A-LEVEL OCR B CHEMISTRY: Developing Fuels
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What is the molar volume of gas?
One mole of any gas at RTP will take up the same volume.
The volume is 24000cm3/24dm3.
What is RTP?
298K/25C
100kPa
What is the ideal gas constant?
8.31 JK-1mol-1
What is the ideal gas equation?
pV=nRT
p = pressure (pascals)
V = volume (m3)
T = temp (Kelvin)
n = moles
m = mass (g)
How do you measure volume of gas released?
Use a gas syringe to measure volume of gas produced.
Measure mass lost on weighing balance and calculate moles of gas produced.
Collect gas and place in upturned test tube filled with water.
What does a solid line indicate (bonds)?
Bond is in the plane of paper.
What does a wedged line indicate (bonds)?
Bond comes out plane of paper.
What does a dotted line indicate (bonds)?
Bond goes into plane of paper.
What are sigma bonds?
Single bonds.
Overlap of orbitals is directly between two atoms and there is free rotation around sigma bond.
What are pi bonds?
Sideways overlap of adjacent p-orbitals above and below bonding atoms.
What bonds do double bonds consist of?
Sigma and pi.
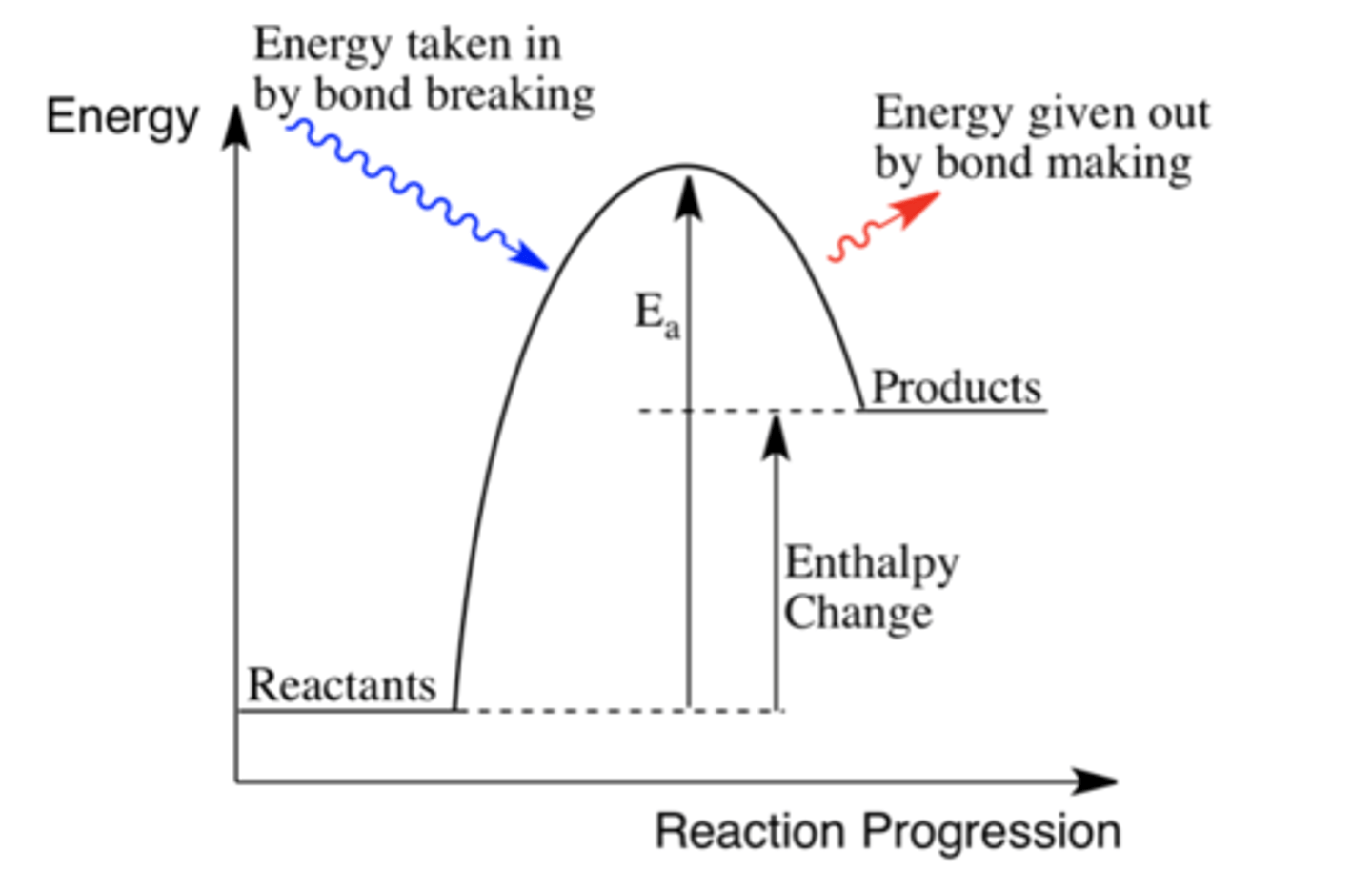
What is enthalpy change?
The heat energy transferred in a reaction at constant pressure.
What type of process is bond breaking?
Energy is taken in from surroundings so is endothermic.
What type of process is bond making?
Energy is given out to surroundings so is exothermic.
In endothermic reactions is the enthalpy change positive or negative? Why?
Positive.
More energy is needed to break bonds than make new ones.
How is the overall enthalpy change calculated?
Energy to break bonds + energy to make bonds.
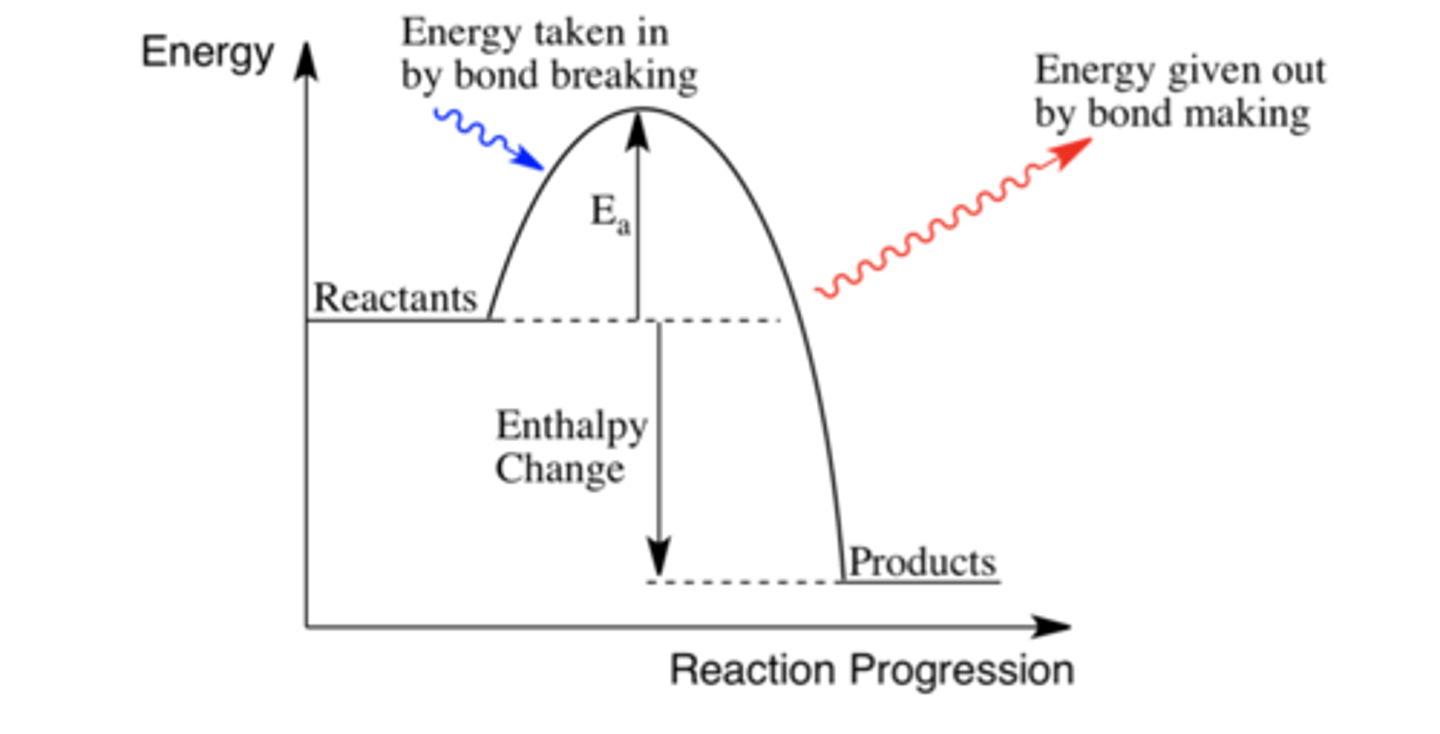
In exothermic reactions is the enthalpy change positive or negative? Why?
Negative.
More energy is needed to make bonds than break existing ones.
What does an endothermic energy level diagram look like?
What does an exothermic energy level diagram look like?
What is bond enthalpy?
The energy required to break one mole of the stated bond in a gaseous state, under standard conditions.
Which bonds are strongest out of single, double and triple? Why?
Double and triple stronger than single bonds as they have shorter bond lengths.
Define enthalpy change of reaction...
The enthalpy change when quantities of a substance in standard states react completely under standard conditions, with substances in their standard states.
Define enthalpy change of formation...
The enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is produced from its elements in their standard states and under standard conditions.
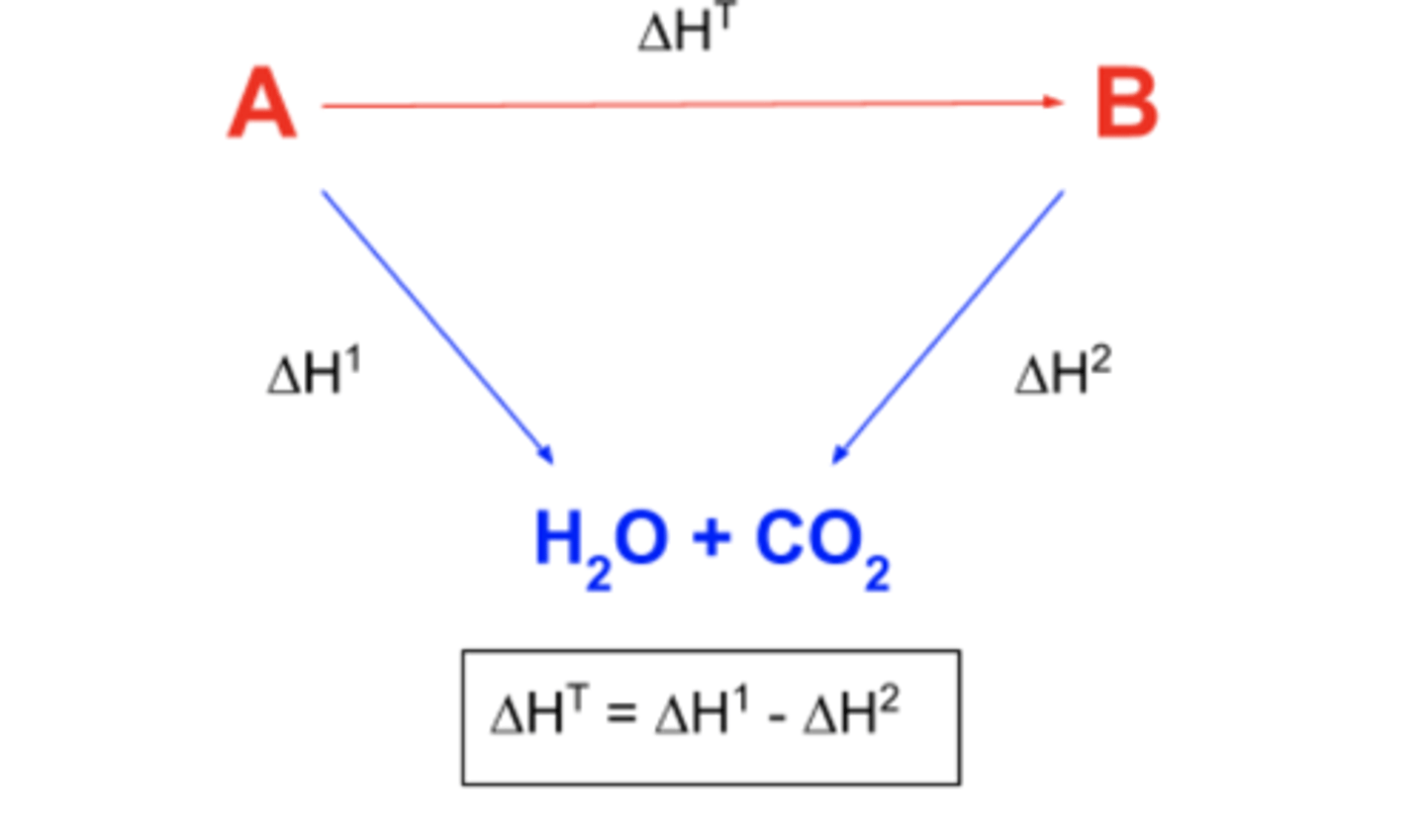
Define enthalpy change of combustion...
The enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is burned completely in oxygen under standard conditions, with all their substances in their standard states.
Define enthalpy change of neutralisation...
The enthalpy change when solutions of acid and alkali react together under standard conditions and in solutions containing 1moldm-3 to produce one mole of water.
What are standard conditions?
100kPa and 298K
Solution concentration at 1.00 moldm-3
q=mc∆T
q = energy change (J)
m = mass (g)
c = specific heat capacity (J g-1 C-1)
ΔT = temp change (C)
Define specific heat capacity...
The energy required to raise 1g of a substance by 1K without a change of state.
ΔH = q/moles
q = energy change (J)
ΔH = energy change per mole (J mol-1)
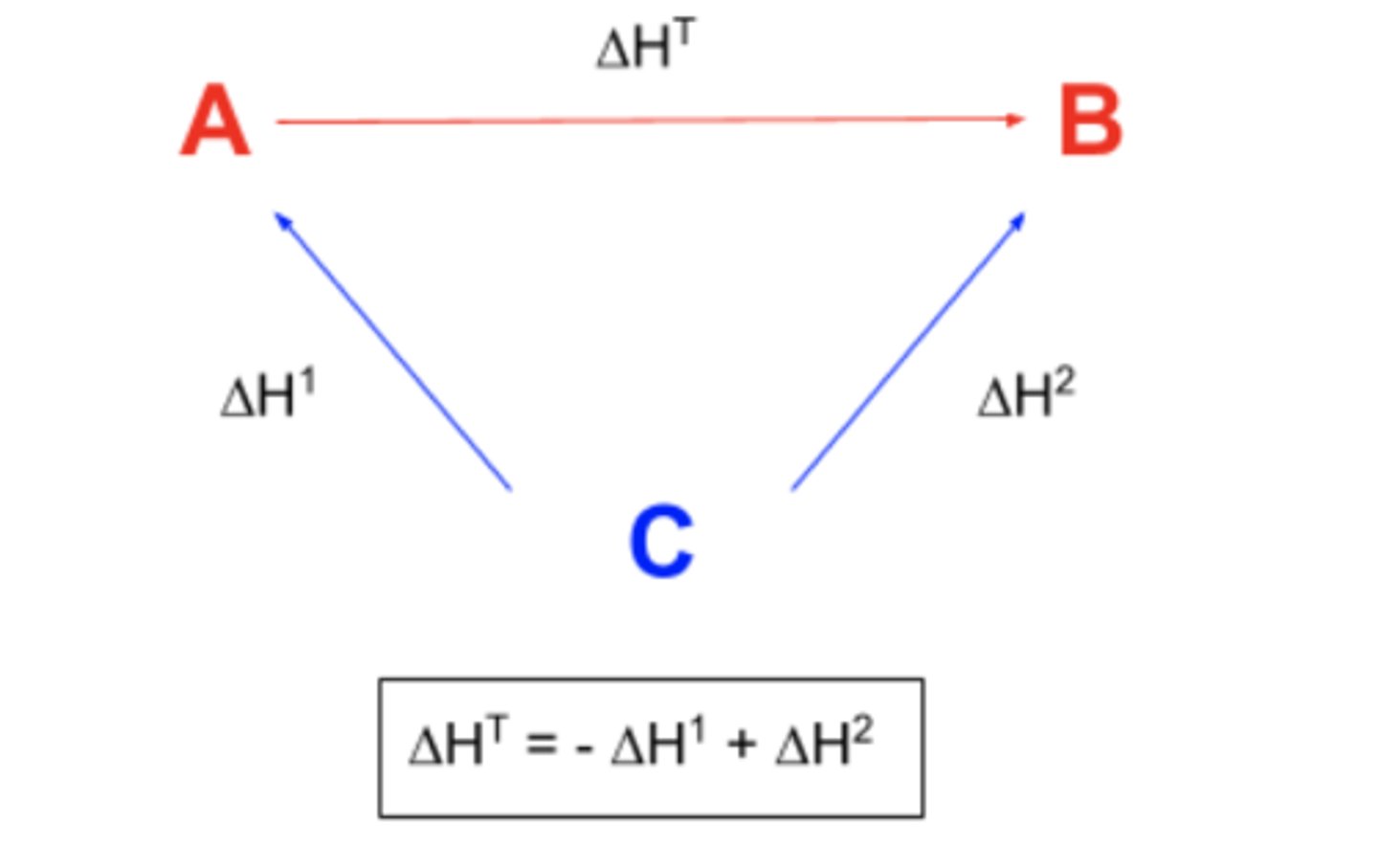
Define Hess's Law...
The total enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the route taken.
Draw an enthalpy of formation cycle...
Draw an enthalpy of combustion cycle...
What are catalysts?
Lower activation energy by providing and alternative reaction route.
what are homogenous catalysts
Catalysts that are in the same state as the reactants.
What are heterogeneous catalysts?
Catalysts that are in a different phase to the species in a reaction.
Describe how a solid heterogeneous catalyst works...
1. reactant molecules adsorb onto active site of surface of catalyst.
2. bonds within reactant molecules break
3. new bonds form, making product molecules
4. the product molecules leave catalyst surface, desorbed
What is catalyst poisoning?
Impurities in reaction mixture may bind to heterogeneous catalyst surface more strongly than reactant molecules and block reactants being adsorbed and reacting
What is cracking?
Long-chain hydrocarbons are split into shorter, more useful hydrocarbons.
What conditions does thermal cracking use?
High temp and pressure.
What conditions does catalytic cracking use?
Lower temp - around 720K - normal pressure and a catalyst.
Hydrocarbon vapour passed over heated catalyst.
Why is carbon monoxide dangerous? How is it produced?
Incomplete combustion.
Toxic, odourless and colourless.
Replaces oxygen in blood which starves brain and other organs -> suffocation.
Why are oxides of nitrogen and sulphur dangerous? How are they produced?
Byproducts of alkane combustion.
React with water to produce dilute acids -> acid rain.
Acid rain erodes infrastructure made from limestone and can make river/lakes acidic -> kills wildlife.
Why are particulates dangerous? How are they formed?
Unburned hydrocarbons.
Respiratory problems and contribute to global dimming.
What do catalytic converters do?
Remove unburnt hydrocarbons and oxides of nitrogen from systems.
Use rhodium catalysts to convert harmful products into stable ones such as CO2/H2O.
What are aliphatic compounds?
Compounds that contain branched or straight carbon chains.
No benzene ring.
What are aromatic/arene compounds?
Contain a benzene ring.
What are saturated compounds?
Compounds containing only single carbon-carbon bonds.
What are unsaturated compounds?
Organic compounds that contain at least one carbon-carbon double/triple bond or an aromatic ring.
Why are double bonds susceptible for attack by electrophiles?
Area of high electron density.
What is the test for alkenes? What causes the colour change?
Alkenes cause bromine water to change from orange-brown to colourless.
C-C double bond can open up and accept bromine atoms -> saturated.
What are electrophiles?
Electron acceptors that are attracted to areas of high electron density.
What is a carbocation?
A carbon with three bonds and a positive charge.
Draw the electrophilic addition of ethene + bromine...
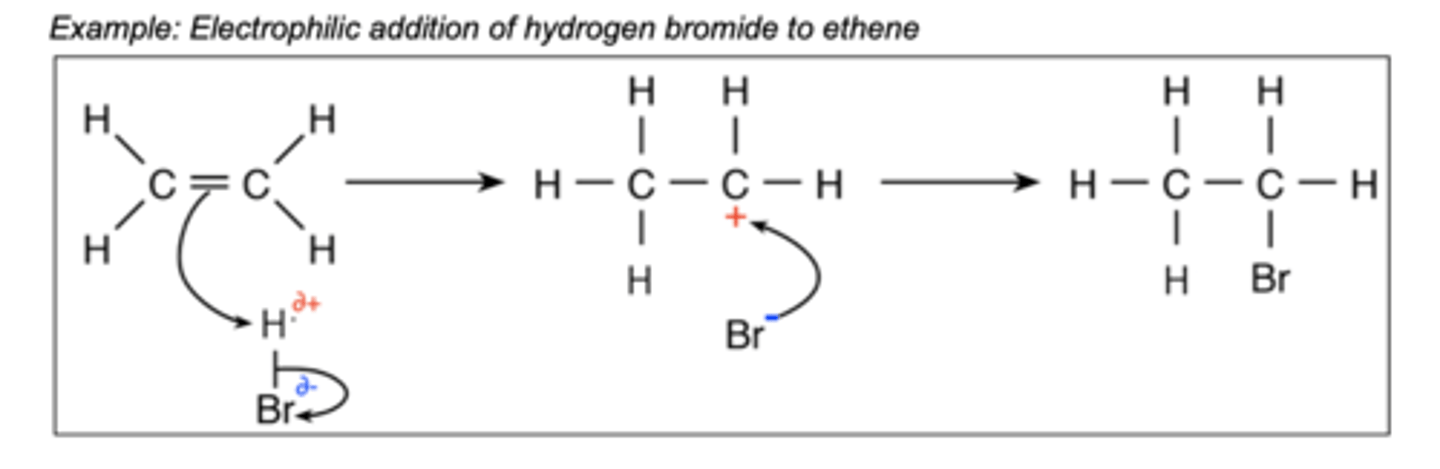
What conditions are required for addition reactions with alkenes and hydrogen?
Nickel catalyst
High temp/pressure
OR
Platinum catalyst
RTP
What conditions are required for addition reactions with alkenes and water?
Concentrated sulfuric acid, then add water
OR
Steam, phosphoric acid and high temp + pressure
What are addition polymers?
Produced from alkenes where double bond is broken to form a repeating unit.
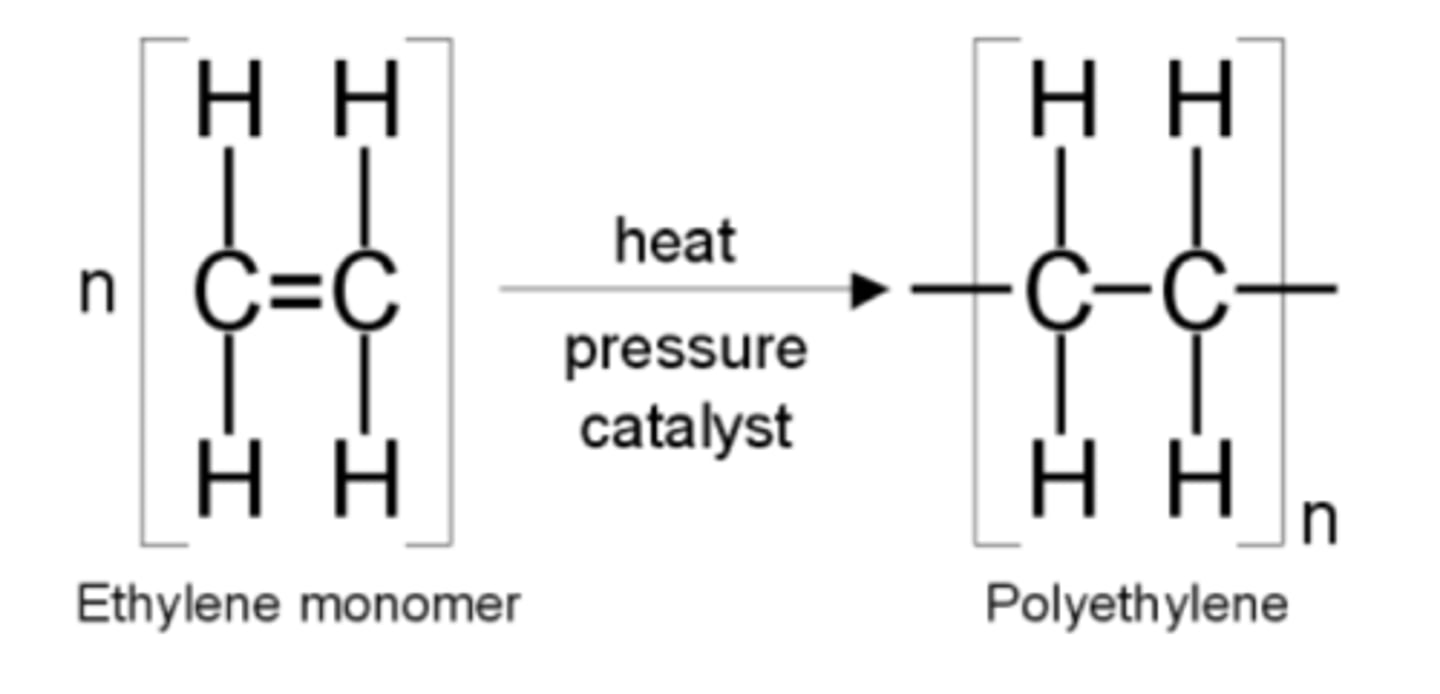
Define molecular formula...
The actual number of atoms of each element in a compound.
Define structural formula...
Shows arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Define displayed formula...
Shows every atom and every bond in a molecule.
Define skeletal formula...
Shows only bonds and any non-carbon atoms.
What are stereoisomers?
Compounds with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement of the atoms in space.
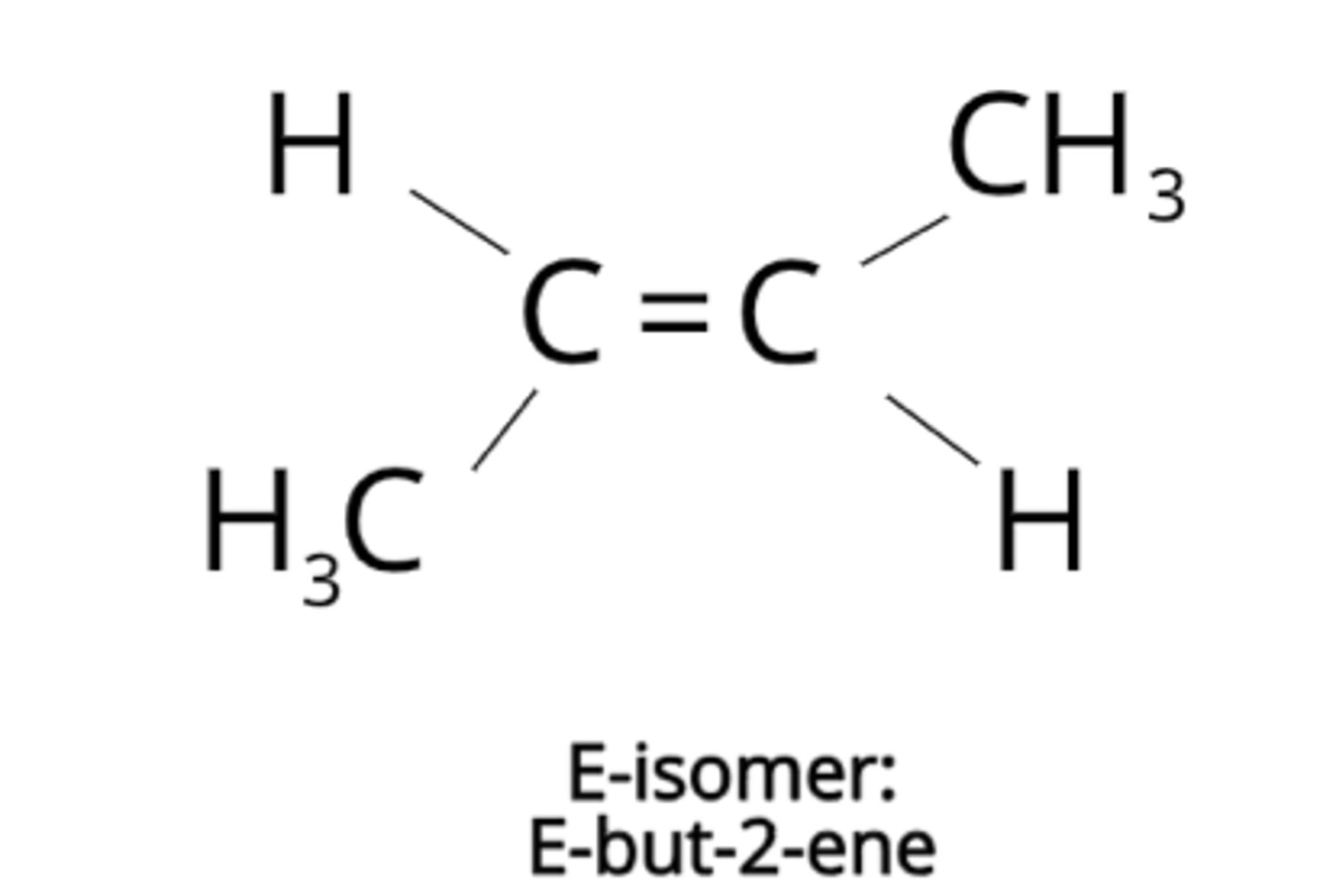
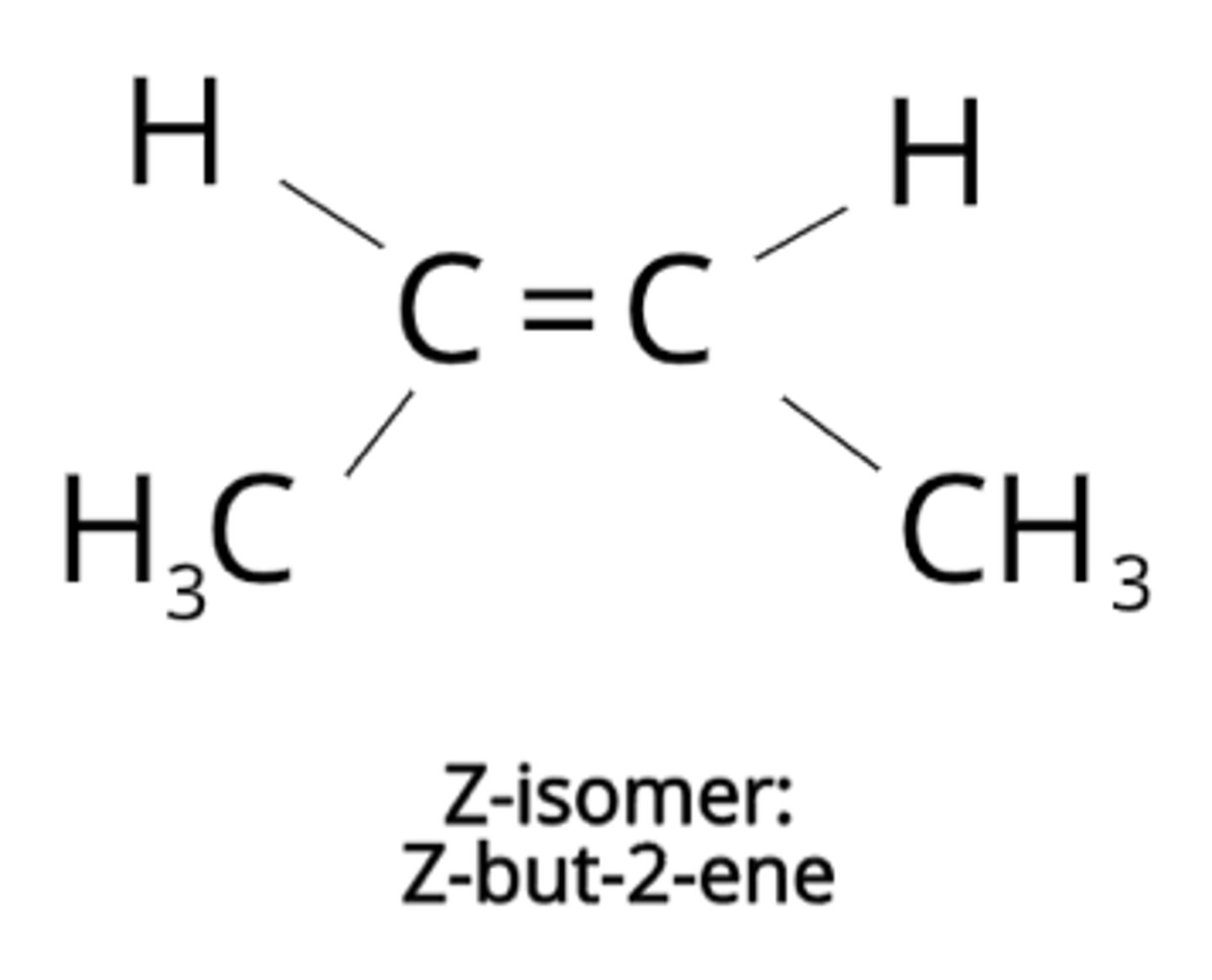
What is E-Z isomerism?
A form of stereoisomerism that occurs in compounds with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom on C=C bond.
There is limited rotation around bond.
Draw an E isomer...
Draw a Z isomer...
What are cis-trans isomers?
Can only be used when groups on each side of carbon atoms is the same.
What is an example of alternative fuels? Benefits?
Biofuels release fewer, less harmful products.
Ethanol + hydrogen are carbon neutral.
Sustainable so will not run out.