Biology Digestion Test revision
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Function of Carbohydrates, lipids, protein
Source of energy for respiration and chemical reactions in the body - starchy foods like potato pasta rice - true polymer
longer term energy store and insulation (electrical + thermal )and protection of organs - oily fish, butter, cream - not a true polymer, and also for cell membranes
needed for growth and repair of cells and tissue, meat, eggs, beans - true polymer
contains the elements c,h,o,(protein has n also)
need for digestion
To breakdown large insoluble food molecules to small and soluble molecules to be absorbed into the bloodstream (and be assimilated) - e.g. glycogen polymerisation or rebuilding glucose
Vit A,C,D
good eyesight and healthy skin and hair found in carrot, leafy veg and liver
citrus friut and veg, healthy immune function, and to prevent scurvy - bleeding gums, weak immune system
Body can make using sunlight, oily fish, eggs
needed for calcium absorption
Fe and ca ions
needed for haemoglobin for carrying oxygen in the blood and to prevent anaemia
red meat, leafy vegetables
milk, leafy veg
for healthy bones and to prevent rickets, deformed bones
water and dietary fibre
medium of transport substances, chemical reactions, cell cytoplasm, major component of blood plasma. Constantly lost by excretory processes so requires replenishment
fibre, (cellulose) fruit and veg and doesn't digest .
Adds bulk to the food, to help intestinal muscles contract and move food through the intestines (against the bulk) (peristalsis)
Balanced diet and misconception of food
all the quantities of each food group in the right proportion for each person varying by their metabolic rate
food doesn't contain only one type of nutrient, it may be rich in one type but that doesn't stop it from having other nutrients aswell
metabolic rate, and factors that affect it
rate of chem reactions occuring inside the body
gender, male norm. has slightly faster m. rate
growth rate , children or adolescents
body mass, muscle mass, fat mass
genetics
activity
enzymes
a biological catalyst made of protein molecules (that increase the rate of reaction,) they catalyse the breakdowns of large ins. food molecules to smaller sol. food molecules
they have a groove on their surface called the active site, and this is where the substrate attaches to - the molecule that the enzyme breaks down
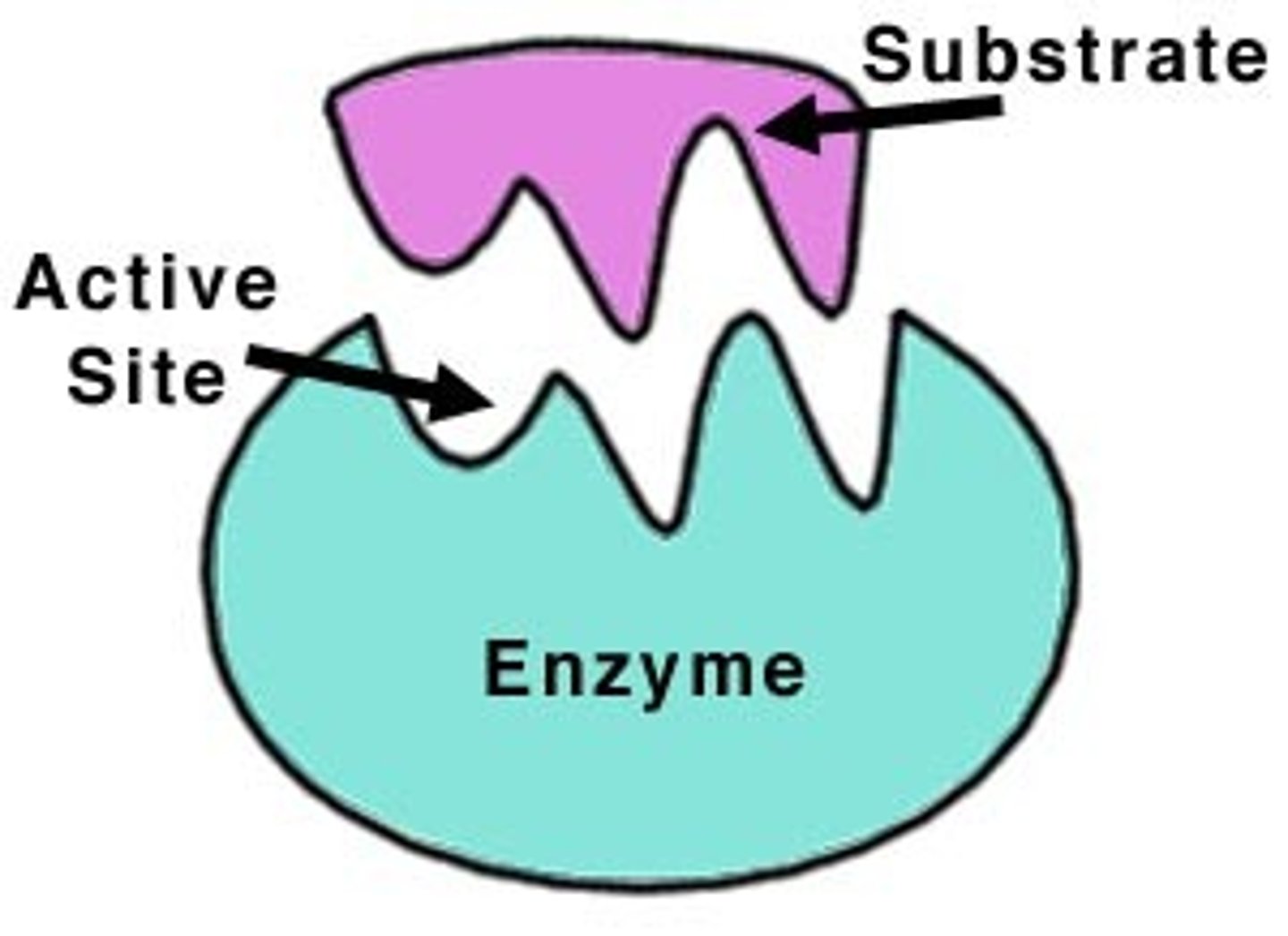
lock and key theory
substrate fits into the active site of an enzyme perfectly and then it gets broken down or built up into products, if the substrate does not fit perfectly then the enzyme cannot break it down.
The substrate and active site shape is exactly complementary, substrate must fit perfectly into the active site for the reaction to be catalysed
there are diff types of enzymes for diff substrates that break down or build up substances
Food molecules broken down by enzymes
proteins are long chains (polymer) of amino acids and are broken down into amino acids by protease enzymes - then joined together in a different order to make human proteins
starch are long chains (polymer) of glucose molecules and are broken down by amylase into glucose - other carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars by carbohydrases
some of the glucose is used in respiration
starch is broken down into maltose in the mouth then broken down to glucose by maltase in the small intestine
lipids are one molecule of glycerol connected to 3 molecules of fatty acids, and are broken down by lipase
Rate of Reaction
How much of a chemical reaction takes place IN A GIVEN TIME
ROR = 1/t (s)
effect of temperature on enzyme ROR
as the temperature increases the rate of reaction (enzyme activity increases)
, at first, the enzyme and substrate are supplied with more energy so they are moving faster so there are more collisions per sec between substrate and active site
- and at a certain temp. the enzyme is working at the fastest possible rate (optimum temp) this is the stage with the highest freq. of active site substrate successful collisions -
most human enzymes optimum temperature is 37c as that is human body temp
-passing the optimum enzyme rapidly decreases to 0 as the enzyme vibrates and the active site shape changes. Now the substrate no longer fits into the active site and the enzyme is permanently denatured - cannot catalyse the reaction
effect of pH on enzyme ROR
each enzyme has a specific optimum pH e.g. stomach protease enzyme low optimum pH and lipase small intestine high optimum pH
but the gradient is always steep both ways so if the conditions are more acidic or alkaline then rate of reaction rapidly decreases to 0 and enzyme denatures
different enzymes have diff optimums e.g pepsin has a very acidic optimum and lipase would have a higher optimum
effect of pH on amylase practical set-up
Place one drop of iodine solution into each well of a spotting tile, take 3 test tubes . S - is starch solution A - amylase solution B - buffer solution pH 5 (used to control pH)
leave them in a water bath for 10 minutes to get to the desired temperature, then combine them into one test tube and and mix with a stirring rod, return to the water bath and start a stopwatch
every 30 s use the rod to transfer a few drops from the mixture to a well in the spotting tile, the iodine should turn blue-black , starch present, (keep on doing this until the iodine remains orange where no starch is present in the solution)
repeat the whole experiment several times using pH buffers of 6 , 7 and 8
problems with the amylase pH practical
sample only taken for 30s so we only have an approximate time for the reaction to complete, address this by taking a sample every 10 seconds
we are looking for the time where the iodine does not go blue-black, which is not always obvious as the colour change tends to be gradual - some of the blue black can be mixed with orange, so its difficult to see when the reaction has finished
address this by asking several people to look at the spotting tile and decide whether the reaction has completed
sugars
soluble carbohydrates, simpler
glucose - boy uses most in respiration
lactose - milk sugar
sucrose granulated sugar
glycogen and cellulose
a large carbohydrate molecule similar to starch and can be stored in liver and muscles
cellulose is another large carbohydrate molecule found in plant cell walls, we cannot digest cellulose
ingestion digestion absorption assimilation
ingestion - taking in food
digestion - breaking down large, insoluble molecules into smaller soluble molecules
absorption - taking in small soluble food molecules from the gut (small int) into the bloodstream
assimilation - absorbed food molecules are taken into the cells of tissues for respiration and/or growth and repair
egestion- (not excretion) the removal of undigested food and other waste materials through the anus.
egestion and excretion difference
egestion - UNDIGESTED food products that were not absorbed from the digestive system
metabolic waste - waste chemicals produced by cells e.g. CO2 and urea
digestion in the mouth
chewing of food, mechanical digestion which increases SA of food, salivary amylase starts the digestion of carbohydrates breaking down to maltose (mucus helps food move down the oesophagus)
Oesophagus
passes food (bolus) down to the stomach by peristalsis - waves of contraction and relaxation of muscles to push food to the stomach and through the gut, breaks down the food a little bit
stomach
where digestion of proteins start (pepsin), contains acid for optiumum, HCL kills ingested microbes,
mucous cells lining protects the stomach walls withstands pH -
churns food into the chyme, which is a liquid food to give a much larger SA for further digestion by enzymes
function of liver
produces bile which has two functions :
neutralises the stomach acid and makes the conditions in the duodenum slightly alkaline for lipase and pancreatic enzymes including lipase
emulsifies fats (convert into smaller droplets ) which gives a greater SA (of droplets) for increase rate of lipid breakdown by lipase
bile is stored in the gall bladder
however when lipids are broken down, the fatty acids lower pH
what happenes in duodenum
in duodenum several digestive enzymes and bile are added to the chyme, this is where most and final chem digestion takes place before the products are absorbed in the illeum
illeum + jejunum
where the smaller food molecules are absorbed into the blood stream through villi.
They are folded and long to give a large SA for absorption and microvilli with folds further increase the SA.
have a really good network of blood capillaries that rapidly take away the products of digestion to ensure a steep conc. grad.
one cell thick membrane to provides a short diffusion path
lacteal and lymph take away glycerol and fatty acids as they cannot be directly absorbed into the bloodstream
many well developed mitochondria for active transport
small intestine is 5m long to give a large SA for absorption
where are all enzymes produced and secreted
all enzymes are produced in the pancreas and secreted in the small intestine, but with an optimum pH slightly alkaline, but there are some other enzymes found :
carbohydrase (amylase) produces in salivary gland and secreted in the mouth
protease (pepsin) produced and secreted in the stomach with an acidic pH optimum
lipase is only secreted in the small intestine
food tests precautions - benedicts
chemicals may be hazardous, so safety goggles must be worn , and also gloves
1. grind food sample into a liquid using distilled water and mortar + pestle used to make a paste, transfer the paste to a beaker with more distilled water so the food molecules dissolve , then filter to remove suspended particles
Benedicts reagent tests for glucose and reducing sugars (not sucrose) , add reagent, a few drops to a little of the sample and place in an 80 deg water bath and leave for 5 mins
should go from blue -> green -> yellow -> orange -> brick red
food tests for biuret starch and lipids
biuret reagent is blue and tests for protein, add a few drops to a little sample and shake, should turn purple
starch is iodine solution add a few drops to a little sample and it should turn instantly from orange brown to blue black
when preparing sample for ethanol emulsion do not fliter as lipid molecules can stick to the paper, add a few drops of distilled water and ethanol and shake - white cloudy emulsion
ethanol is flammable so no naked flames near
large int
absorbs and removes water from any waste material in the intestine , mainly composed of cellulose (fibre)
semi-solid waste is called faeces and is egested through the anus and stored in the rectum
visking tubing experiment
Visking tubing containing starch and amylase can model absorption in the small intestine,
where water outside of the tubing represents blood
mixture inside the tubing is the small int
and the visking tubing is villi
sample the water outside of the tubing w Benedicts and iodine
and no starch and glucose present
then sample around the end and there should be a little bit of glucose and no starch as the amylase broke the carbs down to glucose which was small and soluble enough to diffuse from a high to low conc. out of the visking tubing into the water
the experiment takes place in a controlled temperature
limitations of the visking tubing experiment
the small int has a larger SA due to villi
water doesn't maintain the same diffusion conc grad as blood in capillaries
uses of the products of digestion
To make new carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
proteins are used for growth and repair
lipids - insulation , organ protection , making cell membranes
glucose - respiration release of energy or glycogen store
molecules are re-polymerised