Applications from Molecular Spectroscopy
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
220 Terms
What is spectroscopy a measurement of?
Changing alterations in molecular structure
→ e.g = Vibrations and electronic energy
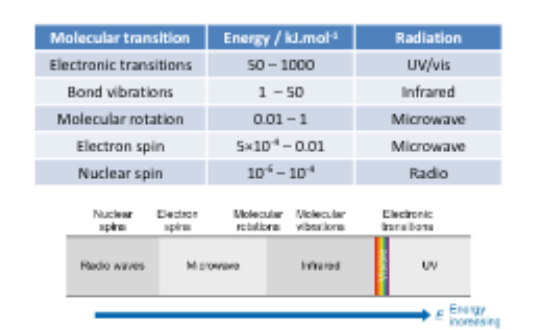
Show the common spectroscopic methods

What quantum number does nuclei have?
I = n/2 where n = integer
What is the quantum number for electron spin?
mI = I, (I-1), (I-2), … -I
What happens when magnetic is applied to nucleus?
Energy levels become degenerate

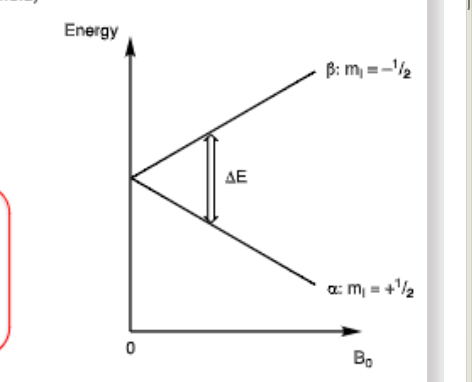
What are the selection rules for change in electron spin quantum number (mI)?

→ Formula is the working out for energy gap difference

How does sensitivity depend on population difference?
A larger population difference will make absorption stronger producing a more sensitive signal
What does population mean?
Number of atoms/molecules that occupy a specific energy level at a time
What happens to nuclei in magnetic field?
There will be net alignment of nuclei in direction of field (z axis) and nuclei will favour lower energy state

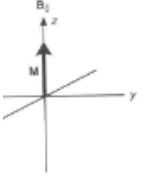
What is magnetisation?
When nuclei favours the lower energy state
What happens of electromagnetic radiation when frequency is applied to z axis in magnetic field with nuclei?
Net magnetisation (M) is perturbed (spins) towards xy plane and will precess around z axis
→ Oscillating magnetisation can induce a current causing a spectrum to be shown

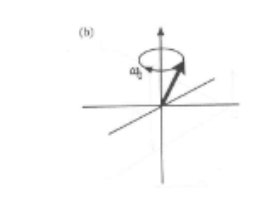
Whats the difference between laboratory frame and rotating frame?
Laboratory frame considers precession of magnetisation
Rotating frame removes time dependence (rotating)


Why is there a small difference between excitation and resonance frequency?
Nucleus is shielded from full magnetic field by electrons so difference must be measured
How do you produce free induction decay?
Amplify and measure induced current
→ Induced current decays overtime as system returns to equilibrium
Measure difference between frequency of NMR signal and excitation (this measures relative frequencies rather than absolute)
Free induction decay can be seen and compared to excitation frequency
Spectra is calibrated to known standard
Why is free induction decay important?
Can measure many resonance frequencies simultaneously
. Each different signal (frequency) gives a different FID resulting with overlapping signals
What is Fourier transform used for?
Separating different signals (frequencies) by converting time domain to frequency domain
How do electrons affect the magnetic field?
Electrons “shield” nucleus from magnetic field (B0) reducing the effective field so field observed will be weaker than theoretical field
Why are chemical shifts present?
Extent of electron cloud around nucleus affects precession frequency (How fast nucleus spin precesses around z axis)
What is AX spin-spin coupling?


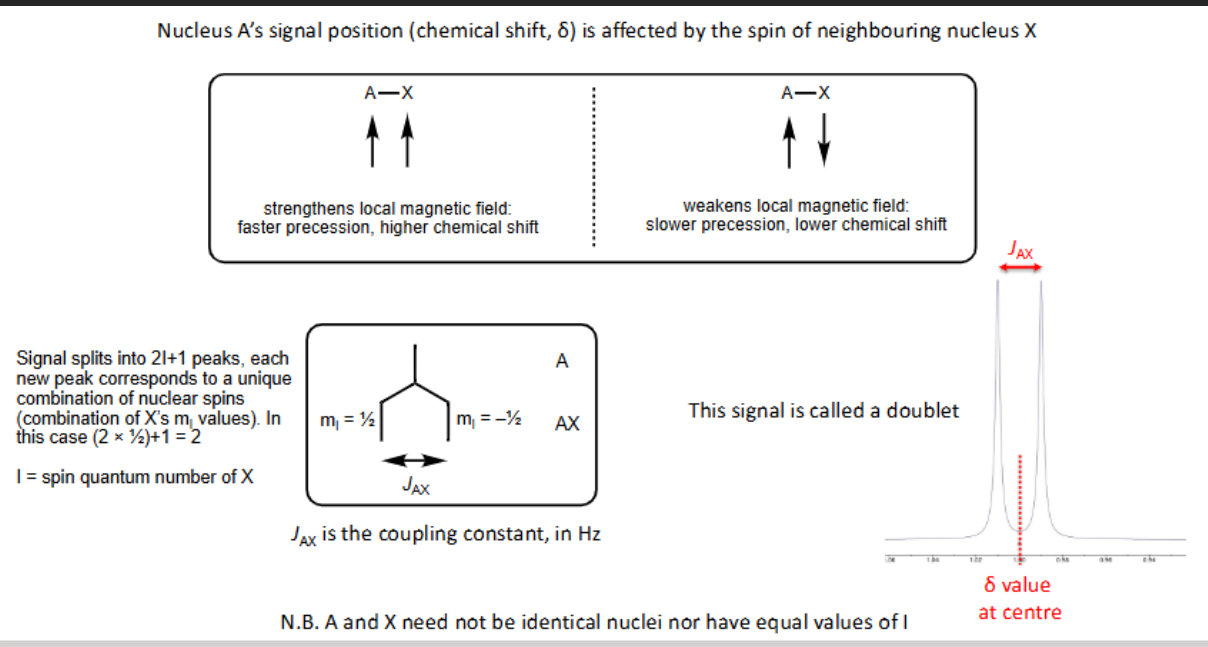
What is coupling to 2 equivalent nuclei: AX2?

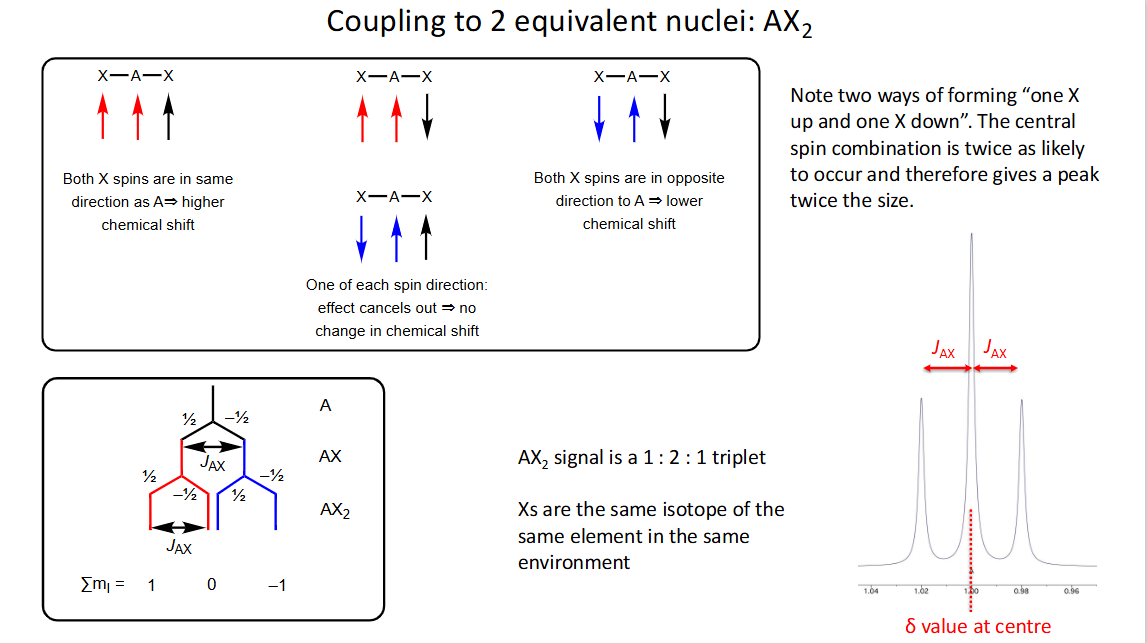
Why is there a peak twice the size in the middle in AX2 ?
There are 2 ways of forming one up spin and one down spin in X so combination is twice as likely to occur
What are coupling to 3 equivalent nuclei: AX3?

There is overlap with drawing out pascals triangle

How must nuclei couple and how do you define distance between coupling ?
They must be connected through chemical bonds and distance is defined by number of bonds between coupling nuclei (nJAX)
What happens to coupling constants as coupling nuclei get further apart?
Coupling constant gets smaller
What is inequivalent coupling (Represented as AMX)?
-Occurs when nucleus couples to non-identical nuclei

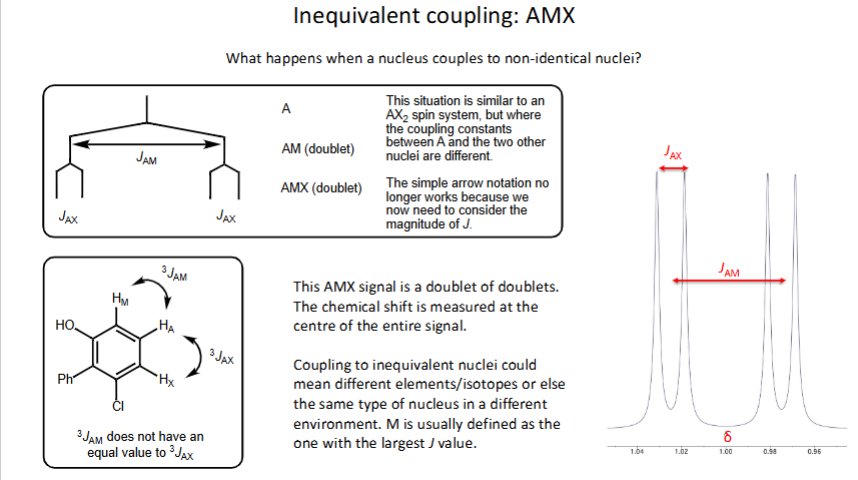
How do you measure chemical shift?
Take value in centre
How do you couple to I > ½ nuclei (When x has more mI values)?

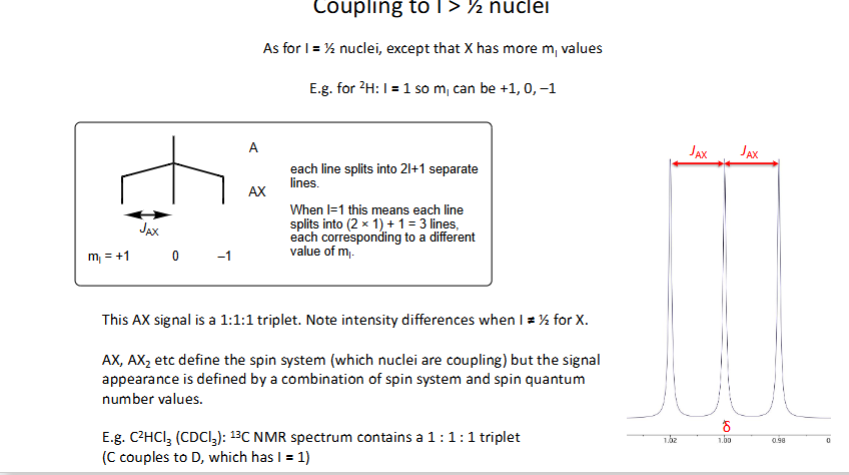
When can coupling occur?
1) Nucleus must have a population difference between ground and excited states
2) I must be greater than 0
Why is 1HNMR important?
Found in nearly all organics and most inorganic metal complexes
Has ½ spin nucleus giving off well-defined signals and multiplets aids structural interpretation
Has abundant isotope (99.9885%)
5870x more sensitive than 13C
What is the typical spectrum range for 1HNMR?
0-10ppm
What reference can you use for 1HNMR?
SiMe4
Why does 1HNMR show mostly solvents?
Most solvents contain protons
Why can you use deuterated solvents in 1HMR and give an example of a deuterated solvent
Spectra can only detect protons therefore the deuterium isotope will appear invisible
e.g = CDCl3 gives off an impurity signal at 7.26ppm
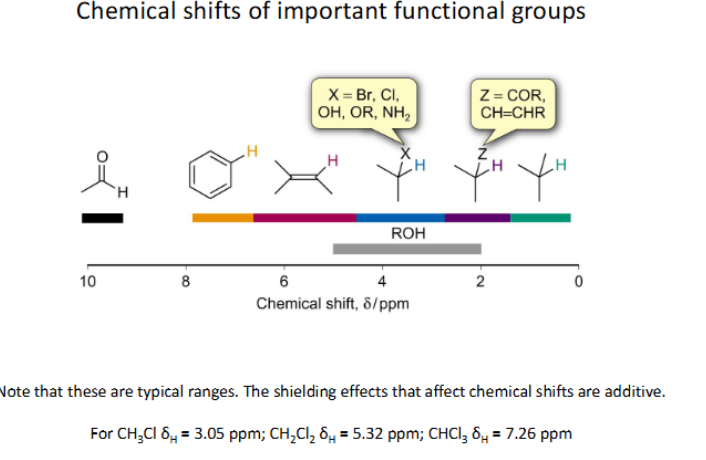
Show the chemical shifts of the important functional groups (For 13C)
TYPICAL RANGES (Shielding effects from neighbouring atoms can affect shift)
What does measuring the height of each integration curve do?
Indicates relative number of hydrogen atoms
What does the integration curve measure?
The area under the resonance signals
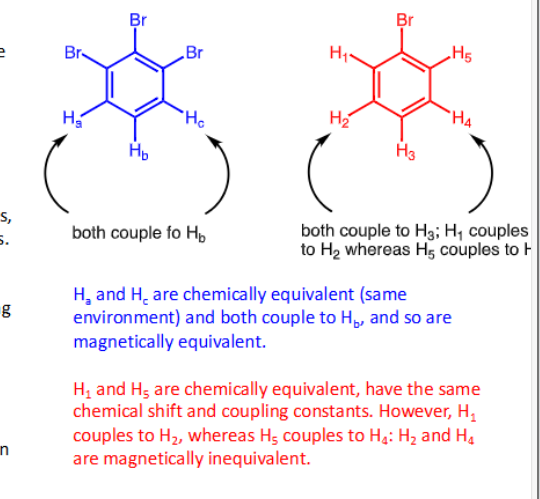
What is chemical equivalence?
Nuclei that have same chemical environment with same proximity to other nuclei in the molecule e.g= symmetry
What is magnetic equivalence
Have identical chemical shifts, coupling constants and coupling pertners
→ If nuclei are chemically inequivalent then they must be magnetically inequivalent
Whats the problem with trying to use 12CNMR?
Spin (I) = 0 but 99% abundance
Having no spin means that the NMR is silent and cannot obtain any data
Reason why 13C is used
Whats a con of using 13CNMR?
Although spin is I= 1/2, it only has 1% abundance so although almost all H can participate, only 1 out of 100 carbon nuclei will contribute to NMR
What is receptivity?
When some nuclei are more sensitive to others regardless of abundance
Does 13CNMR spectra run the same solvents as 1HNMR?
Yes
Does a typical 13CNMR spectrum have a smaller chemical shift range than 1HNMR?
No
What is the typical shift range for 13CNMR?
0-220ppm
Why isn’t 13CNMR coupling constants not as useful for structural interpretation compared to 1HNMR?
13C coupling to non-13C nuclei can be supressed by saturating the non-13C nucleus → Decoupling causing no splitting in the spectra of spin-spin coupling effect being effected (split) by decoupling
What is decoupling?
To supress coupling to another nuclei/thing
How do you resolve decoupling?
By applying additional resonance frequency → Results in singlets
What is proton-decoupled?
When 13C nuclei do not couple to 1H nuclei
What is a scan?
When spectrum quality can be improved by making multiple identical measurements and averaging the signal
→ Averages out unnecessary noise
What should you confirm before performing a scan?
Make sure all nuclei is completely relaxed (magnetisation has returned to z-axis)
→ 13C relaxes back to equilibrium slowly giving weak signals, but can wait
How do you ensure all nuclei (especially 13CNMR) relaxes before each scan?
Irradiating (saturating) nearby nucleus to relax faster increasing decoupling
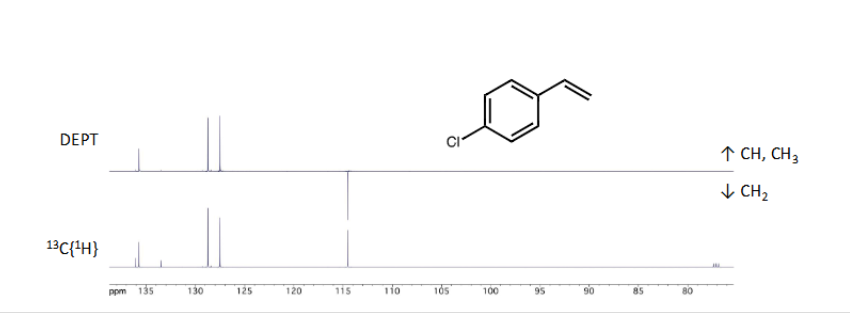
What is DEPT?
Modification of 13CNMR providing more information relating to number of protons attached to carbon. Odd number of protons point upwards on spectrum and even number of protons point downwards and quaternary carbons (no carbons attached) will not show up
What is the spin of 19FNMR spectroscopy ,its abundance and typical range?
I = ½ ,100% abundance and +500 - -500 ppm
What are satellites?
When you use 1HNMR spectrum containing a less abundant nuclei e.g = 29Si (4.7% abundance) and so the remaining 95.3% is silent ( I= 0 )
→ The NMR spectrometer doesn’t detect the difference but only measures entire contents of sample
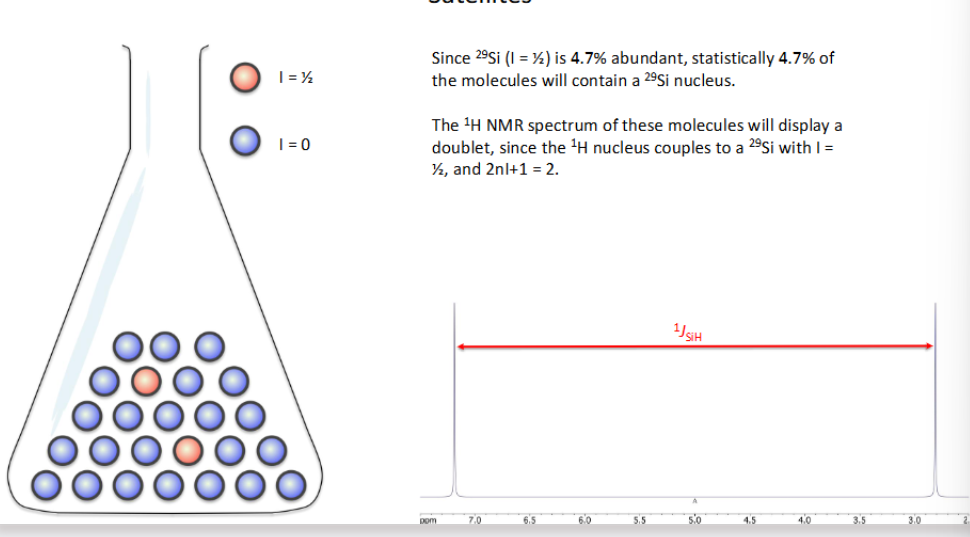
What is paramagnetic?
1 or more unpaired electrons
What nuclei(s) can you perform when running NMR on metal complexes?
1H, 13C, 31P and 15N
Why does paramagnetic metal ions make it hard for NMR spectroscopy?
Broadening of signals and large changes to chemical shifts
What is the difference between running 1HNMR spectra on coordination complexes and normal compounds?
Chemical shifts in coordination complexes will be shifted downfield a bit
→ Exceptions are if nuclei is in close proximity to metal ion or flexible ligand molecule becomes less flexible on coordination

Why is the typical chemical shifts for a hydride ligand (-H) 0 - -20ppm?
Nucleus will be highly shielded due to negative charge
→ Can couple to other 1H nuclei
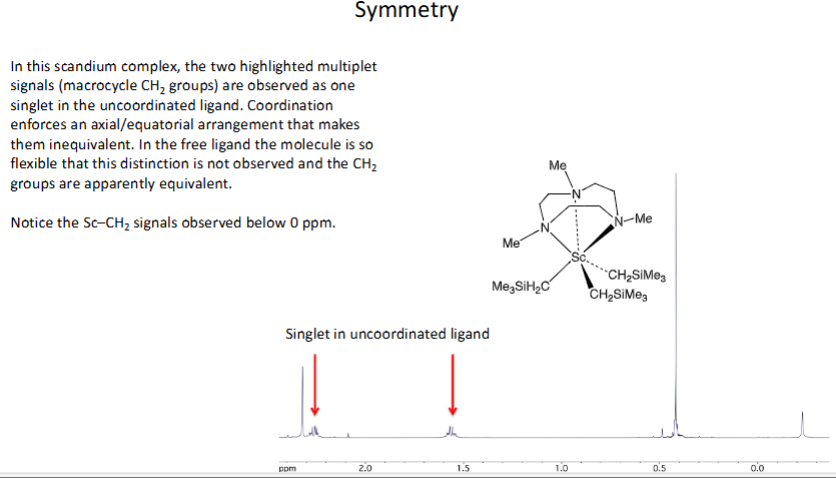
How do you show symmetry in coordination complexes? (look at example)
Can electron density of a ligand be affected by neighbouring ligands?
Yes
→ e.g = in tungsten complexes, 13C chemical shift of carbonyl ligands strongly influenced by phosphine ligand. Stronger the pi-accepting ability of phosphine, the higher the carbonyl chemical shift
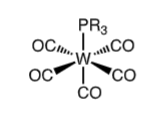
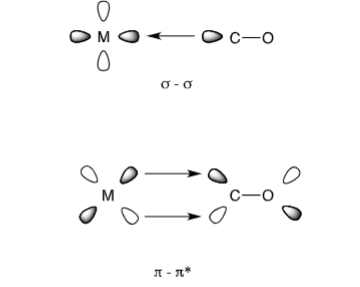
Show the pi-acceptor model and explain how chemical shift changes between C-O and a metal ligand (phosphine)
-Pi accepting phospihne ligand (M) competes for same orbitals as CO ligands. If phosphine is a strong pi-acceptor then there will be less pi-electron density for CO ligands making carbon nuclei less shielded
What is the spin value, typical shift range and abundance for 31P
I = ½
100% abundance
200 - -150(negative) ppm
→ Very sensitive
What happens to NMR spec when you measure in Hz instead of ppm?
Small difference
→ Slow frequency compared to how fast bonds move in molecules making it a ‘slow method’
What is dynamic NMR spectroscopy?
Considers situation when inequivalent parts of molecule move around faster than frequency difference of their NMR signals
How are signals and fluxionality averaged in NMR spectra?
Consider frequency difference between signals of exchanging nuclei (change of frequency) : distinct signals will only be observed if rate of exchange (in Hz) is lower than difference in angular frequency
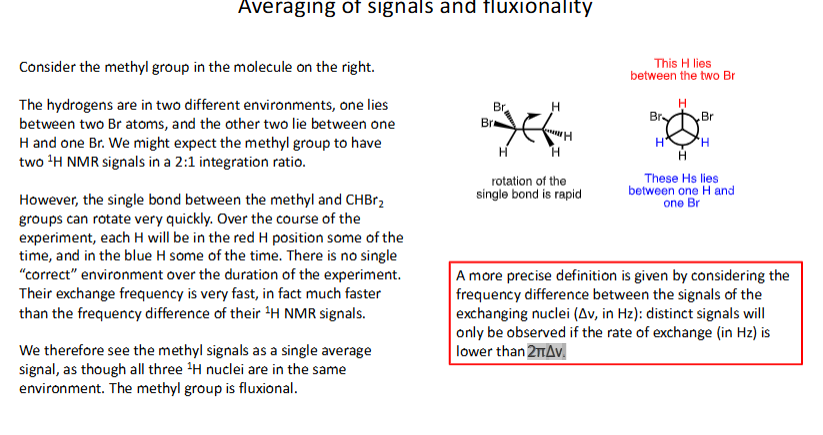
How does averaged signals change into separate signals when temperature is cooled causing rate of exchange of molecule to slow down?
Exchange process slows down
NMR signal starts to broaden and separates into 2 distinct signals
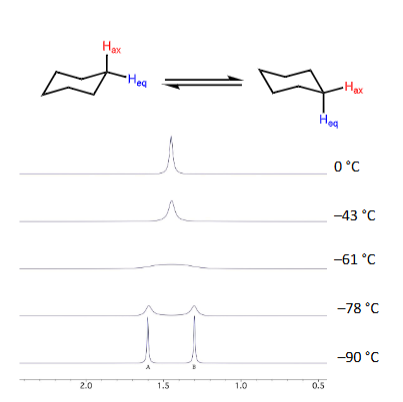
What is coalescence temperature?
Temperature at the one/two signal interchange (when splits)
How does fluxionality affected by temperature effect coupling?
Observed coupling mirrors no. of environments so simpler at higher temperatures

What is the typical chemical shift range for a CH3CHO bond in 1HNMR?
9.7-10ppm
What is the typical chemical shift range for an aromatic ring in 1HNMR?
6.8-7.8ppm
What is the typical chemical shift range for an alkene bond in 1HNMR?
4.3-6.4ppm
What is the typical chemical shift range for a H-CX bond in 1HNMR? (X=Halide)
2.4-4.7ppm
What is the typical chemical shift range for a HC-COR or HCH=CHR bond in 1HNMR?
1.7-2.7ppm
What is the typical chemical shift range for a HC-CH3 bond in 1HNMR?
0.2-1.4ppm
What is the fingerprint reigon in the IR spec?
500-1500cm-1
Why does carbonyl vibrational frequency change in IR spectrum?
Changes due to bond strength → Acidic carbonyl bonds have strong bond strengths

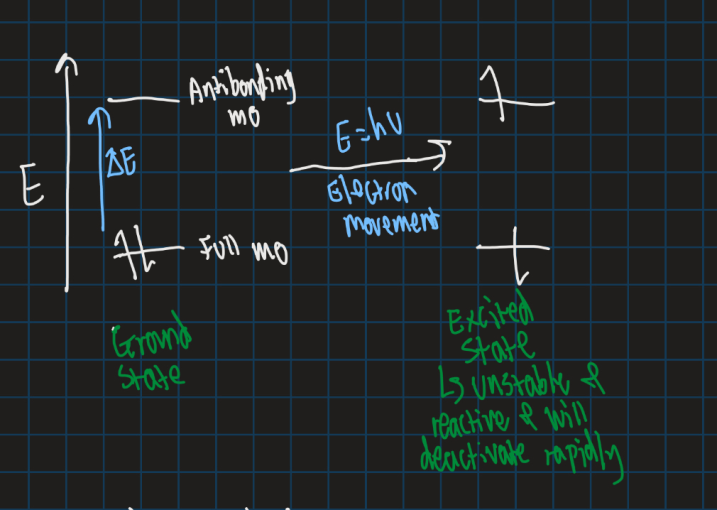
Show the types of energy transitions
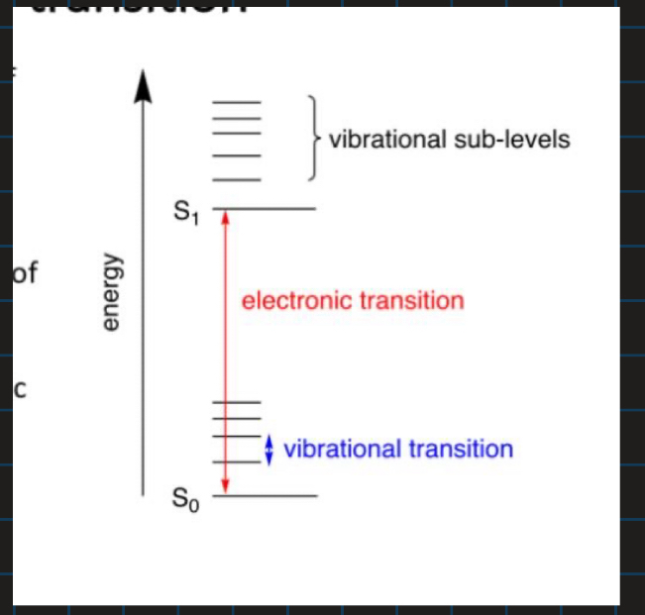
What are electronic transitions?
Movement of electrons between orbitals
How can electrons move up energy levels?
By moving from HOMO to LUMO orbitals
What energy transitions does UV and visible light promote?
Electronic transitions
What energy transitions does IR promote?
Vibrational transitions
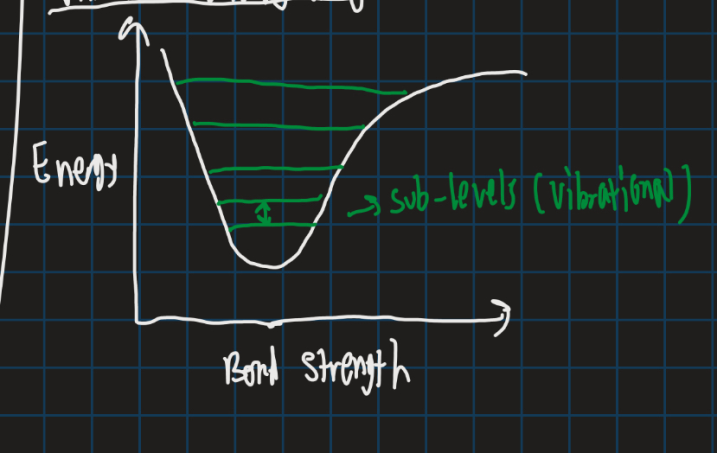
Show the vibrational energy diagram
How are UV-vis spec measured?
Done on dilute solutions at a known conc
How does UV-vis work?
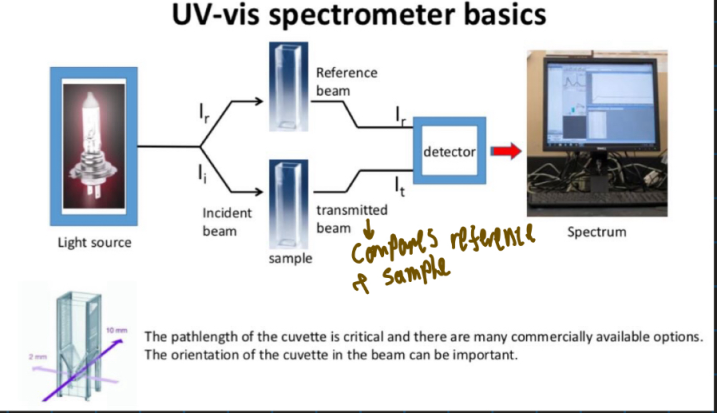
What is the formula for Beer-Lamberts law?
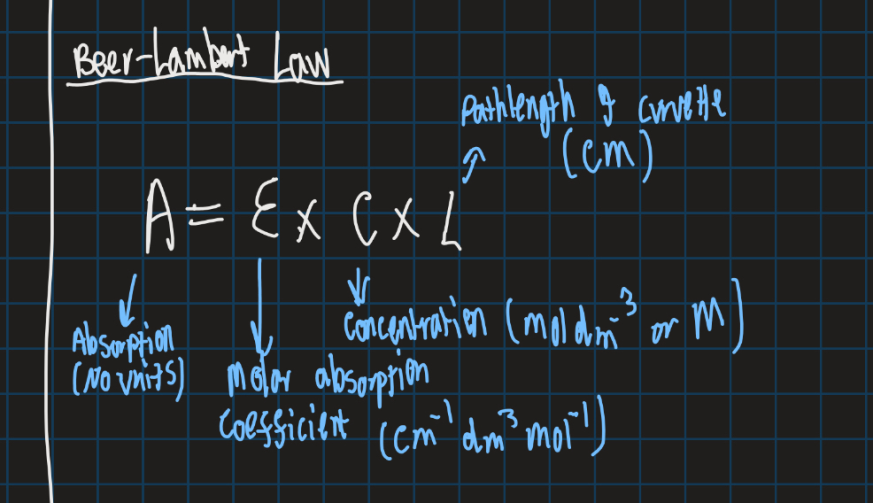
What happens is absorption of a material is 0?
Transmission = 100%
What are some applications for electronic (UV-Vis) spectroscopy?
High performance liquid chromatography (UV - Vis spec adapted as detection mode in HPLC)
Pharmaceutical analysis
UV-Vis used to measure absorbance of haemoglobin
What is a chromophore?
Any light absorbing molecule or molecular fragment
What is auxochrome?
Group of atoms attached to chromophore that modifies its absorption properties
What is bathochromic shift (red shift)?
Shift to longer (lower energy) wavelength
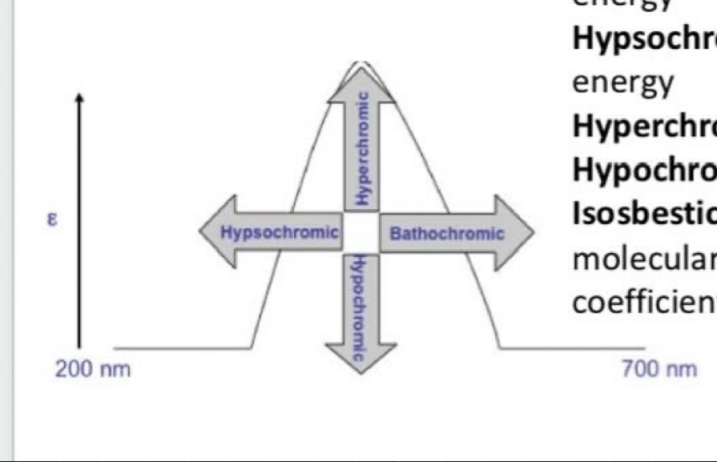
What is hypsochromic shift (Blue shift)?
Shift to shorter (higher energy) wavelength
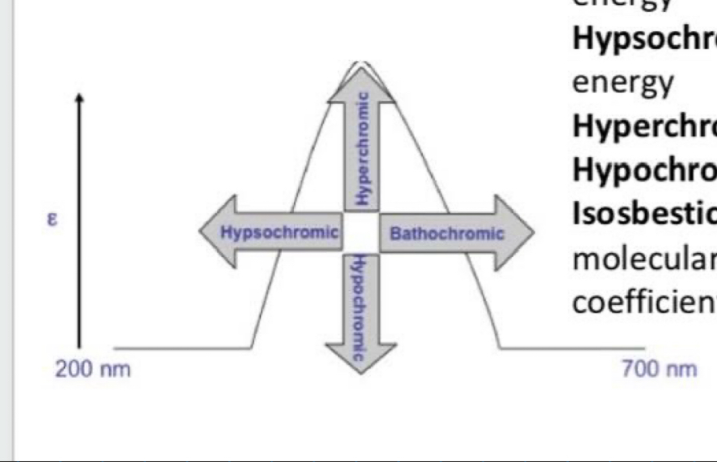
What is the hyperchromic effect?
Increase in intensity
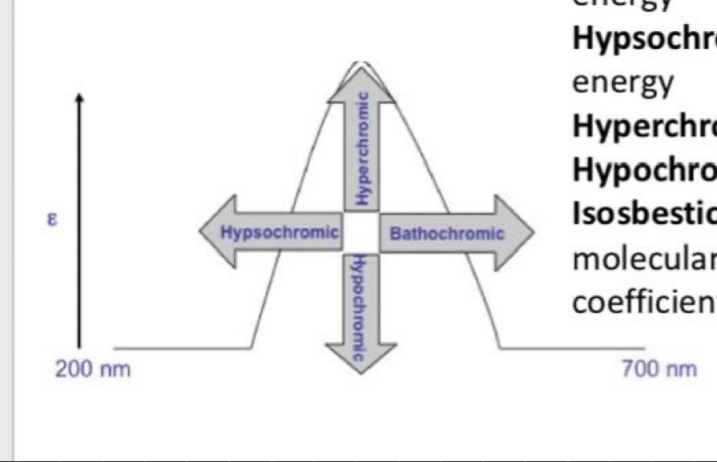
What is the hypochromic effect?
Decrease in intensity
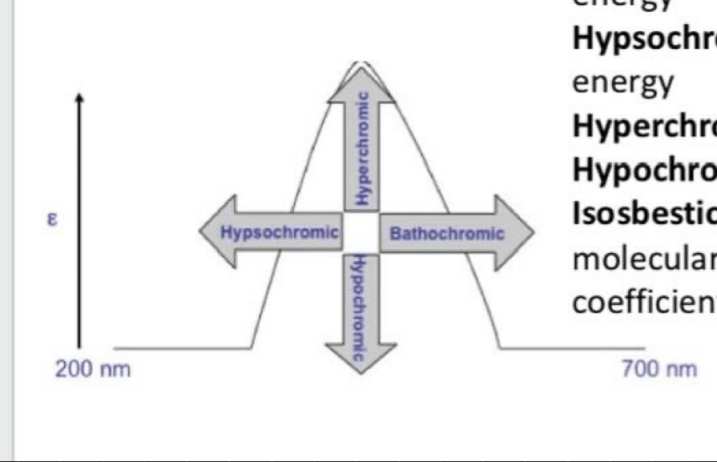
What is the isosbestic point?
Wavelength where 2 or more molecular species of a mixture exhibits the same extinction coefficient
How do you describe electronic transition?
If wavelength of absorbed light has enough energy, this excited electron from bonding or non-bonding orbital to empty anti-bonding orbital