CHEM0011 - Section D
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is molality?
Moles per kilogram of solvent.
How do you calculate activity?
a = k x (c/c0)
What is the activity of a solid or pure liquid?
1
(This means solids or pure liquids are emitted out of equilibrium constants).
When Q < K, a reaction will favour...
Products
What are the Arrhenius definitions of an acid and a base?
Acid increases [H3O+]
Base increases [OH-]
What are the Bronsted-Lowry definitions of acids and bases?
proton donor
proton acceptor
What are the values of pKa for a strong acid?
Small values
For an acid and its conjugate base, pKa + pKb = ...
14
Recall the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
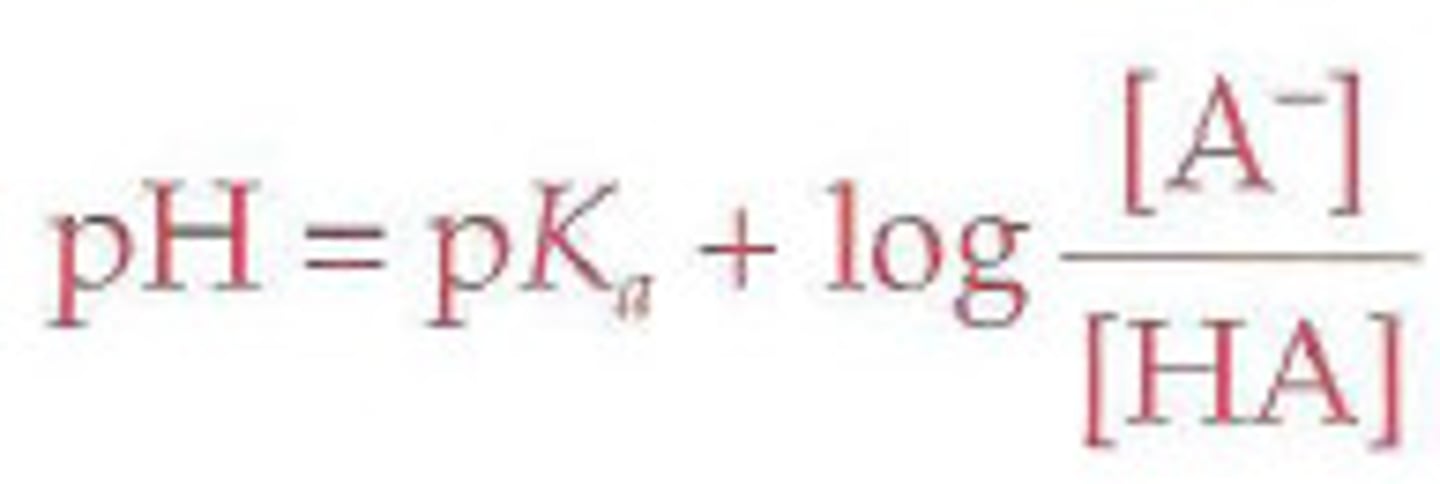
What is the solubility product constant?
An equilibrium constant which describes the equilibrium between undissolved salt and ions when a sparingly soluble salt is dissolved in water, assuming the dissolved salt is fully dissociated.
For the reaction MX(s) -> M+(aq) + X-(aq),
Ksp = [M+][X-]
MX is solid so is emitted out of the constant.
What happens to the solubility when a sparingly soluble electrolyte is dissolved in a solution containing one of those ions?
Solubility decreases
(Therefore the concentration of that ion is dominated by the concentration in solution, not of the added sparingly soluble salt)
What is the buffer of the blood?
CO2 + H2O -> H2CO3
Catalysed by carbonic anhydrase
H2CO3 + H2O -> HCO3- + H3O+
What is voltage and current?
Voltage is the driving force of a reaction, 1 V = 1 JA-1s-1
Current gives the quantity of electricity, 1 A = 1 Cs-1
What do | and || represent?
Phase boundary
Salt bridge
What is the purpose of a salt bridge?
Completes the circuit - has charged ions that do not react with half-cell species. Balances the charges in each cell.
The Calomel electrode can be used as a standard electrode instead of SHE. Write the electrode reaction, conventional cell representation and state the potential difference observed.
1/2 Hg2Cl2(s) + e- -> Hg(s) + Cl-(aq)
Pt, Hg(s), Hg2Cl2(s) | Cl-(aq) ||
0.2676V
What is E°? How do you calculate it (using two delta G equations)?
Standard redox potential at defined standard conditions.
E° = RT/nF x lnk
(ΔG = -nFE°)
What is the Nernst equation? What is the similar equation with Gibbs free energy?
E = E° - RT/nF x lnQ
E is measured EMF not at standard conditions, Q is reaction quotient.
ΔG = ΔG° + RTlnQ
What are galvanic cells?
Electrochemical cells in which spontaneous oxidation-reduction reactions produce electrical energy (electricity).
What are electrolytic cells?
A cell which has a non-spontaneous reaction that is driven by an external source of current.
Recall Faraday's electrolysis laws.
amps x time = coulombs
96485 coulombs = 1 Faraday
1 Faraday = 1 mole of electrons
What are the units of a Faraday?
C mol-1
(coulombs per mole of electrons)