Endocrine system
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
.Glucocorticoids (e.g., Cortisol)
1. Produced By: Adrenal cortex.
2. Functions: Regulate metabolism, immune response, and stress response
Steriod Hormoe
Paravocellular neurosecreting cells
Paravocellular neurosecreting cells = small hypothalamic neurons that release regulating hormones into blood to control the anterior pituitary.
Mineralocorticoids (e.g., Aldosterone)
Produced By: Adrenal cortex.
Functions: Regulate sodium and potassium balance and blood pressure.
Steriod Hormone
What hormone in a bit the growth hormone
Somatostatin
. what is dopamine inhibits
Prolactin
What is Sheehan syndrome?
Sheehan syndrome is when a woman develops hypopituitarism (low pituitary hormones) because her anterior pituitary gets damaged after severe bleeding during childbirth.
What causes it?
Postpartum hemorrhage (major blood loss)
→ low blood flow to the pituitary
→ ischemia/infarction of the anterior pituitary
What is used to make T3 and T4 and where is it stored?
Iodine is used to make it and stored in the thyroid gland
What are the types of receptors in ADH?
Osmoreceptors: “Blood is too salty” → ADH + thirst
Baroreceptors: “Pressure is too low” → ADH + save water
what is it called a thyroid gland and what happens
This is hypothyroidism and it’s gonna be much harder to lose the fat
What is thyroid peroxide?
This is an enzyme used in the T3/T4 synthesis. It does oxidation which turns I- to iodine two which is its active form. this also couples up MITTDIT to make T3/T4
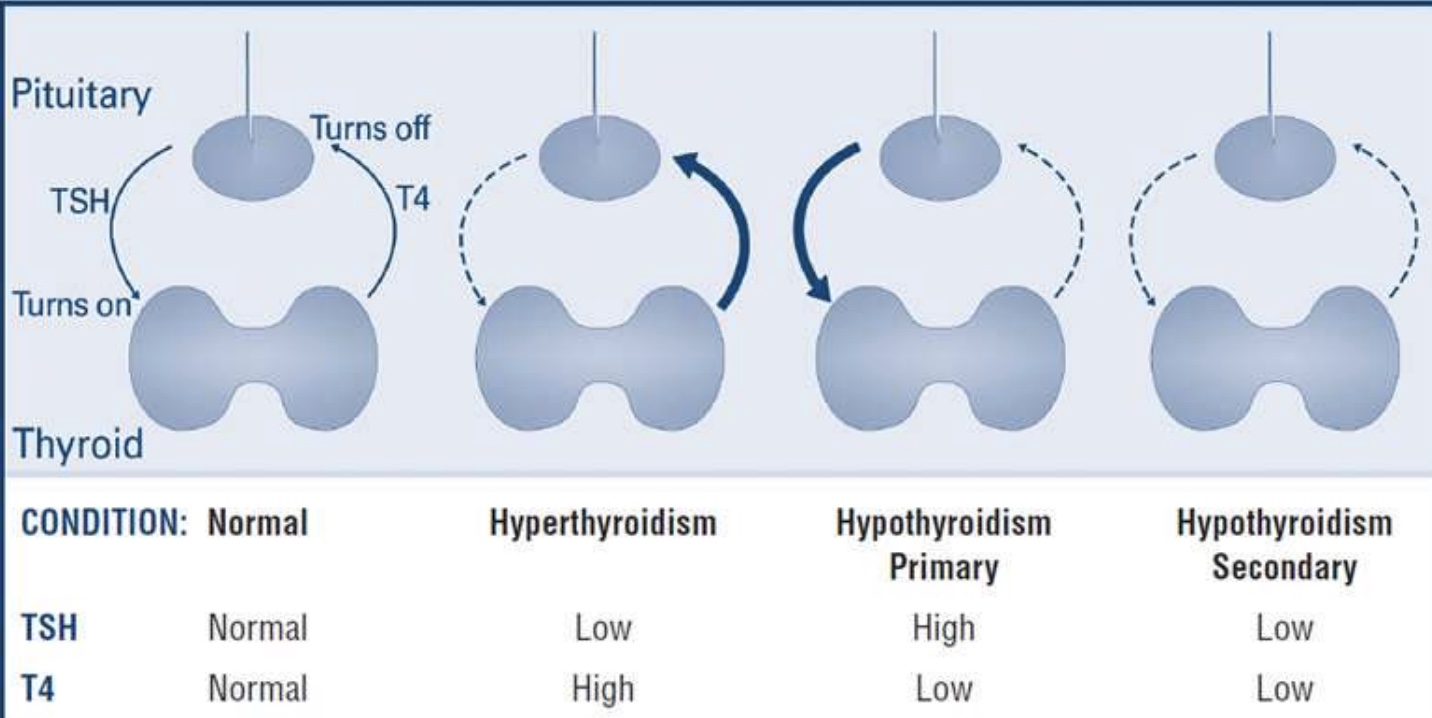
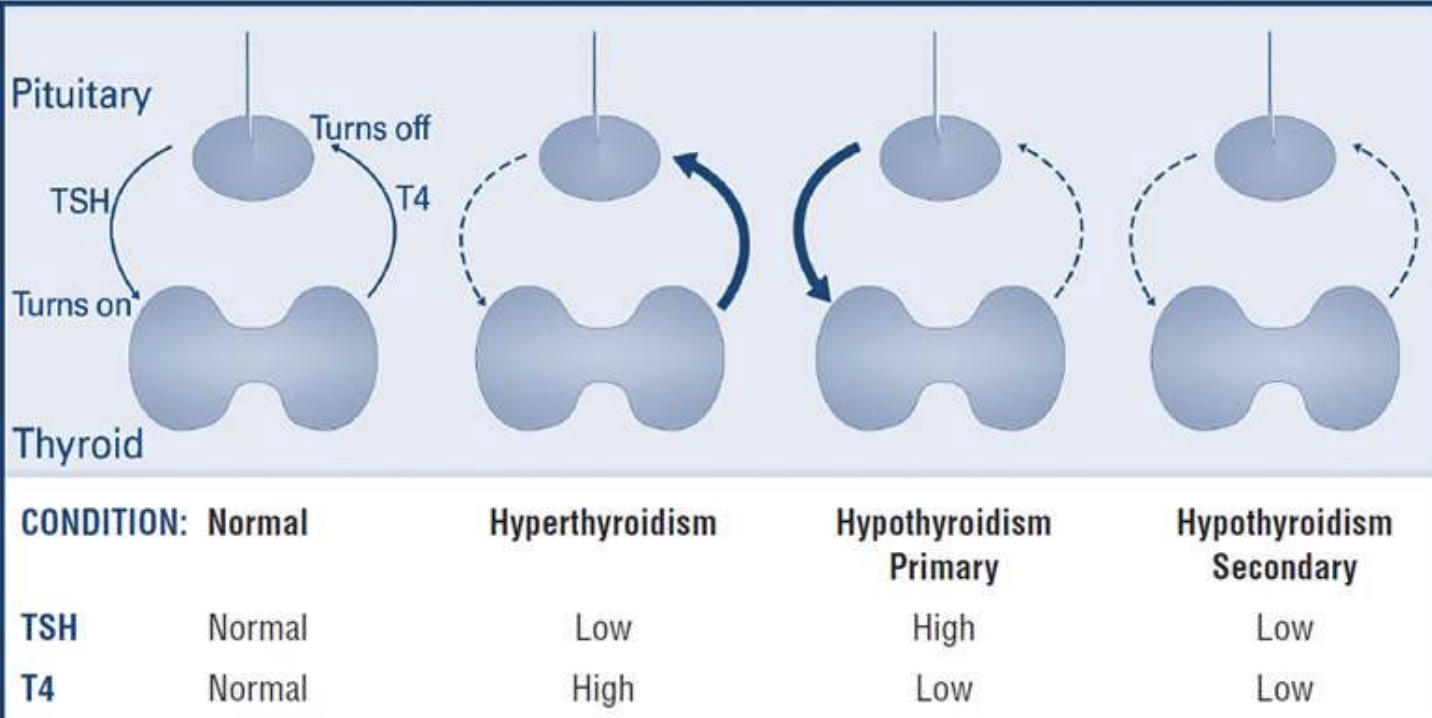
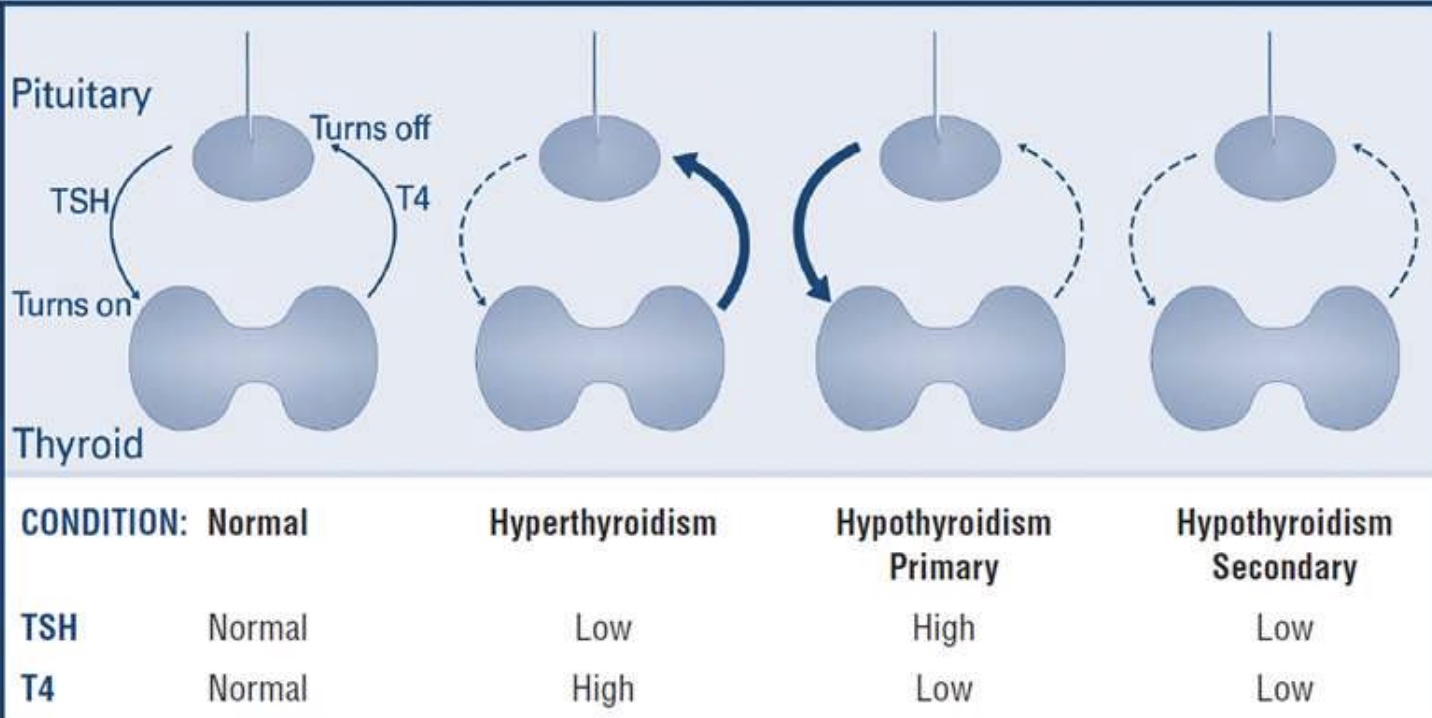
What is hypothyroidism primary?
When the TSH is high, and T4 is low
What are melanotrophs
A chromophobe that secretes melation secreting hormone
What is hypothyroidism secondary?
When both the TSH and the T4 is low
What is hyperthyroidism?
When the TSH is low and the T4 is high
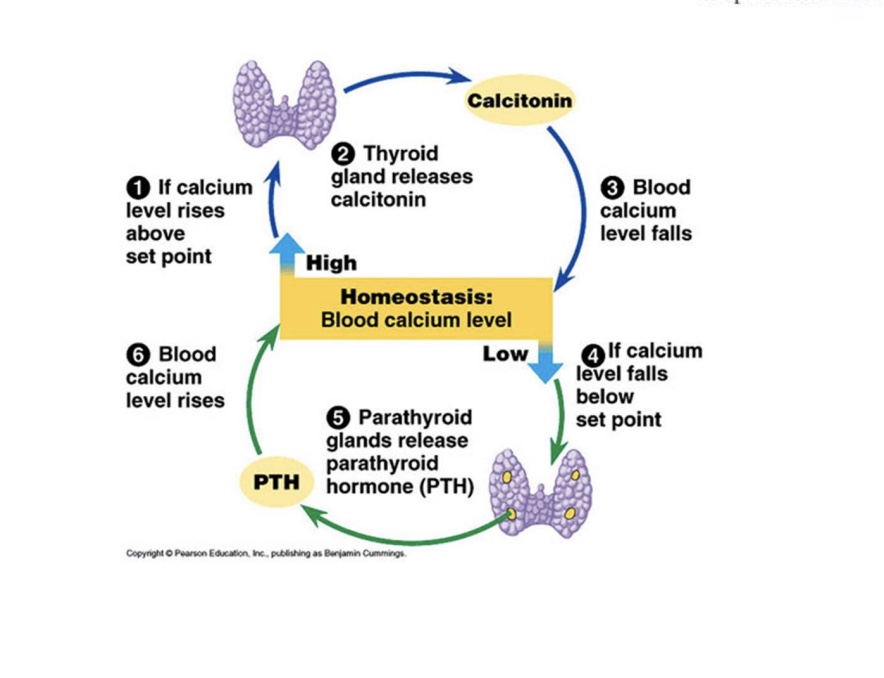
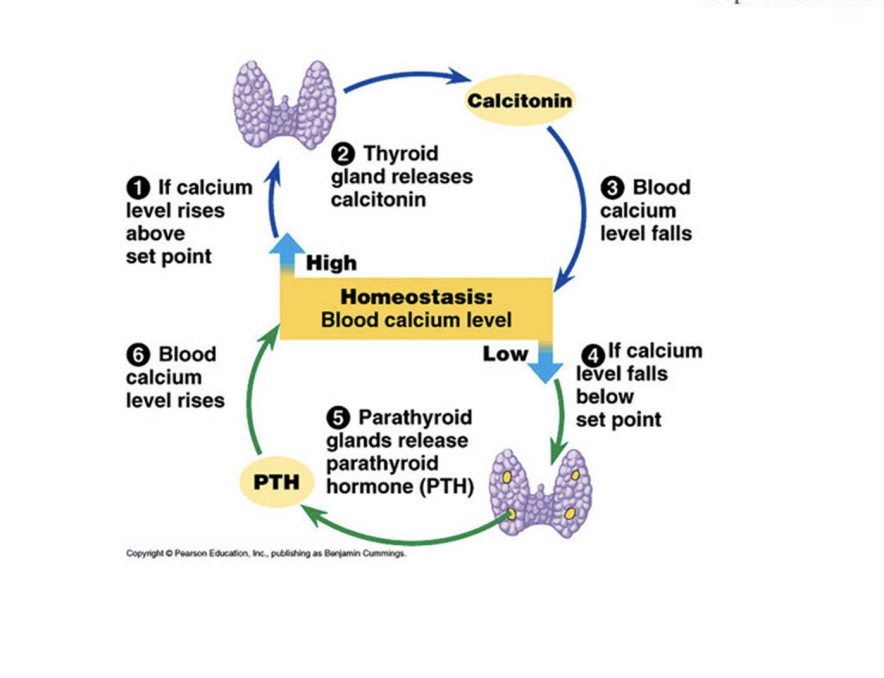
What happens if there’s an increase in the hormone to the bone kidney and the intestines
overall, this will cause an increase of calcium
In the bone, this will increase osteoblast
And the kidney this will increase absorption so you don’t pee it out
In the intestines, this activates vitamin D and increases absorption in the intestine
The steroid creates what
Sugar, salt and sex
Aldosterone
Cortisol
DHEA
Testosterone
Estrogen
So the key idea is:
What is cushioning disease?
Cushing disease = specifically pituitary ACTH tumor
High acth
Acidophil make up what percent of addendhypopsis
‘ 65%
What is Cushing syndrome?
Too much cortisol in the body (hypercortisolism)
The 3 signs (the “warning”)
High blood pressure (hypertension)
Slow heart rate (bradycardia)
Irregular breathing (abnormal respirations)
Somatotraphs are the first group of acidophils what do they secrete?
Growth hormones
MammotrophsAre the second group of aceta fills? Would they secret ?
Prolactin
Hereditary Elliptocytosis
E = Ellipse / Egg shaped
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Small round-no by concave shape
What is a neurophysin II
Carrier protein to transport antidiuretic to the posterior pituitary gland
A immature antidiuretic hormone is known as and what type of cell bodies is used to make it?
Known as a pro hormone when it’s immature
Supraoptic nucleus
What does vasopressin mean?
This is another name for adh this means blood vessel pressure which can also be known as vasoconstriction
Explain how vasopressin
Hypothalamus -pituitary gland-vasopressin-constriction in the blood vessels and kidney reabsorption
What does the thyroid hormones do?
Increased growth and metabolism: it increases basal metabolic rate and brings up bodily functions(like heart rate body temperature nervous reactivity)
Rage is apart of the neurotransmitter, but also the endocrine system
Rage is apart of the neurotransmitter, but also the endocrine system
Steroid hormones
are lipid-soluble (fat-soluble) hormones made from cholesterol.
They can pass through cell membranes and bind to receptors inside the cell (in the cytoplasm or nucleus) to change gene activity.
Difference between endocrine and nervous
Endocrine
chemical signals
slower hormones go everywhere
adapt slowlys
Nervous
chemical and electrical signals
response quickly and stops quickly
targets locally
What is the epithalamus?
The epithalamus is a small part of the diencephalon (the same brain region that includes the thalamus and hypothalamus).
Main structures
Pineal gland (most important one)
Habenular nuclei (sometimes included)
Main function
⭐ sleep/wake timing control. which releases melatonin.
Pinealocytes
Pinealocytes are the main cells in the pineal gland.
Produce and secrete melatonin, the hormone that helps control your sleep-wake (circadian) rhythm
What is a brain sand(corpora arenacea)?
Crystallized deposits are made of calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate.
This will increase with age
This can be found in the pineal gland
What is the pineal body surrounded by and its function
The pineal gland is covered by pia mater
The pia mater forms a capsule
That capsule sends connective tissue partitions inward into the pineal gland
What is a pineal gland consist of in terms of cell types
pinealocytes 95% large and Light Round nuclei
astrocytes dark elongated nuclei
What is the most prominent secretory product of the pineal body, and what does it do?
Melatonin; it has anti-gonadotrophic effects that may delay puberty by blocking gonadotropin (LH & FSH) secretion from the anterior pituitary, which reduces ovarian/testicular activity and affects reproductive development.\n
What is the prominent secretory product of the pineal body and what are the bad effects
Melatonin which can "delay" puberty through anti-gonadotrophic effect
anti-gonadotrophic = reduces or blocks hormones that normally stimulate the ovaries/testes, specifically:
Think will lock FSH and LH production
Melatonin effect/graphs?
Higher in kids
Lower in those who have autism
Lower in old people
Serotonin
What it does
Helps regulate mood
Neruotransmitetr
Helps regulate sleep
Affects appetite
Helps with digestion
Can cause vasoconstriction (tightening of blood vessels)
Pineal gland connection
The pineal gland uses serotonin to make melatonin.
It means the pineal gland affects your sleep cycle and seasonal mood changes because of the hormones it releases.
Breakdown:
Pineal hormones (mainly melatonin) act on the:
adenohypophysis = the anterior pituitary gland
and also affect sex hormones (LH/FSH → ovaries/testes)
So what does that cause?
Because melatonin changes based on light vs dark, the pineal gland helps control:
✅ Circadian rhythm = your daily sleep-wake cycle
✅ Seasonal phenomena = body changes based on seasons (more darkness in winter)
Example:
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
This is when people feel more depressed in winter because there’s less sunlight → more melatonin changes → affects mood/sleep.
It means the pineal gland affects your sleep cycle and seasonal mood changes because of the hormones it releases.
Breakdown:
Pineal hormones (mainly melatonin) act on the:
adenohypophysis = the anterior pituitary gland
and also affect sex hormones (LH/FSH → ovaries/testes)
So what does that cause?
Because melatonin changes based on light vs dark, the pineal gland helps control:
✅ Circadian rhythm = your daily sleep-wake cycle
✅ Seasonal phenomena = body changes based on seasons (more darkness in winter)
Example:
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
This is when people feel more depressed in winter because there’s less sunlight → more melatonin changes → affects mood/sleep.
What is the portal system?
A portal system is just a special set of blood vessels that carries hormones from:
Hypothalamus → Anterior pituitary
It’s like a direct hormone delivery highway.
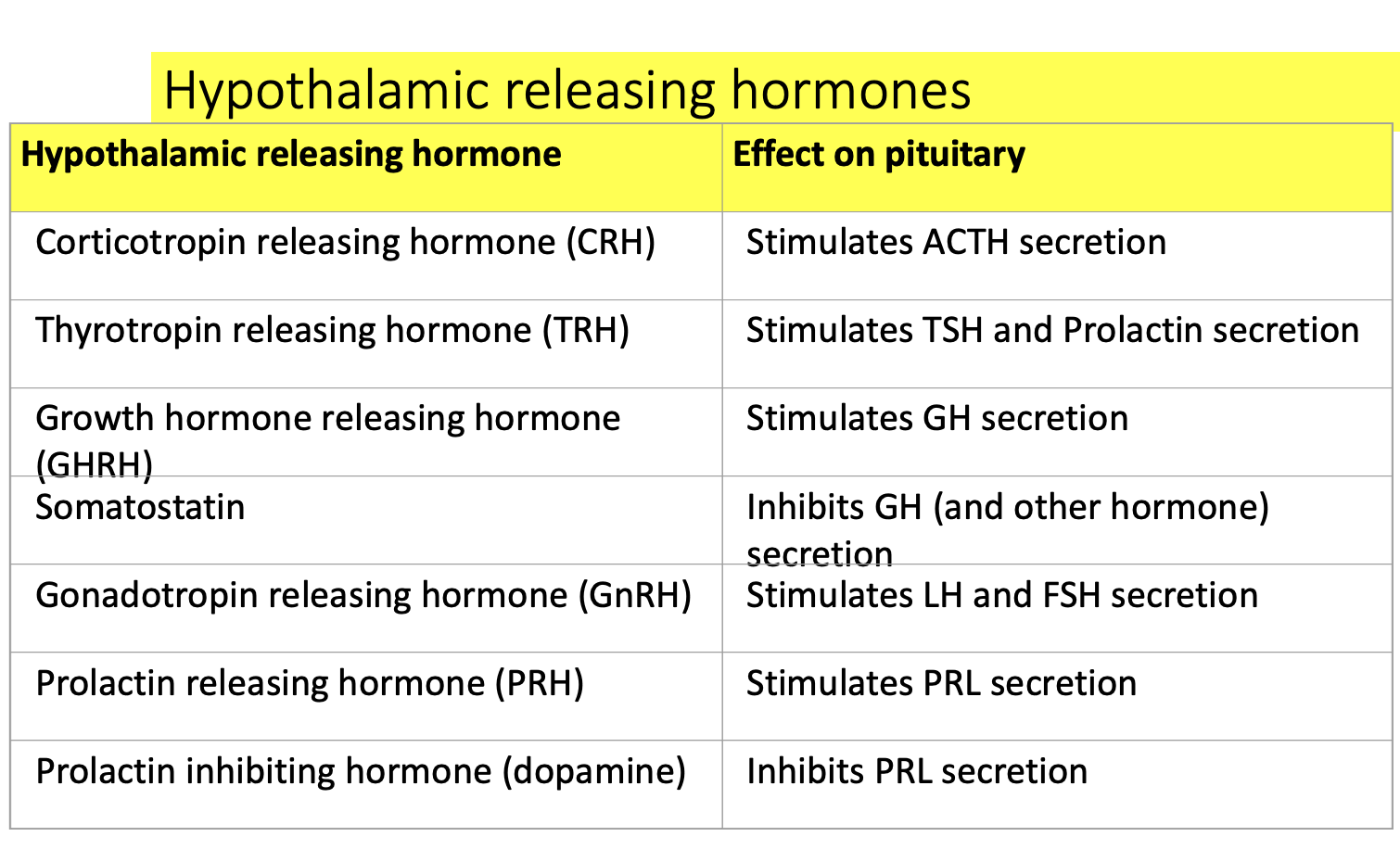
The hypothalamus releases 7 regulatory hormones (mostly releasing/inhibiting hormones)
And those control the anterior pituitary to release 8 hormones (like TSH, ACTH, GH, etc.)
What is Ghrelin
Ghrelin is a hormone that basically tells your brain:
“I’m hungry — feed me.” ✅ Where it’s made
Mostly in the stomach (especially when your stomach is empty)
✅ What it does
Increases appetite
Makes you feel hungry
Helps stimulate growth hormone (GH) release too
Easy way to remember
Ghrelin = “Grrr-lin”
Like your stomach growling: “grrrr” 😭
The hypothalamus sends two types of “messages”:
The hypothalamus sends two types of “messages”:
Releasing hormones
➡ tell the anterior pituitary: “RELEASE this hormone”
Inhibiting hormones
➡ tell the anterior pituitary: “STOP releasing this hormone”
These hormones go into blood capillaries at the base of the hypothalamus
hypophyseal portal system.
The hypophyseal portal system is a special set of blood vessels that carries hormones directly from the:
Hypothalamus → Anterior Pituitary
✅ Why it exists
So the hypothalamus can control the anterior pituitary FAST and without the hormones getting diluted in the rest of the bloodstream.
✅ What travels in it
The hypothalamus sends:
releasing hormones
inhibiting hormones
through this portal system to tell the anterior pituitary what to release.
⭐ Easy way to remember
Portal system = a direct blood “shortcut” between two organs.
What are Paravocellular Neurosecretory
Parvocellular neurons in the hypothalamus make releasing/inhibiting hormones → put them into blood → blood carries them to the anterior pituitary → anterior pituitary releases hormones that control other glands.
what are basophils
Anterior pituitary cells
Stain blue/purple
Produce the main tropic hormones
Tropic hormones stimulate other endocrine glands
Acidophils
Anterior pituitary cells
Stain pink/red
Produce GH and PRL
These hormones are mostly direct-acting (not tropic)
Releasing and Inhibiting hormones

glycoprotein hormones
proteins with sugar attached
(glyco = sugar)
Fat like Tish = FSH, LH, TSH
So they’re grouped based on their structure, not their target.
These are the actual proteins, not the transportation
Somatomammotropins
Somato- = body growth Mammo- = breast/milk -tropin = hormone
So:
GH = somato (growth)
PRL = mammo (milk)
And they’re grouped together because they’re structurally similar hormones.
Corticolipotropins
Corticolipotropins = a hormone family group (NOT a cell type)
The hormones in this group are:
ACTH
MSH (melanocyte-stimulating hormone)
They are grouped together because they both come from the same precursor protein:
POMC (proopiomelanocortin)(parent hormone)
Corticotrophs (or adrenocorticolipotrophs)
secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotropin) and lipotropin (LPH, no known function in humans).
Synthesis products of POMC
ACTH and MSH
Addison’s diseases
In Addison’s disease:
cortisol is low → body makes more ACTH
more ACTH = more POMC being used
more POMC = more MSH
so you get darker skin
So the chain is:
Addison’s → ↑ ACTH → ↑ MSH → darker skin
•Glycoprotein hormones subunits
These hormones are like 2-piece Legos:
an alpha piece
a beta piece
The alpha piece is the SAME for all of them.
The beta piece is DIFFERENT, and that’s what makes it:
FSH vs LH vs TSH
So the beta subunit = the “name tag” that tells your body which hormone it is.
hCG (pregnancy hormone) is similar because it also has:
the same alpha
its own beta
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
a hormone made during pregnancy (by the placenta).
It is structurally related to the glycoprotein hormones because it is built the same way:
2 subunits (alpha + beta)
hCG has the same alpha subunit as:
FSH, LH, TSH
But hCG has a different beta subunit, which makes it its own hormone.
Somatomammotropins: Growth Hormone (GH)
Secretion pattern of GH (mainly):
Released in a pulsatile pattern (not steady)
Comes out in bursts about every 2 hours
Bursts increase during:
exercise
sleep
Main functions of GH:
Increases linear growth (height / bone growth)
Increases muscle mass
How GH causes growth:
GH stimulates the liver and other tissues to produce somatomedins
Somatomedins = IGFs (insulin-like growth factors)
IGFs are what actually cause a lot of the growth effects
Diabetogenic effect (this is important):
GH can cause insulin resistance
“diabetogenic” means:
GH can raise blood sugar
GH can make you more likely to have diabetes-like effects
GH increases blood glucose
Chromophobe cells
Chromophobes are pituitary cells that are pale cells that are inactive OR empty after releasing hormones
They don’t stain red or purple because they have no visible hormone granules
Most of the time, chromophobes are just:
acidophils or basophils that already released their hormones
(so they look “washed out”)
They can also be:
resting/dormant cells
stem cells
Chromophobe" also refers to a type of renal cell carcinoma (distinct from "clear cell")
30% of patients with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome will also develop chromophobe renal cancer.
Chromophobe" also refers to a type of renal cell carcinoma (distinct from "clear cell")
30% of patients with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome will also develop chromophobe renal cancer.
Types of Chromophobe Cell
Amphophils
They’re called chromophobe-ish because they don’t stain strongly as red or purple
But they are still pituitary epithelial cells
They can still be involved in hormone production
Melanotrophs
These are cells that make MSH
They may look pale on regular staining
But they still secrete hormone
The posterior pituitary consists of 3 parts:
Pars nervosa (main posterior pituitary part)
Infundibular stalk (the stalk connecting it)
Median eminence (part at the base of hypothalamus)
ADH (antidiuretic hormone) = vasopressin
regulate water balance: You get thirstier, which increases the volume which is connected to the kidney, and it makes you pee
Where ADH is made (synthesis site):
Supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus
(the neuronal cell bodies there synthesize it)
Oxytocin
Causes uterine smooth muscle contraction (labor)
Also causes milk letdown (squeezes milk out)
Vasopressin (ADH) effects
Vasoconstriction
tightens blood vessels
helps raise blood pressure
Concentrates urine (MAIN effect)
tells kidneys to reabsorb water
makes urine more concentrated
Gluconeogenesis
helps the body make new glucose (usually in the liver)
Platelet aggregation
helps platelets clump together for clotting
Release of Factor VIII + vWF (von Willebrand factor)
helps with blood clotting
Effects on brain
ADH also acts in the brain to help with water balance/thirst
Estrogen increases oxytocin effects
Estrogen makes the uterus more sensitive to oxytocin
So when oxytocin is released, the uterus contracts stronger
Estrogen also helps prepare the breasts for lactation
“Messages increase oxytocin”
This means oxytocin can rise with social bonding (hugging, affection, trust, emotional connection)
Oxytocin isn’t only for pregnancy — it’s also a “bonding” hormone
Prostaglandins (not “prostat gulin”)
Prostaglandins can cause cramps, bloating, mood changes, and PMS-like symptoms
They stimulate uterine contractions, which is why periods can hurt
Estrogen increases oxytocin effects
Estrogen makes the uterus more sensitive to oxytocin
So when oxytocin is released, the uterus contracts stronger
Estrogen also helps prepare the breasts for lactation
“Messages increase oxytocin”
This means oxytocin can rise with social bonding (hugging, affection, trust, emotional connection)
Oxytocin isn’t only for pregnancy — it’s also a “bonding” hormone
Prostaglandins (not “prostat gulin”)
Prostaglandins can cause cramps, bloating, mood changes, and PMS-like symptoms
They stimulate uterine contractions, which is why periods can hurt
When there is too much growth hormone in kids its called
in kids (before the growth plates close) is called:
Gigantism
The most common cause is a:
pituitary adenoma (a benign tumor in the anterior pituitary)
So
Too much GH in adults
Too much GH in adults (after growth plates are closed) is called:
Acromegaly
It happens because GH is hypersecreted (released too much), usually from a pituitary adenoma.
Since adults can’t grow taller anymore, GH causes bones and tissues to enlarge/thicken instead of lengthening.
Cretinism
This is when a baby has too little thyroid hormone (T3/T4) during development
Causes: thyroid gland not formed, iodine deficiency, or maternal thyroid issues
Effects: poor brain development (intellectual disability), stunted growth, big tongue (macroglossia), puffy face, big belly/umbilical hernia
Myxedema (adult hypothyroidism)
Severe hypothyroidism in adults
Symptoms: fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, slow heart rate, depression, puffy skin (non-pitting edema)
Toxic goiter (hyperthyroidism, often Graves disease)
Thyroid becomes overactive → high T3 and T4
Symptoms: weight loss, heat intolerance, anxiety, fast heart rate
The eye bulging (exophthalmos) happens especially in Graves disease
The thyroid tissue is usually hyperactive, not just “big follicles”
Thyroid Hormone
Quick answer: Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) increase growth and metabolism.
More detailed: T3/T4
stimulate mitochondrial protein synthesis → cells make more energy
increase carbohydrate absorption and use → more glucose is used for energy
regulate fat metabolism → increase fat breakdown
promote cell growth and development (especially brain + bone in kids
Goitrogens
food substances that block iodine use
. The only biological role of iodine is
Formation of
T4 (thyroxine)
T3 (triiodothyronine)
Cabbage and tapioca contain
thiocyanate
blocks iodine uptake into the thyroid
Mustard seeds contain
thiourea
blocks iodination of thyroglobulin (so thyroid hormones can’t be made well)
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3) are the main thyroid hormones
They:
increase the rate of energy release from carbohydrates (boost metabolism)
increase the rate of protein synthesis
accelerate growth (especially in kids)
stimulate activity in the nervous system (more alert/reactive)
Their release is controlled by:
TSH (from the anterior pituitary)
Calcitonin is another thyroid hormone (made by C cells / parafollicular cells)
Calcitonin is another thyroid hormone (made by C cells / parafollicular cells)
Calcitonin:
lowers blood calcium and blood phosphate levels
does this by inhibiting release of calcium/phosphate from bones
increases deposition of calcium/phosphate into bones (helps build bone