8. Management of Bronchial Asthma and Cough
1/47
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Define cough and list some of its features .
Protective reflex
Expulsion of respiratory secretions or foreign particles from air passage
Occurs due to stimulation of receptors in throat, respiratory passage/lungs
Useful (productive)/useless (non-productive)
Specific remedies (antibiotics)
Symptom/non-specific treatment
List the drug classifications that are used to treat cough.
Expectorants/mucokinetics
Antitussives/cough center suppressants
Adjuvant antitussives
List the 2 categories of expectorants/mucokinetics.
Bronchial secretion enhancers
Mucolytics
List the 2 categories of antitussives/cough center suppressants.
Opioids
Antihistamines
Name the category of drugs that comes under adjuvant antitussives.
Bronchodilators
Expectorants/Mucokinetics
List bronchial secretions enhancers.
Vasaka
Guaiphenesin
Sodium citrate
Potassium citrate
Potassium iodide
Ammonium chloride
Expectorants/Mucokinetics
List mucolytics.
Bromhexine
Acetylcysteine
Ambroxol
Antitussives/Cough Center Suppressants
List opioids.
Codeine
Pholcodeine
Dextromethorphan
Antitussives/Cough Center Suppressants
List antihistamines.
Chlorpheniramine
Promethazine
Diphenhydramine
Adjuvant Antitussives
List bronchodilators.
Salbutamol
Terbutaline
Salmeterol
Expectorants/Mucokinetics
How do expectorants work?
Increase bronchial secretions or reduce its viscosity, facilitating its removal by coughing
Expectorants/Mucokinetics - Bronchial Secretion Enhancers
Where do Vasaka and Guaiphenesin come from and what do they do?
Plants products
Enhance bronchial secretions
Expectorants/Mucokinetics - Bronchial Secretion Enhancers
Are Vasaka and Guaiphenesin used alone or in combination?
In combination with antitussives/antihistamines
Expectorants/Mucokinetics - Mucolytics
Describe the mechanism of action of bromohexine.
Potent mucolytic and mucokinetic
Capable of inducing thin, copious bronchial secretions
Breaks network of fibers in sputum
Useful if mucus plugs are present
Expectorants/Mucokinetics - Mucolytics
When should bromohexine NOT be used?
Dry cough
Expectorants/Mucokinetics - Mucolytics
List the adverse effects of bromohexine.
Rhinorrhea
Lacrimation
Gastric irritation
Antitussives
Describe the mechanisms of antitussives.
Act in CNS to raise threshold of cough center
Act peripherally in respiratory tract to reduce tussal impulses
Aim to control rather than eliminate cough
Antitussives
When should antitussives be used?
ONLY dry unproductive cough
Antitussives - Opioids
Describe codeine.
Antitussive
Opium alkaloid, like morphine
More selective for cough center
Suppresses cough for about 6 hours
Abuse liability is low (but present)
Other substitutes: pholcodeine, dihydrocodeine
Antitussives - Opioids
List the adverse effects of codeine.
Constipation
Respiratory depression (at high doses)
Drowsiness (at high doses)
Antitussives - Opioids
When is codeine contraindicated?
In asthmatics (worsening due to histamine release and build up of mucus)
Antitussives - Opioids
Describe dextromethorphan and its effectiveness.
Synthetic compound
As effective as codeine
Antitussives - Opioids
Describe noscapine and its mechanisms.
Naturally occurring opium alkaloid
Devoid of analgesic or dependence inducing properties
Minimum constipating effects
Popular cough suppressant
Can release histamine, produce bronchoconstriction in asthmatics (hence, contraindicated)
Antitussives - Antihistamines
Describe the use of antihistamines.
H1 receptor antagonists
Provide relief for cough due to antihistamine, sedative, and anticholinergic actions
Added to antitussive/expectorant formulations
Used for cough in respiratory allergic states
Adjuvant Antitussives - Bronchodilators
Describe what bronchodilators are used for.
Relieve cough in bronchial hyper-reactive patients (bronchospasm can induce/aggravate cough)
Improve effectiveness of cough in clearing secretions by increasing surface velocity of airflow during cough
Used ONLY when bronchoconstriction is present
Describe asthma, its symptoms, and mechanisms.
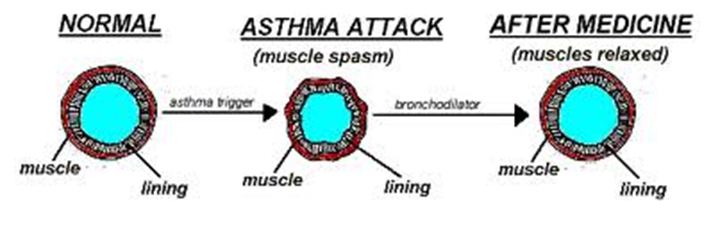
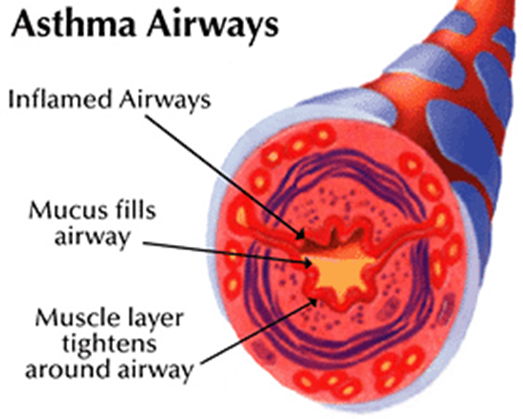
Hyper-responsiveness of tracheo-bronchial smooth muscles to a variety of stimuli
Symptoms: dyspnoea, wheezing, cough
Mast cells (lungs) and inflammatory cells release mediators like
histamine
TNF-α
prostaglandins
leukotriene
interleukins
These mediators constrict bronchial smooth muscle, mucosal edema, produce viscid secretions, resulting in reversible airway obstruction
List the classifications of drugs to treat asthma.
Bronchodilators
Corticosteroids
Mast Cell Stabilizers
Leukotriene modulators
Anti-IgE antibody
List the categories of bronchodilators.
Selective β2-agonists
Non-selective sympathomimetics
Anticholinergic
Bronchodilators
List selective β2-agonists.
Salbutamol (short-acting)
Terbutaline
Salmeterol (long-acting)
Bronchodilators
List non-selective sympathomimetics.
Epinephrine
Ephedrine
Isoprenaline (non-selective action, use has been declined)
Bronchodilators
List anticholinergics.
Ipratropium
Tiotropium
List the categories of corticosteroids.
Inhalational
Systemic
Corticosteroids
List inhalational corticosteroids.
Beclomethasone
Fluticasone
Budesonide
Corticosteroids
List systemic (oral) corticosteroids.
Prednisolone
Hydrocortisone
Prednisone
List mast cell stabilizers.
Sodium cromoglycate
Nedocromil (reserved for prophylactic use in chronic/seasonal asthma; ineffective in acute conditions
List leukotriene modulators.
Montelukast
Zafirlukast
List the anti-IgE antibody.
Omalizumab (monoclonal antibody)
Bronchodilators
Describe salbutamol/albuterol and their mechanisms.
Highly selective β2 agonist; cardiac side effects less prominent
Improves pulmonary function by relaxing bronchial smooth muscles, relieves asthmatic symptoms
Do not control disease process
Bronchodilators
Briefly describe salbutamol and terbutaline and how they can be administered.
Widely used
Short-acting
Oral/inhalational/SC/IM
When inhaled, produce bronchodilation in 5 mins that lasts up to 2-4 hours
Bronchodilators
Describe the mechanism of action of salbutamol.
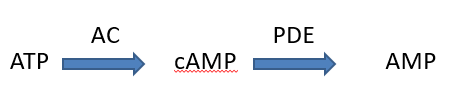
Activates β2 receptors present on airway smooth muscles; activates adenyl cyclase (AC), enhancing release of cAMP (relaxes smooth muscles)
They relax airway smooth muscles, inhibit release of chemical mediators (bronchoconstricting) from mast cells
(PDE - phosphodiesterase)

Bronchodilators
List the adverse effects of salbutamol.
Minimal when inhaled
Oral:
Tremors
Tachycardia
Restlessness
Nervousness
Ankle edema
Throat irritation
Continued use causes desensitization/down regulating of β2 receptors (diminished responsiveness)
Bronchodilators
Describe theophylline.
Used with β2 agonists
Narrow therapeutic angle = second choice in asthma
Bronchodilators
Describe the mechanism of theophylline. What is it used for?
Inhibits phosphodiesterase (PDE); PDE III (airway smooth muscles) and IV (eosinophils and mast cells)
Responsible for degradation of cAMP and cGMP
cAMP/cGMP levels get elevated = bronchodilation
Used in asthma, COPD, and dyspnea associated w/pulmonary edema that develops after congestive heart failure
Bronchodilators
List the adverse effects of theophylline.
Dose-dependent toxicity starts from upper part of therapeutic concentration range
GI: nausea and vomiting
CNS: agitation, tremors followed by seizure
CVS: arrythmia
Corticosteroids
Describe corticosteroids and their mechanism of action.
Powerful anti-inflammatory agents
Inhaled corticosteroids with β2 agonists are mainstay for chronic asthma
Inhibit the release of mediators (leukotriene, prostaglandins), enhance β2 receptor response
Leukotriene Inhibitors - Montelukast
Describe leukotriene inhibitors (LT) and their mechanisms of action.
Powerful mediators of inflammation
Stimulate bronchoconstriction, increase capillary permeability (leading to pulmonary edema), and stimulate mucus secretion
Montelukast and zafirlukast competitively block the stimulatory effects of LT on LT-receptors
Leukotriene Inhibitors - Montelukast
List the uses and side effects of LT inhibitors.
Prophylactic therapy of mild to moderate asthma as alternatives to inhaled corticosteroids
Safe drugs, produces few side effects like headache and rashes
Leukotriene Inhibitors - Montelukast
How is montelukast administered?
Once daily (advantage), 10mg (evening, usually)
Safe in children