Chapter 14 - DNA
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
Chargaff’s rules
A% = T% and G% = C%;
Purine
Adenine and Guanine; Larger, 2 sugars
Pyrimidine
Thyemine and Cytosine; Smaller, 1 sugar
Rules for complimentary strands
Dna runs antiparallel to its complimentary strand, from 5’ to 3’.
Conservative model for DNA replication
When replicating DNA; The two parent strands rejoin
Semiconservative model for DNA replication
When replicating DNA; each daughter strand will match with a new strand; This is the one we actually use
Dispersive model for DNA replication
Each strand is a mix of new and oldWhen replicating DNA;
Experiment 1: griffith
Found that pathogenic bacteria could cause non pathogenic bacteria to become pathogenic
Experiement 2: Avery
Found that DNA is the transforation consist, not Protein
Experiment 3:Hershey-Chase
More evidence for DNA being genetic material, and discovered virus and backeriophages
Experiment 4: Watson-Crick and Photo 51
Discovered the Shape of DNA using a photo from Rosalind Franklin
Experiment 5: Meselson - Stahl
Using heavy nitroen, they where able to prove semiconservative replication of dna
DNA replication Core Idea
RNA polymerase starts, then DNA polymerase binds to and extends the DNA, DNA is replicated from 5’ to 3’
Origins of replication / Replication Bubble
Two DNA strands are separated opening a space for replication, 1 in bacteria; thousands in eukaryotic chromosomes; Begins in both directions
Helicase
Unzips the double helix
Primase
RNA polymerase that makes the RNA primer
Topoisomerase
Cuts the DNA to prevent it from winding up, then rejoins
DNA polymerase
Transcribes the DNA, must have a RNA primer to be able to bond to the DNA strand; uses dATP for energy; must go in the 5’ → 3’ direction
Sliding clamp
Binds dna polymerase to dna

Leading strand
Moves continously towarsd the replication fork
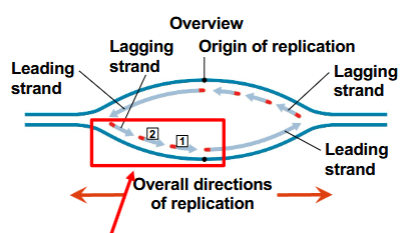
Lagging strand
moves behind the leading strand, replicates towards it; synthesised in a serrises of Okazaki fragments
Okazaki fragments
the lagging strands, joined with DNA ligase
Single stand binding protein
Binds to and stabilized the DNA during replication
DNA proof reading
DNA polymerase proofreads as it goes,
Mismatch repair
Repair enzymes correct the base pair error
nuleotide excision repair
Nuclease cuts out and replaces the damages streach
The End replication problem
Dna gets shorter and shorter each time it is replicated
End replication solution; Telomere
Found at the end of eukaryotic chromosomes; repeating base sequence of TTAGGG; 100-1000 repetitions; extended by Telomerase
Euchromatin
Loosly packed chromatin
Heterochromatin
Highly condensed and prevents expression