Exam 1 rabbits, ferrets
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
For rabbits where are injections preferred
Epaxial (dont use legs)
What is the preferred venipuncture in rabbits
Lateral saphenous
marginal ear vein last resort
What type of breathers are rabbits?
Obligate nasal breathers
When taking a radiograph of rabbits should there be any food in their stomach or no?
Rabbits should always have food in their stomachs.
GI microbiome of rabbits is mostly made of
Gram-positive bacteria
Dont use antibiotics that selectively target gram positive or you will get a overgrowth of gram-negative (endotoxins)
What drugs do you not use in rabbits?
Front line
place acronym
What type of teeth do rabbits have?
Aradicula, hypsodont (*elodont)
like horses, all grow entire life (3mm/wk)
must be constantly worn down
occlusal surface cheek teeth slightly angled
all teeth are open rooted and contiually grow
Rabbit vision
monocular
how many nasal lacrimal ducts do rabbit have?
one located medial ventral
Rabbits commonly get cataracts, ulcers (high atropinase levels) and phacoclastic uveitis
What causes phacoclastic uveitis
E. canniculi
sporizoite goes into lens capsule and causes a rupture
opportunistic of immunocomprised
E cuniculi tropism
Neuro/Reno tropic
granulomatous meningoencephalitis
chronic interstitial nephritis
phacoclastic uveitis
blamed for acute head tilt
Rabbit presents with bilateral exophtalmis is 100% of the time due to
Thymoma
check thoracic chest compliance, T3-6
What are the temperature regulators in rabbits?
Ears
Dilate in hot temperatures
What ear mites do rabbits get?
Psoroptes cuniculi
How do you treat ear mites in rabbits
Ivermectin or selamectin
Do NOT clean ears
do NOT use frontline
Messy front paws/for limbs are indicative of
Darcrocystitis
Asymmetric at jaw in rabbit may be indicative of
abscess
Should rabbits be fasted before surgery
no DO NOT fast rabbits before surgery
In rabbits fracture of which vertebrate can occur with struggle
L7
what should not be used on the floor of cages for rabbits?
Cedar pie grates
Note: keep away from other animals including other rabbits
Due to rabbits not having any foot pads what can they be prone to?
Pododermatitis called sore hock
If kept outdoors rabbits can be prone to?
heat stroke
can rabbits vomit
no
How much hay should you feed a rabbits?
unlimited
should make up most of their diet
only give them unlimited amounts of pellets
You should give rabbits up to 4 cups of
fresh darkley coloured vegetables
young rabbits have a PH of 5-6.5 in their stomach once they are weaned it drops to
1
young rabbits diet contains up to 18% of protein what is a good source?
Alfalfa
Since rabbits are like horses can you change the diet rapidly or slowly
you must change the diet slowly
should rabbits have food in their stomachs always
yes rabbits should always have food in their stomach and some GIT sounds
they eat frequently
diet: high fiber, low CHO
What are good OTC food for rabbits
canned baby food or canned pumpkin
When should rabbits be spayed and why is it important
4-8 months old all females
will get uterine adenocarinoma if not
What intestinal parasites do rabbits get
Tapeworms
coccidia (most common)
pinworms (oxyruis ambiqua)
What is Cyniclomycoes gluttulatus?
Pseudo parasite
it is a yeast that lines the stomach of rabbits, guinea pigs, and chinchilla
Rabbits are susceptible to rabies what vaccine do you use?
all susceptible to rabies but few transmit it (peracute death)
not considered important threat
no approved rabies vaccines for rabbits or rodents
Rabbit presents with peracute death, (fever >greater than 104) anorexia, lethargy, and bleeding
what virus?
Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus - 2
signs:
peracute death
fever (>104)
anorexia
lethargy
bleeding
spread:
fomites
other rabbits
persist for a long time
wildlife
Rabbits have what type of inguinal rings
large open rings
testicles can retract into abdomen
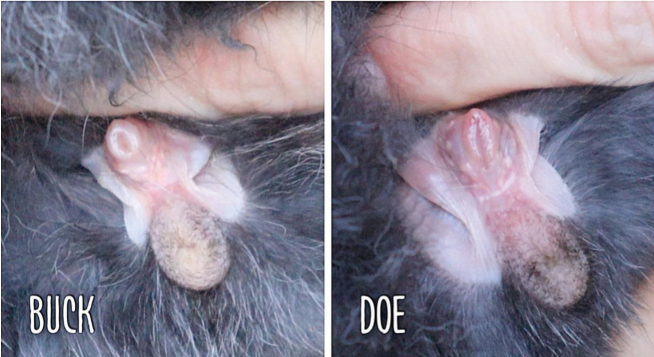
In rabbits who has a dewlap male or females
Females contain the dewlap

80% of unspayed rabbits develop uterine adenocarcinoma at three years or older which can metastasize to chest liver, skeletal system
when should they be spayed
around six months
Rabbits have how many uterine horns and cervix do they have
two separate uterine horns each with its own cervix
Dental disease presentations
Dacryocystitis
messy front paw/forelimbs, mouth
weight loss and inappetence
malocclusion
abscesses
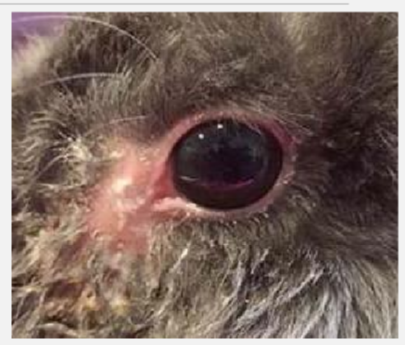
zoonotic fur mites that may be a asymptomatic that can cause dry flaky skin
non burrowing
Cheyletella parasitovarax
wealking dander
exacerbated by stress
treatment = revolution
cecotropes contain bacteria and good vitamins and energy.
where are they absorbed
Jejunum
three differentials if a rabbit presents with anorexia
stasis
GI obstruction
liver lobe torsion
what is the first thing you do when a rabbit presents anorexic
obtain rectal temperatue (low is red flag)
next do a palpation for belly pain listen to a GIT sounds and check for stool production
then do diagnostic test
stasis/Dysbiosis in rabbits
normothermia
smaller or abnormal stools
non-painful abdomen
gut sounds diminished / not absent
anorexia can be >12hr
rads: food in stomach, segmental gas in colon
How do you treat stasis in rabbits
supportive care
fluids and nutrition and pain meds if painful
with rabbits should you give pmotility drugs with stasis
no evidence that it works
signs of obstruction in rabbits
anorexia <12hr
may be shocky
hypothermia (<99F)
BG (high 200’s over 300)
painful to palp
gas in stomach (tympanic)
What woyld you see on radiographs that is indicative of gastric obstruction in rabbits
large distended stomach that passes L2
stomach is filled with fluid and jester
small intestines have gas or fluid
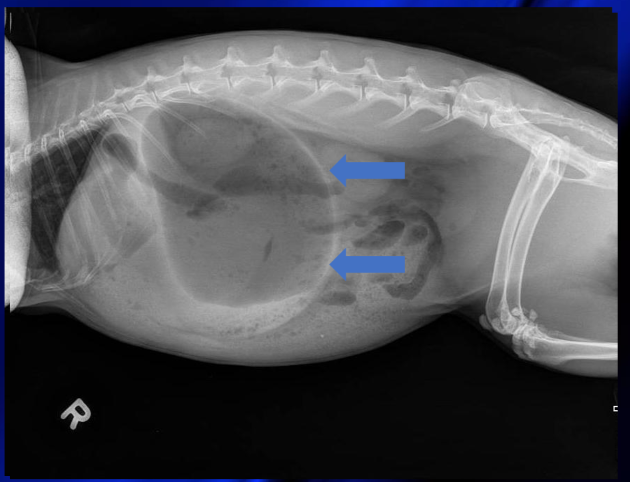
How to treat rabbit gastric obstruction
stabilize; warm pt
IV/IO fluids - shock doses
pain meds - hydro
lidocaine CRI
orogastric decompress under sedation/anesthesia - ASAP
assess
surgical or medical management
Liver lobe torsion
Signs:
lethargy
hypothermia
decreased fecal production
tachypnea
pain in cranial abdomen
CRT prolonged
ACUTE <12hr
Diagnostics:
POCUS: no blood flow to area
ALT, ALKP, AST 3-10x elevated
±anemia
(± rads - less helpful)
abdominal palpation
radiographs (enlarged liver past last rib)
liver anlaytes: increase ALT
ultrasound - right caudate lobe
Treatment:
stablize (warm)
pain meds
transfuse or hypertonic saline
surgery - remove lobe
medical management alone >60% fataltiy
rabbit summary that presents with an acute abdomen
low body temp and moribund
sick for less 12hrs
moderate to severe pain
most common rules outs: LLT vs OBSTRUCTION
Pasteurellosis
common bacterial disease of rabbits
respiratory, then blood to any organ system; brain, bone, repro

Wry Neck - Rabbit
etiology unknown
otoconia (BPPV)
Iatrogenic
Otitis Media/iterna
rarely e. cuniculi
Urolithiasis rabbits
unknown cause
high calcium diet NOT been shown to cause
multifactorial
herbivores
high pH
all calcium based
surgery necessary
Which antibiotics are toxic to pocket pets
penicillin
lincomycin
aminoglycosides
cephalosporin
erythromycin
safe = chloramphenicol, enrofloxacin
ferrets hedgehogs and and sugar gliders do not have the sensivitivies
Sedative and anasthetics are strongly recommended specifically
Midazolam
espcially in respiratory distress
Why are ferrets susceptible to heat stroke
they are cold weather animals
you see a ferret with two tattoos what doses it mean
descented and neutered
one means = descented
they come from marshals
ferrets from marshalls are released at eight weeks old with two vaccines
are they fully vaccianted?
no they become fully vaccinated at 12 weeks old
ferrets GI tract
they contain a shorter GI tract than cats so they poop every 4 hours
protein and fat needs are higher than cats
they do not tolerate fiber
ferrets can conhabitate with other animals except with
Birds
like dogs ferrets are susceptible to
heartworm
vaccines for ferrets
canine distemper (mucopurulent ocular/nasal discharge and hard pad)
rabies
Q3 weeks until 14 weeks old
if you see conjunctivites pretty much only time they get it is with distemper
near 100% mortality with distemper
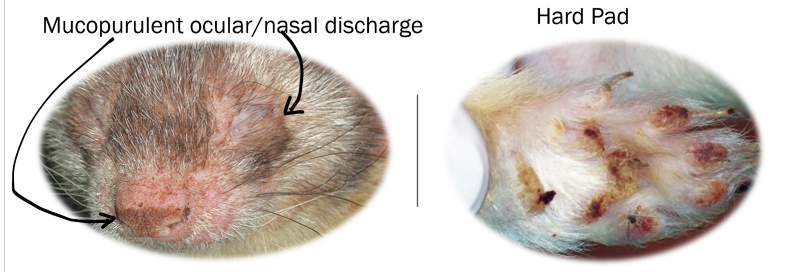
When giving a ferret distemper vaccines in clinica. What should you do?
wait 15 to 30 minutes after and assess for any reactions
type one hypersensitivity reactions
if happened once then increase of 80% with subsequent vaccine
treatment:
antihistamine, epinephrine, dexamethasone, O2, fluids prn
can premed with diphenhydramine
can you test ferrets for microfiliaria
No (cannot do snap test)
definitive diagnosis is ultrasound
Can you treat ferrets with Melarsomine
no they die
best way is used preventative early such as advantage multi (labeled)
Where do you auscultate heart in ferrets?
Near xiphoid
is it pahtological when you see a large spleen in a ferret?
No, they naturally have big spleen
Ferret has red brown earwax. is this normal?
Yes, they are asymptomatic to otodectes cynotis
ferrets are genetically deaf completely
white body with dark eyed and badger face
Which ferret has dminished hearing
White ferrets that have red eyes because they lack pigmeent in iris
Ferrets commonly get dental disease specifically
cracked canine teeth
Ferrets have what type of teeth
Brachydont
Number one hematopoetic disease of ferrets
Lymphoma
physical exam why should you generally compress an anterior mediastinum
want to see if theres compliancy because if not then thymoma possible
you shaved a ferret for a surgery. A week later owner brings ferret back because skin is blue is this normal?
yes normal
All ferets have what GI bacteria
Helicobacter mustelidae
can get ulcers and is zoonotic
What happens if female ferret in estrus is not bred or spayed?
severe bone marrow suppression and fatal anemia
slow takes about a year
First sign of adrenal disease in a ferret
symmetrical alopecia of tail
ferrets do not tolerate fiber very well true or false
true
require high protein and higher fat than cats
younger ferrets and older ferrets usual GI obstruction
younger ferrets:
any household item, espeically rubber items
older ferrets
fiber or hair dont usually obstruct from household items
ferrets may not show radiographic obstructive pattern
ferrets shouldnt have food in their stomach on radiograph. true or false
true
due to their fast GI transit time
Adrenal disease ferret tumor occurs where
Zona reticularis (sex hormones)
symptoms of adrenal disease in ferrets
alopecia
pruitus
increased aggression
dry brittle hair coat
prostatic changes (may not have signs of hair loss)
vulvar enlargement
why do ferrets become obstructive?
what type of stones?
uroliths due to grain free diets
cysteine stones
second theory is genetic disorder that blocks proximal to build absorption
in ferrets what is the only treatment for uroliths
surgery
dissolution diets do not work because may predisosed to struvite
females less likely to be obstruvtive
How do you treat hyperplasia prostatic disease secondary to adrenal disease
Decompress/catheterize
GNRH agonist (deslorelin)
flutamide (shrink prostate)
is cystic hyperplasia prognosis good
No if from hyperplasia prostate becomes cysic, then it is guarded and harder to treat
need ultrasound to tell difference
radiograph = double bubble
What is the best management practice for stopping adrenal disease in ferrets
Deslorelin acetate implants (start first visit)
Insulinnoma symptoms in ferrets
ptylism
hypoglycemia
seizures
run blood glucose with alpha track (less than 65 is indicative)
Treatment for insulinnoma
prednisone, diazoxide
frequent small high protein meal, high fat, low carbs
if you add surgery, can give you an additional one year plus survival time
combination is preferable
what does green poop mena in ferrets
food moved through the GI tract too fast and has not been brocken down by biliverdin
occurs with ECE, rapid food changes, lymphoma
top two common causes of GIT disease
foreign body obstruction
epizootic catarrhal enteritis (coronavirus)
both preent the same time
What is the typical history for ECE
older ferret exposed to a new ferret within last two weeks
newer ferret usually asymptomatic
ferret breaks with watery, greenish-yellow, mucoid stool, anorexia
ECE good prognosis
mild regenerative anemia, mid increase in WBC
ALT<800, ALP<400
ECE poor prognosis
marked increase WBC, it shift, non-regenerative anemia
ALT>1000 ALP>400
Main treatment for ECE
supportive care
triple antibiotics
gastro protectant
chinchillas can live 10 to 15 years, whereas guinea pigs live
4 to 6 years
should guinea pigs and chinchillas be housed separately or in groups
groups