human transport
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
advantages of a single circulatory system :
less complex
disadvantages of a single circulatory system :
lower delivery rate because of lower pressure
organism moves slower
advantages of a double circulatory system :
higher pressure so that blood can pump further
faster blood flow
description of a insects circulatory system :
no blood
open circulatory system
haemolymph pumped by heart, diffuses through short channels to the haemocoel, when heart relaxes, blood is sucked back through the ostia
slow metabolic rate
high surface area to volume ratio
transports molecules e.g. hormones, nutrients
what is heamolymph?
fluid equivalent to blood without red blood cells and haemoglobin
What is haemocoel?
the primary body cavity in insects that fills with circulatory fluid
description of a fish’s circulatory system :
single circulatory system
countercurrent system with blood
higher metabolic rate
large surface area to volume ratio
transports molecules e.g. hormones, enzymes
description of a human circulatory system :
molecules transported through the blood
double circulatory system
small surface area to volume ratio
what is a double circulatory system?
blood flows through the heart twice per heart beat
why do fish have a single circulatory system?
don’t have to pump blood as far
don’t have to fight against gravity
what is a single circulatory system?
the blood is contained within blood vessels
what is a partial double circulation?
oxygenated blood isn’t completely separate
ventricles and aorta not separate
blood still passes through the heart twice per heart beat
why is a partial double circulatory system less effective than a double circulatory system?
oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is mixed
lower saturation of oxygen in blood
lower pressure
why do larger organisms need a circulatory system?
higher metabolic rate - need a more rapid supply
small SA : Vol ratio - diffusion doesn’t supply sufficient oxygen
what do elastic fibres do in blood vessels?
stretch and recoil
what does smooth muscle do in blood vessels?
contract and relax with the beat of the heart changing the size of the lumen
what does collagen in blood vessels do?
provide structural support maintaining shape and volume
features of arteries :
less muscle more elastin - can pulse to move blood
narrow lumen - creates high pressure
high collagen to prevent rupture
features of veins :
valves - prevent back flow of blood
no vein pulses because blood pressure is low
wide lumen - to move blood quickly back to heart
little smooth muscle - does not need to contract
features of a venule :
no elastin or smooth muscle
features of an arteriole :
more muscle less elastin - helps pulse surges maintain high blood pressure
features of a capillary :
one cell thick - more efficient diffusion to deliver oxygen
thin epithelium tissue
gaps in capillary wall (endothelium) for larger substances
large surface area
what are the two types of circulatory systems involved in a double circulatory system?
systemic and pulmonary
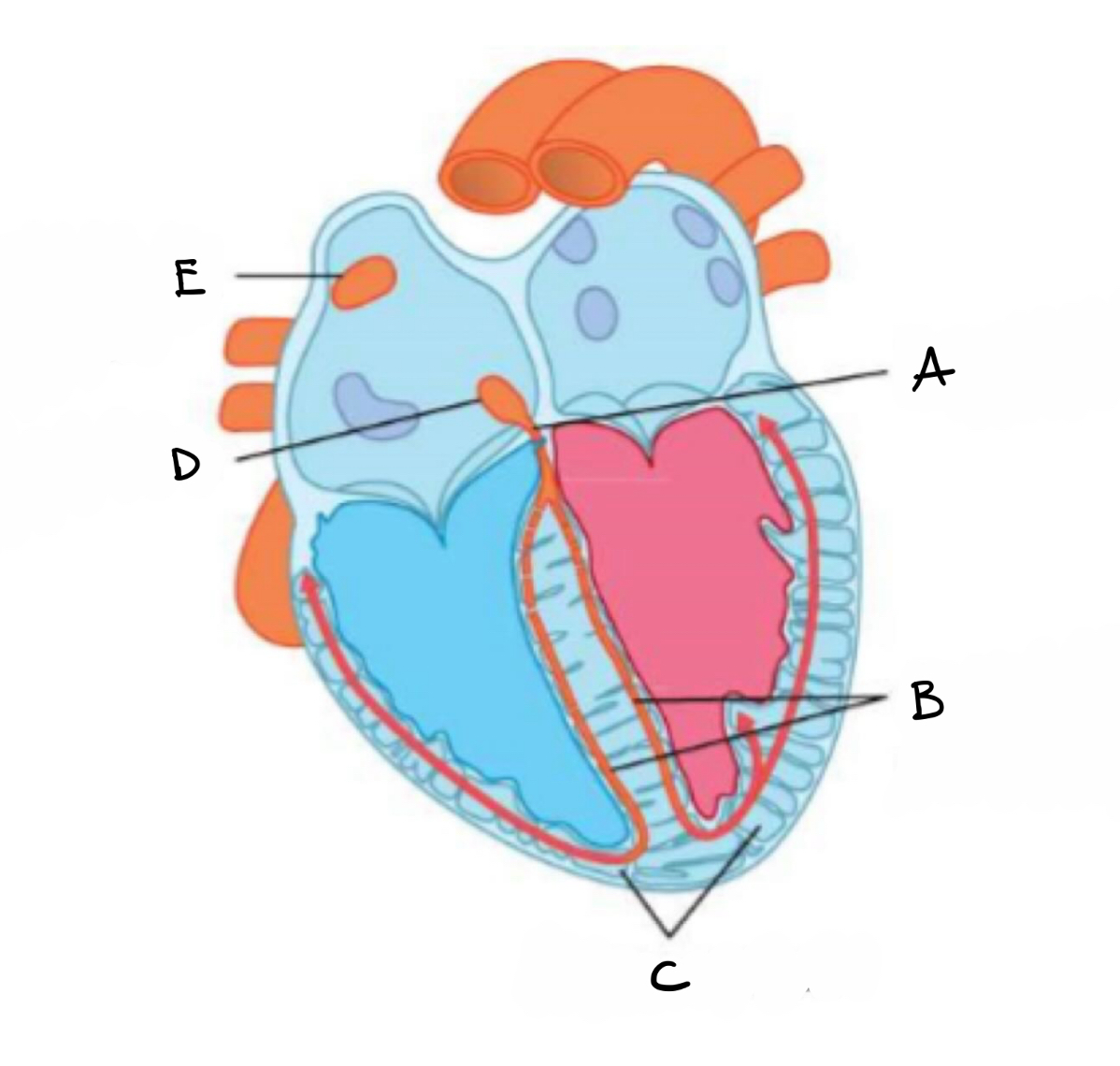
what is A?
bundle of his
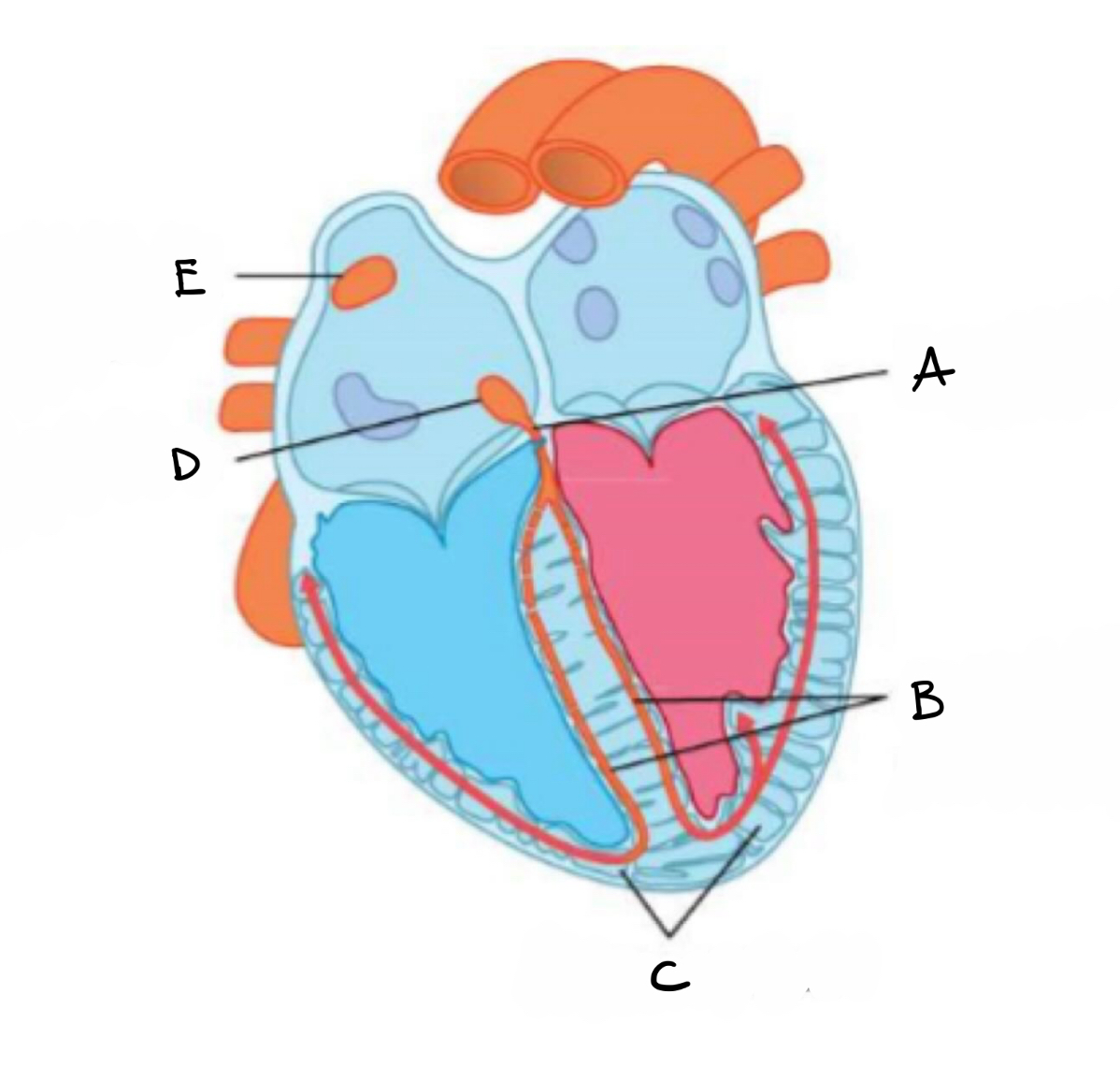
what is B?
right and left branches of purkyne tissue
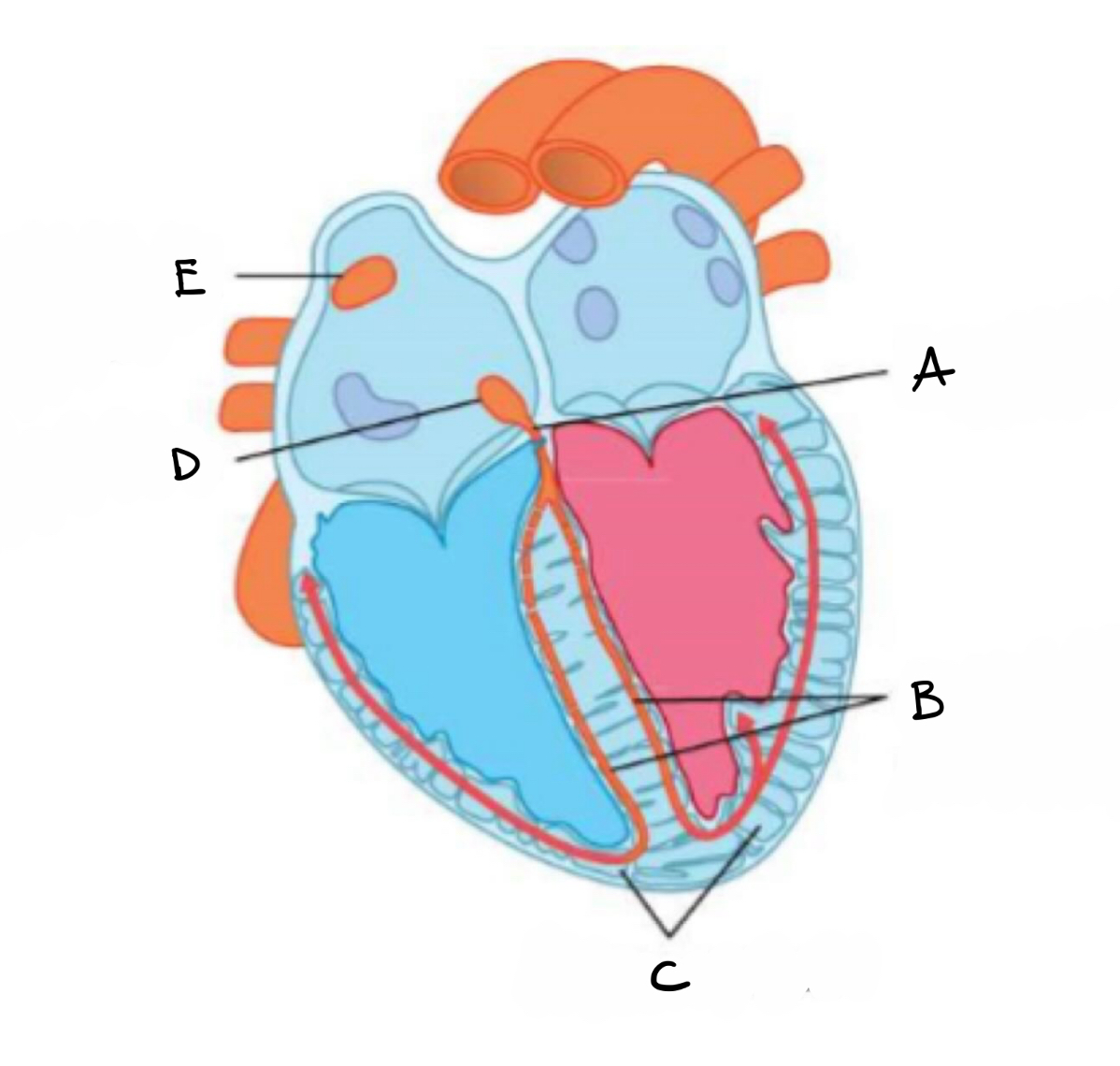
what is C?
purkyne fibres
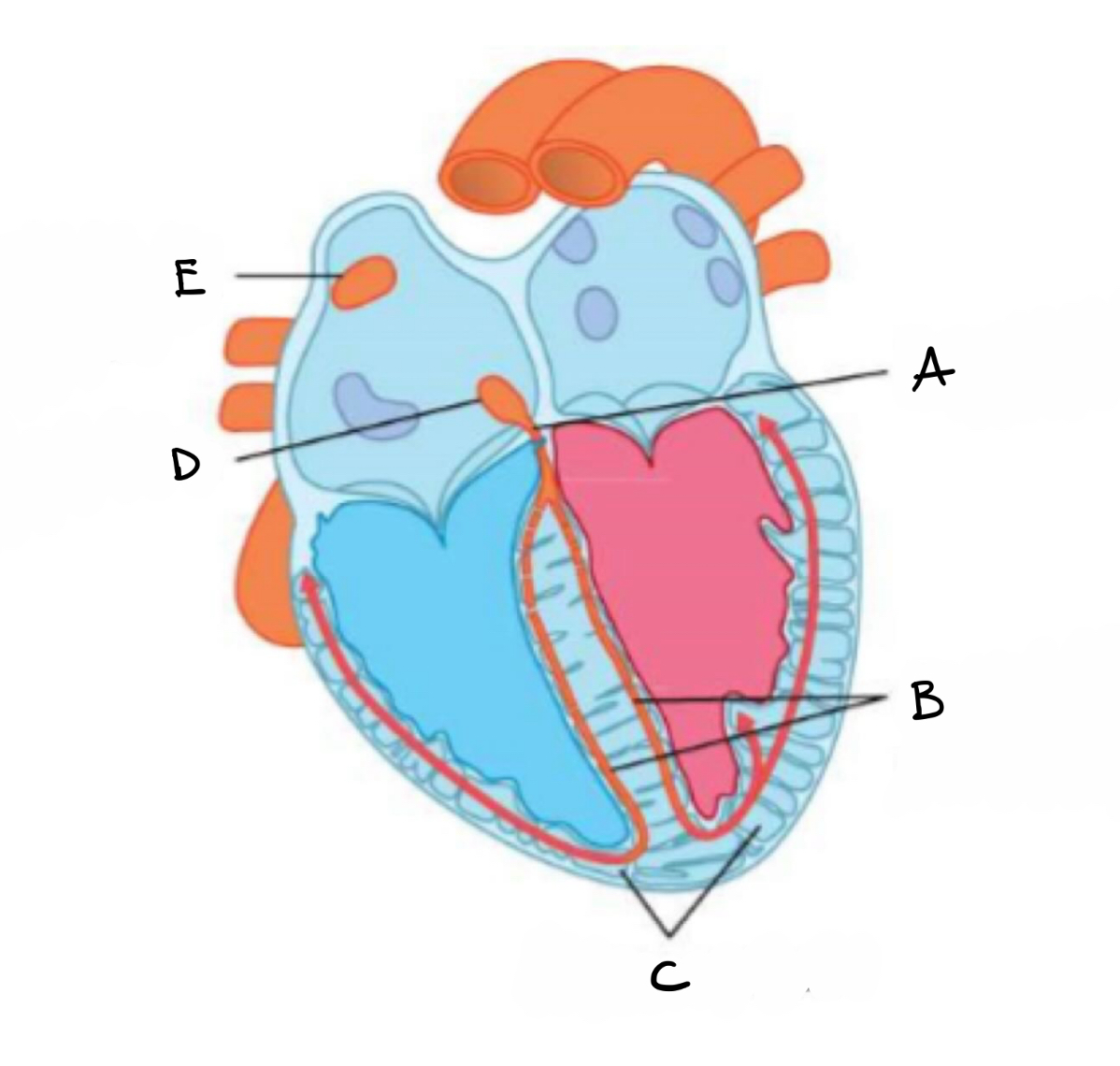
what is D?
atrio- ventricular node
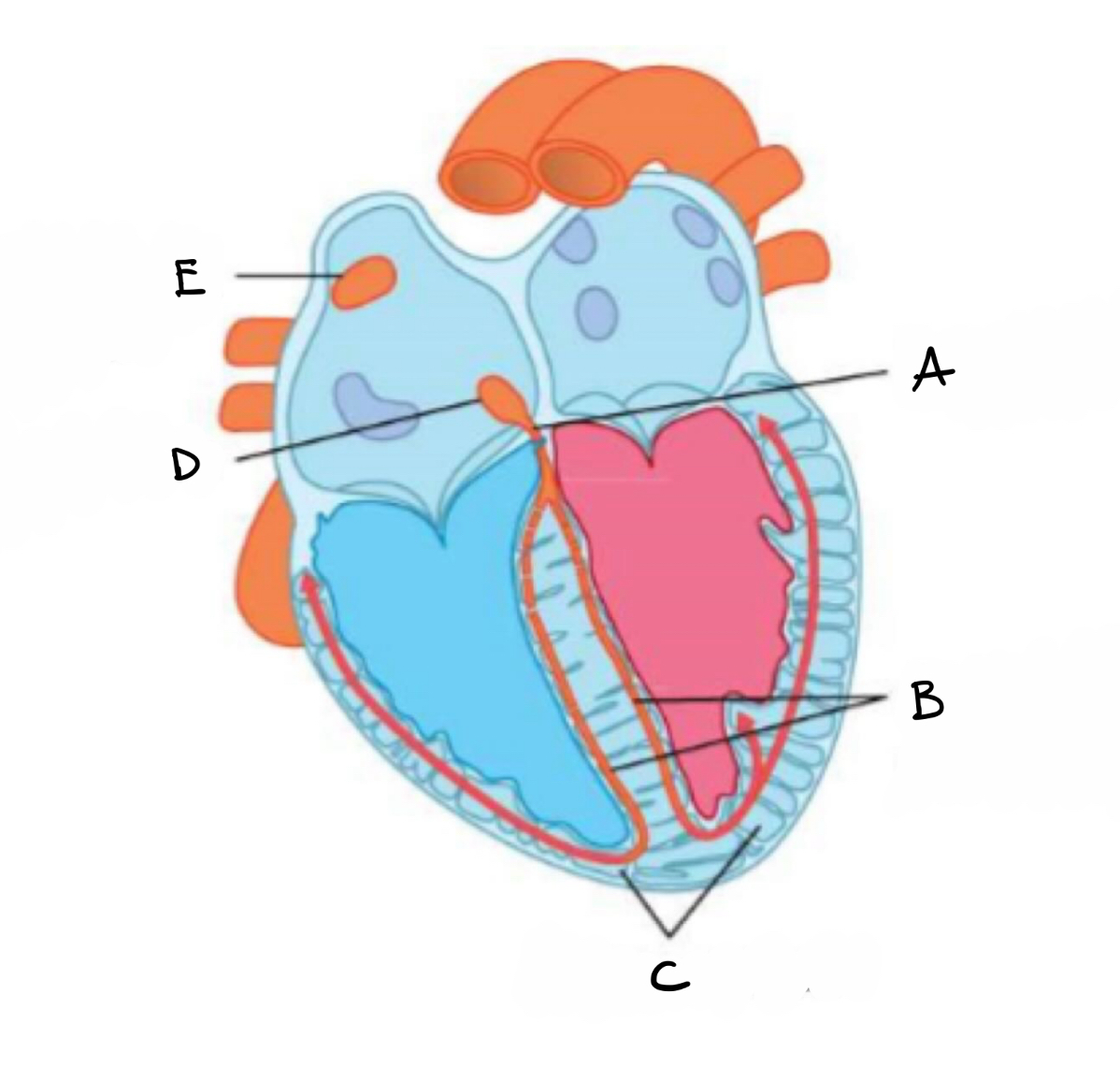
what is E?
sino - atrial mode
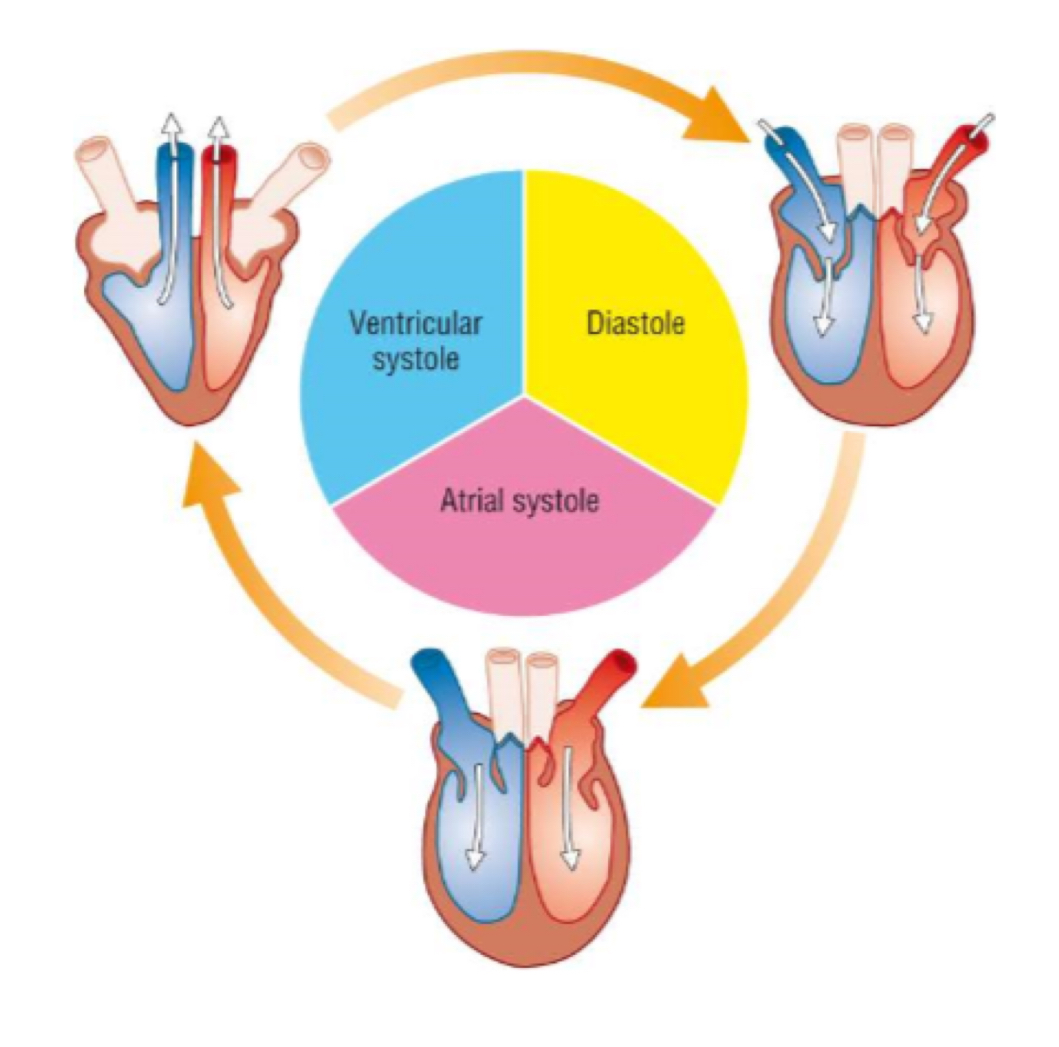
what happens during diastole?
semi lunar valves close
all heart muscles relax
blood flows into atria
blood pressure remains low
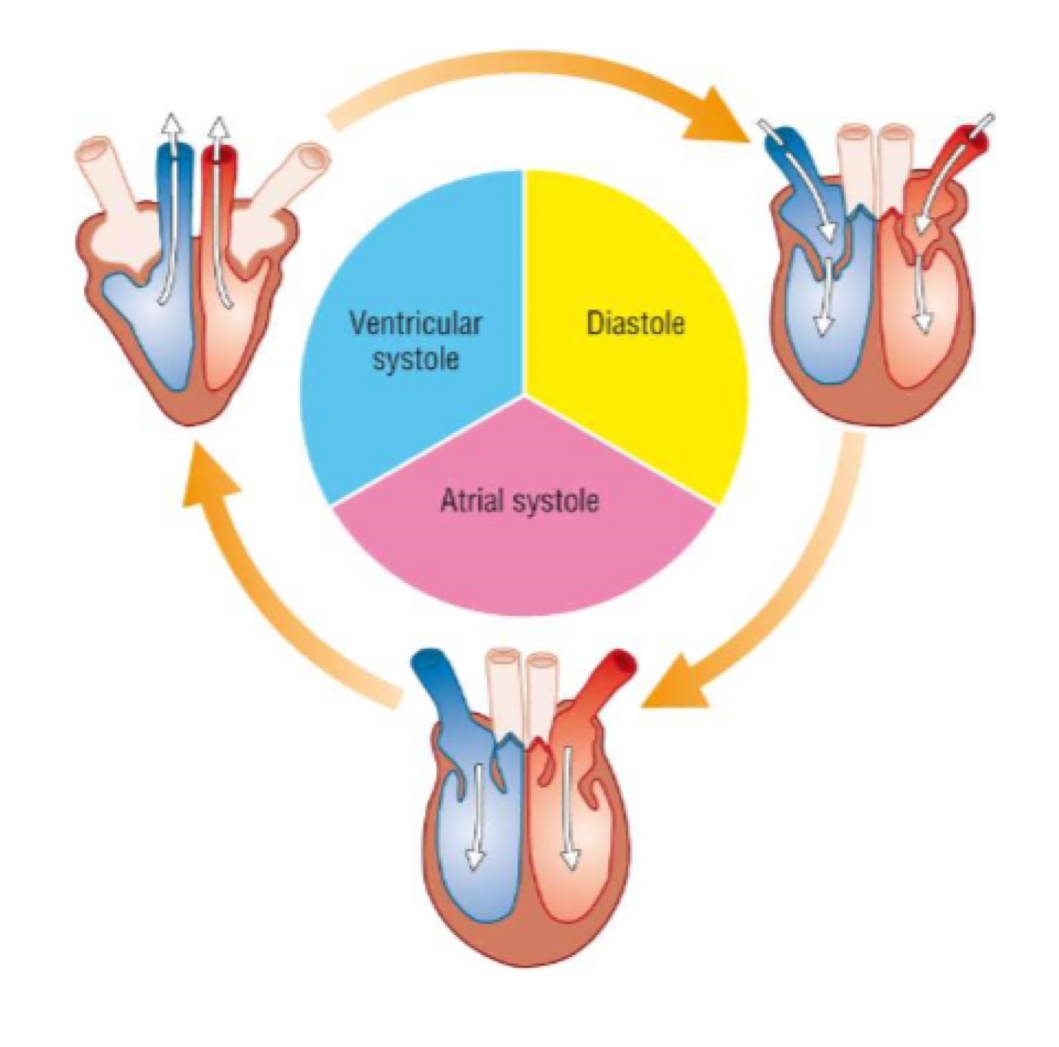
what happens during atrial systole?
muscles in the atria contract
pressure increases
semi lunar valves close
atrioventricular valves open
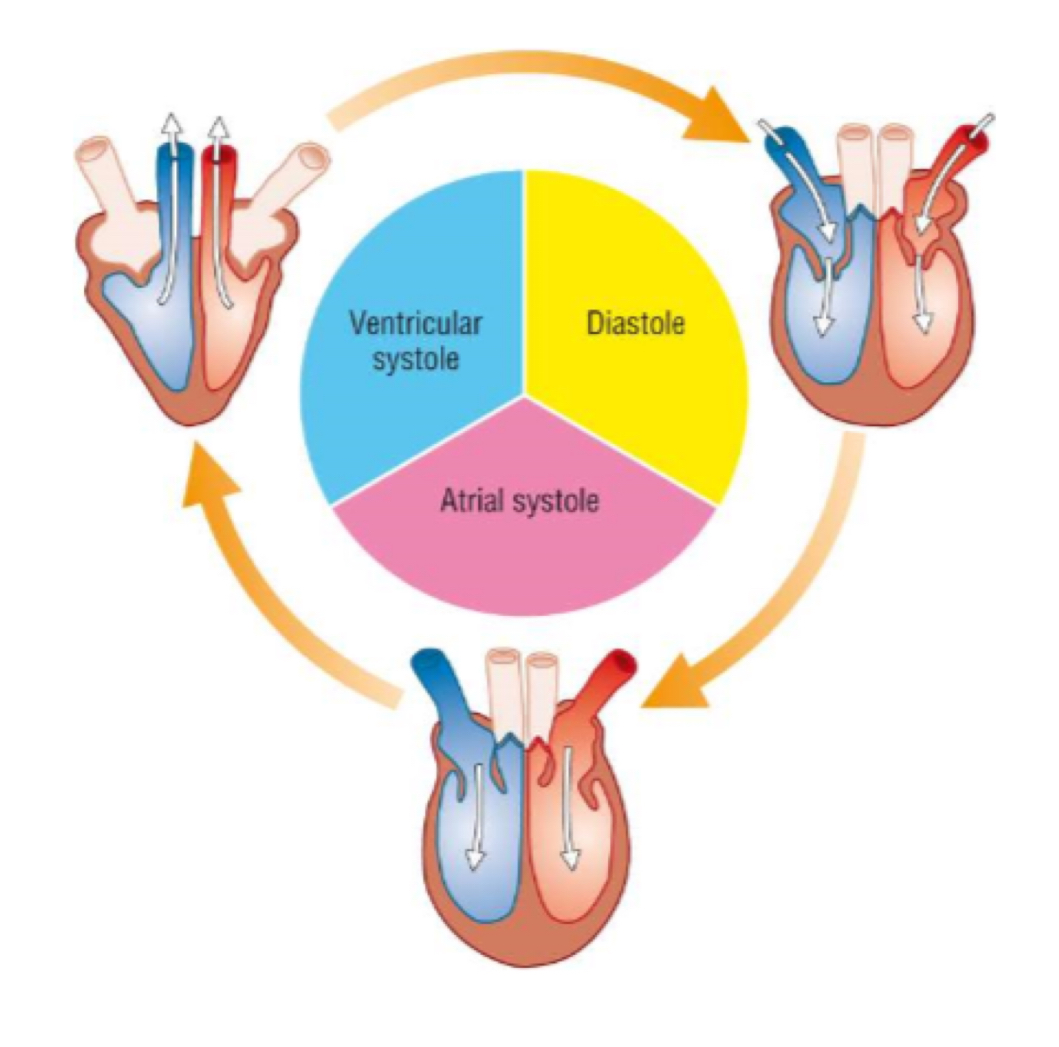
what happens during ventricular systole?
ventricle muscles contract
pressure increases
atrioventricular valves close
semi lunar valves open
blood flows out through aorta and pulmonary artery
what is haemoglobin made of?
four polypeptide chains each bound to one haem group
each haem group can combine with one oxygen molecule
what is the term when all haem groups of haemoglobin have bound to a oxygen molecule?
oxyhaemoglobin
what is partial pressure?
the concentration of gas in a mixture of gases
what is partial pressure measured in?
kilopascals (kPa, PO2)
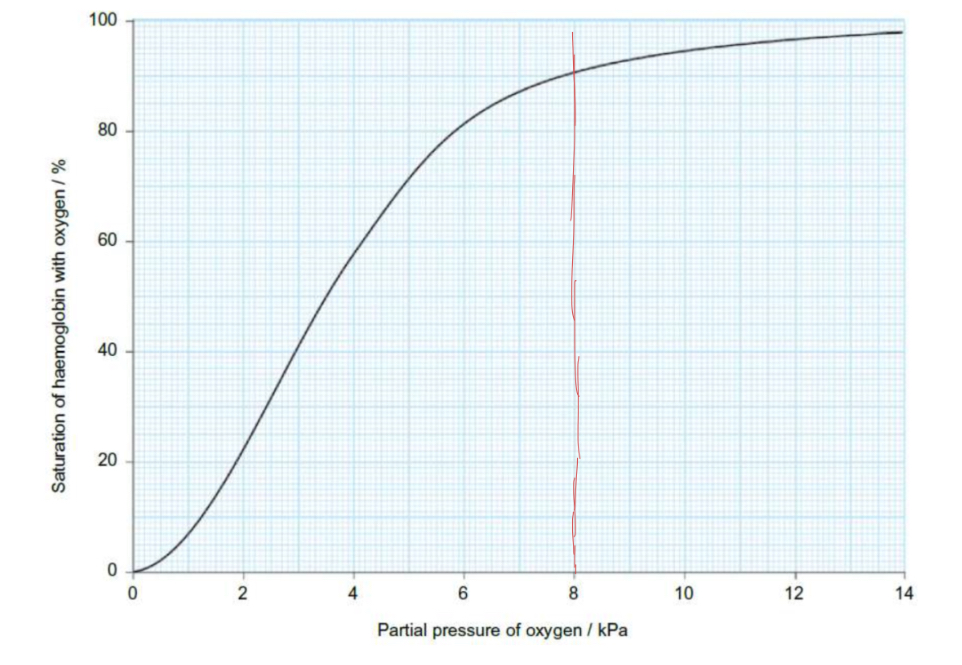
describe and explain the graph :
at start rapid increase - when one oxygen binds it changes shape of the protein therefore increasing affinity
higher partial pressure - higher affinity and therefore higher saturation
plateaus as the haemoglobin becomes saturated
what are three ways carbon dioxide is transported?
dissolved in plasma (5%)
combined with amino groups to form carbaminohaemoglobin (10-20%)
converted to hydrogen carbonate ions in cytoplasm of rbc (75-80%)
how does carbaminohaemoglobin form?
when carbon dioxide binds to haemoglobin
what is the bohr shift?
affect of high carbon dioxide concentration on haemoglobins affinity for oxygen
line drawn to right of normal curve
decrease haemoglobins affinity for oxygen
more oxygen is released for respiration
more carbaminohaemoglobin is formed
why does foetal haemoglobin have a higher affinity for oxygen?
needs to be able to bind with oxygen at a lower partial pressure
maintain a diffusion gradient from placenta
line to the left of normal curve
what is myoglobin?
similar to haemoglobin but with only one haem group
higher affinity for oxygen at very low partial pressure
reserve storage molecule found in muscle cells
how are hydrogencarbonate ions produced in ethrythrocytes?
carbon dioxide diffuses into ethryocytes
reacts with water
forming carbonic acid
the carbonic acid dissociates to form hydrogen carbonate ions and hydrogen ions
what is hydrostatic pressure?
blood pressure - wants to force fluid out of the capillaries
what is oncotic pressure?
pressure caused by plasma protein which reduce the water potential encouraging water to move into capillaries
plasma protein are too big to leave
what is happening at the arterial end of a capillary?
hydrostatic pressure larger than oncotic
net movement of fluid out of capillaries
tissue fluid bathes the cells and exchanges substances with them
what happens at the venous end of the capillaries?
oncotic pressure stays the same - same concentration of plasma proteins
blood moves slower - lower hydrostatic pressure
net movement is into the capillaries
what is the order of layers of a artery inwards to outwards?
endothelium
smooth muscle
connective tissue
what is the sound of ‘lub dub’ in the heart caused by?
closing of the atrioventricular valves then semi lunar valves
why would animals living in high altitudes dissociation curve be to the right?
their haemoglobin needs a higher affinity for oxygen to gain enough oxygen when partial pressure is low
how does electrical the sino atrial node do?
send a charged wave of depolarisation flows through atria walls
causes walls to contract
blood forced through atria ventricular valves
slight delay then ventricle walls contracts
blood flows out of the aorta and semi lunar valves
what does collagen (non-conducting tissue) do within a heart beat?
prevents electrical activity from entering the ventricles
what does the atria ventricular node do?
picks up wave of depolarisation
sends to bundle of his
what does purkyne tissue do?
conduct the electrical activity of the heart
why do maggots have a less developed transport system than flies?
lower metabolic rate
- larger surface area to volume ratio
shorter diffusion distance
sequence of a ECG of a healthy heart :
PQRSTU
what is the P wave of a normal ECG?
depolarisation of the atria causing them to contract
what is the QRS complex of a normal ECG?
depolarisation of the ventricles causing them to contract
largest wave as ventricles have the largest muscle mass
what is the T wave of a normal ECG?
repolarisation of the ventricles causing them to relax
what is the U wave of a normal ECG?
potentially repolarisation of the purkyne fibres
what is tachycardia?
when the heart beats too fast
what is bradycardia?
when heart beats too slow
what is an ectopic heartbeat?
an early heartbeat followed by a pause
what is fibrillation?
an irregular heartbeat which disrupts the rhythm of the heart