Week 1
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Notion of trade-off in operations capabilities
You cannot achieve one capability without sacrificing another
To achieve high-quality production…
Costs will increase
To achieve flexibility…
Costs will increase and quality will decrease

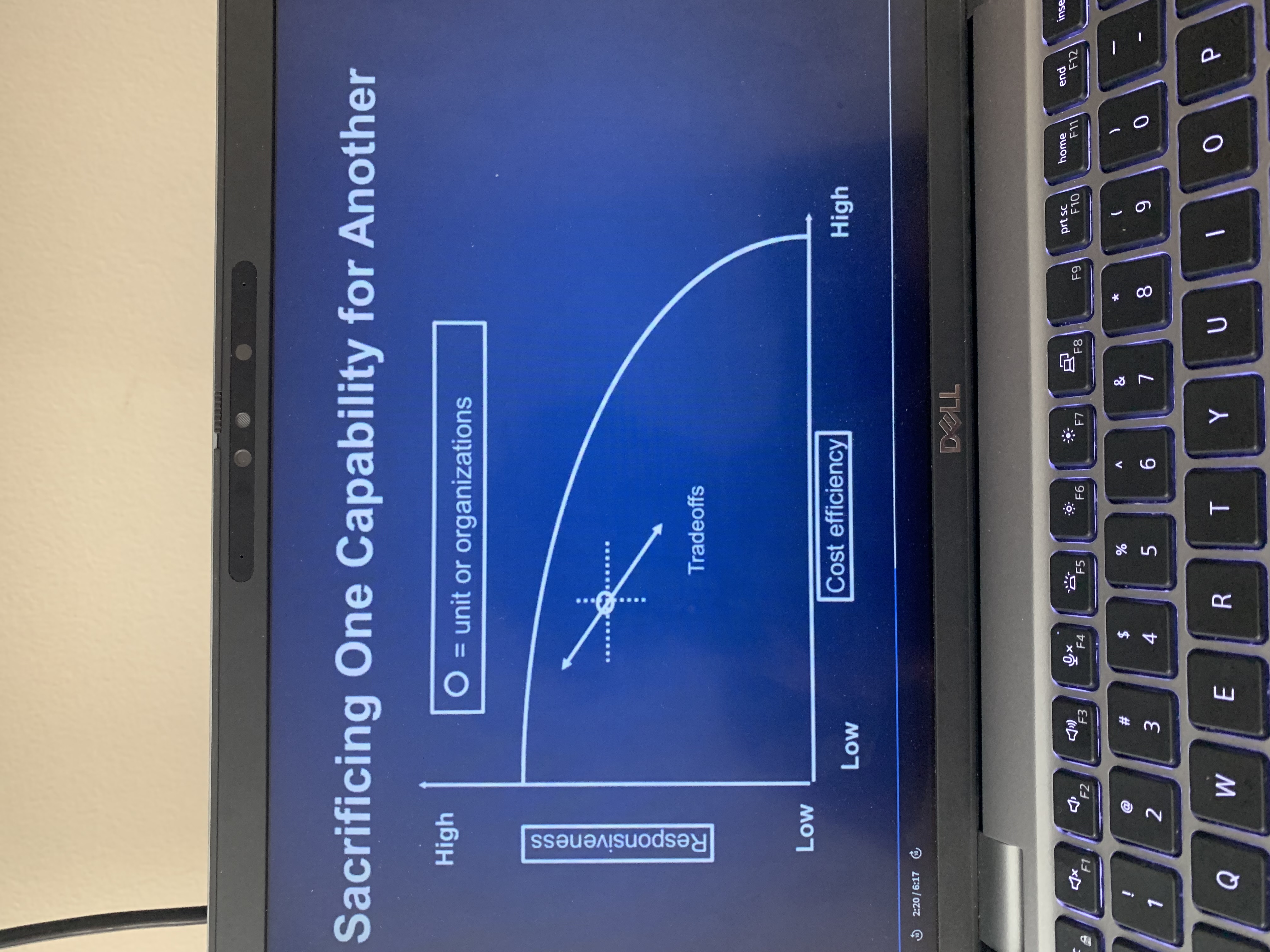
This visual shows a company sacrificing one Capability for another.
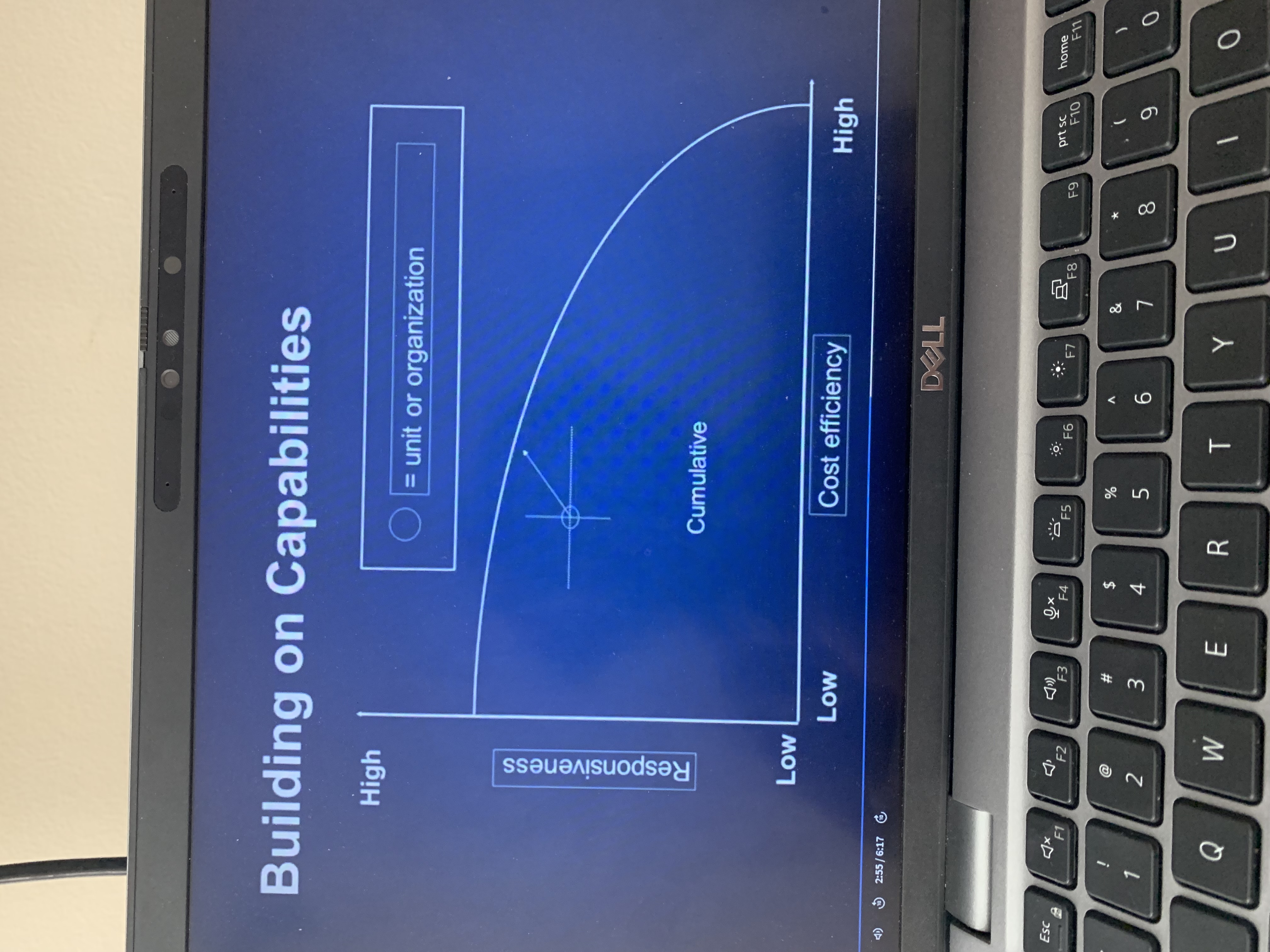
This visual shows building on capabilities. Building capabilities is generally more challenging than sacrificing one capability for another.
What is an example of trade-off versus cumulative capabilities?
Ford versus Toyota
Ford only making their cars in black in order to control costs
Toyota was able to offer different versions of cars without sacrificing costs. They Pioneeredcumulative capabilities
Mass customization
is the capability of Producing products that are customized to meet specific customer needs while charging low prices
additive manufacturing for single unit production
Using 3-D printing for specific use cases. Can eliminate the need for dyes and molds while keeping costs low

Quality is harder to define for?
Services
Production and consumption for services is mostly
Simultaneous
Three main service management concepts
Customer variability
Front and back office
Service profit chain
What are the sources of customer variability in services?
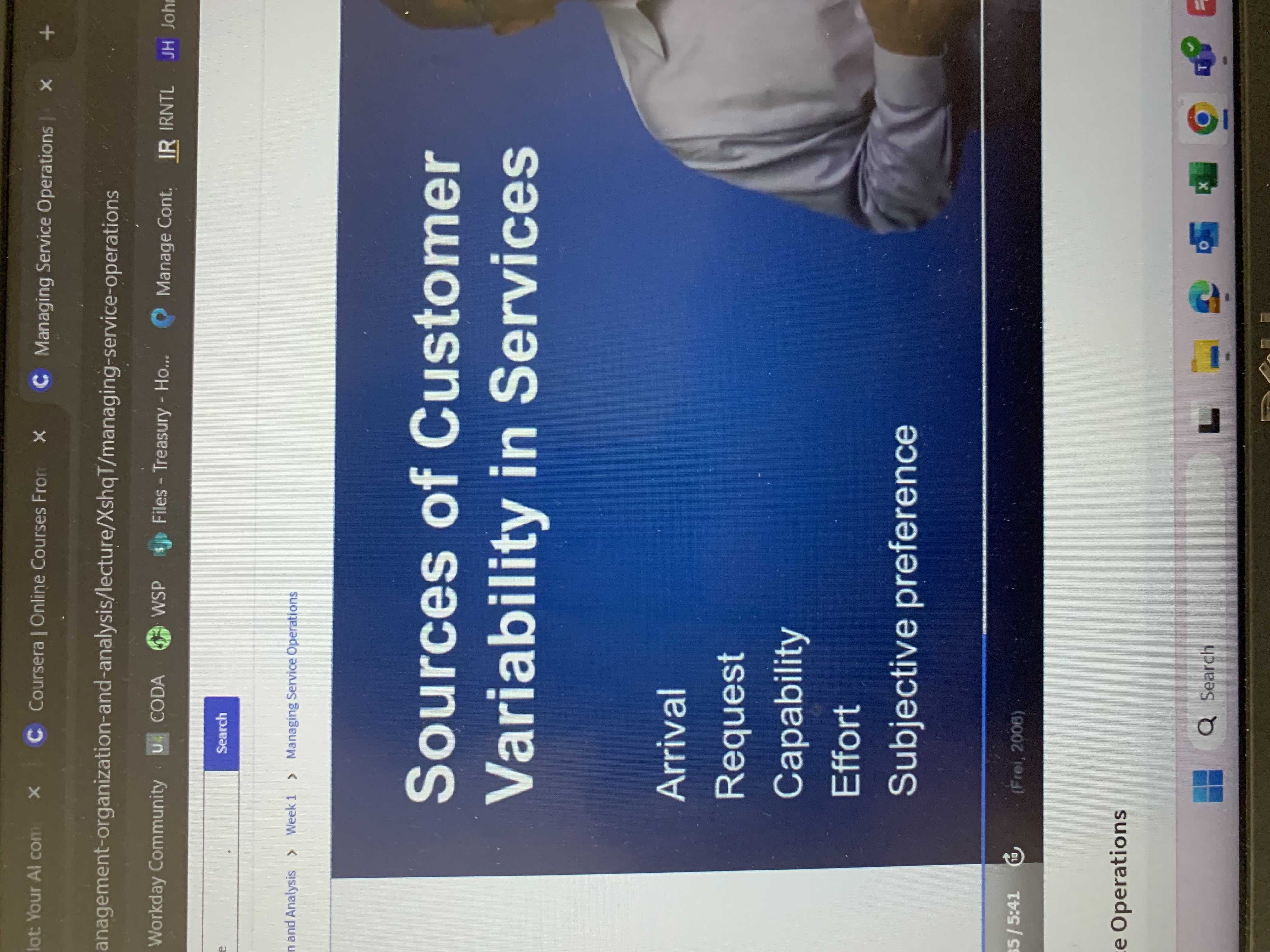
Arrival
The timing of demand of customers is uncertain
Request
What the customer demanded varies. Each customer can have a completely different demand.
Capability
Customers having different levels of ability In the things they need to do To have a good service experience
Effort
Customers have different motivation levels
Subjective preference
Different customers have different ideas of what good service means

implications of the front office
Direct customer encounters
Provide opportunities to delight
Provide openings for mass customization
Increase uncertainties in service delivery parameter
Result in inefficiencies in service delivery
Service profit chain in short
Happy employees can lead to happy customers and happy shareholders or owners
Common operations capabilities
• Cost
• quality - Control, Features
• delivery - Speed, Reliability
• flexibility - mix, Volume
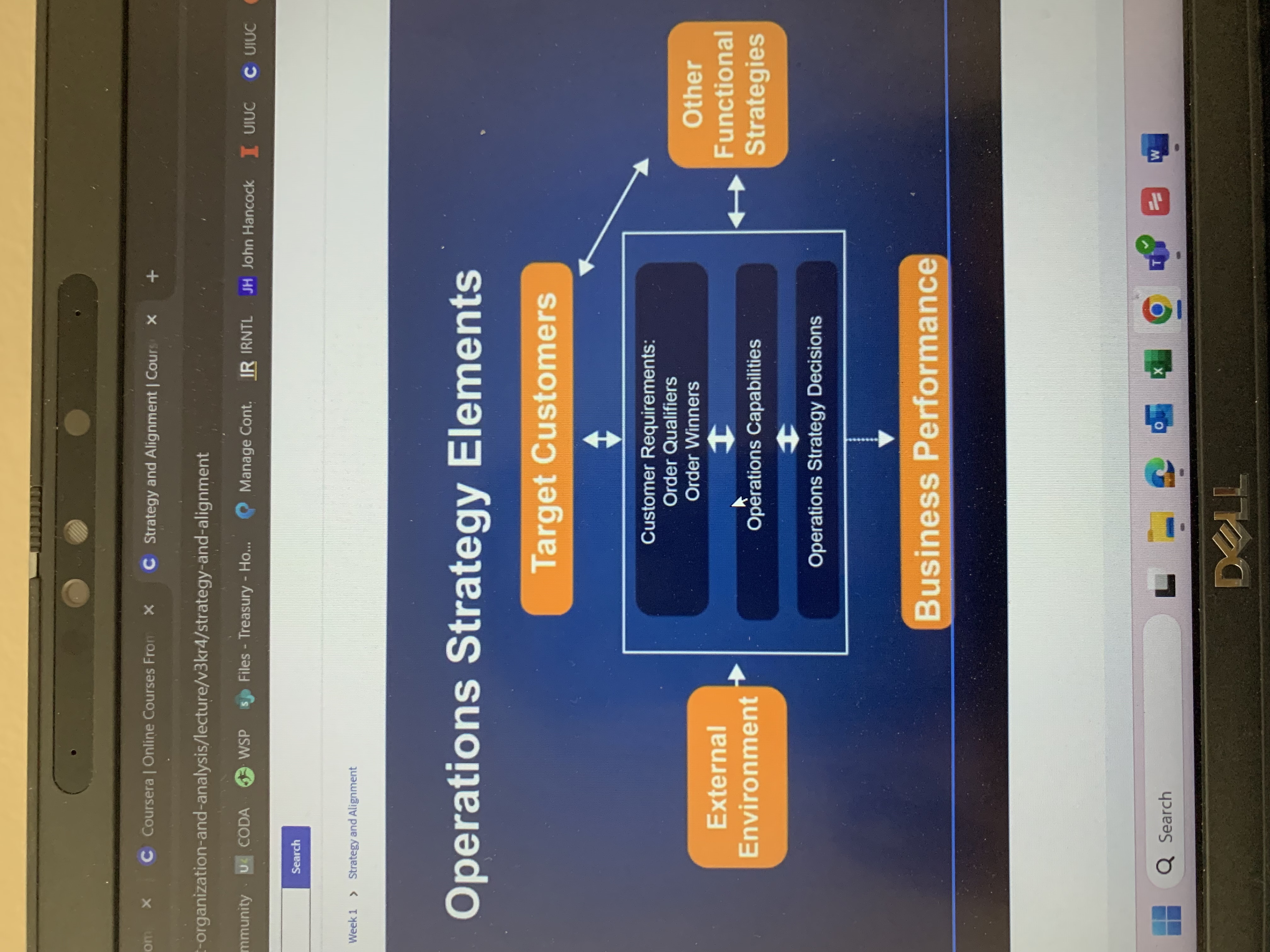
Operations strategy, decision areas
Investments
Organization
Investments
Location and size of facility
Layout of facility
Technology choice
Extent of vertical integration
Organization
Salaries and incentives and employee training
Quality management
Scheduling of production
Centralized versus decentralized control
Order qualifier
Minimum selection criterion that permits, products or services to be even considered by potential customers
Order winner
Criterion that differentiates the products or services from competitors thus resulting in winning orders of customers
Order winners in order qualifiers May get interchanged for different customer segments
Definition of operations strategy
The total pattern of decisions which shaped the long-term capabilities of any type of operation and their contribution to overall strategy, Through the reconciliation of market requirements with operations resources.
Definition of business strategy
Integrated and coordinated set of commitments and actions designed to exploit core competencies and gain a competitive advantage
Alignment among strategies
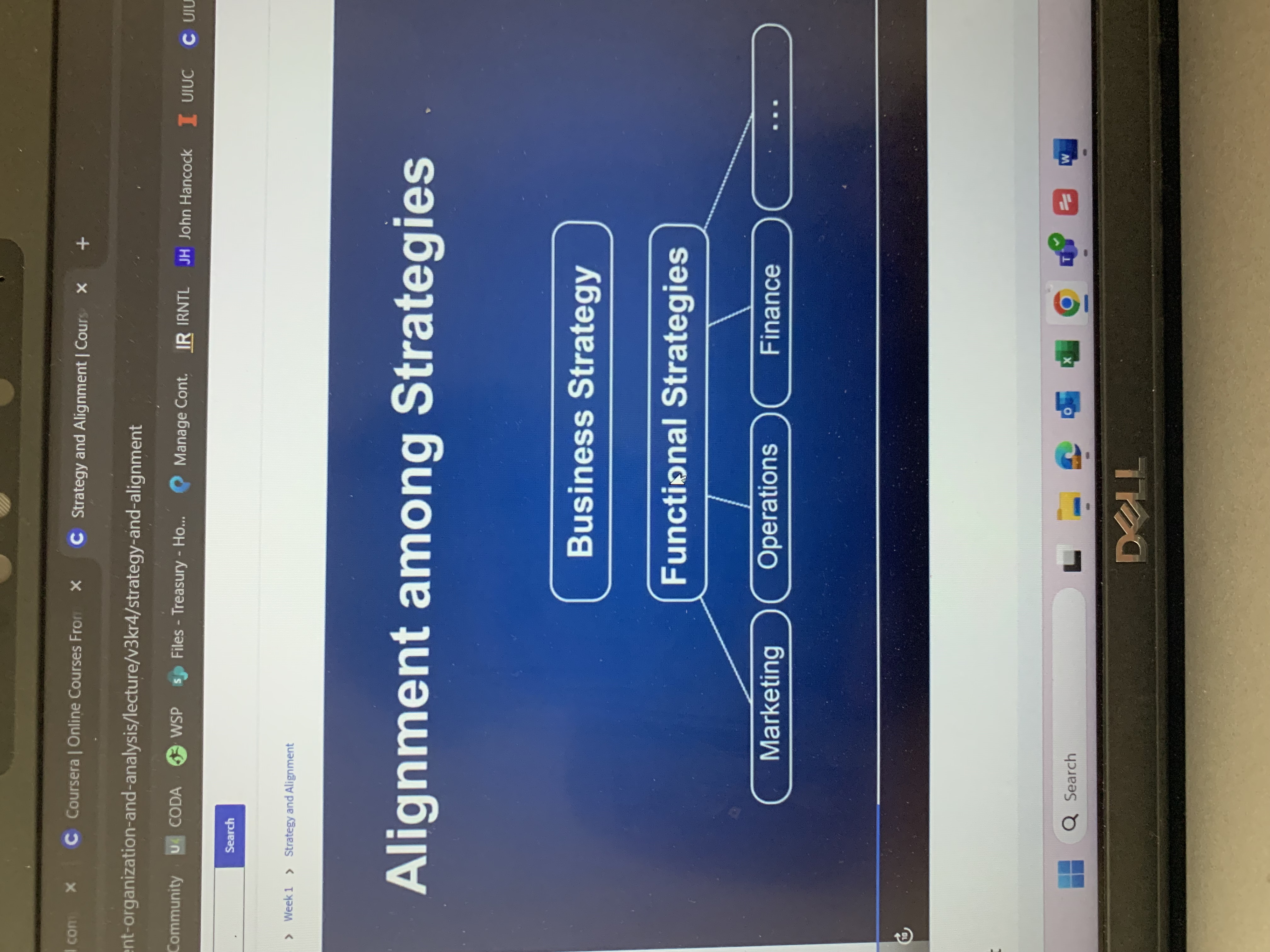
Method of organizing and doing work
Role of operations
Design
Manufacturing
Sales and distribution
After sales service
Upgrades
Disposal
Defining operations management
Objective is to efficiently and effectively Utilize resources To design produce and deliver products, goods and services. They must be the right quality, right quantity right cost, and available at the right place at the right time to meet customer expectations.