Giant Covalent structures
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
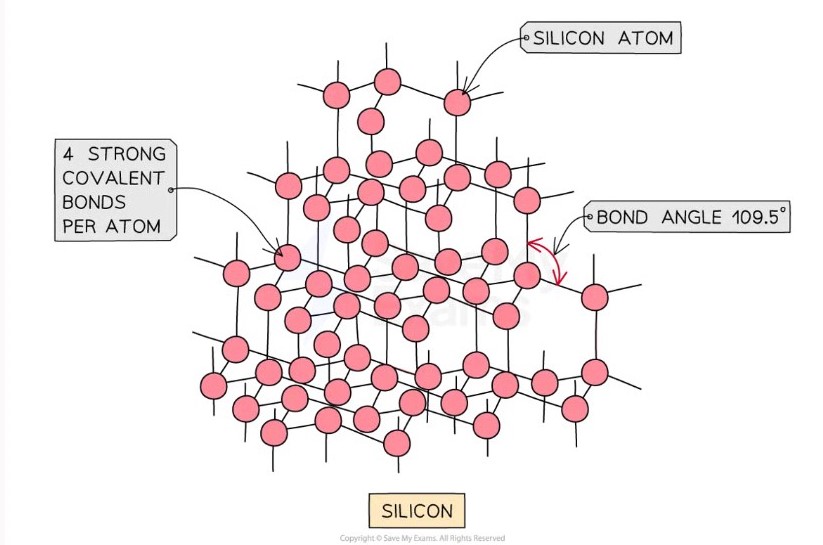
Silicon
Each silicon atom is covalently bonded to four others
Tetrahedral geometry
Bond angle of approximately 109.5
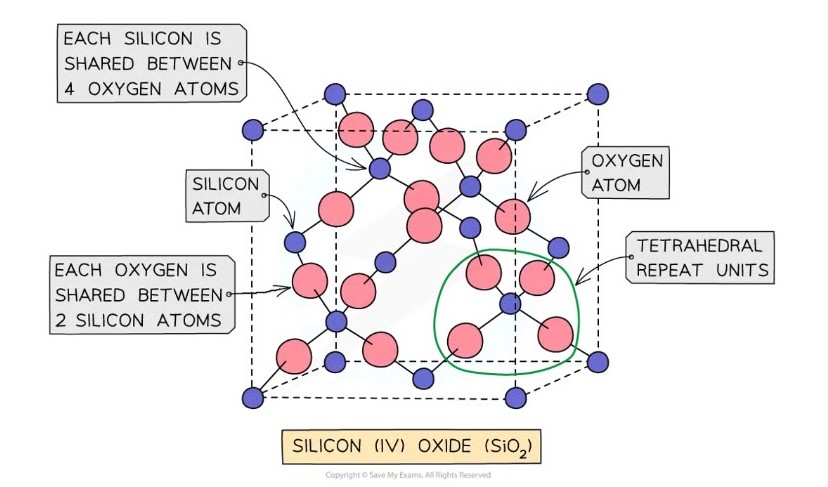
Silicon (IV) oxide
Also known as silicon dioxide
Main component of sand
Each silicon atom is covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms
Each oxygen atom is bonded to two silicon atoms
Tetrahedral geometry
Structure extends in all directions
The empirical formula is SiO2 because the structure is based on a repeating ratio rather than discrete molecules.
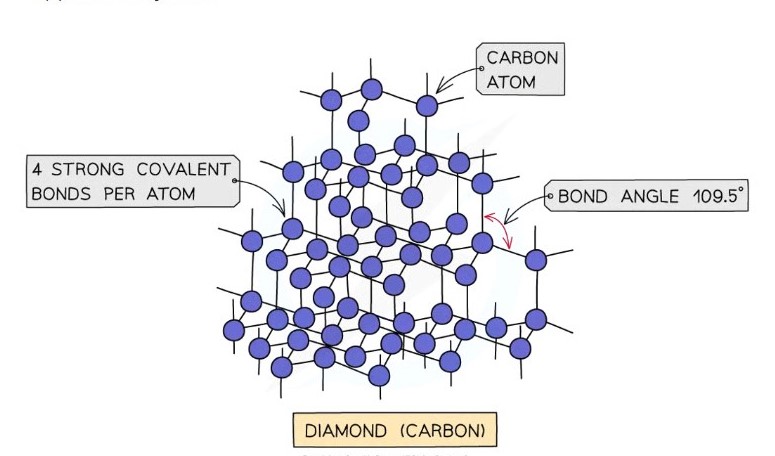
Diamond
Each carbon atom is covalently boned to four others
Tetrahedral geometry
Bond angles of 109.5
Diamonds are very hard because breaking the structure requires breaking many strong covalent bonds
Does not conduct electricity because all four outer electrons on each carbon atom are bonded.
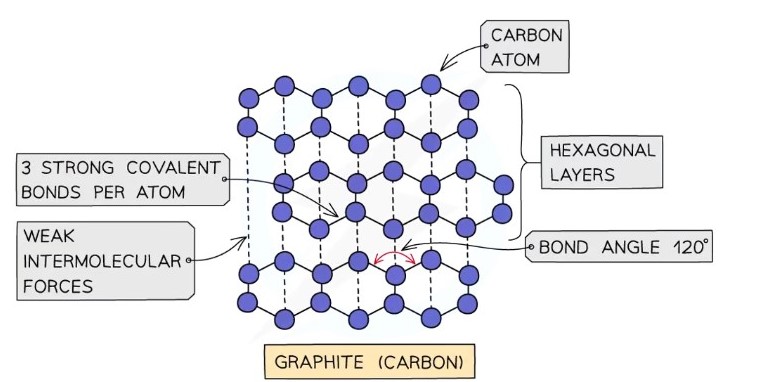
Graphite
Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three others in hexagonal rings arranged in flat layers
Molecular geometry is trigonal planar
Bond angle of 120
Graphite conducts electricity because the fourth outer electron of each carbon is delocalised and moves freely between the layers
Graphite is soft and slippery because the layers are held together by weak intermolecular forces and can slide over each other
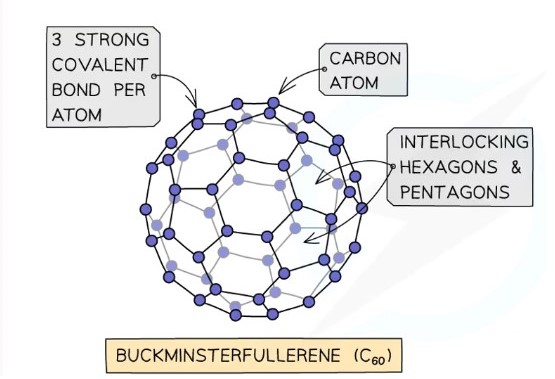
Buckminsterfullerene
A molecular form of carbon made of 60 atoms boned in a spherical structure
Each carbon forms three covalent bonds, creating a pattern of interlocking hexagons and pentagons
The remaining electron on each carbon is delocalised, allowing limited, but some electron movement, hence it is a semiconductor
Graphene
A single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice
Each carbon atom is bonded to three others with trigonal planar geometry
Bond angle of 120
Conducts electricity because the fourth outer electron of each carbon is delocalised
The structure of graphene is two-dimensional, and is one atom thick
Strong and flexible