Lipids and Lipoproteins (Exam 2)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What are the 6 types of lipoproteins?
- Cholymicrons
- Very-low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
- Intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL)
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
- Lipoprotein (a)
What is the order of groups, from least to most dense (largest to smallest)?
Chylomicron --> VLDL --> IDL --> LDL --> HDL
What are the three transport pathways of lipoprotein metabolism?
- Exogenous
- Endogenous
- Reverse cholesterol
In the exogenous pathway, ______ transfer ______-derived lipids to the liver.
chylomicrons, dietary
In the exogenous pathway, chylomicrons from the diet enter the capillaries where ______ breaks it down into what two fractions?
lipase
free fatty acids and chylomicron remnant
The free fatty acids go to ______ and ______.
muscles, adipose tissues
The chylomicron remnants go to the ______.
liver
In the endogenous pathway, ______ transfers ______-derived lipids to cells via LDL.
VLDL, hepatic
In the endogenous pathway, VLDL from the liver enters the capillaries where ______ breaks it down into what to fractions?
lipase
free fatty acids, IDL
The free fatty acids go to the ______ and ______.
muscles, adipose tissue
The IDL goes to the ______ or becomes ______.
liver, LDL
This LDL can go either to the ______ or ______.
liver, peripheral tissues
In the reverse cholesterol transport pathway, ______ removes excess cholesterol.
HDL
The excess cholesterol comes from ______.
macrophages
After it is removed by HDL, the excess cholesterol enters the ______.
liver (bile --> excreted)
Cholesteryl ester byproducts enter ______.
circulation
Apolipoprotein is the ______ portion of lipoproteins, located on the surface.
protein
Lipoprotein lipase deficiency is caused by a deficiency in ______.
lipase
Lipoprotein lipase deficiency is characterized by ______.
hyperchylomicronemia
Patients with lipoprotein lipase deficiency have extremely high ______ levels (5,000-10,000 mg/dL).
triglyceride
This causes a _______ serum.
milky
Physically, ______ are observed with lipoprotein lipase deficiency.
xanthoma (rash due to excess lipids trying to escape through the skin)
Familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCHL) causes increased plasma concentrations of ...
- Cholesterol and LDL (type 2a)
- Triglycerides (type 4)
- All of the above (type 2b)
In a patient with FCHL, triglyceride levels are usually between ______, but can be much higher.
200-400 mg/dL
Familial hypertriglyceridemia is very common and causes a moderate increase in serum ______.
triglycerides
Familial hypertriglyceridemia also causes increased ______.
VLDL
Familial hypertriglyceridemia is commonly associated with low ______.
HDL
Type V hyperlipoproteinemia causes an increase in both ______ and ______.
chylomicrons, VLDL
What would a blood tube of a patient with type V hyperlipoproteinemia show?
Almost the entire tube will have look like butter (see slides)
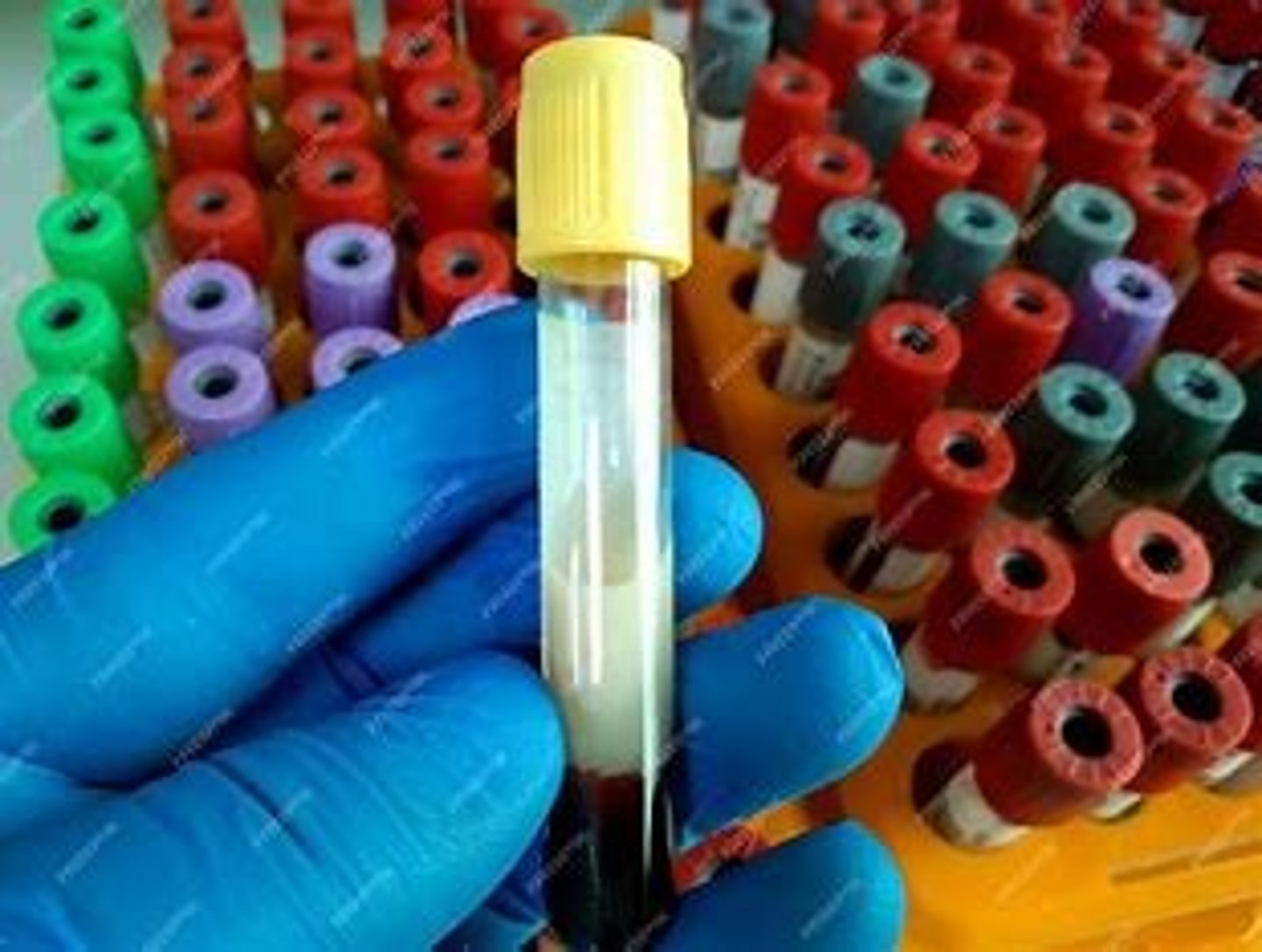
______ and altered ______ are common with type V hyperlipoproteinemia.
Pancreatitis, glucose tolerance
Dysbetalipoproteinemia is caused by a mutant form of ______.
Apo E
Dysbetalipoproteinemia patients will have an accumulation of ______ and ______ in the serum.
chylomicron remnants, IDL
Premature ______ is possible with dysbetalipoproteinemia.
atherosclerosis
Familial hypercholesterolemia is caused by a defect in the ______ pathway.
LDL receptor
Familial hypercholesterolemia causes there to be increased deposition of ______ in what areas of the body?
LDL
skin, tendons, arteries
A patient with familial hypercholesterolemia will have ______x the normal plasma LDL level.
2-3
Hypoalphalipoproteinemia causes a decrease/absence of ______.
HDL
Hyporlaphalipoproteinemia causes an increased risk of ______ in patients.
CVD
______ (disease) is associated with hypoalphalipoproteinemia.
Tangier's disease
Tangier's disease is a ______ of alpha liproproteins.
total absence
Tangier's disease is due to massive ______ deposits in macrophages.
cholesterol
Excess fats present in Tangier's disease cause the tonsils to be ______.
orange
Tangier's disease patients are susceptible to ______.
atherosclerosis
LDL and VLDL are ______ associated with CVD.
directly
HDL is ______ associated with CVD.
inversely
Lipoprotein (a) is measured to asses the likelihood of ______ in an individual with normal ______ values but a strong history of CVD.
CVD, normal
Presence of lipoprotein (a) indicates ______.
risk for CVD
What are the three lipid storage diseases?
- Niemann Pick
- Gaucher's
- Tay Sach's
Excess chylomicrons causes a ______ in plasma upon overnight refrigeration.
creamy layer
Chylomicrons are not normally present in a ______ sample.
fasting
A high concentration of VLDL will make serum appear ______ after overnight refrigeration.
milky (creamy layer)