orgo ch6
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
nucleophilic substituation reaction
electrophilic carbon and nucleophilic atom make new bond
leaving group
halogen or oxygen group
sn1 step
leaving group leaves, formation of carbocation is rate determining step, undergo rearrangement hydride shift or ring expansion, nucleophile attack electrophile carbon, if chiral center then pair of enantiomers form
product formation depends on stability of carbocation
late ts carbocation like product, early ts carbocation like reactant
inductive effect- stability of carbocation
electronic effect due to polarization of sigma bonds within molecule
hyperconjugation- stability of carbocation
sigma bonding electron of ch bond fill empty p orbital of e deficient c
resonance- carbocation stability
tertiary greater than secondary greater than primary benzyl
tertiary greater than secondary greater than primary allylc
rate determining step
formation of carbocation
solvolysis
solvent itself act as nucleophile
nuclephile, best nucleophile
electron donating, neg charge, large size, less steric hinderence
sn1 reaction
nucleophile substitution at carbon with 4 single bonds, weak bases are good leaving group
weak bases
stronger acid will have weak conjugate base
sn1 final product stereochem
formation of product with chiral center, which form a pair of enantiomers
carbocation rearrangment
alkyl carbocation undergo rearrangement to form stable carbocation
ring expansion
rearrangement to relieve ring strain
sn2 reactions
bimolecular reactions, one step reactions, break bond and forming bond happen at same time, inversion of configuration at electrophile carbon
leaving group for sn2 reaction
stronger base is better leaving group
nature of substrate for sn2
methyl, primary benzylic and allylic, secondary benzylic and allylic
base strength of sn2
stronger base has weaker conjugate acid
polarizability of sn2
large size nucleophiles are better than smaller
steric factors sn2
bulky nucleophiles disfavor sn2 reactions
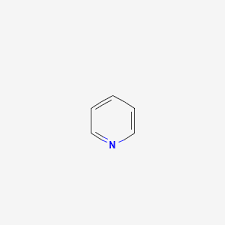
sn2 polar aprotic solvent
pyridine
sn2 polar aprotic solvent
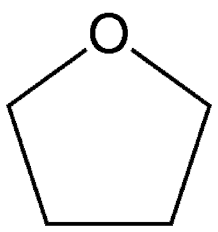
tetrahydrofuran