The UK economy - performance and policies
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
What is the acronym to remember macroeconomic indicators?
TIGER
What are the macroeconomic indicators?
Trade
Inflation
Growth
Employment
Redistribution of income
Stability
What are non core macroeconomic objectives?
Sound government finances
Environmental sustainability
Productivity growth
What is the macroeconomic objective for trade?
Balanced
What is the macroeconomic objective for inflation?
Low and stable
What is the inflation target for the UK?
2% +/- 1
What is the macroeconomic objective for growth?
Strong sustained and sustainable
What is the macroeconomic objective for employment?
Full employment
What is the macroeconomic objective for redistribution?
Fair
What is productivity?
output per worker per hour
What is a trade deficit?
when a country imports more than it exports
What is a trade surplus?
when a country exports more than it imports
What is a current account?
The balance of trade in goods and services
What is the circular flow of income?
The movement of spending and income across the economy
What are 3 leakages in an economy?
Savings
Imports
Tax
What are 3 injections into an economy?
Investment
Exports
Government spending
What is investment?
When firms spend on capital goods to increase their productive capacity
What are the 3 methods to calculate GDP?
Output
Income
Expenditure
What is the output method relating to calculating GDP?
The value of all final goods and services produced in a year
What is the income method relating to calculating GDP?
Adding up all factor incomes in a year
What is the expenditure method relating to calculating GDP?
C+I+G+(X-M)
Why are index numbers good?
To make numbers more appealing
To allow for quick and easy data comparisons
What is the equation for an index number?
Index number = raw number/ base year raw number x 100
What is the index value of a base year?
100
What is aggregate demand?
the total demand for a countries goods and services at a given price level at a given time
What is aggregate demand a measure of?
Expenditure
What is the equation for aggregate demand?
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
What does the graph for aggregate demand look like?
What are the 3 factors causing AD to slope downwards?
Wealth effect
Trade effect
Interest effect
What is the wealth effect in regards to AD?
As price level decreases the purchasing power of income increases therefore increasing consumption
What is the trade effect in regards to AD?
As the price level decreases exports become more competitive and imports become less competitive, hence increasing net exports
What is the interest effect in regards to AD?
As the price level decreases interest rates can be kept lower increasing consumption investment and net exports
What is consumption?
Total spending by households on goods and services in the economy
What is the marginal propensity to consume (MPC)?
A measure of the proportion of an increase in income that a person is likely to spend on consumption
What are 5 determinants of consumption?
Level of real disposable income
Interest rates
Consumer confidence
Asset prices
The level of household debt
What are 6 determinants of saving?
Level of real disposable income
Interest rates
Level of consumer confidence
Trust of financial institutions
Tax incentives
Age structure of the population
What are 6 determinants of investment?
Interest rates
Business confidence
Corporation tax
Spare capacity
Level of competition
Price of capital
What are 4 parts of government spending?
Current spending
Capital spending
Welfare spending
Debt interest payments
What is current spending?
maintenance of public sector services and payment of public sector wages
What is a budget deficit?
Where government spending is more than taxation in a fiscal year
What is a budget surplus?
Where government spending is less than taxation in a fiscal year
What is national debt?
The total stock of a nations debt
What are 5 determinants of net exports?
Real disposable income abroad
Real disposable income at home
Strong/weak exchange rate
Protectionism at home and abroad
Relative inflation rates at home
What does SPICED stand for?
Strong Pound Imports Cheap Exports Dear
Why does the pound being strong mean imports are cheap?
As it requires less money to buy the same good/service
What does WIDEC stand for?
Weak Pound Imports Dearer Exports Cheaper
What does the classical model of SRAS look like?
What does the classical model of LRAS look like?
What does the position of the SRAS curve depend on?
The costs of production
What are 5 costs of production?
Wages
Raw materials
Oil prices
Tax
Import prices
What does the classical model of LRAS represent?
One level of output the economy will always produce in the long run
What is YFE?
The maximum level of output an economy can produce using all of its factors of production at sustainable levels
Why does LRAS shift?
Due to an improvement in the quantity and quality of the factors of production
What are 6 factors that cause a shift to LRAS?
Labour productivity
Investment
Infrastructure
Quantity of labour
Competition
Discovery of new resources
What does the Keynesian LRAS curve look like?
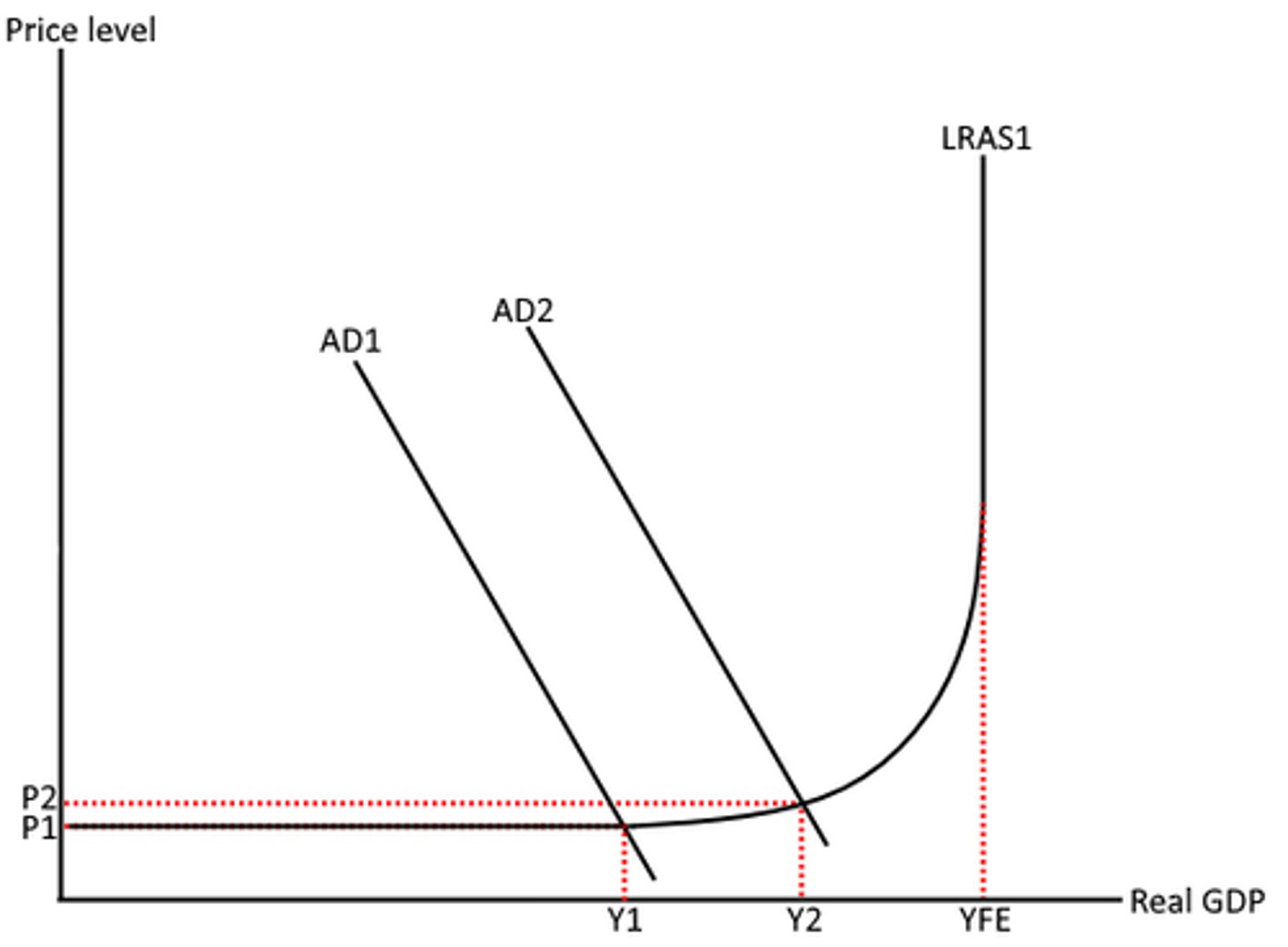
Why is the Keynesian model different to the classical model of LRAS?
To depict how there is spare capacity in the economy due to unemployment of the factors of production
Why does the price level increase dramatically when approaching YFE?
As there is more pressure put on the existing factors of production
When does macroeconomic equilibrium occur?
When AD=AS
When does short run macroeconomic equilibrium occur?
When aggregate demand is equal to SRAS but not equal to LRAS
When does long run macroeconomic equilibrium occur?
When AD is equal to SRAS and is also equal to LRAS
What 4 things happen in the economy due to a shift in AD to the right?
Increased economic growth
Decreased unemployment
Increased inflation
Worsened trade position
Why does the trade position worsen when there is a shift in AD to the right?
As when the price rises exports become less competitive leading to a contraction in demand for exports
What 4 things happen in the economy due to a shift in LRAS to the right?
Increased economic growth
Decreased unemployment
Decreased inflation
Improvement in trade position
What is the multiplier effect?
Process by which any changes in the components of AD will lead to an even greater change in national output
What are the 2 equations for the multiplier effect?
1/1-MPC or 1/MPW
What can the multiplier effect do to an initial shift in AD?
It can make it shift again
What is the accelerator effect?
changes in investment can be directly linked to changes in the rate of GDP growth
Why does the accelerator effect occur?
If the rate of GDP growth occurs firms may be more encouraged to invest to meet future demand
When can output gaps occur?
When the actual output is not equal to the potential level of output
What is a negative output gap?
Where actual output is less than potential output
What is a positive output gap?
where actual output is greater than potential output
Can an economy produce more than YFE?
Yes however this would only happen unsustainably and would lead to high inflation
What are 4 reasons why measuring economic growth important?
-Allows government to see if they are reaching their objectives
-Allows the evaluation of policy
-Allows businesses and government to forecast to change future policy or investment
-Allows for comparison between economies
What are 4 measures of economic growth?
GDP
GDP per capita
GNI
Green GDP
What is GDP?
The value of all final goods and services produced in an economy in a year
What are 3 negatives of using GDP?
Disregards inequality
Disregards negative externalities
Illegal activity not accounted for
What is the equation for GDP per capita?
GDP/population
What are 3 negatives of using GDP per capita?
Disregards income earned abroad
Illegal activity not accounted for
Errors with data collection
What is GNI?
the total income generated by a country's factors of production regardless of where those factors of production are located
What is the equation for GNI?
GDP + net factor income
What are 3 negatives of using GNI?
Errors with data collection
Illegal activity not accounted for
Disregards income inequality
What is the equation for green GDP?
GDP - environmental costs
What are 3 negatives of using green GDP?
Putting a value on pollution is difficult
Would decrease the value significantly
Disregards income inequality
What is actual growth caused by?
An increase in AD using spare capacity to increase real GDP
What are 5 factors that can increase AD?
Low interest rates
Lower taxes
Higher consumer/business confidence
Higher government spending
Weak exchange rate
What is potential growth caused by?
An increase in LRAS increasing the productive capacity of the economy
What does the graph look like showing potential growth and actual growth?
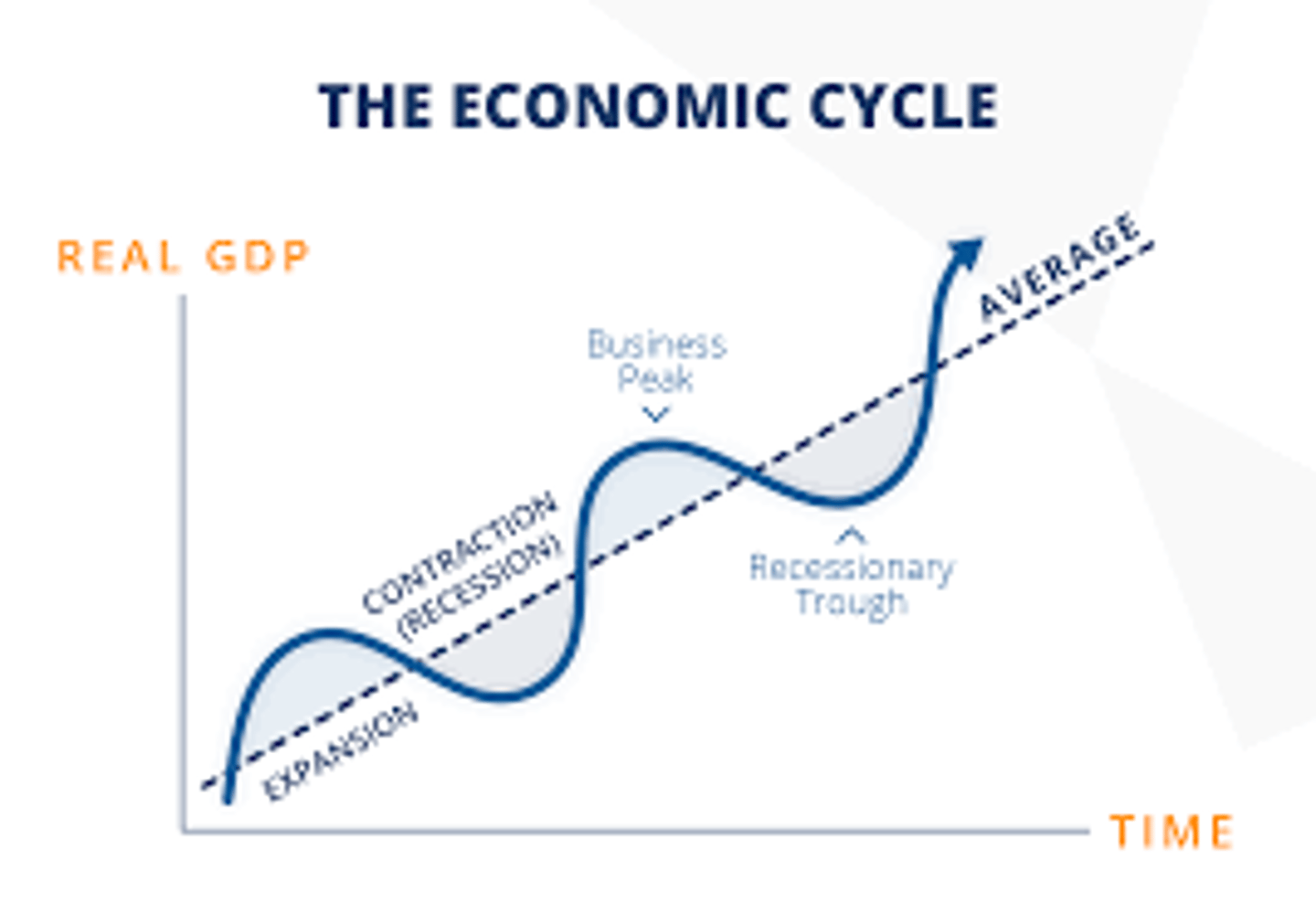
What do we call it when actual growth peaks?
An economic boom
What do we call it when actual growth falls?
An economic recession
What is a recession?
Where real GDP falls for 2 consecutive quarters
What is the lowest point of a recession called?
A trough
What do we call it when the economy starts to get better?
An economic recovery
When actual growth is greater than potential growth what is this known as?
Positive output gap
When actual growth is lower than potential growth what is this known as?
Negative output gap
What are 4 benefits to economic growth?
higher disposable income
higher employment
higher profit for firms
fiscal dividend for Government (increase in tax revenue)
What are 4 costs of economic growth?
inflation (demand-pull)
income inequality
environmental costs
current account deficit
What makes an individual unemployed?
Working age
Willing and able to work
Actively seeking work
Do not have a job
What does it mean to be economically inactive?
Individuals who are of working age but are not willing to work
What are 2 ways we can calculate unemployment?
Labour force survey
Claimant count
What is the labour force survey?
Survey conducted by the ONS to UK households