VTNE Review: Pharmacology
1/451
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
452 Terms











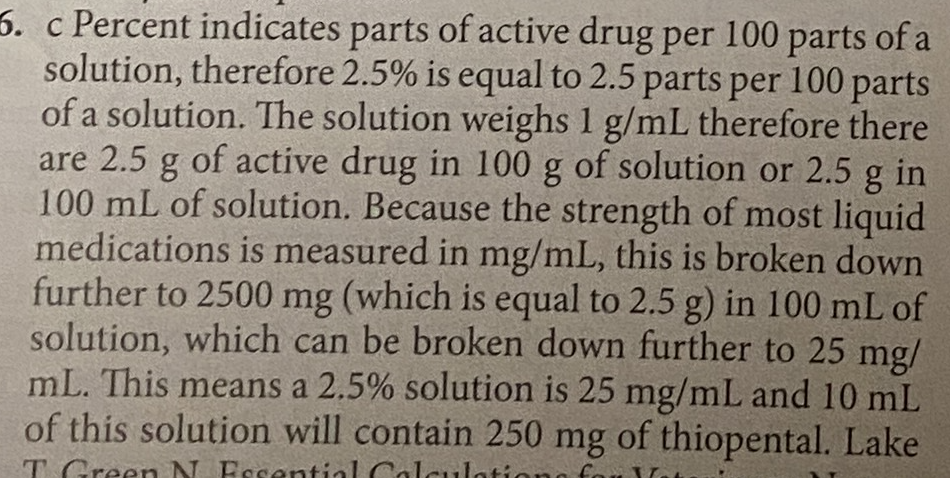


















c Penicillin is a beta-lactam, which is excreted by the kidneys. Some beta-lactams are excreted via the liver through the bile, but only a small portion, hence the liver is not the primary method of excretion. The stomach and small intestine are not involved in the excretion of medications.





c Diazepam will be absorbed by the plastic and should not be drawn up until you are ready to administer it to the patient. This is not known to occur with acepromazine, atropine, or ketamine.

d Xylazine is an alpha-2 agonist. These are reversed with yohimbine, which is an alpha-2 antagonist. Naloxone is a reversal for opioids, whereas flumazenil is used to reverse benzodiazepines. Atropine is an anticholinergic and is not used to reverse any medications, although it can be used to treat organophosphate toxicity.

d Griseofulvin is an fungistatic antibiotic used to treat dermatophyte fungal infections in dogs and cats, as well as ringworm in horses.



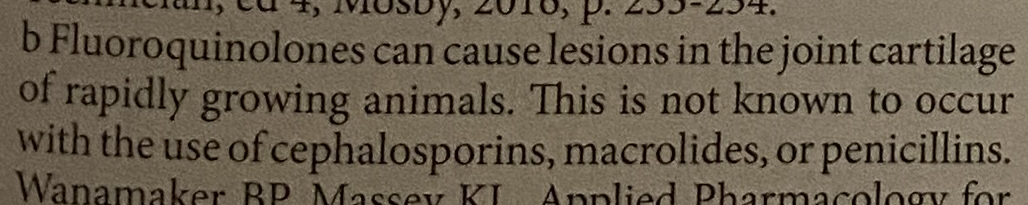

c Bacteria that contain the beta-lactamase enzyme inactivate penicillin. They do this by attacking the beta-lactam ring of the penicillin, which causes it to be ineffective. Potentiated penicillins are penicillins combined with another drug that will inactivate the beta-lactamase enzyme. This is seen in Clavamox (amoxicillin and clavulanic acid) and Unasyn (ampicillin and sulbactam). These drugs will have a wider spectrum of action because of the resistance to beta-lactamase bacteria. Penicillin is commonly used to treat mastitis and cephalosporins are not penicillins.







b Butorphanol is a synthetic opioid that is used as an analgesic in dogs and cats, as well as being used in dogs for its antitussive activity. Because it is an opioid, it is reversed with naloxone and not yohimbine.

a An iodophor is made up of iodine and a carrier that allows the iodine to be released with time, providing prolonged activity (although it may need to be applied more than once to provide adequate disinfection). Organic materials can inactivate it and the area should be thoroughly cleaned before application. It should also be diluted before use to avoid irritation of the tissues.



















d The half-life of aspirin is very different in dogs (8 hours) than it is in cats (40 hours).





d Corticosteroids are known to have several short-term side effects, including polyuria and immunosuppression (which would cause a delay in healing). Osteoporosis can be a long-term effect of corticosteroid therapy.

b There are multiple histamine receptors in the body including Hl found in smooth muscle and the endothelium, H2 found in the gastric cells, H3 found in the central nervous system, and H4 found in the cells of the immune system. Antihistamines cause sedation via blocking of H3 receptors in the central nervous system.
They are also used to treat pruritus and are not known to cause panting or polyuria.

a H2 receptors are found in the parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. These receptors are not found in saliva, the carotid arteries, or the aortic arch.













a Biotransformation occurs in many organs including the liver, lungs, skin, and kidneys. Of these, the liver is where the majority of the biotransformation occurs.





d Drugs are eliminated via the kidneys (in urine), liver (in bile), and lungs. The spleen is not involved with elimination of drugs.

























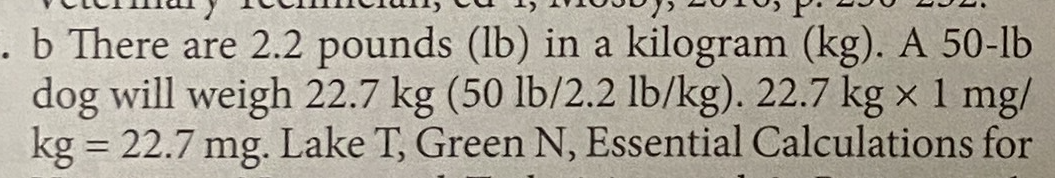





d Rabbits are sensitive to medications that are known to kill off the normal flora of the gastrointestinal tract, causing dysbiosis and/or enterotoxemia. Because of this, antibiotics that should be avoided include pencillins (Clavamox), cephalosporins (cefotaxime), incosamides (clindamycin), and some macrolides (erythromycin). Enrofloxacin does not have this side effect and is therefore safe for use in rabbits.













b Fibrinolytic drugs will break down clots in a controlled manner, which would be most beneficial in this patient. Anticoagulant drugs are used to prevent or to decrease the formation of clots and may benefit this patient in the future but they will not treat a pre-existing clot. Hemostatic drugs are used to induce clotting and to stop hemorrhage which would not be appropriate in this patient. Hematinic drugs increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood, which would not help this patient.