Anatomy Lab 1 practical.
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Broken up by action and Nerve connection
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
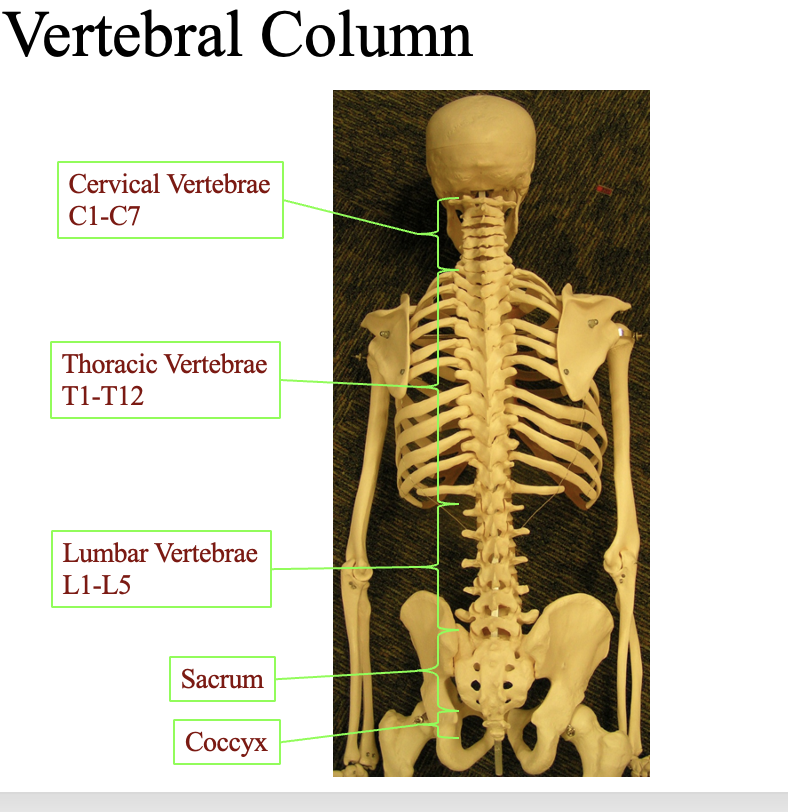
where can you find each vertebrae? cervical, thoratic, Lumbar, Sacrum, Coccyx
look at the diagram
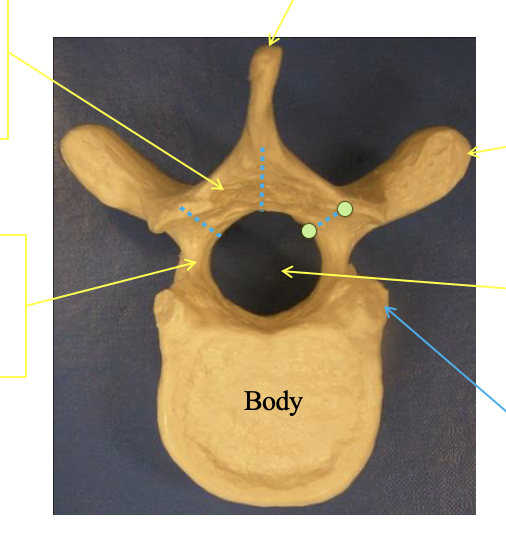
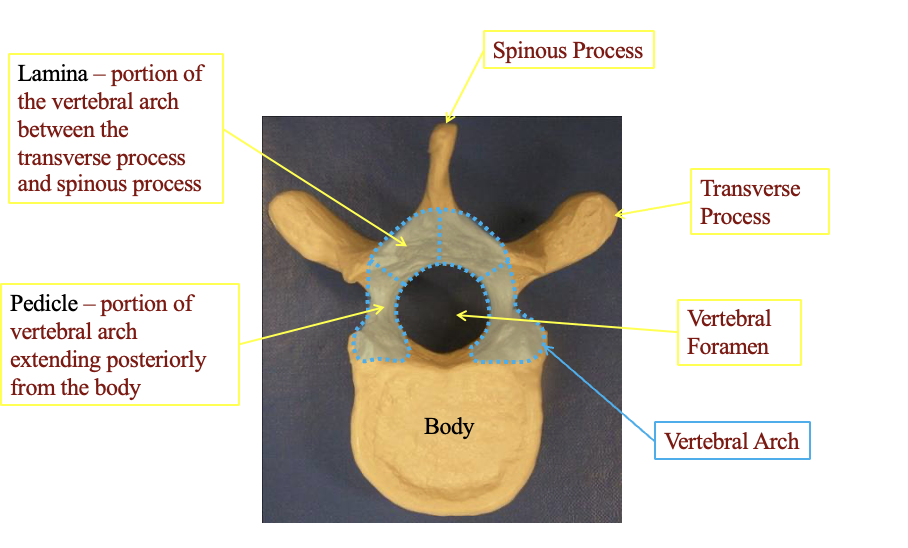
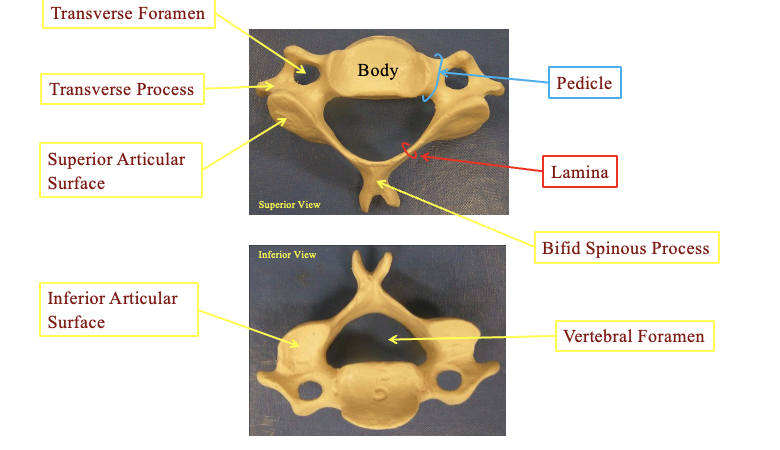
What are some of the general featers of the vertibrae
lamina
portion of the arch between the transverse process and the spinous process
p
pedicle
portion of the vertebral arch extending posteriorly from the body
spinous process
the tip at the top
transverse process
Transverse proess. there are two and sticks out
Vertebral formen
the little part in the centrer where the spinal nerves go
Vertebral Arch
the connection the arch part in the center
the body
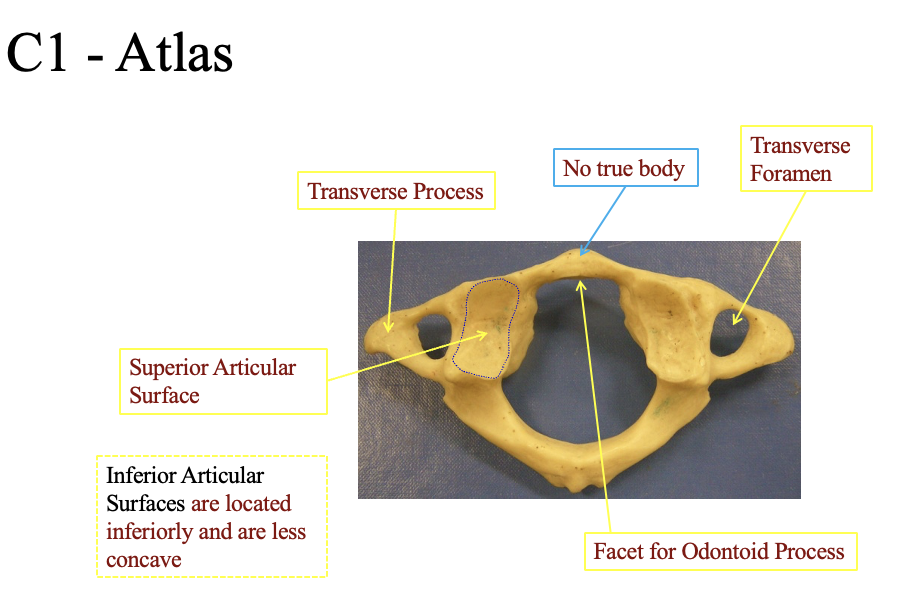
Describe the components of the C1- Atlas. What makes it unique?
has no true body
no hard part in the center for support
Transvere formen
place where the arteries goes to the head (two sides)
inferior Articular
located inferiorily and are less concave (on the other side
Facet for odontoid process
The flat ridge in the front. slight bump
Superior articular surface
The divivit on the side (both sides
C1 and c 2 are used for pivoting
note that thepivod section of C2 (ridge is closeted to the anteiror side (the facet for ontoind process
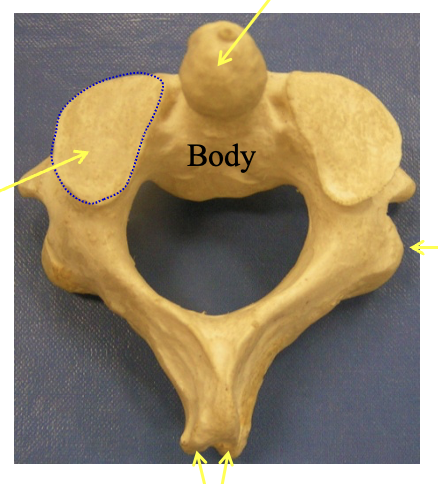
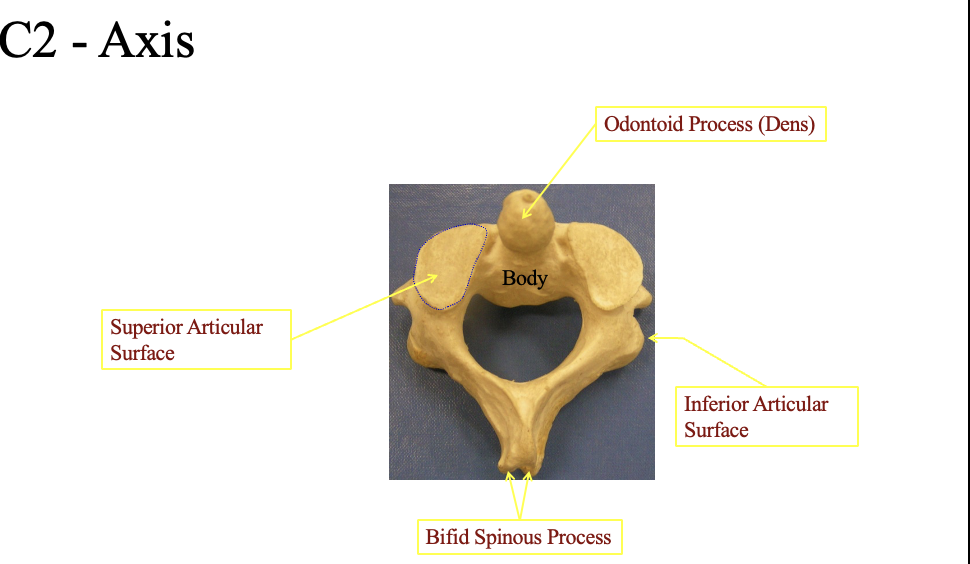
C2 - Axis
Ontoid process (Dens)
where the pivot point
Supeiror articular surface
The top flat part (on both sides
Inferior articular surface
bottom flat part posterior
bifid spinous process
The bumpy portion in the back posteiror)
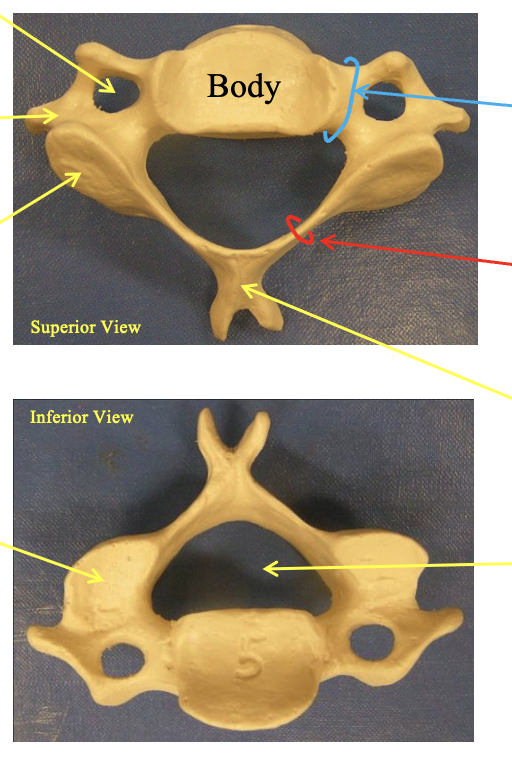
Cervical Vertebrae (C2-C7). How can you identify it vs the thoractic and lumbar.
Transverse forament
holes on the side for the artieres to the brain. posterior sectio
Transverse process
the little divit on the side next to the transverse forament
Pedicle
the joining section beween the body and the forament
Lamina
the little thin area on the sides next to the articular surfaces
Bifid spinous proess
space at the posterior of the vertibrae
supirior articular surface
fat area at the side top portion
inferior articular surface
flat area at the side bottom portion ( you can tell inferior if the binfid spinous process is at the top) (posteriro
vertebral forament
the hole in the center
you can tell because it has the holes
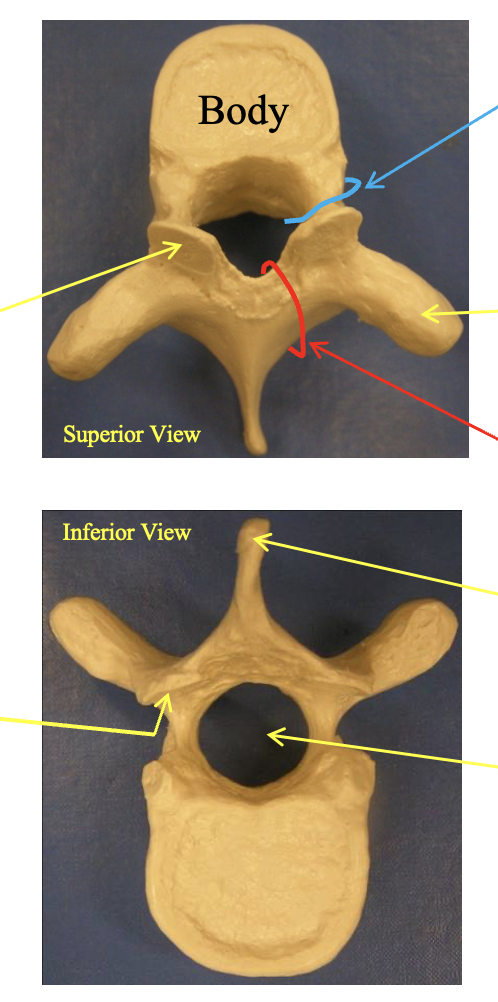
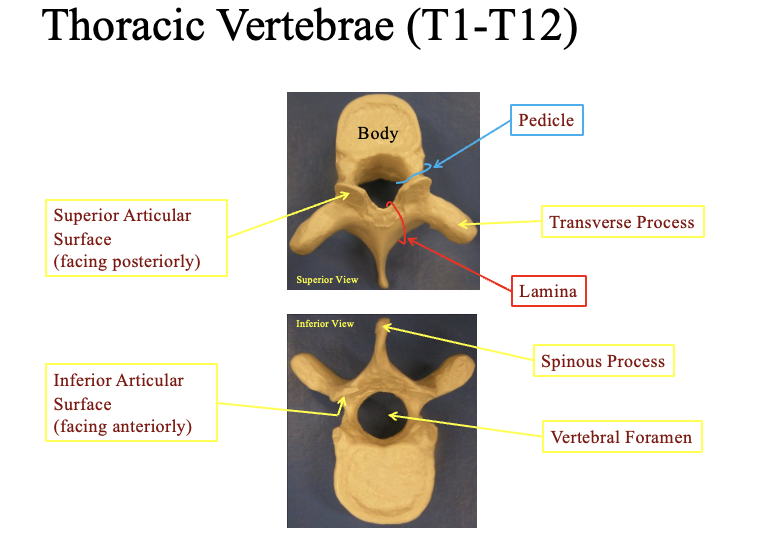
Thoractic vertebrae? Describe the anatomical structure. how can you tell whats waht? whats special about the lateral view
note that to tell it looks like a young moose
posterior = with the pointy part facing backwards out your spine
Superior articular surface (faces posteriorly)-
flat ridged bumps above the pointy parts
inferior articular surface
the inner part of the bumps facing the hollow shell of the vertebrae
pedicle
cercumferance area by the body
Transverse process
transverse process = the horned areas on two sides
spinous process
the most posterior part jutting out
Vertebral foramen
the hollow center
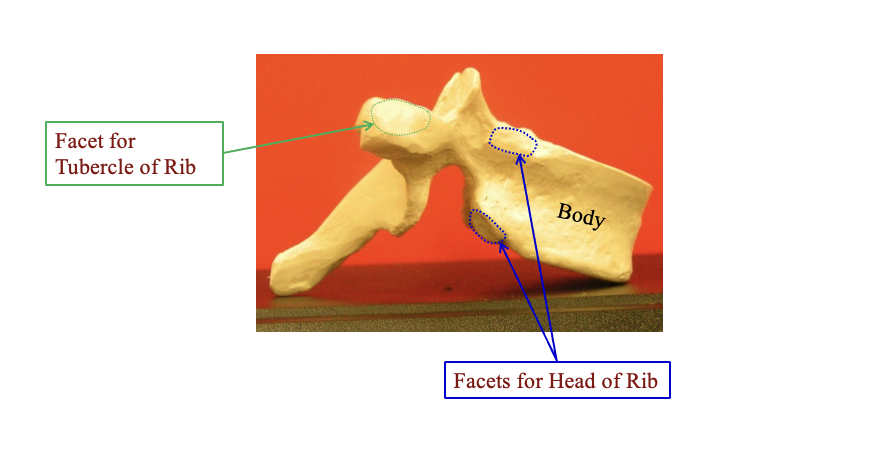
Lateral view: where the ribs connect
by the body you have two facetts for the head of the rib
on the transverse processes = facet for tubercle of rib
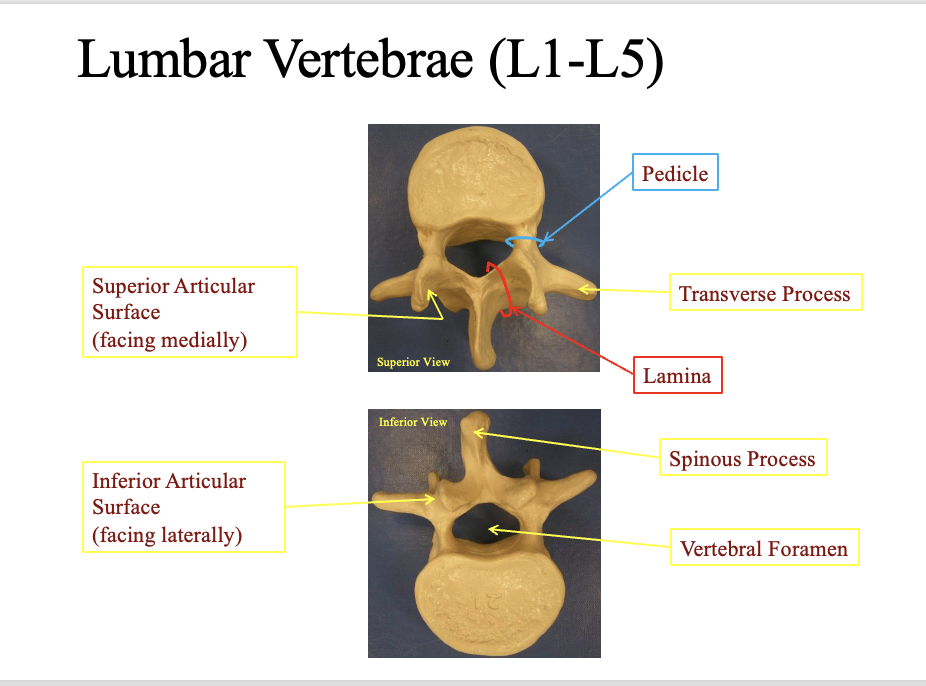
Lumbar vertabrae (what are its components and how do you identify it from the rest
Superior articular surface
faces medially close to the spinous process (facing)
Inferior articular surface
faces laterally (sideways) away from the spinous process on the bottom
Pedice
rounded ara by the vertebral foramen
Transverse process
the most lateral horned areas
Lamina
he cercumferance combining the spinous process and the articular surfaces
Pinous process
the most posteiror/ jutted part
Vertabral foramen
the hole in the center for the spinal nerves
hint: looks like an elephant
pointy part is the posterior
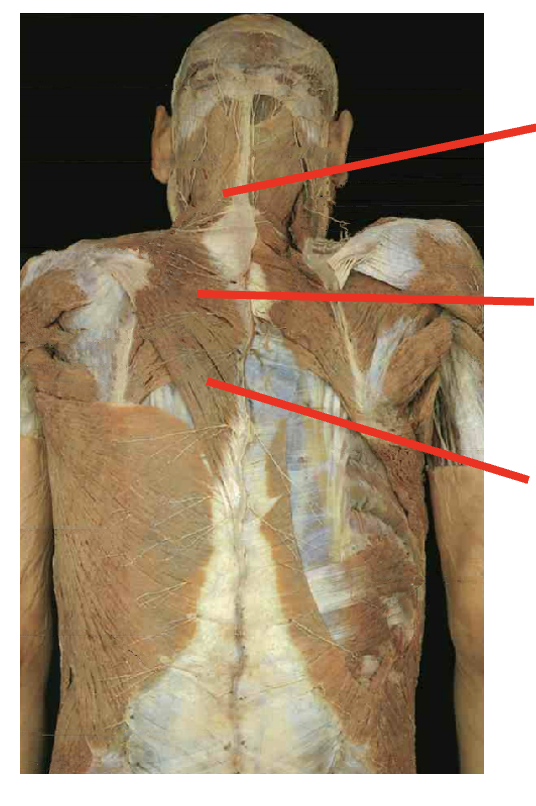
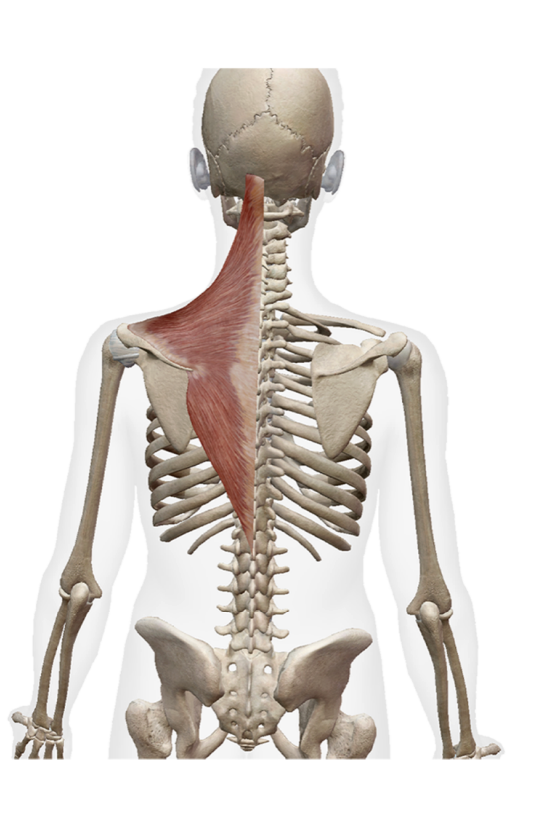
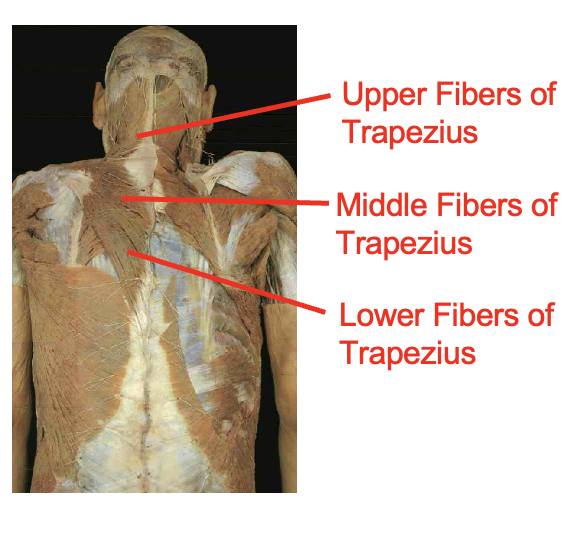
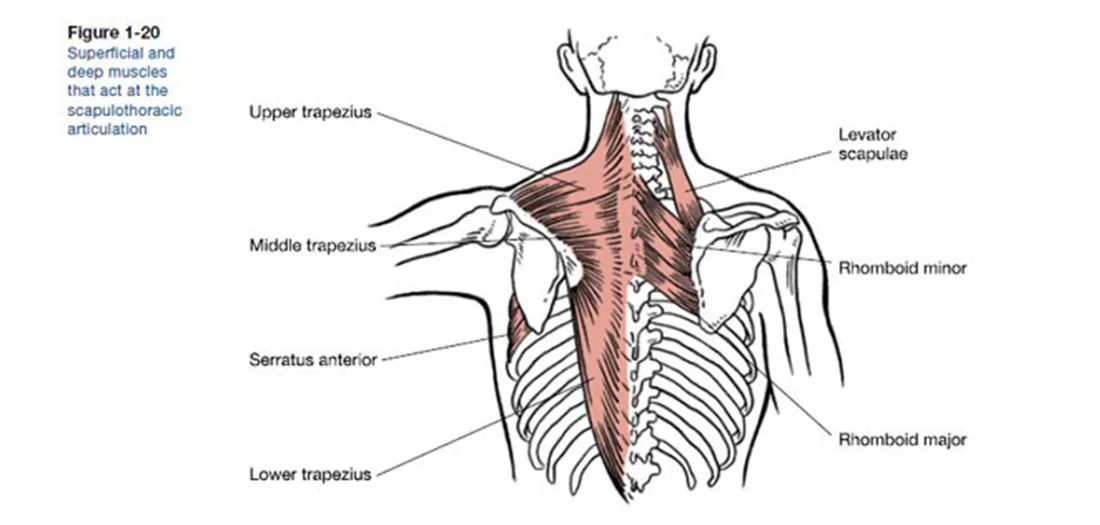
What are these muscles. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
Trapezius
origin
occipital proturberance
ligament nuchae
spinous process fo c7-t12
insertation
upper- lateral calvical
middle - spine of scapula
lower fivers - root of the spine scapula
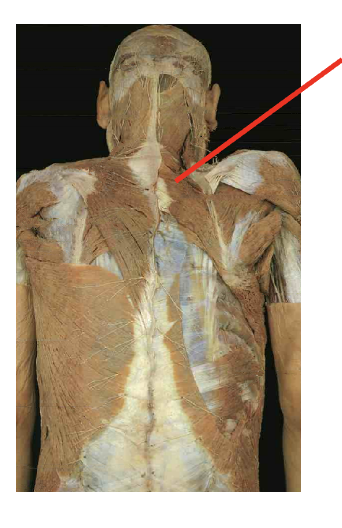
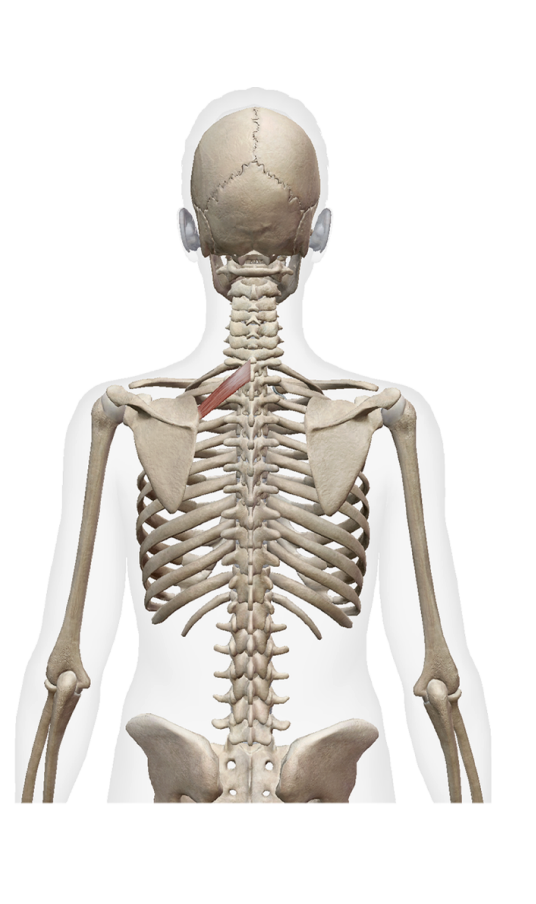
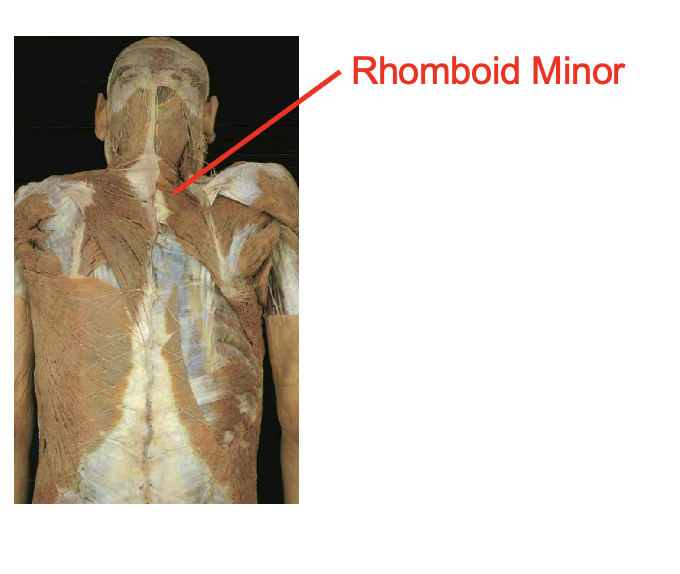
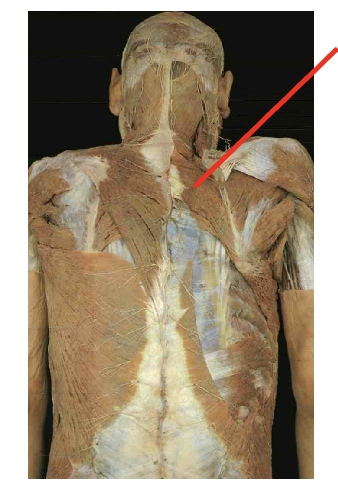
What is this muscle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
Rhomboid minor
origin
spinous process of C7-t1
insertation
root of spine of sclpula
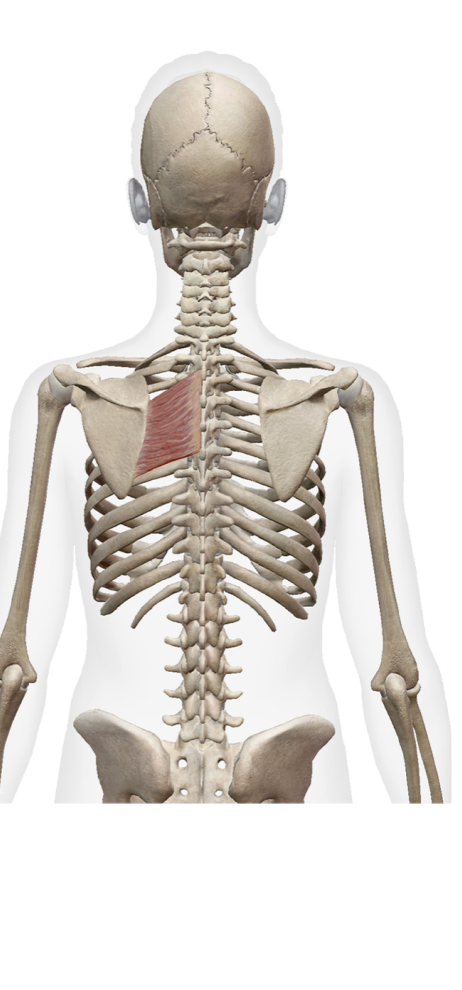
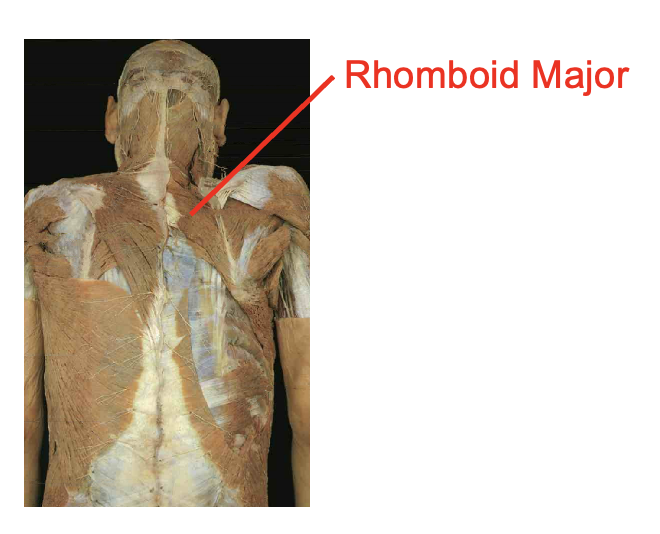
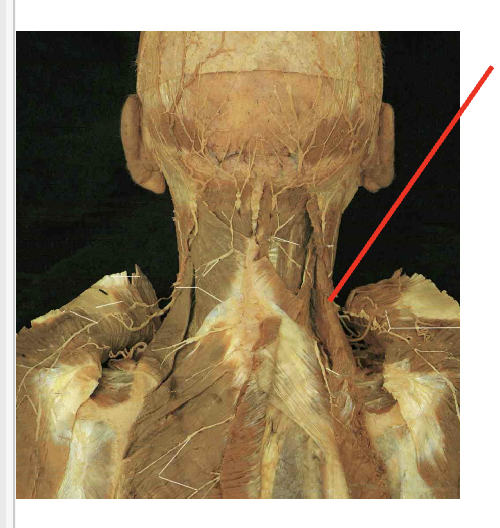
What is this muscle. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
Romboid Major
Origin
Spinous process of T2 -T5
Insertation
vertebral border of scapula inferior to root of spine
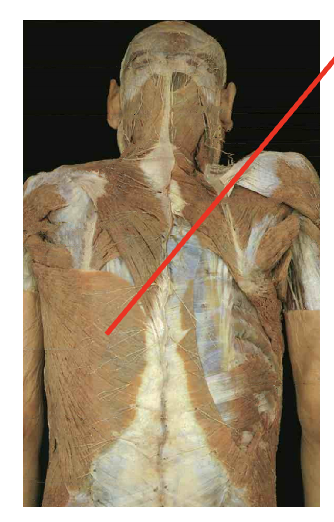
what is this muscle. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
levator scapulae
Origin
Transeres process of C1-C4
Insertation
Vertebral border of scapula superiror to root of spine
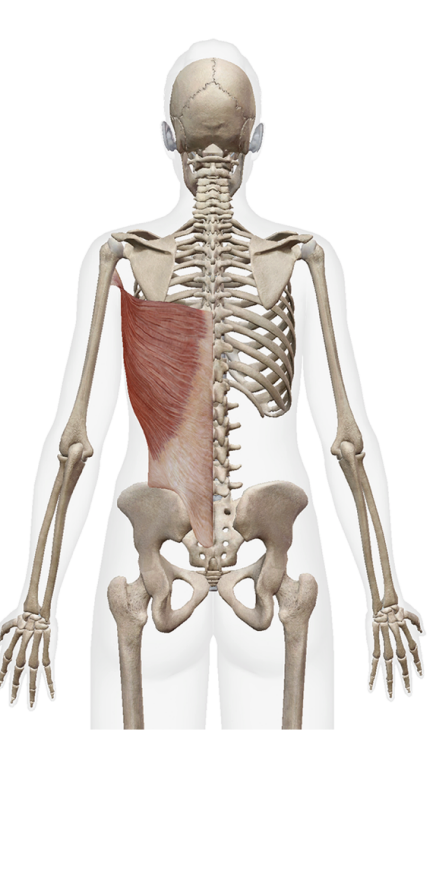
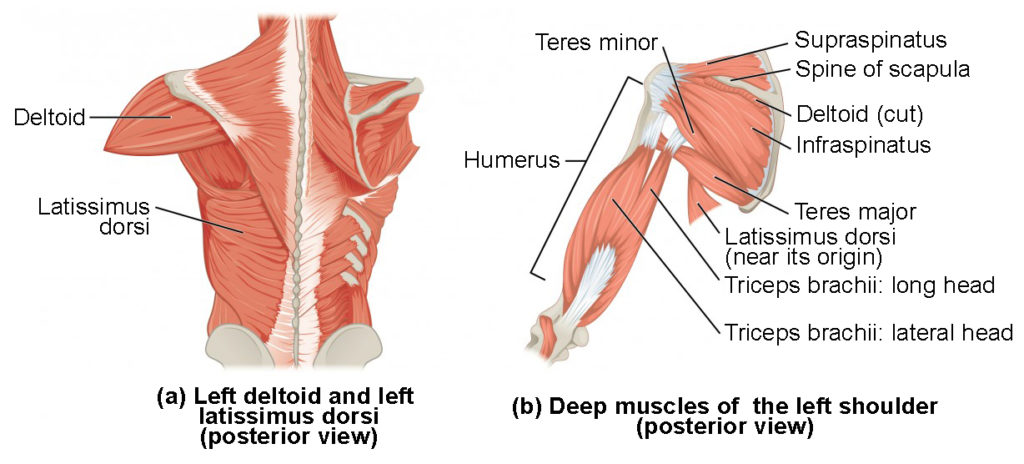
What is this muscle. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
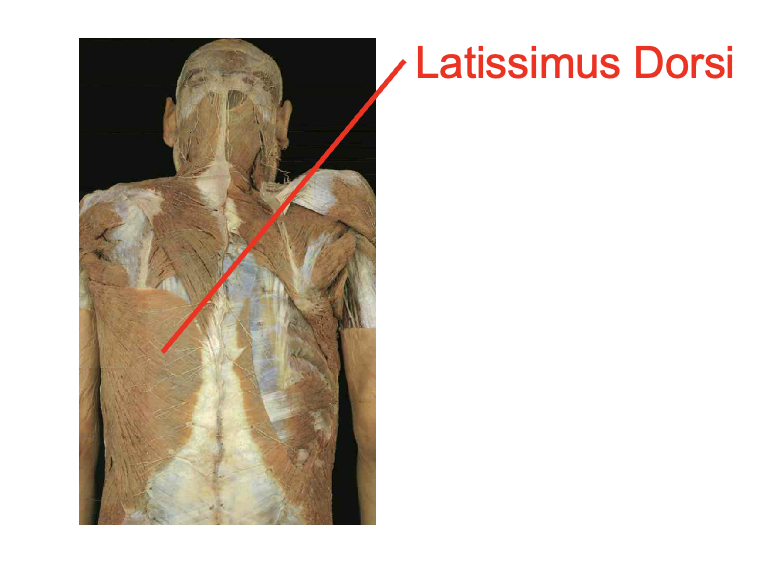
latissimus Dorsi
Origin:
Spinous process of T7-T12
lower ribs
Thoracolumbar aponeurosis
iliac Crest
Insertation
Bicipital Groove of humerous
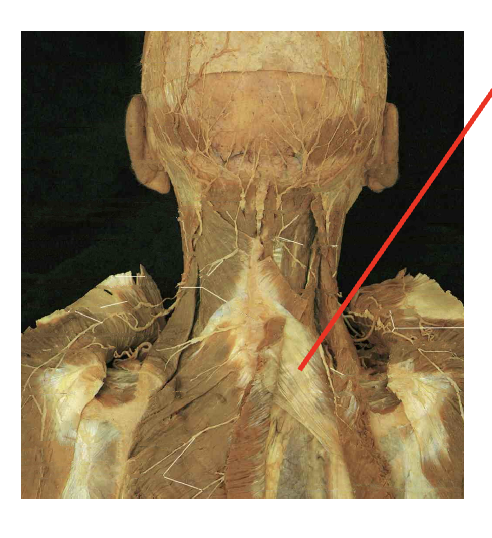
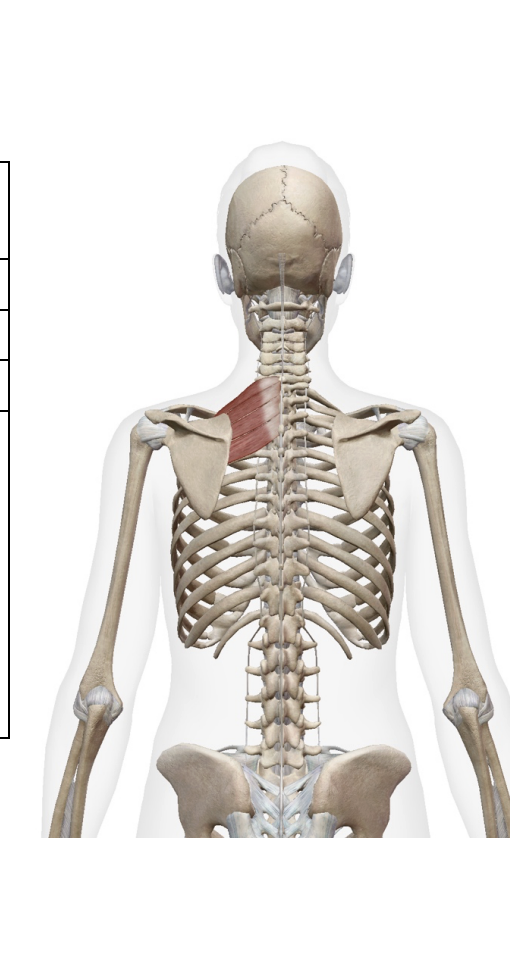
what is this muscle. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
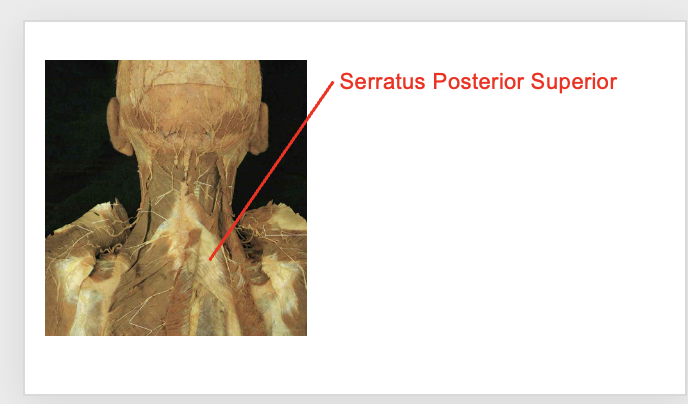
serratuss Posterior supeiror
Origin
Ligamentum nuchae
Spinous process of C7-T3
Inseration
supeiror border of ribs 2-4
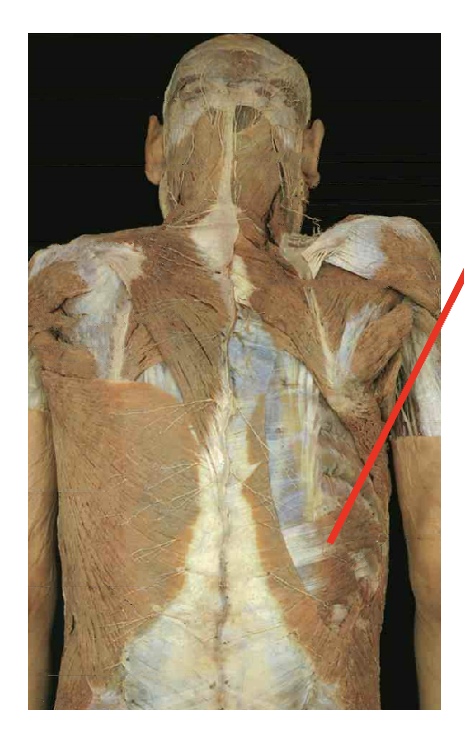
What is this muscle. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
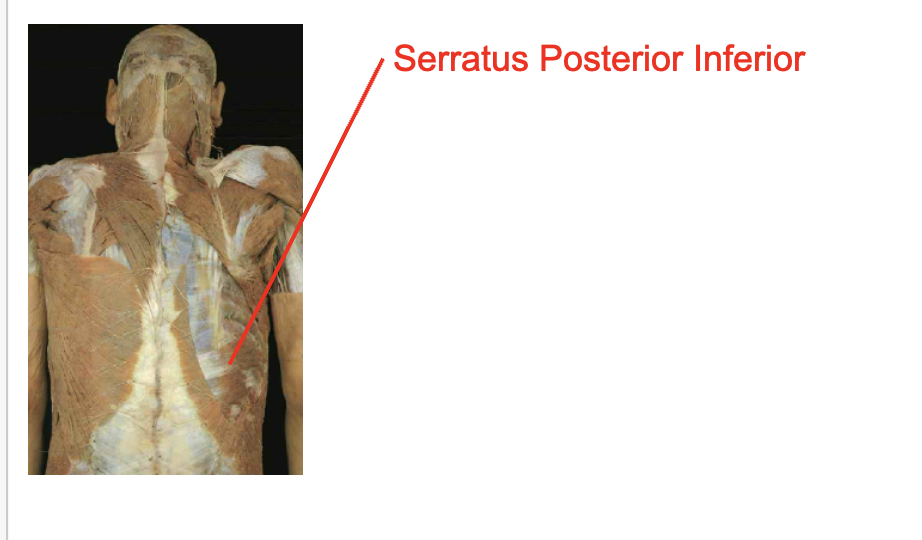
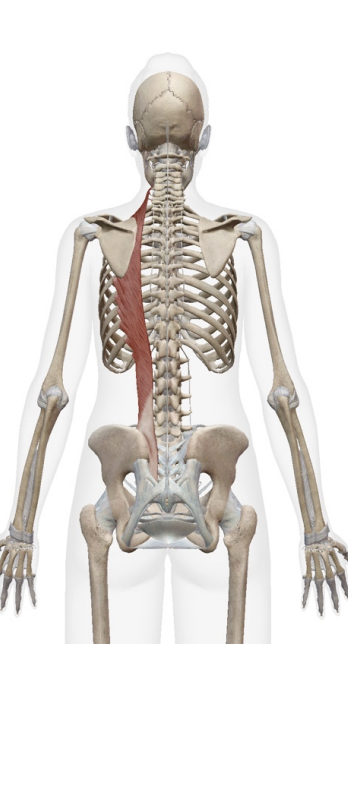
Serattus postierior inferior
Origin
Spinous process of T11-L2
Inseration
Inferior border of ribs 9-12
what is this muslce. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
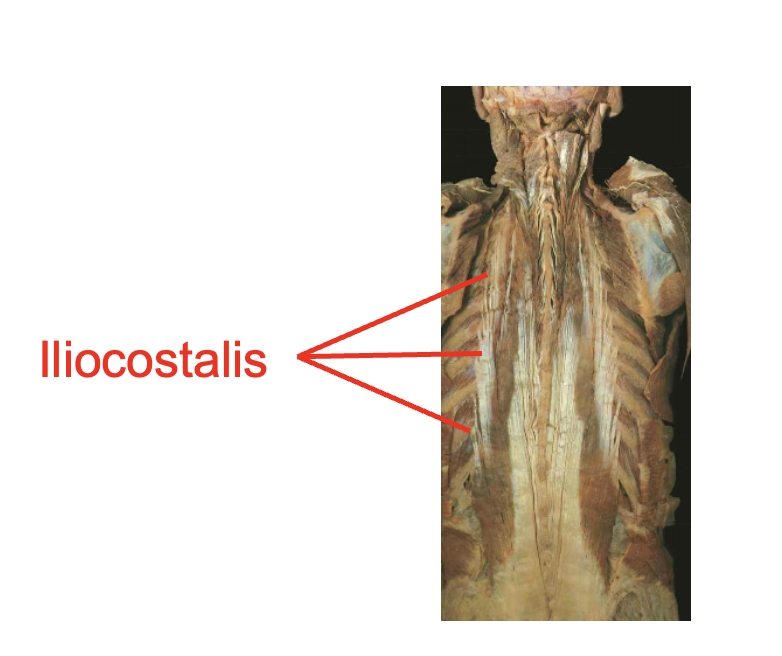
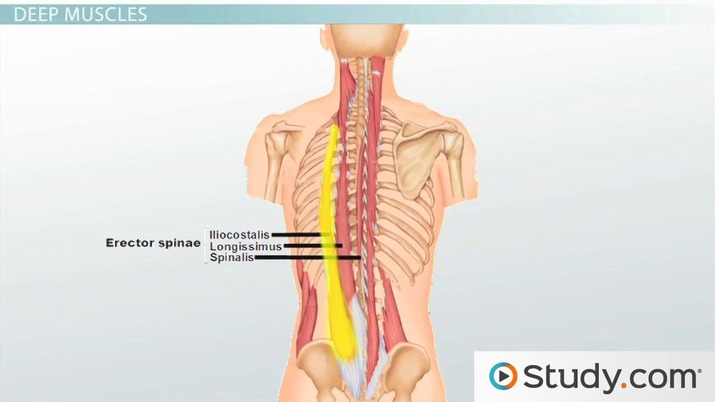
illiocostalis
Origin
Posterior ribs
Thoracolumbar aponeurosis
iliac crest
sacrum
Inseration
Trasnverse process of cervical vertebrae
Posterior ribs
Action
what is this muscle. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
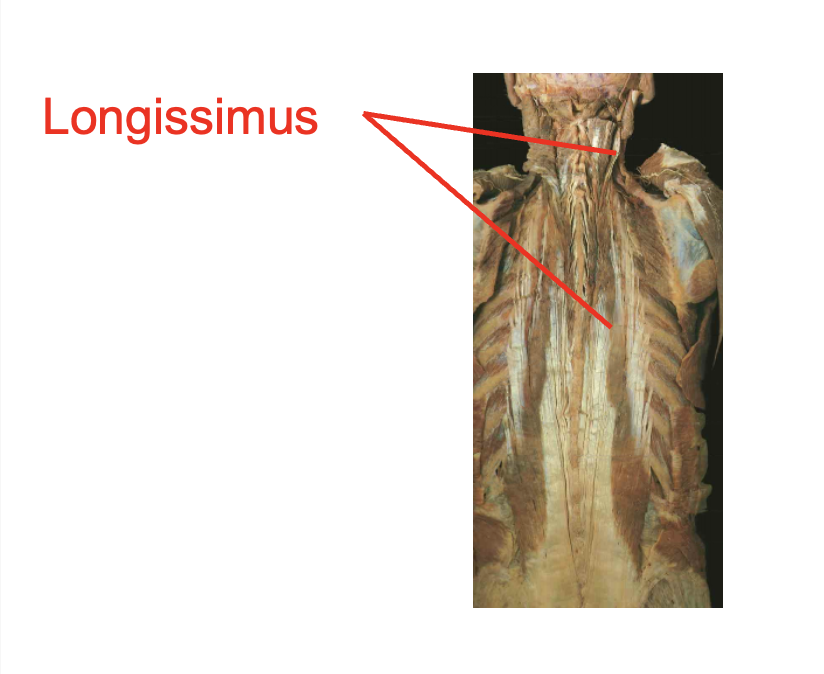
Longissiumus
Origin
Transverse process of cervial ant thoractic vertibrea
Thoracolumbar aponeurosis
liac crest
sacrum
Insertion
mastoid process
transverse process of cervical and thoractic vertibrea
Action
What is this muscle. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
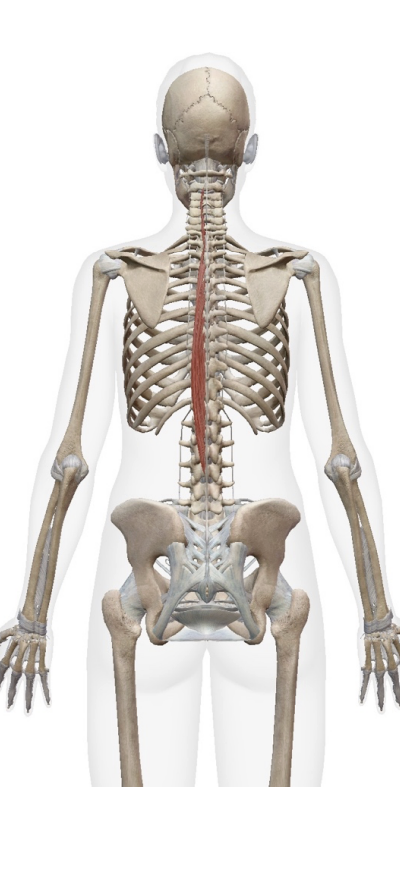
spinalis (notes runs along the spineal area).
Origin
ligamentum nuchae
spinous process of cervical thoractic and lumbar vertibrea
Insertion
occipital bone
spinous process of cervical and thoractic verterael column
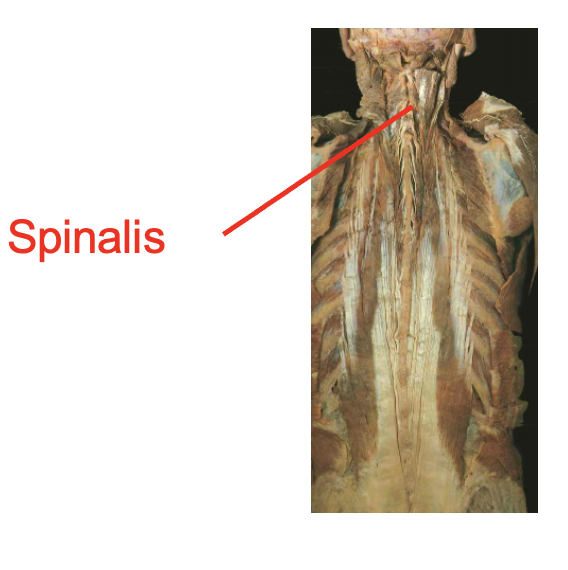
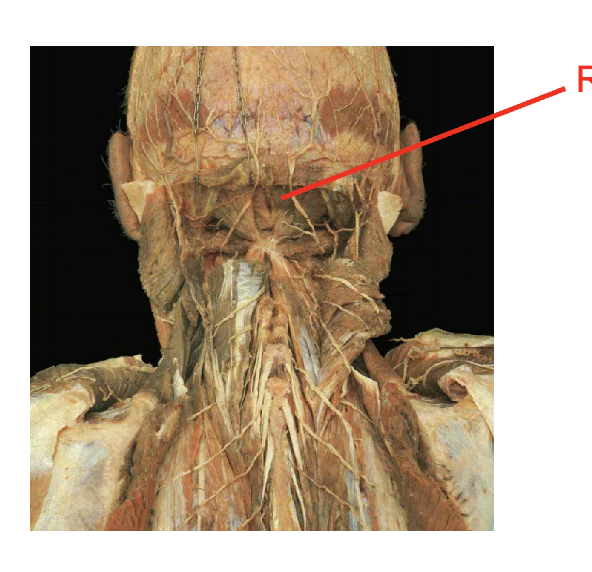
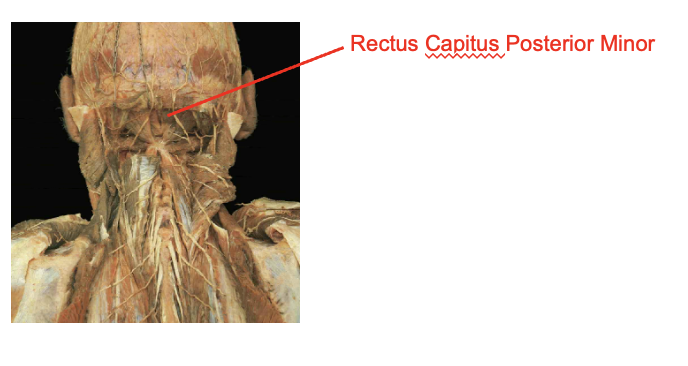
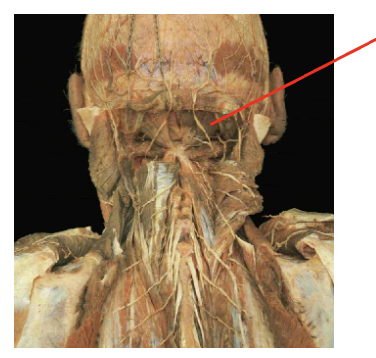
What is this muscle:What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
rectus capulus posterior minor
Origin
posterior tubercel of the atlas
Insertion
occipital bone
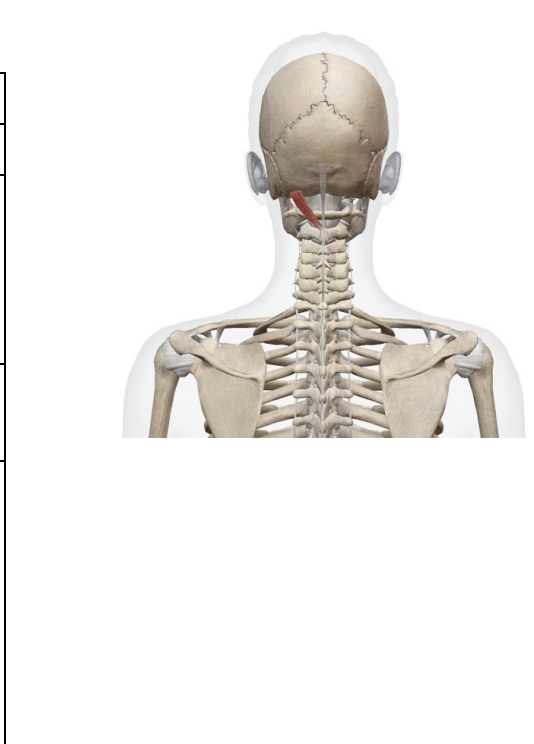
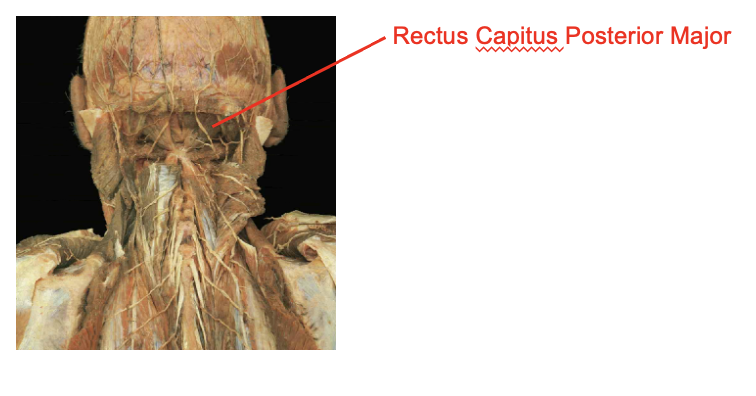
What is this muscle: What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
rectus capitus posterior major
Origi
spinous process of axis
Insertion
extension of the atlano-occuoutak hiubt
ipsilateral rotation of the atlano-axial joint
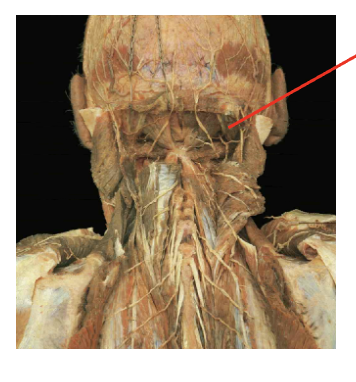
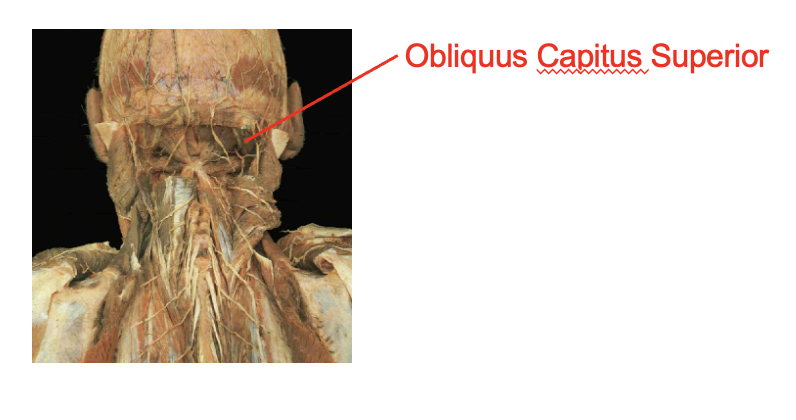
What is this muscle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
obliquus capitus superior
Origin
transverse process of atlas
insertion
occipital bone
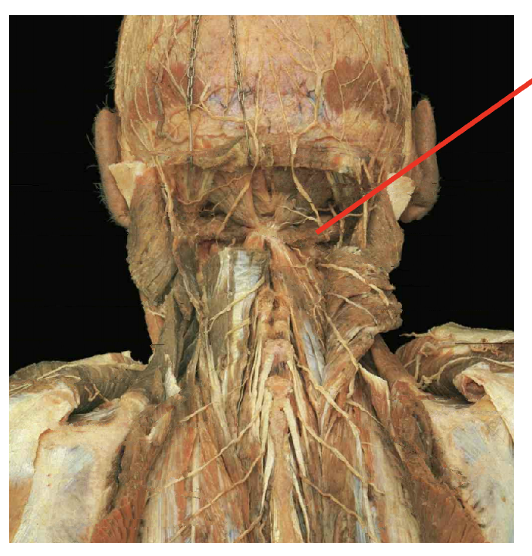
What is this muscle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
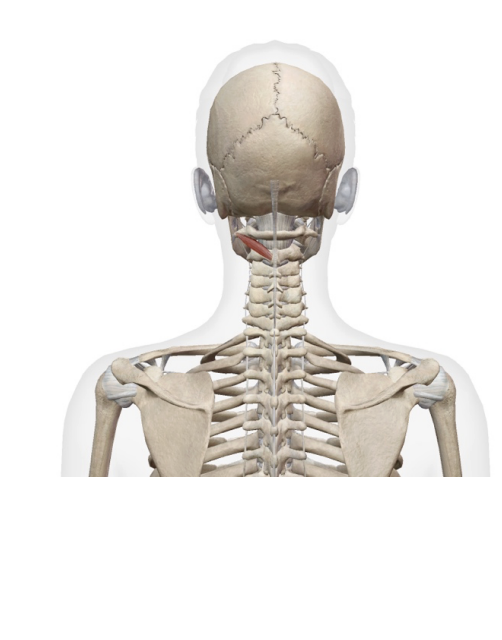
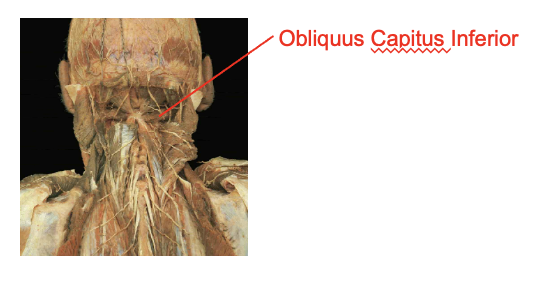
Obliquus capitus inferior
Origin
supeiror process of the axis
Insertion
transverse rocess of teh atlas
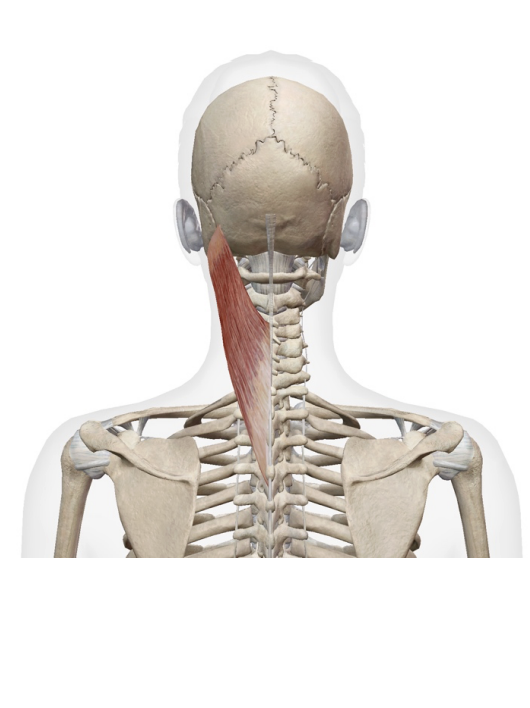
What is this muscle: What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
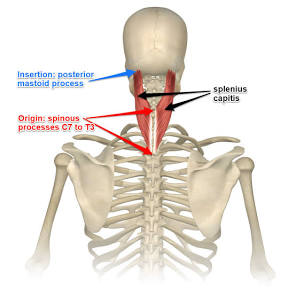
splenius capitus
Origin
spinous process fro c7-t3
ligamentumm nuchae
insretion
occipital bone
mastoid process
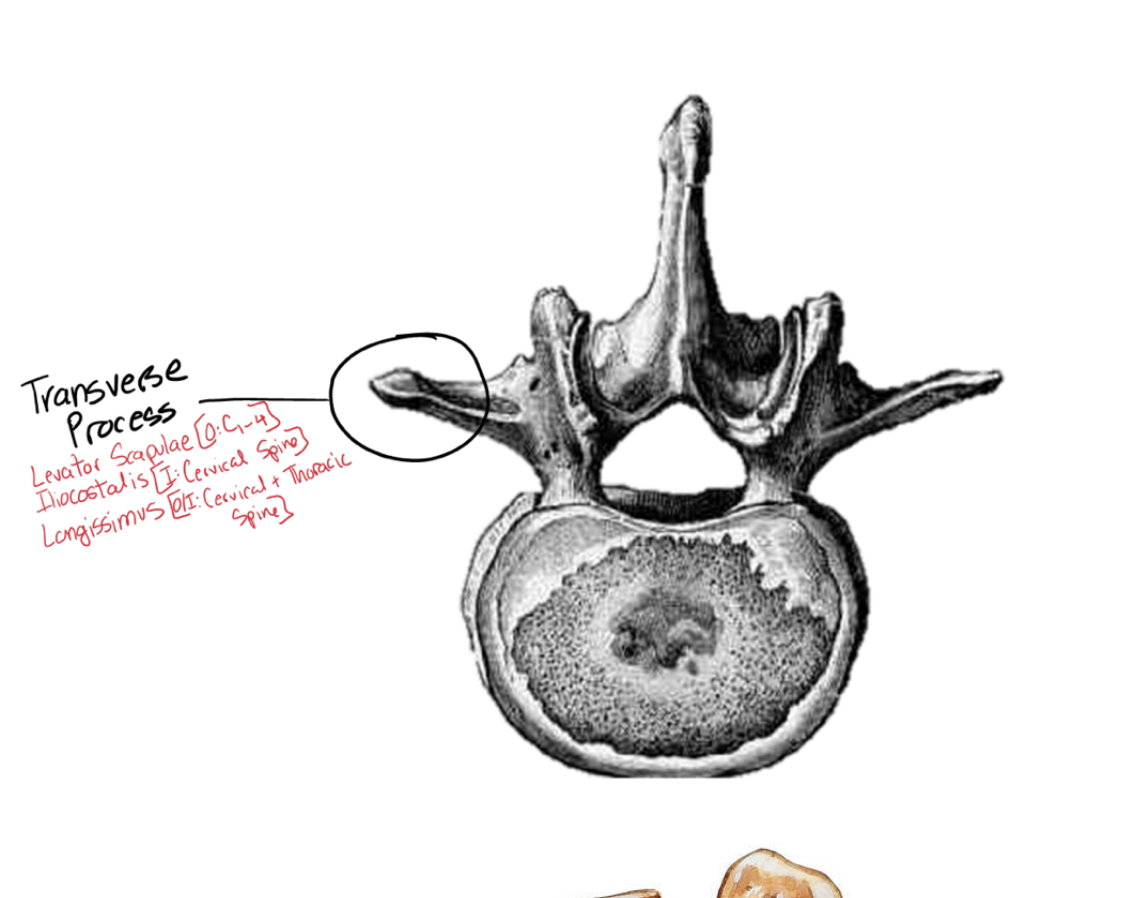
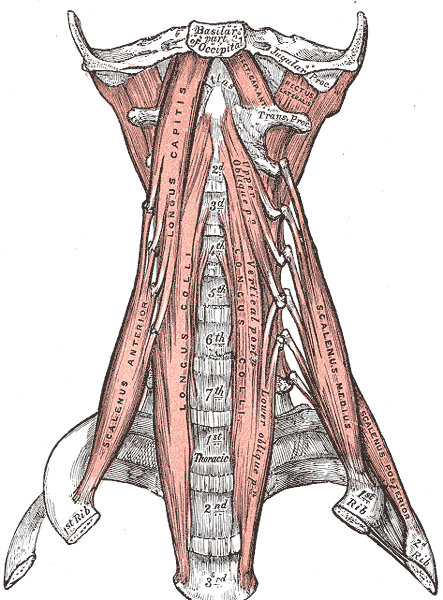
Describe the Tansverese process. What muscles attach to it and how does it differ per spinal segment
the most lateral part of the vertibrae (all sections)
connects the levator scapulae from (C1-c4)
illiocostallis ( found also on the cervical spine)
longissimus (cerviacal s pine and thorastic spine)
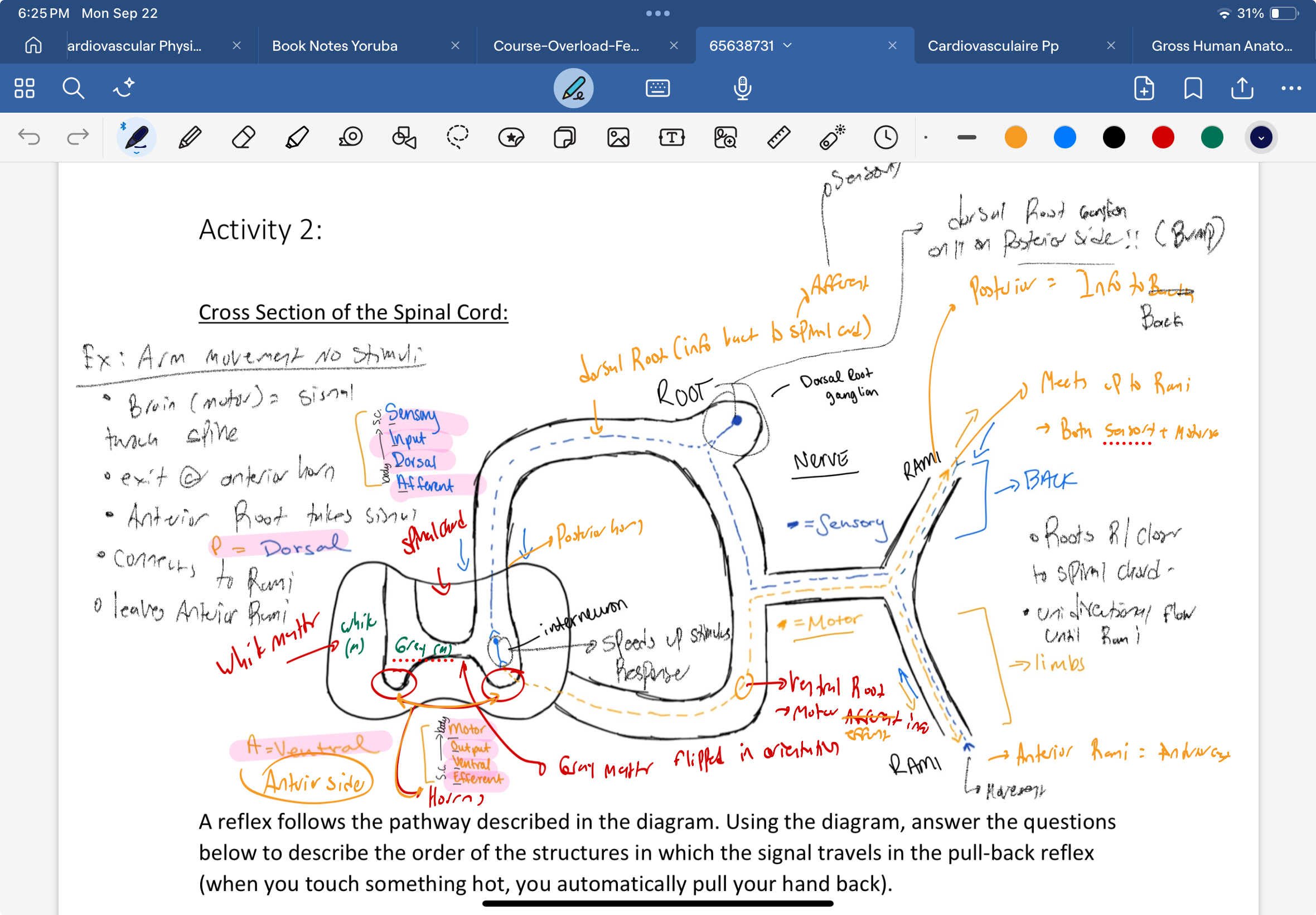
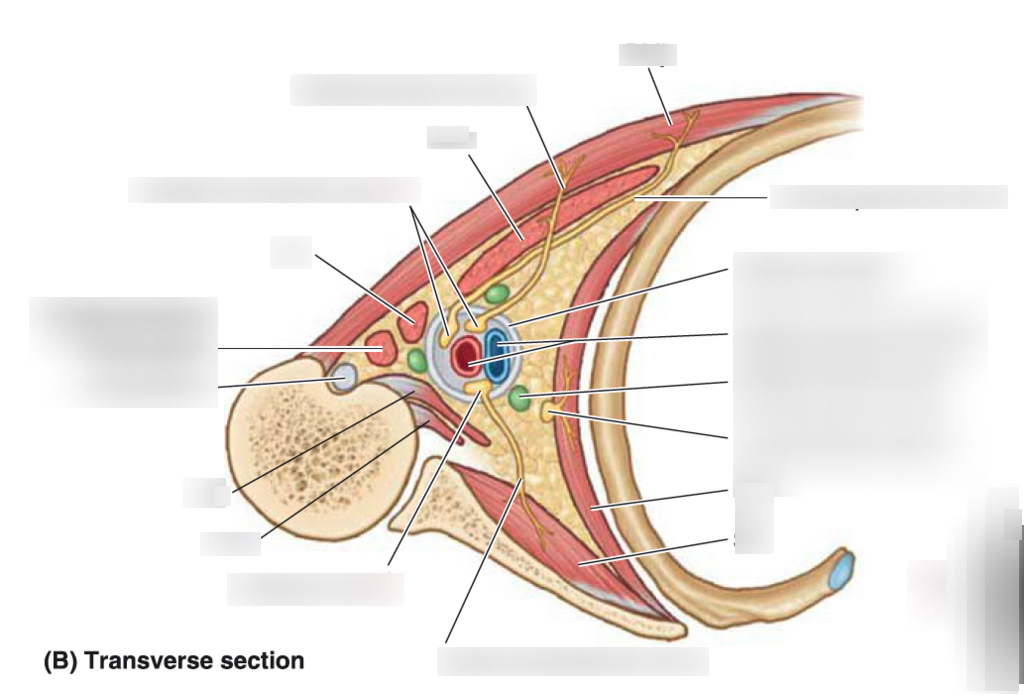
Describe the cross section of the spinal cord. What is found in each section and what are thier oriontations Posteriorally and anteriorally.
Where is the gray matter and white matter
where are the seonsory neurons
where are the motor nearons
where is the interneuron
where is the root (dorsal root ganglion
what is /are the rami
what innervates the back and limbs
where is the ventral root
where are the horns
Where is the gray matter and white matter
gray matter is in the center of the spinal bone
white matter is in the exterior
where are the seonsory neurons
sensory neurosn are found posteriorally being sent towards the spinal cord. uses interneurosn to spee d up the responses
where are the motor nearons
motor neurons are on the antirorside going outside the spinal cord
where is the interneuron
used to speed up conections between sensory neurons
where is the root (dorsal root ganglion
found posteiroally that sends informatio nback to the spinal cord (Afferent)
what is /are the rami
theere are two rami. the anterior rami = efferent (movement
posterior rami sends information back
the sensory and motor neurons connect and spread out at this point
what innervates the back and limbs
the motor neurons innervates the limbs (anterior)
back and stuff (posteiror
where is the ventral root
sconnected to the anteiro side with the motor neurons
where are the horns
hors face anteriorally in the spinal cord
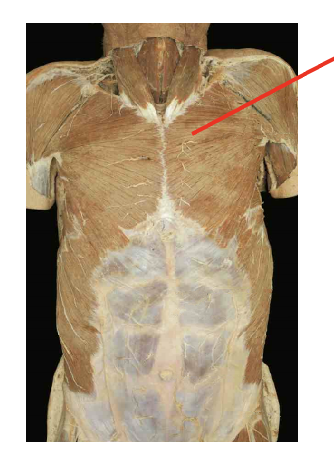
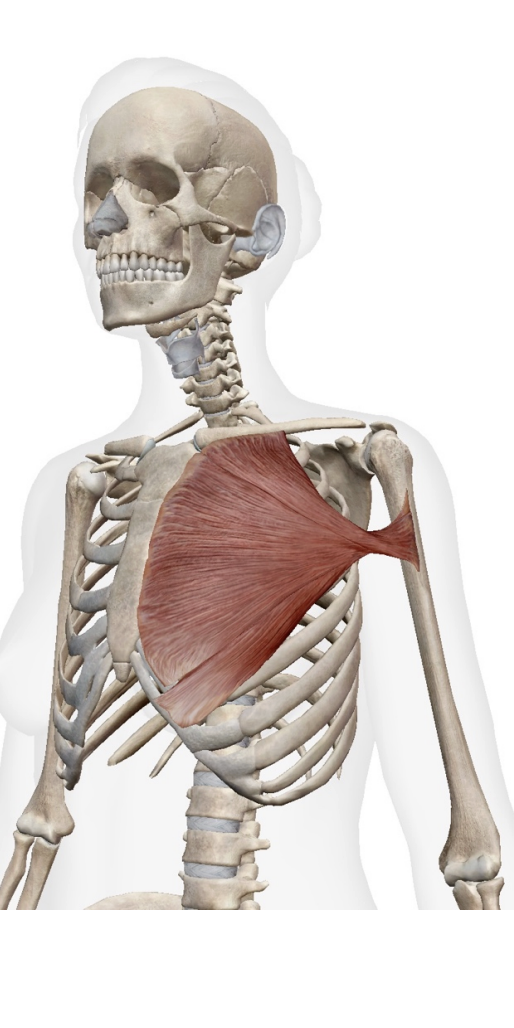
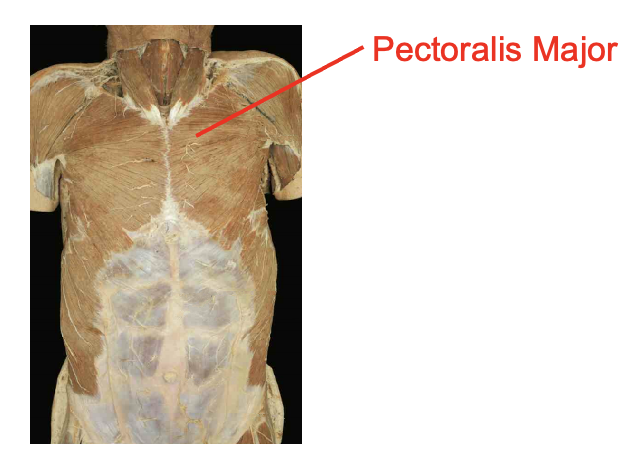
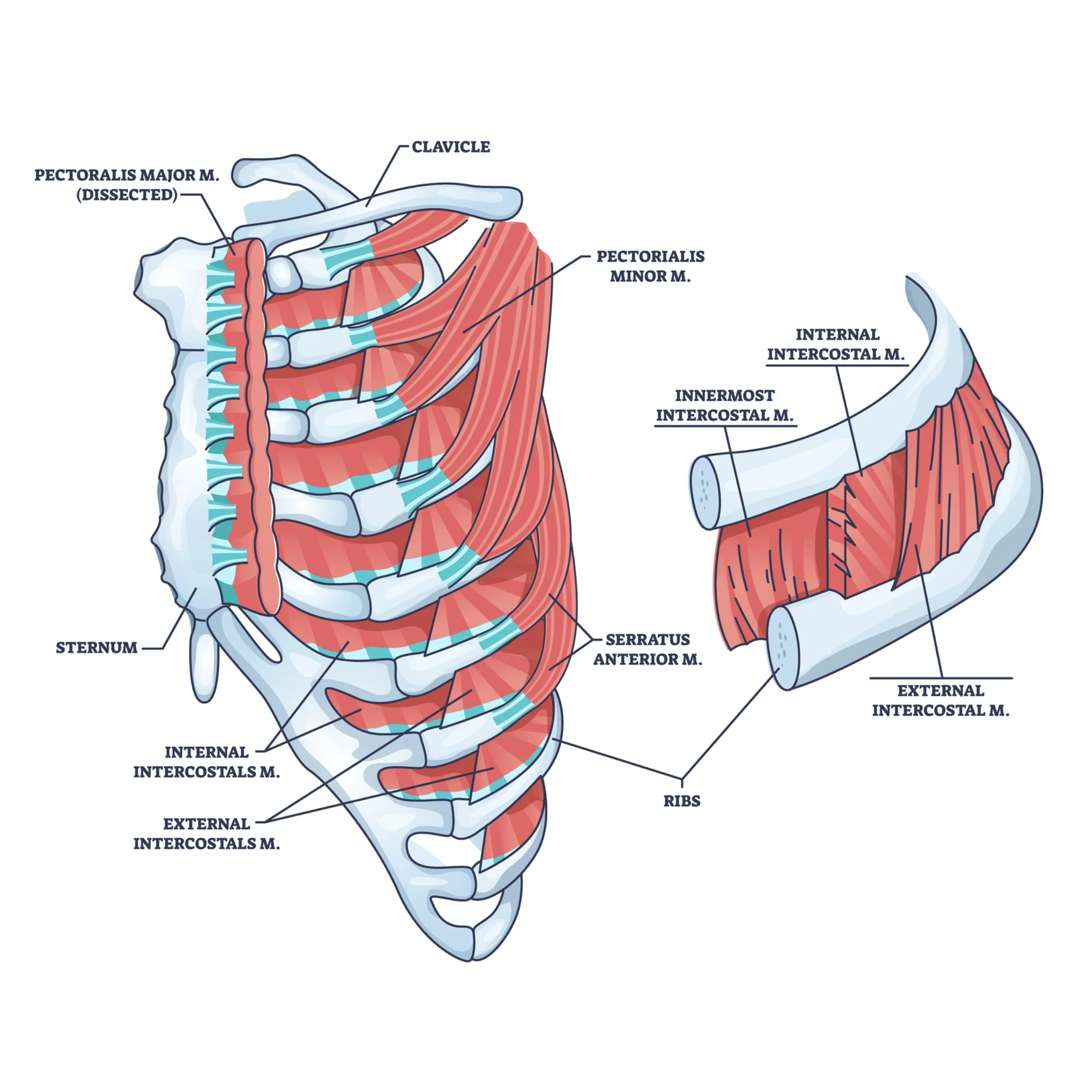
What is this muscel. What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
perctoralis. major
Origin
clavicular head- medial clavicle
sternal head- seternum and costal cartilatges of superior ribs
Insertion
lateral bicipital (intertubercular) groove of humerus
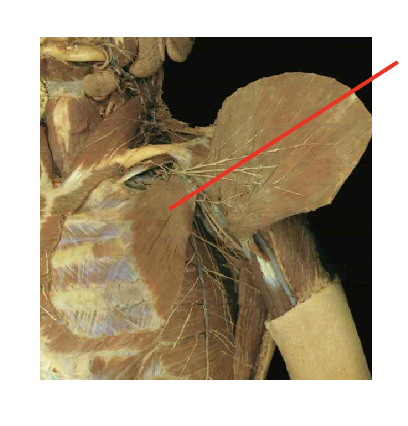
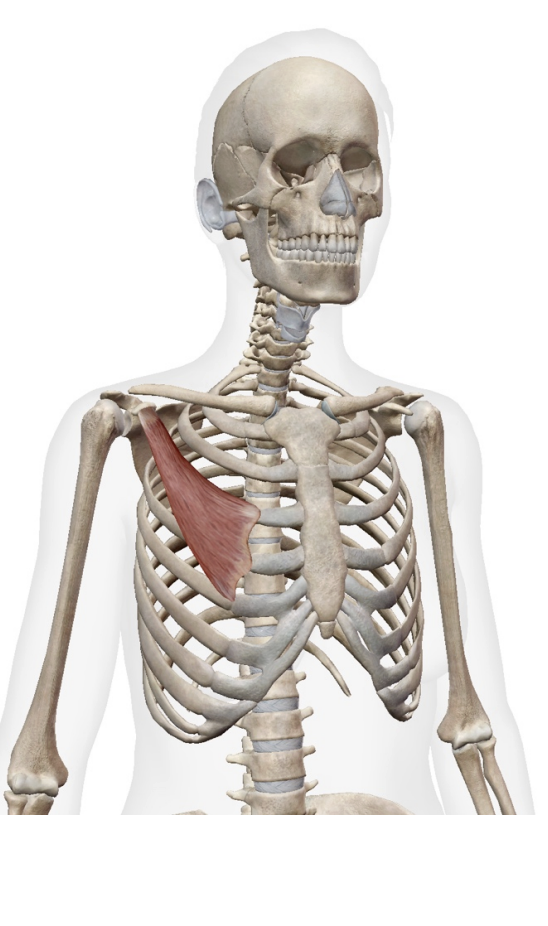
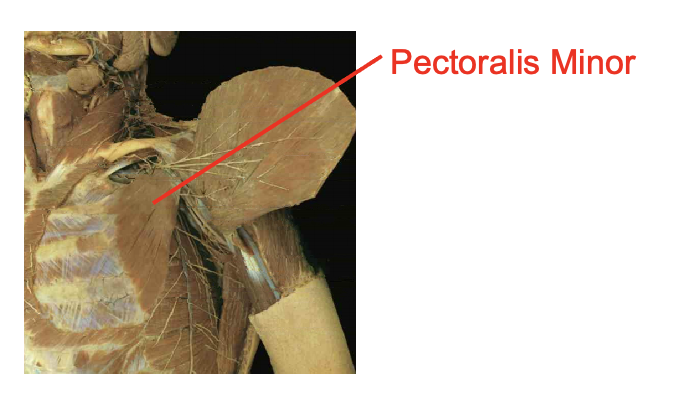
What is this muscle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
Pectoralis minor
Origin
anteiror surcface of ribs 3-5
insertion
coracoid process of scapula
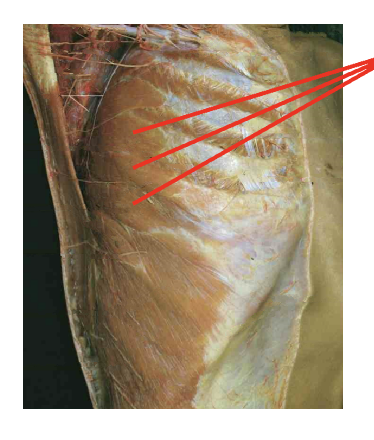
What is this muscle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
serratus Anteiror
Origin
lateral surface of superior ribs
Insertion
meidal (vertebral) border of scapula
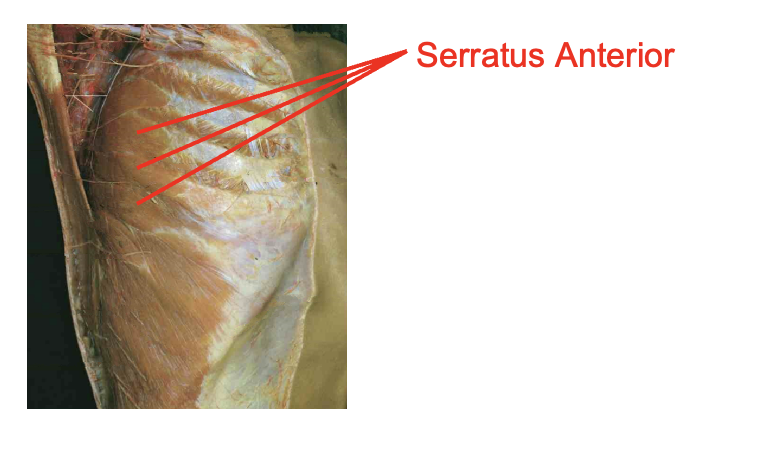
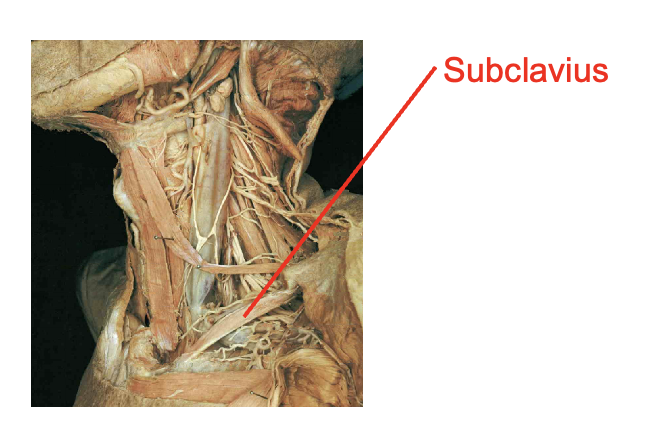
What is this muscle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
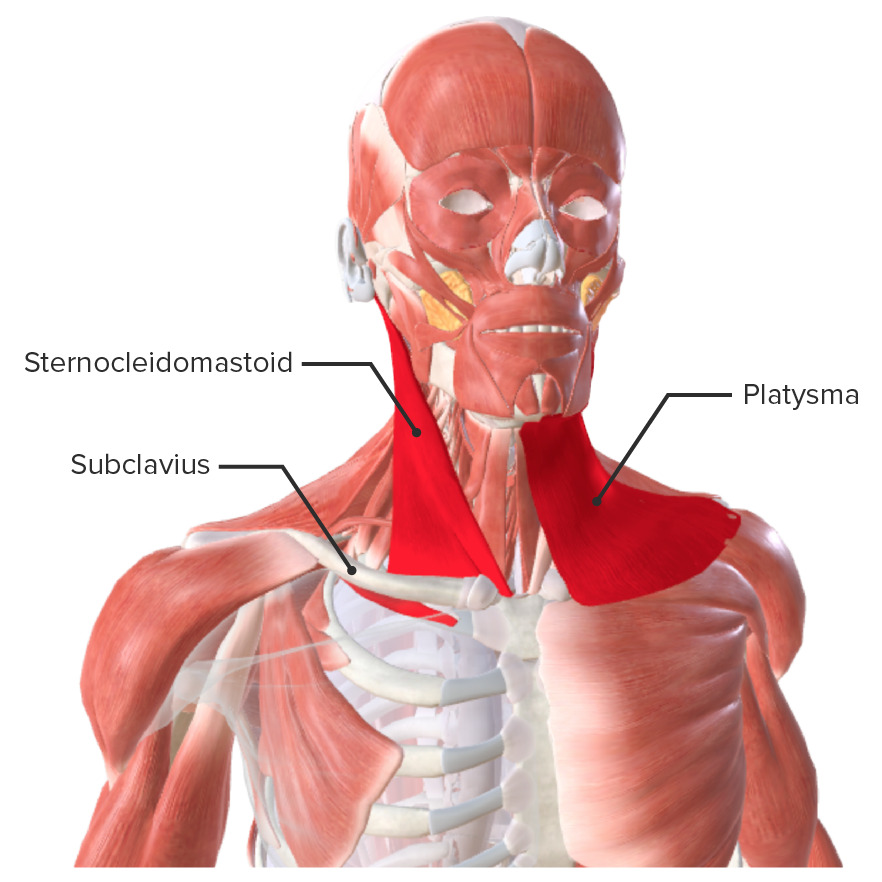
subclavius
Origin
costal cartilage of rib 1
insertion
inferior border of calvicle
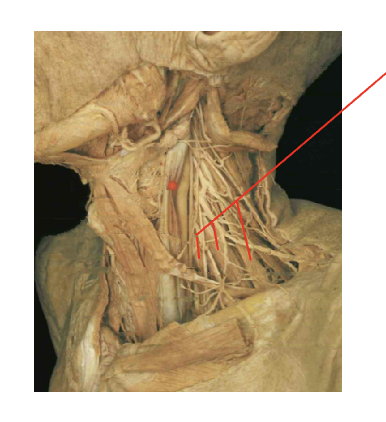
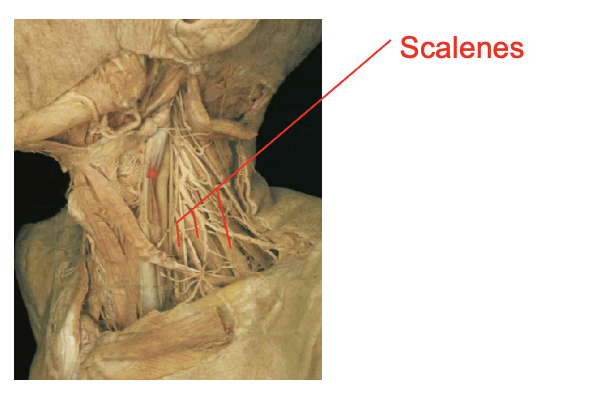
What is this muscle: What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
scalenes
origin
transverse process of cervical vertebrae
insertion
ribs one and two
erves
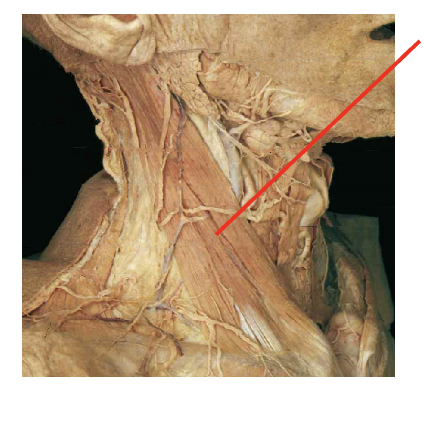
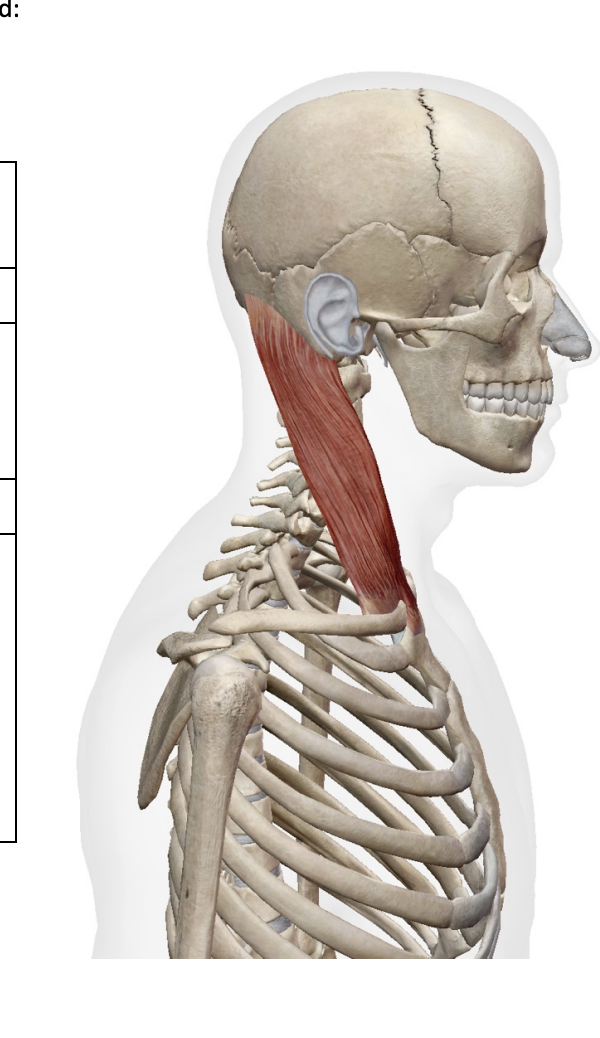
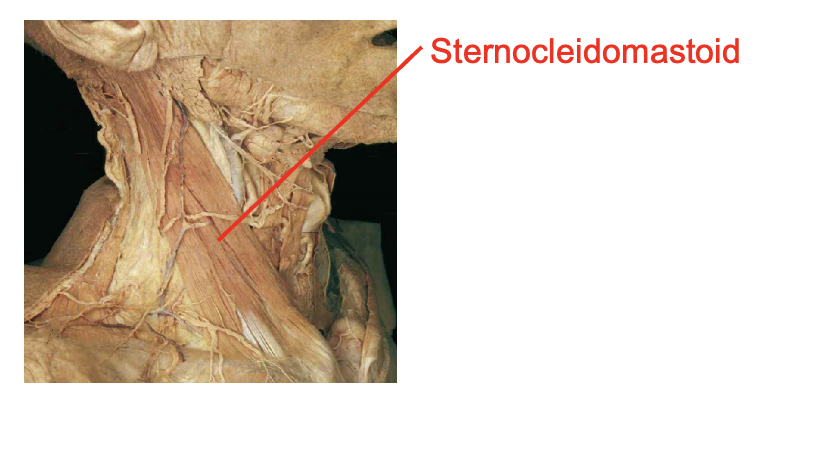
What is this muslcle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
Sternoceiomastoid
Origin
Sternal head- manubrium
Clavicular head - medial clavicle
insertion
mastoid rocess
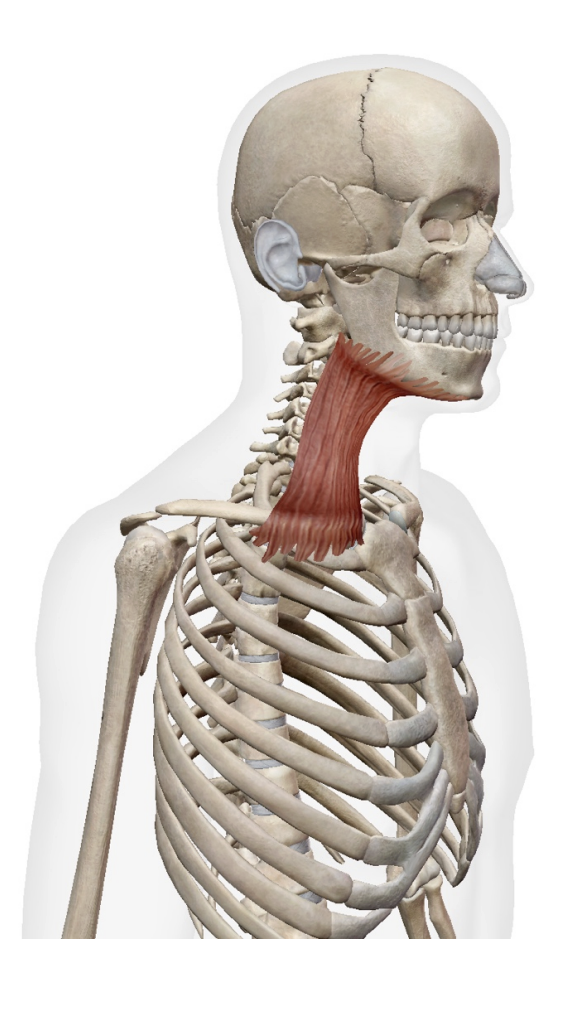
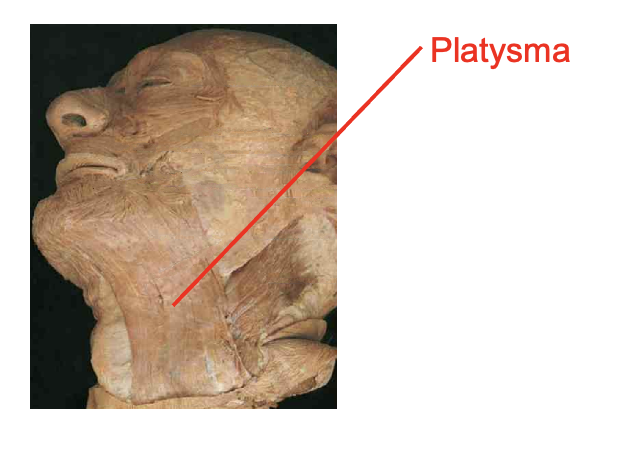
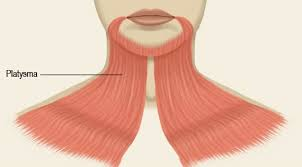
What is this muscle: What is its origin and insertion
platysma
origin
fascia over upper chest
insertion
mandible
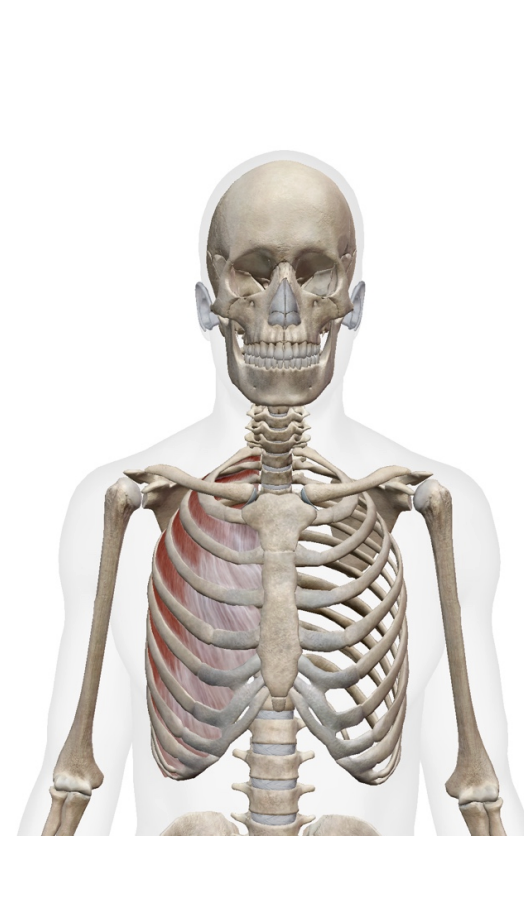
What is this muscle: What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
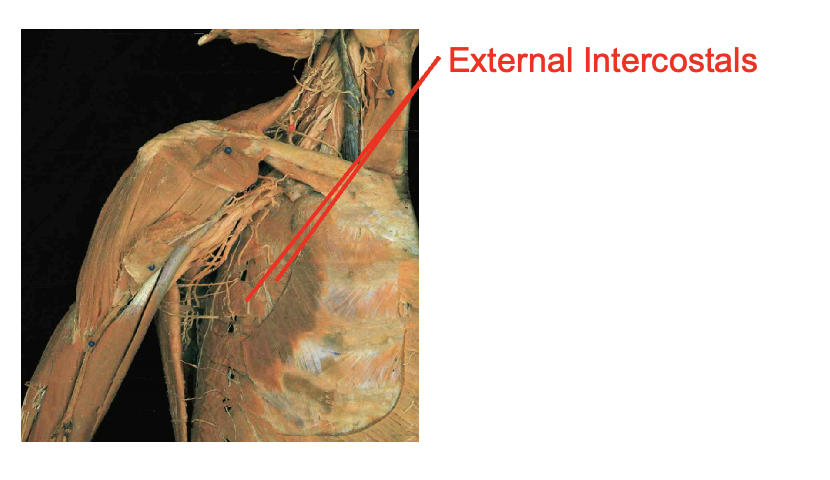
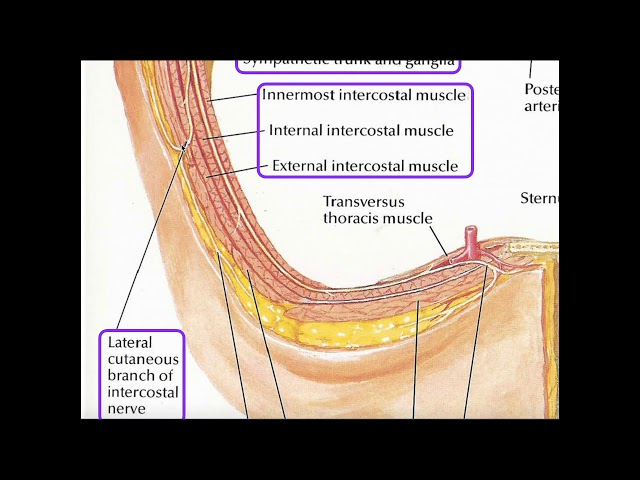
External Intercostals (ex to sex—- serrations face downard towards your plevice)
Origin
inferior margin of rib aboce
insertion
0 superior margin of rib below
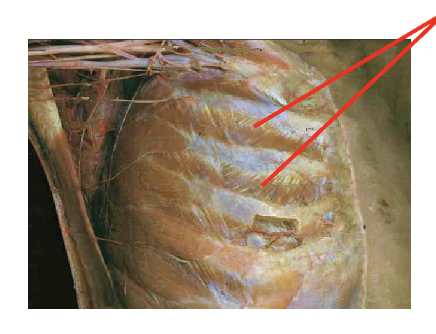
What is this muscle: What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
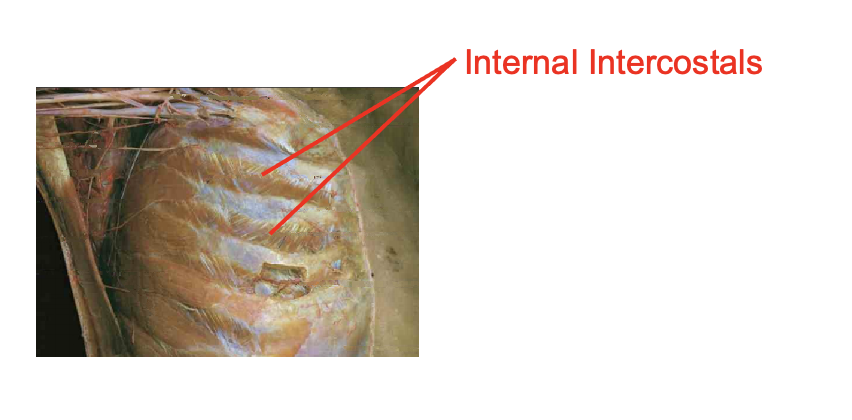
internal intercostalas
note that the muscles face upwards towards our chin in a serrated mannor
Origin
superiro margin of rib below
INsertion
inferior margin of rib above

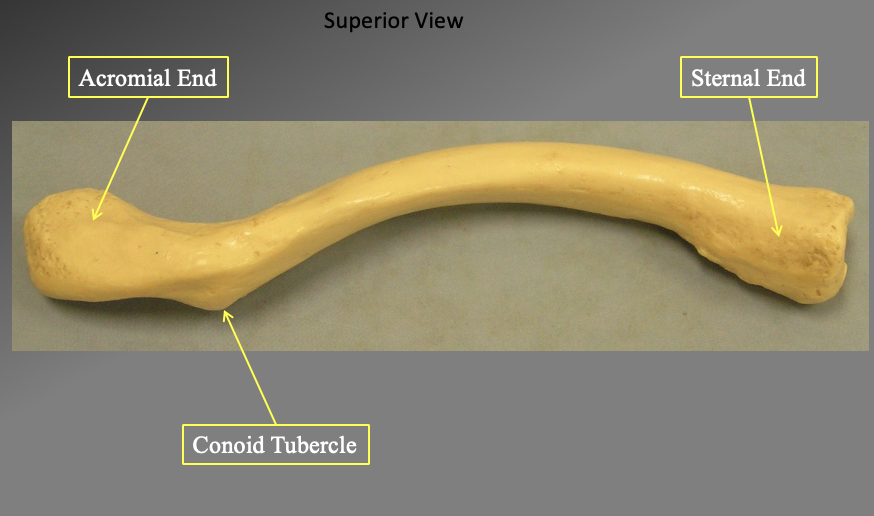
What are the different components of this bone. What is the name of this bone? what view is ti in
The clavicle
The acromial end
the more flat ide (cant be seein in this section but is flat like a soon
The sternal end
connects to your sternum… slightly rounded (more medial)
The conoid tubercle
found inferiorly
its in a supperior view
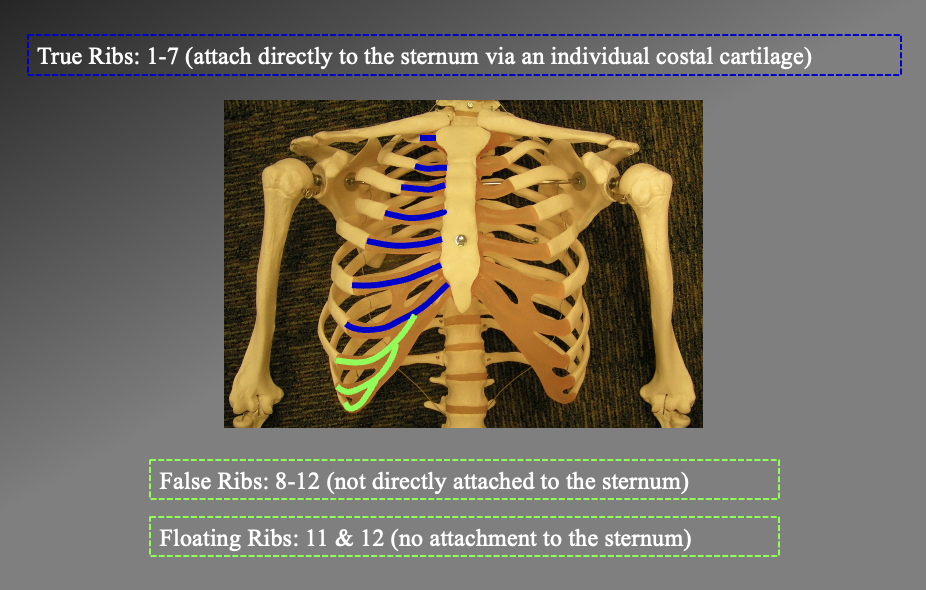
How many ribs do you have, what are the different types and their numbrs.
just look at this image ig

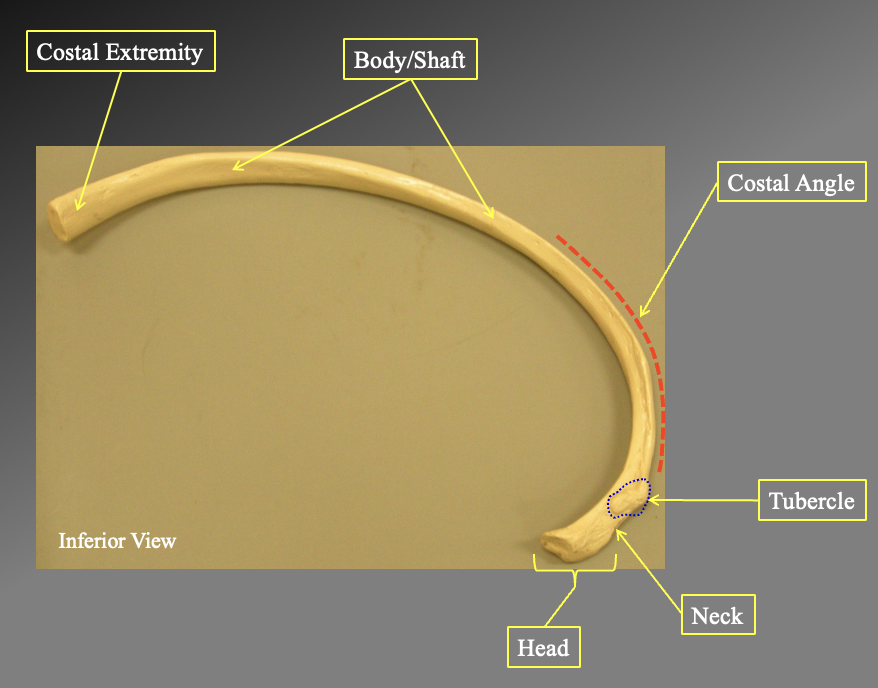
What are teh different portions of this bone? what bone is it?
Costal extremety
body/shaft
costal angle
tubercle
neck
head
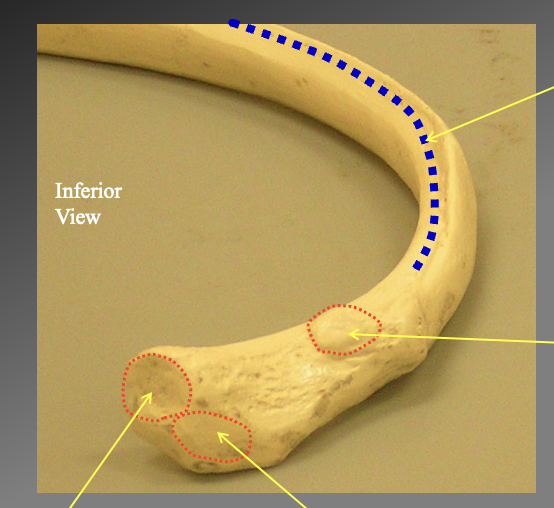
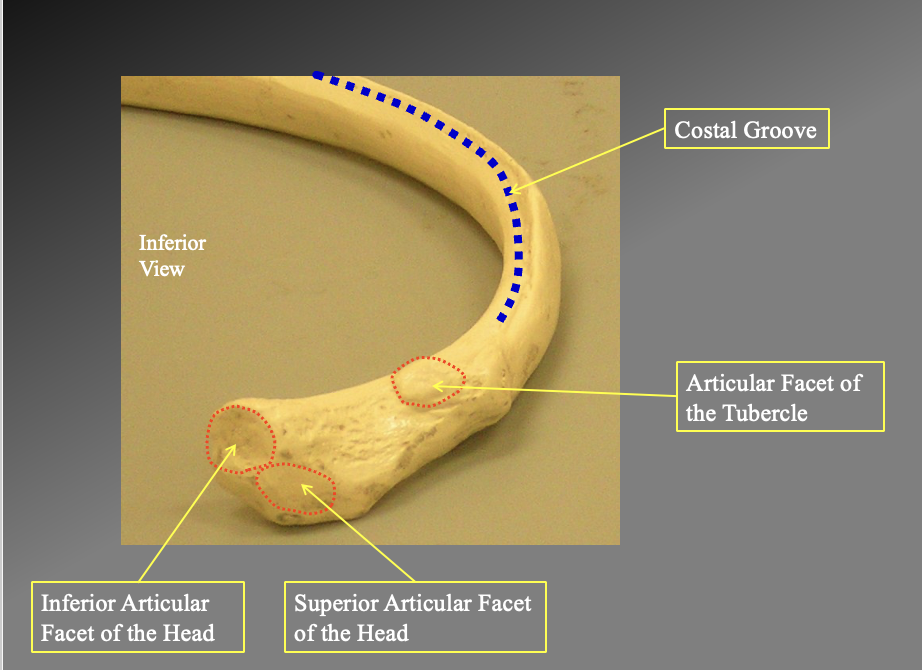
What are the distinct parts of the head of the ribs
The costal grouve
-only seein inffeiorly
Thear articular facet of the tubercle
superior facet of the head
inferior facet of the head
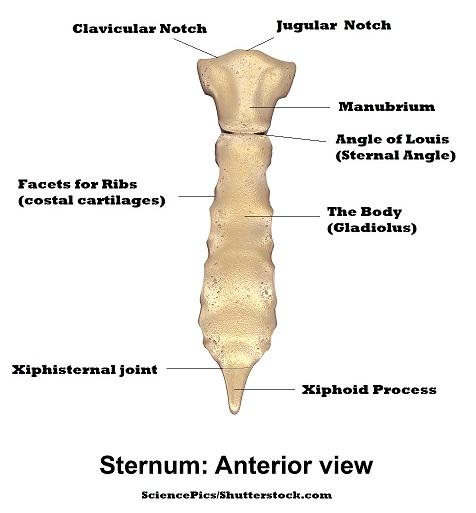
What bone is being highlighted and what are teh different parts
the sternum… look at the image for the parts
- what are the costal facets
whrere the ridge attaches
juglar notch
clavicular notch
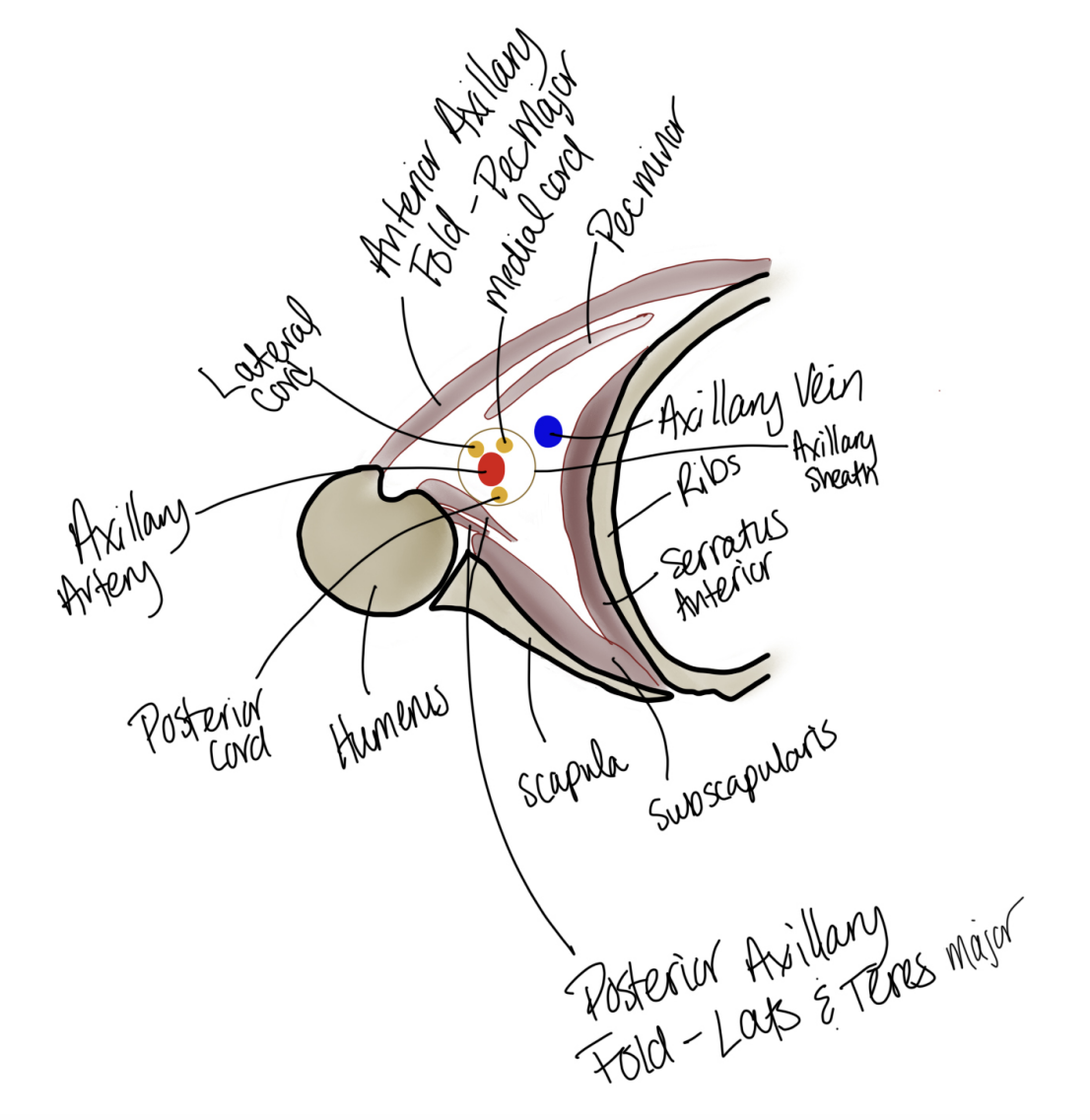
What are the components of the cross-section of axilla. Where is the lateral cord, axillary artery, posterior cord, humerous, scapula, subscapulaus, serratis anterior, ribs, auxillary ein, axillary sheath, pec minor, medial cord, anterior axillary fold- pec major, posterior axillary fold- lats and teres major
note the arteries are protecte
The scapula side is the posterior side
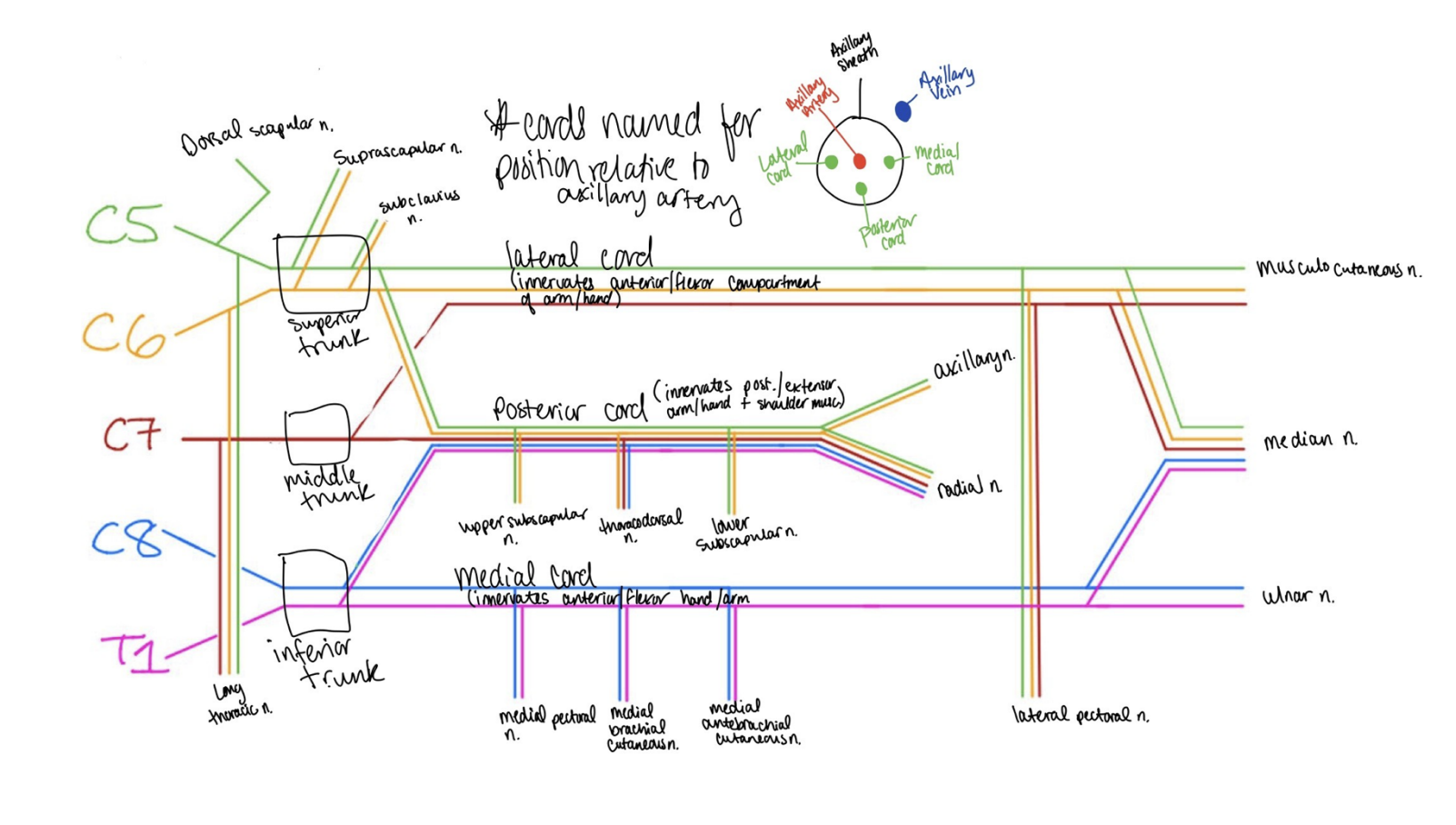
Draw out the brachial plexus. C5 to T1. what are the trunsk, what are the cords, what are the different nerves, where is the m sections, which nerves are which (prayers girl). Which nerves are connected and which are individual . where are the arteries
prayers girl
Pre trunk Nerves
dorsal scapular nerves
c5
long thoratic nerve
c5-c8 past t1
Trunks
superior trunk
suprascapular nerve nerves (c5-c6)
supra scapularis (c5-c6)
middle trunk
C7
inferior trunk
C8-T1
Cords
lateral cord (innervates the anterior/ flexors of the arm and head) +picks up C7
c5-c7
runs straight to m portion
Posterior cord (innervates posteiror/extensor part of hte arms and head amd shoulders)
c5-t1 Innervates all nerves
Upper scapular nerves
c5-c6
theacrodorsal
c6-c8
lower scapular nerves
c5-c6
breaks of into two
auxiliary
C5-C6
Radial nerve
all nerves
Medial cord (flexors in the hand and arm)
c8-t1
medial pectoral
c8-t1
medial brachial cutanious nerves
c8-t1
medial antibrachial cutanious nerves
c8-t1
End cords
Lateral pectoral nerves (just before the m)
c5-c7
M section
musculocutanious
c5-c7
median
all nerves
ulnar
c8-t1
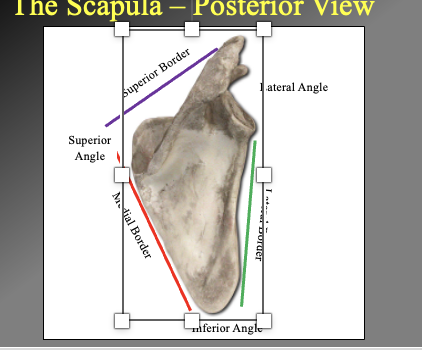
What are the different boarders and angles of athe scapula
Superior vorder
Lateral angle
attaches to humerous
Superior angle
Lateral vordder
axillery border
medial border
vertebral border
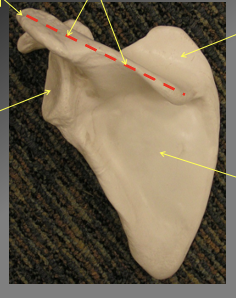
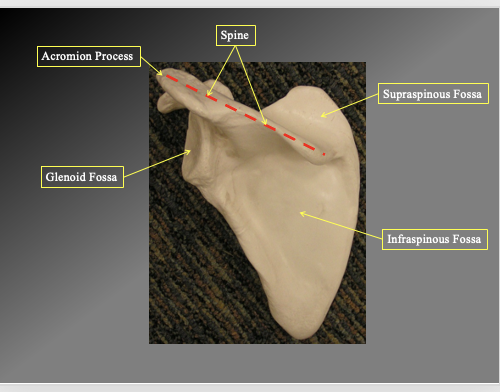
Waht are the different components of the posterior angle of the scapula
Acromion process
the top of the ridge
Spine
the long flat part
Supraspinous Fossa
the flat part above the spine
Infraspoinous Fossa
the flat triangular section inferior to spine
Glenoid fossa
the depressio nwehre the head of the humerous goes
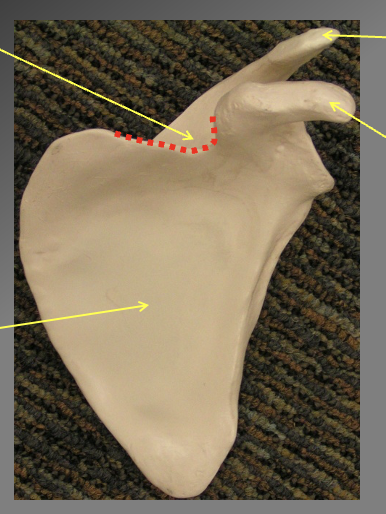
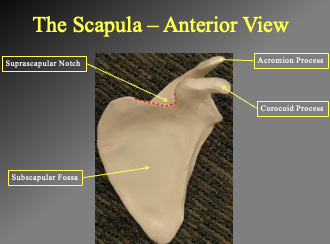
Components of the scupula (anterior view). how do we know its anterior
we know its anteiorr ecause the processes stick out
Suprascapular notch (allows way for suprascapular nerve to pass through
triagngual knotch on the top
Acromion process
shoulder connection
Corocoid process
Subscapular fosa
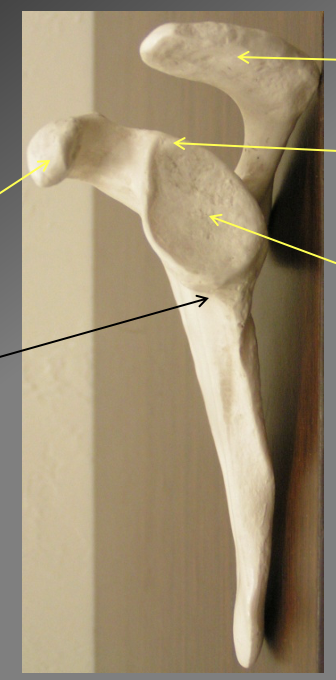
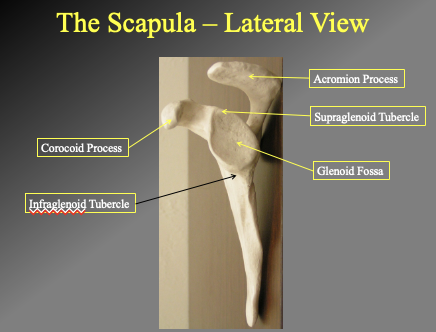
What are the comonents of the lateral view of teh scapula
-Acromion oprocess
where teh scapula meets
Supraglenoid tubercle
protection of the superior segment
Glenoid fossa
Corocoid process
INFFRAGLENOID TUBERCLE
the litle rige/ origin point for msucle
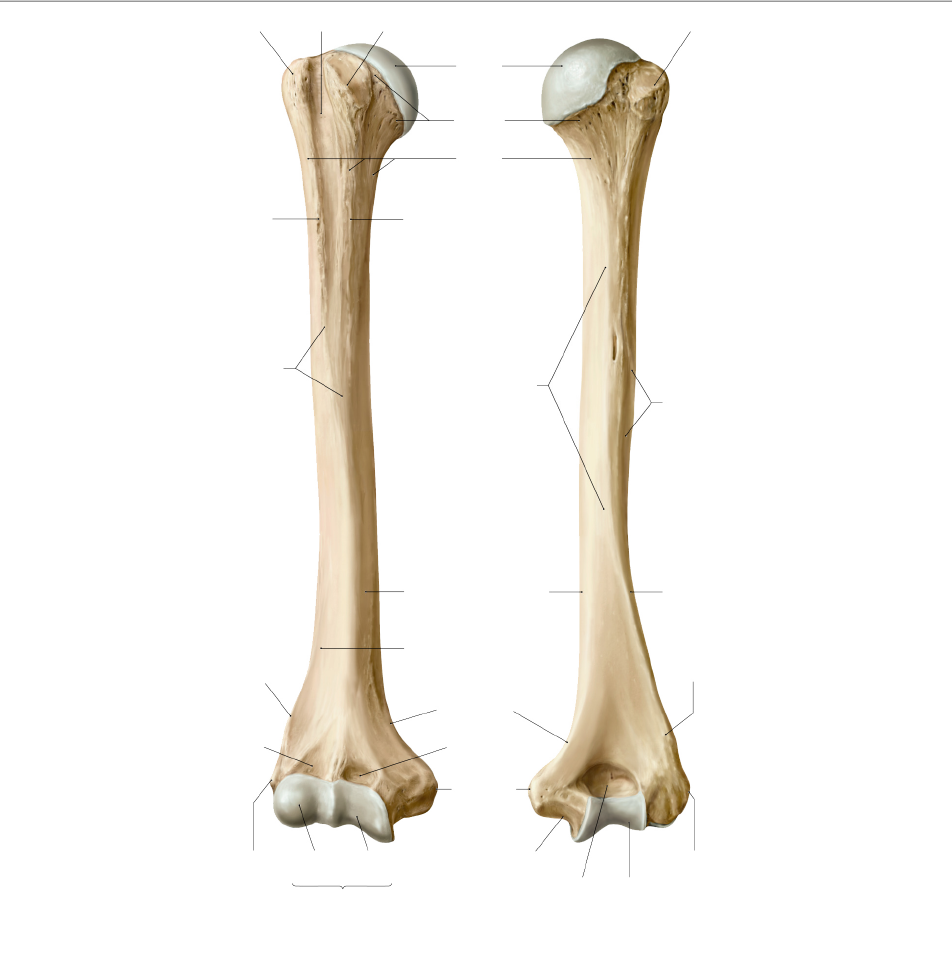
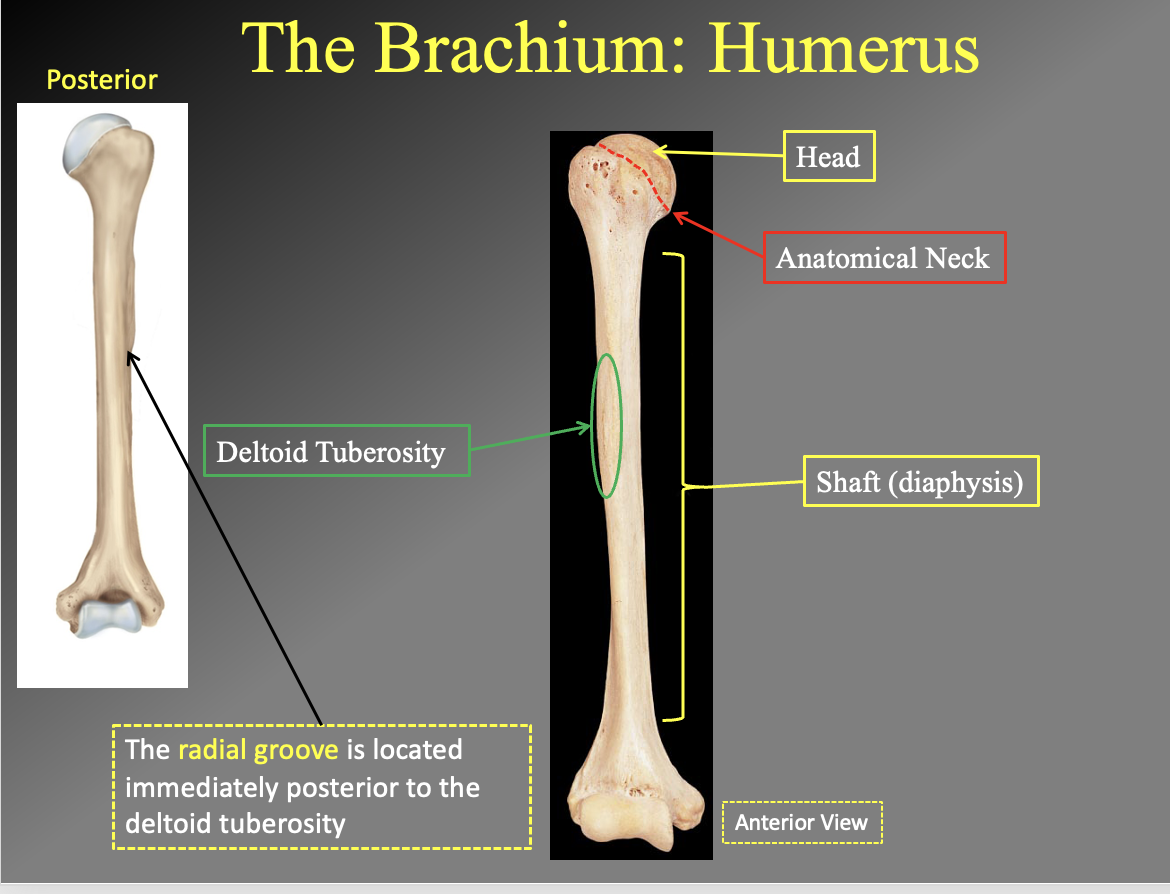
What are the parts of the humerus. which side is anterior and which is posterior
posteriror side has the deep rivit in in the most distal portion
you can see the radial grove in the poserior
What are the different parts of. the humerous
Anterior
head
anatomical neck
spiral grouve in the miiddle holds the radial nerve)
the little divit in the middle of the shaft
the shaft
deltoid tubersity
insertion poitn for the delts (look at the bump)
posterior
has the radial groove
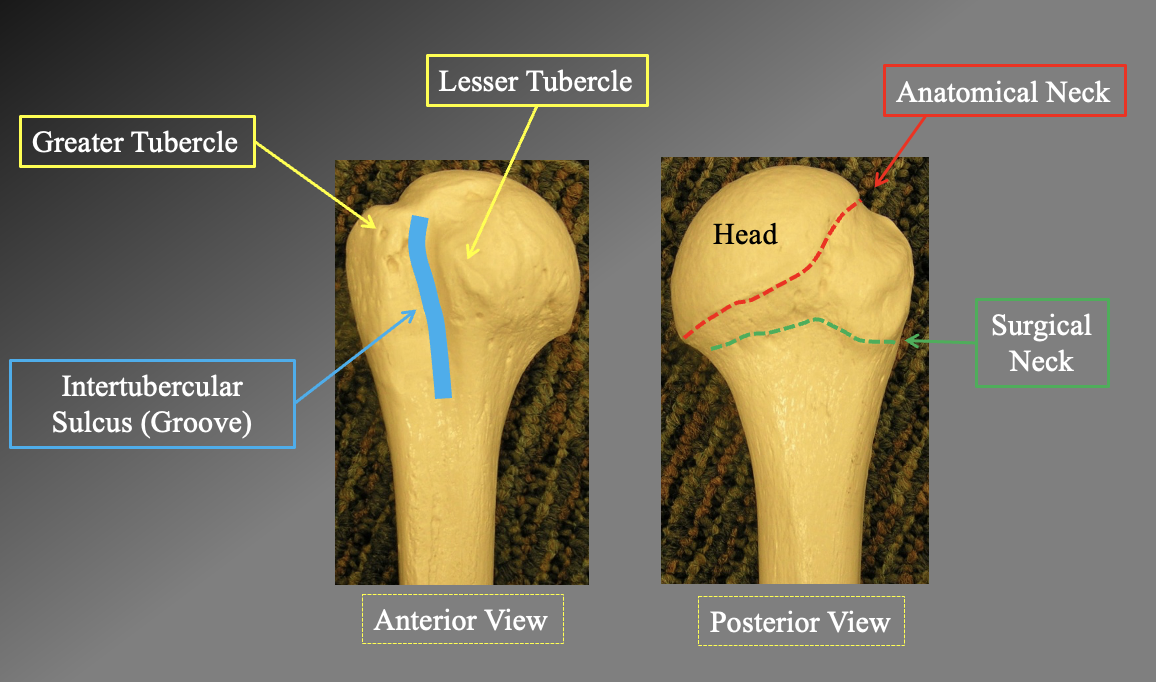
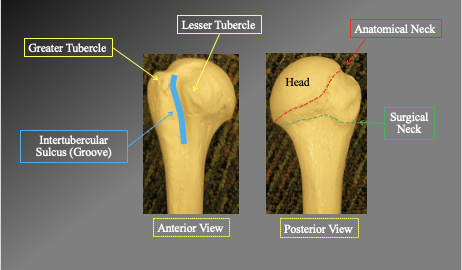
What are the arts of the Proximal humerous anteriorly and posteriorly
Anterior view
greater tubercle
leser tubercle
intertublear suclus Groove
Posterior view
anatomical neck
surgical neck
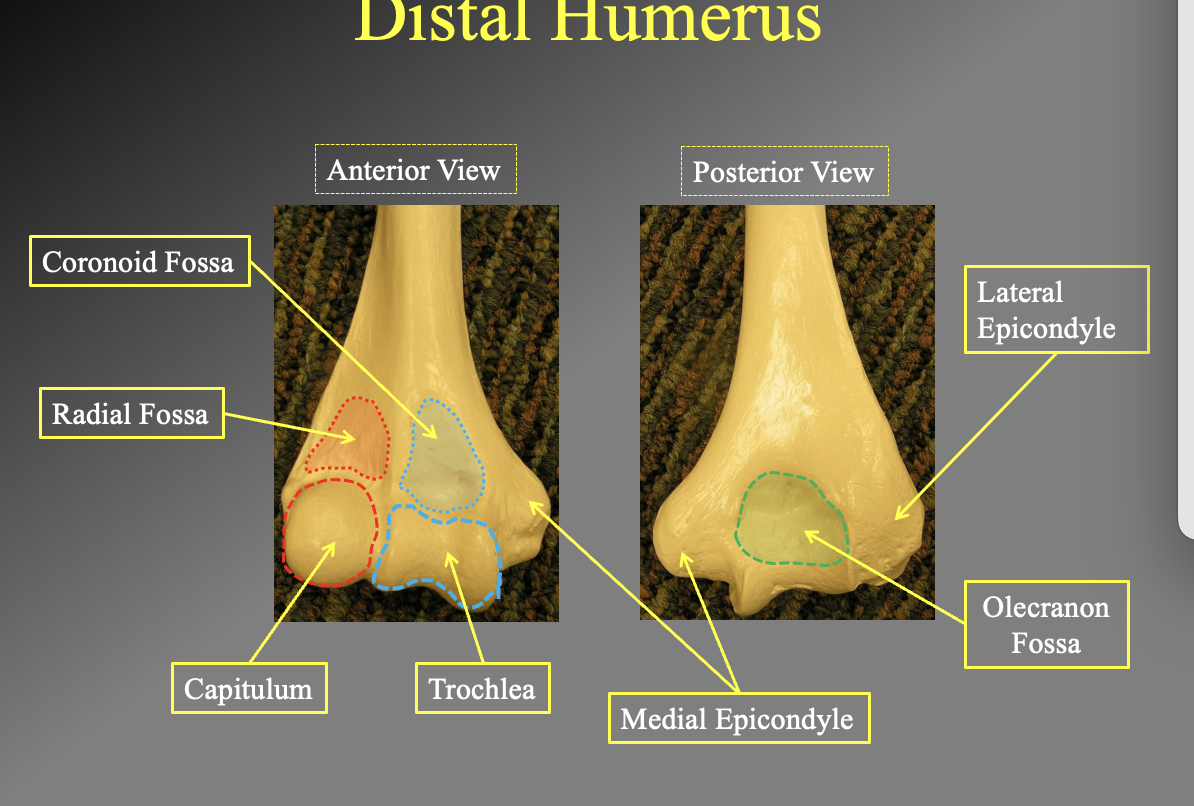
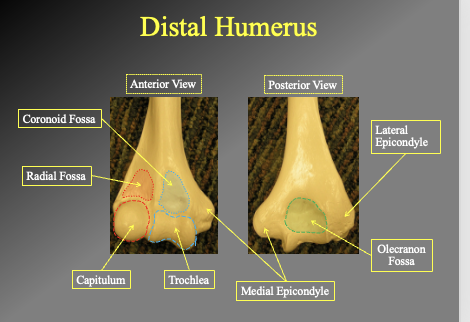
What are the different parts of the distal humerous posaterior and anterior
anterior view
cornicouid fossa
Radial fossa
Capitulum
Trochlea
poterior view
lateral epicondyle
olecranon fossa
medial epicondyle
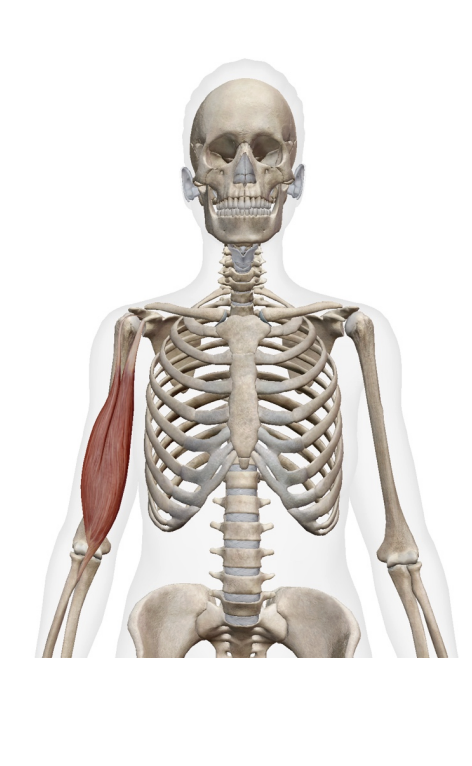
What muscle is this? What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
short head of bicepts brachii
long head of biceps brachii
Origin
short head- coracoid process
long head- supralenoid tubercle
Insertion
tendon- radial tuberosity
bicept aponeurosis- antebrachilal fascia medial side)

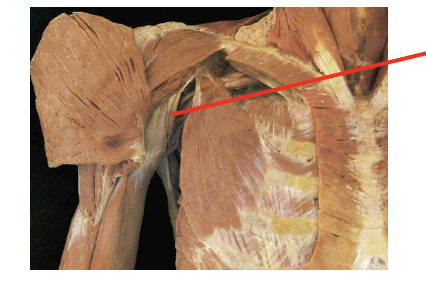
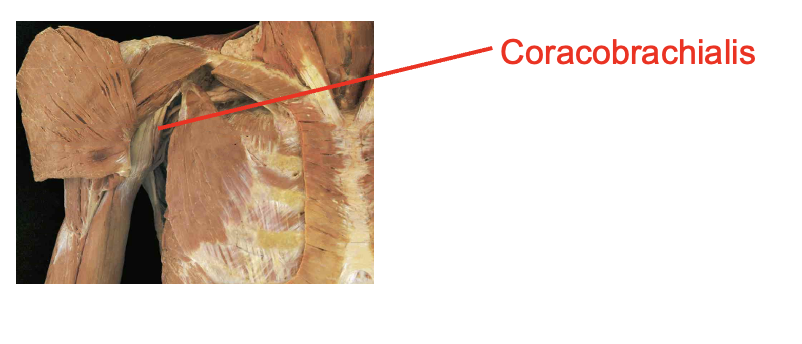
What i this muscle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
Coracobrachialis
Origin
coracoid process
Insertion
middle of medial humerous
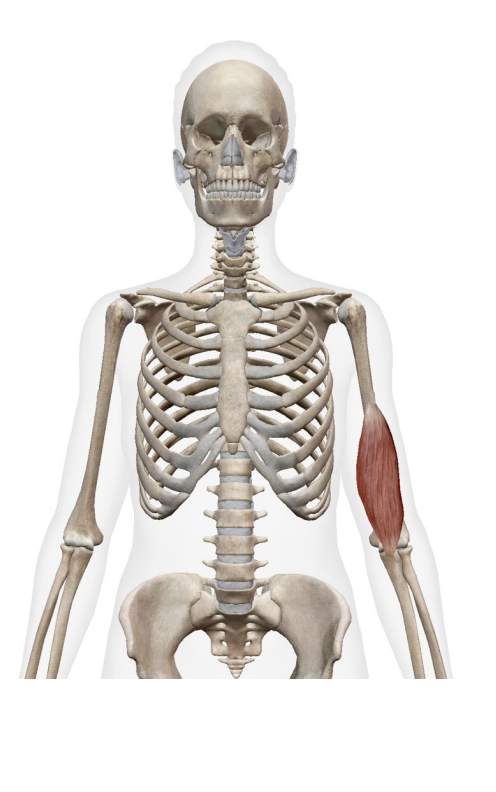
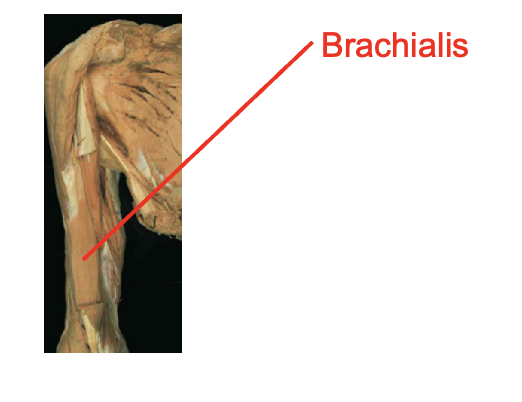
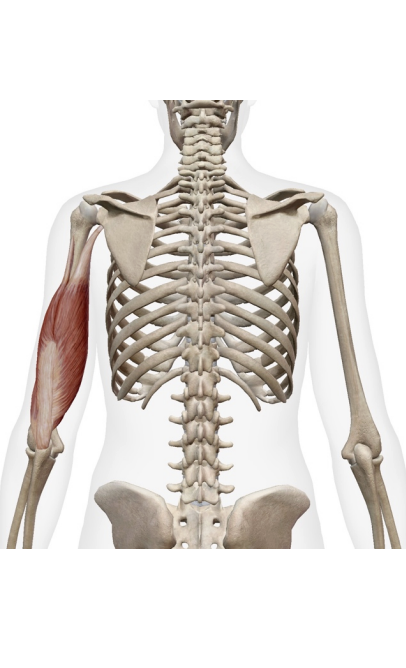
What is this muscle What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
Brachialis
Origin
distal anterior humrous
Inserition
ulnar tuberosity
coroid process
nerve
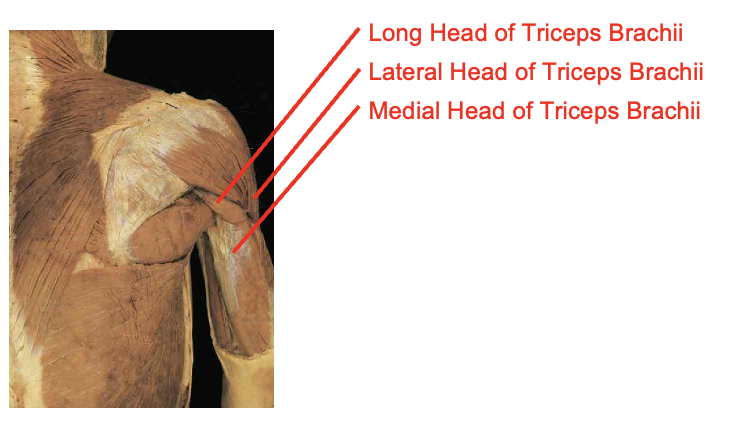
What musclees are these?What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
long head of tricepts brachii
lateral head
medial head
Origin
Long head
infraglenoid tubercle
Lateral head
posterior humerous bove spiral grove
Medial head
posteiors humerous below siral groube
Inserition
oleranon process
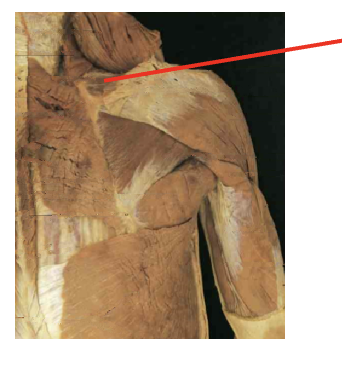
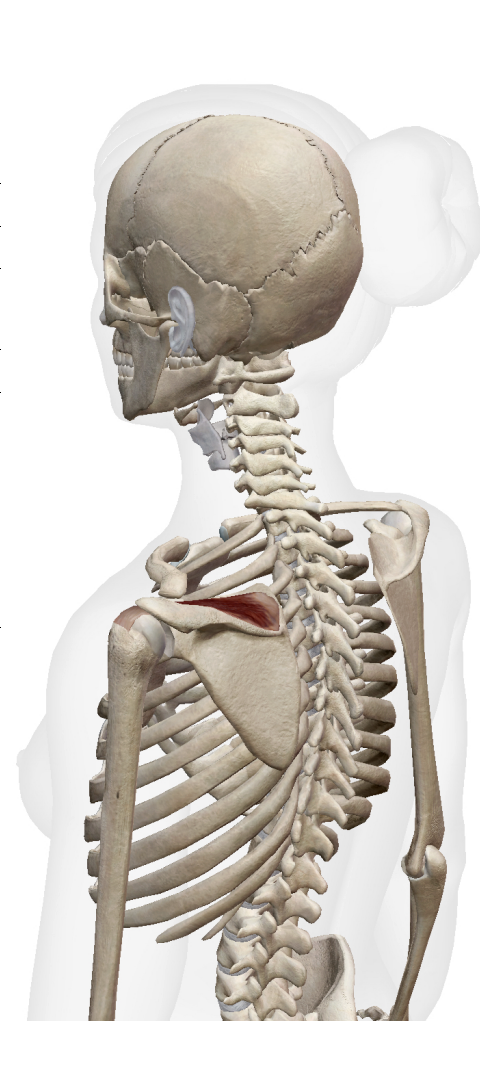
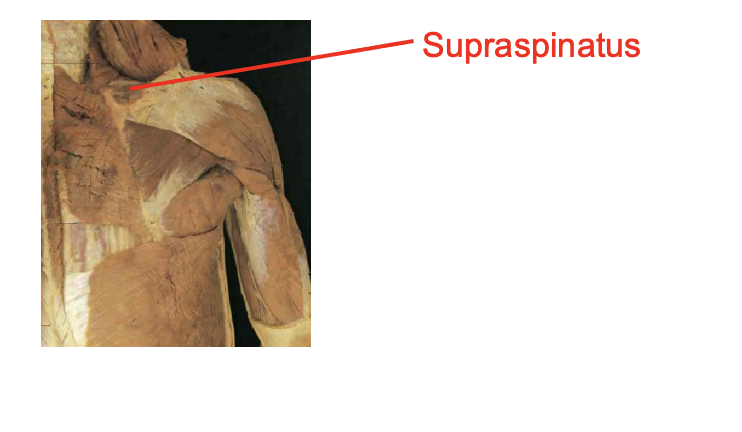
What muscle is thisWhat is its origin. Where does it inserts.
supraspinatus
Origin
supraspinous fossa
Inserition
superiro greater tubercle
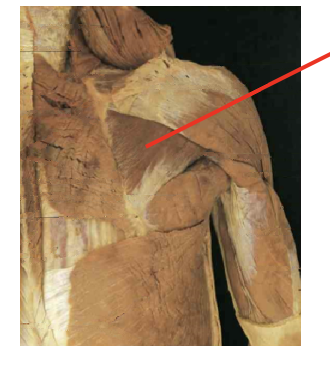
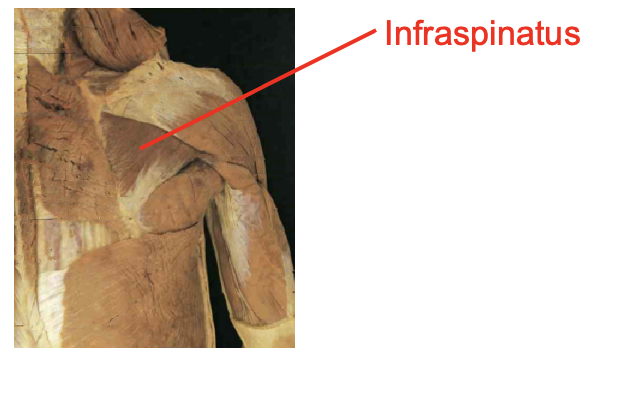
What muscle is this? What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
infraspinatus
Origin
infraspinous fossa
Inserition
middle greater tubercle
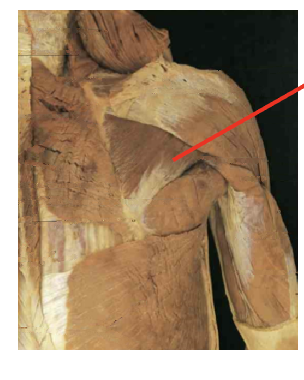
What muscle is this What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
Teres minor
Origin
superior axillary border
Inserition
inferiro greater tubercle
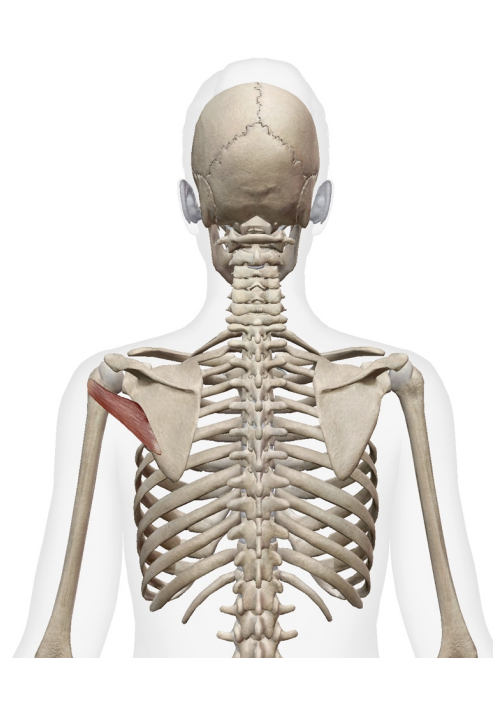


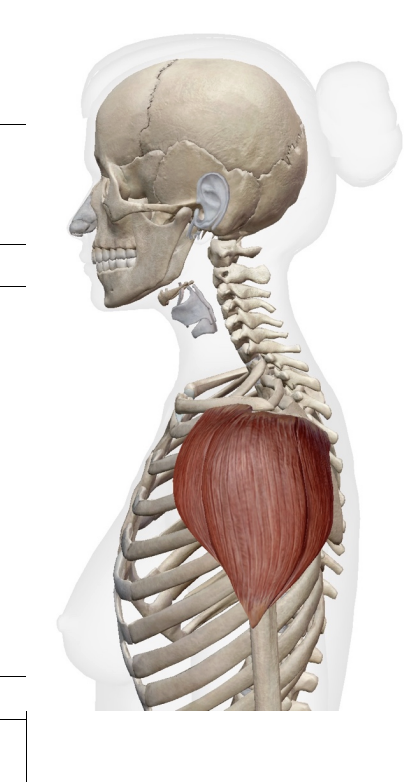
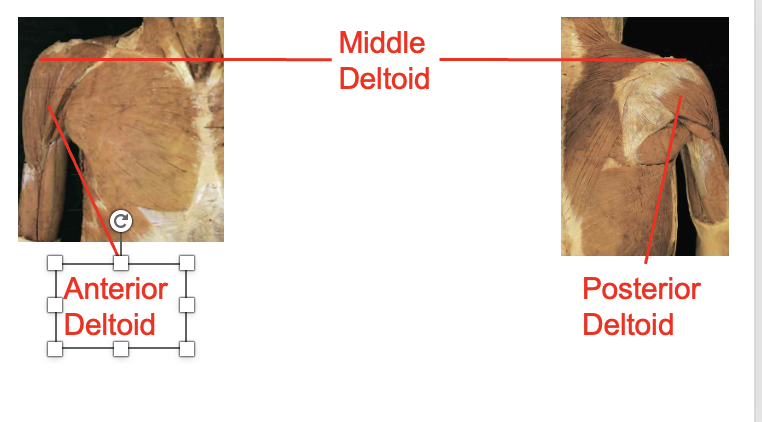
What muscles are these. which isde is posteiror and anteiror What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
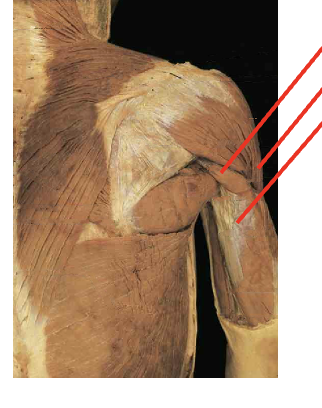
Middle deltoid, anteiroor deltod, posterior deldoid
ORIGIN
- Anterior deltoid – Lateral clavicle
- Middle deltoid – Acromion
- Posterior deltoid- Spine of scapula Insertion
insertion
deltoid tuberosity

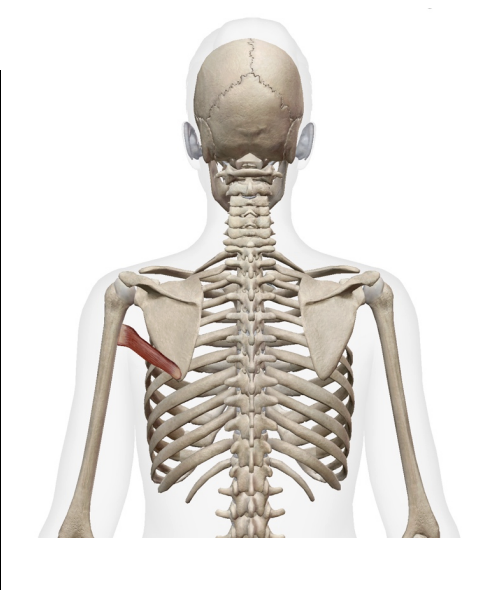
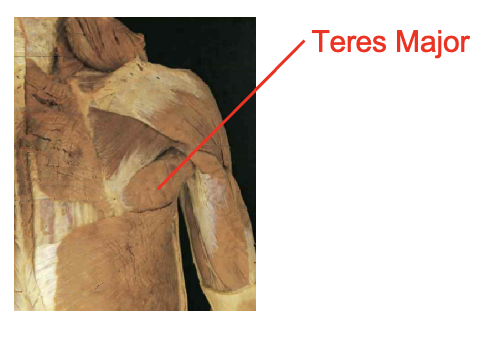
What muscle is this What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
teres major
Origin
inferior angle of scapula
inferor axillary border of scapula
Inserition
medial bicepital grove
What muscle is this What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
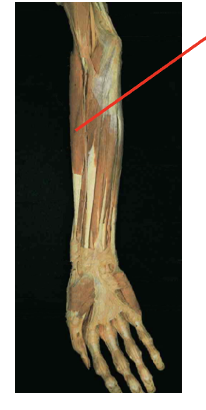
Brachiordaialis
Origin
supracondalr ridge of humerous
Inserition
styloid process of radius
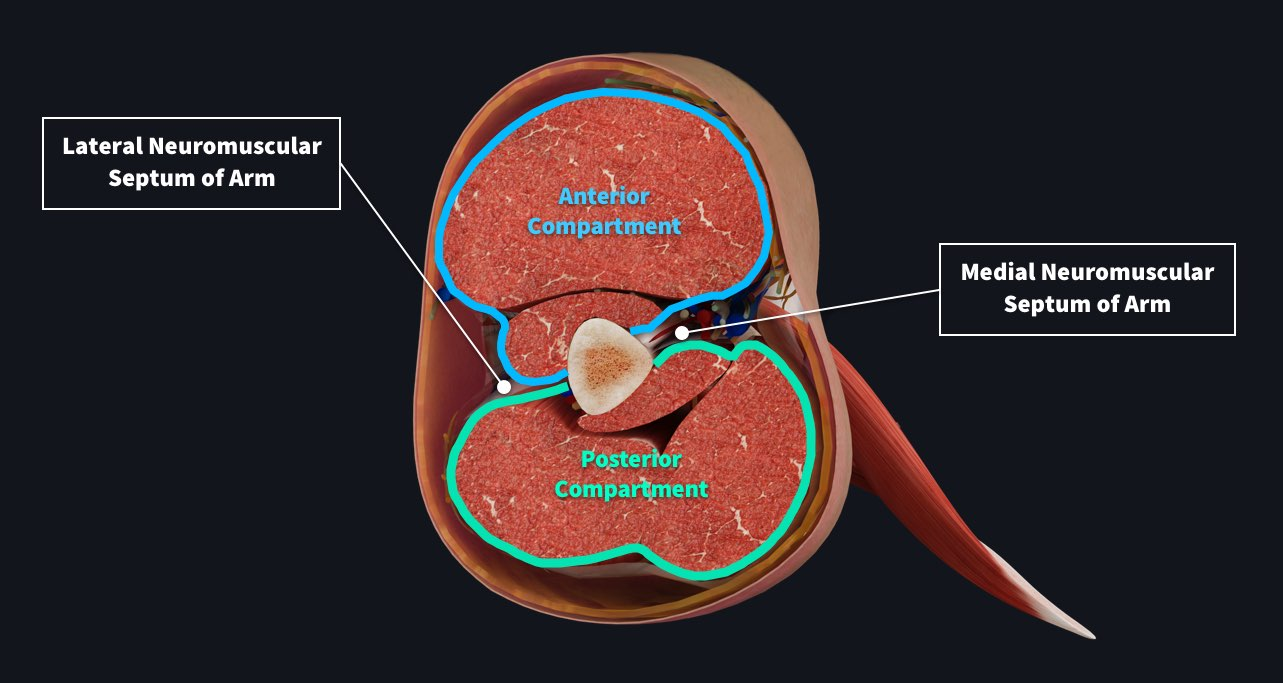
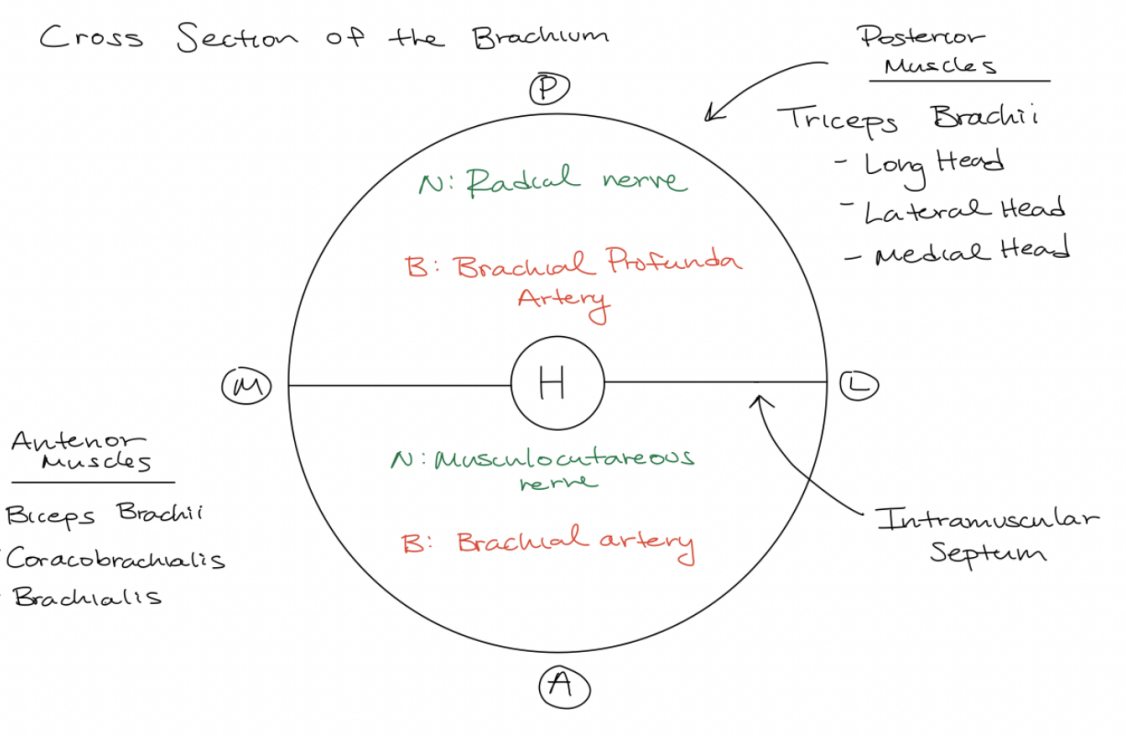
Draw out the cross section of the brachium. Whats in the posterior? Whats in the anteiror? what do they innervate? what are the major nerves and arteries
look at diagram
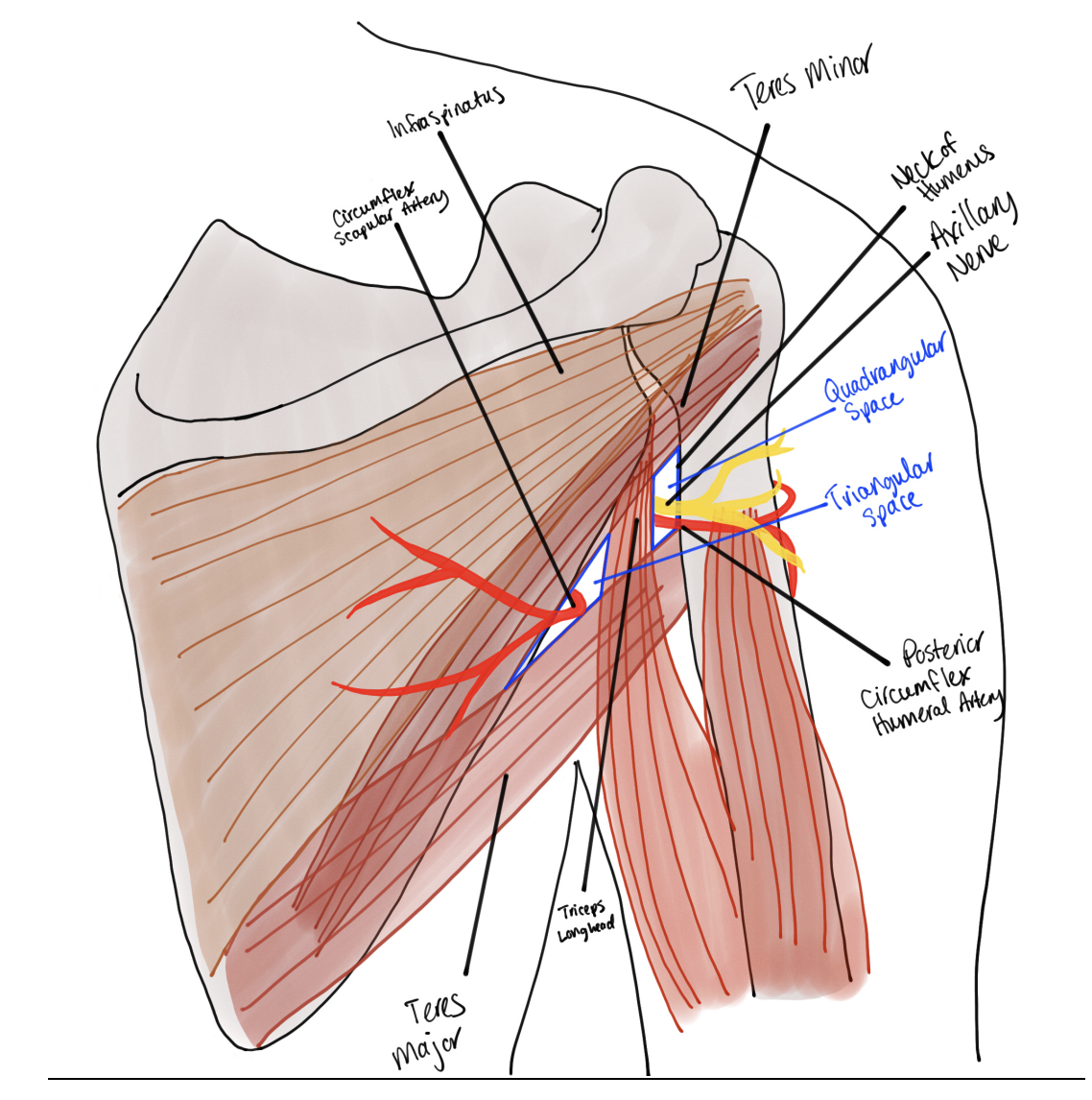
What are the quadrangular and triangular anatomical spaces of the arm. What is found there? what muscles make up this space? what nerves and artieeres and what. makes it special? what muscles. make up the triangular spcace directly
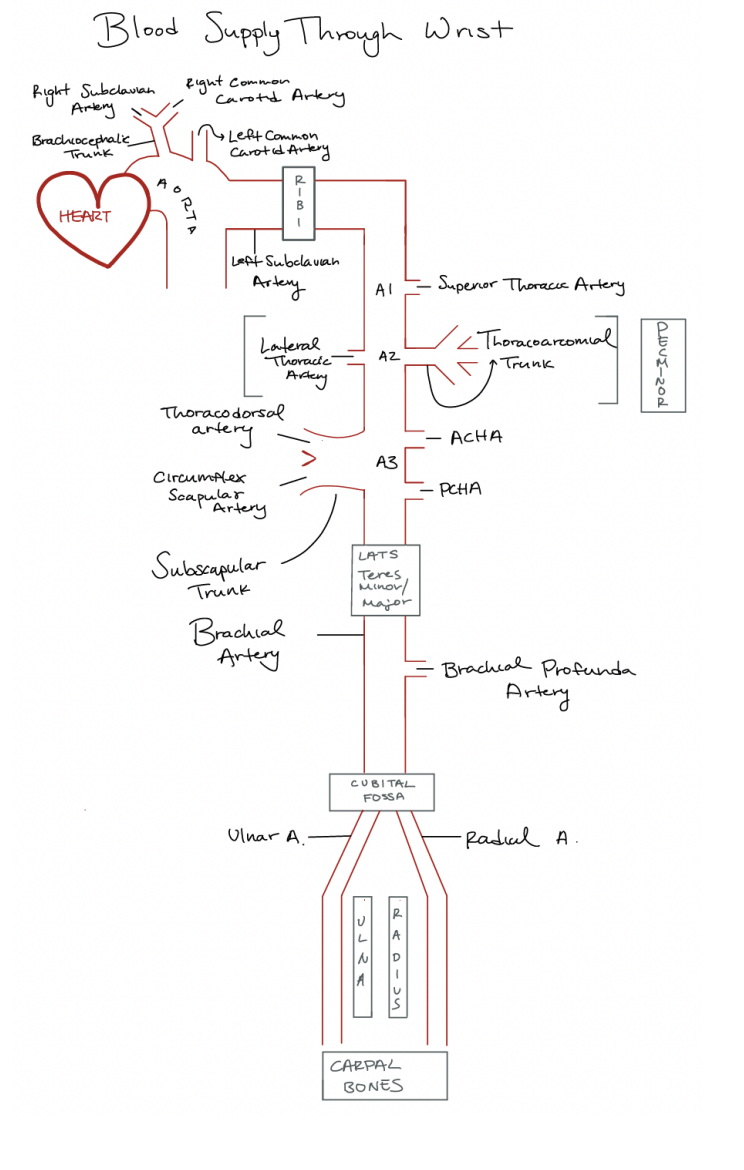
Draw out the diagram for blood supply thorughg the wrist. What are the different sections (A1-3), What are the major artieres. Where are they found and where do they branch off to? what are the trunks? where do they connect to
goes from a1-a3
ends atht the wrist
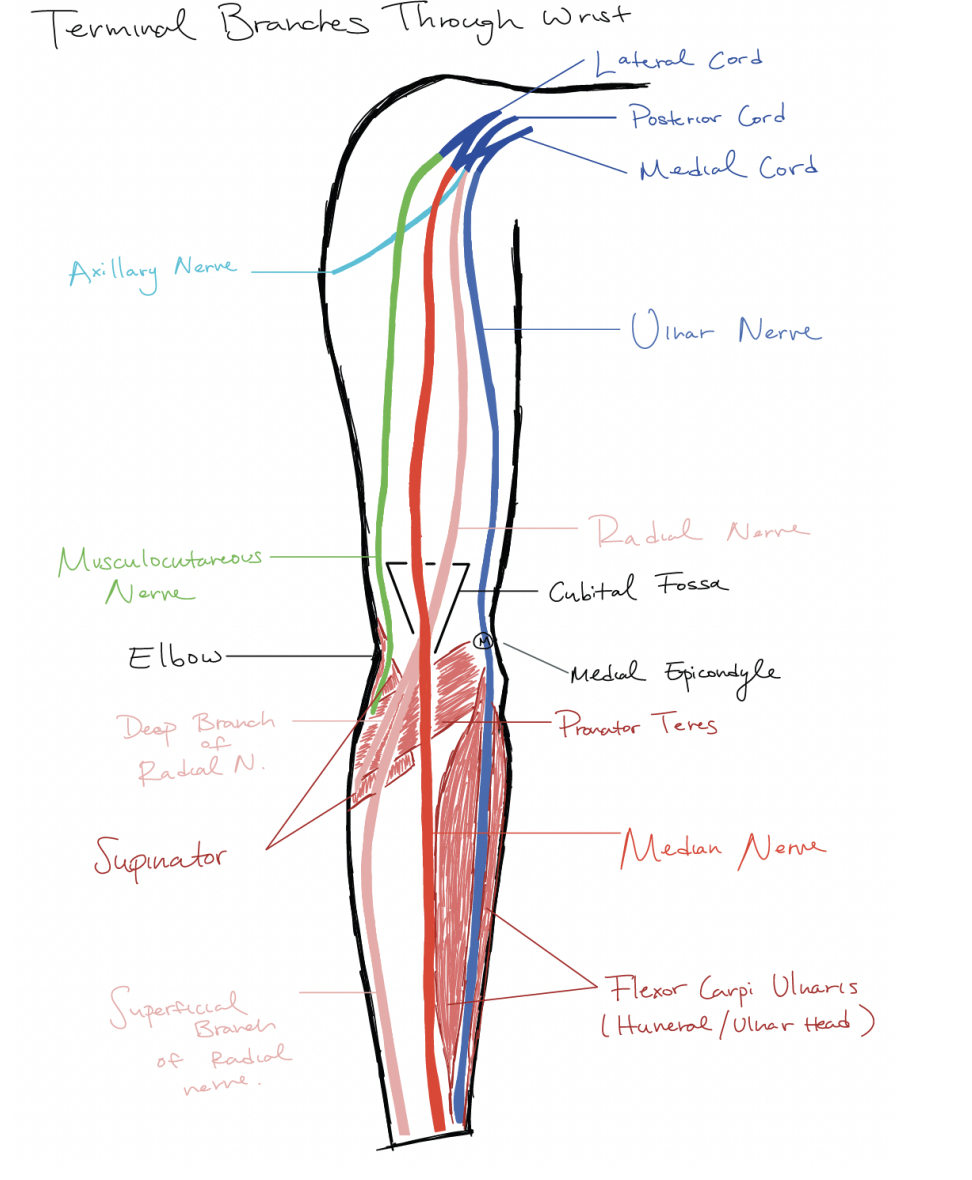
What are the terminal branches through the arm. the different nerves and all that crap
the M cord
extension of the lateral cord posterior cord(found behind the artery) and and medial cord
Medial cord
Ulnar Nerve
Posterior cord
holds the radial nerve
laterna nerve
musculcutaneous nerve
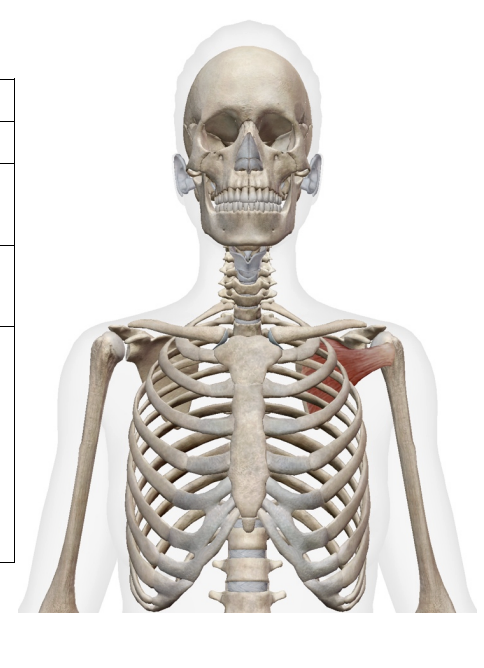
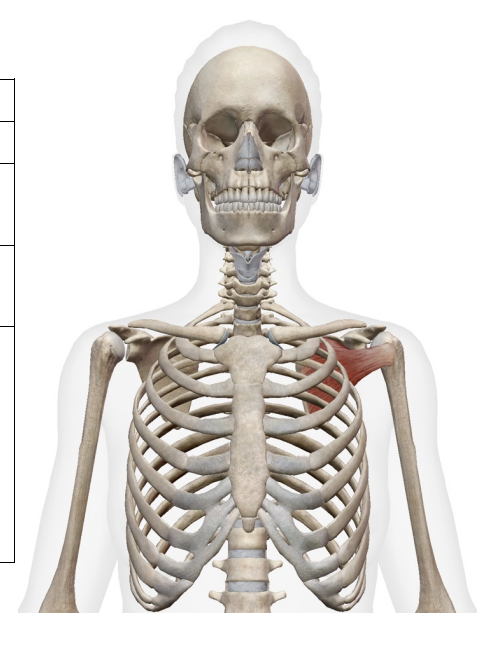
What muscle is this; What is its origin. Where does it inserts.
subscapularis
Origin
subscapular fossa
Inserition
lesser tubercle
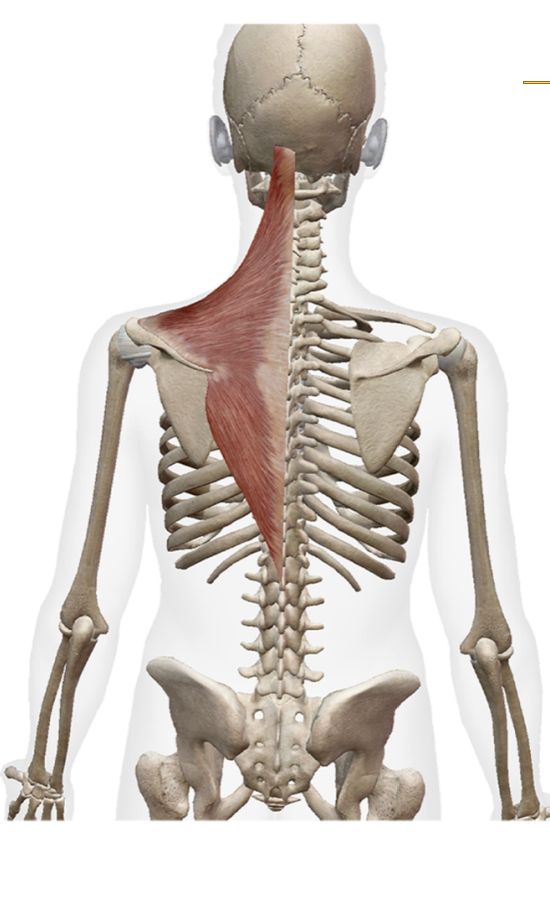
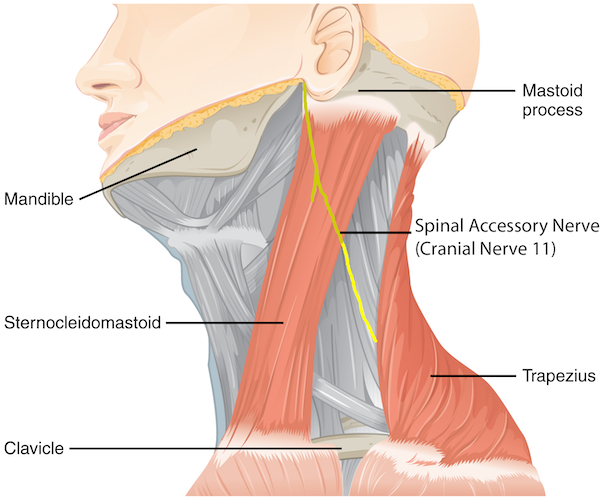
What does the Spinal accessory nerve innervate
The trapezius
What muscles are in control of these actions of of the scapula:
elevation
upward rotation
Downward rotation
retraction
depression
protraction
holding to thoratic wall
elevation
Upper fibers of the trapezius
Levator Scapulae
upward rotation
Lower fivers of the scapula
upper fibers of the trapezius
Serratus Anterior
retraction
middle fibers of the trapeizus
Rhomboid Minor
Rhomboid Major
depression
lower fibers of the trapezius
Pectoralis Minor:
Downward rotation
Rhomboid minor
Rhomboid Major
Levator Scapula
Pectoralis Minor:
protraction
Pectoralis Minor:
Srratus Anteior
Holding
Serratus Anterior
What is innervated by the Dorsal scapular nerve
rhomboid Minor
Rhomboid Major
Levator scapulae.
What muscles are in control of these actions of the shoulder
Extension
Addiction
Abduction
Internal rotation
external rotation
Horizontal adduction of the shoululder
flexion
Extension
Latissimmus dorsi
Pectoralis major (sternal end)
long head of the triceps brachii
posteior deltoid
teres major
Flexion
pectoralis Major (clavicular head)
bicepts brachii (short head
Coracobrachialis
anterior deltoid
Adduction
Latissimus dorsi
Pectoralis Major (whole) (regular and horizontal)
coracoibrachiallis
teres major
Abduction
Latissimus dorsi
supraspinatus
middle dletoid
Internal rotation
latissimus dorsi
Pectoralis Major
anterior deltoi
teres major
external rotation
infraspinatus
Teres minor
posteiror deltoid
horrizontal Adduction of the shoulder
Anterior deltoid
horizontal abduction of the shoulder
posteiror deltoid
What is innervated by the Thoracodorsal nerve
the Lats
What do these innervate: the intercostal nerves T1-T4
The serratus Posterior Superior
What muscles are responsible for the movement of the ribs:
Elevation
Depression
Elevation
Serratus Posterior Superior
Scalenes (ribs 1 and 2)
external intercostalis (inspriaition)
Depression
Serratus Posterior Inferior
internal intercostal (expiration)
What do these innervate: the intercostal nerves T9-T12
Serratus posterior inferior
What do these innervate: posteiror rami of spinal nerves
Iliocostalis
longissimus
spinalis
What msucles are responsible for the movements of ther vertebral column:
Extension
Lateral flexion
Extension
iliocostalis
longissimus
spinalis
Lateral flexion
iliocostalis
longissimus
spinalis
What msucles are responsible for the movlements of the atlanto-axial joint:
Extension
ipsilateral rotation
Lateral flexion
Extension
Rectus Capitus Posterior Major
Rectus Capitus Posterior Minor
Obliquus Caitus Superior
Ipsilateral Rotation
rectus Capitus Posteior Major
Obliquus Capitus Inferior
Lateral Flexion
Obliquus Capitus Superior
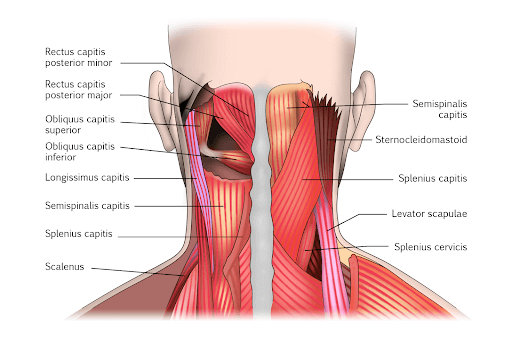
What is innervated by the posterior ramus of spinal nerve C1
Rectus Capitus Posterior Major
Rectus Capitus posterior Minor
Obliquus Capitus Superior
Obliquus Capitus Inferior
What muscles are innervated by the Posterior ramus of spinal nerve C2-3
Splenius Capitus
What muscles are responsible for the movements fo the head:
Extension
Lateral Flexion
Extension
Splenius Capitus
Lateral Flexion
splenius Capitus
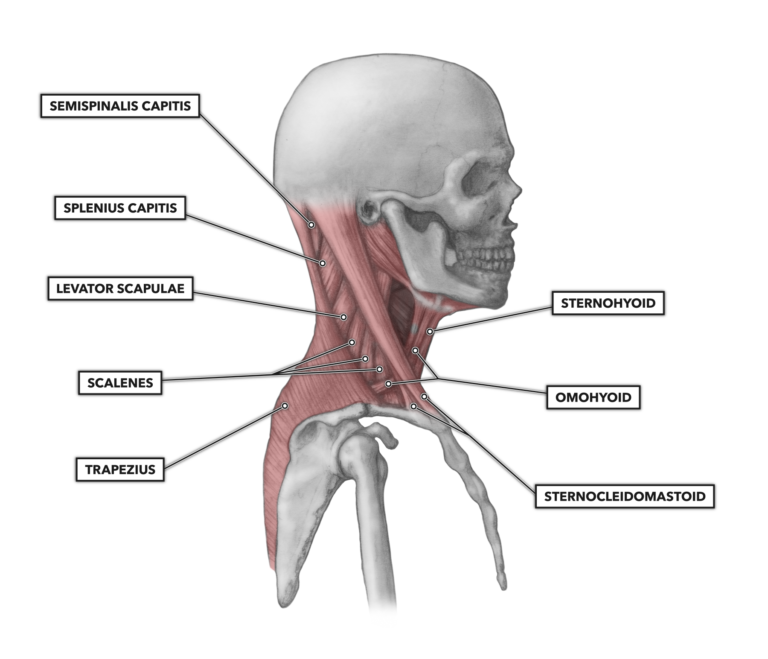
Which muscles does this nerve innervate: lateral pectoral nerves
medial pectoral nerves
Lateral
clavicular head of pecs major
Medial
Clavicular head of pecs major
Sternal head of pecs major
pecs minor
What muscles does this innervate:
long thoratic nerve
the serratus Anterior
What muscle does this innervate:
Nerve to subclavius. What does the muscle do
subclavius
stablizes the clavivle
What muscles do this action:
Flexion of the cervical vertabrae
Lateral flexion ofthe cervical vertibrae
scalines
Waht muscles does this innervate:
Anterior rami of spinal nerves
Scalenes
What muscles are responsible for these movements
flexion of neck
ipsilateral flexion of the neck
contralateral rotation of the neck
flexion of neck
Sternocleidomastoid:
ipsilateral flexion of the neck
Sternocleidomastoid:
contralateral rotation of the neck
Sternocleidomastoid:
What muscles do these nerves innervate:
Cranial nerve XI
Crania nerve VII
Cranial nerve Xi
Sternocleidomastoid:
Cranial nerve VII
Platysma
What is the function of the platysma
Tension of the skin of neck
What musles does this nerve innervate:
intercostal nerves
extrnal intercostalas
internal intercostalis
What muscels are responsible for the movements of the arm/forearm
Supination of the forarm
flexion of the elbow
extension of the elbow
Pronation of the forearm
Supination of the forearm
biceps brachii
Supinaotor
Flexion of the elbow
biceps brachii
brachialis
brachiordialis
Pronator Teres
extension of the elbow
triceps brachiii (all heads)
Pronation of the forearm
Pronator Teres
Pronator Quadratus
What muscles does this nerve innervate:
musculocutaneous nerve
biceps brachii
coracovrachialis
brachialis
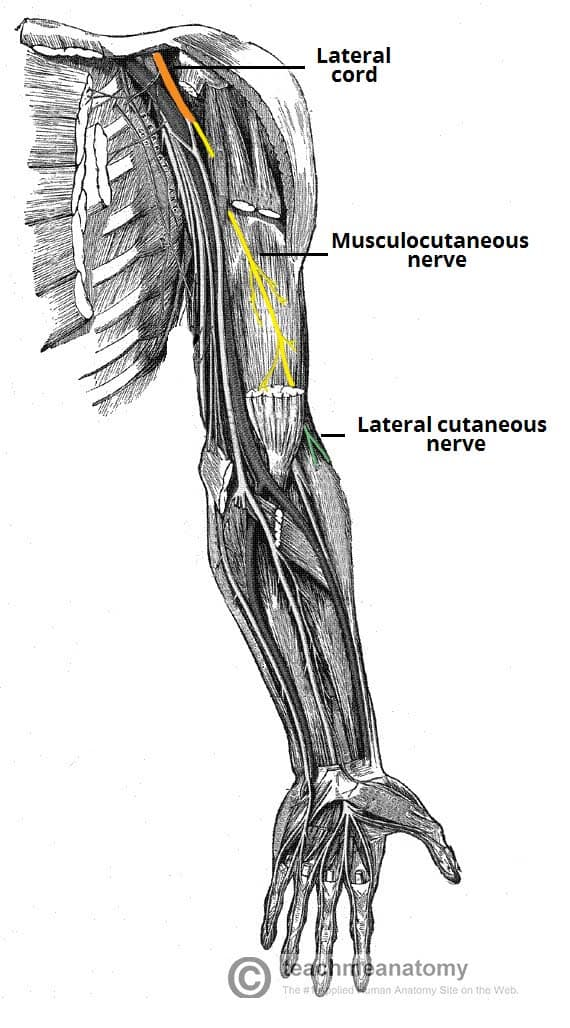
What muscles does this nerve innervate:
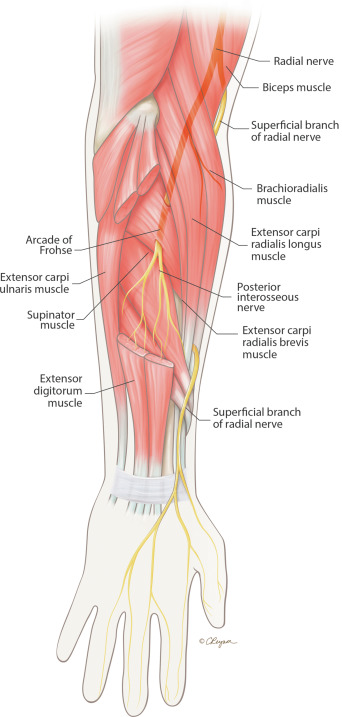
Radial nerve
brachiodrailis
triceps brrachii
What muscle does this nerve innervate:
supra scapular nerve
supraspinatus (used to stabilize glenohumeral joint and abduct shoulder)
Infraspinatus (external rotation of the shoulder, stablilizes glenohumeral joint)
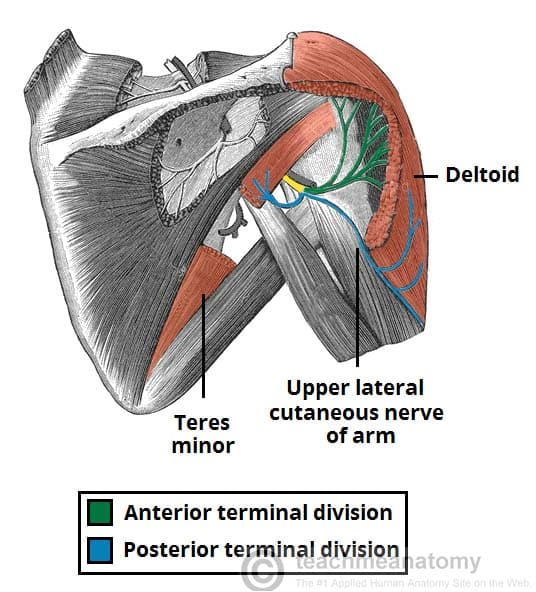
What muscles does this nerve innervate
axillary nerve
Teres Minor (stabilized glenohumeral joint and external rotation of the shoulder)
deltoid
What does this nerve innervat
lower and upper subscapular nerve
subscapular fossa
Teres Major
What is the differnece betwen the radial unar joint and the distal radial ulnar joint
proxima; elbow
Distal: wrist

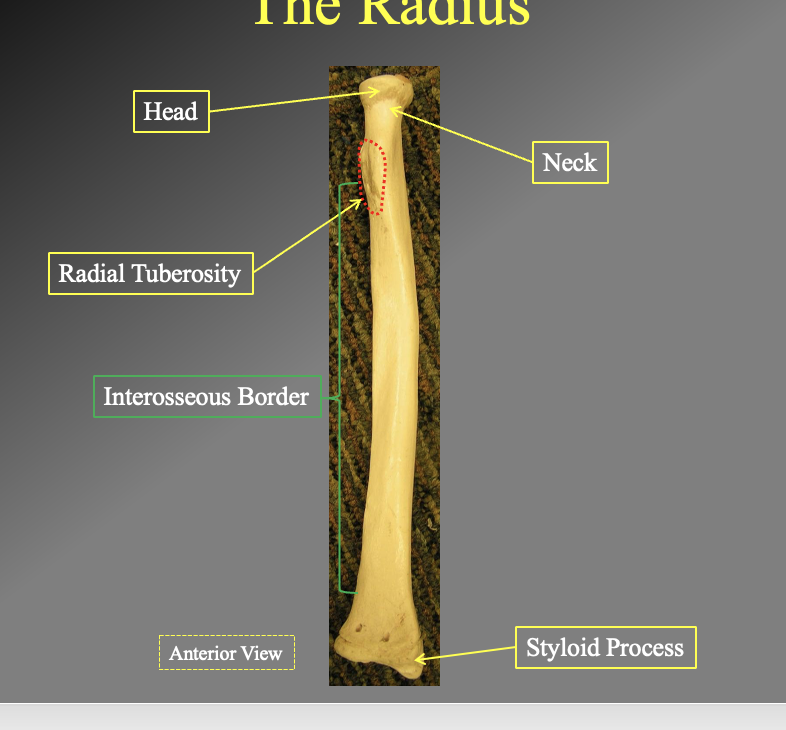
What are the components of the radius? how do you know what is proximal dn distal? left and right? anterior and posteirior`
head
the flat rounded side
neck
the pinched off part of the head (under)
Radial Tuberosity
thers a bump where muscles attach
Interosseous Border
medial boarder- faces most inward to the body
Styloid process
faces most laterally
ulnar knotch
faces medially
The anterior side
more smooth while the posterior side is bumpier
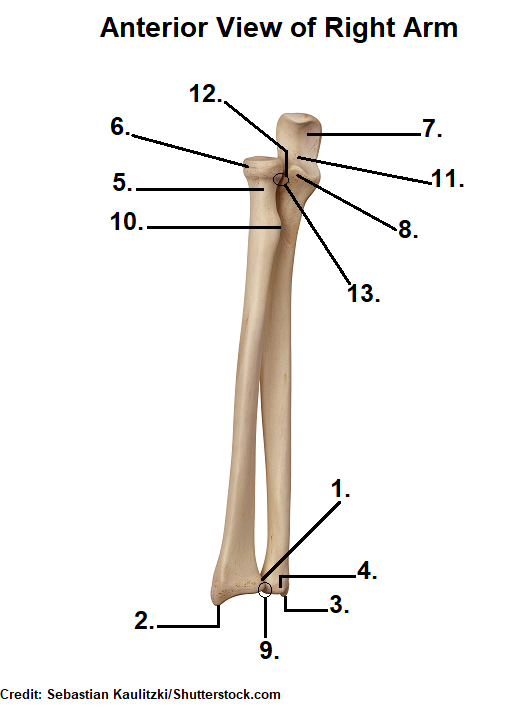
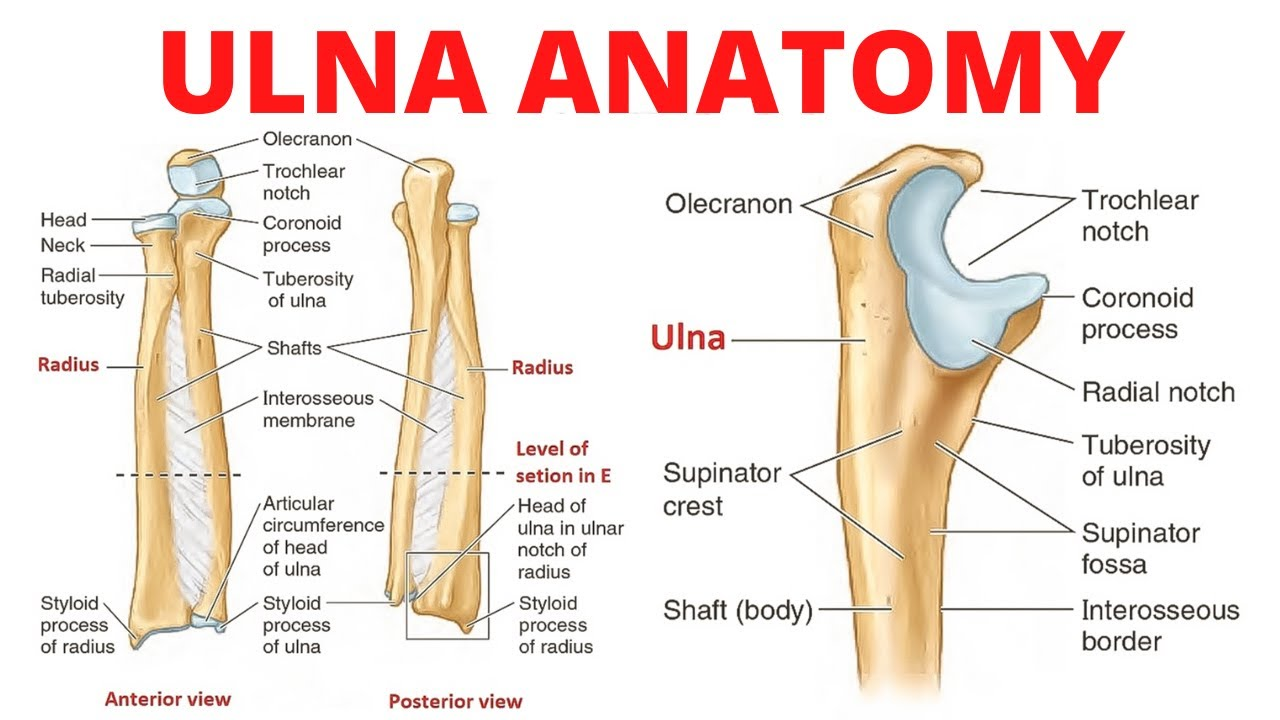
What are the different parts of the Ulnar? Proximal Ulna, Distal Ulna, Full body Ulna? what is medial and lateal? anterior, posterior?
proximal Ulna
Cornoid process
goes into the gornoid fossica of the humerous
Olecranon Process
Attaches to the olecranon fossa of the humerous
Radial Notch
faces Lateral
Trochelular notch
faces you on the anterior side
Distal Ulna
Head
Styloid process
little pointed bump on the end of the body. faces laterally
Full body
shaft
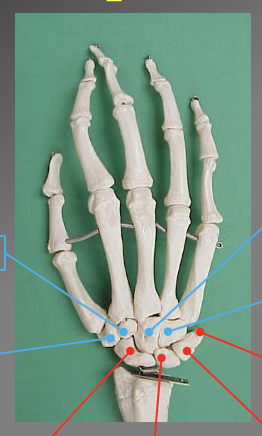
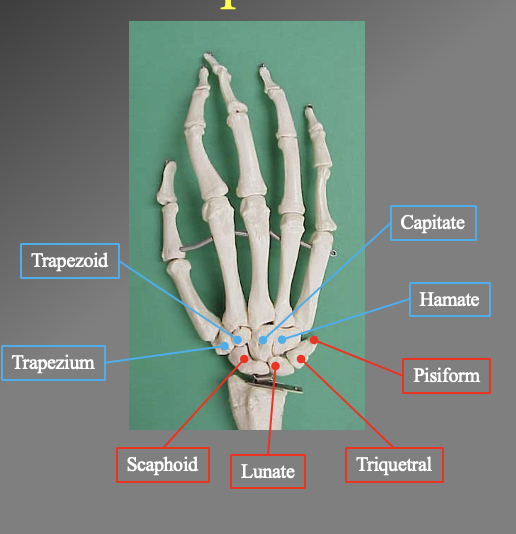
What are the different carle bones? which ones are attached to the ulnar and radius
proximal bones
Scaphoid
unate
Triquertral
Phisiphorm
distal bones'
Hanate
Capitate
Trapezoid
Trapezium
note this follows from the bone under the thumb to the pinkey and back to the thumb
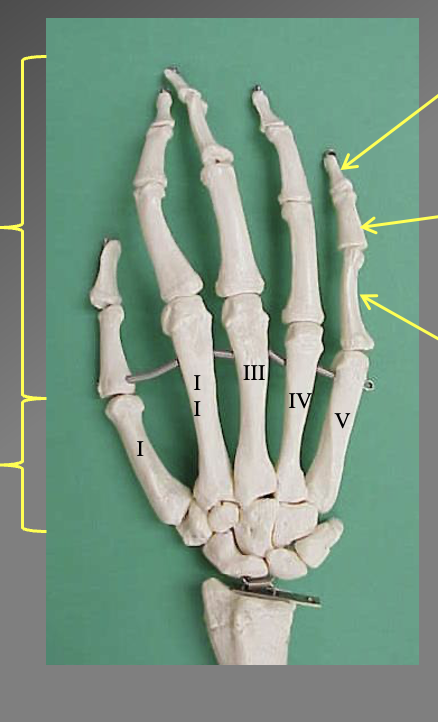
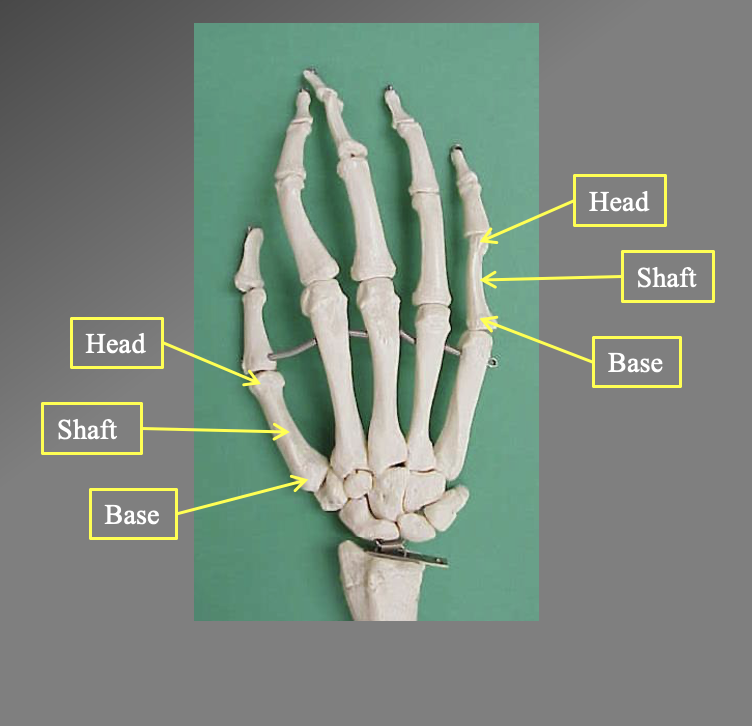
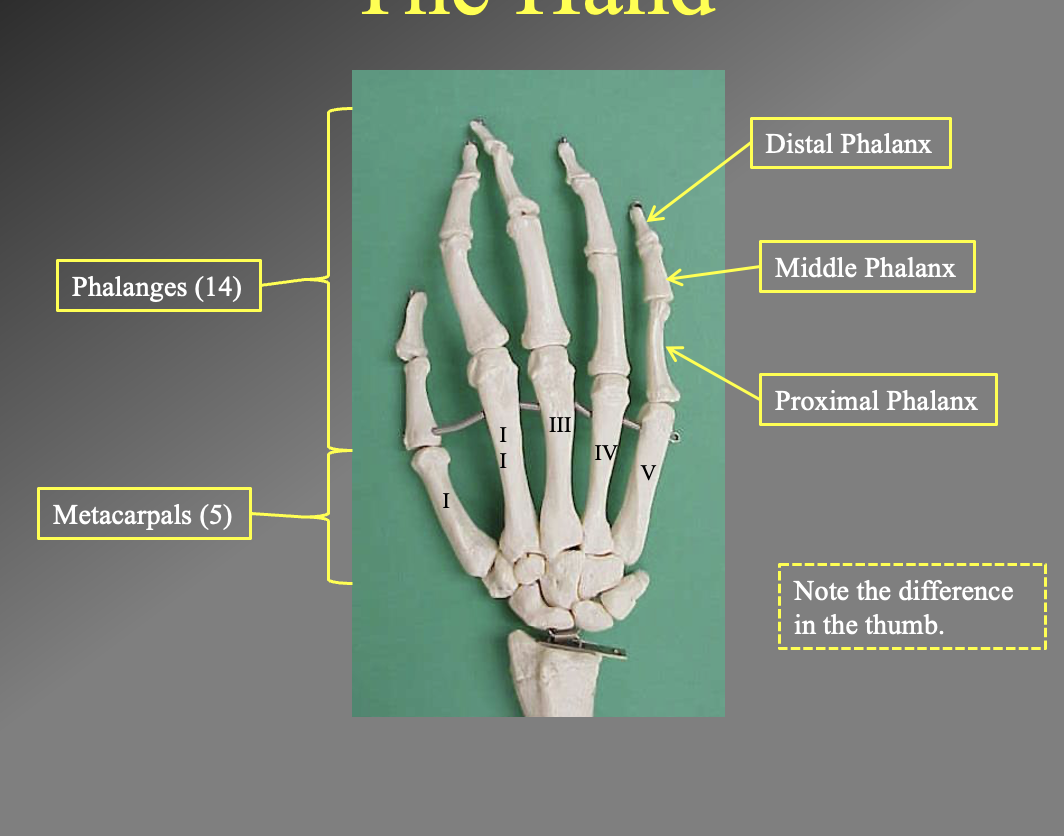
What are the differrent bones of the hands. What are the different sections
There are 14 philangeis (upper finger bones)
5 metacarles (lower finger bones)
Proximal phalanx
iddle phalanx
Distal philanix
note the thumb only has the proximal and distal since there are only 2 philangies
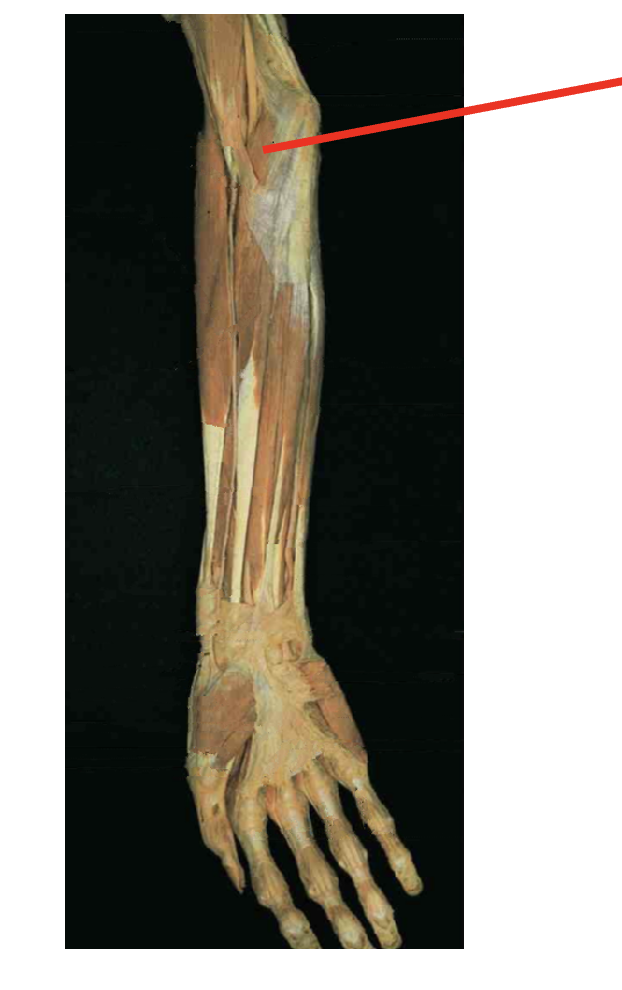
What is this muscle? where does it insert? where is its origin
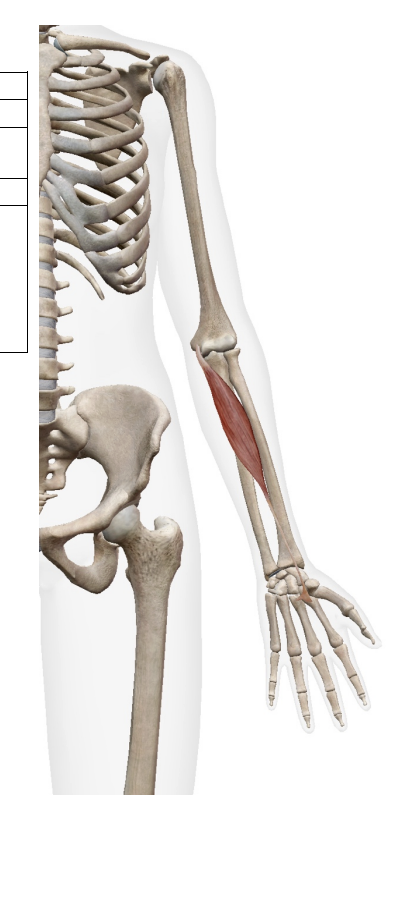
pronator Teres (flexor)
origin
Humeral head - medial epicondyle of humerous
Ulnar head (coricoid process of ulna)
insertion
middle of lateral radius
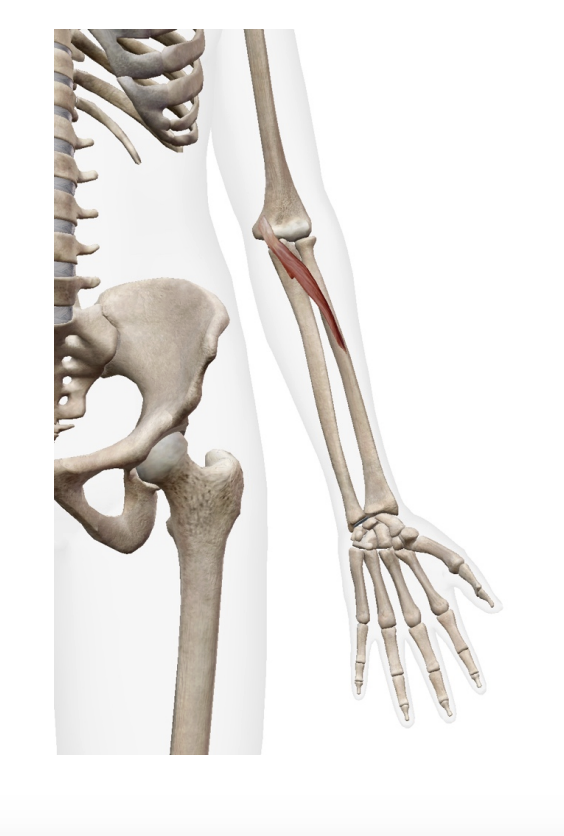
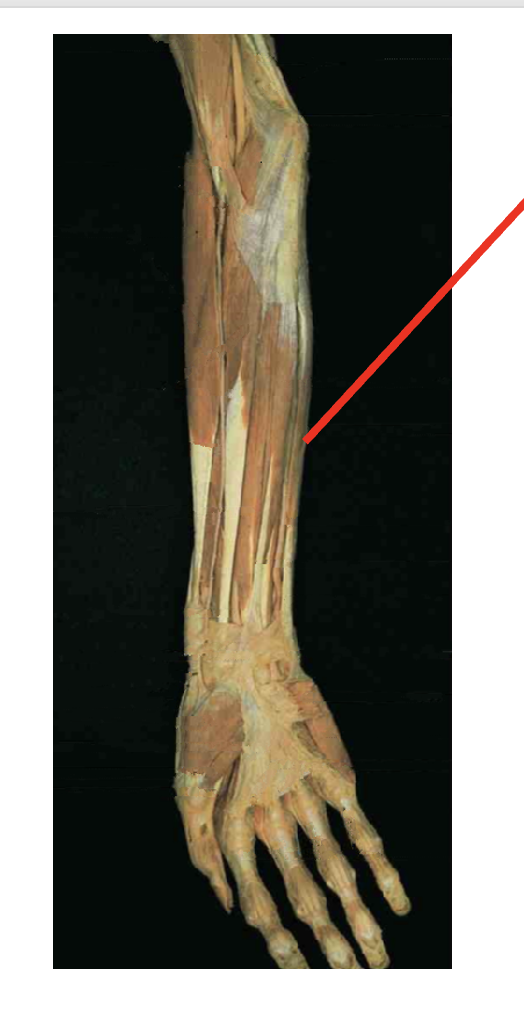
What is this muscle? Where does it insert? What is its origin
Flexor Cari Unaris (flexor)
Origin
Humeral head: medial epicondyle of humerous
Ulnar head: olecranon process and proximal posterior ulna
Insertion
phusiphorm
hok of hamate
base of 5th metacrale
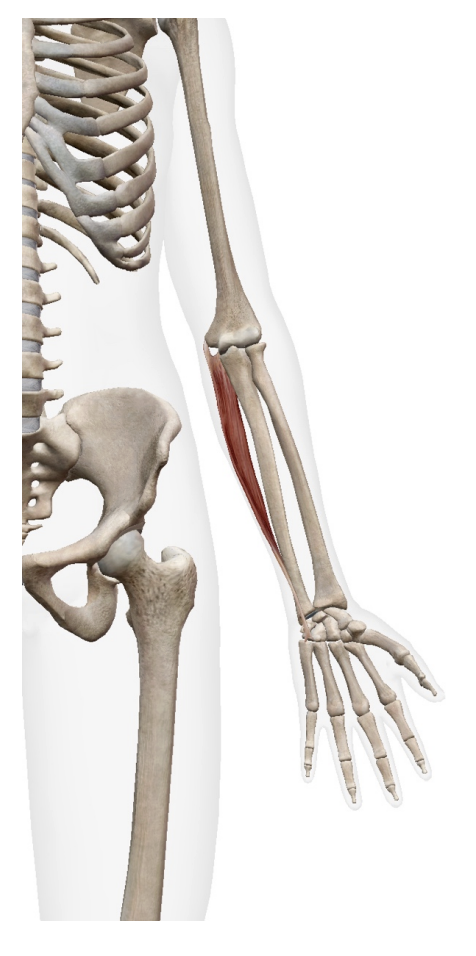
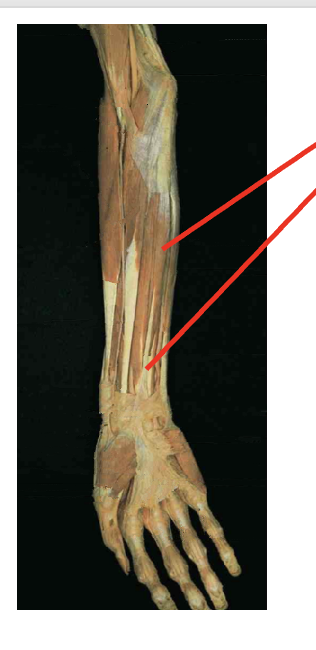
What is this. muscle? where does it insert? Waht is its origin
Palmaris Longus (flexor)
Origin
Medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion
palmar aponeurosis
flexor retinaculum
bases of proximal phalanges
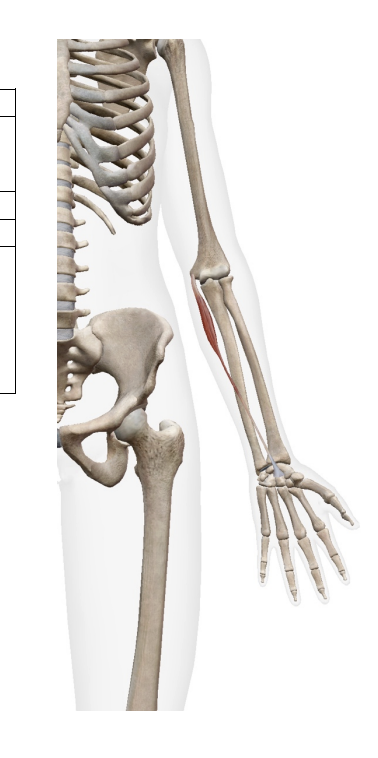
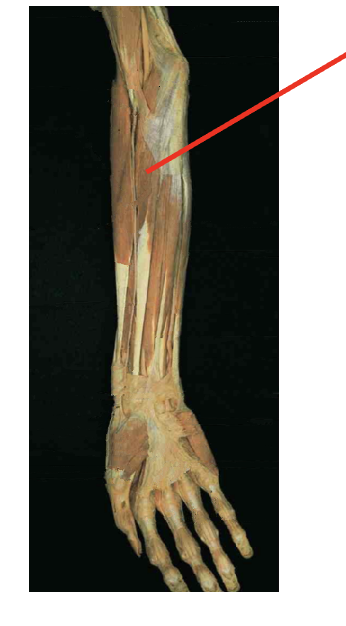
What is this muscle? What is its origin? Where is its insertion
Flexor Carpi Radialis (flexor)
Origin
meidal epicondyle of humerous
Insertion
Base of 2nd and 3rd metacarals