Cranium, Ventricles, & Meninges
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
cranium
bony framework of the head that protects the head and houses special sensory organs
neurocranium
houses the brain, meninges, supporting vasculature, and cranial nerve nuclei and associated fibers until they exit
"cranial vault"
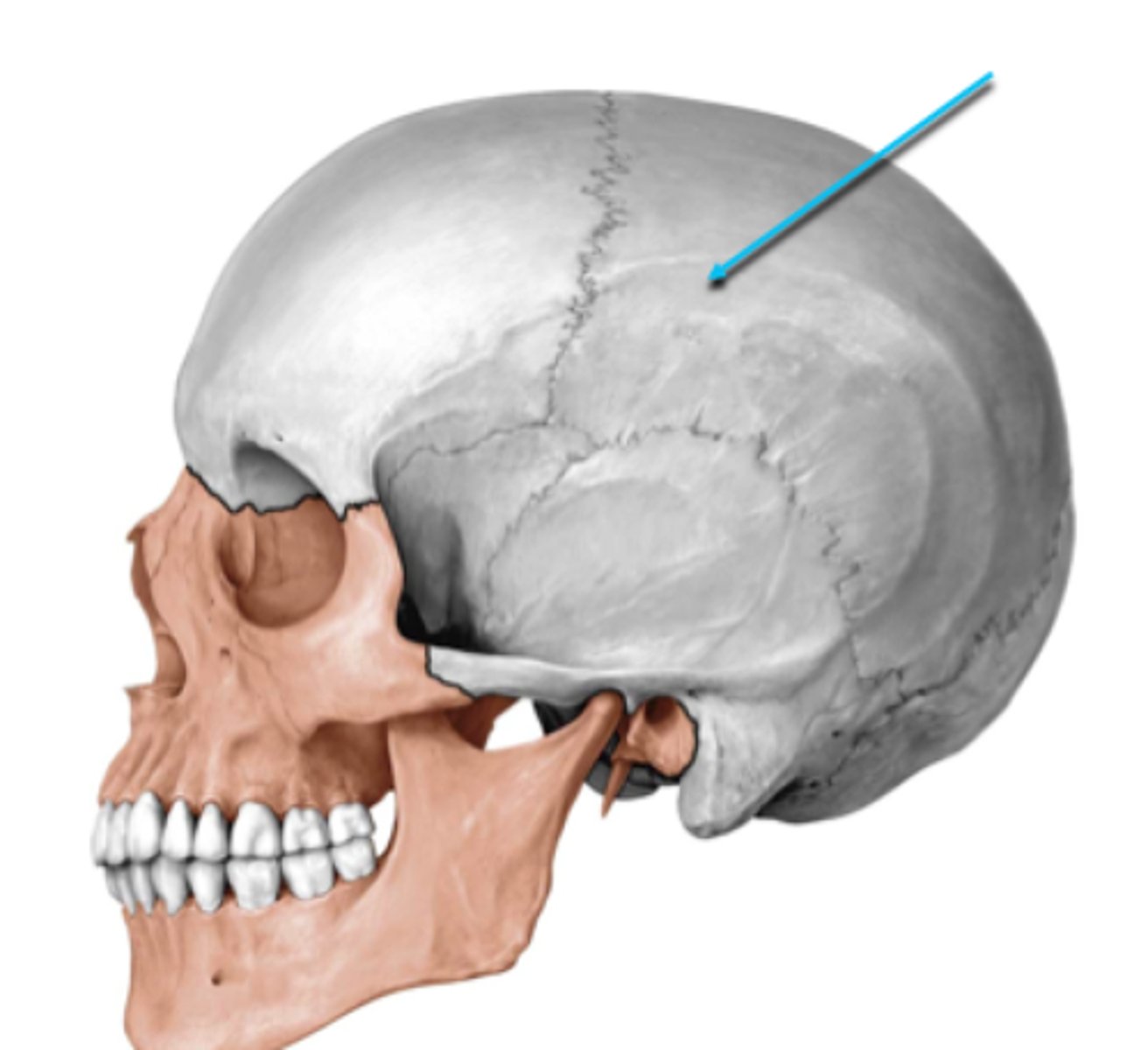
calvaria
roof of the neurocranium
cranial base
floor of the neurocranium
- frontal
- ethmoid
- sphenoid
- occipital
- temporal (2)
- parietal (2)
what bones make up the neurocranium (6)?
viscerocranium
forms the anterior part of the cranium and consists of bones surrounding the mouth, nose, and most of the orbits

- mandible
- ethmoid
- vomer
- maxilla (2)
- inferior nasal conchae (2)
- zygomatic (2)
- palatine (2)
- nasal (2)
- lacrimal (2)
what bones make up the viscerocranium (9)?
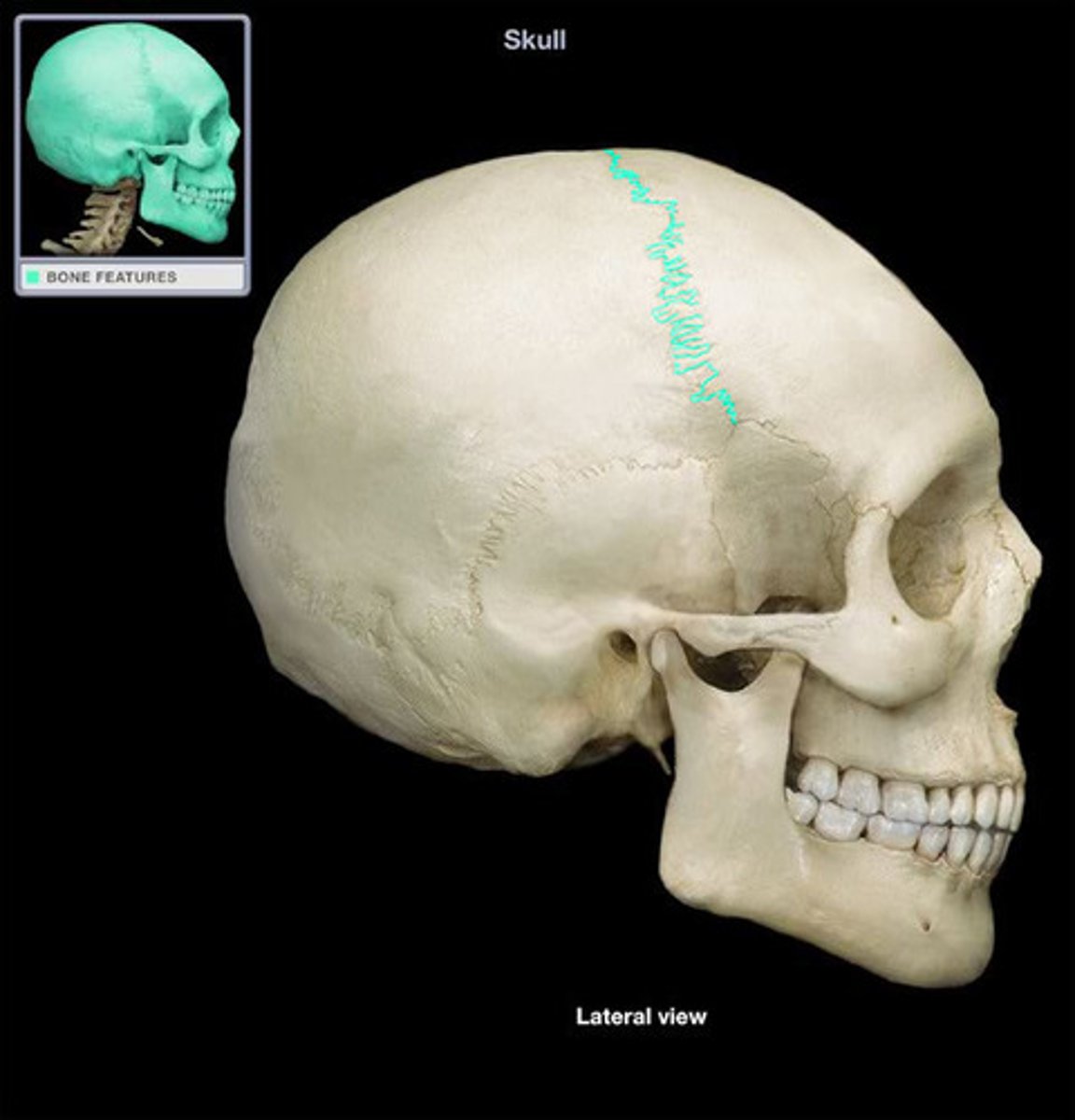
coronal suture
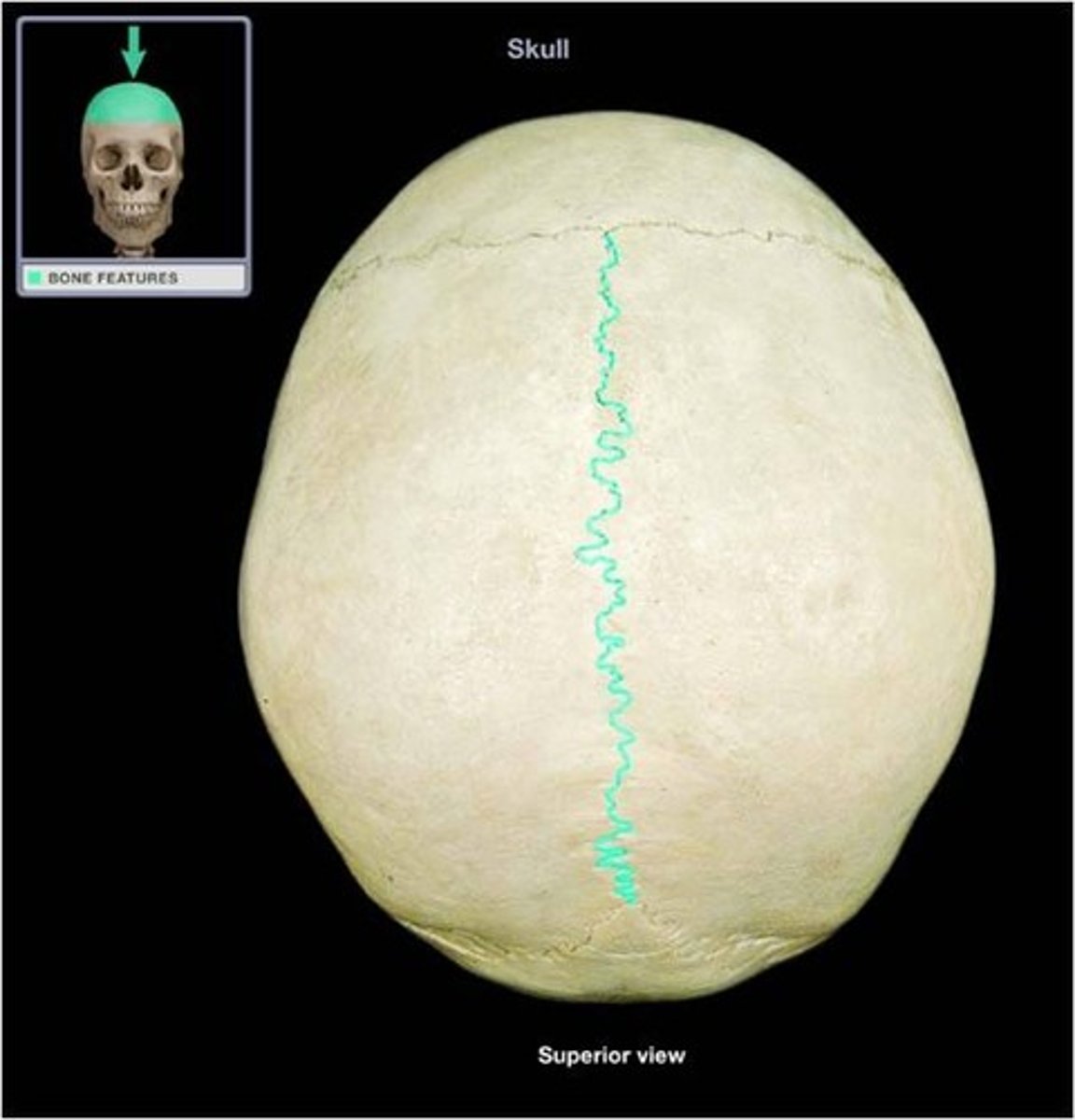
sagittal suture
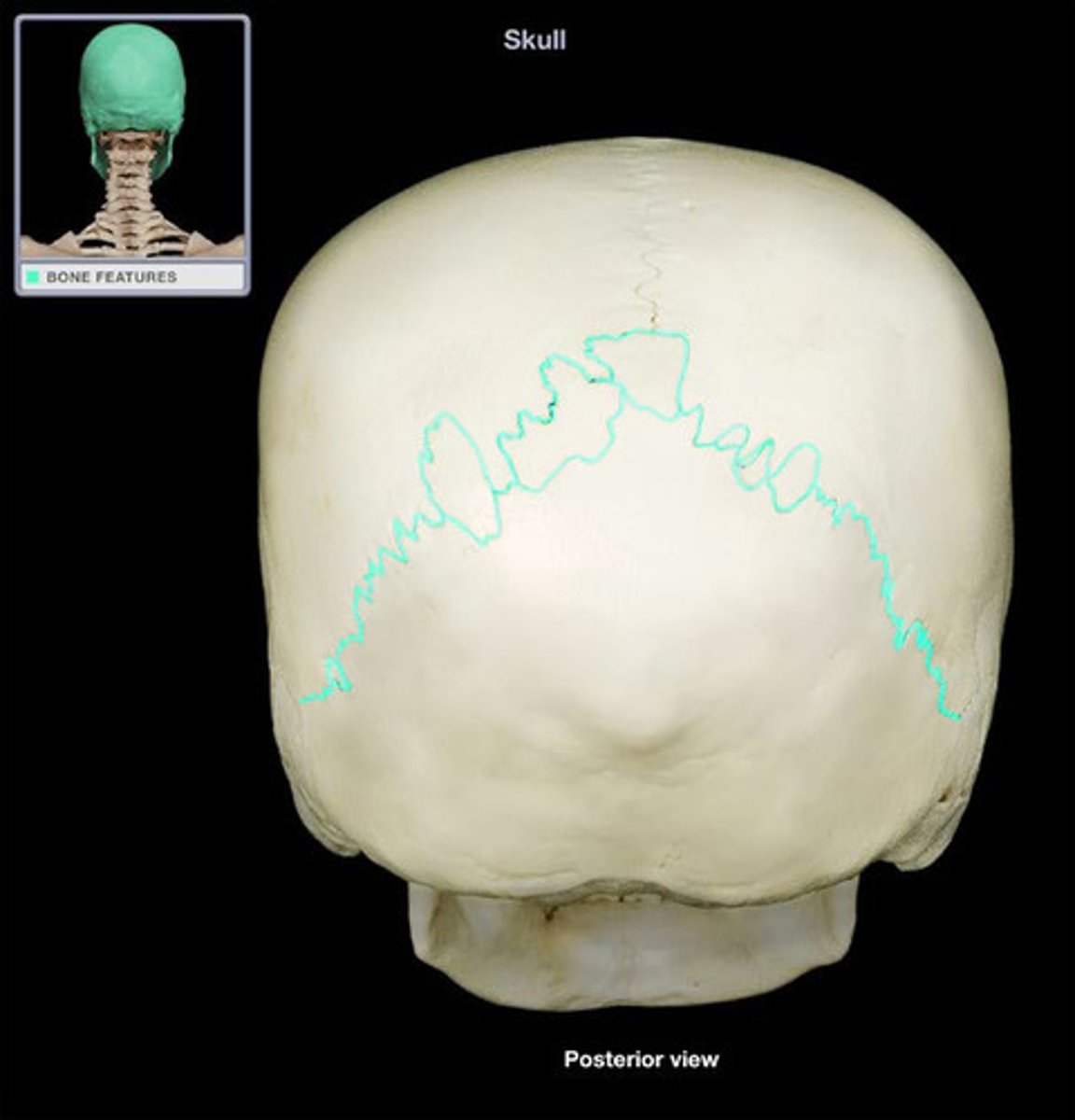
lambdoid suture
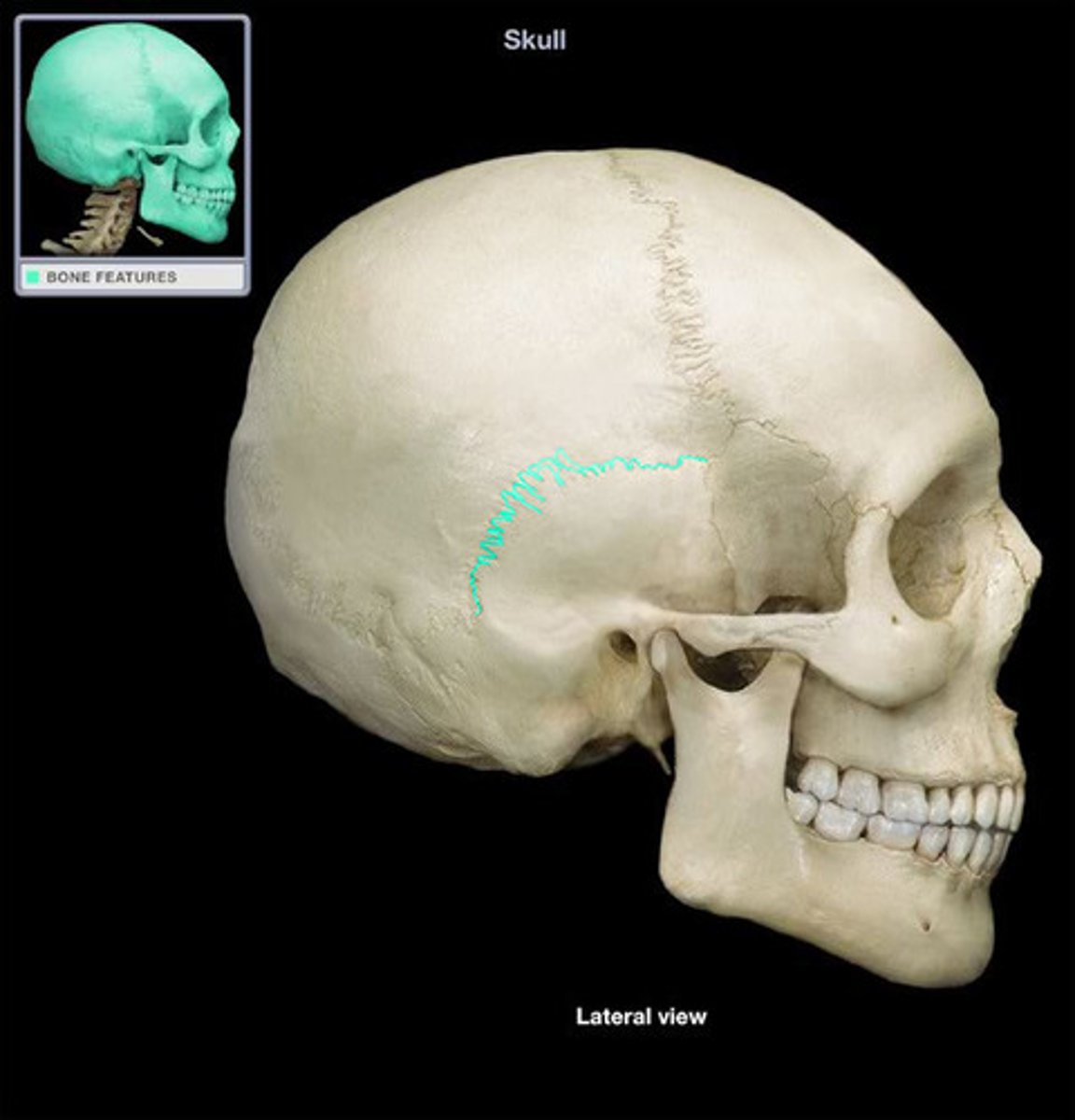
squamous suture
suture
interlocking line of union between bones
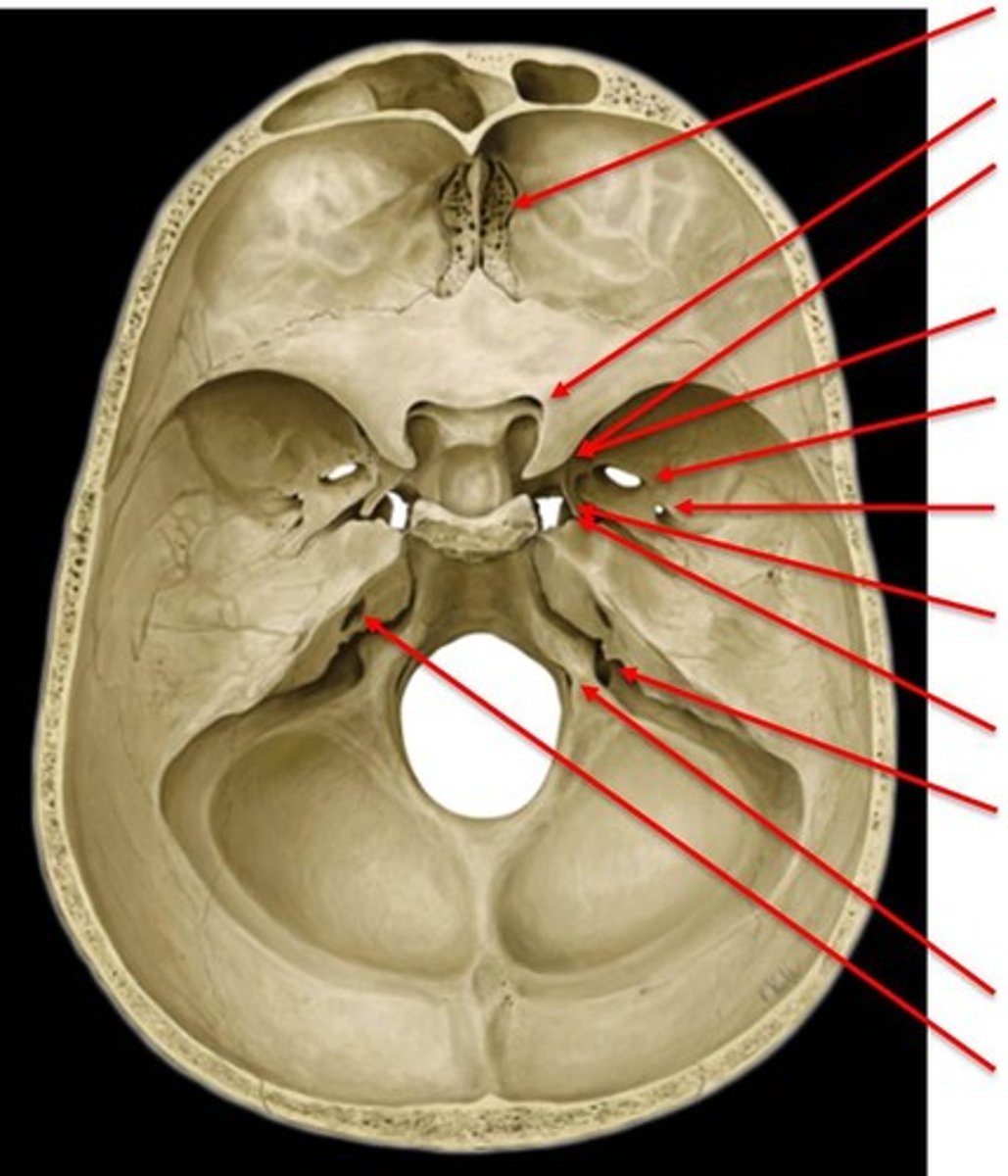
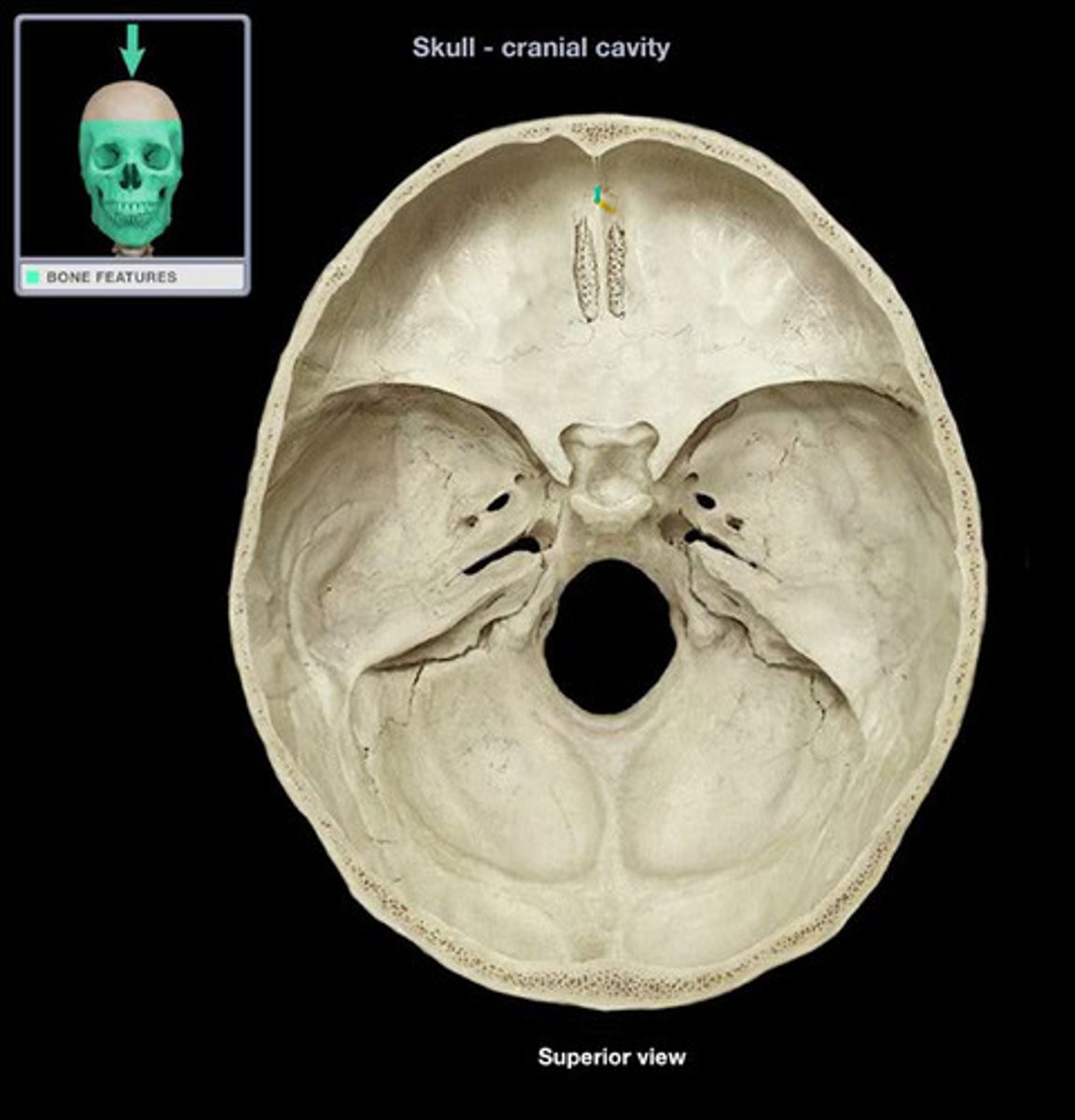
cranial fossa
three paired, tiered depressions (anterior, middle, posterior) on the internal base of the skull that cradle and protect the brain
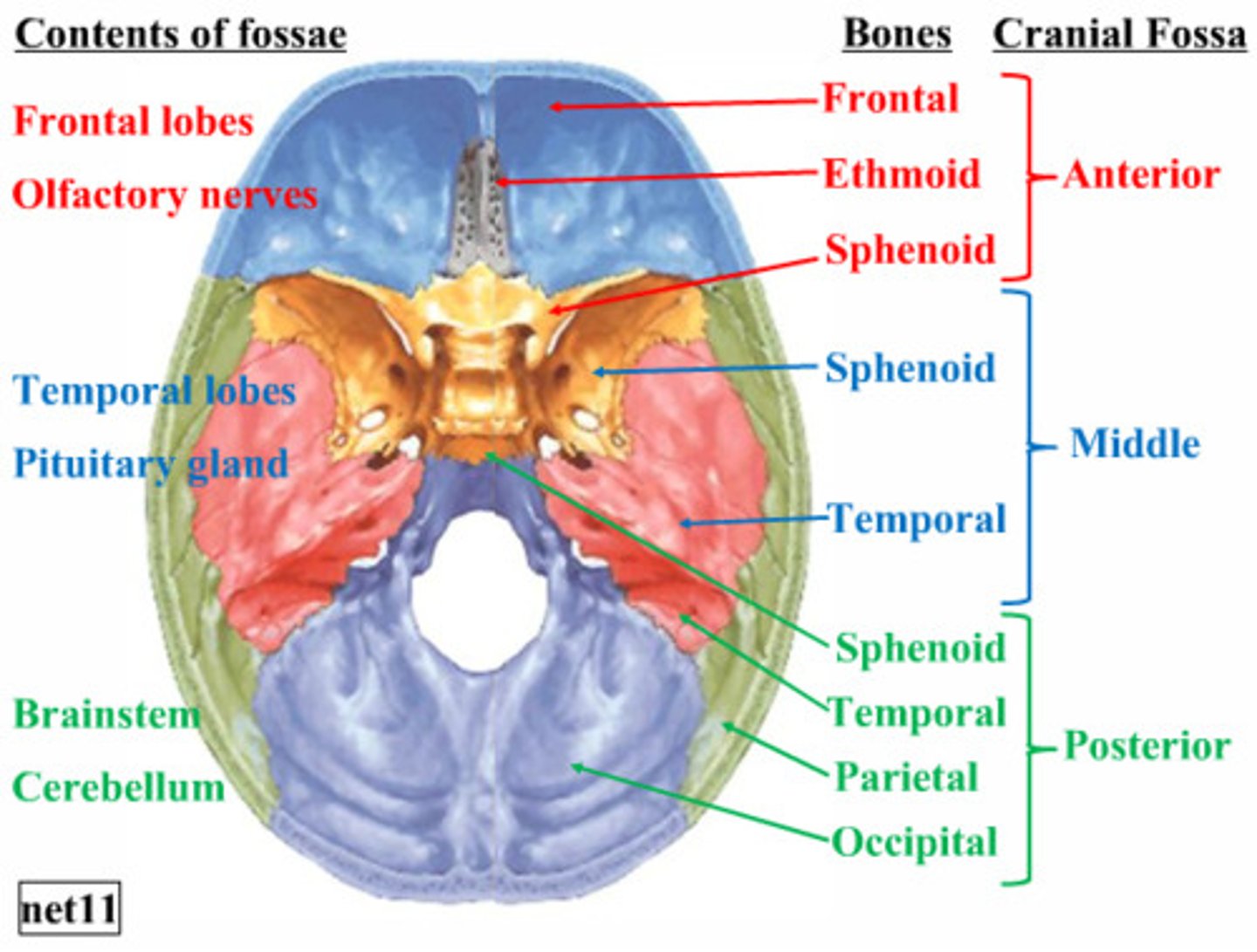
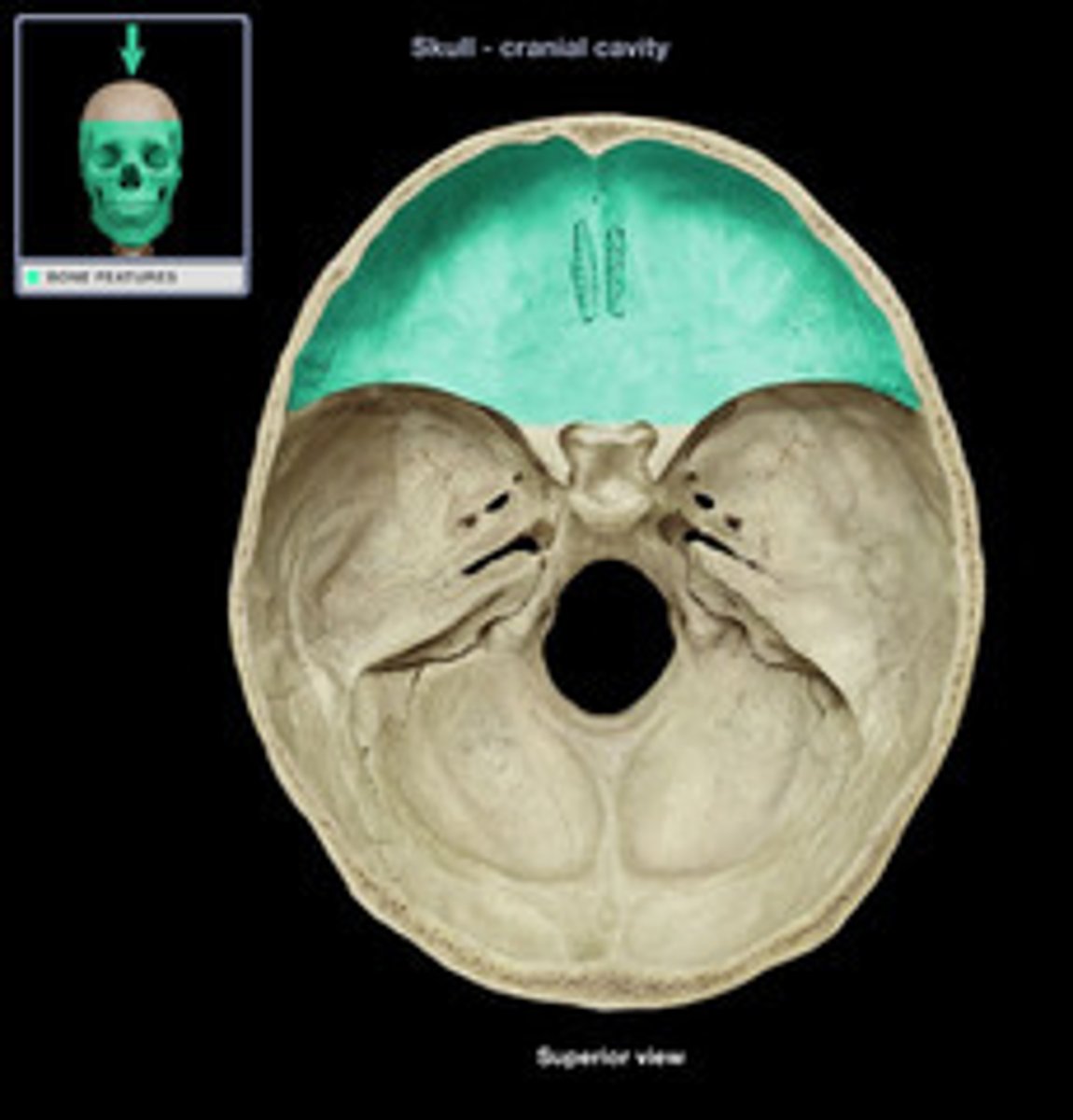
anterior cranial fossa
part of the cranial fossa that contains openings for olfactory and ethmoidal structures & supports the frontal lobes
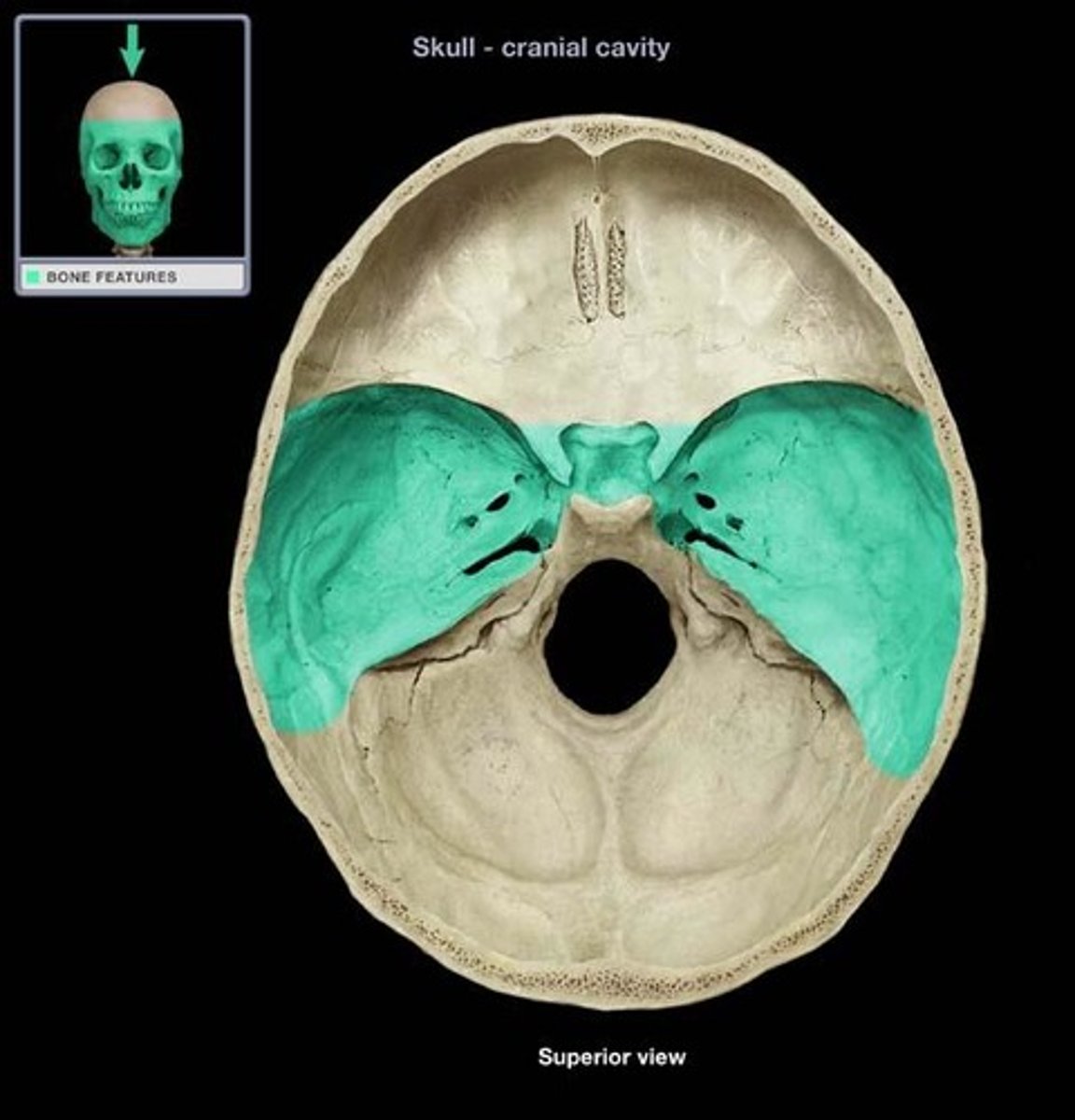
middle cranial fossa
part of the cranial fossa that is the major passageway for cranial nerves 2-6, and houses the temporal lobes & pituitary gland
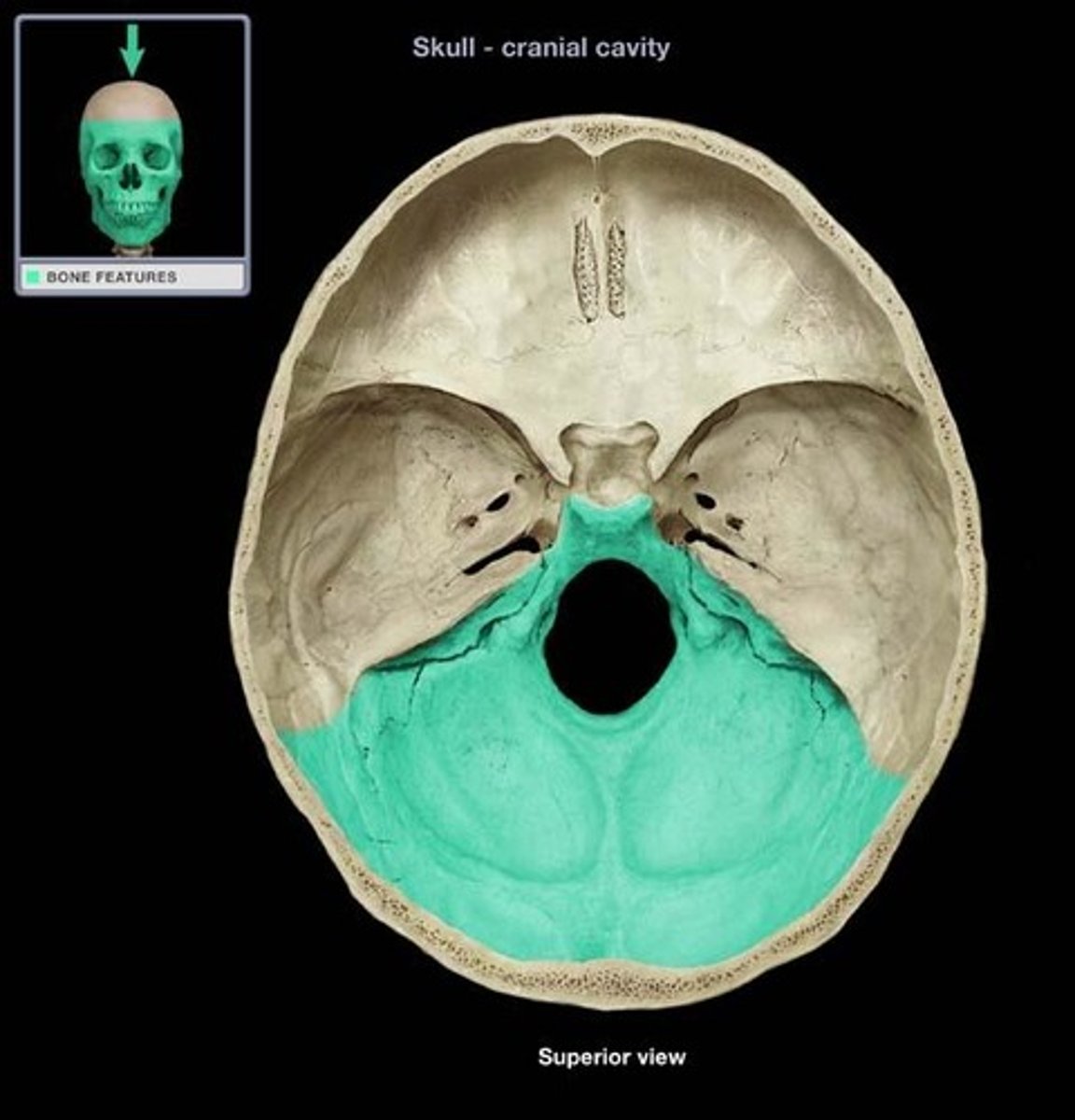
posterior cranial fossa
part of the cranial fossa that is a major passageway for cranial nerves 7-12, and houses the cerebellum, pons, medulla, and the fourth ventricle
1. ethmoid
2. frontal
3. lesser wing of sphenoid
what 3 bones make up the anterior cranial fossa?
foramen cecum
hole that is typically closed, but may transmit the emissary vein
cribiform foramina
hole that transmits olfactory nerve filaments
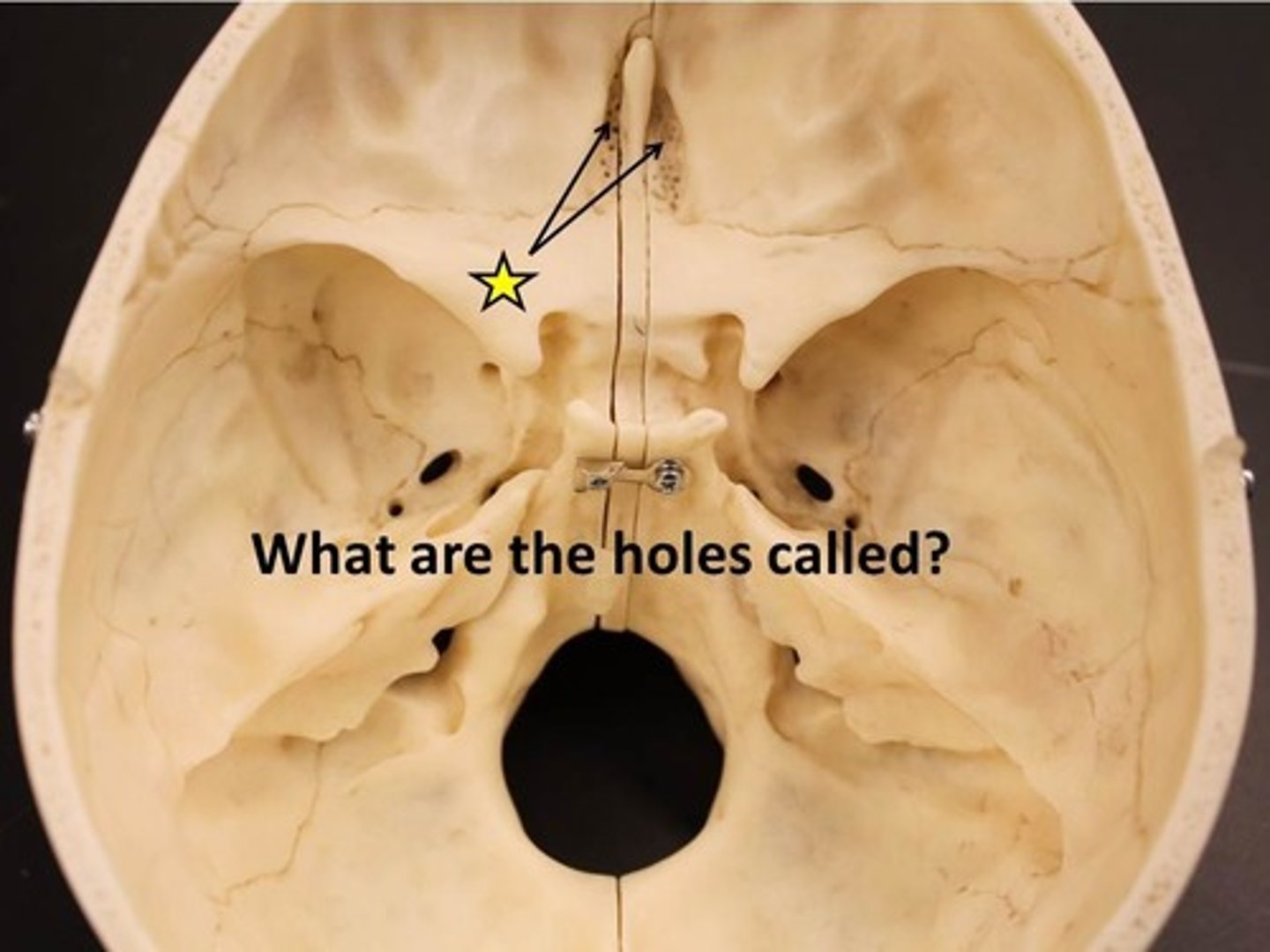
ethmoidal foramina
hole that transmits ethmoidal nerves, arteries, and vessels

sella turcica
region of the middle cranial fossa that houses the pituitary gland
1. sphenoid (body/greater/lesser wings)
2. temporal bone (squamous & petrous)
what 2 bones make up the middle cranial fossa?
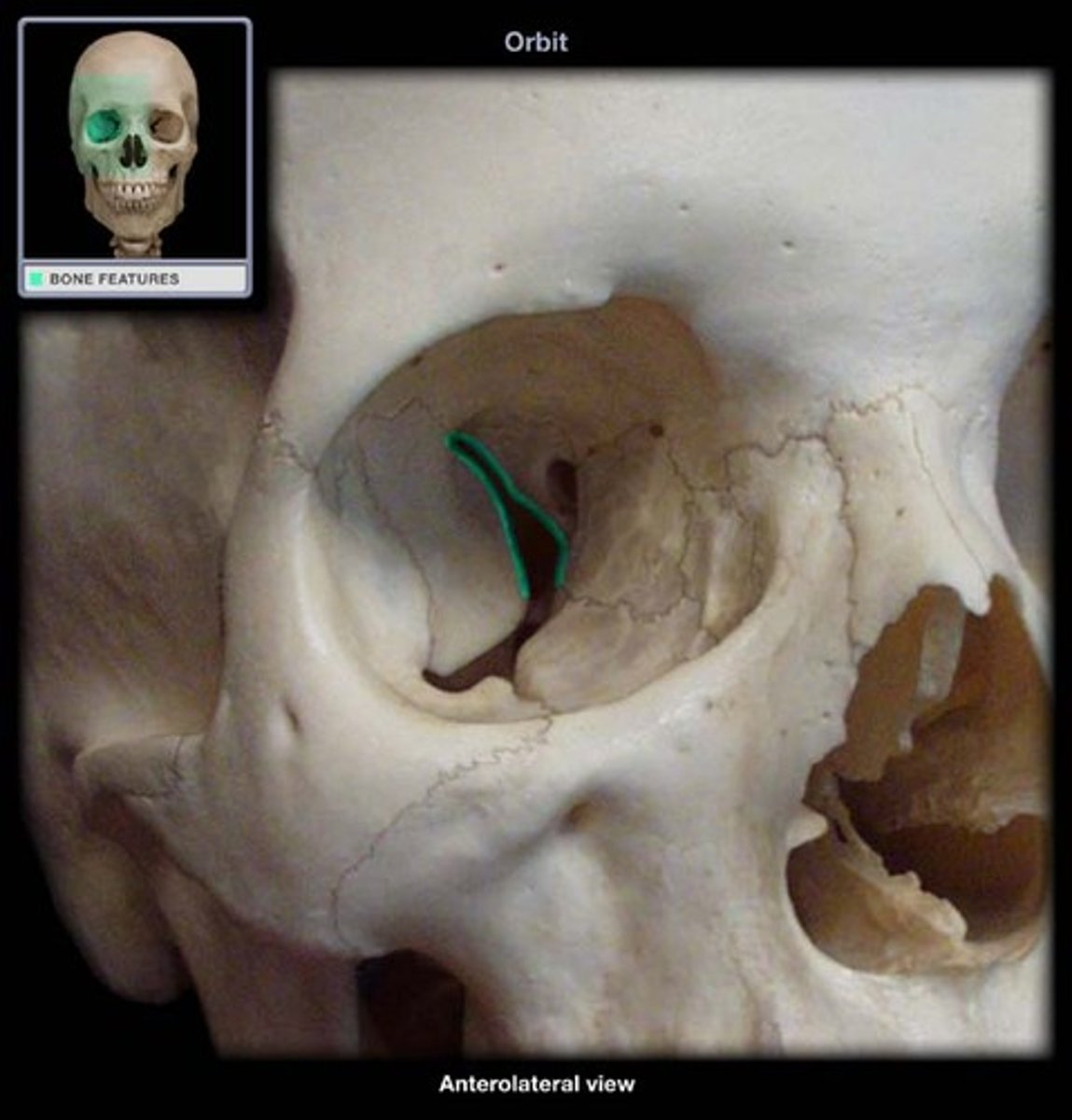
optic canal
hole that transmits the optic nerve (CN II) & the opthalmic artery

superior orbital fissure
opening that transmits cranial nerves III, IV, V1 and VI, and the superior opthalmic vein
foramen rotundum
hole that transmits the maxillary nerve (CN V2)
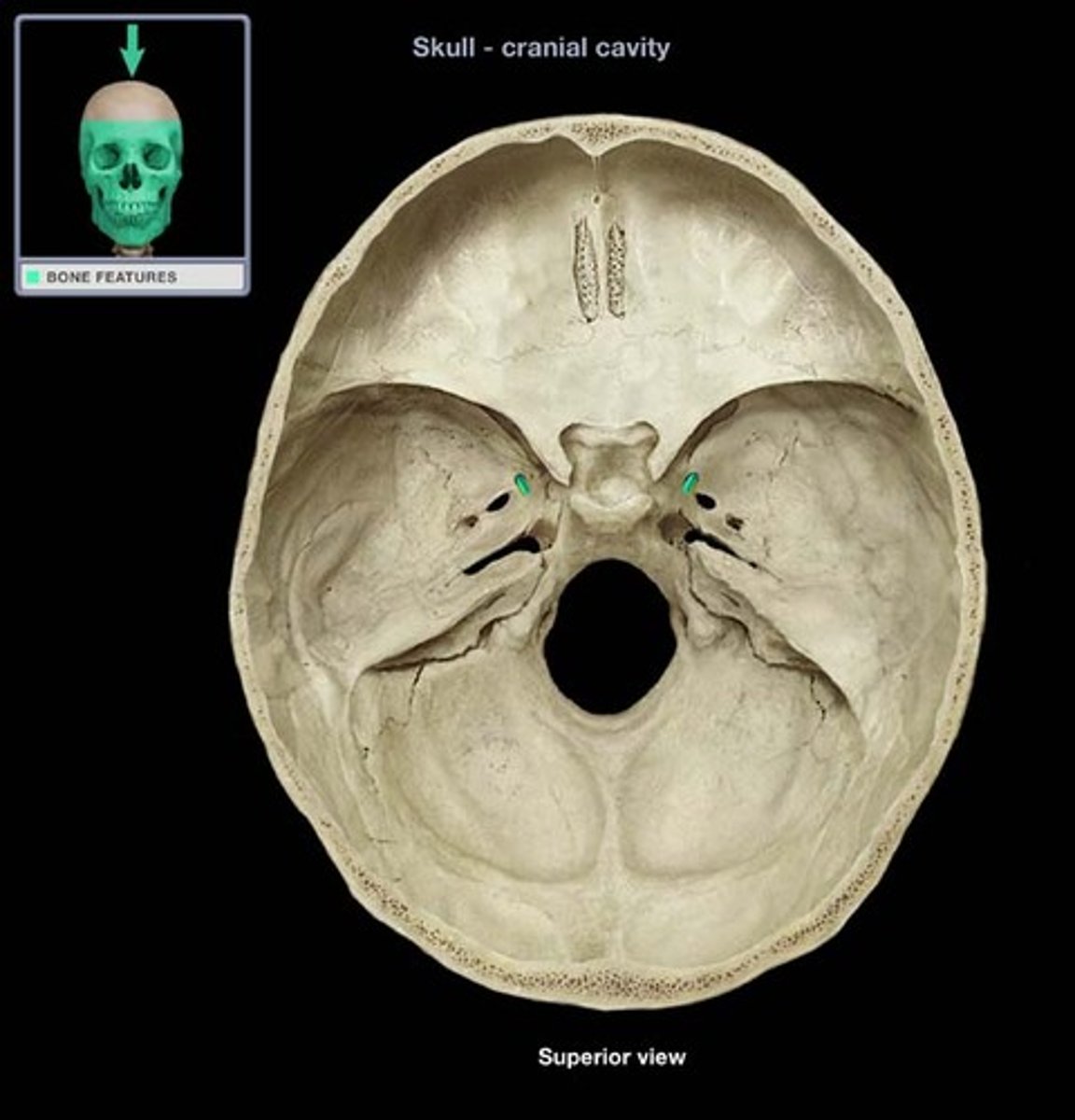
foramen ovale
hole that transmits the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and the accessory meningeal artery
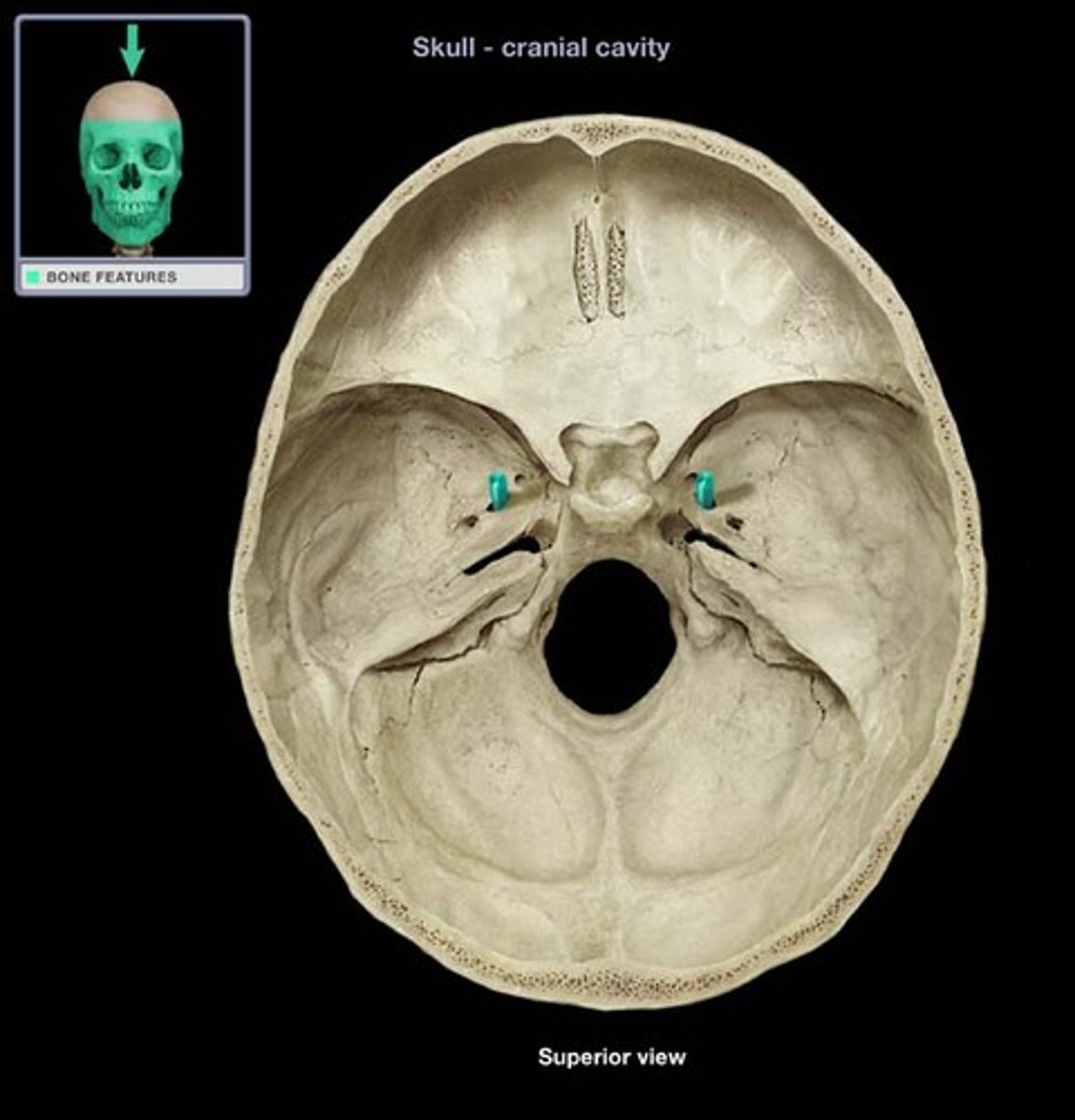
foramen spinosum
hole that transmits the middle meningeal artery and vein
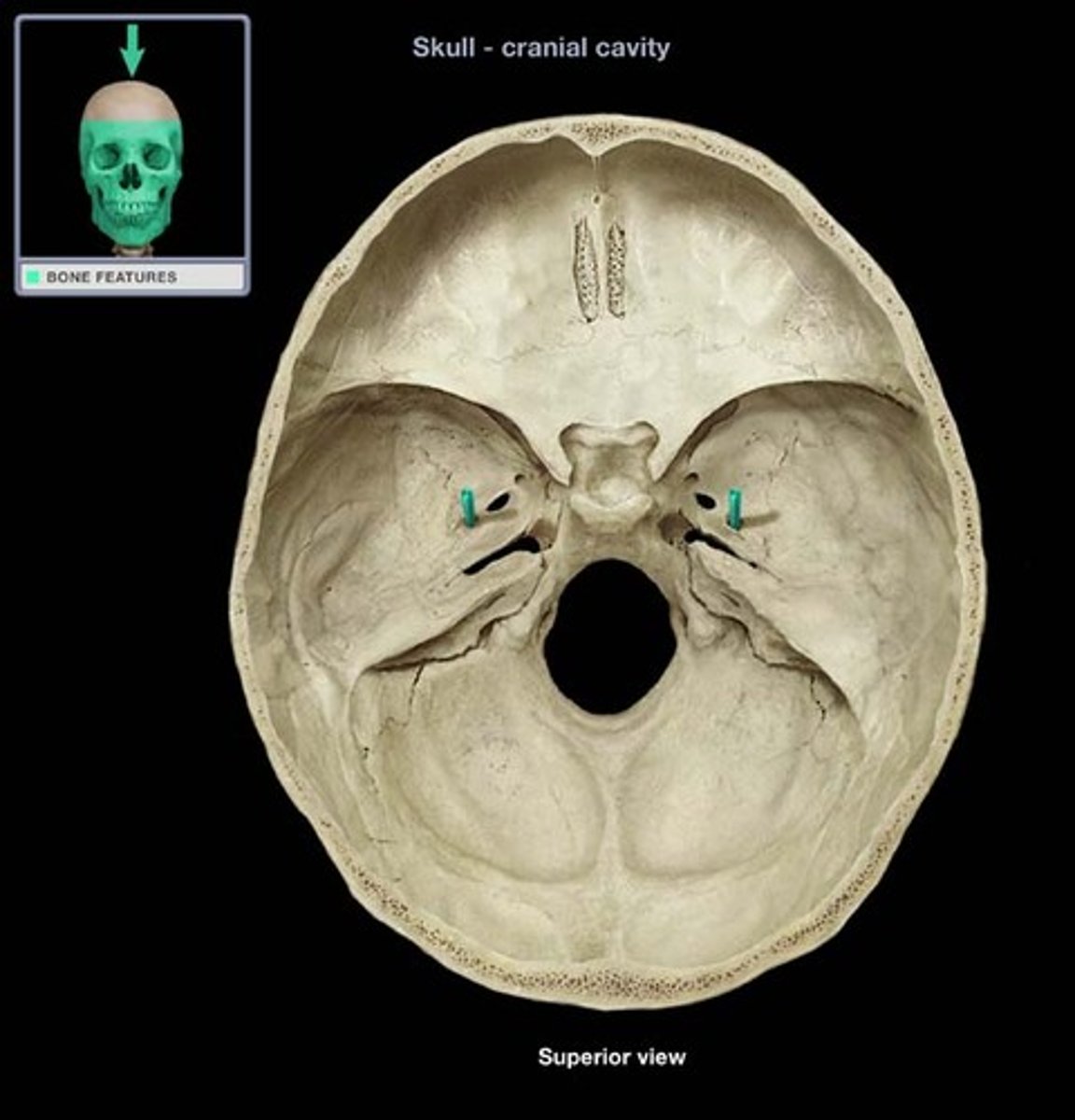
1. occipital
2. temporal (petrous part)
3. sphenoid (posterior)
what 3 bones make up the posterior cranial fossa?
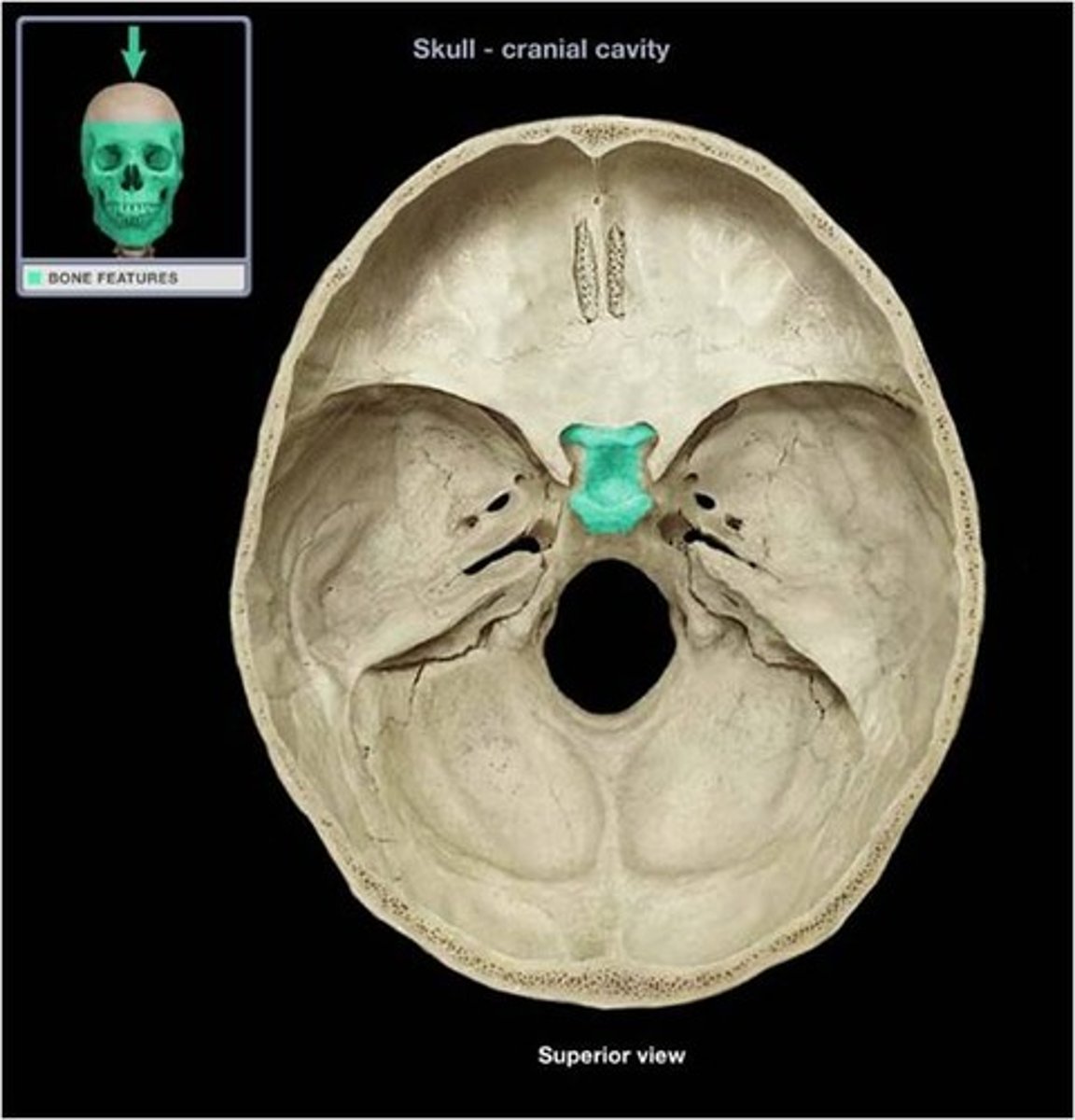
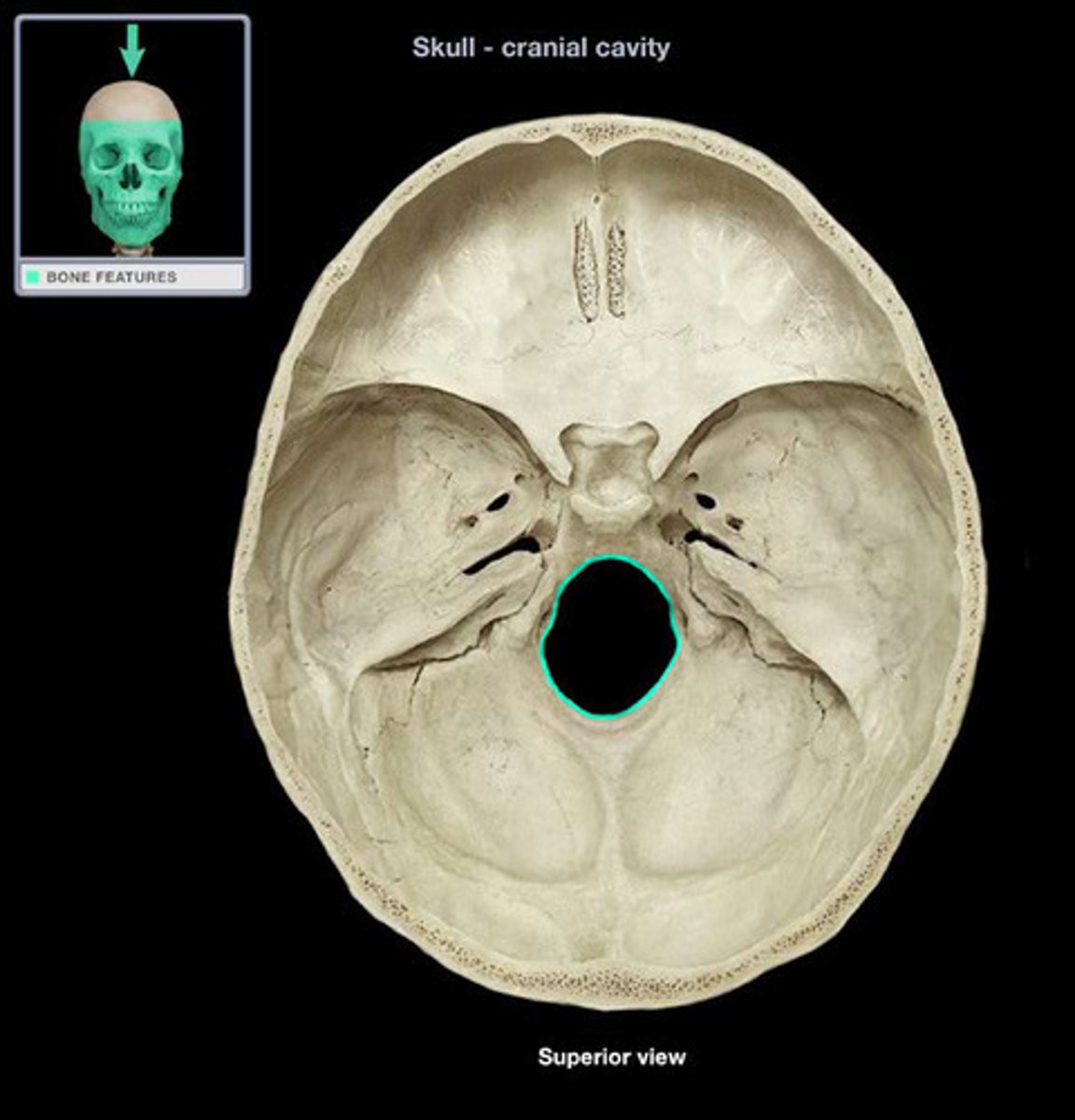
foramen magnum
large opening at the based of the skull that transmits the spinal cord, vertebral arteries, and spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
internal acoustic meatus
passage for facial (VII) and vestibulocochlear (CN VIII) nerves
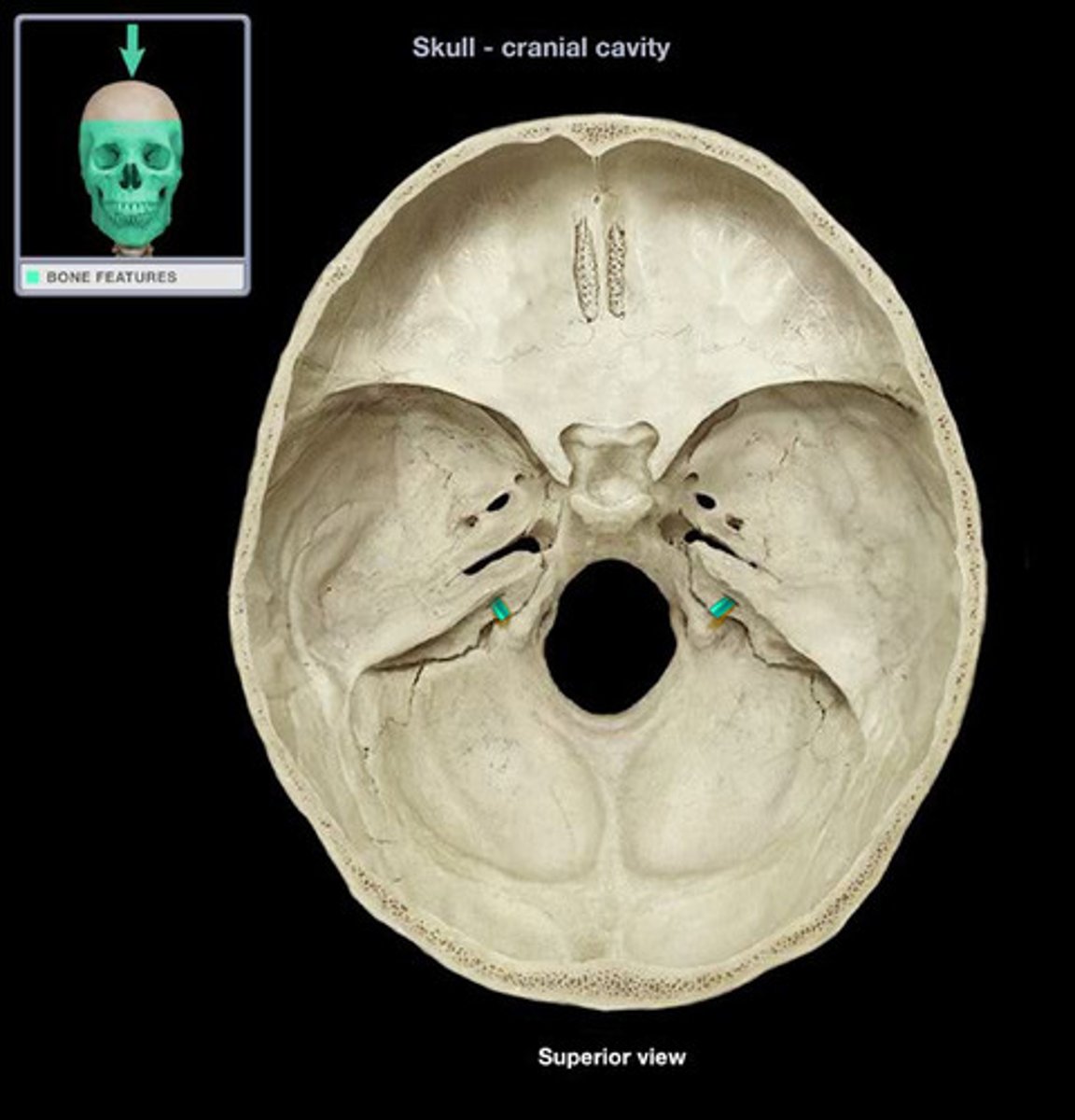
jugular foramen
opening that transmits the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XI
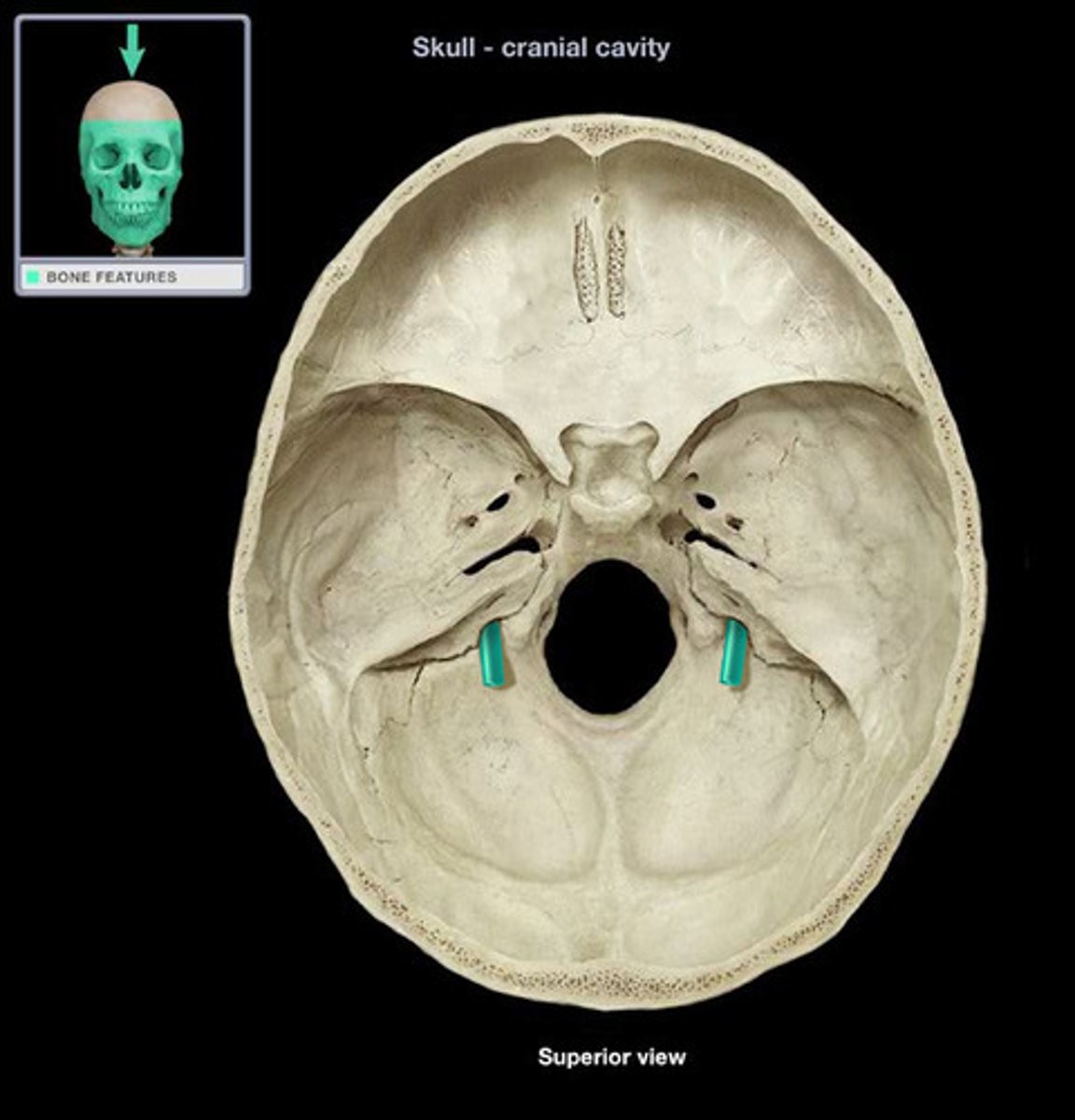
hypoglossal canal
hole that transmits the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
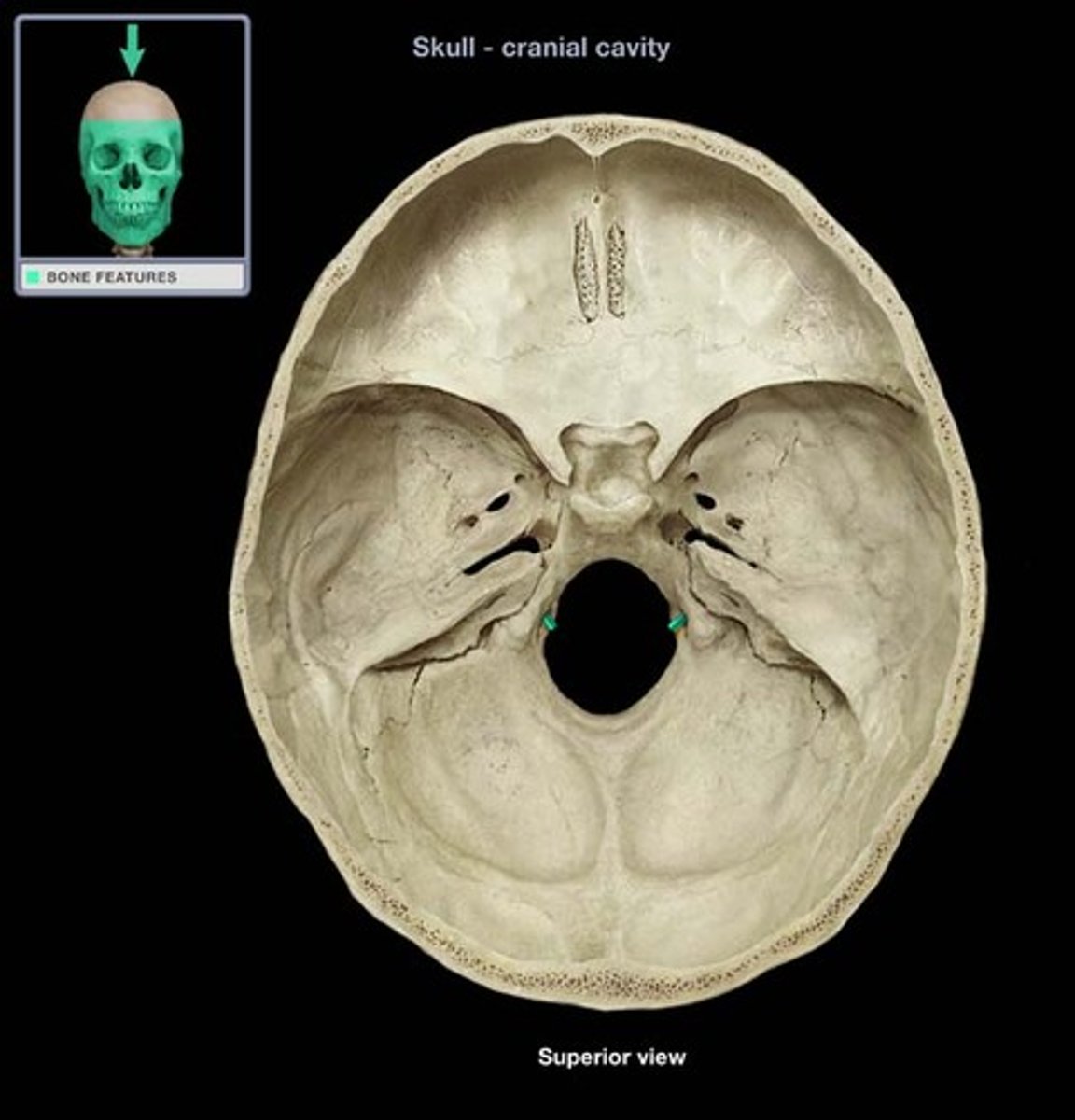
cervicomedullary junction
transition between the medulla oblongata and upper cervical spinal cord (C1-C2) that is located at the level of the foramen magnum
*houses ascending/descending tracts (decussation) and nuclei that influence breathing, CV control, and CN 9-12
*orange line on picture
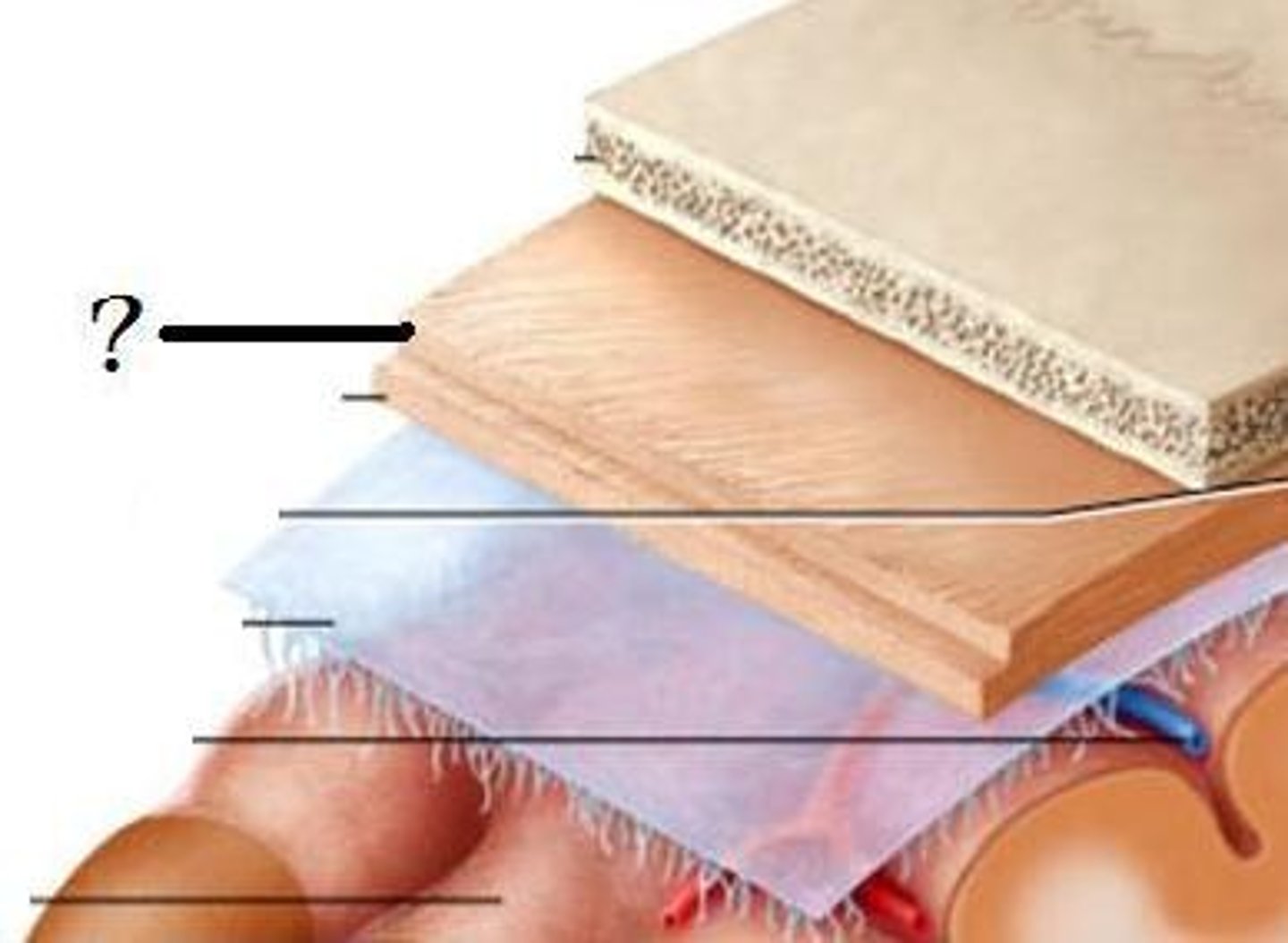
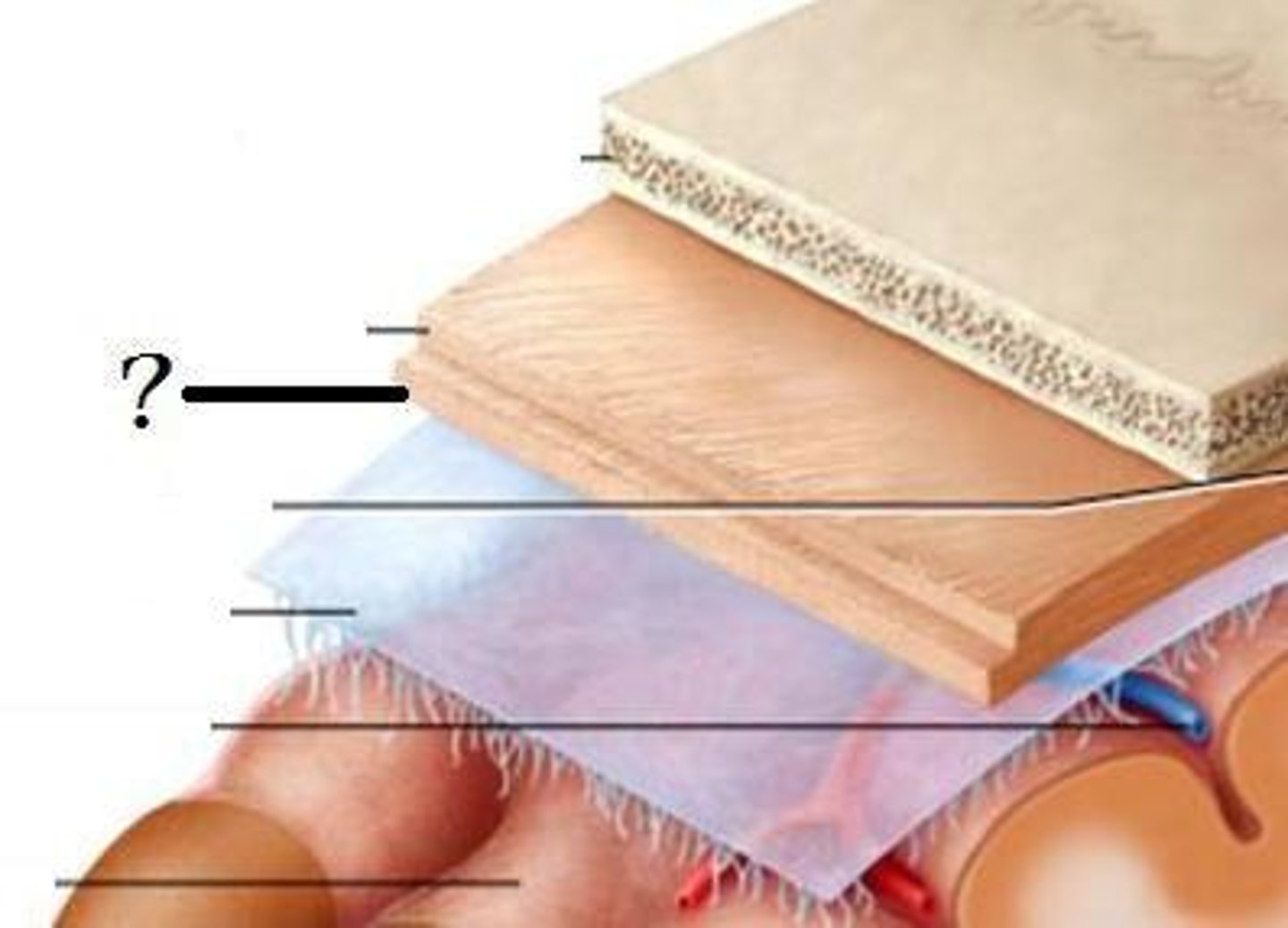
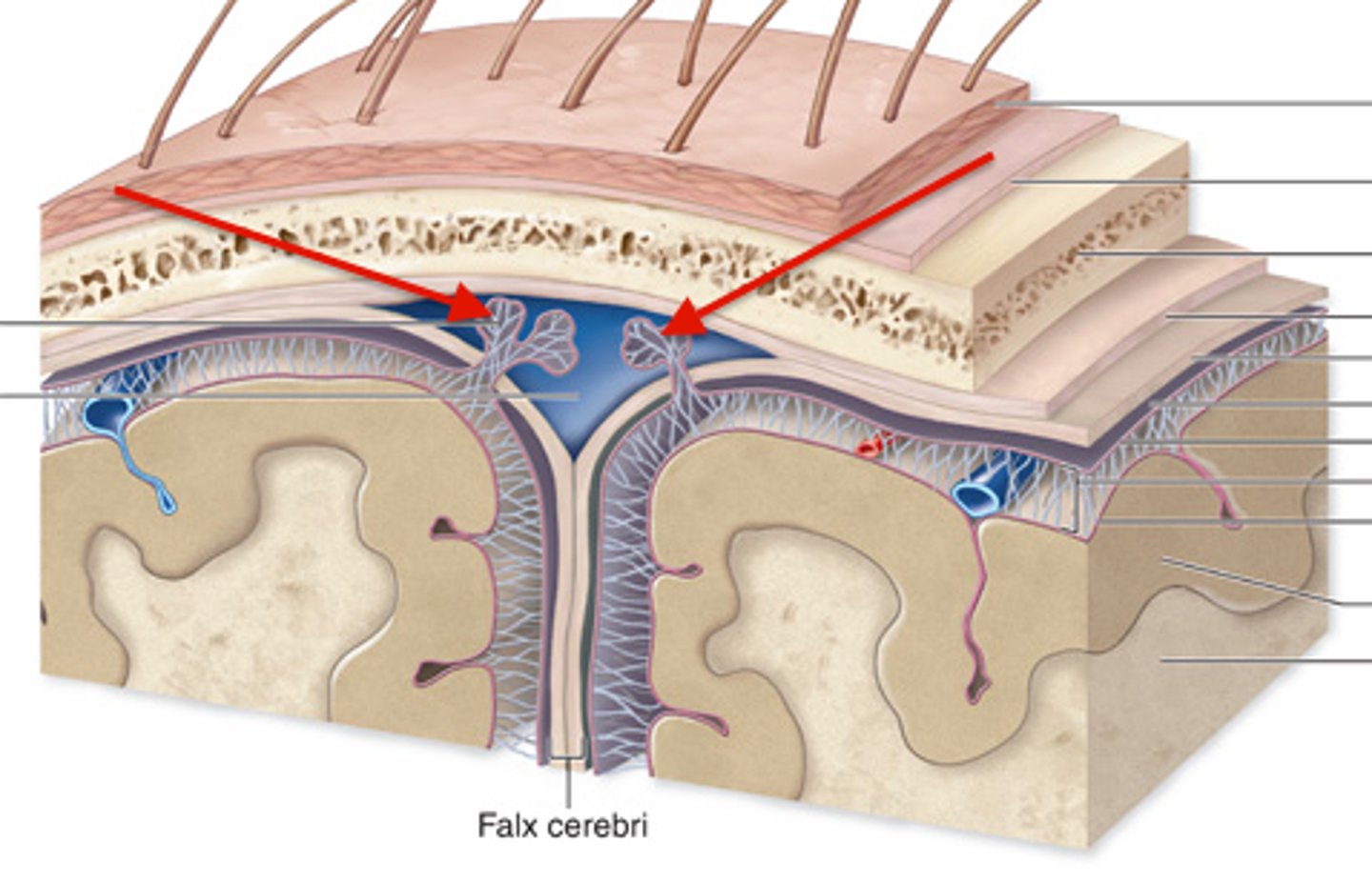
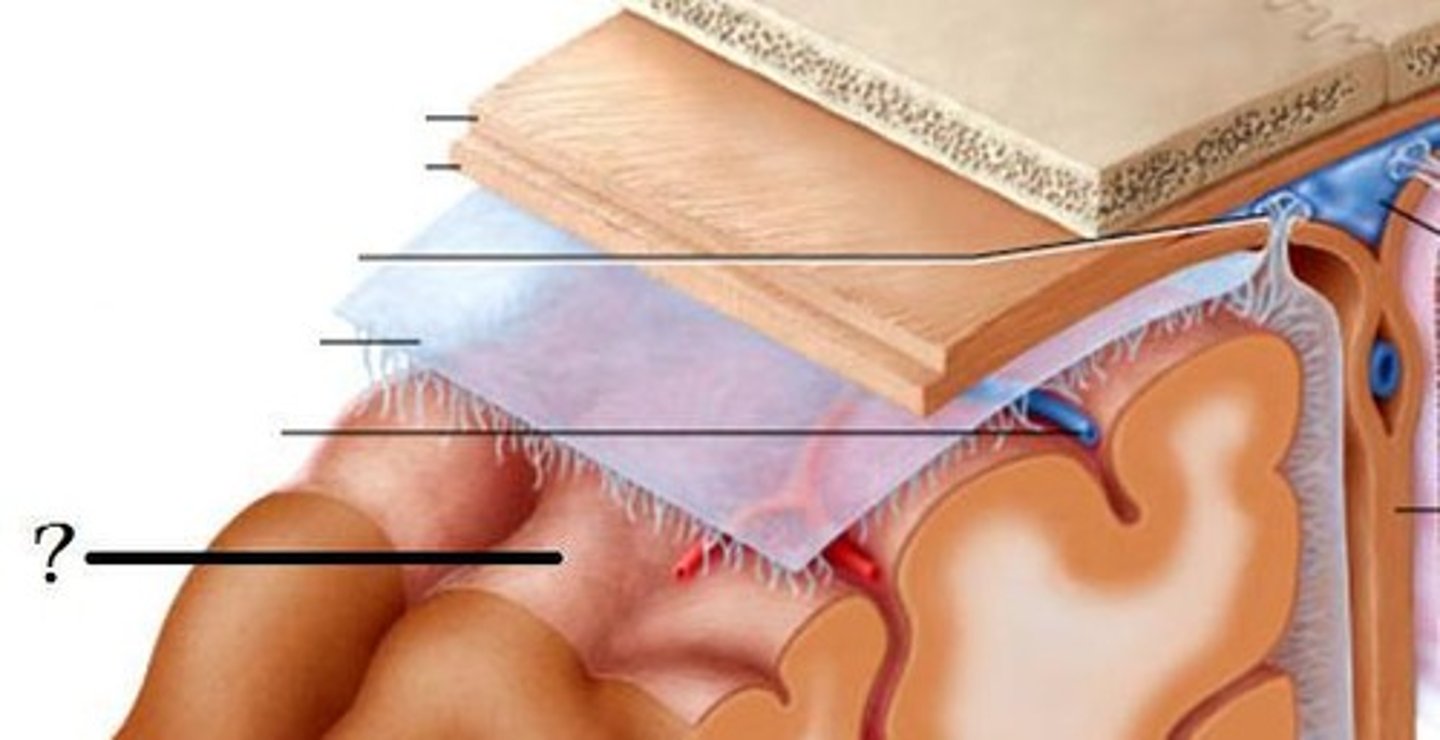
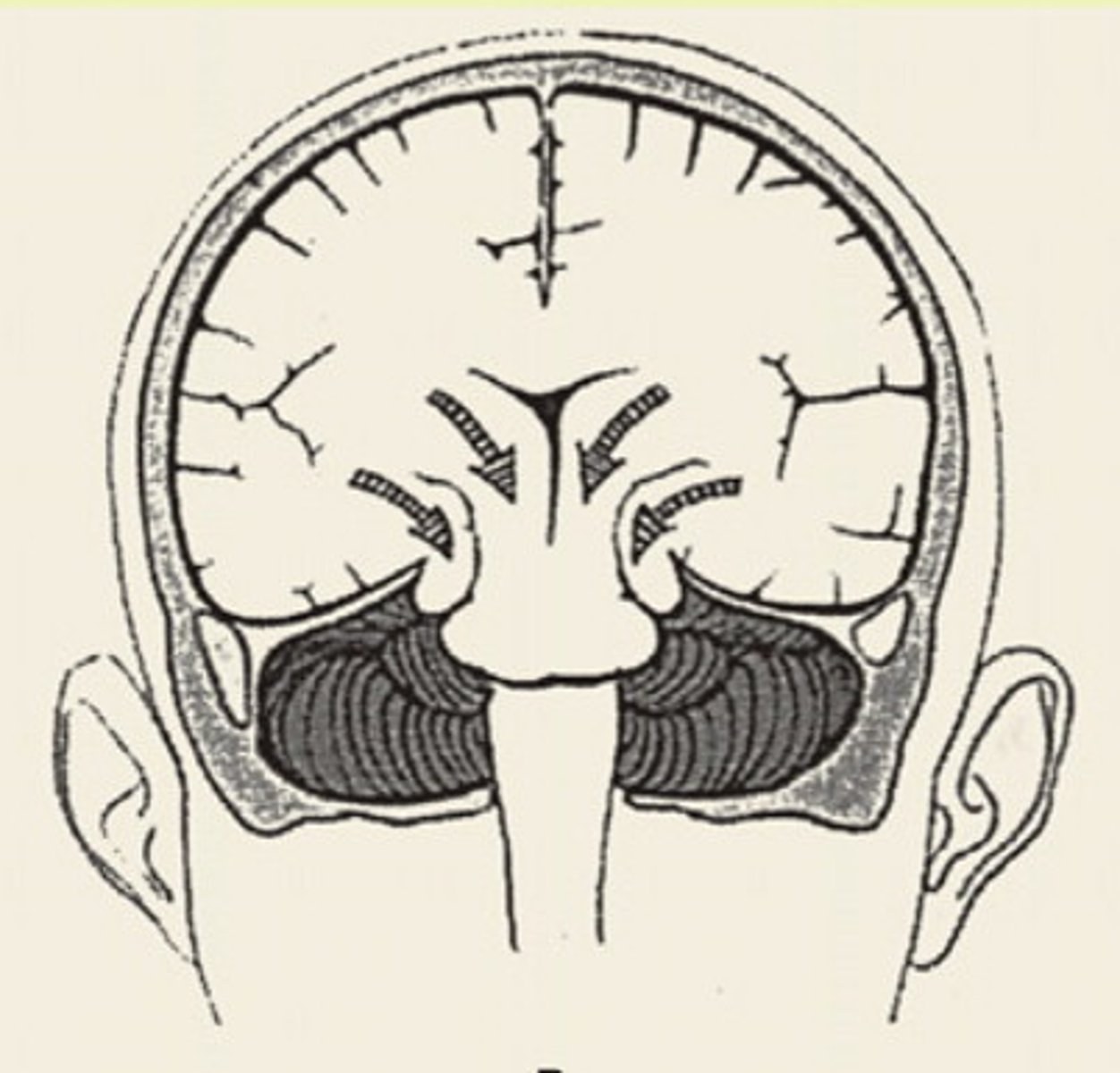
1. skin
2. connective tissue
3. aponeurosis
4. loose connective tissue
5. pericranium
5 layers of the scalp?
1. dura mater
2. arachnoid mater
3. pia mater
3 meninge layers?
dura mater
dense, tough, outermost meningeal layer that adheres to the inner surface of the skull
*provides mechanical protection & stabilizes brain
1. periosteal layer
2. meningeal layer
2 layers of the cranial dura mater?
periosteal layer
outer layer of dura mater that is attached to the skull
meningeal layer
inner layer of the dura mater that contains the falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli
"true dura"
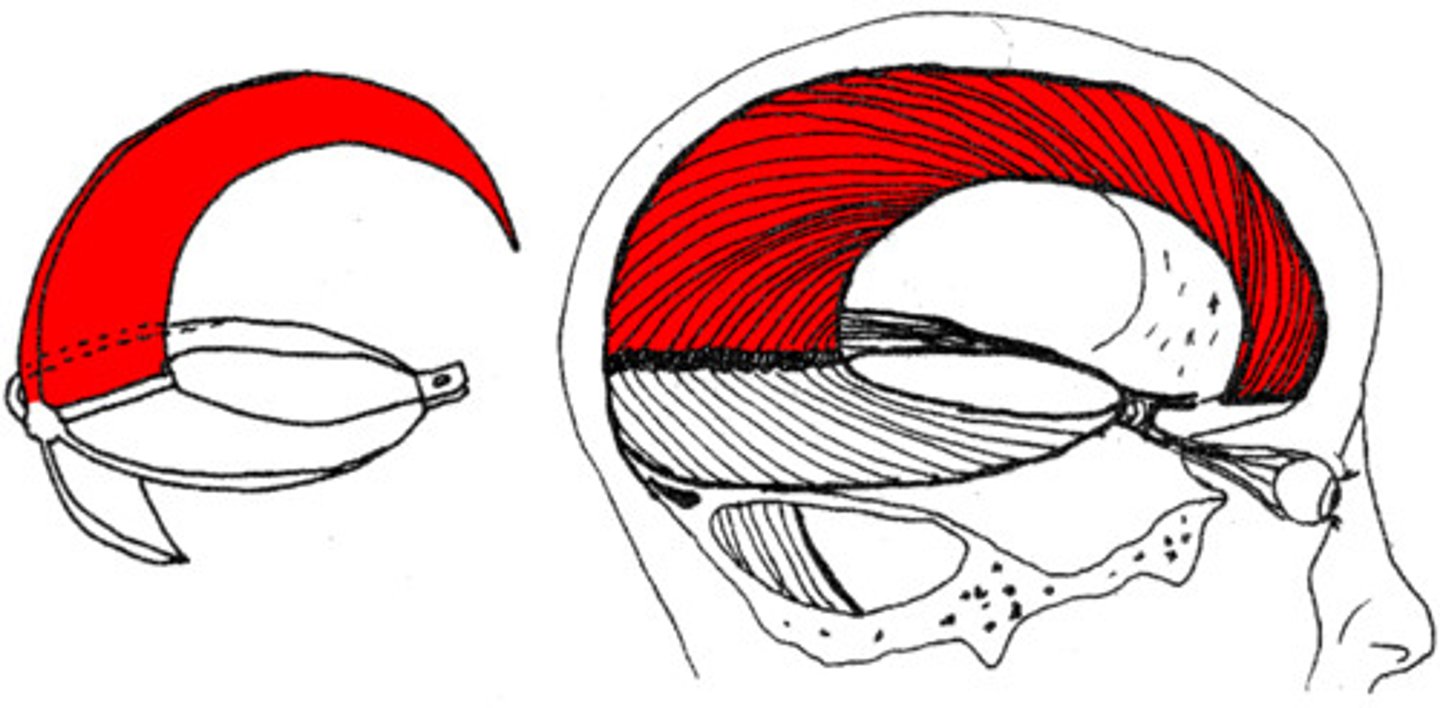
falx cerebri
sickle-shaped meningeal fold of the dura mater that lies between L & R cerebral hemispheres
*sup. sagittal sinus along superior margin
*inf. sagittal sinus along inferior margin
ethmoid, internal occipital protuberance
the falx cerebri runs from the ____ bone to the ______ _____ _____
tentorium cerbelli
horizontal meningeal fold of the dura mater that separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobe
*contains passage for brainstem (tentorial notch)
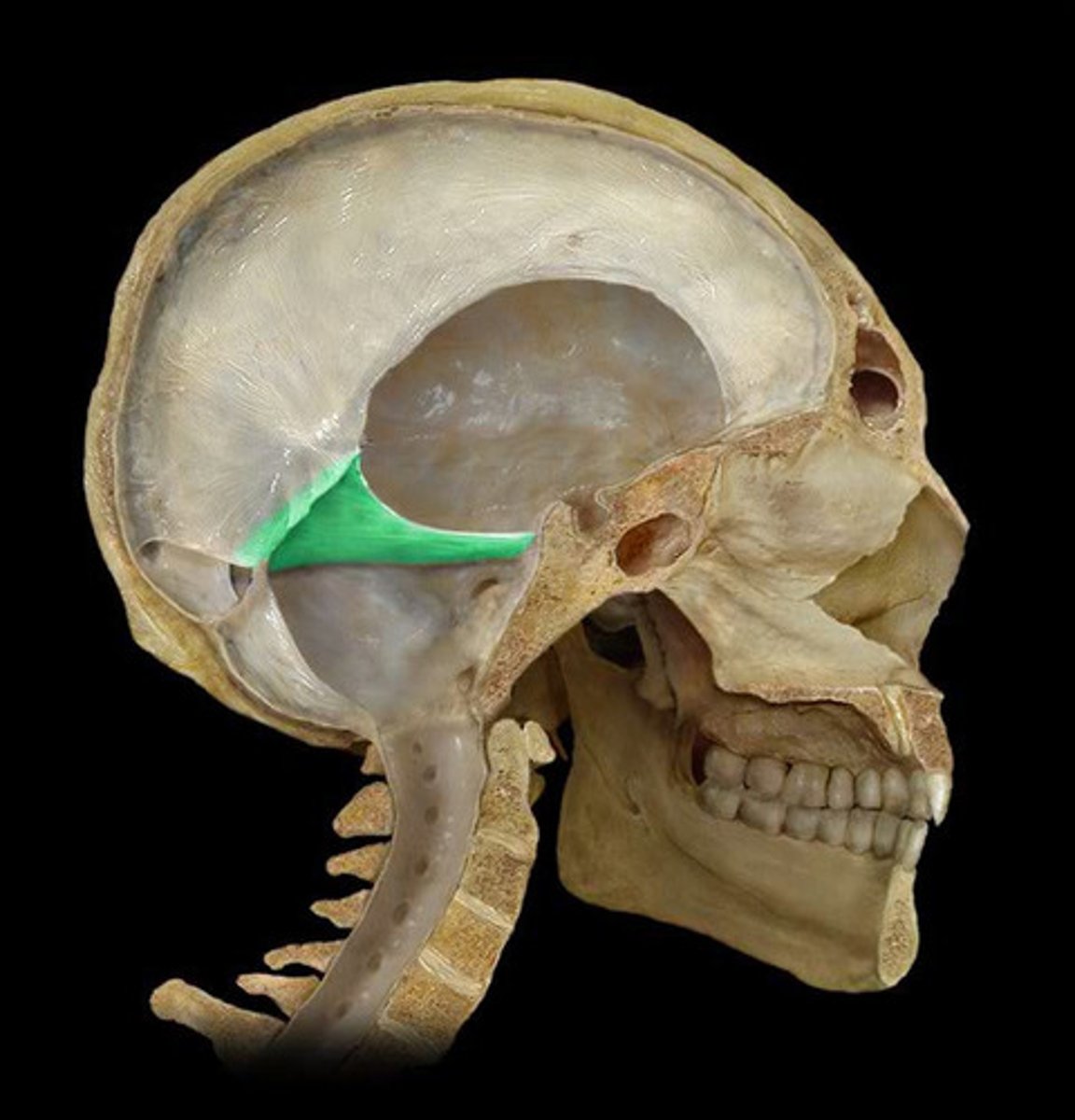
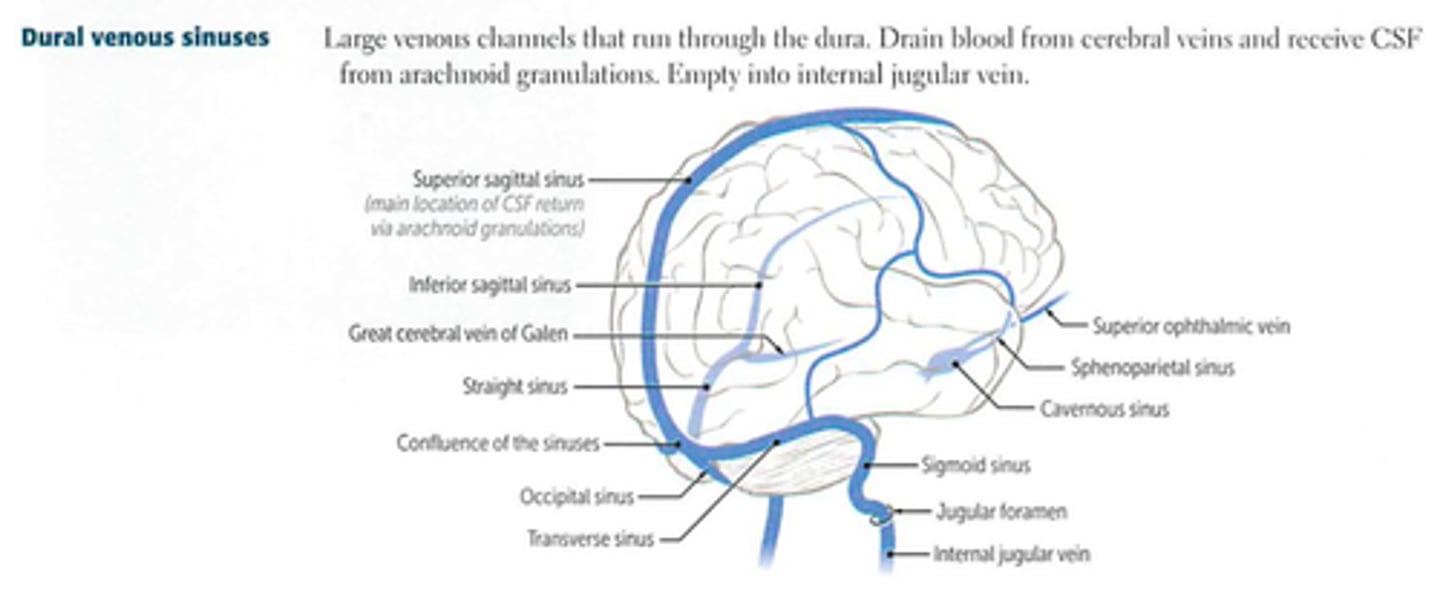
dural venous sinuses
large veins in the dura mater that drain venous blood and CSF from the vein
*superior & inferior sagittal
*transverse & sigmoid
epidural space
potential space between the inner surface of the skull and the dura mater
*contains meningeal arteries, veins, and nerves
*ARTERIAL injury
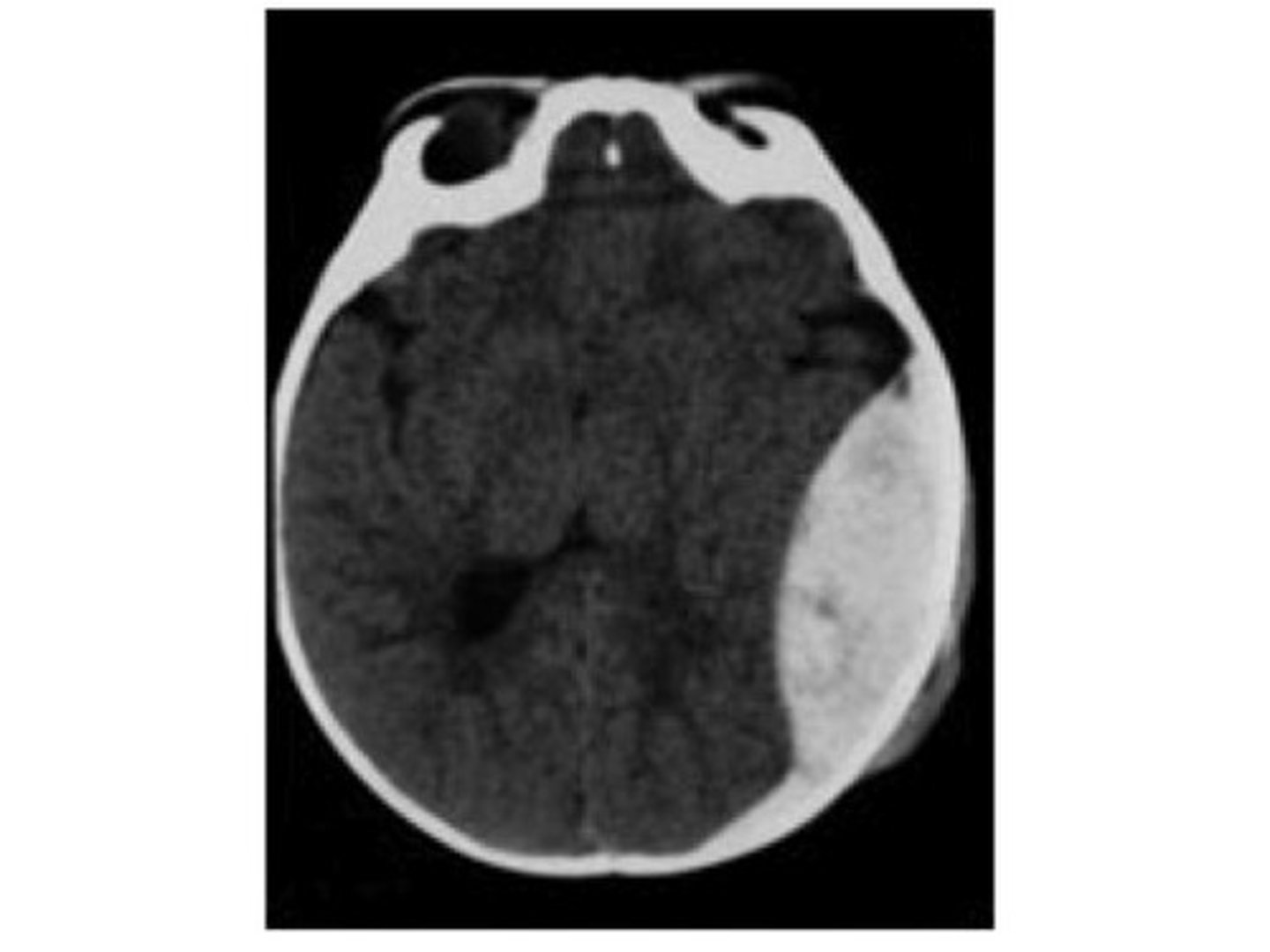
epidural space, middle meningeal
______ _____ is the common site for epidural hematomas and is commonly associated with ____ _____ artery
epidural hematoma
presentation of what cranial disorder?
brief loss of consciousness → lucid interval (short period of restored consciousness & mental clarity) → rapid decline → death (if no immediate treatment)
subdural space
potential space between dura mater and arachnoid mater that contains a thin film of fluid
*VENOUS injury
subdural hematoma
venous bleeding under the dura mater that presents with delayed or gradual symptoms and is often common in adults that take anticoagulants
subdural hematoma
presentation of what cranial disorder?
- headache
- confusion
- weakness
- gait changes
arachnoid mater
middle meningeal layer between the dura mater and pia mater that has a thin, avascular membrane resembling a spider
*protective barrier around brain
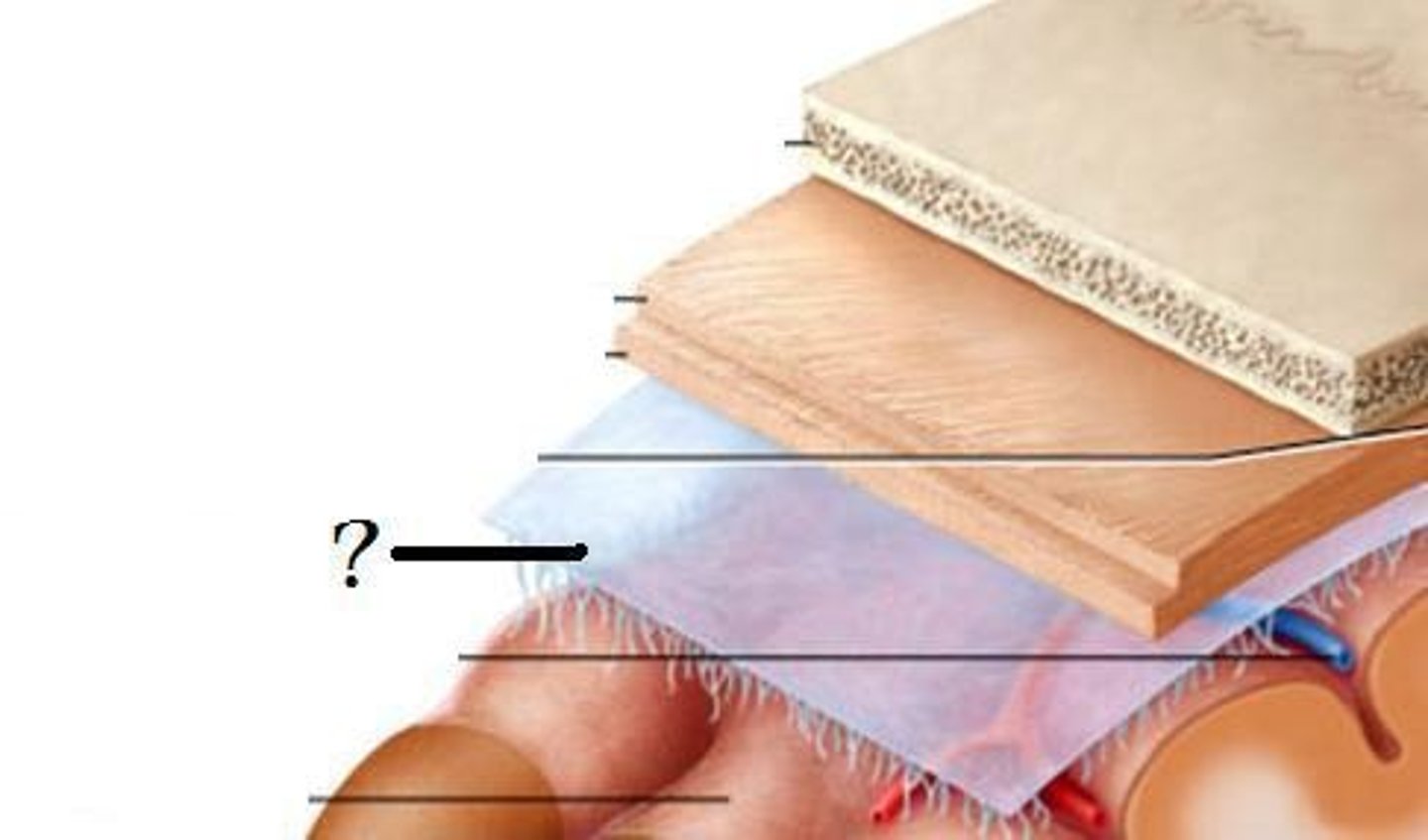
subarachnoid space
space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater that is filled with CSF
*contains major cerebral arteries and veins
*CSF cushions the brain and spinal cord, nutrient delivery, and waste removal
arachnoid granulations
extensions of the arachnoid mater that allow excess CSF to be absorbed by the dural venous sinuses
*↓ fluid build up
subarachnoid hemorrhage
bleeding into the subarachnoid space that disrupts CSF flow and can lead to ↑ intracranial pressure
subarachnoid hemorrhage
presentation of what cranial disorder?
- headache
- sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- neurological deficits
pia mater
thin, delicate, innermost meningeal layer that provides structural support to neural tissue and contributes to the blood brain barrier
pia mater injury
commonly seen in meningitis or inflammatory conditions, and may affect cortical function seen in surface-level brain injuries (TBI, infection)
CSF, ependymal cells
ventricles of the brain are filled with _____ and are lined by _____
lateral ventricles
set of paired ventricles lying within the cerebral hemispheres that contain the choroid plexus for CSF production
*largest
choroid plexus, ependymal cells
the _____ _____ in the lateral ventricles produce CSF, and _____ ______ distribute CSF
third ventricle
the ventricle located between thalami and are close to autonomic centers & hypothalamus
interventricular foramen
the lateral ventricles and third ventricle are connected by what structure?
cerebral aqueduct
structure that connects the third and fourth ventricles, and is located at the midbrain
*vulnerable to obstruction due to narrow nature
*common cause of non-communicating hydrocephalus
fourth ventricle
the ventricle located between the cerebellum and brainstem, connecting to the subarachnoid space via lateral foramina of Luschka and medial foramina of Megendie for CSF distribution
*connects spinal cord to central canal
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
clear fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord that is essential for CNS protection and homeostasis
*total volume ~ 150 mL
* ~ 500 mL produced daily
CSF
5 functions of what structure?
1. cushion & protect brain and spinal cord
2. reduce brain weight (buoyancy)
3. deliver nutrients and remove waste
4. regulate intracranial pressure
5. provide stable chemical environment for neurons
CSF impairments
presentation of what impairment/issues with what cranial structure?
- balance
- gait
- cognition
- hydrocephalus
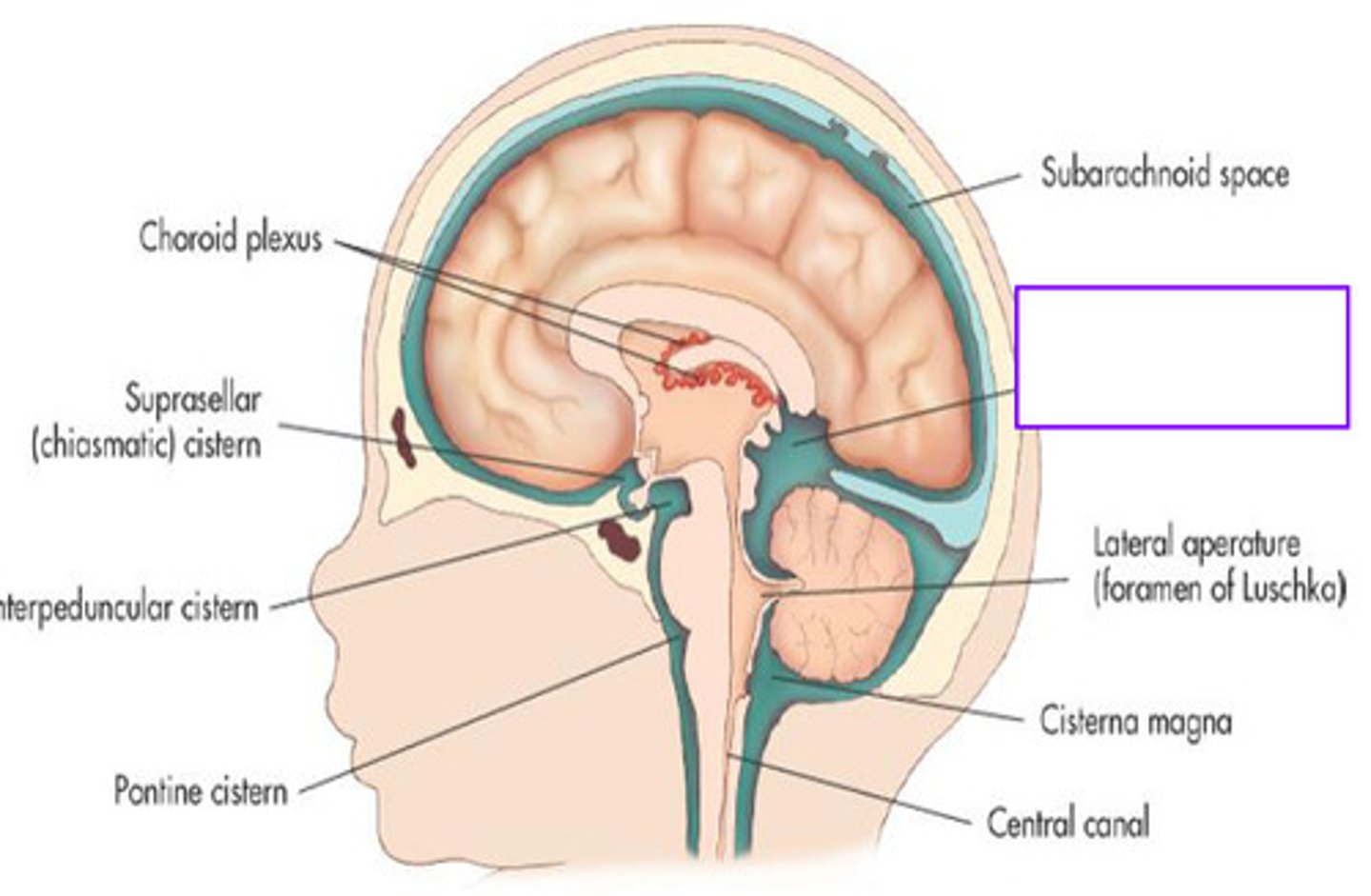
cisterns
enlarged spaces within the subarachnoid space that act as reservoirs facilitating CSF circulation
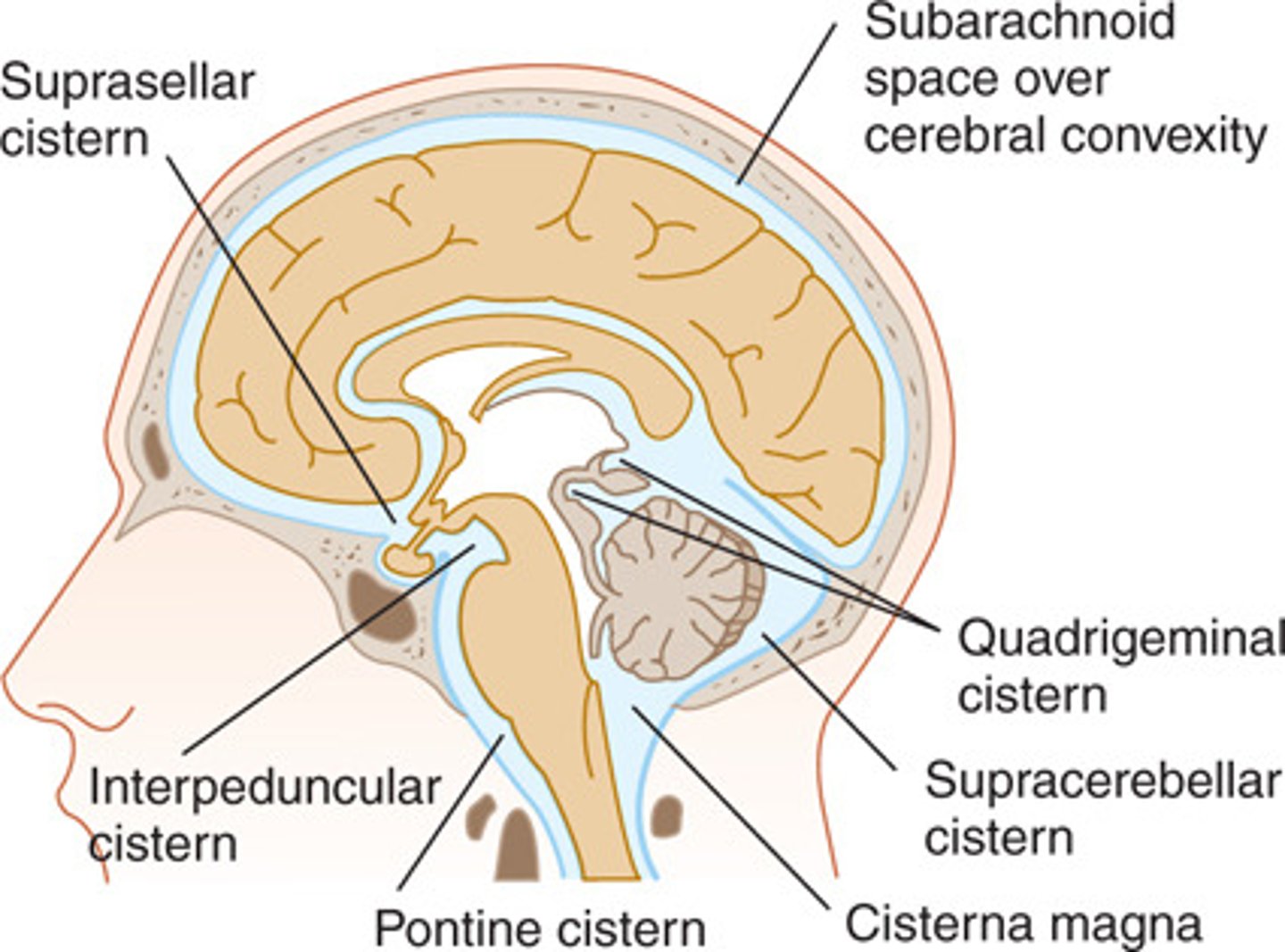
cisterna magna
cistern found between the cerebellum and medulla
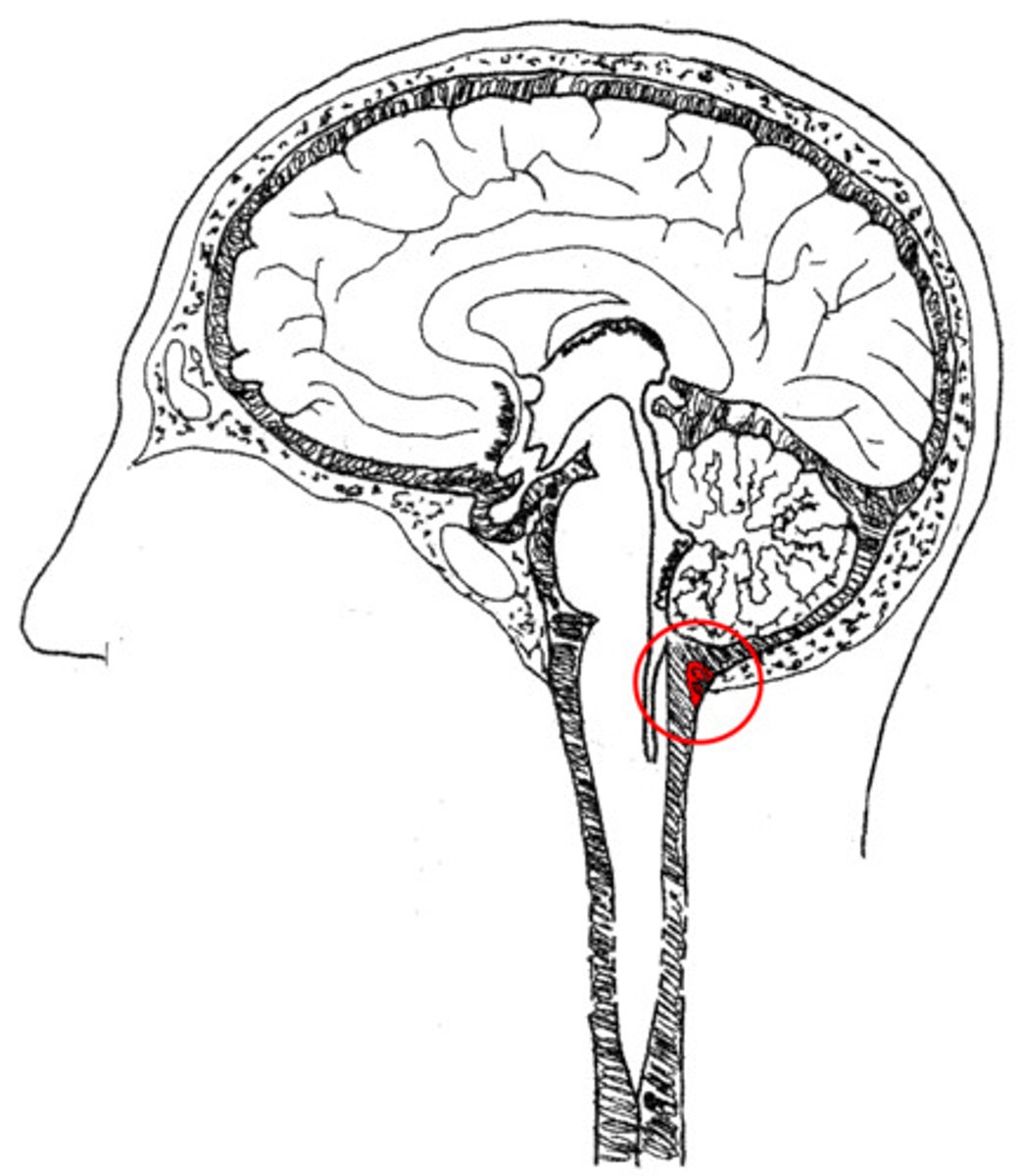
interpeduncular cistern
cistern found at the base of the midbrain
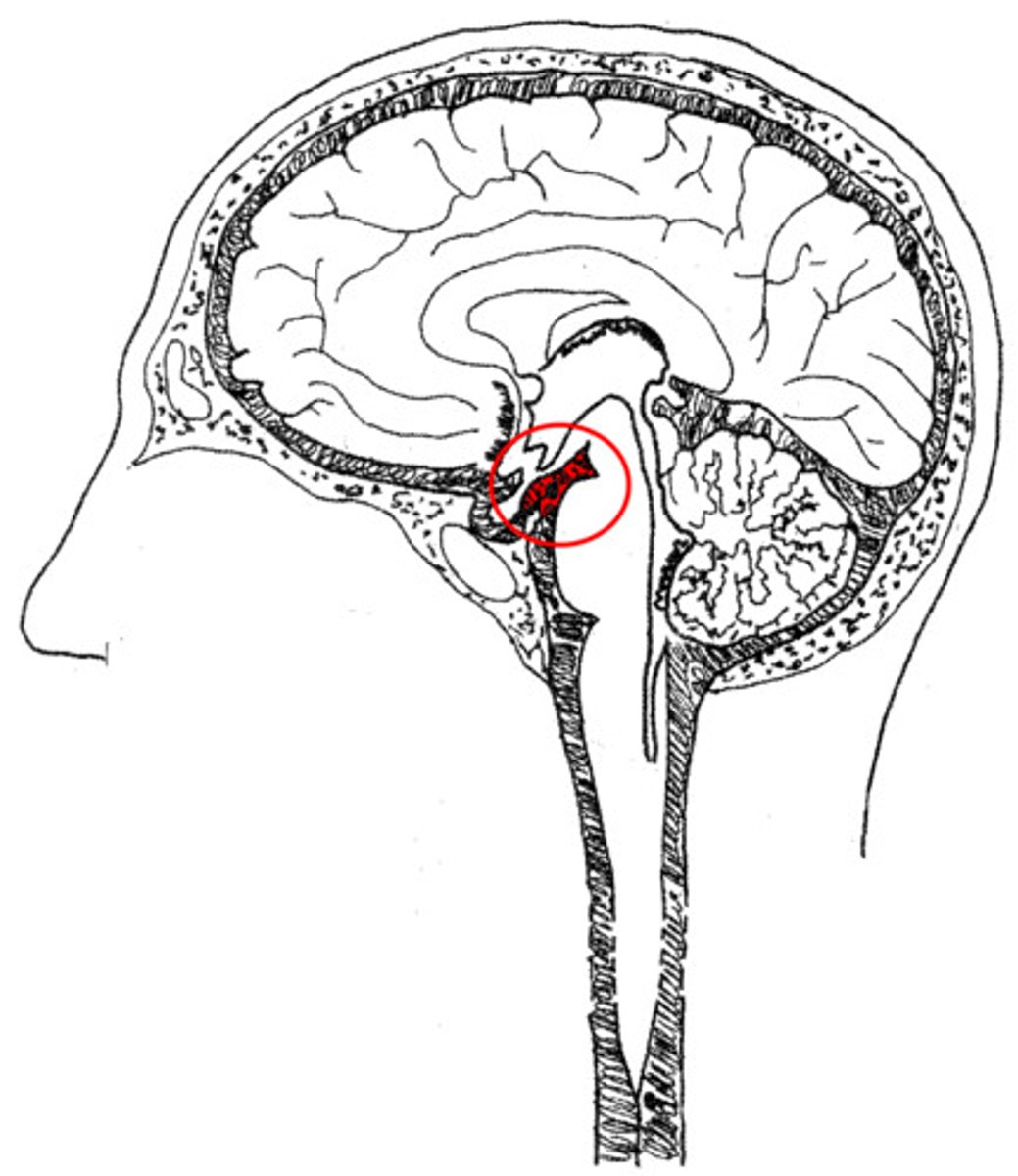
suprasellar (chiasmatic) cistern
cistern that surrounds the optic chiasm
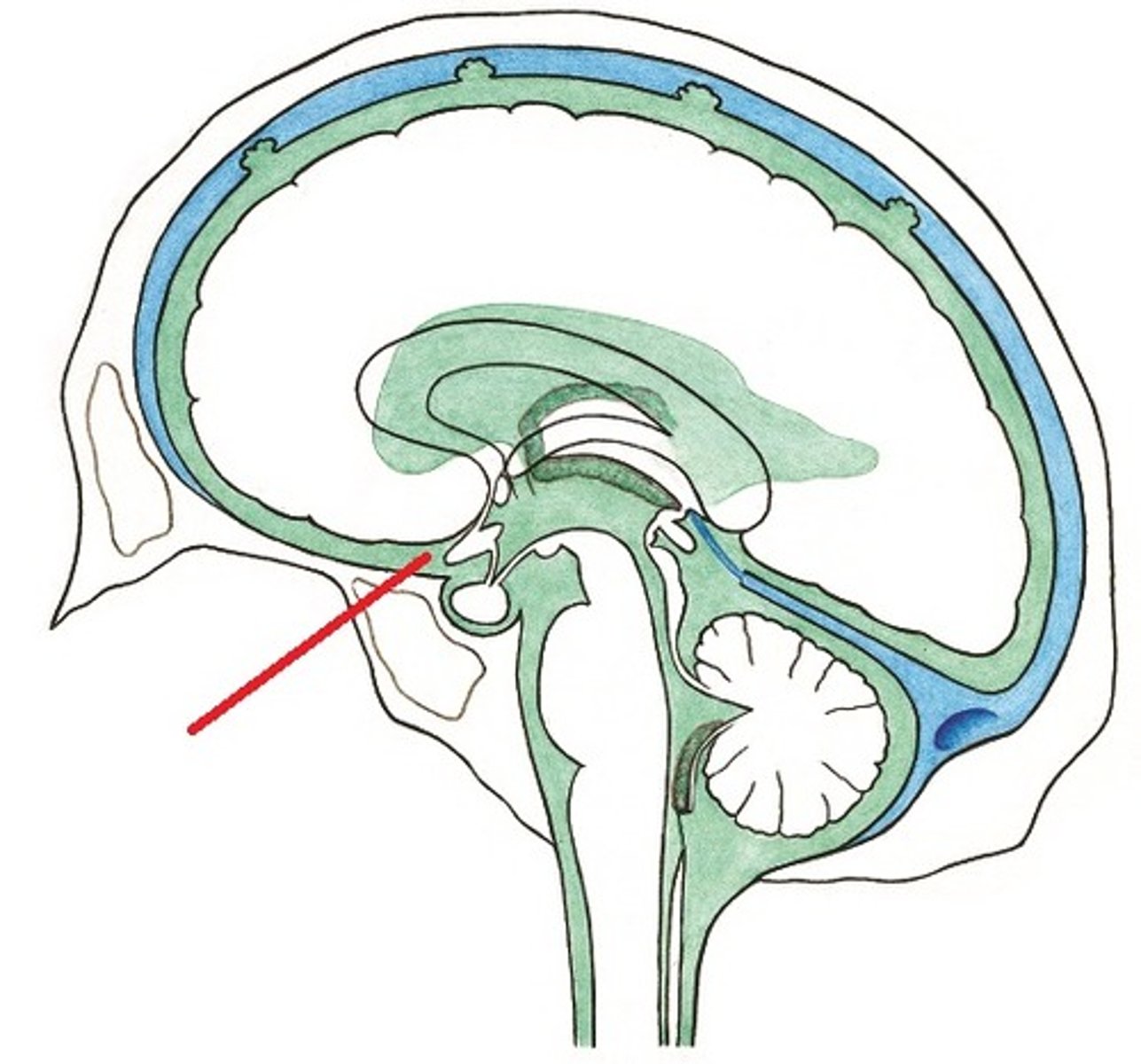
quadrigeminal cistern
cistern posterior to the midbrain
pontine cistern
cistern anterior to the pons
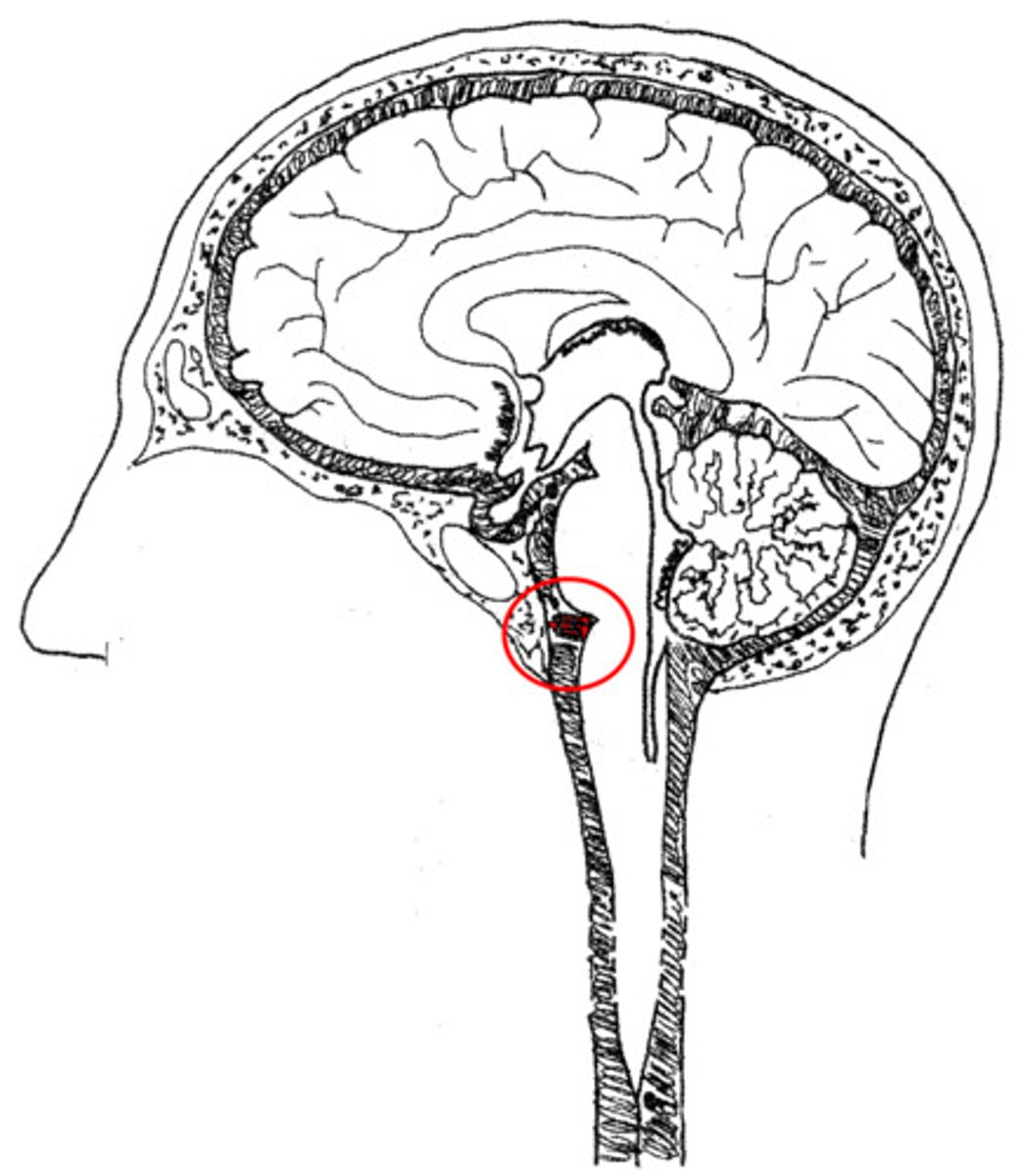
basal
subarachnoid hemorrhage often accumulates in _____ cisterns
blood brain barrier
protective separation between blood and CNS tissue that regulates what substances enter the brain and spinal cord
*capillary endothelial cells, basement membrane, astrocyte end-feet, pericytes
*infection control!
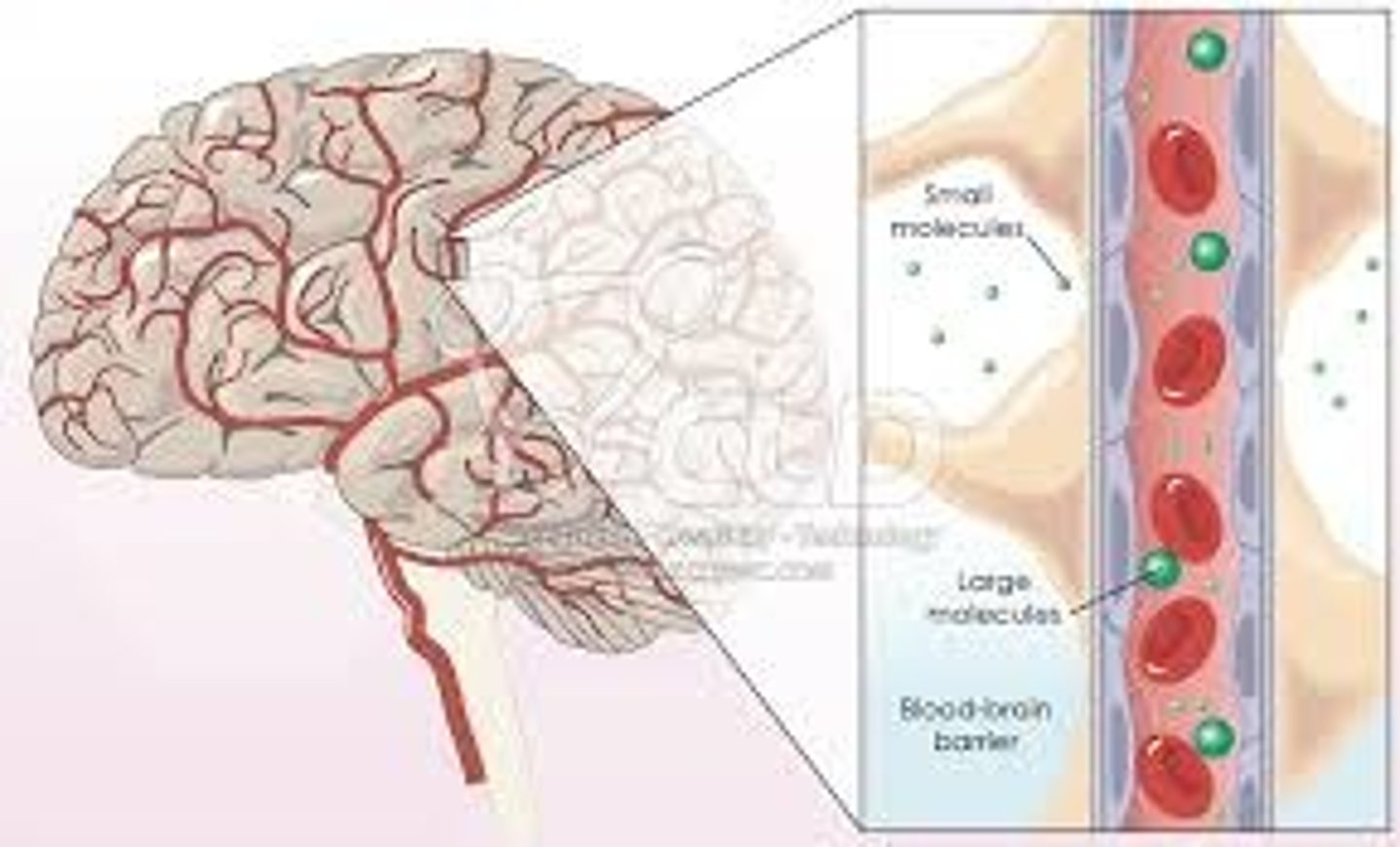
1. oxygen
2. carbon dioxide
3. lipid-soluble substances
3 substances that can cross the BBB?
glucose, amino acids
the blood brain barrier allows substances through, which are transported by _____ and _____
blood brain barrier (BBB)
presentation of what impairment/issues with what cranial structure?
- spasticity
- fatigue
- immune cell infiltration
- infection
- increased cytokines
- cerebral edema
blood-CSF barrier
barrier regulating exchange between blood and CSF, overall maintaining a stable chemical environment for the CNS
*located at choroid plexus (lateral, third, fourth ventricles)
*vascular tissue, fenestrated capillaries, epithelial cell layer
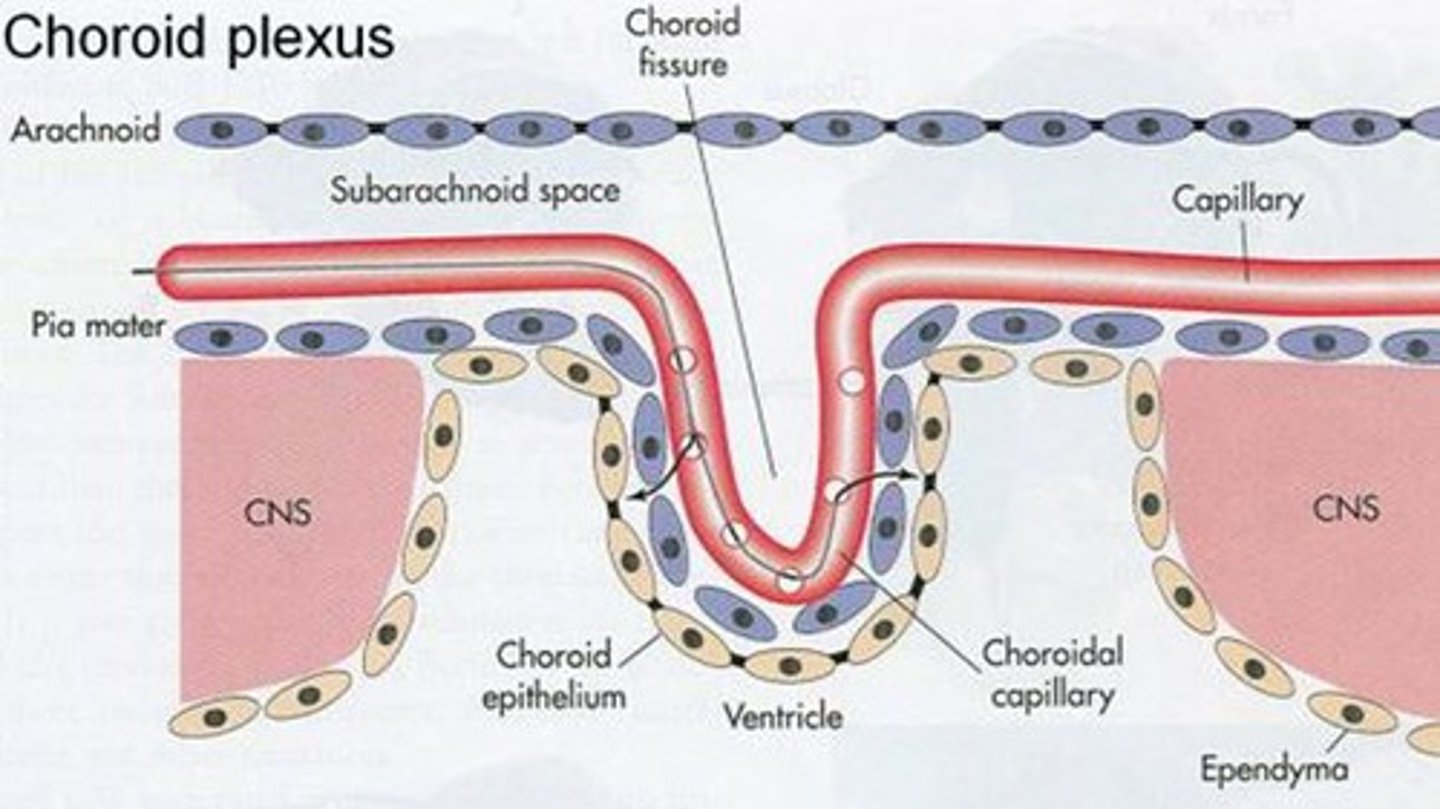
choroid plexus, brain capillary
the blood CSF barrier is contained within the _____ _____ epithelium, and the blood brain barrier is contained within the ____ ____ endothelium
sodium, chloride, water
transporters of CSF (ependymal cells) regulate _____, ______, and _____ movement
neonates
barrier immaturity within ______ increases vulnerability to infection (pia mater)
older age
_____ may reduce barrier efficiency and commonly contributes to neurological risks
5-15
normal intracranial pressure (ICP) is around _____ to _____ mmHg in adults
monro-kellie doctrine
states that due to rigidity of the cranium.... brain tissue, blood, and CSF share a fixed cranial volume
1. TBI
2. intracranial hemorrhage
3. edema
4. hydrocephalus
5. tumors
6. impaired venous drainage
6 common causes of increased ICP?
elevated ICP
presentation of what impairment/issues with what cranial structure?
- headache
- nausea/vomiting
- altered consciousness
- pupillary changes
- cushing's triad (HTN, bradycardic, irregular respiration)
cushing's triad
three classic signs—bradycardia, hypertension, and bradypnea—seen with increased ICP
1. valsalva
2. excessive exertion
3. improper positioning
what 3 things should be avoided when working with a pt that has increased ICP?
brain herniation
displacement of brain tissue to due increased ICP
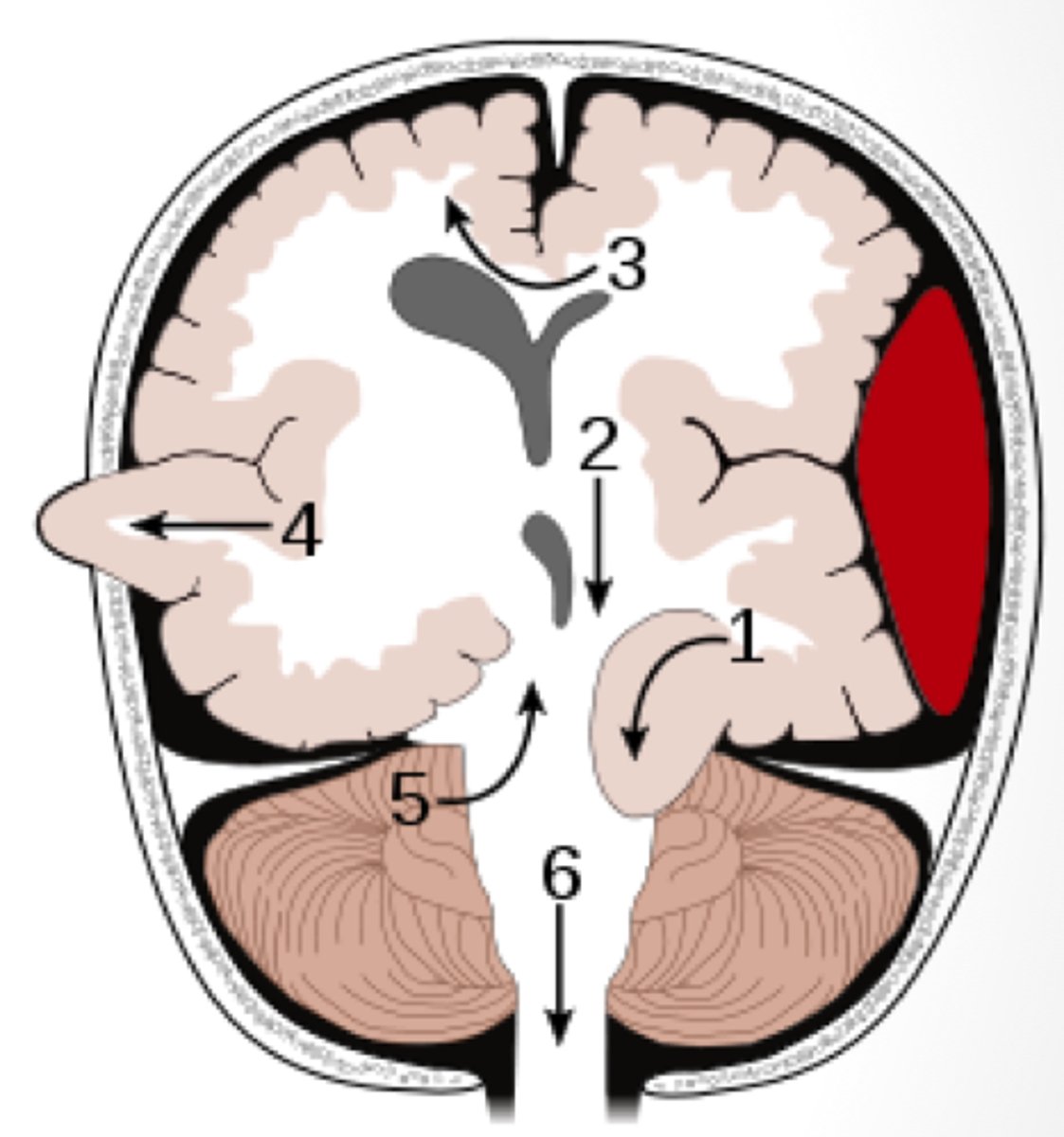
subfalcine (cingulate) herniation
herniation of the brain where the medial frontal lobe shifts under the falx cerebri
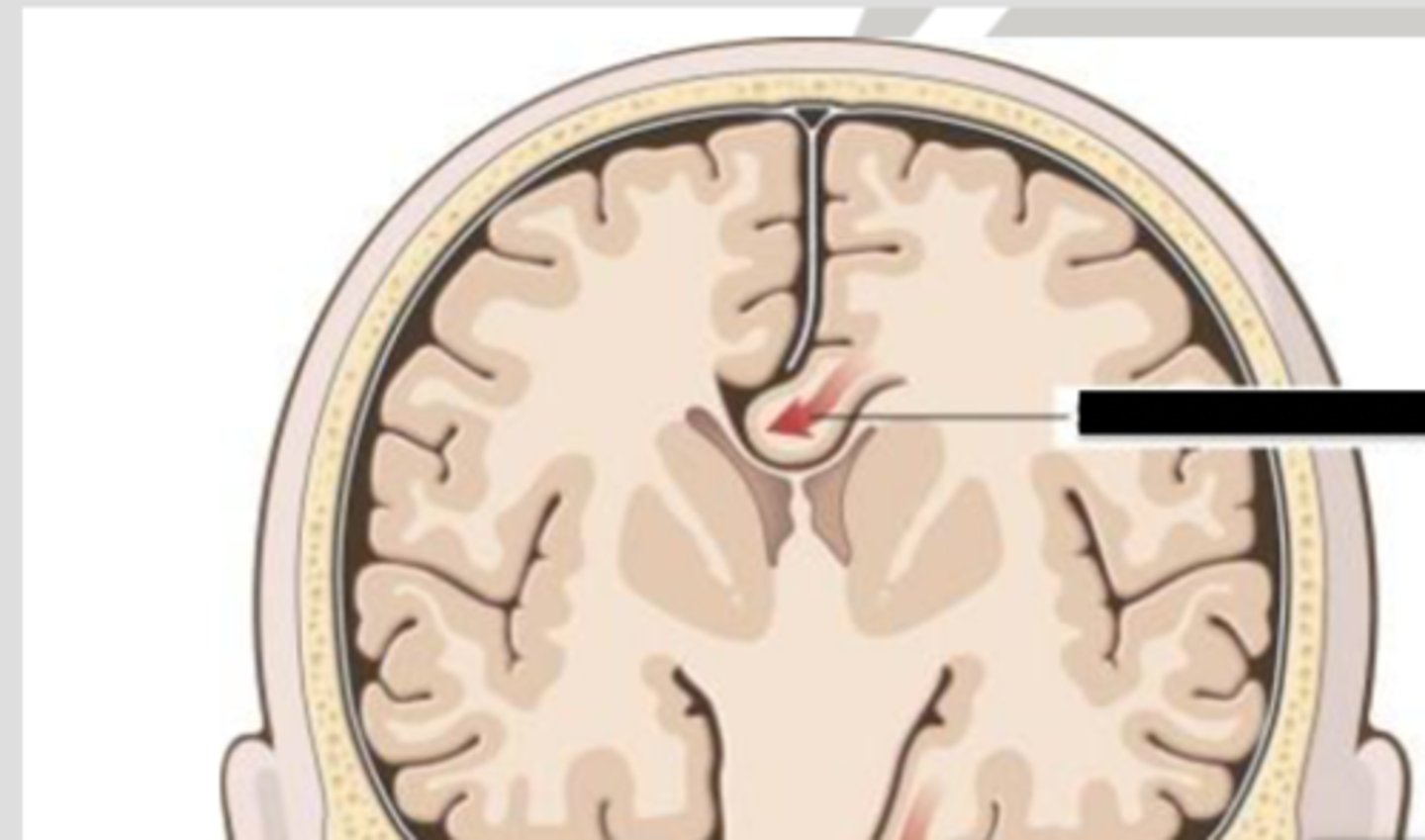
transtentorial (uncal) herniation
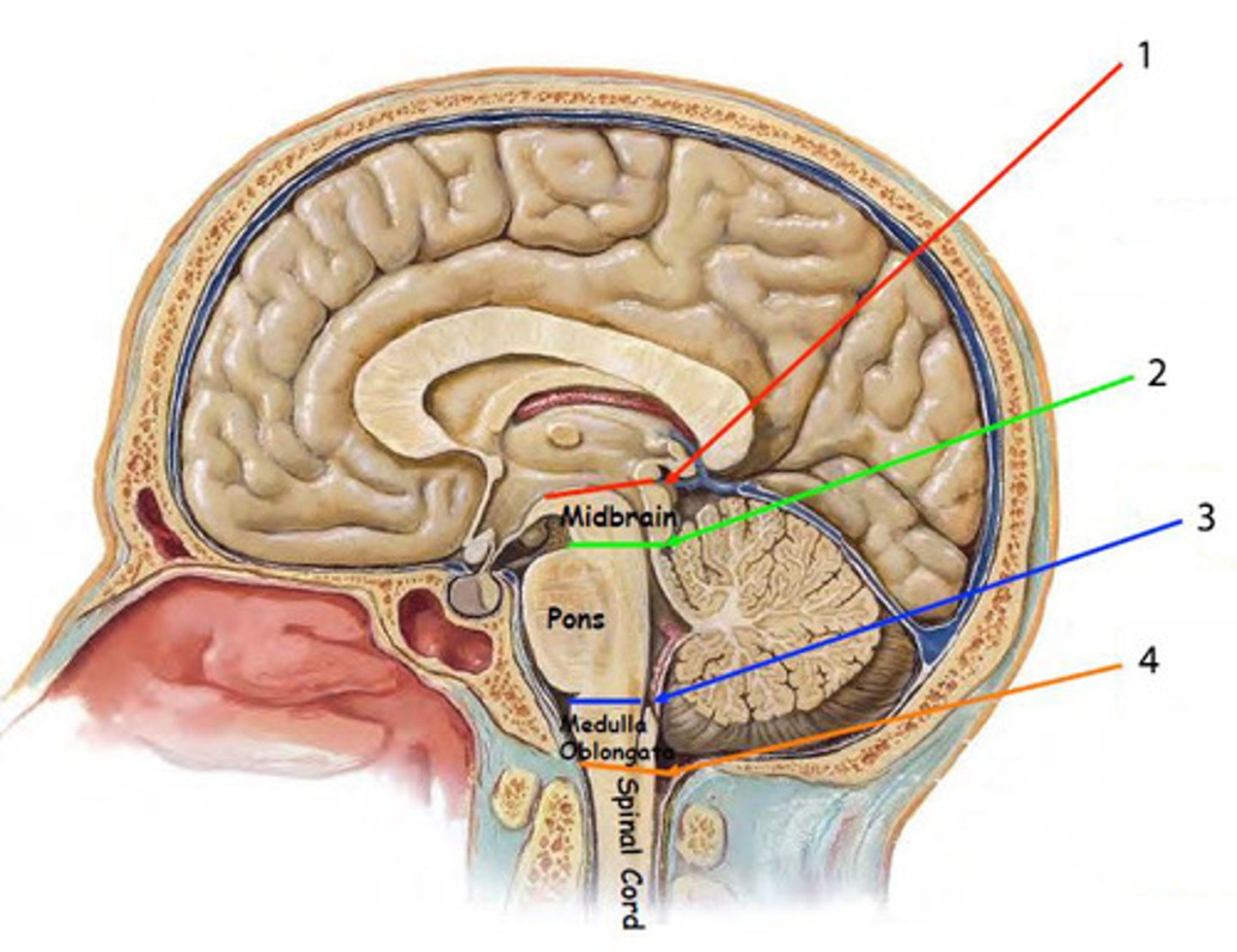
herniation of the brain where the temporal lobe shifts through the tentorial notch
*1 on diagram
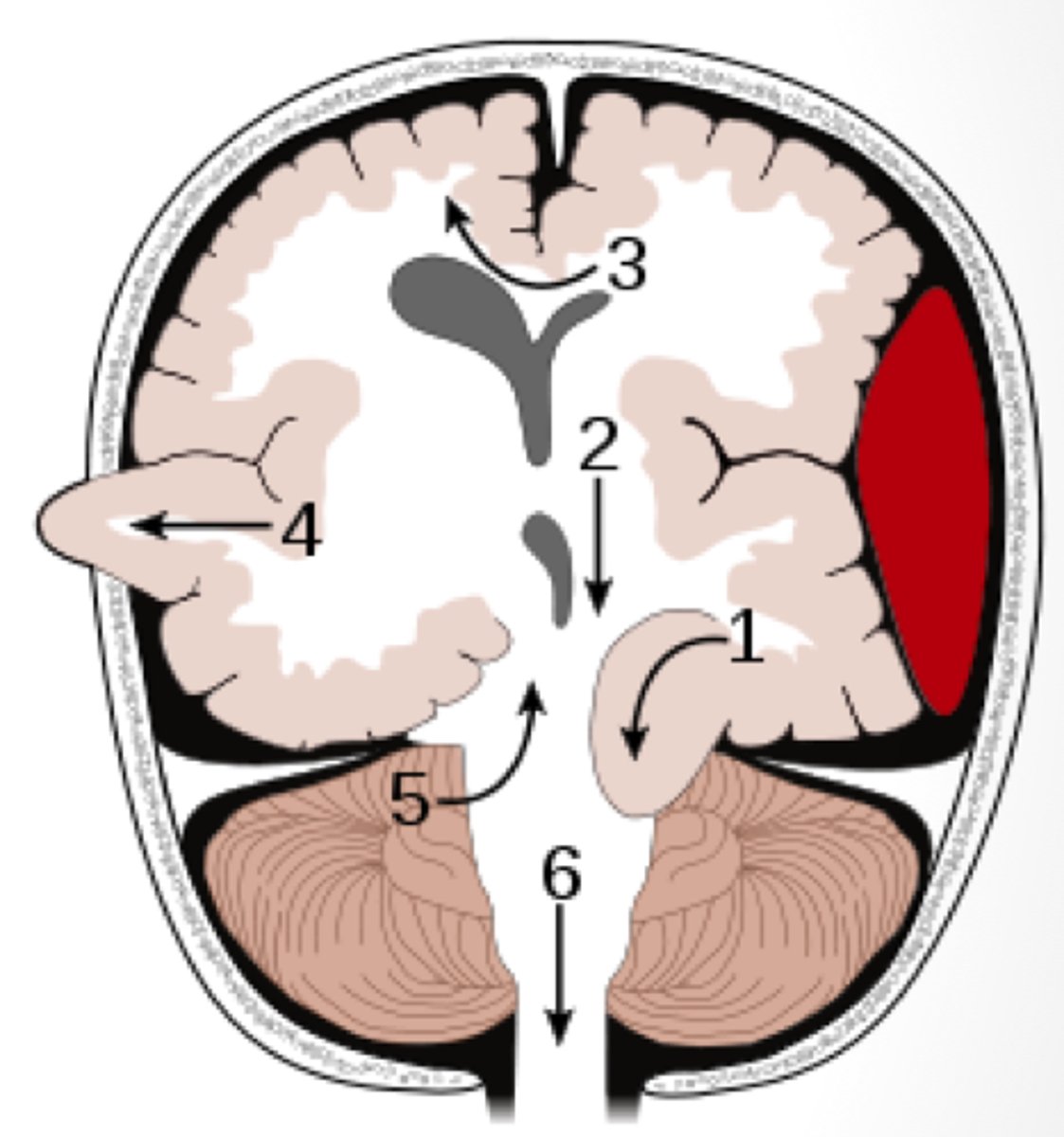
tonsillar herniation
herniation of the brain where cerebellar tonsils descend through the foramen magnum
central herniation
herniation of the brain where there is downward displacement of the brainstem
brain herniation
presentation of what impairment/issues with what cranial structure?
- altered consciousness
- pupillary asymmetry or non-reactive pupils
- abnormal posture
- respiratory and CV instability
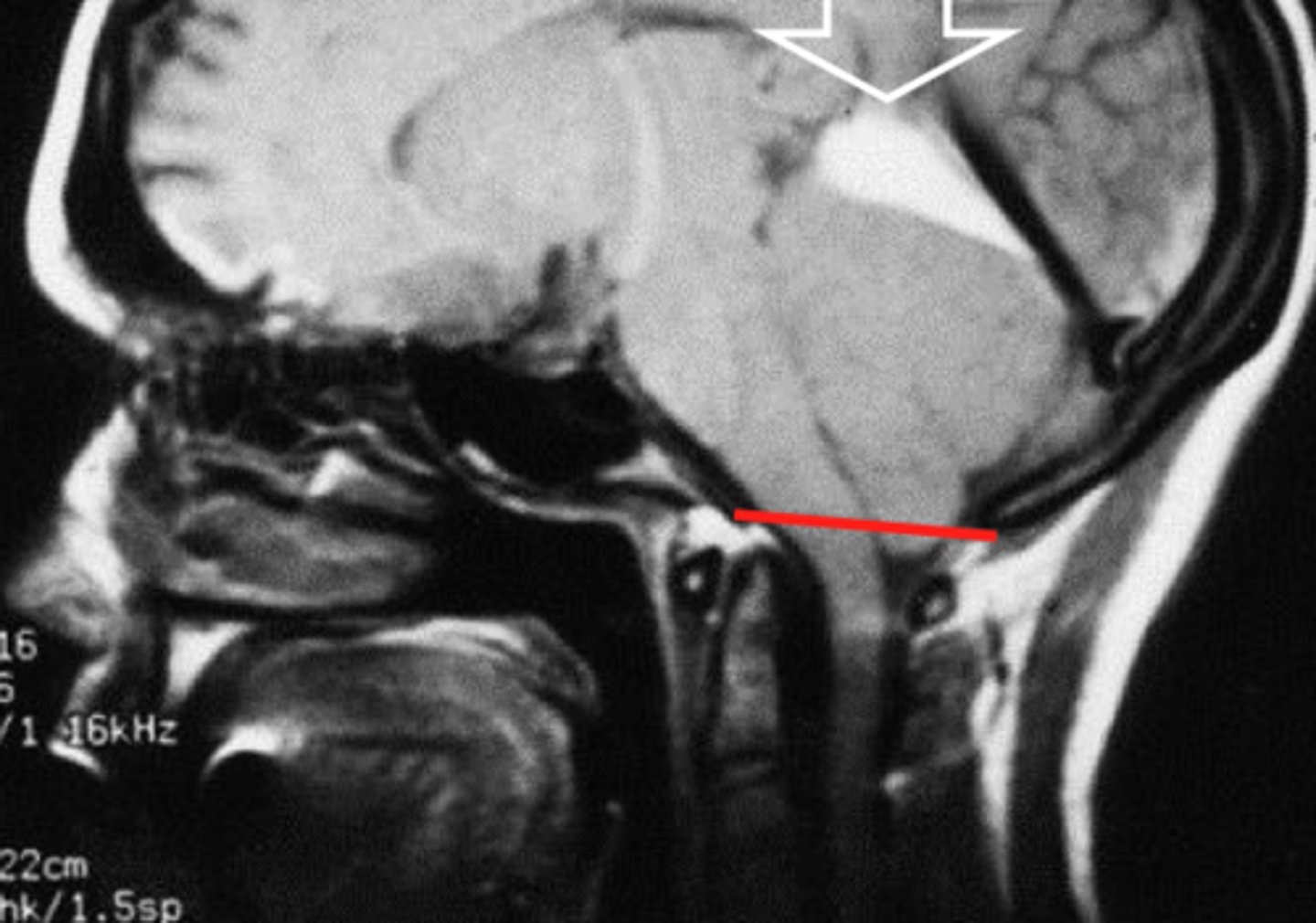
intracranial hemorrhage (ICH)
bleeding within the skull that leads to increased ICP and reduced cerebral perfusion
*traumatic or spontaneous
*major cause for neurologic morbidity and mortality
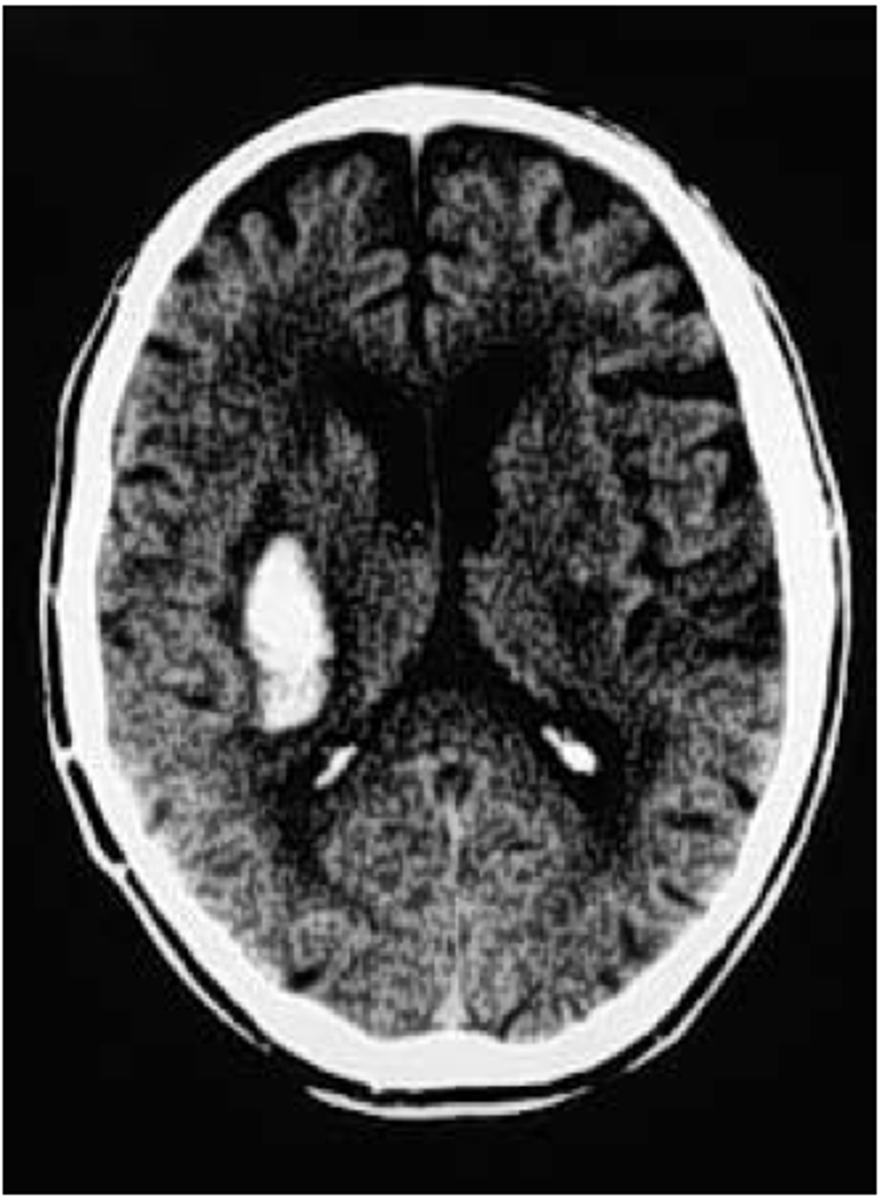
epidural hemorrhage
arterial bleeding between the skull and dura
*middle meningeal artery affected
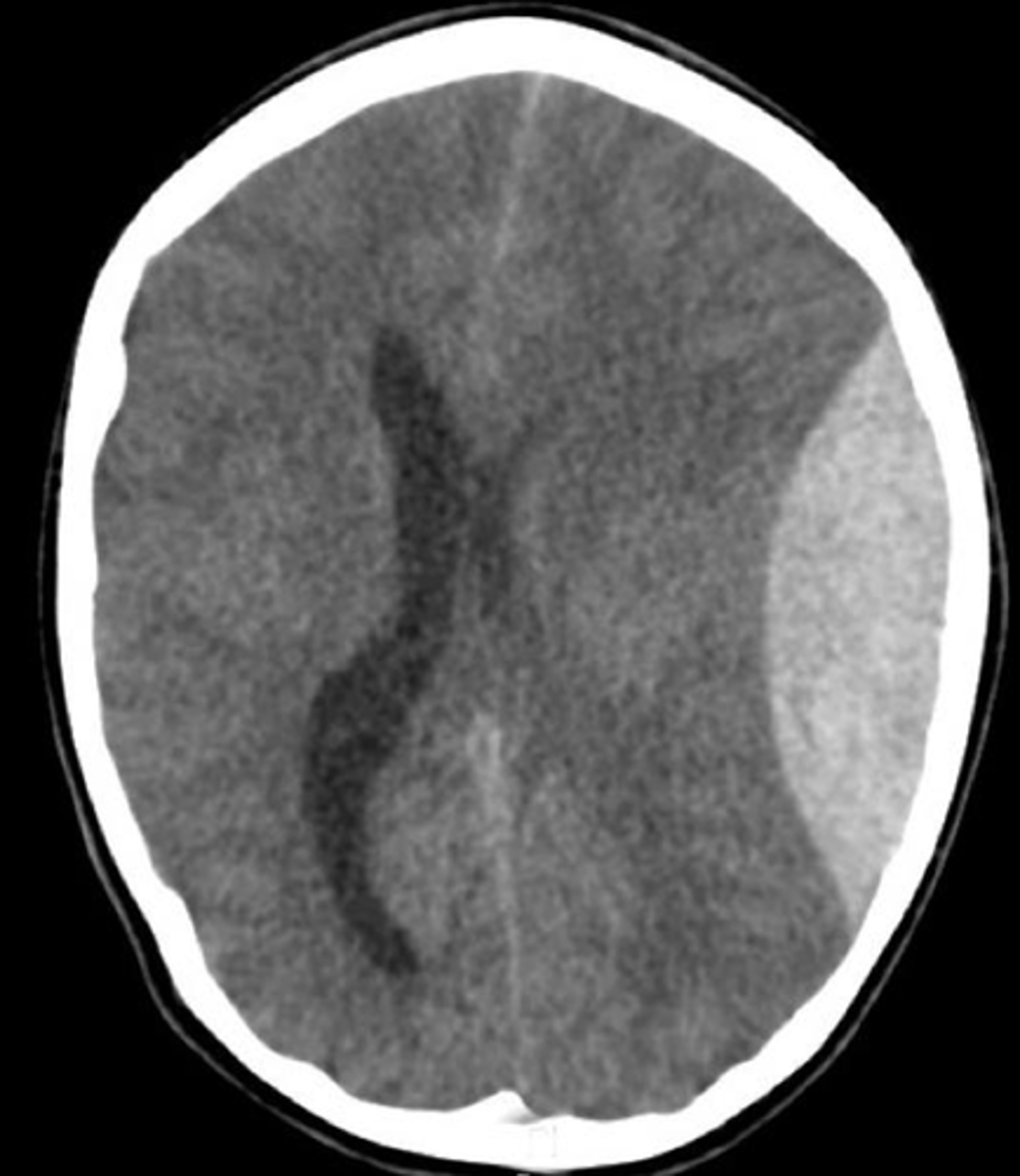
subdural hemorrhage
venous bleeding between the dura and arachnoid
*due to rupture of bridging veins
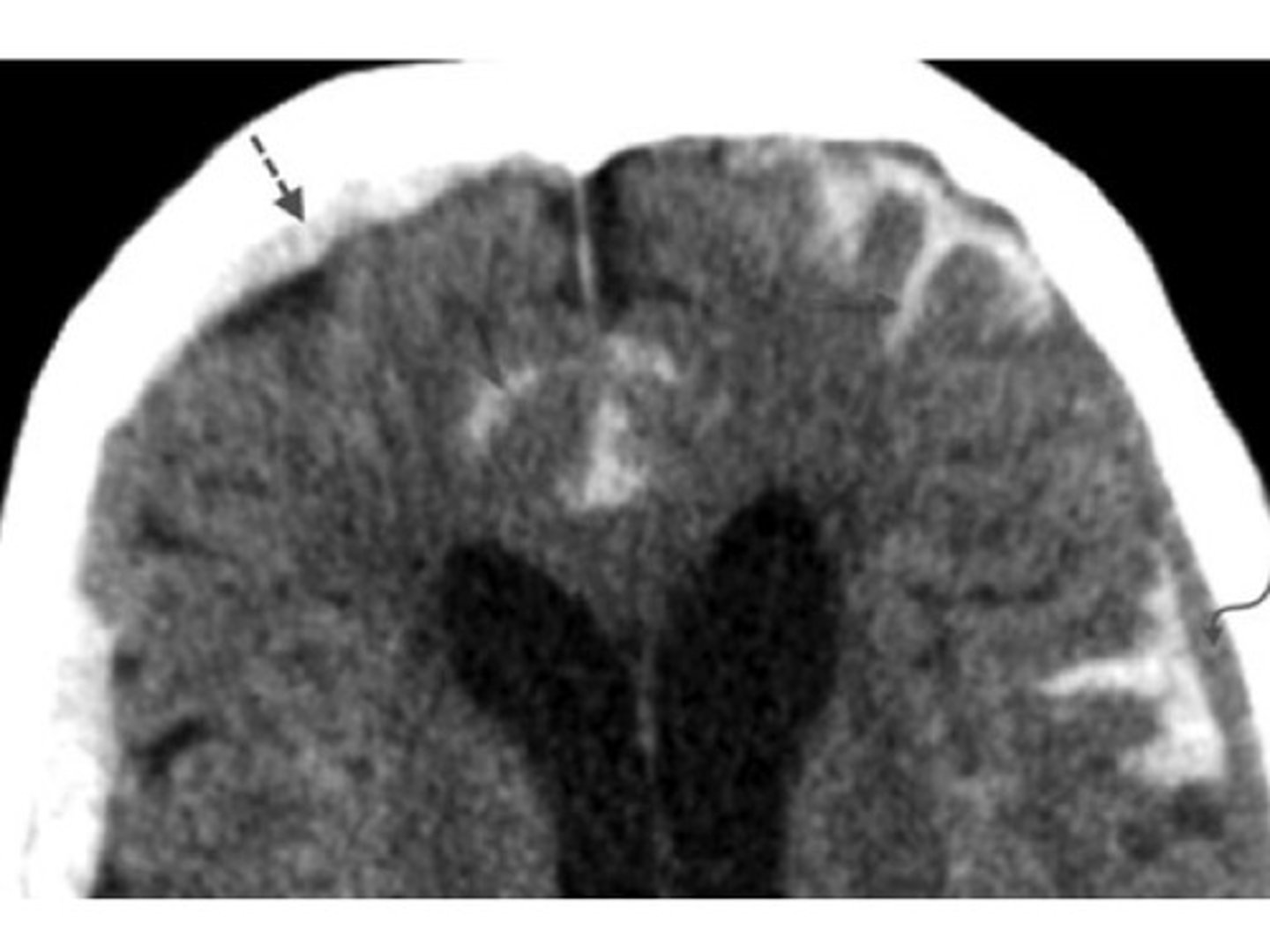
intracerebral hemorrhage
bleeding within the brain tissue
ICH
presentation of what impairment/issues with what cranial structure?
- headache
- nausea/vomiting
- altered consciousness
- weakness
- speech or vision deficits
- seizures
- rapid neurological decline
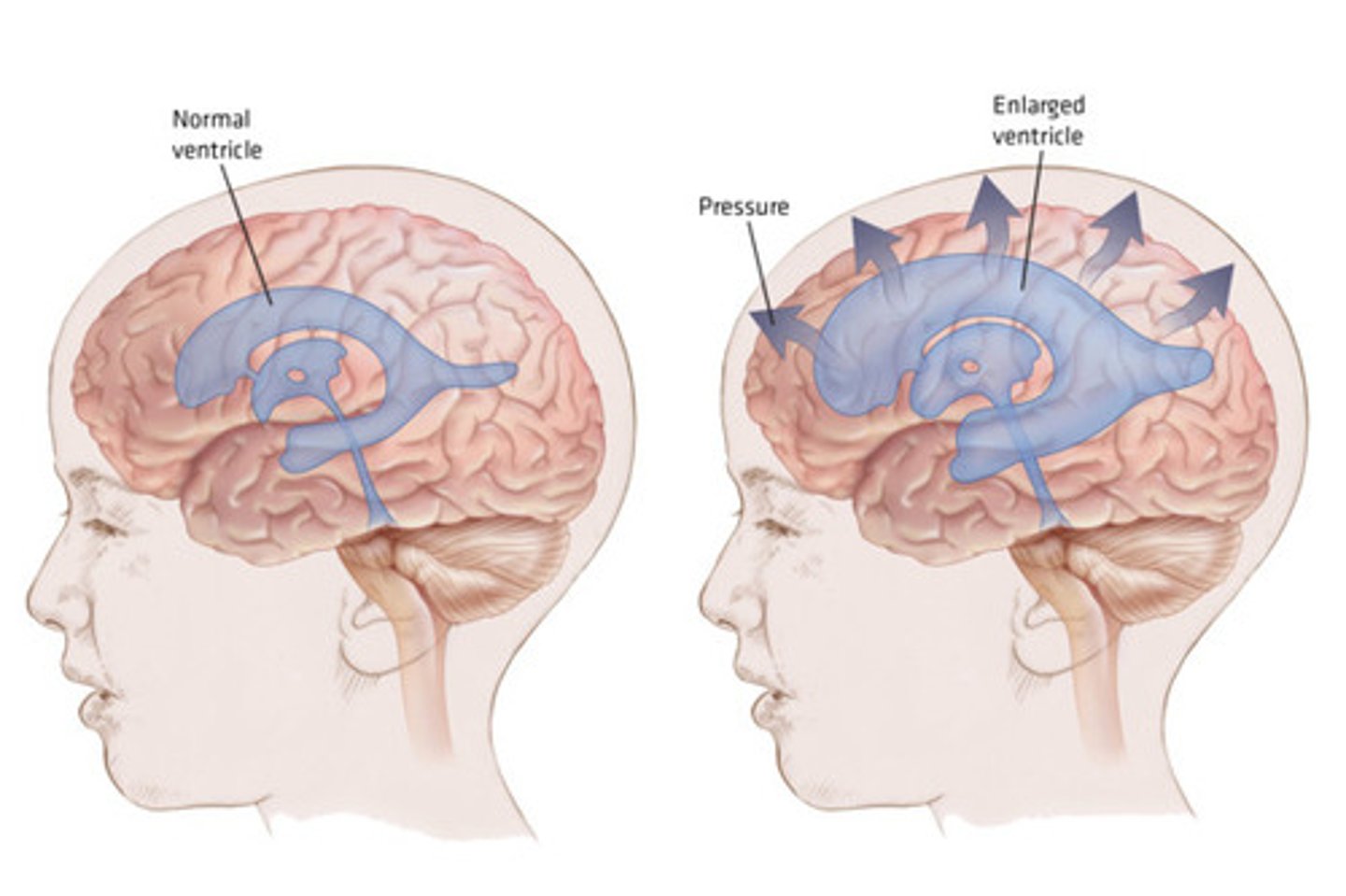
hydrocephalus
excess CSF causing ventricular enlargement