Genetics Week 3 (Mitosis)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
The cell cycle alternates between
Interphase (normal cell activity) and mitosis (cell division
G0 stage
Terminally differentiated cells stop dividing and enter the G0 stage.
How long does the cell cycle take (human vs embryo cell)
Rapidly proliferating human cells go through the cell cycle in 24 hours.
In an early embryo, it’s ~30 minutes.
Order of cell cycle phases
G1, S, G2, M
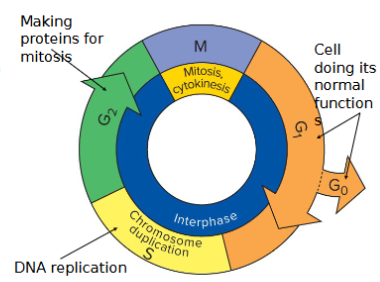
G1 interphase gap 1
Cells actively producing products specific to their biological role in the body.
Varies in length, depending on cell type.
Cells like human nerve cells do not divide and stay in G1.
S phase - DNA synthesis (chromosomes, centromere, open)
Duplication of chromosomes to produce identical sister chromatids.
Sister chromatids remain joined at centromere.
DNA must be open for replication not condensed.
Centrosomes also need to replicate to produce two centrosomes.
G2 interphase gap 2
Phase just before mitosis
Cell synthesis proteins necessary for mitosis and cell division are produced.
You observe a cell under the microscope and it has two centrosomes. By the appearance of the chromosomes, you know that the cells have not yet entered mitosis. What phase(s) could the cell be in?
G2 or S
Mitosis Products
Two daughter cells.
Genetically identical to each other and parent cell.
Have the same number and kind of chromosomes as parent.
Mitosis vs Binary Fission
Mitosis - eukaryotic process
Eukaryotic nuclei typically have multiple linear chromosomes.
Binary fission - prokaryotic cell division/reproduction
Prokaryotes do not have nuclei and usually have a single circular chromosome.
Mitosis Phases
Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Prophase + # of chromosomes and chromatids
Chromosomes condense and become visible.
Two centrosomes move apart, one migrating to each pole.
Microtubules begin to extend from centrosomes.
Nucleoli begin to disappear.
46 chromosomes
92 sister chromatids
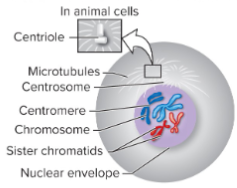
Centrosome vs centriole
Centrosome = 2 centrioles plus matrix and microtubules.
Prometaphase + # of chromosomes and chromatids
Nuclear membrane breaks down.
Microtubules attach to kinetochores in centromere of each sister chromatid.
Sister chromatids attach from opposite poles.
Mitotic spindle forms.
46 chromosomes
92 sister chromatids
23 homologous pairs
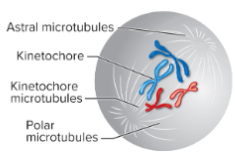
Three types of microtubules forming mitotic spindle
Kinetochore microtubules attach to kinetochores.
Polar microtubules are directed to the middle of the cell.
Astral microtubules extend toward the cell’s periphery.
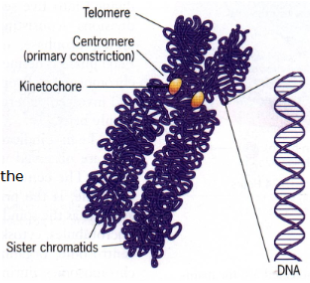
Centromere vs Kinetochore
Centromere - region of DNA
Kinetochore - protein structure on the DNA
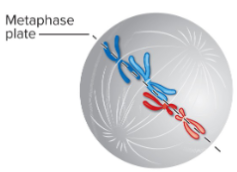
Metaphase + # of chromosomes and chromatids
Chromosomes align on the metaphase plate.
Sister chromatids face opposite poles of the cell.
Forces pushing/pulling chromosomes to or from each pole are balanced, which keeps chromosomes in place.
46 chromosomes
92 sister chromatids
23 homologous pairs
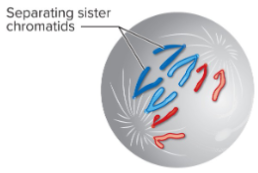
Anaphase + # of chromosomes and chromatids
Sister chromatids of all chromosomes simultaneously separate at their centromere.
Separated sister chromatids move to opposite poles via shortening kinetochore microtubules (disjunction can occur)
Chromatids have a characteristic v shape at this stage.
92 chromosomes
92 chromatids
0 homologous pairs
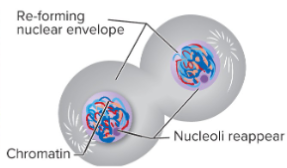
Telophase + # of chromosomes and chromatids
Nuclear membrane (envelope) forms around each group of chromatids.
Nucleoli re-form.
Spindle fiber disappears.
Chromosomes uncoil and reform as chromatin.
46 chromosomes
46 chromatids
23 homologous pairs
Cytokinesis + # of chromosomes and chromatids (begins when?)
Cytoplasm of parent cell splits into two daughter cells with identical nuclei.
Begins during anaphase, but isn’t complete until after telophase.
46 chromosomes
46 chromatids
23 homologous pairs
Cytokinesis in plants vs animal cells
Cleavage furrow in animal cells.
Cell plates in plant cells.