active 17 fuck my life
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is gene expression
process where a gene’s dna is used to make rna and proteins
what is transcription
copying of dna to mrna
what is translation
reading mrna to make a protein
Three ways RNA differs from DNA
Different sugar
Different nitrogen base
Different structure
monomer of dna and rna
nucleotide
monomer of protein
amino acid
transcription product synthesized
mRNA
transcription template
DNA
transcription location in euk cell
nucleus
translation template
mRNA
translation product synthesized
protein (polypeptide)
translation location in euk cell
cytoplasm on ribosome
central dogma
genetic information flowing from DNA to RNA by transcription and from RNA to protein by translation
proteins are made up of
amino acids
how many different types of amino acids are used in protein synthesis
20 amino acids
in what organ in humans is the crystallin gene expressed
lens of the eye
what is produced when crystallin gene is expressed
crystallin proteins
crystallin protein function
maintain lens transparency and focus light onto retina
three main types of crystallin
alpha beta gamma (a b y)
do skin cells have the crystallin gene?
yes, but no expression, only lens cells activate genes
dna letters
atcg
rna letters
aucg
how is rna different from DNA
single stranded, in nucleus and cytoplasm, carries and translates genetic info
how many nucleotides in a codon
three
how many total codons are there in dna langauge
64
which dna strand is used to produce mRNA transcript
template strand
is dna single or double stranded
double, but only template strand is used during transcription to make mRNA
two strands of dna and function
template strand, used to make mRNA
coding strand, matches mRNA sequence
dna to mrna A turns into
U
dna to mrna T turns into
A
dna to mrna C turns into
G
dna to mrna G turns into
C
what are codons
group of three nucleotides in mRNA that tell the cell which amino acid to add
how many codons code for amino acids
61
stop codons
UAA UAG UGA
where is the start codon
AUG
Which amino acid does AUG code for
Met, start codon that signals beginning of protein synthesis
why is genetic code redundant and not ambiguous
redundant because multiple codons can code for same amino acid
not ambiguous because each codon always codes for only one specific amino acid
what is a reading frame
way nucleotides in mRNA are grouped into codons during translation
what happens when reading frame is shifted
all codons change, producing wrong amino acids
what sets the correct reading frame
start codon AUG
where does the amino acid attach on t RNA
3’ end
where is the anticodon located
bottom loop of tRNA molecule
what is an anticodon
set of three nucleotides on a tRNA molecule that pairs with complementary codon on mRNA during translation
anticodon example if mrna is aug trna is
uac
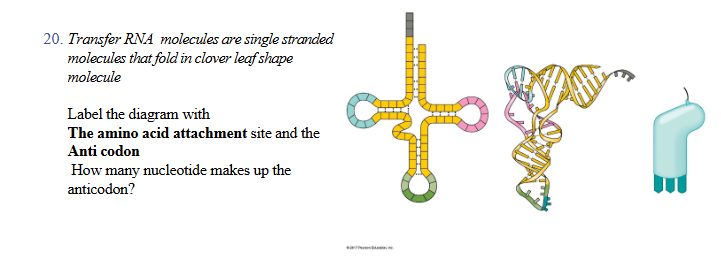
top of clover
3’ end of trna where a specific amino acid binds
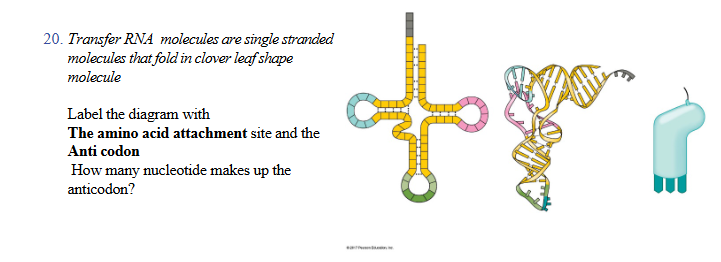
bottom of clover green loop
anticodon loop, three bases forming anticodon
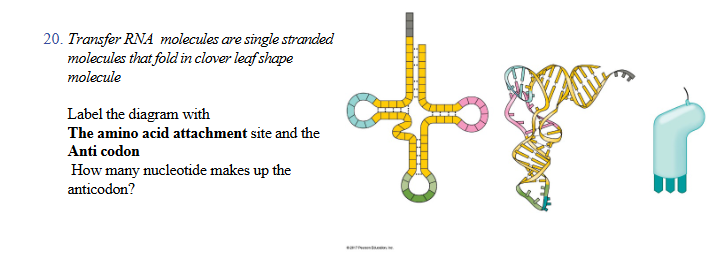
middle pink blue loop
D loop and TYC loop, helps molecule fold properly and interact with ribosome
left groove of large subunit
e site, trna exits
middle groove of large subunit
p site, peptidyl site holds tRNA with growing peptide chain
right groove of large subunit
A site, aminoacyl, entry site where tRNA carrying new amino acid binds to mRNA codon
what are two units of euk ribosome
large 60s small 40s
total size of euk ribosome
80s
mrna description
single stranded copy of a gene made during transcriptionm
mrna function
carry genetic code from dna to ribosome
trna description
cloverleaf shaped molecule with anticodon and aminoacid attachment site
trna function
bring correct amino acid to ribsome by matching anticodon to mrna codon
rrna description
structural rna that combines with proteins to form ribosomes
rrna function
form ribosome and catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acid
why is anticodon important during protein synthesis
ensures correct amino acid is added to growing protein chain
enzyme that uses dna template strand to transcribe new mrna strand, doesnt require primer
rna pol
what is a transcription unit
stretch of dna that is transcibred into rna by rna pol
promoter
where rna pol binds and starts transcription
the gene of transcription unit
part that is actually copied into rna
terminator of transcription unit
sequence that signals rna pol to stop transcription