Data Analysis for A Level Biology
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What does Standard Deviation (SD) measure?
It measures the spread (or dispersion) of data around the mean.
Why is Standard Deviation considered a better measure of dispersion than the Range?
SD uses all the data points, whereas the range only uses the highest and lowest values.
SD is less affected by anomalies (outliers) than the range.
SD reveals the spread around the mean, giving an indication of reliability.
When interpreting a graph, what conclusion should you draw if the error bars of two data sets overlap?
There is no significant difference between the means.
Any difference observed is likely due to chance.
(Therefore, you cannot claim that the independent variable caused the change).
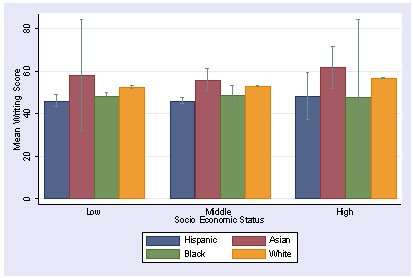
When interpreting a graph, what conclusion should you draw if the error bars do not overlap?
There is a significant difference between the means.
The difference is likely not due to chance.
(You can likely claim the independent variable had an effect).
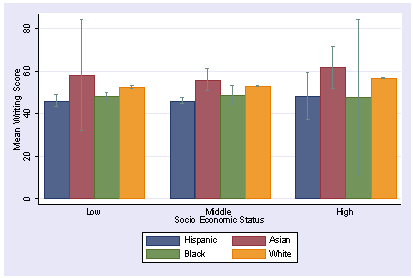
Which statistical test would you use to confirm if a difference between two means (with known SD) is significant?
The Student's t-test (unpaired if separate groups, paired if same individuals before/after).
Question 1 (Evaluate - The "Overlap" Trap) A student investigated the effect of fertilizer on plant height. Group A (Fertilizer): Mean height = 45cm (± 5cm SD). Group B (No Fertilizer): Mean height = 38cm (± 4cm SD). The student concludes that the fertilizer significantly increased plant growth. Evaluate this conclusion.
Calculation: Group A range is 40-50 (45 ± 5). Group B range is 34-42 (38 ± 4).
Observation: The error bars (spread) overlap (between 40 and 42).
Conclusion: The student is incorrect. Because the bars overlap, there is likely no significant difference between the means. The difference in height could be due to chance.
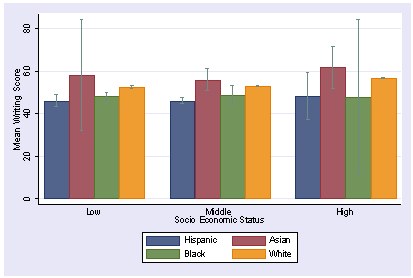
Question 2 (Explain) The standard deviation for the rate of reaction at 60°C is much larger than the standard deviation at 30°C. Explain what this indicates about the data at 60°C.
The data at 60°C is more spread out / less consistent around the mean.
This suggests the results at 60°C are less repeatable / less reliable.
(This might be due to the difficulty of measuring fast rates or rapid denaturation).
Question 3 (Suggest) A researcher presents mean values for blood glucose levels but does not include standard deviation or range. Suggest why this makes it difficult to evaluate their results.
We cannot see the spread of the data.
We cannot identify if there were any anomalies (outliers).
We cannot determine if the differences between the means are significant (cannot check for overlap).
Question 4 (Maths Skill) The formula for Standard Deviation is provided in the exam: see below . Explain what the term (n - 1) represents and why it is used
s = \sqrt{\frac{\sum(x - \bar{x})^2}{n - 1}}
n represents the sample size (number of data points).
(n - 1) represents the degrees of freedom.
It is used to calculate the variance for a sample (rather than a whole population).
Question 5 (Application) You are designing an experiment to measure the effect of caffeine on heart rate. You plan to use the t-test to analyse your results. What condition must your data meet to use a t-test?
The data must be continuous (heart rate is a continuous variable).
The data should be normally distributed.
You are comparing two means (e.g., Mean Heart Rate with Caffeine vs Mean Heart Rate without).