Unit 6 AP Psychology
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
developmental psychology
a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span

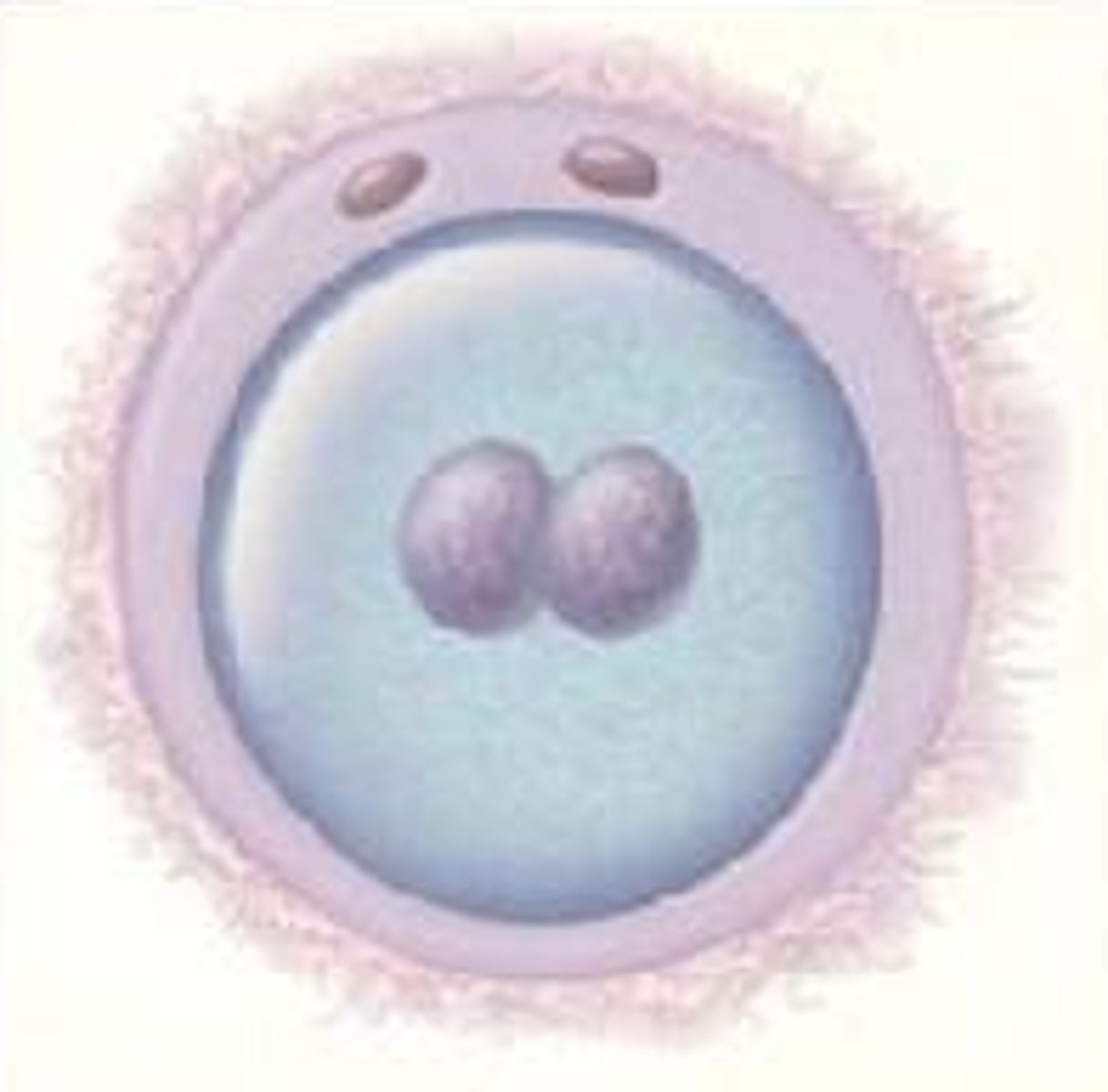
zygote
the fertilized egg; it enters a 2-week period of rapid cell division and develops into an embryo
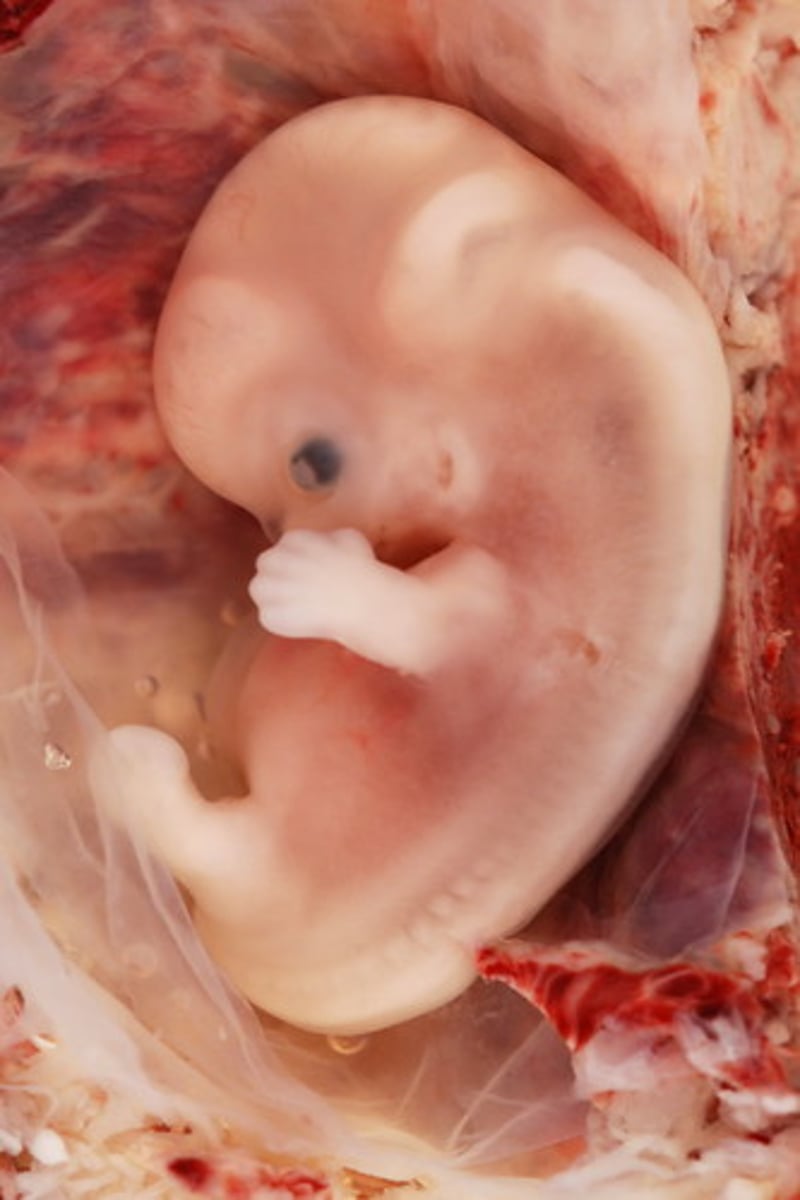
embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month
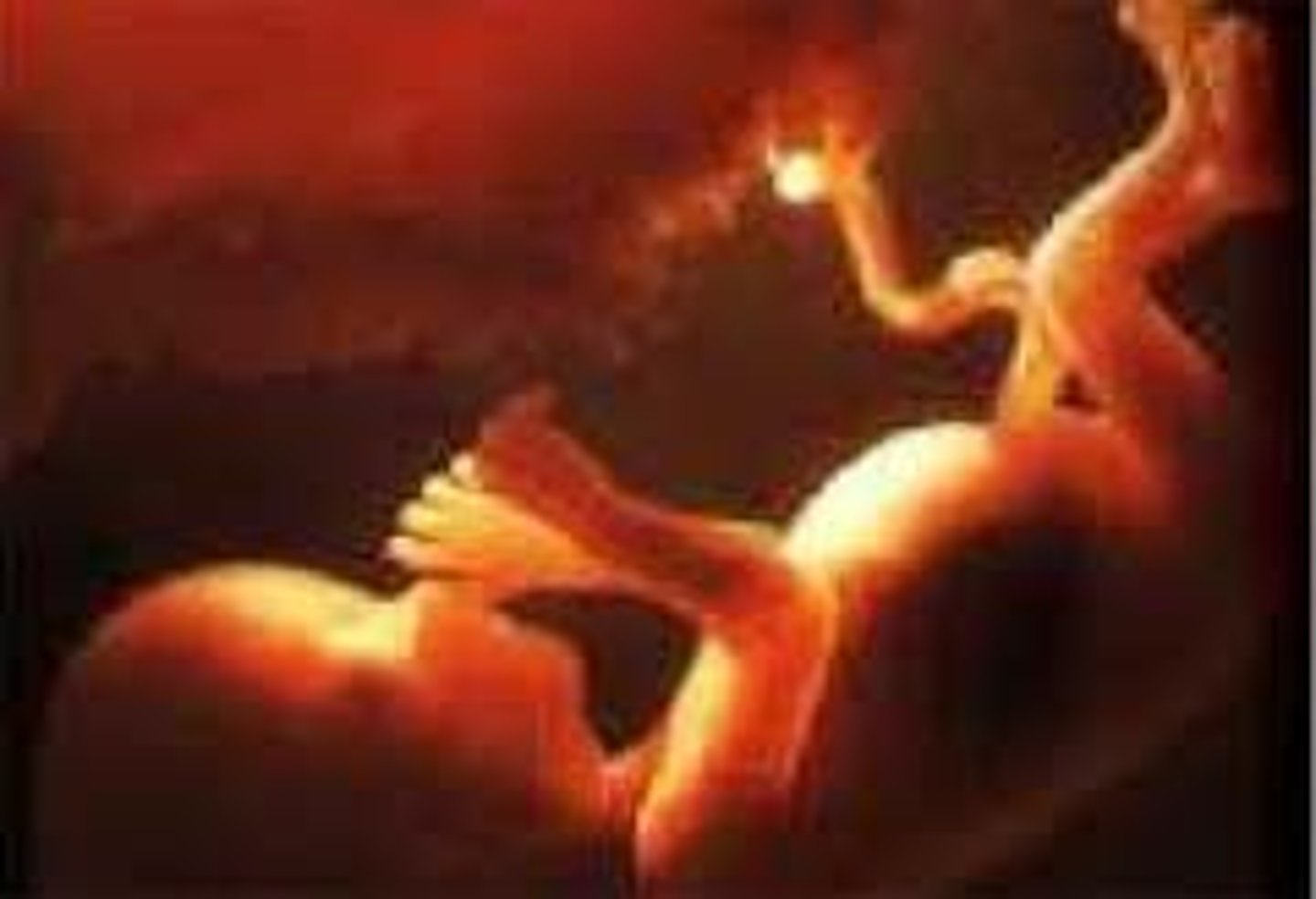
fetus
the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth
teratogens
(literally, "monster maker") agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking. In severe cases, signs include a small, out-of-proportion head and abnormal facial features.

habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.
maturation
biological growth processes that enable in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating

schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
accommodation
adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
sensorimeter stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities
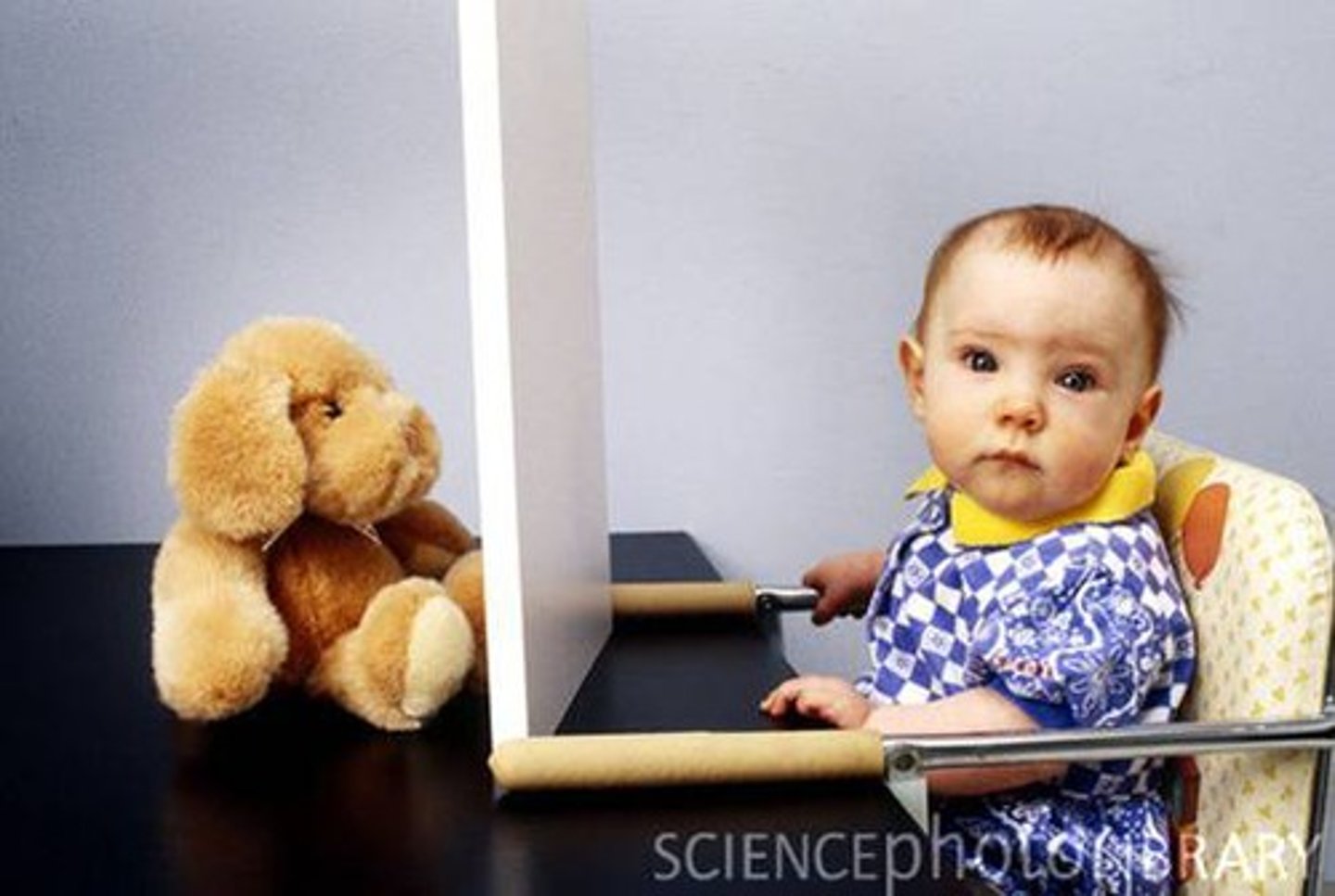
object permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived

preoperational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from about 2 to 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic
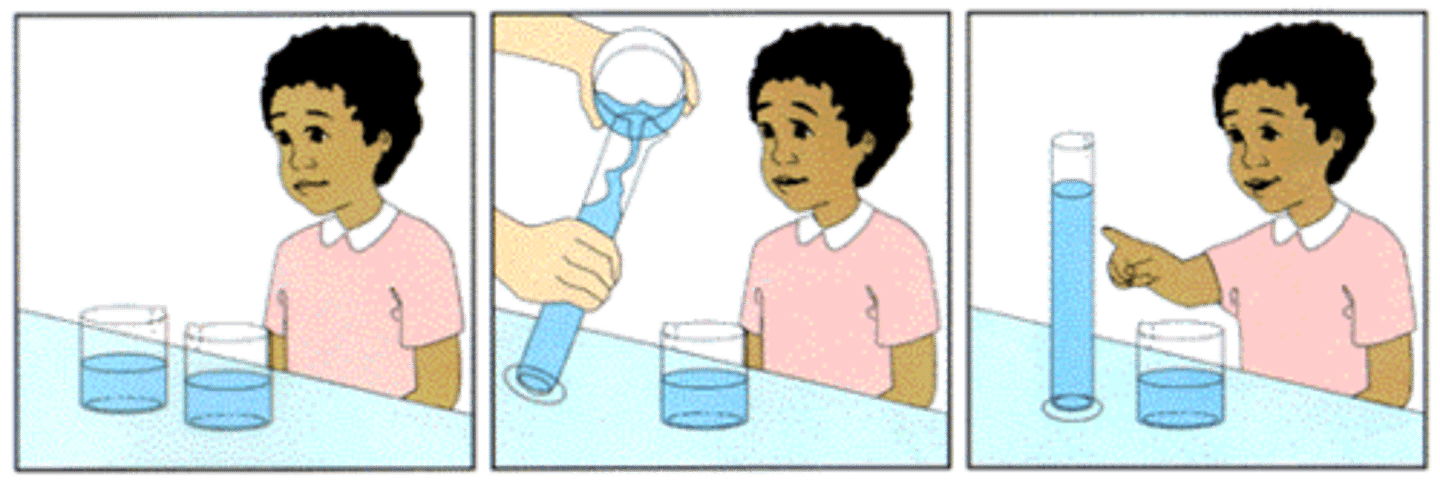
conservation
the principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects

Egocentrism
in Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view
theory of mind
people's ideas about their own and others' mental states—about their feelings, perceptions, and thoughts, and the behaviors these might predict.
conrete operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events
formal operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts
scaffold
a framework that offers children temporary support as they develop higher levels of thinking
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by significant deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and by rigidly fixated interests and repetitive behaviors
stranger anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age

attachment
an emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to their caregiver and showing distress on separation

critical period
an optimal period early in the life of an organism when exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces normal development
imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life

strange situation
A laboratory procedure for measuring attachment by evoking infants' reactions to the stress of various adults' comings and goings in an unfamiliar playroom.
secure attachment
demonstrated by infants who comfortably explore environments in the presence of their caregiver, show only temporary distress when the caregiver leaves, and find comfort in the caregiver's return
insecure attachment
demonstrated by infants who display either a clinging, anxious attachment or an avoidant attachment that resists closeness
temperament
a person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
basic-trust
according to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers
self-concept
all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, "Who am I?"
sex
in psychology, the biologically influenced characteristics by which people define males and females
gender
in psychology, the socially influenced characteristics by which people define boy, girl, man, women.
aggression
any physical or verbal behavior intended to harm someone physically or emotionally
relational aggression
an act of aggression (physical or verbal) intended to harm a person's relationship or social standing
role
a set of expectations (norms) about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave
gender role
a set of expected behaviors, attitudes, and traits for males or for females
gender identity
our sense of being male, female, or some combination of the two
social learning theory
the theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
gender typing
the acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role
androgyny
displaying both traditional masculine and feminine psychological characteristics
transgender
an umbrella term describing people whose gender identity or expression differs from that associated with their birth sex
adolescence
the transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence

puberty
the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
identity
one's sense of self; according to Erikson, the adolescent's task is to solidify a sense of self by testing and integrating various roles
social identity
the "we" aspect of our self-concept; the part of our answer to "Who am I?" that comes from our group memberships
intimacy
in Erikson's theory, the ability to form close, loving relationships; a primary developmental task in young adulthood
emerging adulthood
a period from about age 18 to the mid-twenties, when many in Western cultures are no longer adolescents but have not yet achieved full independence as adults
X chromosome
The sex chromosome found in both men and women. Females have two X chromosomes; males have one. An X chromosome from each parent produces a female child.
Y chromosome
the sex chromosome found only in males. When paired with an X chromosome from the mother, it produces a male child.
testosterone
the most important of the male sex hormones. Both males and females have it, but the additional testosterone in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs in the fetus and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty
primary sex characteristics
the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
secondary sex characteristics
nonreproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair
spermarche
first ejaculation
menarche
the first menstrual period
intersex
a condition present at birth due to unusual combinations of male and female chromosomes, hormones, and anatomy; possessing biological sexual characteristics of both sexes
AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome)
a life-threatening, sexually transmitted infection caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). AIDS depletes the immune system, leaving the person vulnerable to infections.
sexual orientation
an enduring sexual attraction toward members of either one's own sex (homosexual orientation) or the other sex (heterosexual orientation); variations include attraction toward both sexes (bisexual orientation).
menopause
the time of natural cessation of menstruation; also refers to the biological changes a woman experiences as her ability to reproduce declines
cross-sectional study
research that compares people of different ages at the same point in time
longitudinal study
research that follows and retests the same people over time
neurocognitive disorders
acquired (not lifelong) disorders marked by cognitive deficits; often related to Alzheimer's disease, brain injury or disease, or substance abuse. In older adults neurocognitive disorders were formerly called dementia
Alzheimer's disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning
social clock
the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
Sigmund Freud
Developed psychoanalysis; considered to be "father of modern psychiatry"

Jean Piaget
Known for his theory of cognitive development in children

Lev Vygotsky
child development; investigated how culture & interpersonal communication guide development, zone of proximal development; play research

Harry Harlow
Studied attachment in monkeys with artificial mothers with Margaret Harlow

Margaret Harlow
Experimented with infant baby monkeys with Harry Harlow
Konrad Lorenz
researcher who focused on critical attachment periods in baby birds, a concept he called imprinting

Mary Ainsworth
developmental psychology; compared effects of maternal separation, devised patterns of attachment; "The Strange Situation": observation of parent/child attachment
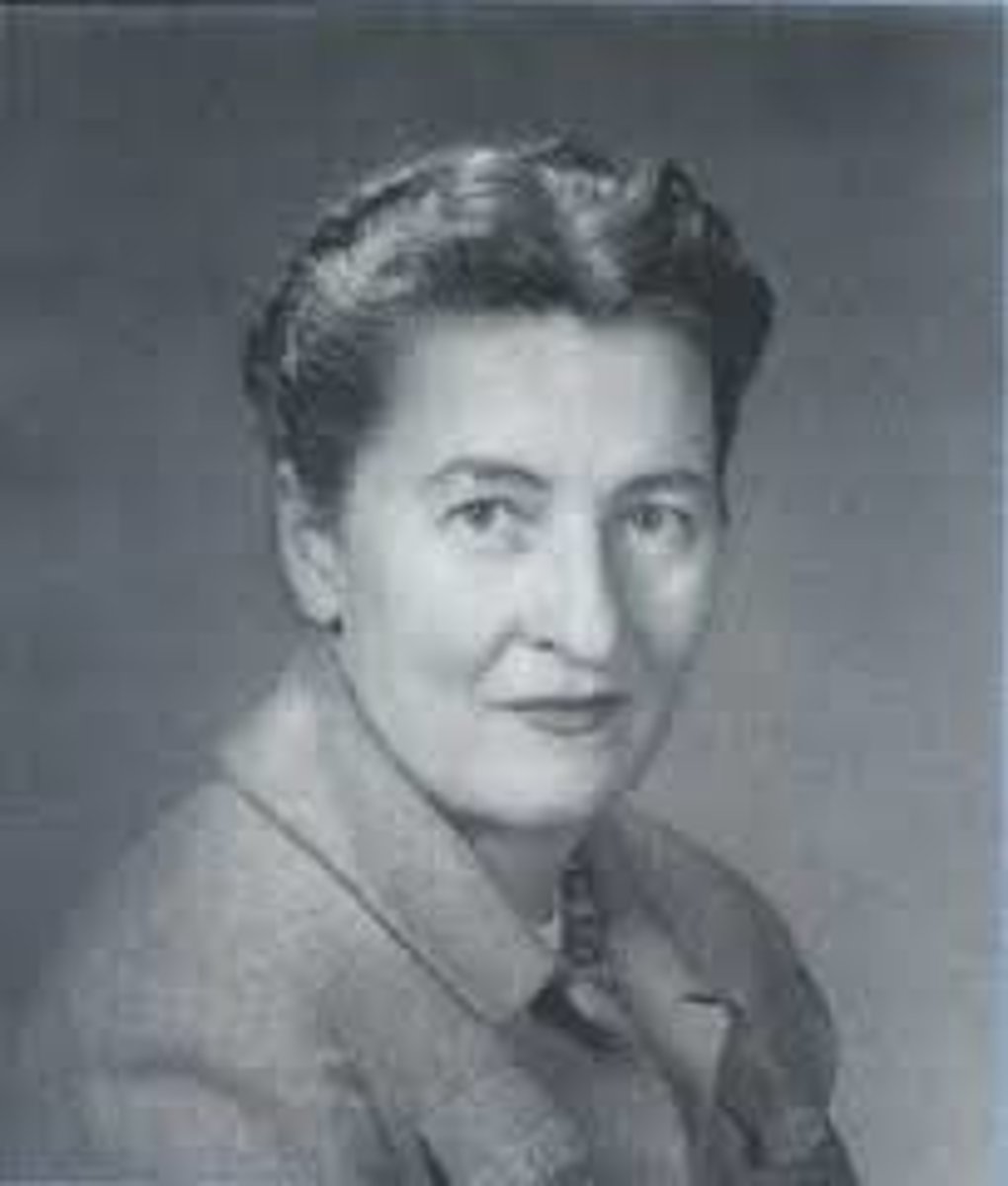

Erik Erikson
basic trust; expanded psychoanalytic theory by exploring development throughout life, including events of childhood, adulthood, and old age
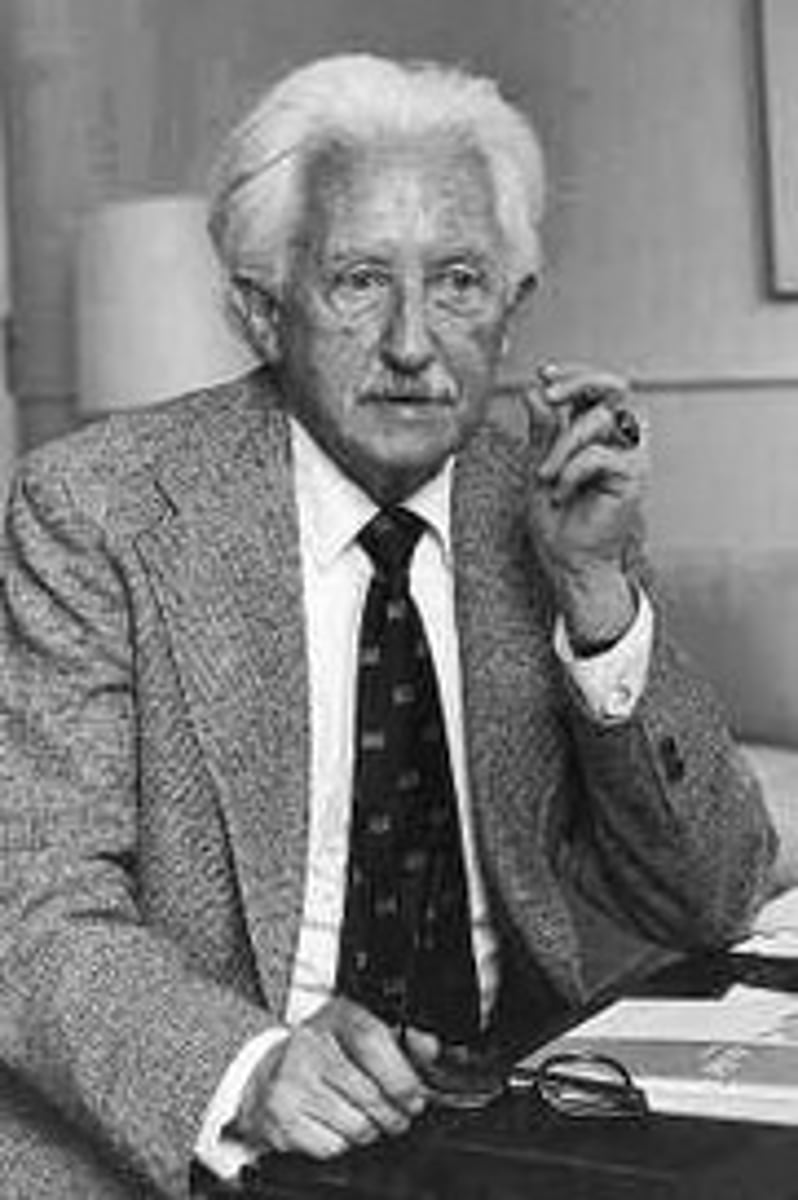

Diana Baumrind
researcher who developed a model of parenting styles that included authoritarian, authoritative, and permissive
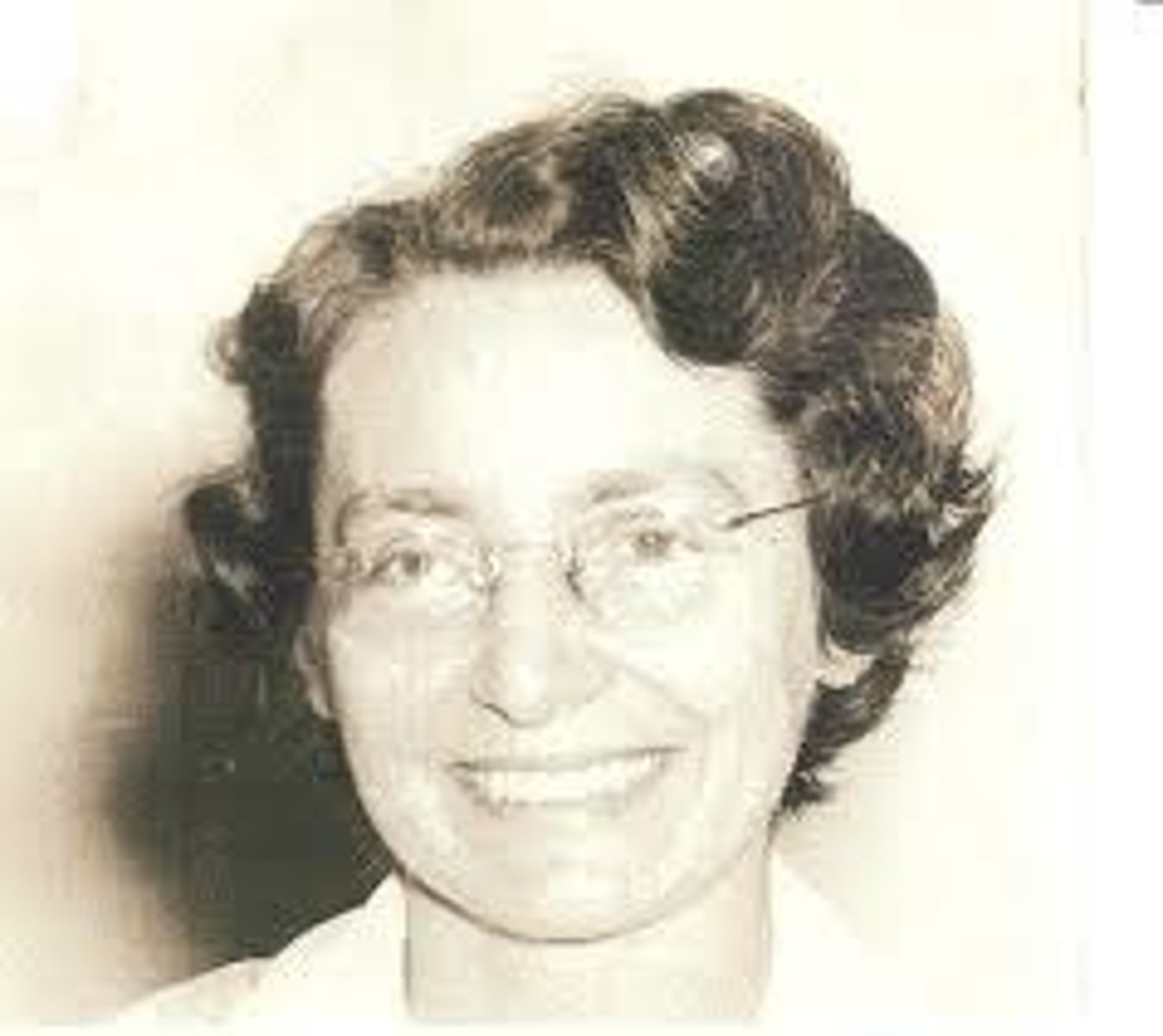

Carol Gilligan
argued that girls exhibit distinct patterns of moral development based on relationships and on feelings of care and responsibility for others; moral development studies
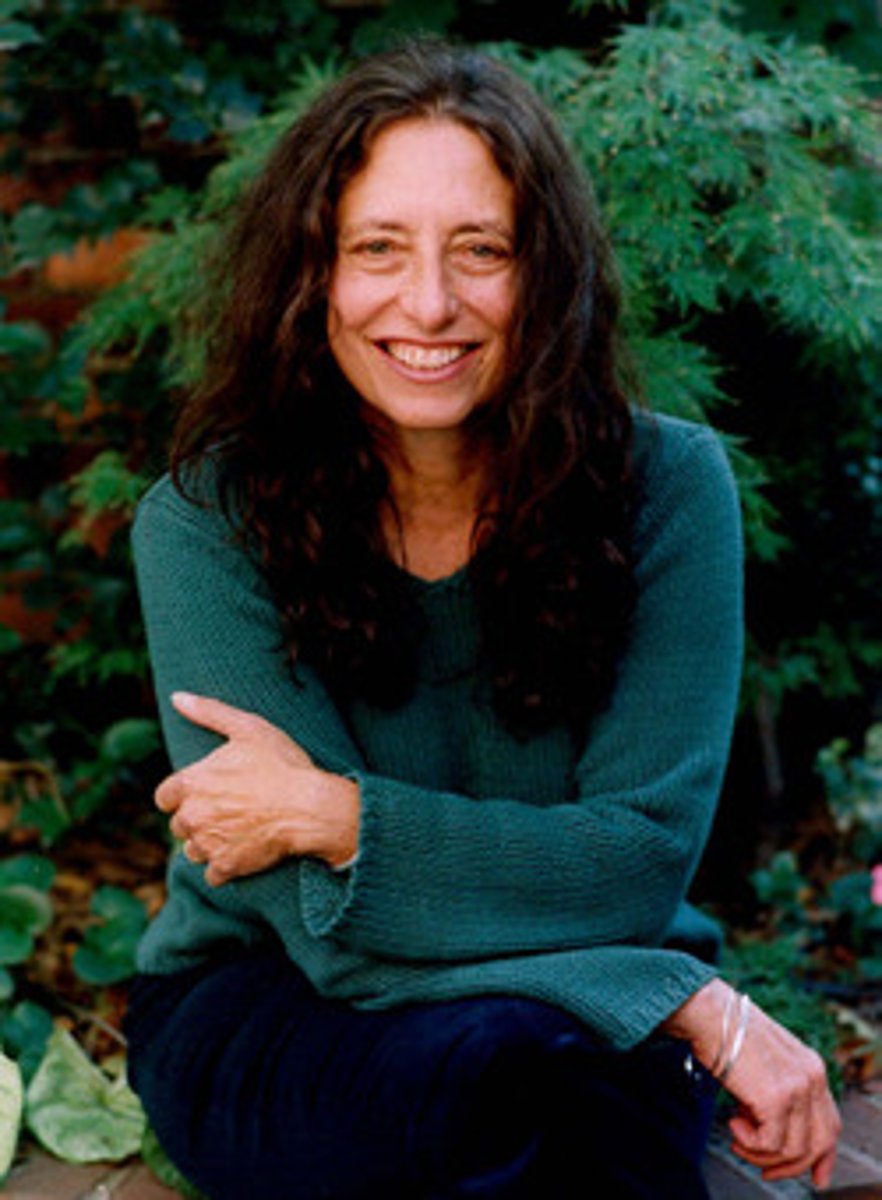

Albert Bandura
Famous for the Bobo Doll experiments on observational learning & influence in the Socio-Cognitive Perspective

Lawrence Kohlberg
Famous for his theory of moral development in children; made use of moral dilemmas in assessment; moral reasoning guides moral actions
