Dichotomous Key Glossary (Fish)
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
Acuminate
Somewhat pointed, but not as extreme as lanceolate
Abdominal
Referring to the belly region.
Accessory Sensory Line
One or more series of sensory pores that diverge from the main lateral line. In soles of the genus Gymnachirus, these occur at right angles to the main lateral line on the right (eyed) side.
Adipose
Referring to fatty tissue. For example, adipose eyelid——a transparent covering over the eye of some fishes——-or adipose fin.
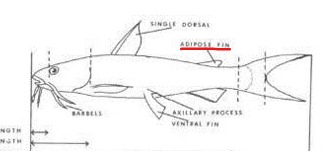
Adnate
Attached
Air bladder
Swim bladder, a gas filled membranous organ responsible for buoyancy in many fishes. Some fish use their air bladder as a lung, and some others use it as a sound producing organ.
Ambicolorate
In the flatfishes, part or all of the blind side having the same or similar pigment as the eyed side.
Anadromous
Living in the sea but entering fresh water to spawn.
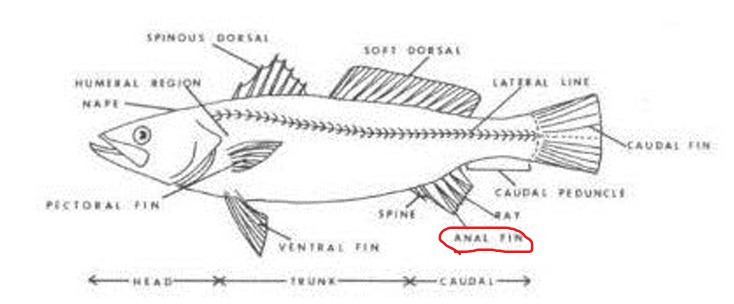
Anal Fin
Circled on figure.
Angulate
Having definite corners, forming an angle, with at least one point.
Antitropical
Distributed in both northern and southern temperate zones, but not common in the tropics.
Axil
The rear side of the pectoral fin base; the “armpit”.
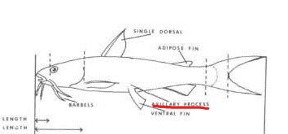
Axillary scale (Axillary Process)
An elongate structure at the base of the pectoral or ventral fins in some fish.
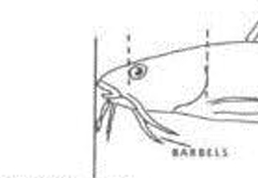
Barbel
A threadlike structure on the head; usually sensory
Bathypelagic
Pertaining to or living in the deep waters of the open ocean (depths usually greater than 1000 meters)
Benthic
Referring to the sea bottom.
Bifurcate
Branching into two lobes or sections.
Bony Stay
A prominent bony ridge running from a suborbital bone to the preopercle.
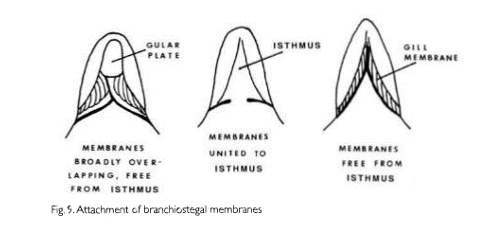
Branchiostegal membrane
A membrane connecting the gill cover or opercle with the throat.
Branchiostegal Ray
Slender bones in the branchiostegal membrane.
Buckler
Large, multi-spined structure in the skin of batfishes.
Canine
A slender, rounded, pointed tooth for holding or tearing.
Catadromous
Living in fresh water but entering the sea to spawn.
Caudal Fin
See Figure
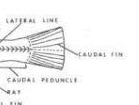
Caudal Peduncle
The region between the last ray of the anal fin and the base of the caudal fin.
Chest
The ventral area just behind the throat.
Ciguatera
A disease of the nervous system caused by eating certain tropical fishes.
Circumtropical
Occurring around the world, in all oceans, in the warm areas extending from the equator to approximately 20 to 30 degrees N and S.
Cirrus
A fleshy appendage, usually on the head or tips of the fins.
Compressed
Laterally flattened.
Corselet
Covering of enlarged, thick scales on the anterior body of some scombrids (mackerel and tuna).
Ctenoid Scale
See photo

Cusp
The base of a tooth, the region where it is attached.
Cutaneous Fold
A low, finlike fold on the tails of rays.
Cycloid Scales
See photo

Deciduous
Tending to shed or break off.
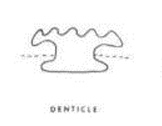
Denticle
Check photo
Disc Lamellae
In remoras, the flattened, overlapping folds in the sucker, actually modified dorsal rays.
Distal
Remote from the point of origin or attachment.
Dorsal
Referring to the back.
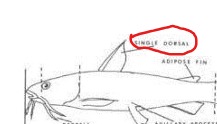
Dorsal Fin
see photo
Dorsum
The upper (or dorsal) portion of the fish’s body.
Electrophoresis
One of several molecular techniques used to demonstrate genetic similarities or differences between organisms.
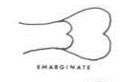
Emarginate
Having the margin indented but not so deeply as to be forked.
Entire
Whole, complete, or smooth.
Epipelagic
Pertaining to or living in the surface waters of the open ocean (depths usually greater than 200 m).
Esca
The fleshy “bait” at the end of the illicium of frog-, goose-, and batfishes.
Estuary
An area where fresh water meets sea water.
Euryhaline
Capable of withstanding large changes in salinity (salty concentration).
Exserted
Extending beyond an otherwise even margin.
Extralimital
Distributed outside the range. The term may be applied to the range of a species or other taxonomic group or to the coverage of a book, paper, or other report.
Falcate
Sickle shaped
Fin
Median or paired structure, usually membranous and supported by soft rays or spines. Fins may be variously modified into other structures such as sucking discs or “fishing poles”.
Adipose Fin
A fleshy median dorsal fin without spines or rays.
Anal Fin
A median fin on the ventral surface between the anus and the base of the tail.
Caudal Fin
The tail fin; the median fin at the base of the tail.
Dorsal Fin
A median fin on the dorsal surface; it may be single or divided into two or more fins.
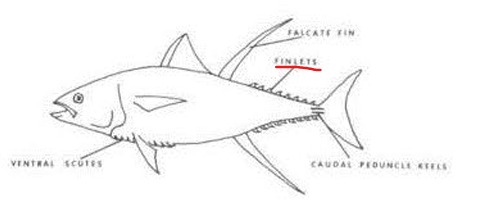
Finlets
Detached median fins following the dorsal or anal.
Pectoral Fin
Paired fins on either side of the body, usually near or just behind the gill opening; these correspond to the arm or foreleg of terrestrial vertebrates.
Pelvic or Ventral
Paired fins below or behind the pectorals, near the anus (abdominally inserted), under the pectorals (thoracically inserted), or in advance of the pectorals (jugular).
Finlet
Typically found in fast swimming fishes, they are thought to improve the hydrodynamics of these species.
Forked
Divided into two parts or branches.
Fusiform
Streamlined “cigar shape” typical of most fishes.
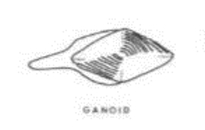
Ganoid Scale
See Photo
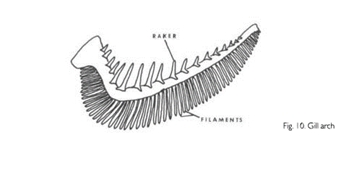
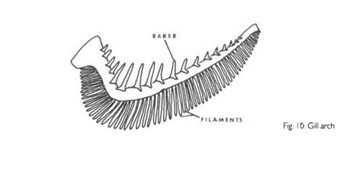
Gill Arch
Unit of respiratory structures on either side of the pharynx.
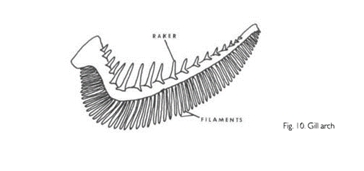
Gill Filament
Slender respiratory structures that compose the posterior part of the gill arch where gas exchange occurs.
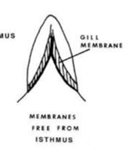
Gill Membrane
See Branchiostegal Membrane
Gill Rakers
Usually, stiff projections on the inner or anterior surfaces of the gill arch, used for straining food.
Gular Plate
A bony median plate between the lower jaws of some fishes.

Head (Head Length)
The region from the tip of the snout to the posterior edge of the gill cover.
Heterocercal Tail
Look at figure.

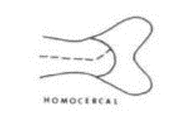
Homocercal Tail
See photo
Humeral
Pertaining to the shoulder region, just behind and above the pectoral fin in most marine fishes.
Hyoid
Of or pertaining to the tongue.
Hypural Plate
Posterior end of the vertebral column, noticeable as a vertical crease when the tail of the fish is bent forward.
Illicium
Modified dorsal spine that serves as the “fishing rod” in angling fishes; see also ESCA
Incisor
A long but sharp-edged tooth for scraping or cutting.
Interhaemal
Bones connecting the ventral vertebral arches.
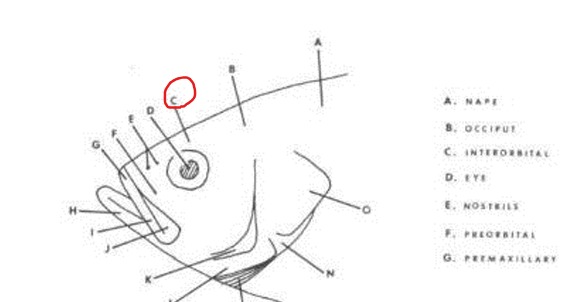
Interorbital
Region (or bone) on top of the head between the eyes.
Intromittent Organ
A modified structure (fin) in the male of fishes with internal fertilization that is used for transfer of sperm to the female.
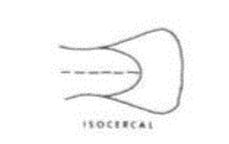
Isocercal tail
Look at photo
Isthmus
Fleshy region extending forward on the throat between the gills.

Jugular
Of or pertaining to the throat.
Keel
A raised ridge, often on a scale or on the caudal peduncle.
Lachrymal Plate
In searobins a bone under the eye and above the maxilla.
Lanceolate
Tapering to a long, lancelike point.

Lateral line
A line of modified scales with pores in them connected by tubes usually running the length of the fish from behind the gill opening to the base of the caudal fin. The pressure-sensitive pores, but not the scales of the lateral line, usually extend onto the head of the fish and sometimes onto the caudal fin as well. The position, shape, and number of scales in the lateral line is of taxonomic importance in many fishes.
Lateral Scale Rows (Vertical scale rows)
The number of scales in a vertical row between the gill opening and the base of the caudal fin, used instead of the lateral line scale count in fishes that lack a lateral line.
Length
Measured in various ways.
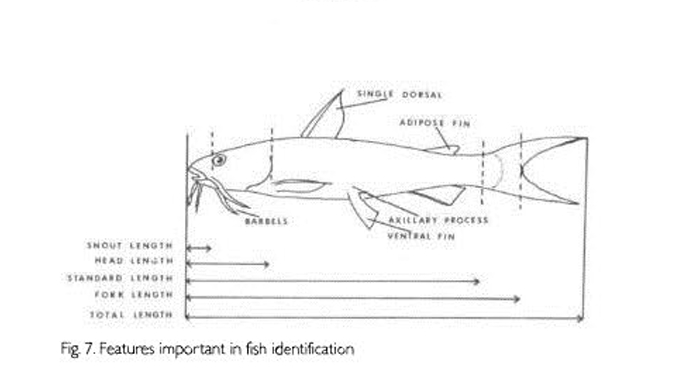
Fork Length
From the tip of the snout to the fork of the caudal fin. Standard length (sl). From the tip of the snout to the tip of the hypural plate. Total length (TL). From the tip of the snout to the tip of the caudal fin.
Leptocephalus
A laterally flattened, transparent larval stage of eels, bonefish, tarpon, and ladyfish. It has a small head and decreases considerably in size and body depth during metamorphosis.
Lunate
Deeply forked, with curved branches.
Mandible
Lower Jaw
Maxilla
One of the bones comprising the upper jaw.
Medial
Near the centerline of the body.
Melanophore
A dark colored pigment cell.
Meristic
Pertaining to the number of serial parts, for example, fin rays or lateral line scales.
Mesopelagic
Pertaining to or living in the midwaters of the open ocean (depths usually 200-1000 m).
Molar
A short blunt tooth for crushing.
Nape
The posterior most part of the head just before the dorsal fin.