Neuro Anatomy
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System
contains the brain and spinal cord. The nerves act as a communication network to relay sensory and motor commands
Somatic Motor Systen
Controls muscles and contains automating nervous system
Automating nervous system
controls automatic functions like digestion, heart rate, tears, etc.
Sympathetic System
aka the fight or flight system. Goal being to get you ready for an action. I.e Heart rate, quicker breathing, secretes adrenaline
Parasympathetic
brance prepares your body to rest and digest
-primarily uses ACH as neurotransmitter
i.e stimulates blood flow, slows heart, increases digestive functions
Enreric nervous system
controls the stomach and gut
-partially controlled by inputs form the vagus nerves that tells your body the time of day it is or when you’re eating
Cerebrospinal fluid(CBL)
Fluid that protects the brain with a cushion and has a part time job of clearing away waste products
Meninges
outside covering w/multiple layers. Almost like a protective wrap around your brain
Choroid Plexus
cells that produce cerebrospinal fluid from blood
Hydrocephalus
Disease where ventricles can become enlarged because of abnormal pressure in the brain or shrink surrounding areas of brain tissue
Nuclei
compact cluster of neurons w/similar inputs and outouts
-typically working to do a job together
Cortext
arranged in a continuous folded sheet on the outside of the brain
Tracts
large white matter bundles
Commissures
when neurons cross to the opposite hemispheres
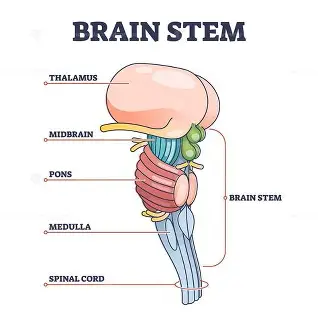
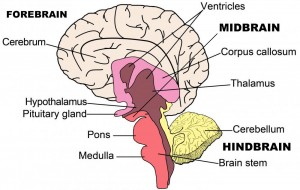
Brain Stem
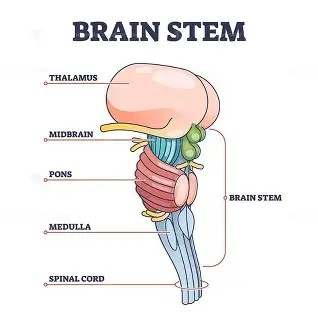
Medull a
critical for life because it controls the motor nuclei, heart rate, breathing, and arousal
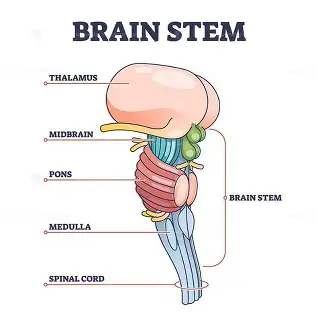
Pons(bridge)
links the brain and cerebellum and contains sensory and motor nuclei for the eyes
-round eye shape on the scan
-controls face and mouth functions
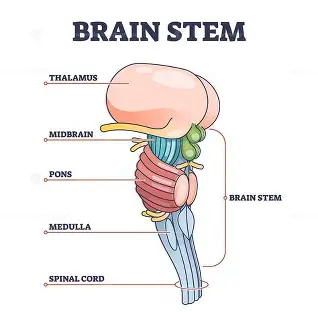
Midbrains
processes anxiety and fear responses
-in charge of automatic orienting attention like if someone claps or raises their voice
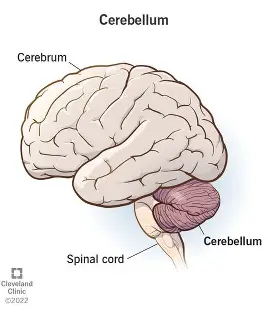
Cerebellum
receives motor plans and sensory iputs about the position of the body in space to help coordinate motor movements like balance or throwing
Thalamus
serves at the gateway for all the sensory info to the brain and body (except smellO
Lateral geniculate nucleus
reciev incoming visual info and contains a retinotopic map of visual locations
Medial geniculate nucleus
receives auditory info and contains tonotopic map of different frequencies
Sagittal View
Transverse
coronal view
Rostral (anterior)
dorsal(superior)
ventral(inferior)
caudal(posterior)
Parts of the brain stem
Lateral geniculate nucleus
receives incoming visual info and contains retinotopic map of visual locations
Medial geniculate nucleus
receives auditory info and contains tonotopic map of different frequencies
hypothalamus
controls hormone production and released thru pituitary gland
Limbic System
subcortical structures surrounding the brainstem
The limbic system functions
1)Bind events and experiences(hippocampus +mammilary body)
2)Focus emotion and motivation on external objects(amygdala)
3)Coordinate social behavior/emotional processing (amygdala)
4)Prrocessing smell, taste,and pain
Basal Ganglia
set of bilateral nuclei surrounding the thalamus
-receives sensory and motor info that aid in action selection and task switching
Reward prediction error
brain predicts the outcomes of our actions and dopamine is released in the nucleus when the outcomes are as good as or better than we predicted
Parietal Lobe
responsible for directing our visual attention in space, locating and interacting with objects, and mathematical processing
Occipital lobe
visual info is processed here
-travels from retina, to the thalamus, to primary visual cortext
Temporal Lobe
Includes Hershel’s Gyrus where auditory info is processed at the top of the temporal lobe
*criticala for speech recognition and language comprehension