very strong contractions - fatigue fast, few mitochondria and myoglobin, anaerobic glycolysis = atp, but larger fibers = more force, for rapid movement for tiny amt of time, muscles has more type of a fiber than another
how do diff types of force excite diff fibers
gentle contractions - small muscle fibers
forceful contractions - generate strong contractions that will fatigue eventually but not fast
strong burst- largest muscle fibers
how is atp produced for muscle contractions
creatine phosphate, anaerobic respiration, aerobic respiration
creatine phosphate
accumulate in muscle tissue, used quickly, stores energy to make atp, where adp and creatine phosphate with a kinase make creatine and atp
anaerobic respiration
occurs without oxygen, breaks down glucose = atp and lactic acid, atp from creatine and anaerobic respiration = 3 mins
aerobic respiration
more efficient than anerobic = needs oxygen and breaks down glucose to make atp co2 and water
endruance training
fast muscle fibers from anaerobic to aerobic fibers
weight lifting
converts fast from aerobic to anaerboic, as anaerobic contract faster and more powerful, but fatigue faster
how does force correlate with motor units
skeletal muscles = functional motor units, and a group of muscle fibers activated by branch of single motor neuron, how total force = num of motor units activated (recruitment), and more motor units = more force
what is optimal length
maximal number of cross bridges needed for contractions = overlap between thick and thin filament without getting in the way,
if muscle fiber stretched too long, not much overlap and cross bridges
if extreme stretch = then no overlap what so ever
if length shorter than optimal = thin filaments overlap and get in the way, binding sites aren’t able to bind to all heads = less tension
why can’t we change the length as much
because our muscles are attached to our bones, and won’t stretch as far from optimal range
isomeric contraction
muscle = at same length, can contract but only exerts force or tension, like holding an object up, force = load
isotonic
muscle length changes - like lifting object at constant speed
two types 1:
concentric = shortening of muscles = generates forces
eccentric : causes muscles to elongate in response to greater opposing force
smooth muscle
found in bladder, reprodu tracts, gastroint tract, respiratory tract and surrounds blood vessels, mechnaically coupled to one another, contract of one cell = another cell, gap junctions couple adj cells chem and electrically = facilitating chemical and ap spread between cells
what is signif abt smooth muscles shortening
it can shorten greater than skeeltal as it surrounds structures that change in diameter, and contraction can be nonlinear, as fibers are slanted position
neural input for smooth muscle and hormonal
ANS can induce or inhibit contraction (either from sns or pns), hormones can stimulate a second messenger molecule = calcium release
how are smooth muscles activated by calcium
calcium enters from outside = voltage/ligand gated channels, others coem from sacroplasmic reticulum but has no t tubules, and calcium binds to calmodulin = and phosphorylates the cross bridges which can bind and pull on thin filaments
smooth muscle contractions
tend to be slower but not fatigued, like diameter of blood vessel will maintain like that for a long time
cardiac muscle
branched, connected through intercalated disks, and similar mechanism as skeletal muscle