Neuro final exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:28 PM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
list the domains of cognition
attention, memory, executive functions, social cognition, perception, sensory/motor control
A M EF SC P SMC
A M EF SC P SMC
2
New cards
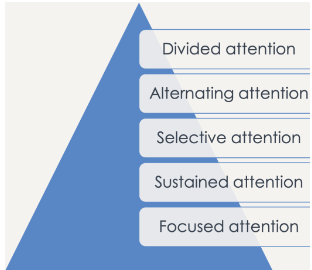
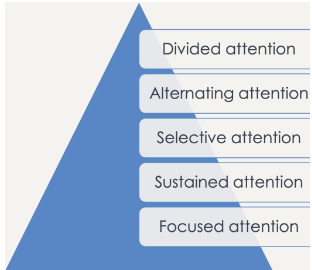
name the divisions of attention
focused, sustained, selective, alternating, divided
3
New cards
what is focused attention?
general ability to notice stimulus
4
New cards
what is sustained attention?
ability to maintain attention over time
5
New cards
what is alternating attention?
ability to focus on one thing and filter out and ignore others
6
New cards
what is divided attention?
ability to focus on two tasks at the same time (multitasking)
7
New cards
what are the divisions of memory?
short-term, long-term, working memory
8
New cards
what is working memory?
type of memory where information is manipulated from short-term memory
lasts same length of time as short-term memory
lasts same length of time as short-term memory
9
New cards
what is short-term memory?
holding space for information to attach recall to it and put it in long-term memory
small amount of information for a short-term
small amount of information for a short-term
10
New cards
what is long-term memory?
stored information for long period of time
11
New cards
what are the types of long term memory?
declarative and nondeclarative
12
New cards
what are declarative memories and their types?
have to work to remember, consciously recall information
episodic: events
semantic: facts
episodic: events
semantic: facts
13
New cards
what are nondeclarative memories and their types?
don’t have to consciously recall, just in your memory
procedural: how to do things like riding a bike
more likely to retain these memories
procedural: how to do things like riding a bike
more likely to retain these memories
14
New cards
what is ischemia?
reduced blood supply to an organ
15
New cards
what is an infarct?
small area of dead tissue
16
New cards
what is an artery?
mechanism that carries oxygenated blood to the brain
divided into arterials and capillaries
divided into arterials and capillaries
17
New cards
what is a vein?
carries deoxygenated blood back to heart
same branching system as arteries- divides into veinals and capillaries
same branching system as arteries- divides into veinals and capillaries
18
New cards
what are capillaries?
connect arteries to veins
smallest dimension of branch where blood moves slowly and allows nutrient exchange
terminal extension
smallest dimension of branch where blood moves slowly and allows nutrient exchange
terminal extension
19
New cards
the carotid system divides into…
external and internal carotid arteries
internal divides into anterior and middle cerebral arteries
internal divides into anterior and middle cerebral arteries
20
New cards
the vertebral basilar system divides into…
posterior cerebral arteries
21
New cards
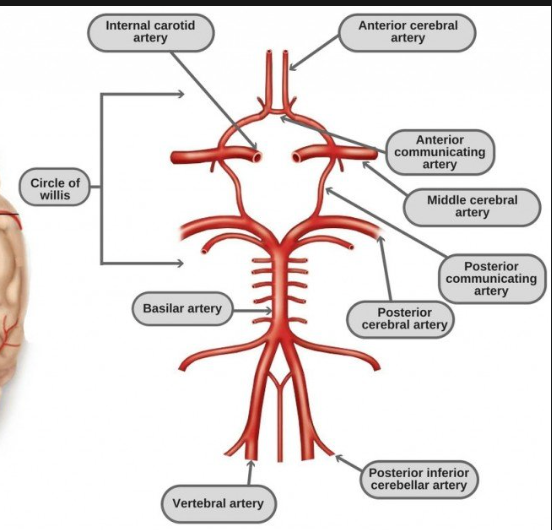
what is the circle of willis?
protective mechanism of branches of blood supply in the brain that allows alternate circulation if there’s injury
22
New cards
what are the three categories of branches of the circle of willis?
internal carotid
basilar
connection
need to be able to label circle of willis
basilar
connection
need to be able to label circle of willis
23
New cards
what is an ischemic penumbra?
area that surrounds infarct
24
New cards
what are the two major artery systems that carry blood to the brain?
carotid artery system and vertebral basilar system
25
New cards
describe the pathway of the carotid system.
ascends both sides of neck, when it reaches the jawline, it splits into two branches- the internal and external carotid arteries
26
New cards
what does the internal branch of the carotid system supply blood to?
large part of brain
enters skull and branches in complex way- anteriorly and middle
enters skull and branches in complex way- anteriorly and middle
27
New cards
the anterior cerebral artery is a branch of the…
internal carotid branch of the carotid system
28
New cards
the vertebral basilar system provides blood supply to…
posterior circulation system of brain and brainstem
29
New cards
describe the pathway of the vertebral basilar system.
arises near level of subclavian arteries and ascends through upper cervical vertebra and eventually merges into one artery (basilar artery), then it branches into posterior cerebral artery
30
New cards
the posterior cerebral artery is a branch of the…
vertebral basilar system
31
New cards
draw and label Circle of Willis
32
New cards
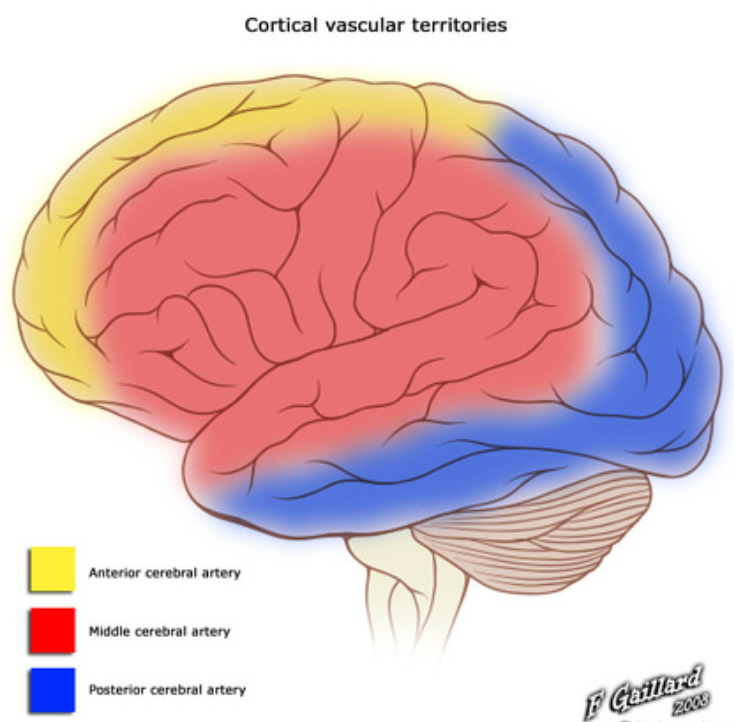
where does the anterior cerebral artery supply in the brain?
orbital and medial cortical surfaces of prefrontal, frontal, parietal lobes
anterior 80% of corpus callosum and caudate head and putamen
anterior 80% of corpus callosum and caudate head and putamen
33
New cards
where does the middle cerebral arteries supply in the brain?
lateral cortical surface of each hemisphere, internal capsule
emerge through Sylvian fissure
emerge through Sylvian fissure
34
New cards
what are the signs and deficits associated with an issue with the anterior cerebral artery?
loss of somatic sensory and paralysis of contralateral leg and foot
mental impairments: lack of spontaneity, easy distraction, problem solving deficits, indecisiveness, altered personality
mental impairments: lack of spontaneity, easy distraction, problem solving deficits, indecisiveness, altered personality
35
New cards
what are the signs and deficits associated with an issue with the middle cerebral artery?
contralateral hemiplegia and hemianesthesia with spared leg and foot
homonymous hemianopsia
aphasia (dominant)
visual-spatial deficit and constructional apraxia (nondominant)
homonymous hemianopsia
aphasia (dominant)
visual-spatial deficit and constructional apraxia (nondominant)
36
New cards
where does the vertebral arteries supply in the brain?
medulla, cerebellum, choroid plexus of fourth ventricle
37
New cards
where does the basilar artery supply in the brain?
lateral pons, cerebellum, cranial nerves
38
New cards
what are the signs and deficits associated with an issue with the vertebral arteries?
contralateral hemiplegia
loss of discriminative touch, temperature, pain sensation from ipsilateral face
loss of pain and temperature from contralateral limbs
ipsilateral ataxia
vertigo, nystagmus and vomiting
dysphagia and dysarthria
loss of discriminative touch, temperature, pain sensation from ipsilateral face
loss of pain and temperature from contralateral limbs
ipsilateral ataxia
vertigo, nystagmus and vomiting
dysphagia and dysarthria
39
New cards
what are the signs and deficits associated with an issue with the basilar artery?
hemiplegia, ataxia, loss of facial sensation, facial paralysis, deafness and nystagmus, vertigo, vomiting
40
New cards
what is collateral circulation?
provision of alternative vascular supply
occurs where vascular supplies overlap
important for recovery
occurs where vascular supplies overlap
important for recovery
41
New cards
the anterior communicating artery connects the…
two anterior cerebral arteries
42
New cards
the posterior communicating artery connects the…
carotid and posterior systems
43
New cards
what are the watershed zones?
points of anastomoses where capillaries join with other systems through terminal arteries
blood supply from at least two different groups of arteries
blood supply from at least two different groups of arteries
44
New cards
why are watershed zones vulnerable to damage?
farthest away from main arterial supply, small capillaries, terminal end of each system, vulnerable to reduction in perfusion from main arterial supply
small terminating capillaries are where lack of perfusion will begin first
small terminating capillaries are where lack of perfusion will begin first
45
New cards
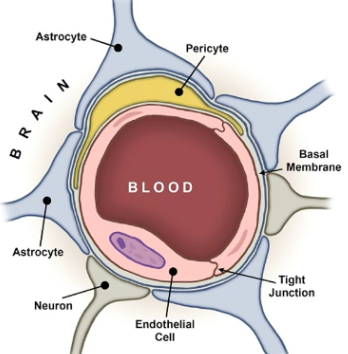
what is the blood brain barrier?
mechanism that regulates arterial permeability CNS
lines of defense that allows certain elements through blood supply into brain
keeps out harmful substances and only allows lipid soluble substances across
lines of defense that allows certain elements through blood supply into brain
keeps out harmful substances and only allows lipid soluble substances across
46
New cards
what are the two components that regulate arterial permeability?
capillaries are lined by tightly packed endothelial cells
endothelial membrane is surrounded by end feet of astrocytes outside of capillary wall
endothelial membrane is surrounded by end feet of astrocytes outside of capillary wall
47
New cards
what is cerebrovascular disease?
generic term for any disease that affects blood vessels in the brain
caused by hypertension and atherosclerosis
caused by hypertension and atherosclerosis
48
New cards
what is cerebrovascular accident?
when diseases processes in the cerebrovascular system intensify to an occlusion or hemorrhage
49
New cards
what is a transient ischemic attack?
mini stroke that has no lasting issues and resolves quickly
causes extremely elevated risk for stroke
causes extremely elevated risk for stroke
50
New cards
what are the signs of cerebrovascular accident?
sudden onset of weakness or numbness on one side
sudden inability to speak or understand others
sudden difficulty seeing with one or both eyes
sudden loss of balance and/or dizziness
headache with cause
sudden inability to speak or understand others
sudden difficulty seeing with one or both eyes
sudden loss of balance and/or dizziness
headache with cause
51
New cards
what is atherosclerosis?
disease process resulting in deposit of fat (plaques) in walls of arteries
constricts amount and ease of blood flow
constricts amount and ease of blood flow
52
New cards
what is hypertension?
disease process resulting in chronically elevated blood pressure
puts pressure on artery walls and may lead to rupture
puts pressure on artery walls and may lead to rupture
53
New cards
what is an aneurysm?
blood vessel rupture caused by weakness or thinness in wall of blood vessel
54
New cards
what is arteriovenous malformation?
congenital tangle of abnormal blood vessels
vulnerable to developing aneurysms
vulnerable to developing aneurysms
55
New cards
what are the different types of CVAs?
occlusive (blockage), hemorrhage (bleeding) and external pressure
56
New cards
what are the two types of occlusive CVAs?
thrombotic: fixed blot
embolic: traveling clot
embolic: traveling clot
57
New cards
what are the two types of hemorrhagic CVAs?
aneurysm and AVM
58
New cards
what can cause external pressure CVAs?
tumor causes pressure on arteries
intracranial pressure from brain injury inside brain that causes blood vessels to collapse or occlude
intracranial pressure from brain injury inside brain that causes blood vessels to collapse or occlude
59
New cards
how does the brain process and comprehend auditory input?
primary auditory cortex → left or right side → planum temporale and planum polare → ventral and dorsal streams → Broca’s area
signal begins in primary auditory cortex & decides where info needs to go in the PAC to be further processed (left part of PAC phonology & right part pitch)
signal is then sent to planum temporale (processes semantics and attaches meaning) & planum polare (might be acoustic analysis but don’t know for sure)
syntactic processing also occurs across entirety of superior temporal gyrus
info is then transported to frontal lobe (Broca’s area) through the ventral and dorsal streams
complex syntactic processing and working memory in Broca’s area
signal begins in primary auditory cortex & decides where info needs to go in the PAC to be further processed (left part of PAC phonology & right part pitch)
signal is then sent to planum temporale (processes semantics and attaches meaning) & planum polare (might be acoustic analysis but don’t know for sure)
syntactic processing also occurs across entirety of superior temporal gyrus
info is then transported to frontal lobe (Broca’s area) through the ventral and dorsal streams
complex syntactic processing and working memory in Broca’s area
60
New cards
what is another name for Wernicke’s area?
planum temporale
61
New cards
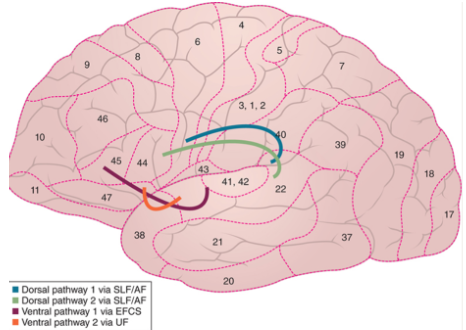
what are the two auditory processing pathways that connect the temporal lobe to the frontal lobe?
ventral (2 pathways) & dorsal (2 pathways)
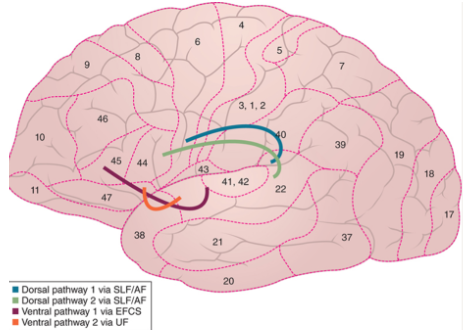
62
New cards
where does the 1st ventral auditory processing pathway connect?
superior temporal gyrus to pars triangularis
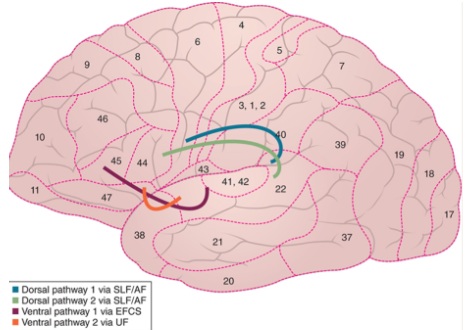
63
New cards
where does the 2nd ventral auditory processing pathway connect?
anterior superior temporal gyrus to frontal operculum (covering of insula)
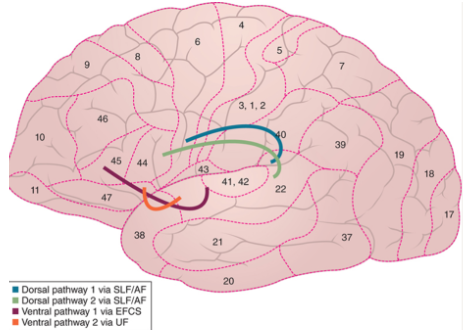
64
New cards
where does the 1st dorsal auditory processing pathway connect?
Wernicke’s area to premotor cortex
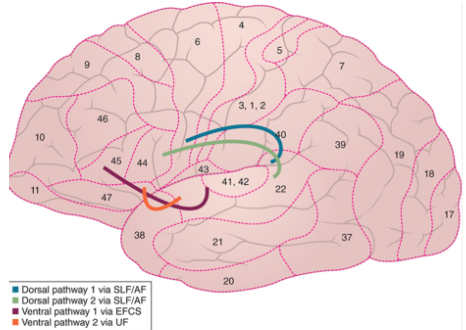
65
New cards
where does the 2nd dorsal auditory processing pathway connect?
Wernicke’s area to pars opercularis
66
New cards
the superior temporal gyrus is highly connected to the ____________ and why is this important?
inferior frontal gyrus
explains that these areas of the brain are highly specific for language
explains that these areas of the brain are highly specific for language
67
New cards
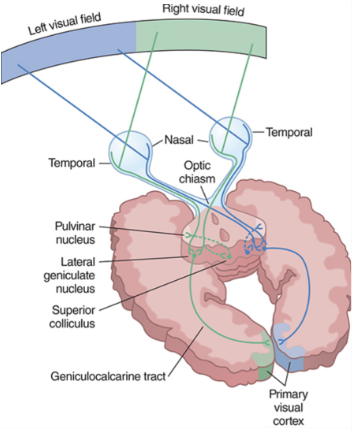
how does the brain process and comprehend visual input?
eye → retina → optic nerve → optic chiasm → thalamus → geniculocalcarine tract → primary visual cortex → dorsal and ventral streams
eye gathers written stimuli and passes it on to visual pathways in retina
info from retina is passed down optic nerve to level of optic chiasm where the information crosses
info then travels to thalamus and the geniculocalcarine tract carries it from thalamus to primary visual cortex where it is divided into two streams: dorsal and ventral
dorsal stream processes where information and sends it to inferior parietal lobe and superior occipital lobe
ventral stream processes what information and sends it to inferior occipital lobe and inferior and posterior temporal lobes
eye gathers written stimuli and passes it on to visual pathways in retina
info from retina is passed down optic nerve to level of optic chiasm where the information crosses
info then travels to thalamus and the geniculocalcarine tract carries it from thalamus to primary visual cortex where it is divided into two streams: dorsal and ventral
dorsal stream processes where information and sends it to inferior parietal lobe and superior occipital lobe
ventral stream processes what information and sends it to inferior occipital lobe and inferior and posterior temporal lobes
68
New cards
The left visual field is processed in the ________ cerebral cortex.
right
69
New cards
where does the dorsal visual processing pathway connect?
primary visual cortex to superior occipital lobe and inferior parietal lobe
70
New cards
where does the ventral visual processing pathway connect?
primary visual cortex to inferior occipital lobe and posterior and inferior temporal lobes
71
New cards
what are the three left hemisphere reading systems?
parietotemporal, occipitotemporal, anterior
72
New cards
what is the function of the parietotemporal left hemisphere reading system?
word analysis (decoding at phoneme level) and comprehension of written and spoken language
73
New cards
what are the associated anatomic locations of the parietotemporal left hemisphere reading system?
angular gyrus, supramarginal gyrus, posterior portion of superior temporal lobe
74
New cards
what is the function of the occipitotemporal left hemisphere reading system?
visual word-form, reading just from the form of the word
75
New cards
what are the associated anatomic locations of the occipitotemporal left hemisphere reading system?
left inferior occipital area, left inferior-posterior temporal area, fusiform gyrus
76
New cards
what is the function of the anterior left hemisphere reading system?
word analysis in spoken language and articulation, silent reading, decoding infrequently encountered words
77
New cards
what are the associated anatomic locations of the anterior left hemisphere reading system?
Broca’s area, premotor areas
78
New cards
explain the oral language production pathway
prefrontal cortex → Broca’s area → SMA → primary motor cortex → UMN → LMN → muscles of speech sound production
prefrontal cortex makes the decision
prefrontal cortex makes the decision
79
New cards
what are the functions of Broca’s area?
speech motor/articulation, phonological processing, complex syntactic processing, working memory, cognition
sm/a pp csp wm c
sm/a pp csp wm c
80
New cards
what are the parts of Broca’s area?
pars triangularis and pars opercularis
81
New cards
how does the brain produce written language?
prefrontal cortex → Broca’s area → premotor cortex → primary motor cortex →UMN, LMN → muscles of hand
left superior parietal lobe provides visuospatial information as the info travels down the UMN pathway
prefrontal cortex makes decision to write, Broca’s area encodes language
left superior parietal lobe provides visuospatial information as the info travels down the UMN pathway
prefrontal cortex makes decision to write, Broca’s area encodes language
82
New cards
what are the four stages of normal swallowing?
oral preparatory, oral, pharyngeal, esophageal
83
New cards
what happens during the oral preparatory stage of normal swallowing?
bolus is formed, mostly mastication with saliva, oral breathing altered, lips sealed
voluntary
voluntary
84
New cards
what happens during the oral stage of normal swallowing?
bolus movement- bolus moves from on tongue and tongue moves it posteriorly, maintains nasal breathing, lips sealed
voluntary
voluntary
85
New cards
what happens during the pharyngeal stage of normal swallowing?
1. bolus makes contact with faucial pillars
2. soft palate elevates
3. VF adduct and close opening to trachea
4. respiration pauses
5. larynx elevates and moves forward
6. epiglottis lowers and covers VF
7. bolus goes down pharynx into esophagus
8. upper esophageal sphincter relaxes
involuntary
86
New cards
what happens during the esophageal stage of normal swallowing?
lower esophageal sphincter relaxes and bolus goes into stomach
peristalsis: smooth muscle movement wave that is meant to push bolus down into stomach
involuntary
peristalsis: smooth muscle movement wave that is meant to push bolus down into stomach
involuntary
87
New cards
what are the nerves involved with the oral preparatory stage?
trigeminal V: chewing
glossopharyngeal IX: gland
facial VII: gland
glossopharyngeal IX: gland
facial VII: gland
88
New cards
what are the nerves involved with the oral stage?
facial VII: labial seal, taste
hypoglossal XII: anterior to posterior bolus movement
hypoglossal XII: anterior to posterior bolus movement
89
New cards
what are the nerves involved with the pharyngeal stage?
vagus X: soft palate closure, laryngeal elevation
facial VII: laryngeal elevation
trigeminal V: laryngeal, velar closure, pharyngeal constriction
hypoglossal XII: laryngeal elevation
facial VII: laryngeal elevation
trigeminal V: laryngeal, velar closure, pharyngeal constriction
hypoglossal XII: laryngeal elevation
90
New cards
what are the nerves involved with the esophageal stage?
vagus X: upper esophageal sphincter control, esophageal peristalsis
91
New cards
what are the two brainstem nuclei needed for swallowing?
nucleus tractus solitarius and nucleus ambiguous
92
New cards
what does the nucleus tractus solitarius do in swallowing?
sensory swallow center
taste, touch, respiratory, cardiovascular input
taste, touch, respiratory, cardiovascular input
93
New cards
what does the nucleus ambiguous do in swallowing?
motor swallow center
innervates muscles
innervates muscles
94
New cards
what are the structures in the cortical and subcortical sensory pathway for swallowing?
NTS → pons → hypothalamus → thalamus → primary sensory cortex
95
New cards
what are the structures in the cortical and subcortical motor pathway for swallowing?
inferior primary motor cortex → substantia nigra → reticular formation → medulla and NA
96
New cards
what are the support areas for the subcortical and cortical sensory and motor pathway for swallowing?
insula: mediate motor and sensory info
anterior cingulate cortex: attention
premotor cortex: motor planning
thalamus, basal ganglia: sensory info
anterior cingulate cortex: attention
premotor cortex: motor planning
thalamus, basal ganglia: sensory info
97
New cards
what is aspiration?
when bolus penetrates airway below level of vocal cords and enters trachea
98
New cards
what are the clinical indicators of risk for aspiration?
dysphonia, dysarthria, abnormal gag reflex, abnormal volitional cough, cough after swallow, voice change after swallow
99
New cards
what type of information does the dorsal visual processing pathway process?
where
100
New cards
what type of information does the ventral visual processing pathway process?
what