Topic V-a : Electricity and Magnetism
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Electrical Force
The attraction or repulsion between charged particles.
Conductor
Something that allows electrons to move freely, the electrons will now space out across the material.
Insulator
Something that tightly bounds electrons to their atoms ; they cannot move as freely.
Static Electricity
Electrical phenomena related to charges that are at rest.
Ways to charge an object
by friction
By conduction
By induction
Electrostatic Series
A chart that ranks materials from those that more easily lose electrons to those that more easily gain them.
Coulomb’s Law
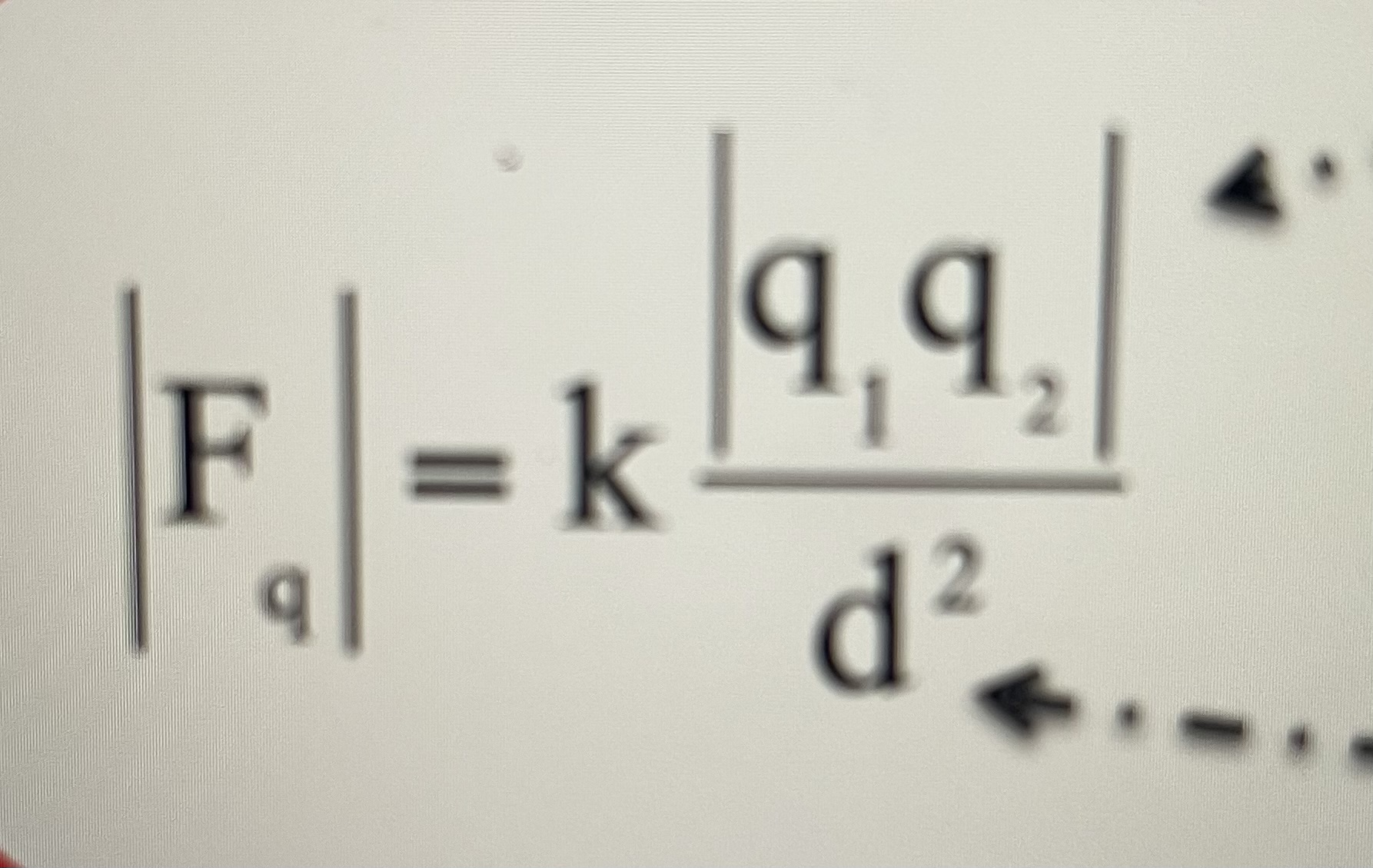
What is an Electroscope
A device that detects the presence of an electric charge on an object.
What is Coulomb’s Constant

What is an Electric Field
A region around a charged object where other charges experience an electric force. It depends on the charge “Q” that creates it and is measured in newtons per coulomb (N/C).
What are lines of force
Visual representations that show the direction a positive test charge would move and the relative strength of the electric field.
The Worldwide Convention
Electric field direction. Positive charges go outward, negative charges go inward
Spacing of electric field lines
Closer lines mean a stronger field, and wider spacing means a weaker field.