L6 Cardiology + Renal Pharm
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Hypertension:
Goal
Risk factor
Symptoms
Alterations
SBP <130
Most prevalent + modifiable risk factor for CVD
Often asymptomatic til severe
Alterations
Nervous system
RAAS
Cardiovascular (vessels)
Firstline HTN Treatment
Thiazide-type diuretics
Calcium channel blockers
ACE inhibitors
ARBs
Signs of fluid overload?
Peripheral edema
SOB, Crackles in lungs, Diminished breath sounds
Elevated BP
JVD
Signs of increased ICP?
HA, N/Projectile vomiting
Agitation → Confusion → Drowsiness → Coma
Vision changes
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS)
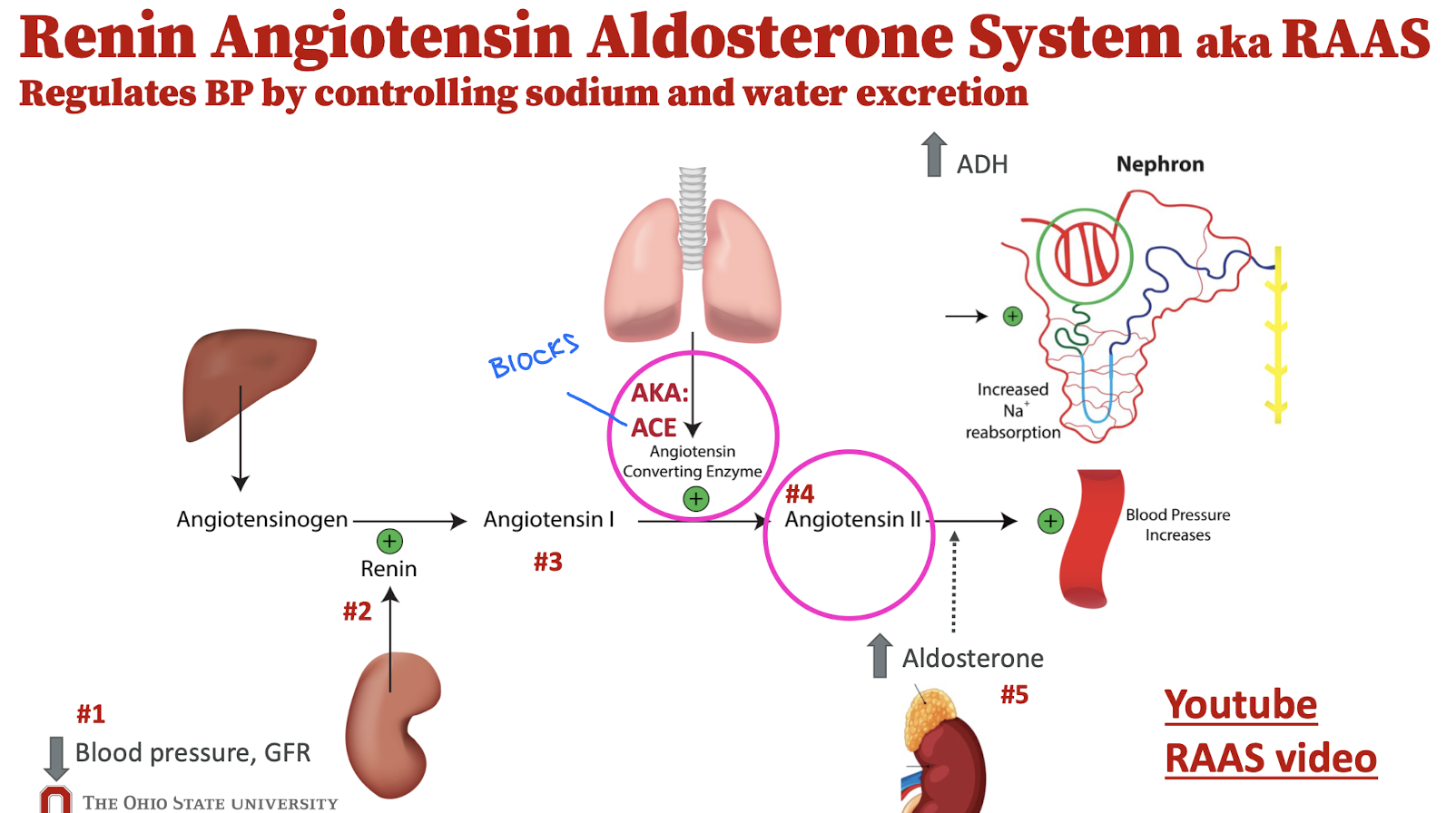
Lisinopril:
Pharm class
Indication
MOA
Therapeutic effects
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
HTN, HF → Decrease mortality = Cardioprotective
Inhibits angiotensin I from converting into angiotensin II → Reduced aldosterone secretion → Less salt + water reabsorbed
Decrease BP
Lisinopril:
Adverse effects
Contraindications
Black box
AE
AKI
Hyperkalemia
Dry cough + Angioedema
CI
Hx Angioedema
Significant renal disease
Concurrent use with NSAIDs, some diuretics, potassium supplements
Fetal toxicity → Contraindicated in pregnancy
Lisinopril:
Pt. Education
Nursing considerations
Pt. Edu
Caution w/ potassium supplements + NSAIDS
Monitor dry cough
NC
Monitor → BP + Potassium + Kidney function
Losartan:
Pharm class
Indication
MOA
Therapeutic effects
Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker (ARB)
HTN + CKD
Blocks angiotensin II → Reduces aldosterone secretion → Less salt + water reabsorbed
Decrease BP
Losartan:
Adverse effects
Contraindications
Black box
AE
AKI
Hyperkalemia
CI
Concurrent use with NSAIDs
CKD → End stages
Fetal toxicity → CI in pregnancy
Losartan:
Pt. Education
Nursing considerations
Caution w/ Potassium supplements
Monitor → BP + Potassium + Kidney function
A client newly prescribed lisinopril reports a persistent dry cough. Which action should the nurse anticipate?
Switch to an ARB such as losartan
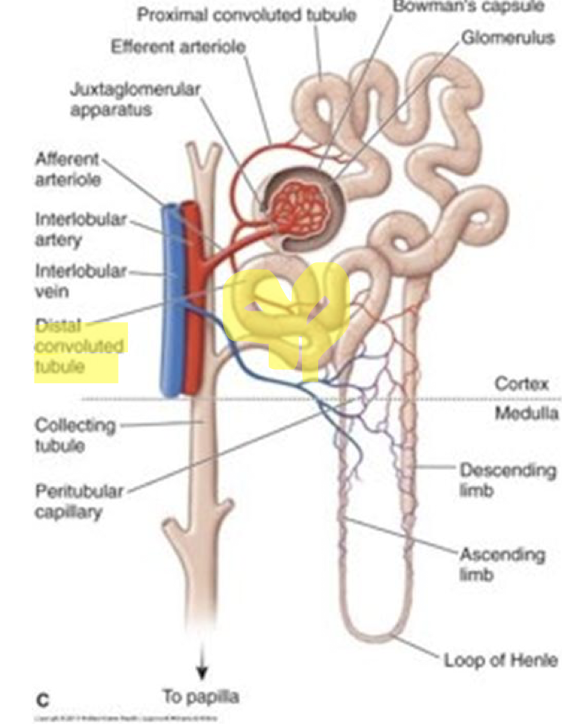
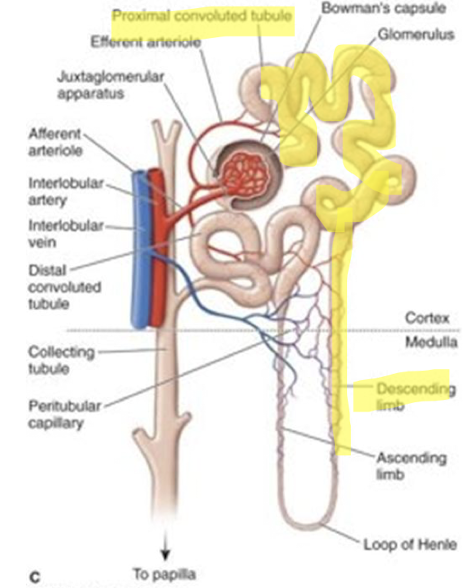
Nephron structure?
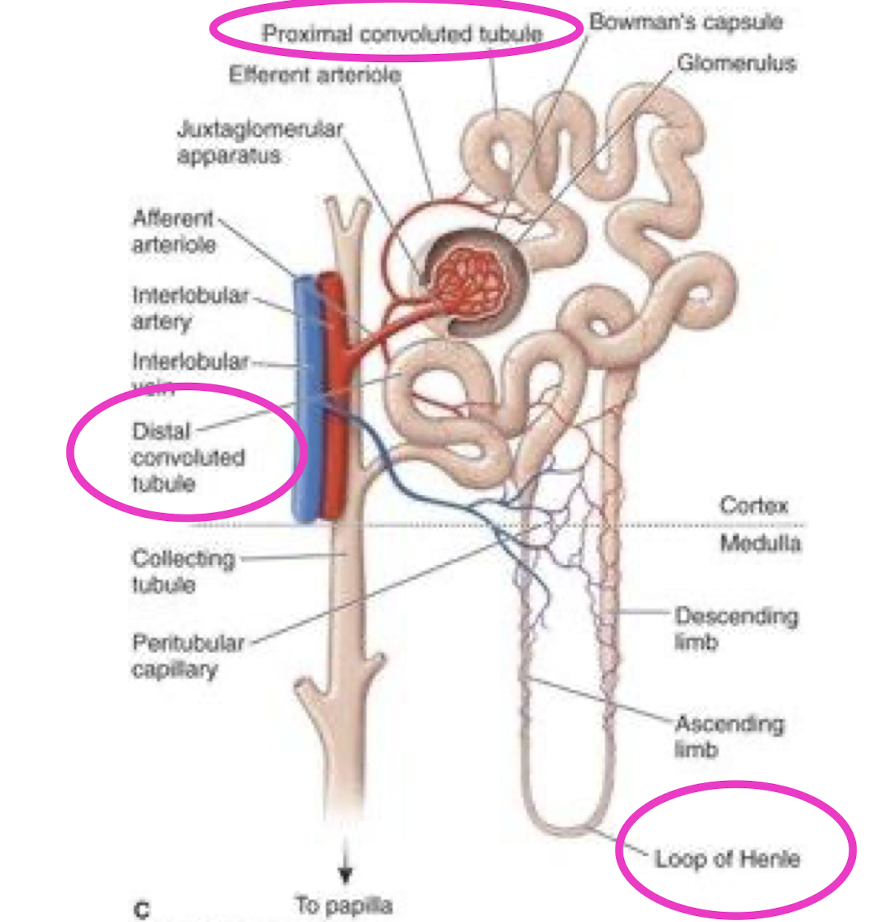
Furosemide (Lasix):
Pharm class
Indication
MOA
Therapeutic effects
Loop diuretic → Strongest
Edema + Fluid overload + HF + Cirrhosis + Renal disease
Inhibits reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the loop of henle + proximal + distal tubule
Diuresis = Getting rid of fluid
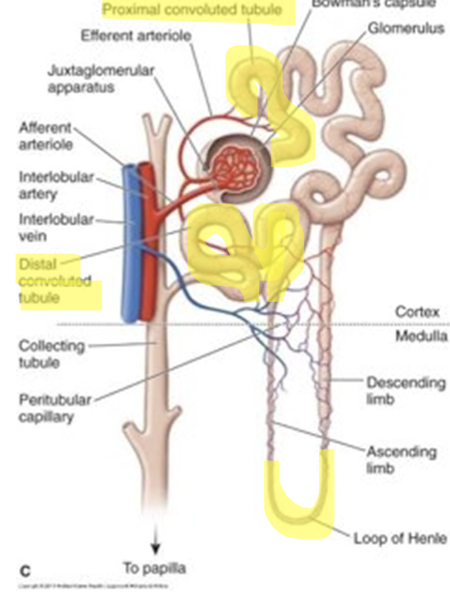
Furosemide:
Adverse effects
Contraindications
Black box
AE
AKI
Fluid + electrolyte loss → HypoK/Ca/Mg
Cross reactive w/ sulfa antibiotics
Ototoxicity → Hearing changes
CI
Dehydration
BPH → May cause urinary retention
Sulfa allergy
Potent diuretic → Can lead to significant fluid and electrolyte loss
Furosemide:
Pt. Education
Nursing consideration
Pt. Edu
Daily weight → Report 2lb change
Stay hydrated
Signs of electrolyte changes → Muscle weakness/cramps
NC
Intake / Output → More urine = sign it is working
Daily weight
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ):
Pharm class
Indication
MOA
TE
Thiazide diuretic → Not as potent as furosemide
Edema + Volume overload (HF) + HTN → 1st line
Inhibits sodium reabsorption in distal tubules → Increased excretion of sodium + water + potassium
Diuresis
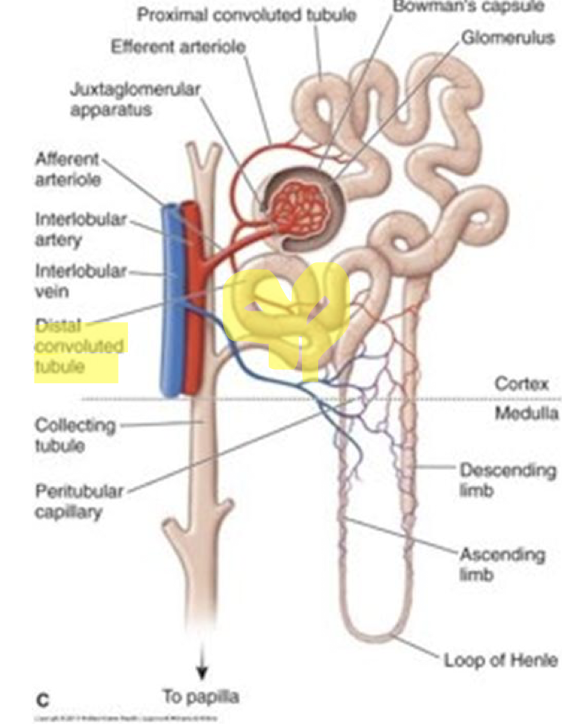
Hydrochlorothiazide:
Adverse effects
Contraindications
AE
Hypo K/Mg/Na + Hyper Ca
Gout → Hyperuricemia
Photosensitivity
CI
Addison’s disease
Cirrhosis → Hyponatremia
Renal disease
Hydrochlorothiazide:
Pt. education
Nursing considerations
Pt. Edu
Daily weight → Report 2lb change
May require potassium supplements
UV exposure
NC
Monitor → BP + K + Renal function
Intake / Output
Metolazone:
Pharm class
Indication
MOA
TE
Thiazide-related diuretic
Edema + Fluid overload (HF / Renal disease)
Given 30-60 min before lasix for “Diuretic resistance”
Inhibits sodium reabsorption in distal tubules → Increased sodium + water + potassium excretion
Diuresis
Metolazone:
Adverse effects
Contraindications
AE
Hypo K/Mg/Na + Hyper Ca
Orthostatic hypotension
CI
Anuria
Severe liver/renal disease
Addison’s disease
Gout
Metolazone:
Pt. Education
Nursing considerations
Pt. Edu
Daily weight → Report 2lb change
Electrolyte changes
May need potassium supplements
NC
Monitor → BP + Electrolytes (K + Uric acid) + Renal function
Intake / Output
Which of the following have a known side effect of hypokalemia?
a. furosemide
b. hydrochlorothiazide
c. lisinopril
d. metolazone
e. losartan
a. furosemide
b. hydrochlorothiazide
d. metolazone
Spironolactone:
Pharm class
Indications
MOA
TE
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist → Blocks aldosterone + Potassium sparing diuretic
Ascites from cirrhosis + HF fluid overload + Acne
Blocks aldosterone in distal tubule → Increases sodium + water excretion
Diuresis
Spironolactone:
Adverse effects
Contraindications
AE
Gynecomastia → “gyno” hormonal
Hyperkalemia
CI
Hyperkalemia
Addison’s disease
Dehydration
Renal disease
Spironolactone:
Pt. Education
Nursing considerations
Pt. Edu
Caution w/ high potassium foods + salt substitutes
Monitor electrolyte changes
Monitor → BP + Weight + K + Kidney function
Mannitol:
Pharm class
Indications
MOA
Osmotic diuretic
Reduction of ICP + Reduction of increased intraocular pressure (IOP)
Increases osmotic pressure in blood + Increase Osmolality and tonicity of blood
Draws water out of blood
Draws water out of eye
Mannitol:
Adverse effects
Contraindications
AE
Dehydration
Hypo K/Na
Renal injury
CI
Anuria
Severe hypovolemia + pulmonary edema
Renal disease
Mannitol:
Pt. Education
Nursing considerations
Pt. Edu
IV only
Requires significant monitoring
Accurate I/O’s
NC
Kidney function
Serum osmolality
Tele + Pulse Ox monitoring
I/O’s
ICP → Neuro status
Which medication is most likely to cause ototoxicity if given rapidly IV or at high doses?
Furosemide
Which conditions/indications are appropriate for spironolactone? (Select all that apply.)
A. Ascites from cirrhosis
B. Heart failure fluid overload
C. Addison’s disease with fluid overload
D. Acne
E. Acute pulmonary edema requiring rapid diuresis
A. Ascites from cirrhosis
B. Heart failure fluid overload
D. Acne