Organic Chemistry Introduction IGCSE Chemistry
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Introduction to organic chemistry IGCSE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is organic chemistry?
The scientific study of the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds. (this does not include carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide or metal carbonates)
What is an organic compound
A chemical compound that contains carbon
Hydrocarbon definition and example
Definition: A compound that only contains hydrogen and carbon
Example: An alkane
How can organic compounds be shown? (5)
Empirical Formulae
Molecular Formulae
General Formulae
Structural Formulae
Empirical formulae and example
Shows the simplest possible ratio of the atoms in a molecule
For example: Hydrogen peroxide is H2O2 but the empirical formula is HO
Molecular formula and example
Shows the actual number of atoms in a molecule
For example:
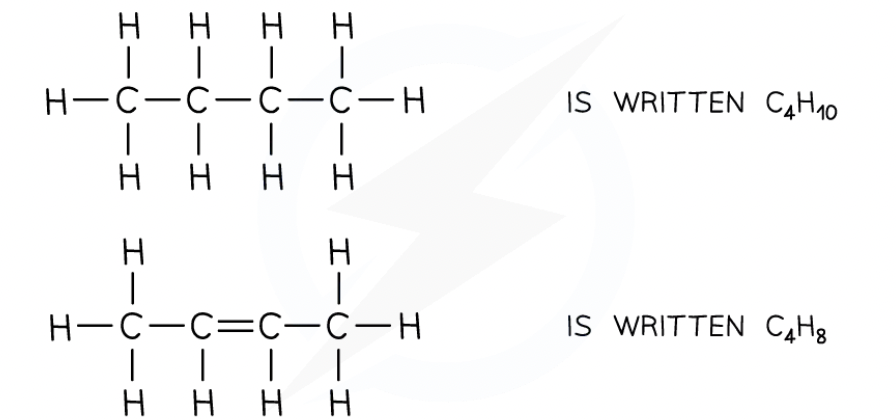
General formula and example
Shows a ratio of atoms in a family of compounds in terms of ‘n’ where n is a varying whole number
For example, the general formula of a molecule that belongs to the alkane family is CnH2n+2
Displayed formula and example
shows the spatial arrangement of all the atoms and bonds in a molecule - this is also known as the graphical formula.
For example:
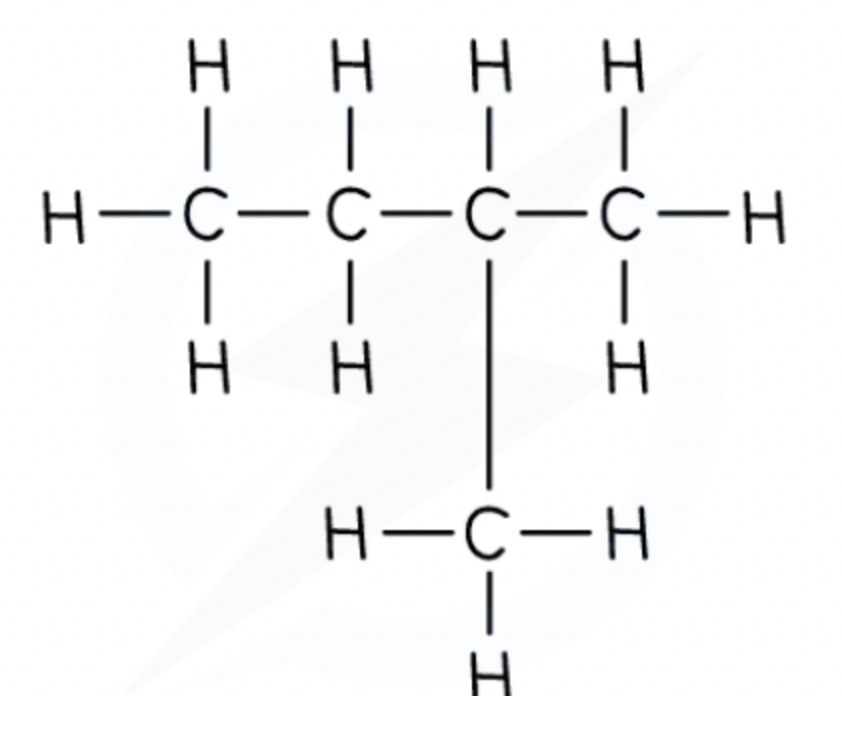
Functional Group
A group of atoms bonded in a specific arrangement that influences the properties of the homologous series
Examples of functional groups (6)
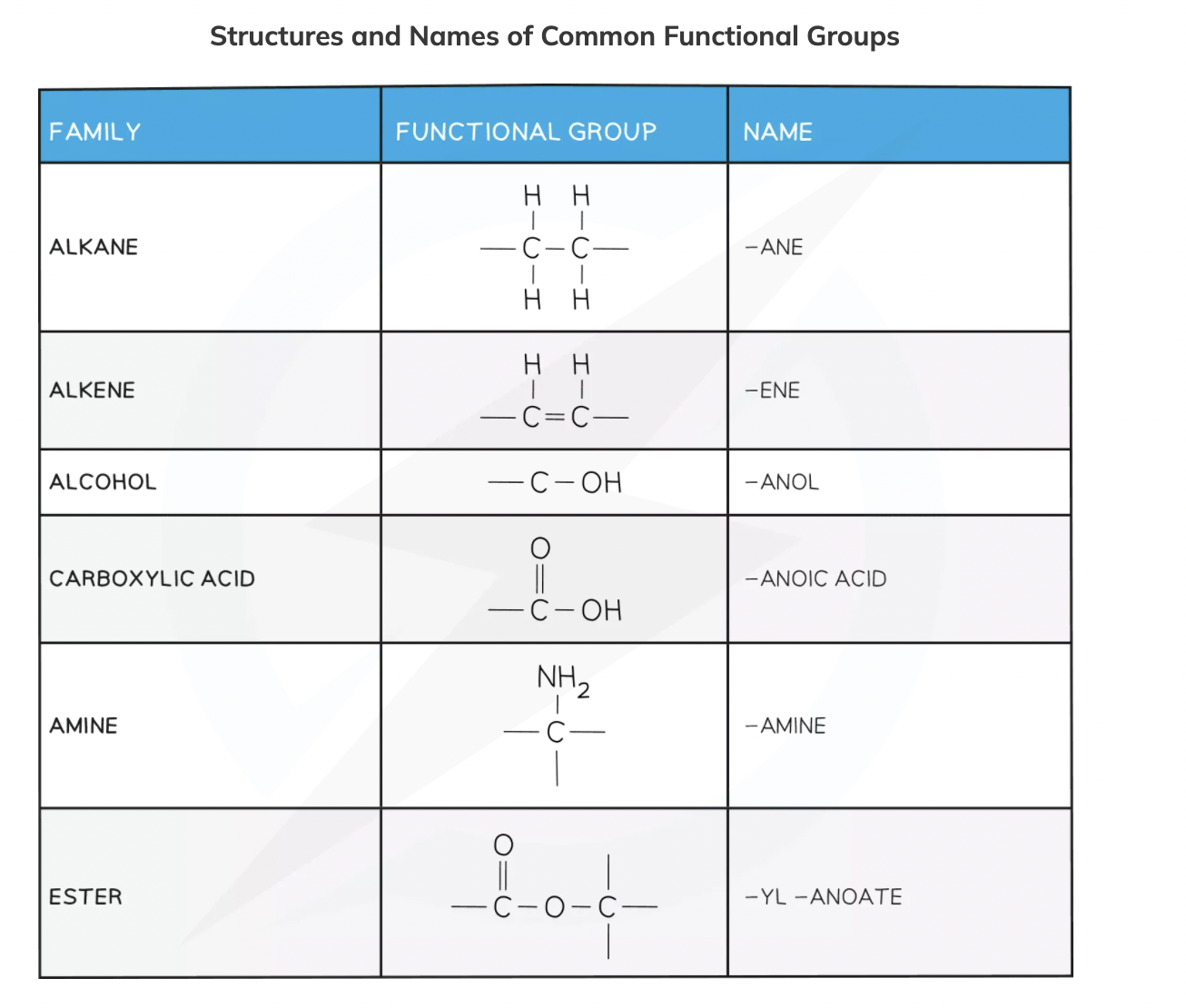
Naming organic molecules
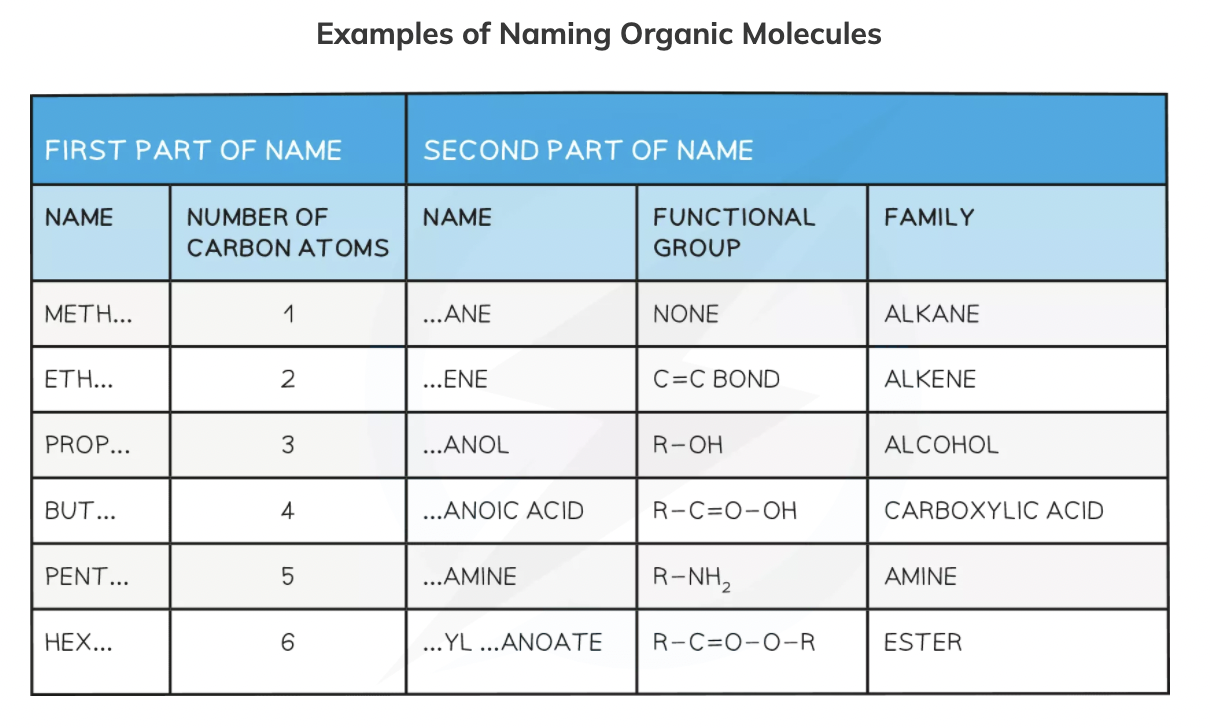
Classifying organic reactions
Substitution
Addition
Combustion
Substitution and example
A substitution reaction takes place when one functional group is replaced by another
Example: Methane reacts with bromine under ultraviolet light
CH4 + Br2 → CH3Br + HBr
Methane + Bromine → Bromomethane + Hydrogen Bromide
Addition and example
Takes place when two or more molecules combine to form a larger molecule with no other products
Example: Bromine will react with ethene and the bromine molecule will react and add across the double bond of the ethene
C2H4 + Br2 → C2H4Br2
Ethene + Bromine → Dibromoethane
Combustion and example
Combustion
This is the scientific term for burning. In a combustion reaction, an organic substance reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (or carbon monoxide if incomplete combustion) and water.
Example: Alkenes burn when heated in air of oxygen
If there is an unlimited supply of air / oxygen, the products are carbon dioxide and water:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Alkane
Are a saturated molecule - enough bonds for
Alkene
Unsaturated molecule - not enough bonds for the carbon and so forms a double bond
How to know if the hydrocarbon is an alkane or an alkene
Alkanes have a single bond and alkenes have a double one
Does crude oil have mainly Alkanes or alkenes
Alkanes
Formula for alkane
CnH₂n+² (fill in N with the humber of carbon atoms to get your formula)
Use the formula for the alkane Ethane - show your working
Ethane has 2 carbon atoms so to fill in the formula:
CnH₂n+² = C(2)H2×2(+2)
= C₂H₈