Respiratory PathSession 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Nasal cavity
Sinuses
Nasopharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
What are the conduction portions of the respiratory tract?
Bronchioles
What is the transitional portion of the resp tract?
Alveoli
What is the exchange portion of the respiratory system?
To hold open the airway to allow air in
What is the purpose of the nasal turbinates (bone) and cartilage portions of the conducting system?
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epitheilum w/ goblet cells
What kind of cells line the conducting portion of the respiratory system?
Nasal turvonates - turbulent airflow and microbe get stuck
Bifurcation - turbulent air flow
Normal flora - outcompete
What are physical barriers of the conducting respiratory system?
Entrapment of particles and movement up the mucociliary apparatus
What is the mucocilliary transport system?
Bronchi to the pharynx
How far does the mucocilliary apparatus extend?
Sol
Gel
____ is a more fluid secretion ___ is a thicker mucus secretion produced by goblet cells
Bronchial associated lymphoid tissue (BALT)
What kind of defense will we see at the bronchial bifurcation?
Viral infections - confections w/ bacteria
Toxic gases (anesthesia)
Immunodeficiencies
What factors can weaken the pulmonary defense?
Aerogenous (inspired air)
What is the most common method of entry of a pathogen into the respiratory tract?
Hematogenous
What method is most common for neoplasia and parasites to get to the lungs?
Direct extension - bites/ penetrating wounds
How can a fighting cat get respiratory issues?
Palatoschisis (Cleft palate) most common congenital dysfunction of upper resp tract
Identify the pathology?
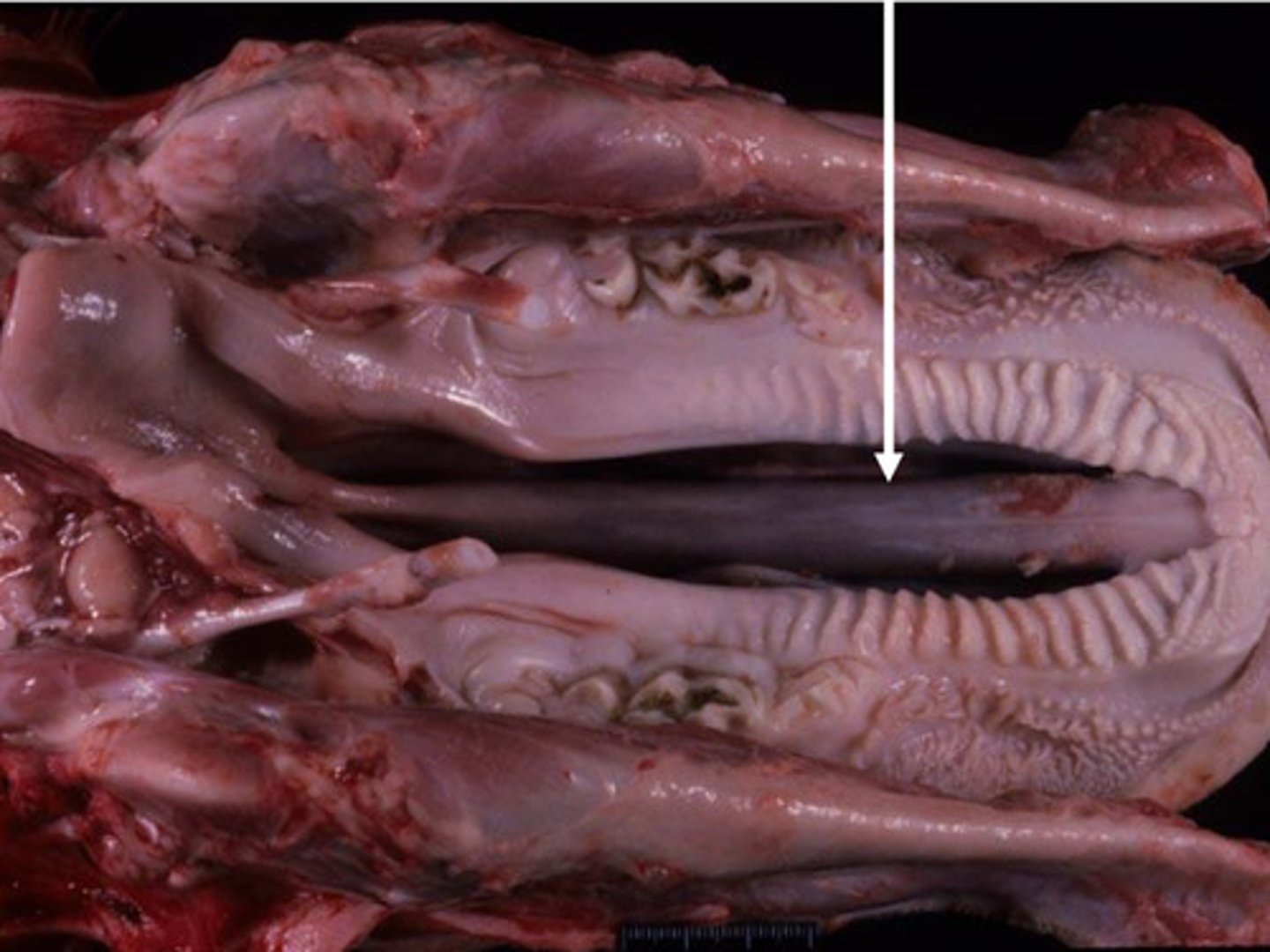
Aspiration pneumonia - communication b/w nasal and oral cavity
What are common sequela of Palatoschisis?
Choanal atresia - opening between nasal cavity and nasal pharynx
Identify the pathology?
Aspiration
Can develop bone/ membrane that obstructs airflow into nasopharynx
What are common sequela of Choanal atresia?
Malformed/ poor functioning cilia
What is ciliary dyskinesia?
Stenotic nares
Elongated soft palate - occudes larynx
Everted laryngeal saccules
Hypoplastic trachea (+/- collapsing trachea)
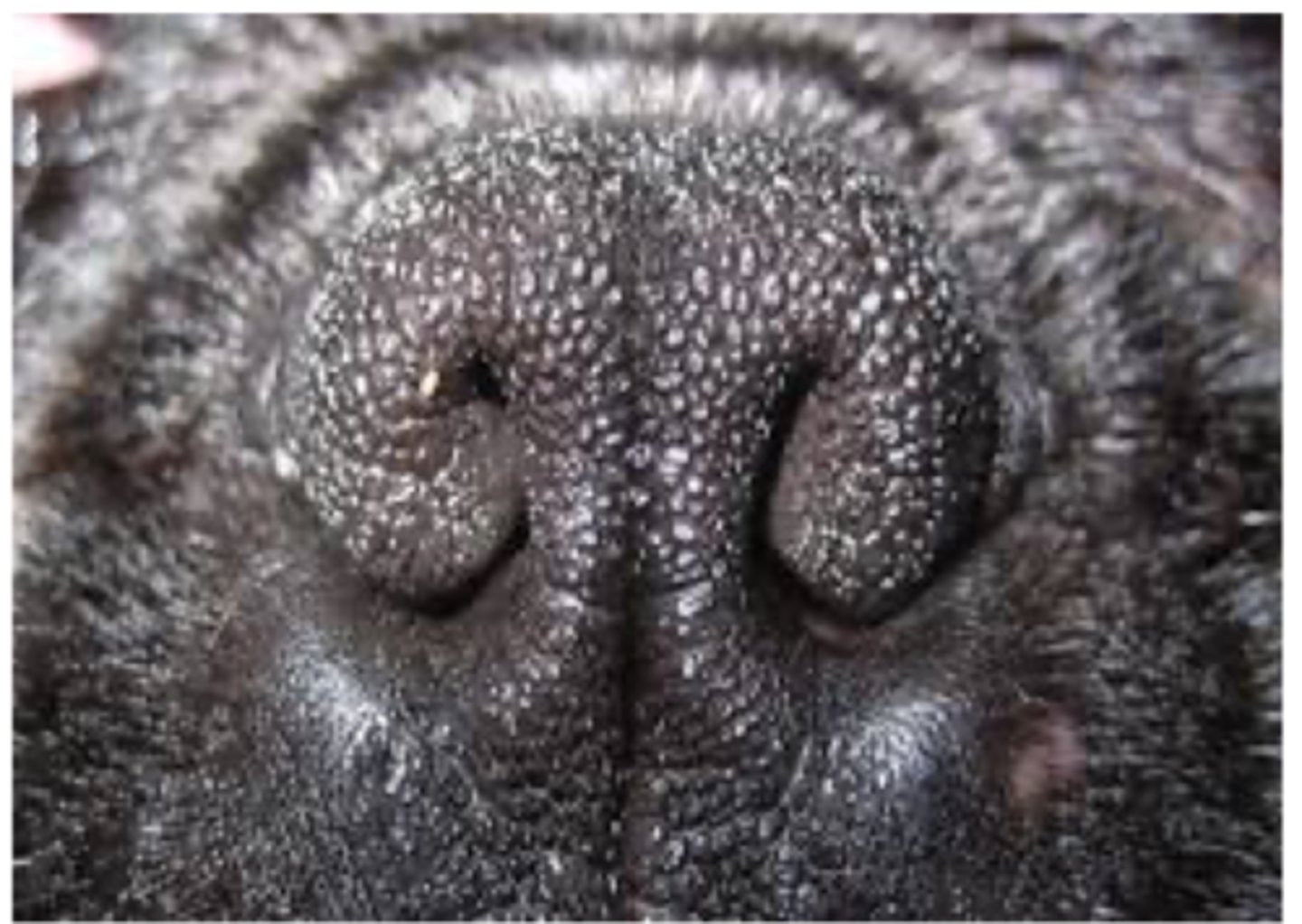
What are signs of Brachycephaic airway syndrom?
Stenotic nares
Identify the pathology?
Elongated soft palate
Identify the pathology?
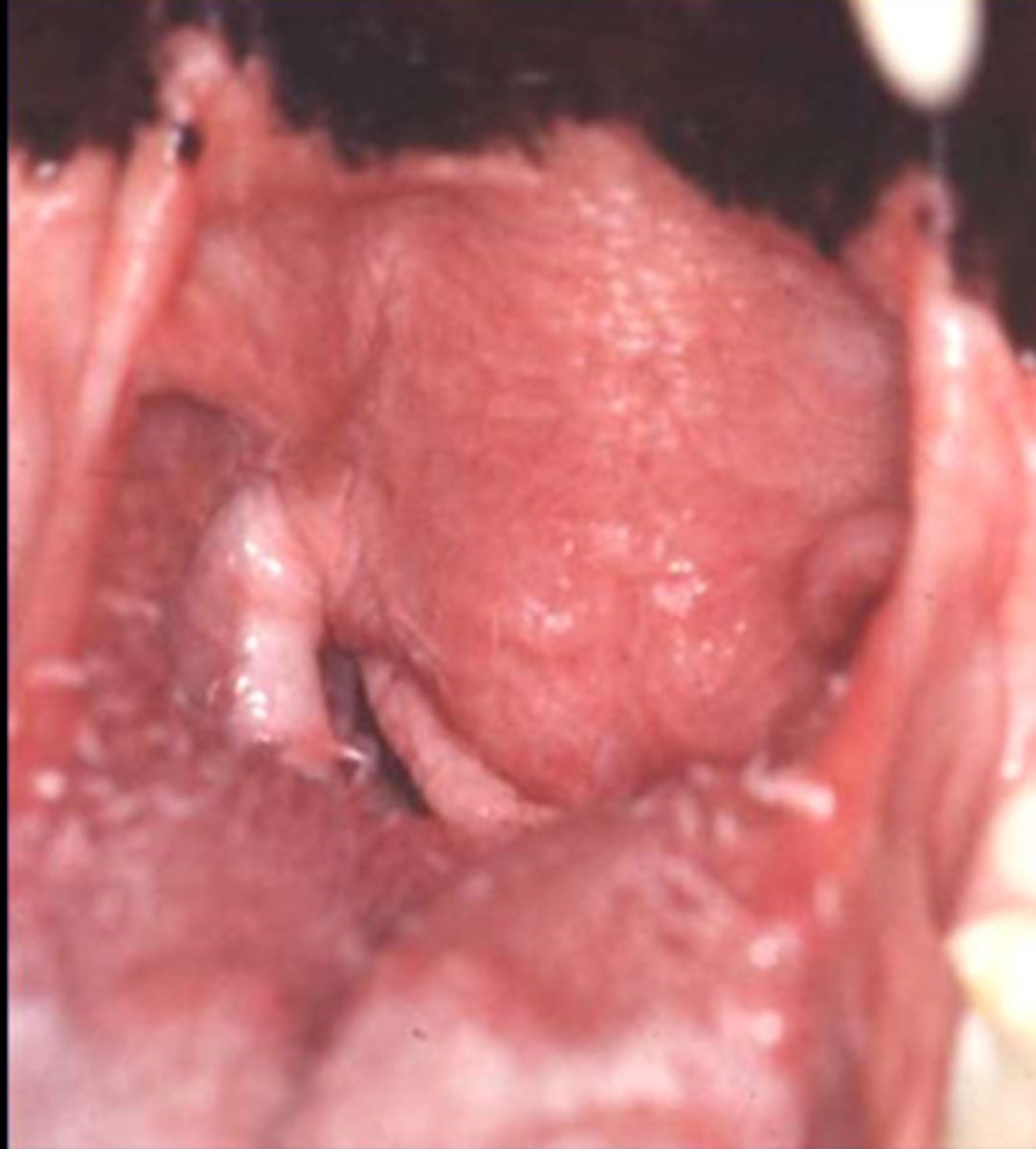
everted laryngeal saccules
Identify the pathology?
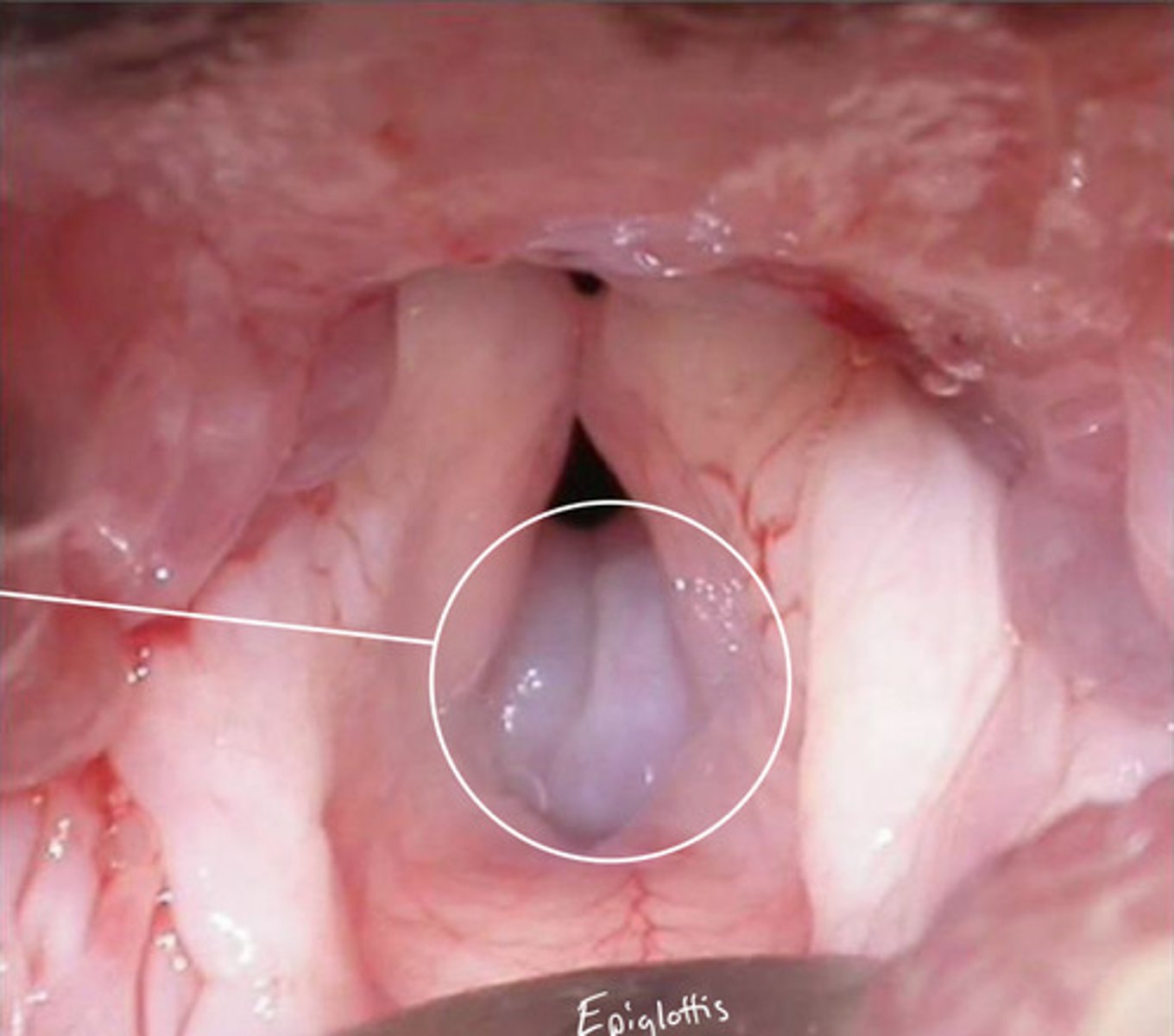
collapsing trachea
Identify the pathology?
Guttural pouch inflammation
Define Eutachitis?
Bleeding from nose
Define epistaxis?
Coughing blood
Define hemoptysis?
Pus accumulation in the guttural pouch
Define Empyema?
Viral/ allergy (clear/ thicker chunky)
Serious/ catarrhal nasal discharge is more likely to be seen in what kinds of infection?
Bacterial ( yellow thick)
Purulent/ suppurative nasal discharge is more likely to be seen in what kinds of infection?
Fungal
Granulomatous nasal discharge is more likely to be seen in what kinds of infection?
Distemper virus
What virus is typically responsible for respiratory dz in dogs?
Bordetella bronchiseptica
Pasteurella multocida
What are the two respiratory bacterial infections that commonly affect the upper resp system dogs?
Aspergillus
What fungal infections that commonly affect the upper resp system dogs?
Bordetella bronchiseptica
-crowding/ mixing of dogs in poor ventilation w/ environmental stressors
What are factors that typically cause Kennel cough?
German Shepards and Dolichocephalic breeds
What dogs does Aspergillus fumigatus?
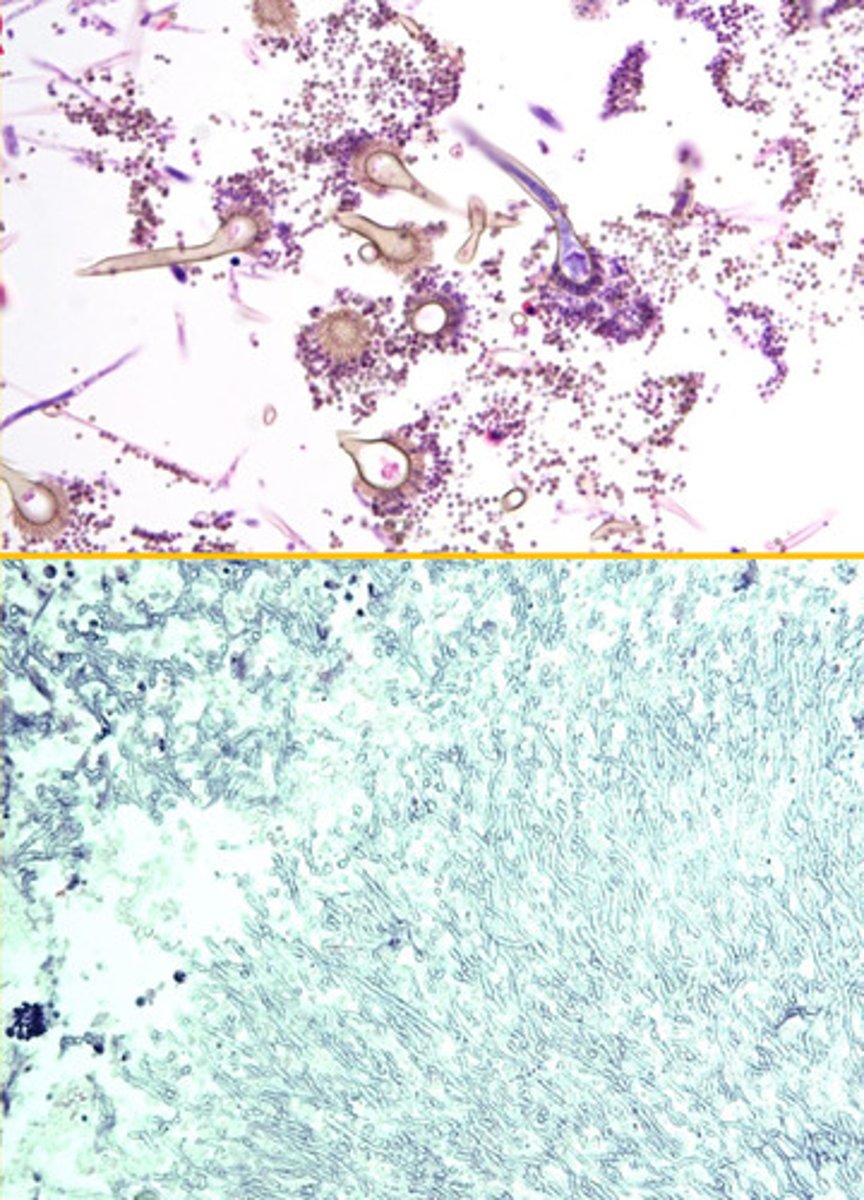
Aspergillus fumigatus
Identify the organism?
Feline calicivirus
Feline Herpies virus 1
What two viruses will cause feline rhinitis and conjunctivitis?
Mycoplasma felis
Chlamydophila felis
What are the secondary infections that can occur from feline Rhinitis?
Cryptococcus
What is the fungal cause of feline rhinitis?
Dendritic ulcerations
What is pathognomonic for felines herpes virus?
Calicivirus but can also be in FHV-1
If you see oral ulceration in a cat what virus would we lean towards?
Gelatinous polypoid masses (in brain or nose)
Swollen nasal cavity (roman nose)
What are signs of Cryptococcus neoformans/ C. gatti?
Cryptococcus
Identify the pathogen?
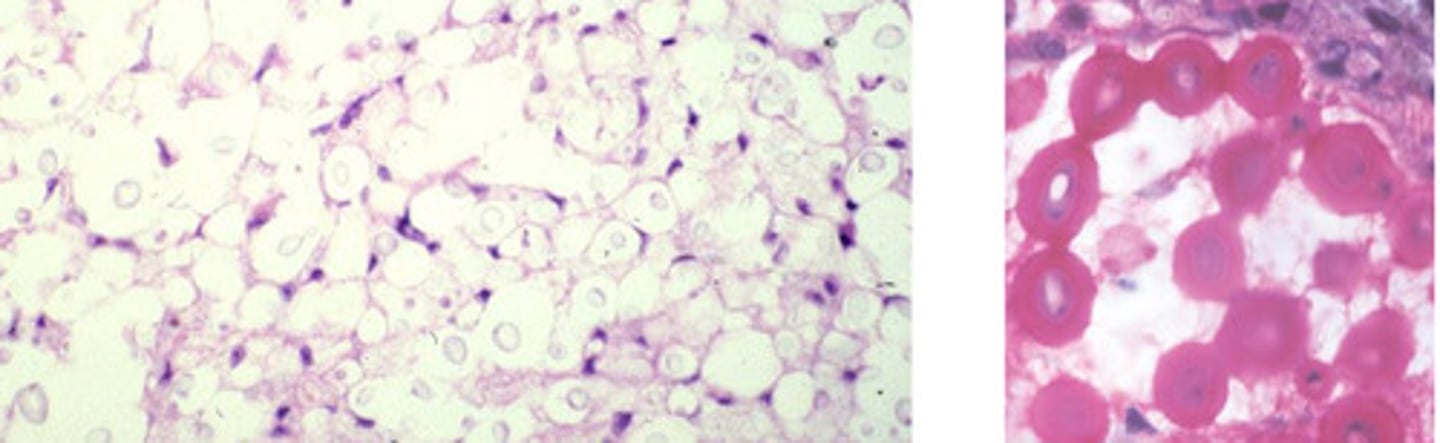
Mucicarmine stain
What stain is used to see Cryptococcus?
IBR - bovine herpes virus
Identify the pathology?
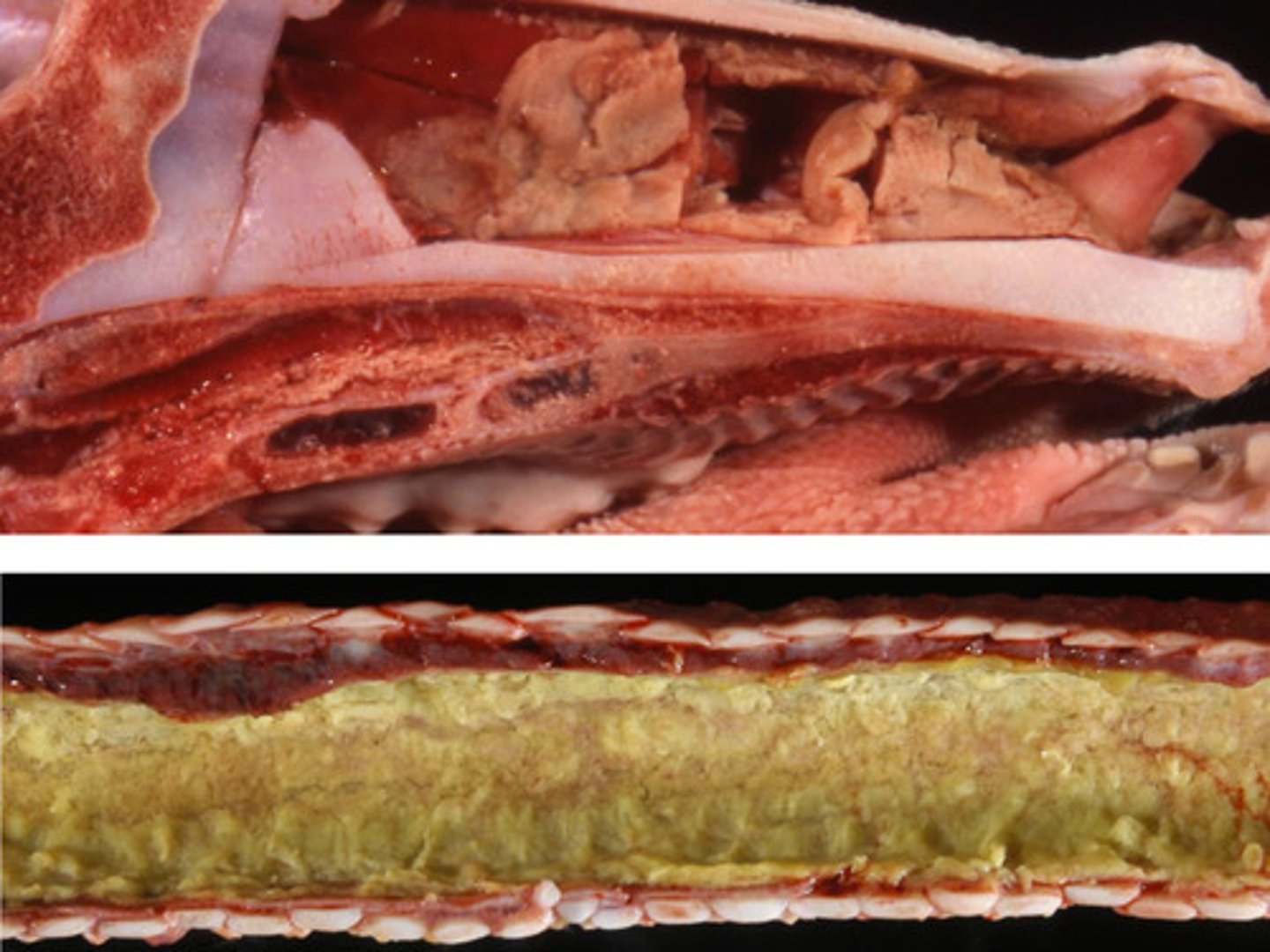
Red nose dz a Necrotic hemoragic dz of the nasal cavity
What is IBR - bovine herpes virus?
Mannheim haemolytica synergism
What bacteria will we see a co-infection with IBR - bovine herpes virus ?
Bordetella bronchiseptica and Pasteurella multocida
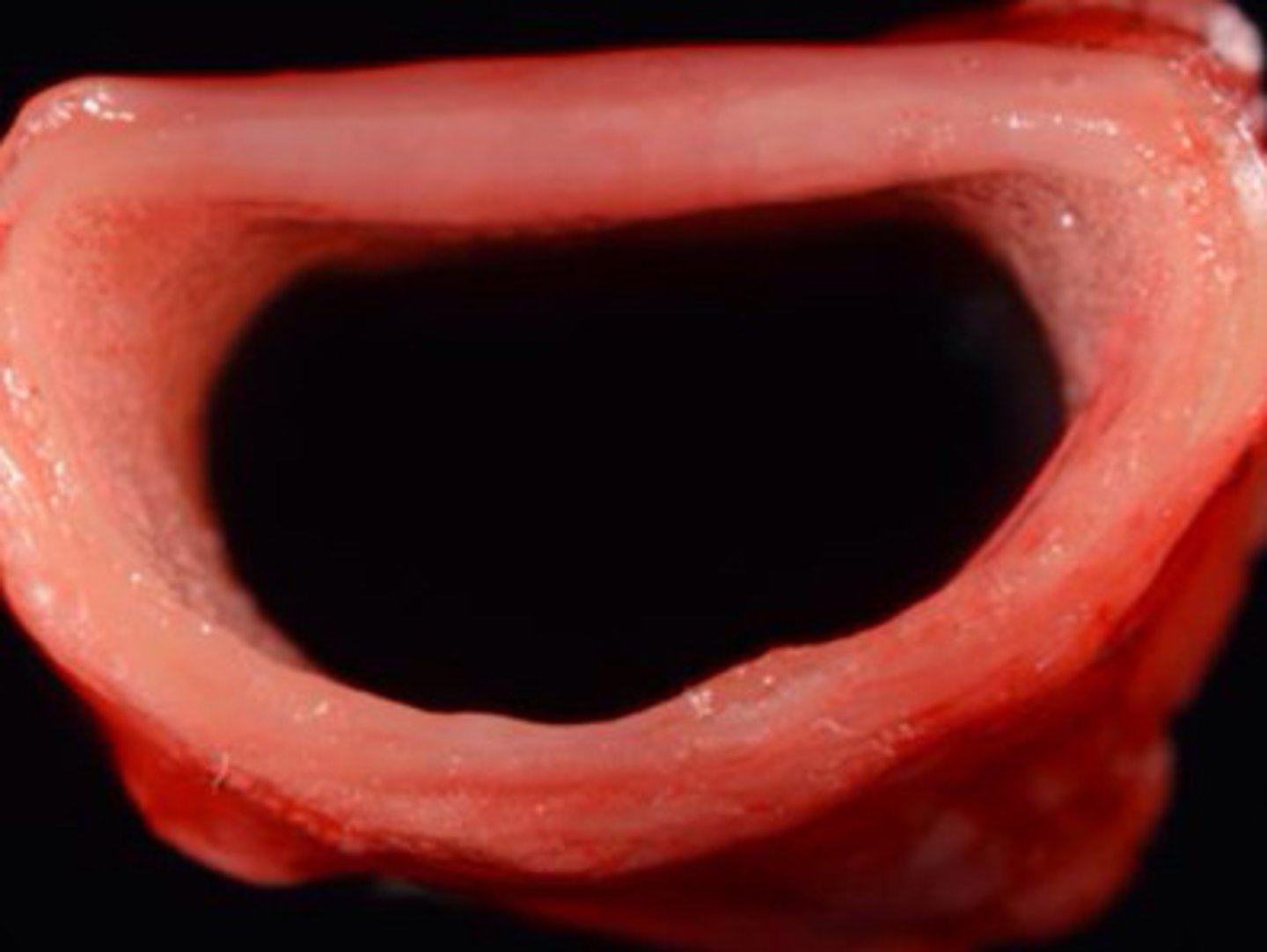
Atrophic rhinitis in pigs
Identify the pathology?
Coinfection will lead to inhibition of osteoblasts and activation of osteoclasts leading to atrophy and loss of nasal conchae and a septal deviation
Explain the pathogenesis of Atropic rhinitis in pigs?
Oestrus ovis
Myiasis fly - larva in living tissue
What is a form of parasitic rhinitis in sheep?
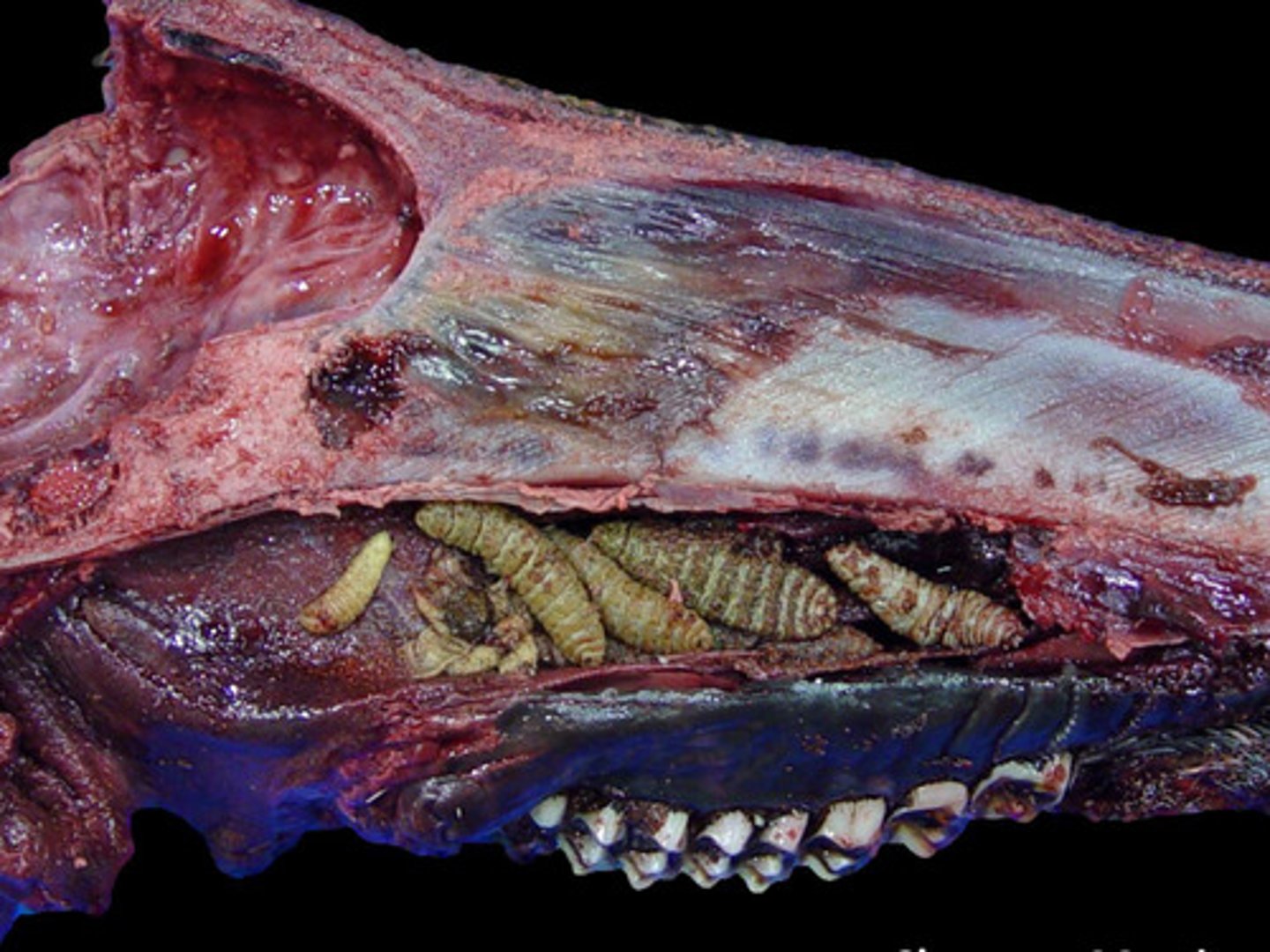
A rodent botfly larval that migrates w/ in the body - goes to nasal cavity, trachea and brain
What is cuterebra spp?
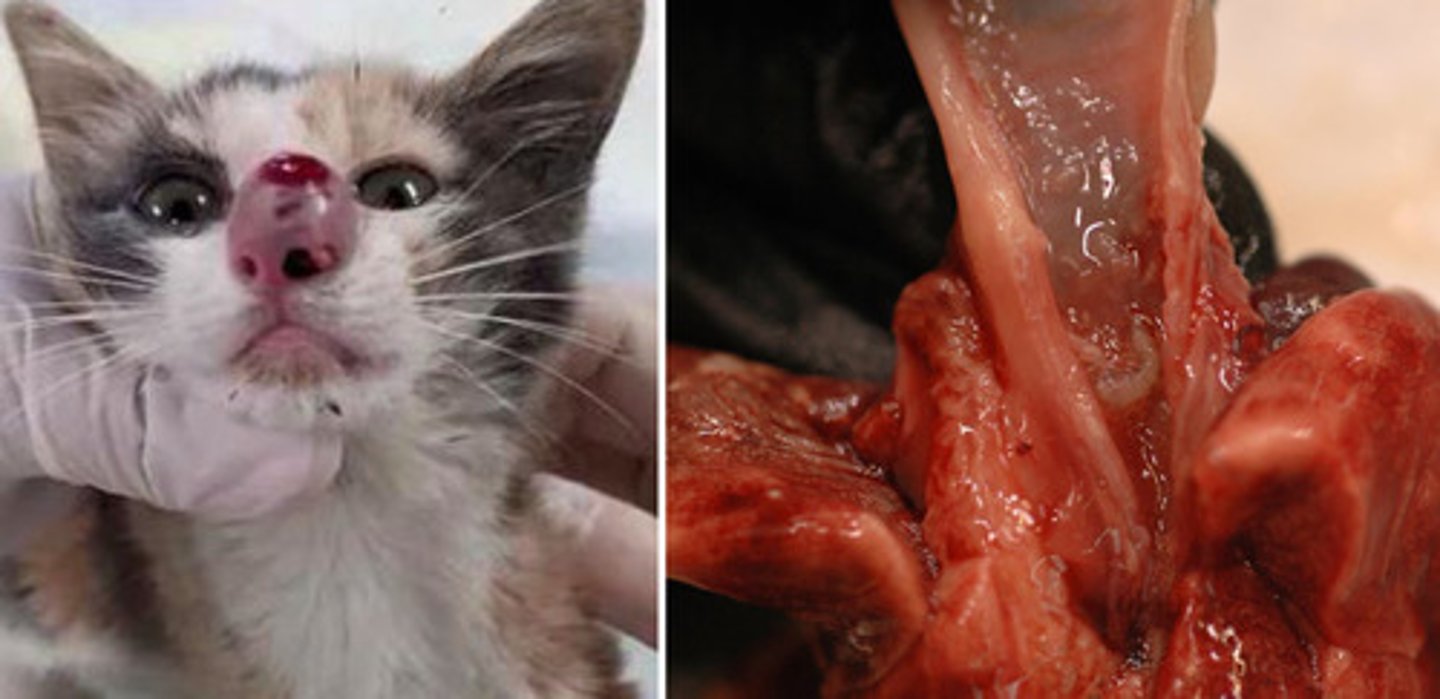
Dehorning complications
Periodontitis/ tooth abscess
What are some issues w/ sinitis?