Final (Old HW + Quizzes)
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
serves the senses of hearing and equilibrium
vestibulocochlear
c1 spinal nerve emerges between the first and second cervical vertebrae
false
structure covering individual neuron
endoneurium
striking funny bone (ulnar nerve) may cause injury to a nerve in this plexus
brachial plexus
a fracture of the ethmoid bone could result in damage to which cranial nerve
olfactory
A patient who received a blow to the side of the skull exhibits the following signs and symptoms on that side of the face: he is unable to close his eye, and the corner of his mouth droops. Which cranial nerve has been damaged?
facial
A fall or improper administration of an injection to the buttocks may injure a nerve of this plexus.
sacral plexus
There are three layers of neurons in the retina. The axons of which of these neuron layers form the optic nerves?
ganglion cells
receptor membranes of gustatory cells
gustatory hairs
Some of the sensation of olfaction is actually one of pain
true
preparing the body for fight or flight response
sympathetic nervous system
rest and digest division of the ANS
parasympathetic division
controls temperature, endocrine activity, thirst
hypothalamus
light passes through the following structures in which order
spinal nerves that make up brachial plexus
C5-C8 and T1
major targets of growth hormone
bones and skeletal muscles
organ responsible for synthesizing ANP
the heart
single most important regulator of calcium levels in the blood
parathyroid hormone
aldosterone
functions to increase sodium reabsorption
parent cell for all formed elements of blood
hemocytoblast
no visible cytoplasmic granules are present
monocytes
A lack of intrinsic factor, leading to a deficiency of vitamin B12 and causing an appearance of large pale cells called macrocytes
pernicious anemia
characteristic of all leukocytes
they are all nucleated
foramen ovale
connects the two atria in the fetal heart
visually discern right and left ventricles by
noticing thickness of ventricle walls
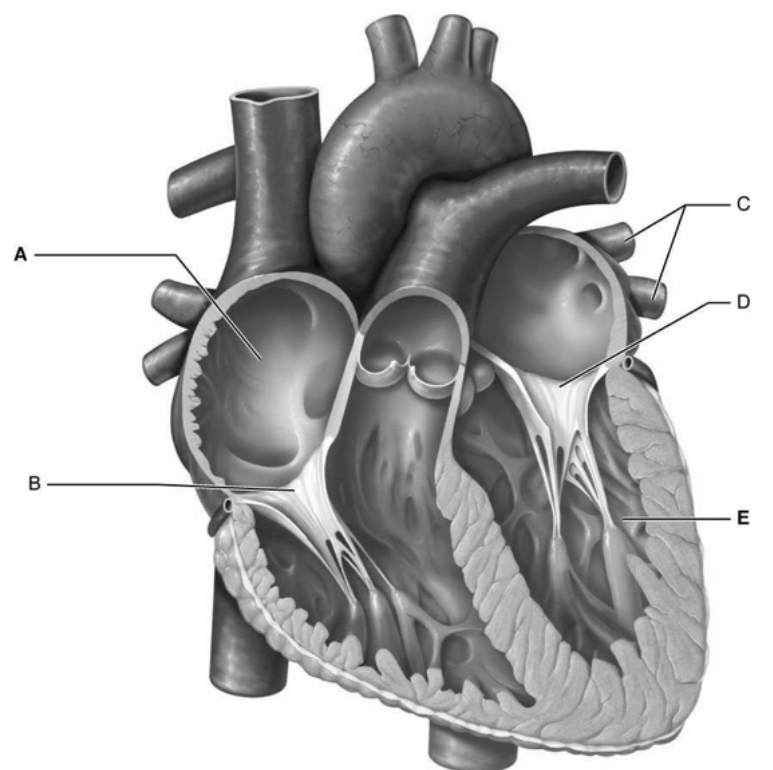
What is A
right atrium
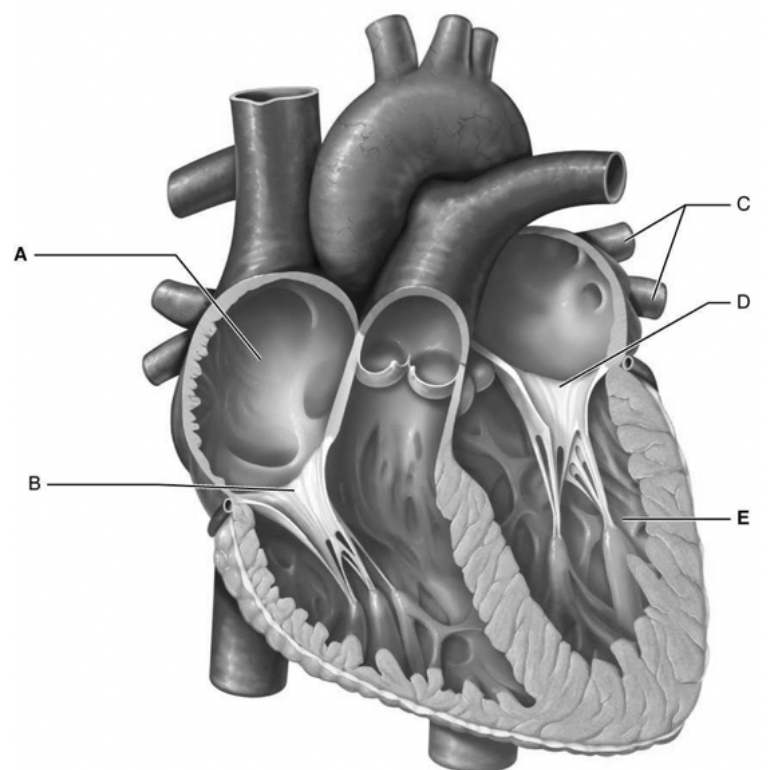
what is B
tricuspid valve
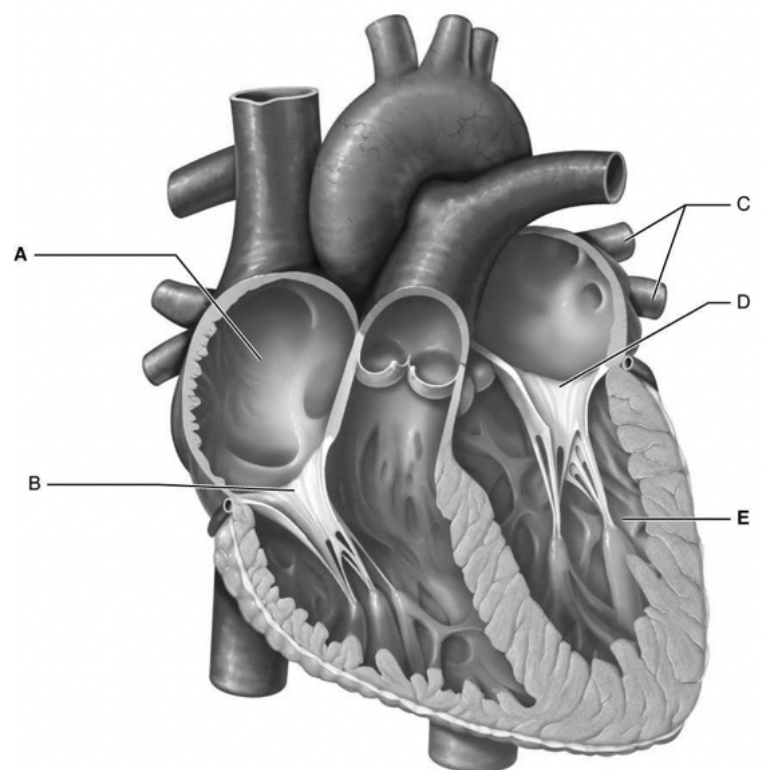
what is c
pulmonary veins
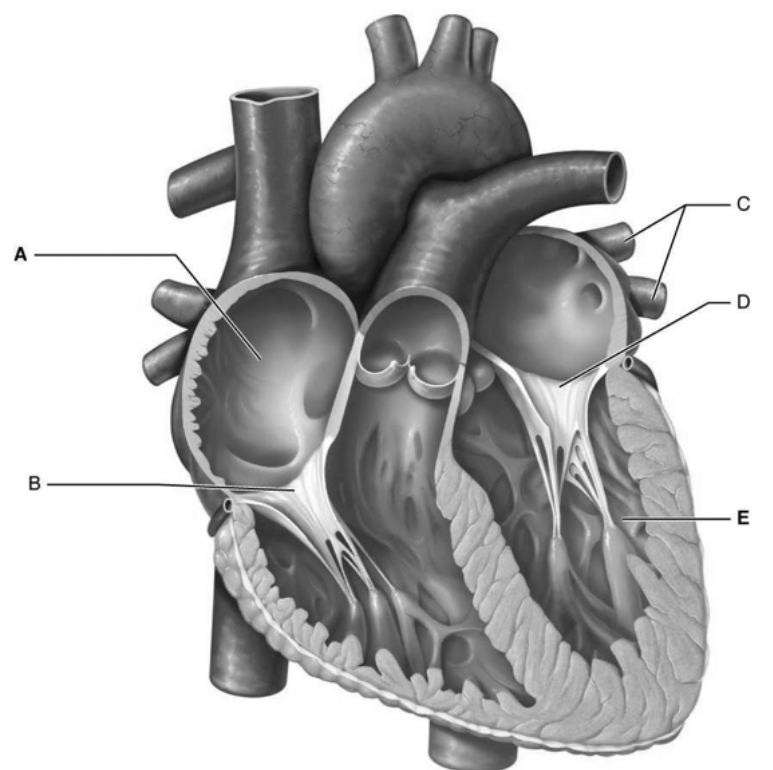
what is d
mitral valve
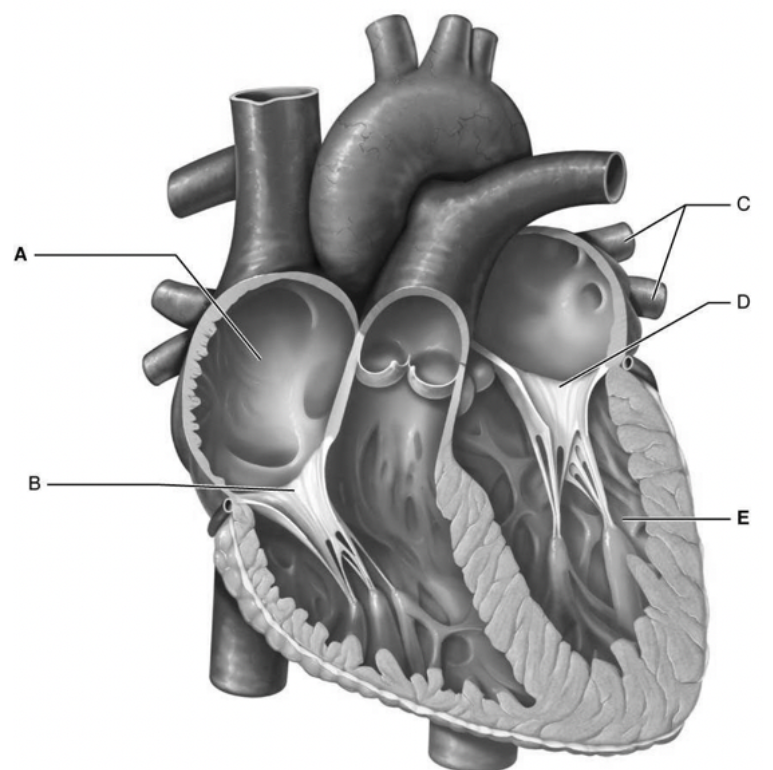
what is e
left ventricle
compared to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle..
has gap junctions that allow it to act as a functional syncytium
prevents backflow into the left ventricle
aortic valve
what cranial nerves supply the extra ocular muscles
CN III, CN IV, CN VI
the central fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres
false
the longitudinal fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres
true
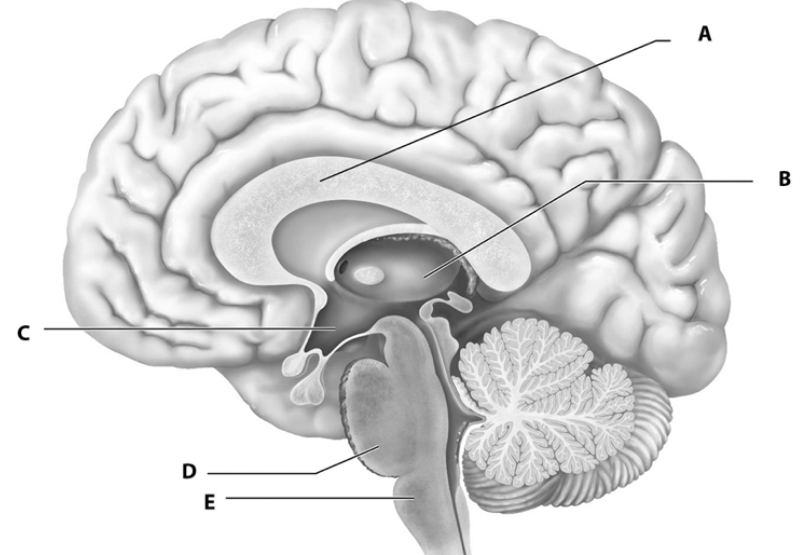
what is a
white fiber tracts
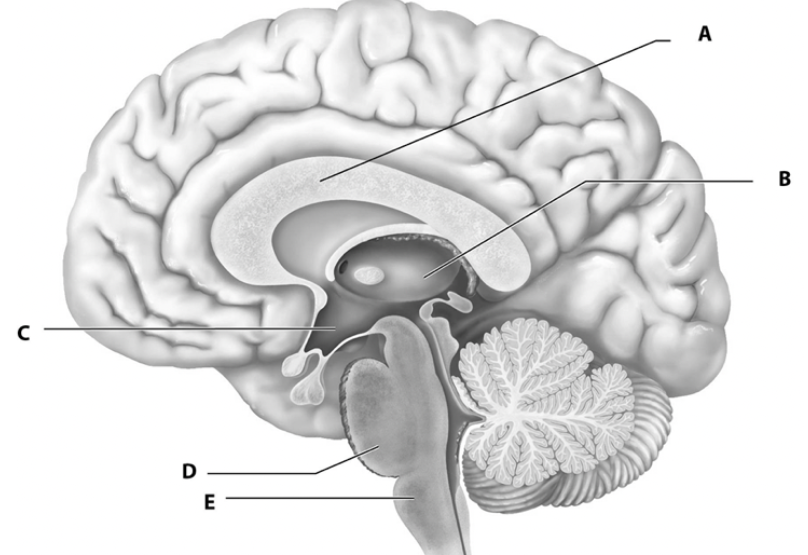
what is b
thalamus
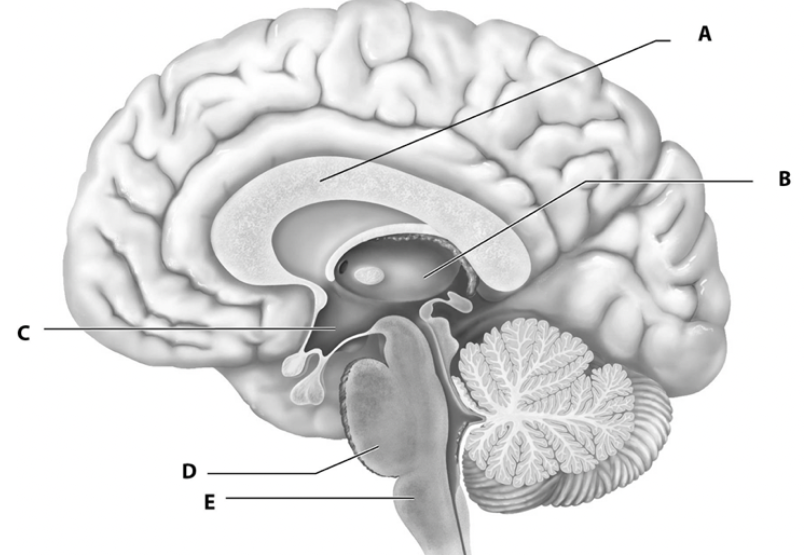
what is c
hypothalamus
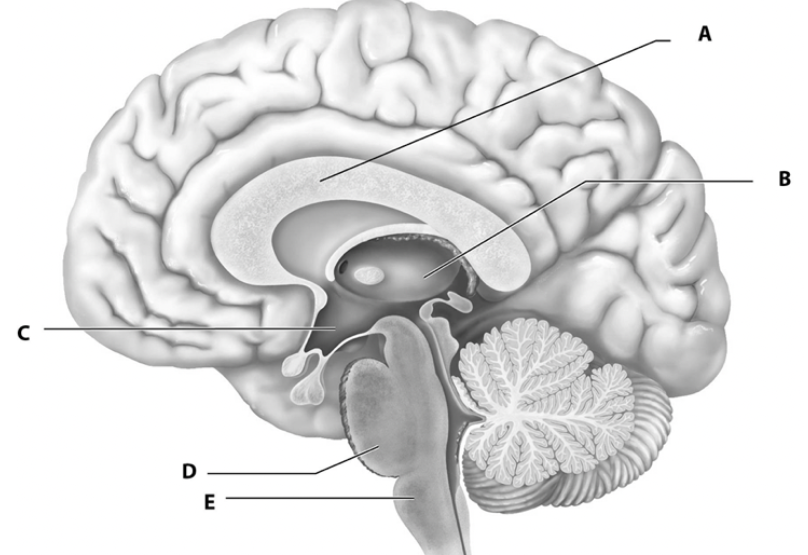
what is d
pons
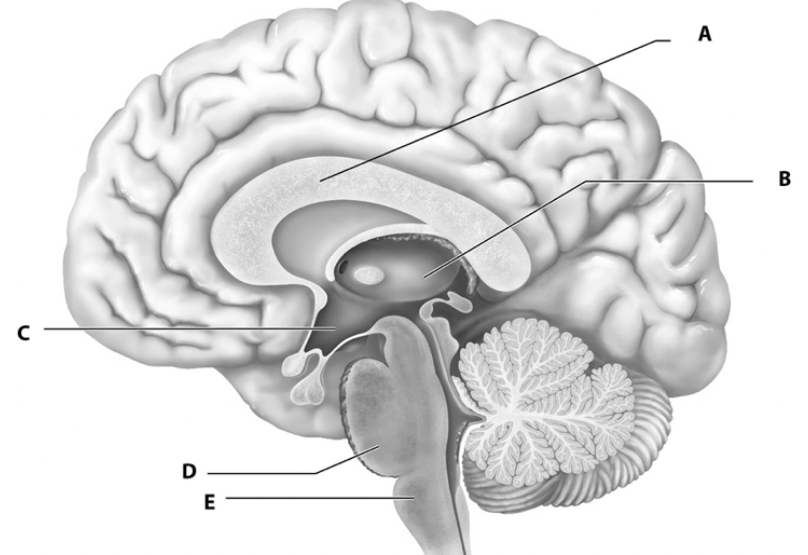
what is e
medulla oblongata
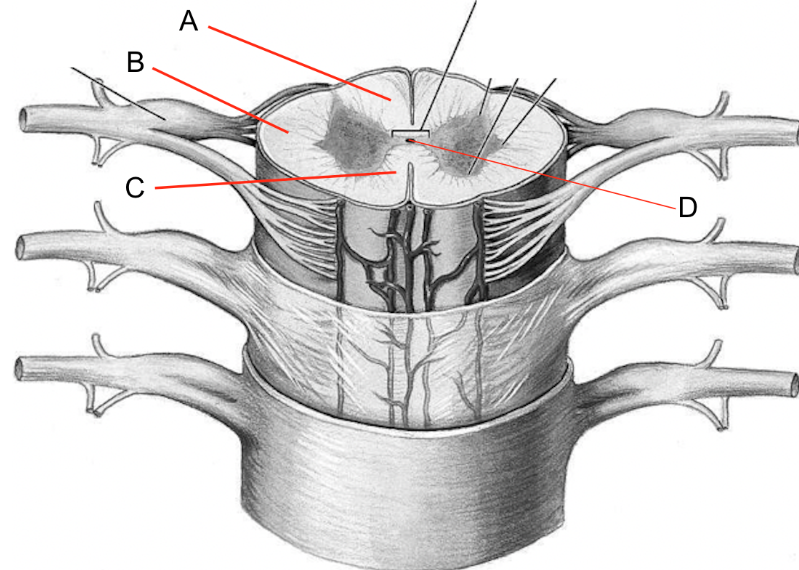
what is a
dorsal columns
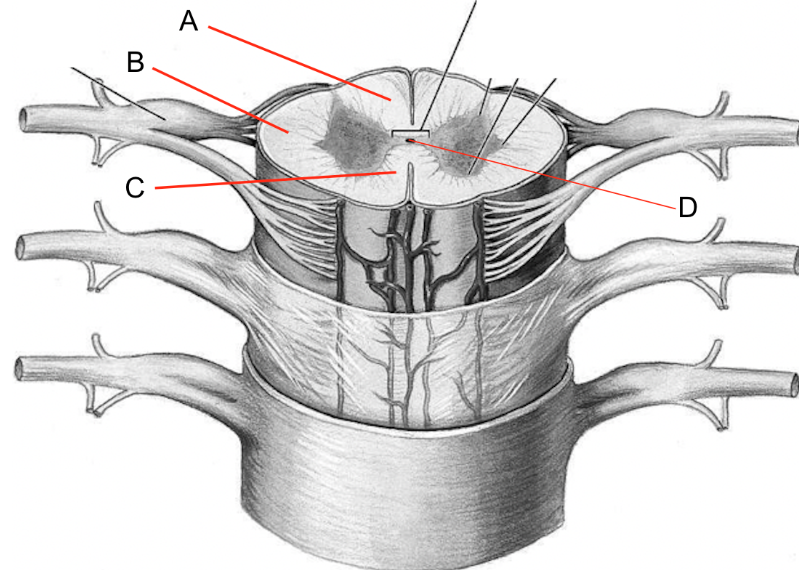
what is b
lateral columns
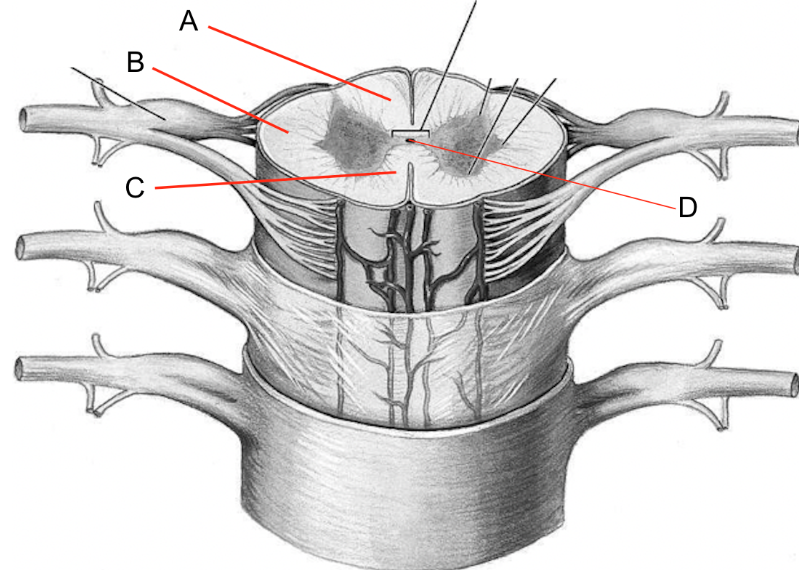
what is c
ventral columns
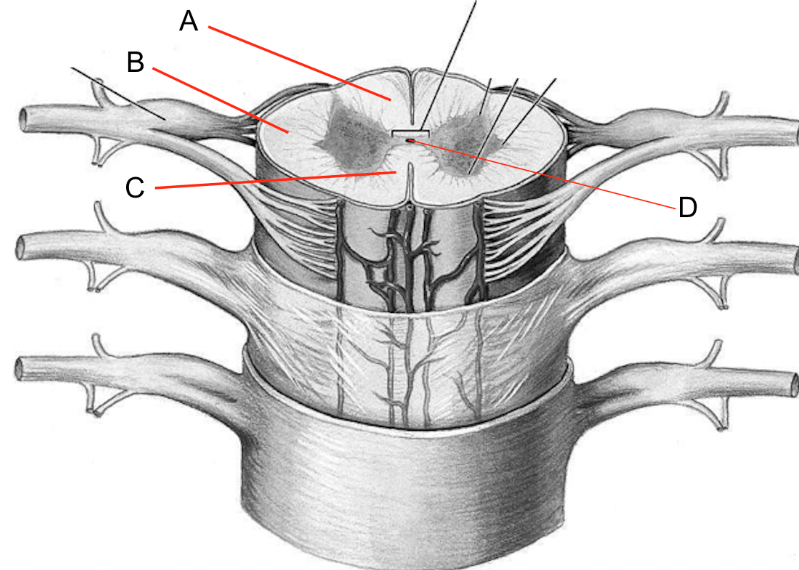
what is d
central canal
temporal lobe
auditory area
insula
gustatory area / taste
occipital lobe
visual area
outer to innermost layer of meninges
dural mater
arachnoid mater
pia mater
structure responsible for production of CSF
choroid plexus
membrane that vibrates after it is struck by sound waves, transmitting sound vibrations to the auditory ossicles
tympanic membrane and/or eardrum
what part of middle ear will you find the stapes
middle ear
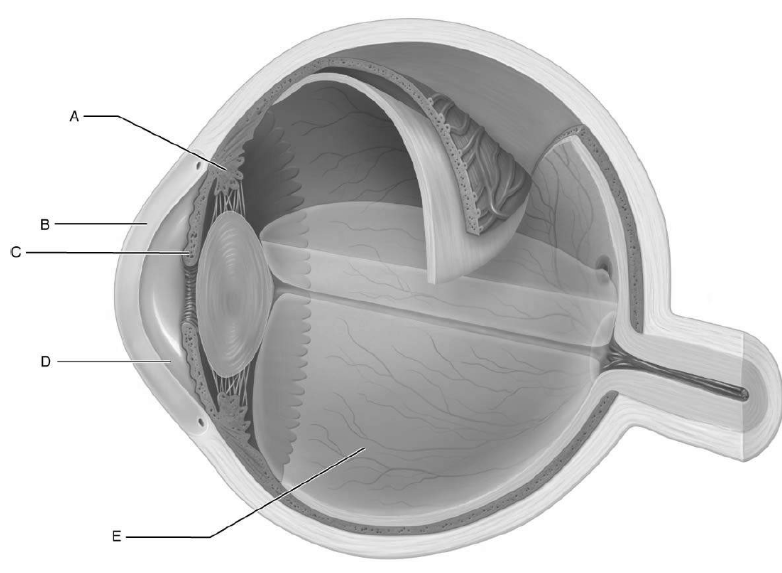
structure responsible for focusing light rays that enter the eye
lens
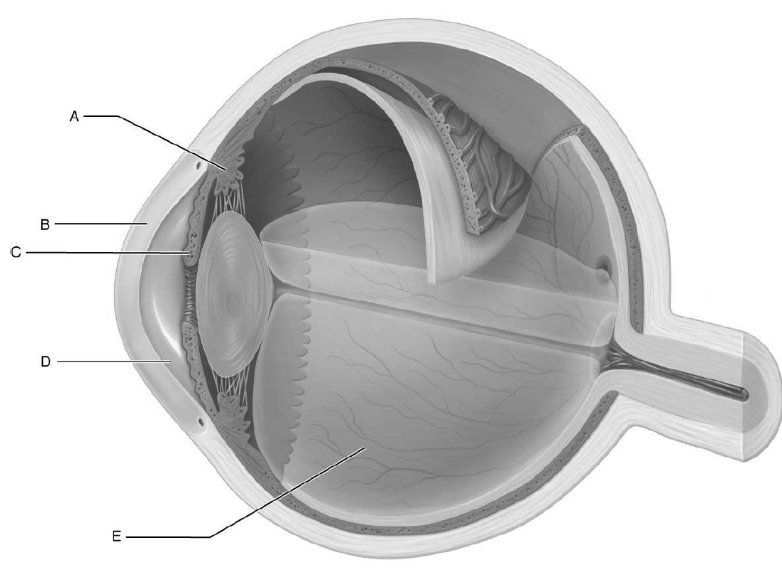
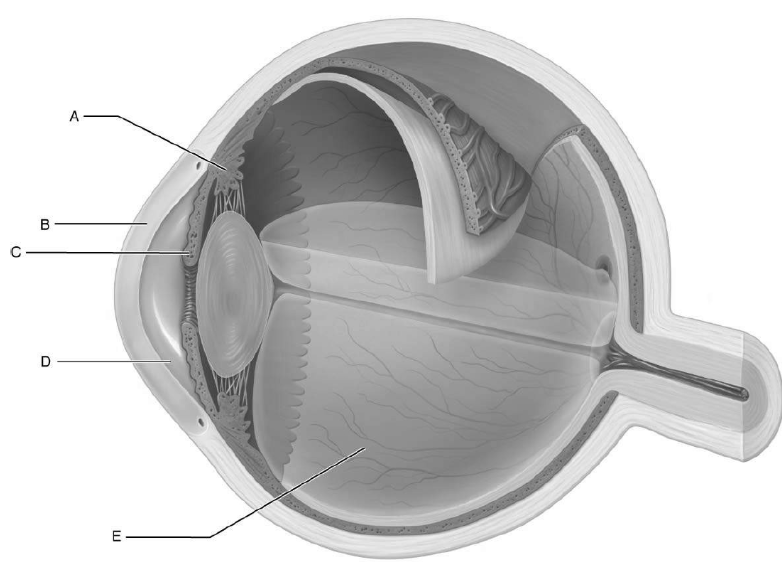
what is a
controls lens shape
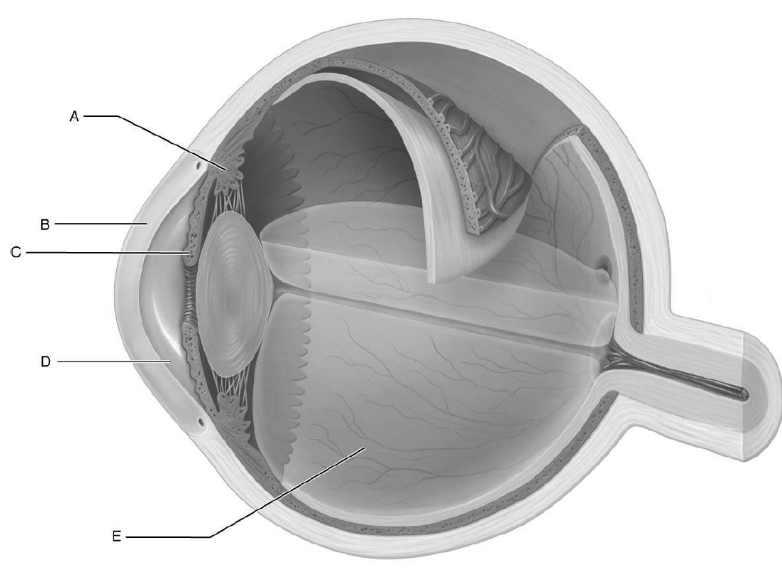
what is b
cornea
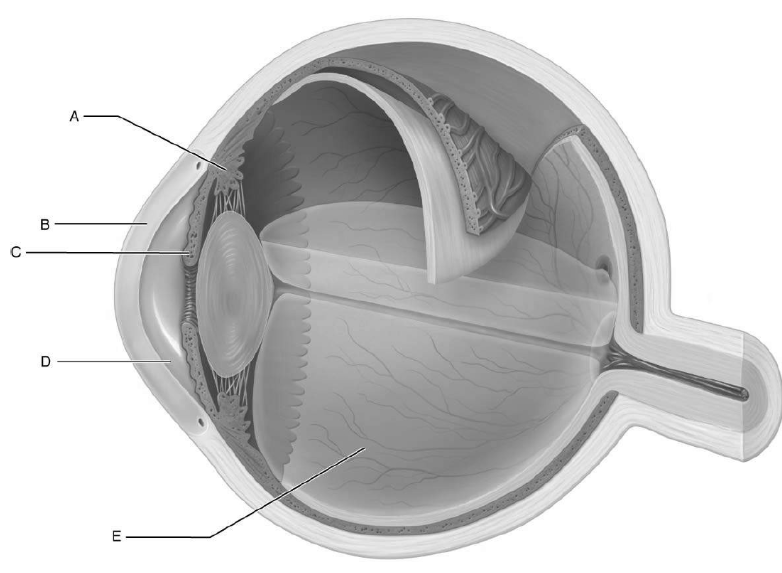
what is c
colored part of eye that opens/closes pupil
what is d
space between cornea and lens
what is e
vitreous humor
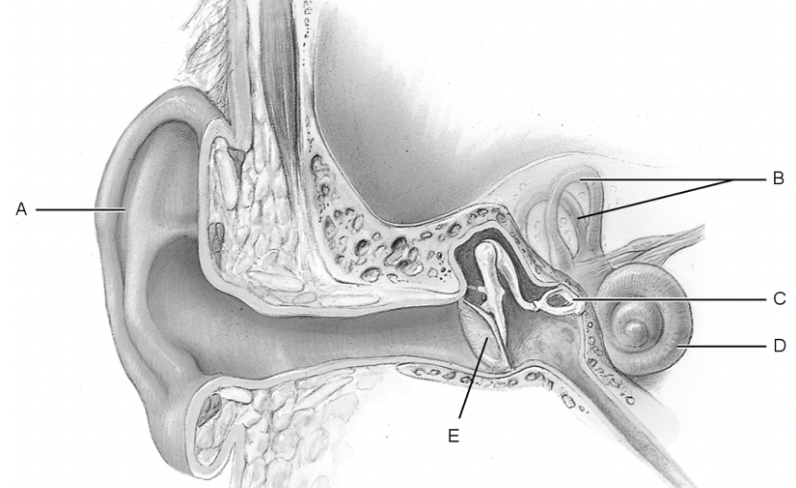
what is a
pinna
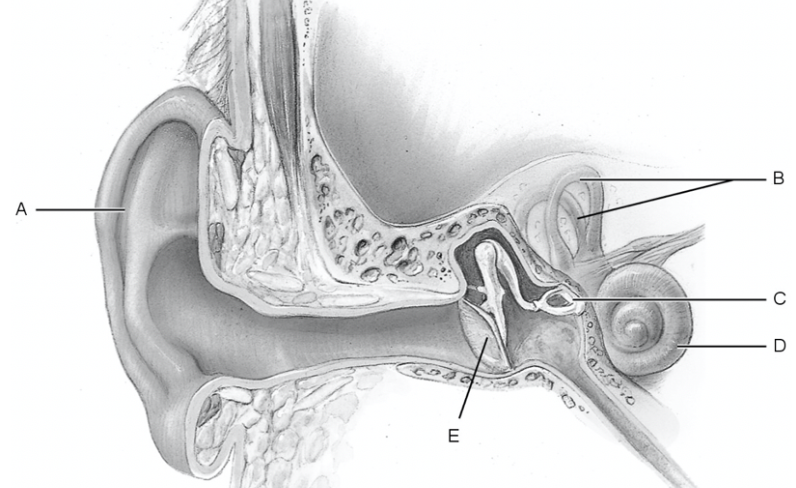
what is b
semicircular canal
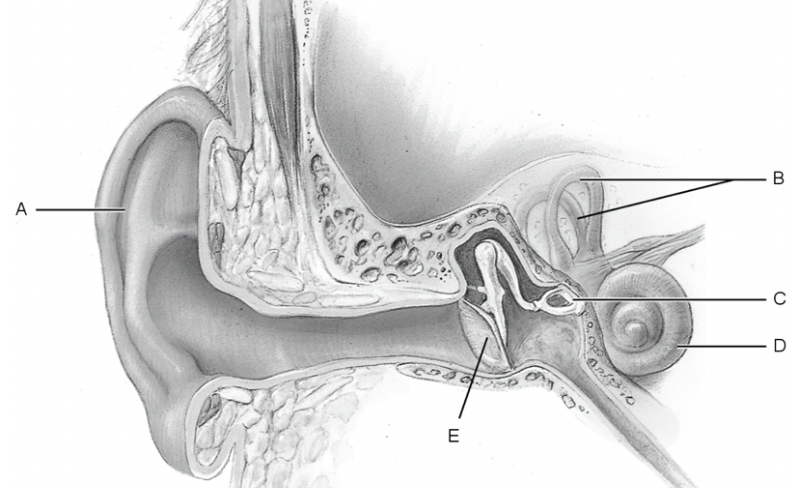
what is c
stapes
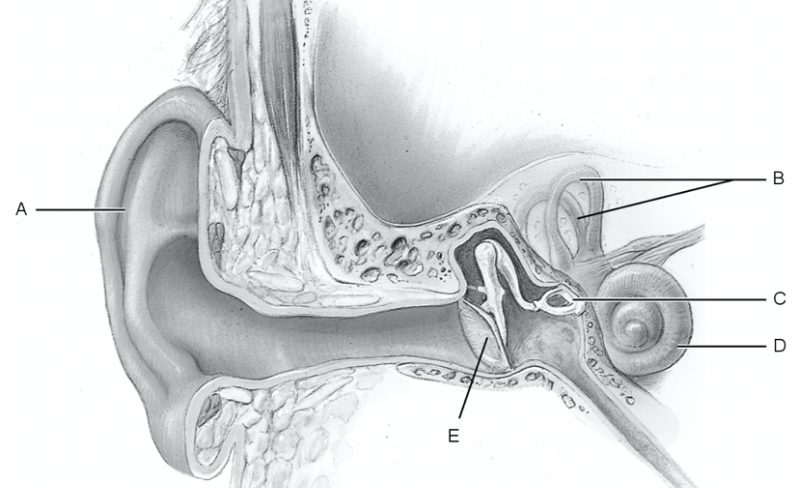
what is d
cochlea
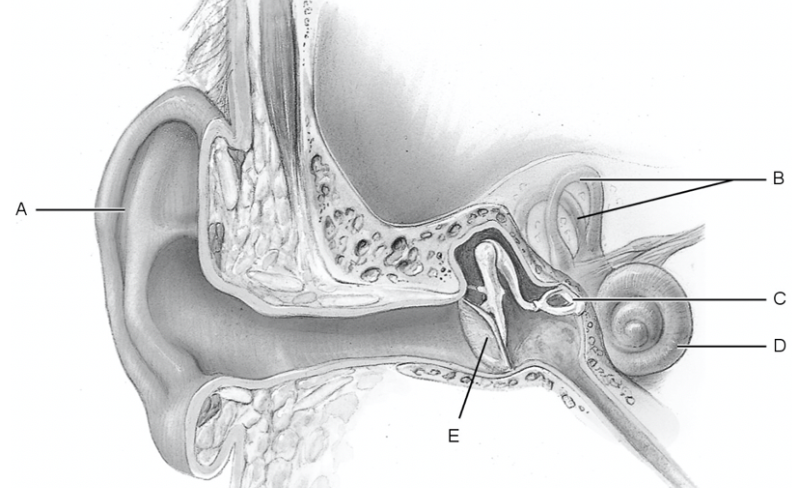
what is e
tympanic membrane
the pupil regulates the amount of light passing to the visual receptors of the eye
false
the iris regulates the amount of light passing to the visual receptors of the eye?
true
Which of the following taste sensations is incorrectly matched to the chemicals that produce it?
umami-amino acids glutamate and lysine
where is visual acuity the sharpest found in the eye
fovea
In addition to chest pain, a person suffering from a heart attack can also fee the pain in the
left arm
How does the somatic nervous system and autonomic nervous system differ from one another?
Effector of the somatic nervous system is the skeletal muscles
Effector of the autonomic nervous system are glands, cardiac muscles and smooth muscles
somatic and autonomic nervous system differs in their efferent pathways and their neurotransmitters
Which of the following is false about the cholinergic signaling molecules?
norepinephrine is released, binds to alpha receptors
All somatic motor neurons release acetylcholine and the effect is either stimulatory or inhibitory on the organ.
false
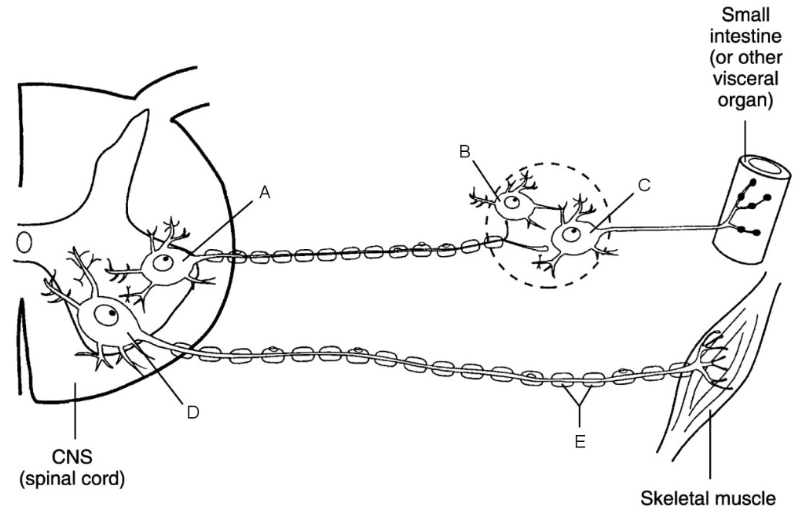
what is a
cell body of ANS preganglionic neuron
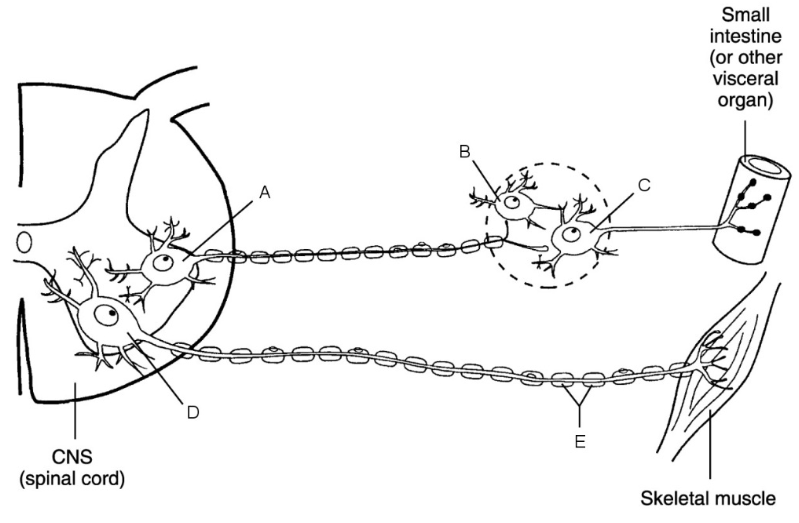
what is b
central neuron
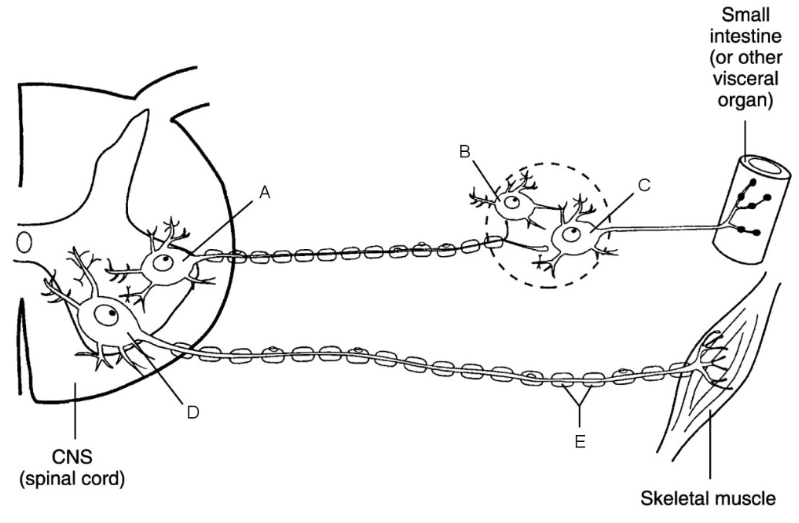
what is c
ganglionic neuron
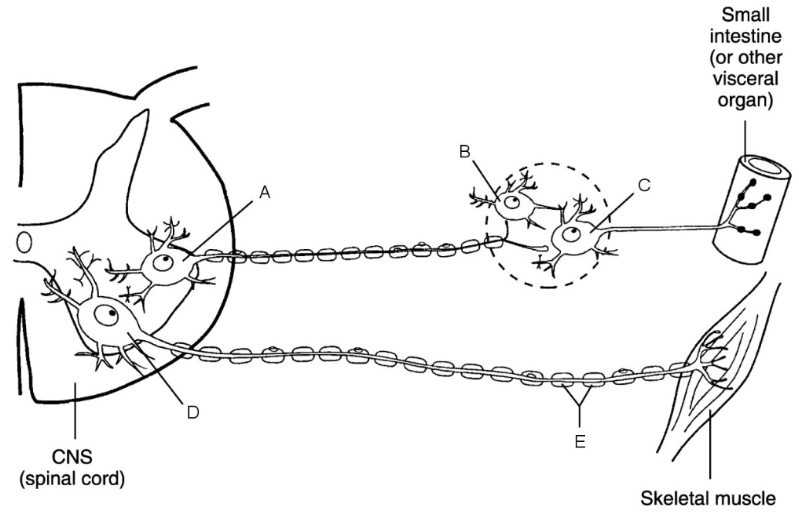
what is d
cell body of somatic neuron
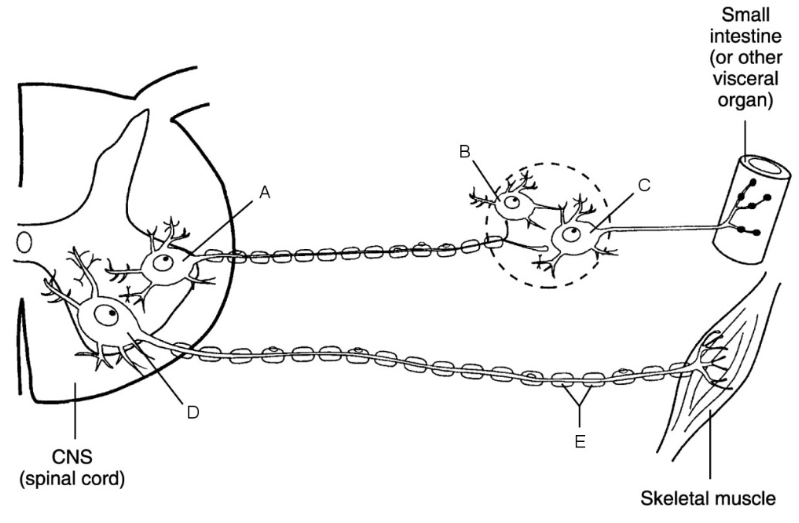
what is e
myelin sheath
effectors of the autonomic nervous system
cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands
efferent neuron of somatic reflex has only ___ neuron
one
efferent neuron of visceral reflex has only ___ neuron
two
Referred pain is a strong visceral sensations that rise to level of conscious perception
true
Almost all visceral organs are served by both divisions of the ANS causing the same effects
false
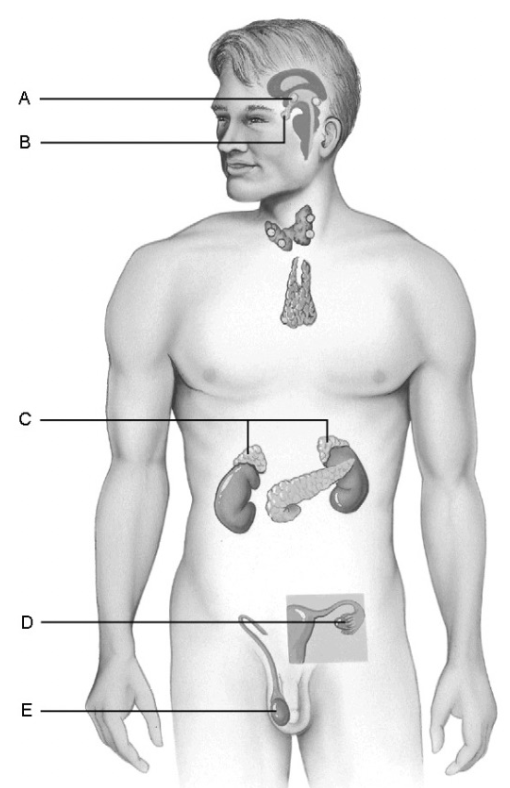
what is b
(pituitary gland) storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus
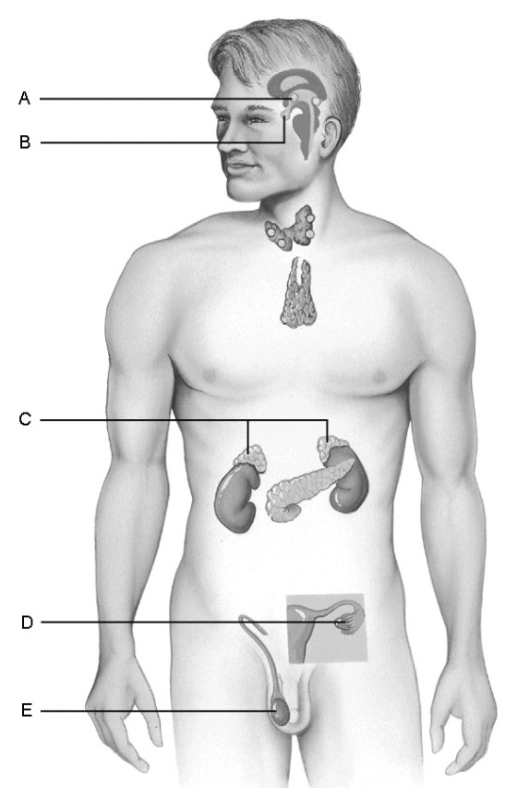
what is c
(adrenal glands) produces steroid hormones, glucorticoids, and mineralcorticoids
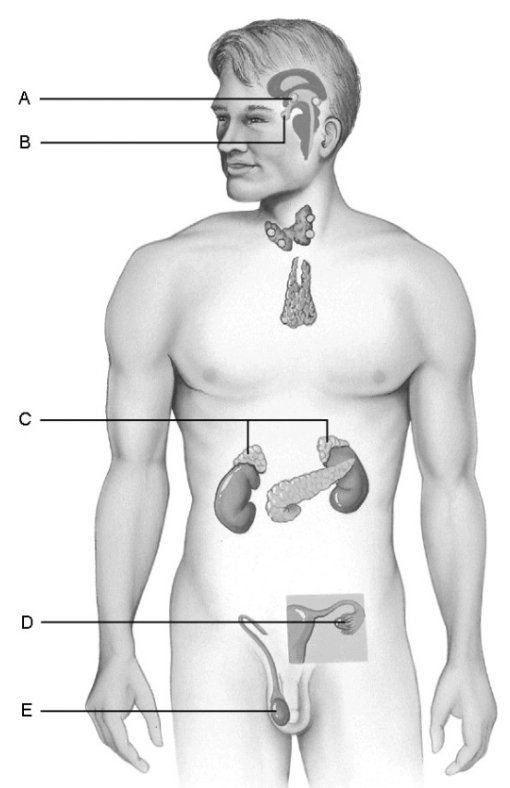
what is d
(ovaries) produces hormones that promote development of female secondary sexual characteristics @ puberty
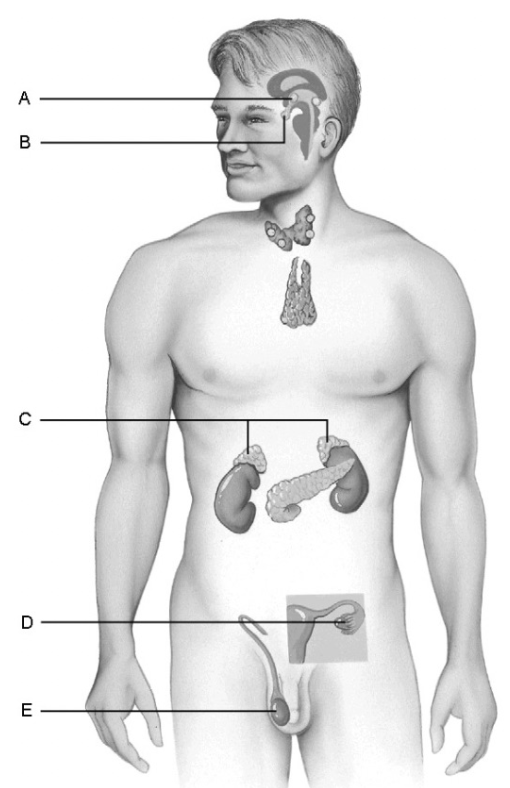
what is e
(testis) produces hormones that promote development of male secondary sexual characteristics @ puberty
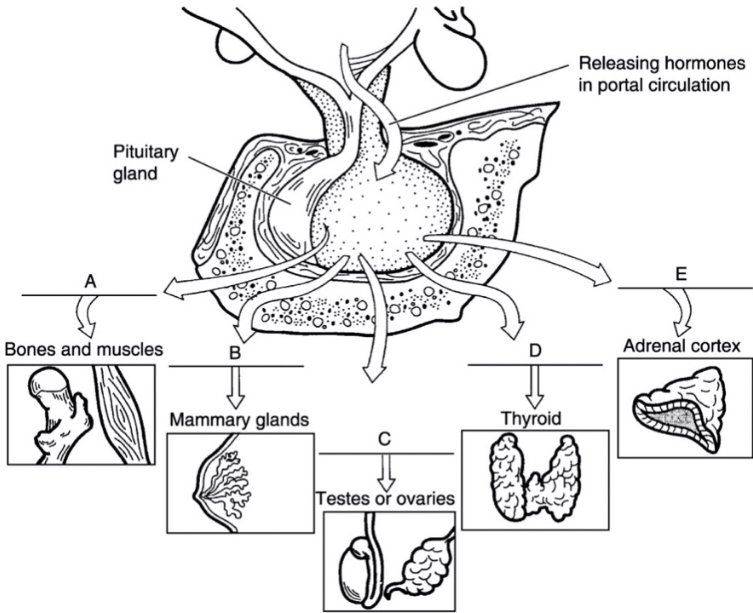
what is a
growth hormone
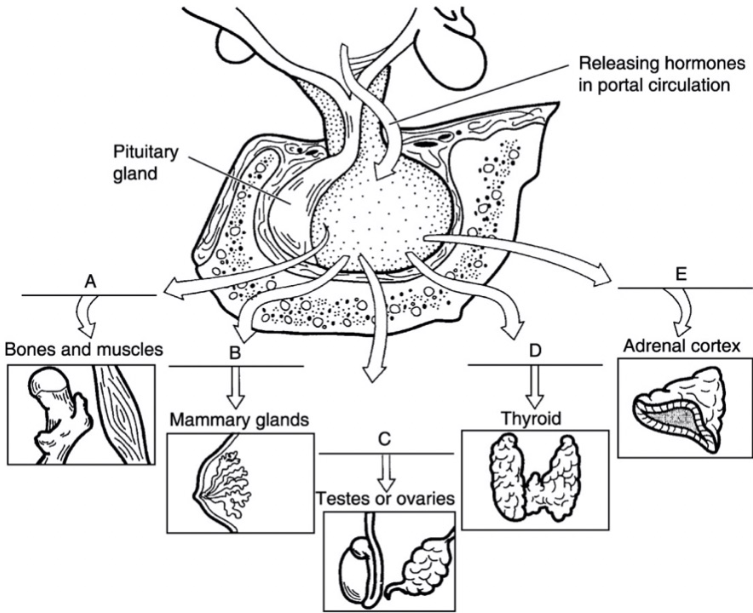
what is b
prolactin
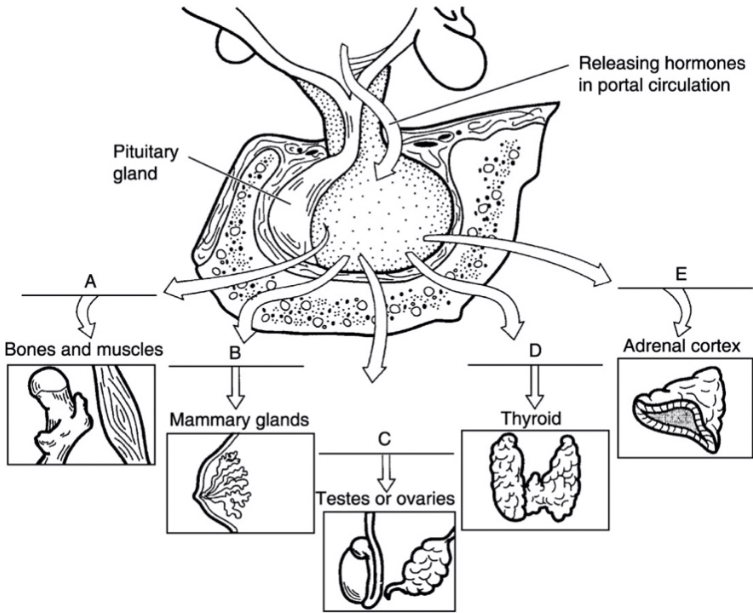
what is c
FSH/LH
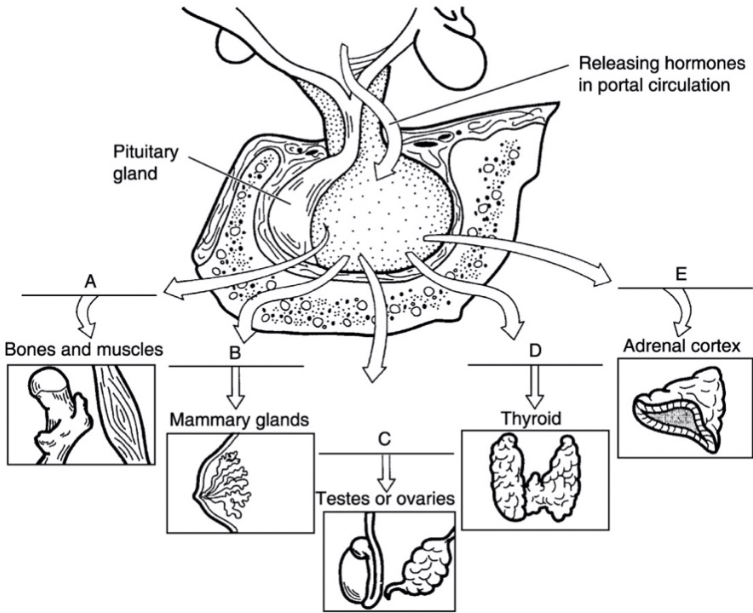
what is d
thyroid stimulating hormone
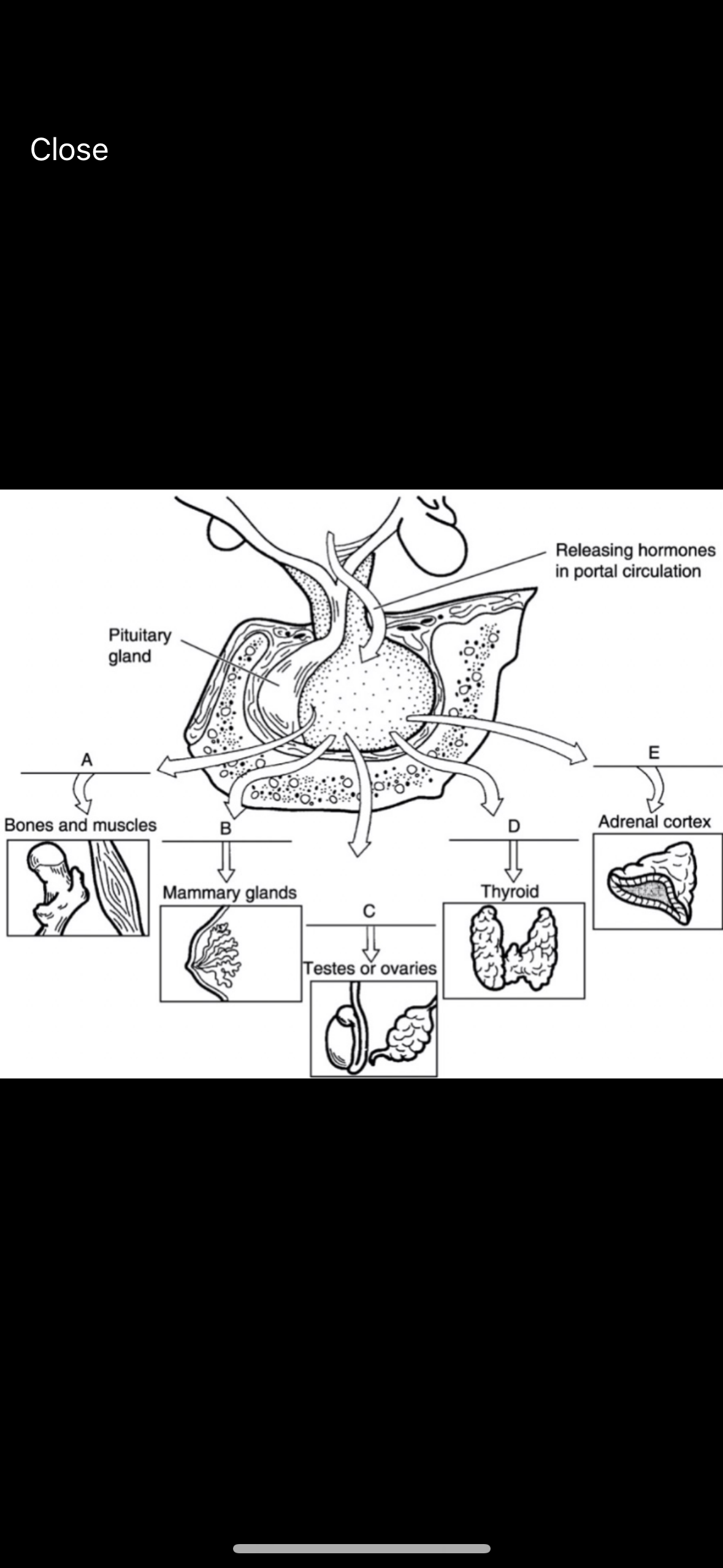
what is e
adrenocorticotropic hormone
Chemical substances secreted by cells into the extracellular fluids and that regulate the metabolic function of other cells in the body are called
hormones
Which of the following is correctly matched regarding hormone production by the pancreas?
beta cells - insulin
stimulates water reabsorption
ADH
Which part of the pituitary gland is responsible to hormone storage only?
posterior pituitary gland
what organ does not produce hormones
spleen
What organ releases a hormone that will stimulate red blood cell production?
kidneys
oxytocin
causes uterine contractions
The single most important regulator of calcium levels in the blood is the ________ hormone. Secretion of this hormone in the blood stream can lead to increase in blood calcium level.
parathyroid
Ridges of tissue on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres
gyrus
what organ is responsible for synthesizing ANP
the heart
axons of this neuron layer form the optic nerve
ganglion cells